Content
Spirulina is a blue-green alga that is widely used as a weight loss and energy supplement due to its beneficial properties. Growing spirulina at home is very simple and realistic. This will require a large but flat aquarium for the algae to have enough sunlight. There is also a water heater, and of course the spirulina itself, which can be ordered via the Internet.
The temperature required for the growth and reproduction of spirulina is 36-38C, with the alkalinity of water approximately 8-10.
Filtered water, purified from any impurities, is suitable before use. For spirulina, sunlight is very important when growing, but not prima, but partial shade so that microorganisms do not die. It is not recommended to expose the aquarium to hot sun rays in summer. Water should be mixed periodically, 2-4 times a day. For this, a sterile glass rod is used. When stirring, you need to be very careful so as not to harm the algae, stir very slowly.
When the water is completely green, you need to harvest the spirulina. To do this, you need to drain and pass through the filter half of the suspension. the spirulina itself should remain on the filter, and clean water will flow down. Then add clean water to the aquarium and add the necessary chemicals.
Video about a scientist who grows spirulina at home.
Live spirulina is considered the healthiest. It can be smeared on a pastry, eaten with a spoon, or added to a cocktail. For long-term storage of spirulina, you can place it in the freezer after dividing it into equal portions for convenience.
Beneficial features

This alga contains a lot of nutrients, active substances such as zinc, chlorine, iodine, iron, manganese, copper, chromium, cobalt, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, vitamins B12, B1, B2, B6 and many others. The digestibility of all the elements contained in spirulina exceeds 95%. This speaks of its high value.
This small plant, packed with trace elements and vitamins, is able to provide nutrition to the entire body. Spirulina can be dried, if desired, outdoors, but not in direct sunlight, to avoid loss of trace minerals.
The best place to dry is polyester, it absorbs moisture well. The result is a dark green, dried algae. It is recommended to take small amounts of spirulina every day, absolutely for everyone. For healthy people, a sufficient amount will be 7-10 g, for healthy people, from 1 to 4 g per day.
3 parts: Prepare everything you need Prepare the aquarium How to care for a spirulina colony
Spirulina is a type of blue-green alga that contains many beneficial nutrients, including proteins, antioxidants and many vitamins and minerals. It is a simple organism that grows well in warm water. But because algae can absorb toxins from the environment, some people choose to grow spirulina at home, in a safe and controlled environment, or simply enjoy the flavor and texture of fresh spirulina. After you make the necessary preparations, the spirulina colony can grow on its own.
Part 1 Prepare what you need
-
 Get an aquarium.
Get an aquarium.
For most people looking to grow spirulina at home, a standard sized aquarium will suffice.An aquarium of this size will be able to supply algae to a family of four.
- If you prefer, get a bigger aquarium, or grow spirulina in a bathtub or outdoor pool (if you live in a warm climate and in a private home). The easiest way to keep track of spirulina growth is in a small aquarium in your home.
-
 Get the items for collecting algae.
Get the items for collecting algae.
The spirulina colony appears to be dense, but it is mostly water. When ready to eat or for other purposes, squeeze out the excess water. If you only want to collect a small amount of spirulina, use a filter cloth or fine mesh strainer. In addition, you will also need a scoop to remove the spirulina from the aquarium.
- If you want to harvest more spirulina to dry, use a cloth or sieve.Olarger sizes.
-
 Buy minerals to stimulate algae growth.
Buy minerals to stimulate algae growth.
Trying to grow spirulina in regular water does not always lead to good results. In order for a colony to grow large, it needs certain minerals. You don't have to be an expert to do this - you can buy spirulina mineral blends at health food stores or online. These mixtures must contain the following substances:
- bicarbonate of soda;
- magnesium sulfate;
- phosphorus nitrate;
- lemon acid;
- salt;
- urea;
- calcium chloride;
- ferrous sulfate;
- ammonium sulfate.
-
 Buy a spirulina crop.
Buy a spirulina crop.
To grow a spirulina colony, you first need to buy some live spirulina. Check with your local or favorite online health food retailer to see if they have spirulina growth kits available.
- Spirulina starter cultures are a common bottle of spirulina algae in a nutrient medium (in water).
- Buy spirulina cultures only from trusted sellers. Since spirulina is capable of absorbing heavy metals and other toxins, make sure the starter culture comes from a safe source.
Part 2 Prepare the aquarium
-
 Place the aquarium in a warm, bright place.
Place the aquarium in a warm, bright place.
If possible, place the aquarium near a south window for plenty of sunlight. Spirulina requires a lot of sunlight and warmth to grow.
- Some manufacturers use artificial lighting, but with natural light, the result will be much better.
-
 Prepare the culture medium.
Prepare the culture medium.
Spirulina growers call the place where the algae grows as a "breeding ground", but in fact it is just water in the aquarium with mineral supplements. Pour filtered water into the aquarium, and then add as much mineral mixture to it as indicated on the instructions on the package.
- Install the filter on the tap (for example, Aquaphor) and draw water from the tap for the aquarium.
- If chlorinated water is running out of your faucet, buy a water dechlorinating kit from an aquarium supply store.
-
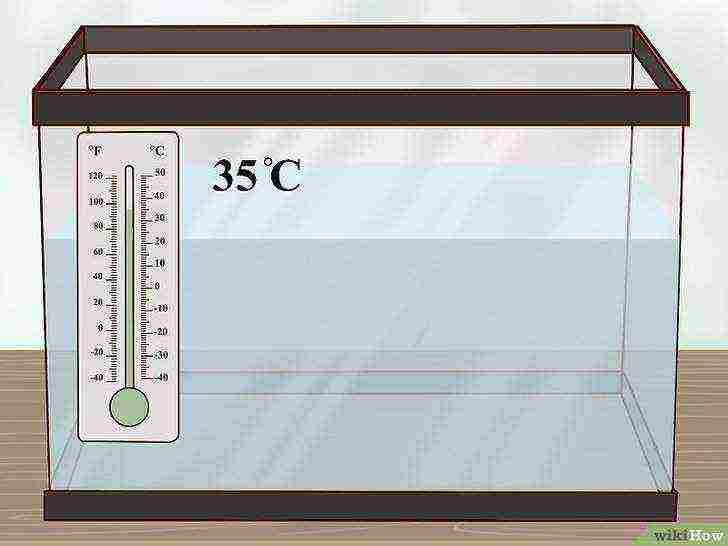 Check the water temperature.
Check the water temperature.
Ideally, the water temperature in the aquarium should be around 35 ° C. Temperatures over 38 degrees are considered too high for algae. Set up an aquarium thermometer to keep your aquarium at the right temperature.
- Spirulina is able to withstand cold temperatures and not die, but it does its best in warm environments.
- If your aquarium is too cold, heat up the water with a special aquarium thermostat, which you can buy at a pet or aquarium store.
-
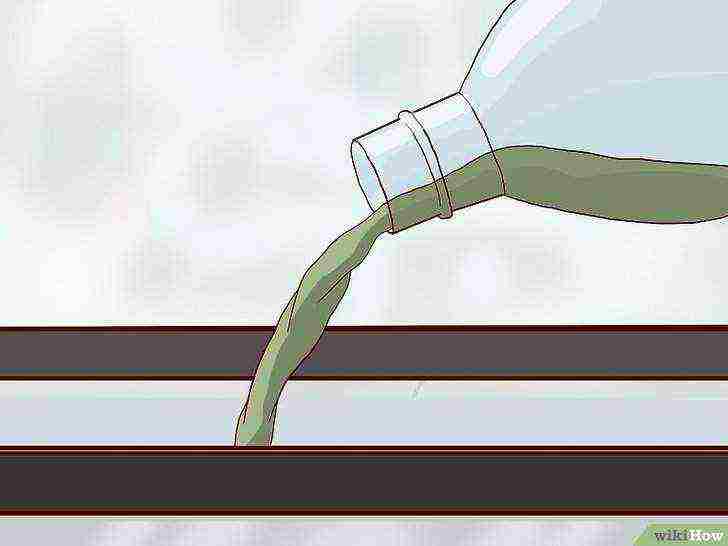 Pour the spirulina starter culture into the aquarium.
Pour the spirulina starter culture into the aquarium.
Follow the directions on the spirulina bottle carefully, but usually just pour the culture into the water. Typically half or three-quarters of the bottle should be poured into the aquarium.
Part 3 How to care for a spirulina colony
-
 Monitor the growth of the spirulina colony.
Monitor the growth of the spirulina colony.
The spirulina colony will appear sparse at first, but over time it will thicken and grow in size. Most of the time, you don't have to do anything other than keep an eye on the growth of the colony!
- If the colony is not growing well, check the pH in the aquarium, which should be 10 during the harvest period. If the pH is not correct, add more mineral supplements.
- You can buy pH strips from your pet store or order online.
-
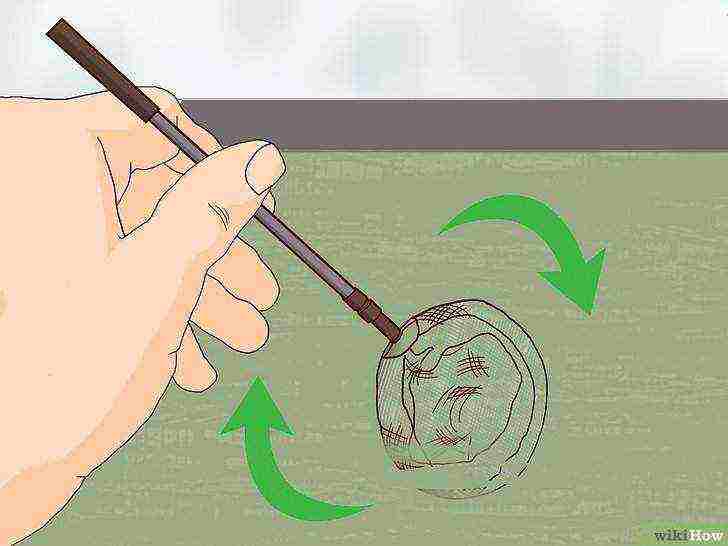 Stir the aquarium water occasionally.
Stir the aquarium water occasionally.
Spirulina needs oxygen to grow well. Some people oxygenate their water with pumps and aquarium pumps, but you can do without them. To get oxygen into the water, just stir it from time to time.
-
 Collect the spirulina after 3-6 weeks.
Collect the spirulina after 3-6 weeks.
When the spirulina has grown, start harvesting it for consumption. You just need to catch it with a scoop! As a rule, people only need to eat one spoonful of fresh spirulina.
-
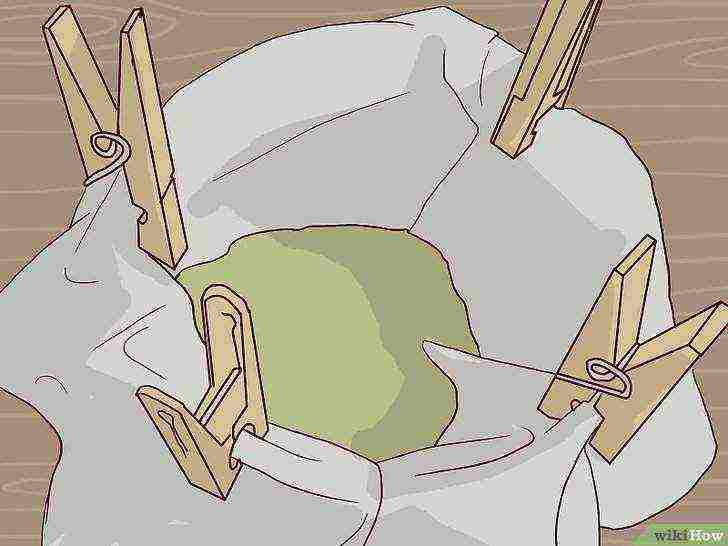 Strain the spirulina through a filter cloth.
Strain the spirulina through a filter cloth.
Take a piece of cloth and place the spirulina you removed from the aquarium on top of it. Hold it over a sink or bowl and gently squeeze out excess water. This leaves you with a thick green paste. Add fresh spirulina to smoothies, sprinkle it on your favorite food, or enjoy the flavor of fresh spirulina!
-
 Replenish your tank's supply of nutrients.
Replenish your tank's supply of nutrients.
Whenever you take some spirulina out of the aquarium, remember to add the mineral mixture to the water. The amount of the mixture should approximately correspond to the amount of algae caught. For example, if you took a tablespoon of spirulina out of the aquarium, add about a tablespoon of minerals to the water.
Article Information
This page has been viewed 560 times.
Was this helpful?
Spirulina growing module
The setup and methods described here are primarily intended for testing, demonstration, and training purposes. However, they can provide a steady production of 40 grams of dry spirulina per day (enough to provide a nutritional supplement for 10-20 children). We strive to show that satisfactory results can be achieved at very low cost (aquarium pump, small amount of initial culture, etc.).

1. The main factors affecting the growth of spirulina
1.1 Nutrient medium
The liquid used to make spirulina is a solution of mineral salts in water. This liquid should provide spirulina with all the chemicals it needs. The PH factor of the culture medium (that is, its alkalinity level) should be between 8 and 11. There are various recipes for the culture medium of spirulina. The one shown here is one of the simplest, but not the cheapest.
Table # 1
Table 2
1.2 Temperature
The temperature of the culture medium has a direct effect on the growth rate of spirulina. This alga is quite resistant to temperatures down to 3-5 ° C above zero. It starts to grow noticeably above 20 ° C. And at 35-37 ° C it reaches its maximum. If this temperature is exceeded, the crop may die from overheating. And after a few hours at temperatures above 43-44 ° C, all spirulina can die. Note that sudden changes in temperature will reduce yields.
1.3 Light
Very strong light (direct sunlight) can be dangerous under the following circumstances:
With a cold culture (below 14-15 ° C), especially with a sudden sharp increase in illumination;
· In a very warm culture, due to the possibility of overheating;
· With a very dissolved culture (transparency is more than 6 cm);
When the culture is recovering (after overheating).
If any of the above happens, you need to worry about shading the pool.
On the other hand, when the concentration and temperature conditions are optimal, the spirulina should be grown in open sunlight.
1.4 Stirring
It is very important, at least from time to time (2-4 times a day), to stir the spirulina.Excessive stirring may damage the spirulina (fragments visible under the microscope) and cause foam to form. Certain types of centrifugal pumps, as well as splashing falling water, are particularly harmful. The module proposed here provides continuous agitation of the culture using an aquarium electric pump. For small crop volumes (less than 100 liters), a small aquarium compressor can be used to mix the culture with air bubbles. The latter method is very convenient for maintaining a reserve culture.
2. Description of the module
2.1 Equipment
A jar of live spirulina;
Covered swimming pool with a total surface of 4 m2, consisting of:
- 2 sheets of 0.2mm polyethylene
- 4 semicircular arcs
- 3 poles 4 m long
- boards or bricks for building walls.
Electric aquarium pump 220V 5-7 W (for mixing and harvesting);
1000 liters of culture medium (water, fertilizers and mineral salts according to the recipe used).
A special measuring ruler with a glued white patch at the beginning, litmus paper to measure the pH, a thermometer.
Harvesting filter.
Possibly: extruder and dryer with removable trays.
Small aquarium air compressor 220V 5W.
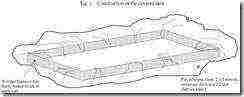
2.2 Covered pool arrangement
The selected area should be an open flat area (or slightly shaded if the climate is very hot), measuring 2 m by 8 m. The pool should be built according to the drawings, using bricks, cinder blocks, planks, adobe or any other material. If termites are present, a minimum of a centimeter layer of ash must be placed under the film. If there are rodents, it is necessary to put a sufficiently fine metal mesh or sheet metal under the film. It is prudent but not necessary to use double film, especially if its thickness is less than 0.2. In all cases, the pool surface must be carefully leveled before laying the film.
The arcs supporting the clear pond cover can be made of 6-8mm iron rods or bamboo. Arcs can be triangular or semicircular. The clear cover (agricultural polyethylene, ANTI-UV if possible) must be fixed on three sides with earth or stones. One long side is left free to allow access to culture.
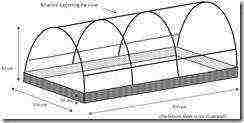

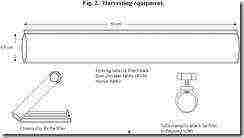
3. Preparation of the culture medium
The water used should be potable and, if possible, low in calcium (less than 100 mg calcium per liter). Slightly salty water can also be used (up to 4-5 g / liter NaCl, then salt should be omitted in the recipe). According to Table 1, you can determine the required amount of substances to prepare the required amount of nutrient medium.
Important: ammonium nitrate cannot be used here!
The substances indicated in parentheses are not necessary, at least initially or depending on the quality of the water used. For example, calcium chloride (or lime) must be added if very soft water is used (less than 10 mg calcium per liter). Water that is even moderately rich in sulphate (more than 20 mg / liter) makes it possible to eliminate potassium sulphate, provided that potassium nitrate is used as indicated (if sodium nitrate is used, potassium sulphate becomes important for its potassium).
The addition of green tea prevents iron deposition (purplish coloration is normal after diluting the iron salts with tea).
Dissolve ferrous sulfate in a glass of water before adding it to the solution; then add magnesium sulfate, which should be dissolved in a little water beforehand. This solution can be stored for several days before using it (in this case, it must be stored away from light).
4. Volume expansion and growth control
4.1 Measurement of Spirulina Culture Concentration
The concentration of a culture can be measured by the intensity of its color, for this a ruler is used, at the beginning of which a small white disc is attached perpendicularly. This instrument is immersed in water until the disc is no longer visible. The immersion depth of the disc is read off the ruler. The culture is dissolved if the disc remains visible at a depth of 5-6 cm; a depth of 2-3 cm shows a crop ready for production. A depth of less than 2 cm indicates that the crop must be dissolved or it is time to harvest. In good conditions, spirulina doubles every 2-4 days until it reaches its maximum concentration (clarity
Spirulina naturally grows in lakes with alkaline water. This water inhibits the growth of other microorganisms. The microalgae grows very quickly on the surface of the lake. This growth continues until the spirulina layer becomes so dense that it ceases to transmit light. But it is he who is so necessary for her growth.
For mass cultivation of spirulina, scientists investigated the conditions of growth, nutrition and growth for growing it on an industrial scale.
Spirulina is produced and consumed in more than 60 countries of the world: in Mexico, USA; Thailand; Japan; Taiwan; India, China, Russia, Ukraine, etc.
Where possible due to environmental and climatic conditions, growing spirulina takes place in open water. Open-type installations are used in Bulgaria, Italy, Israel, Mexico, Chile, Brazil, Thailand, India, China, USA (California), Central Asia, Kazakhstan.
In countries with a temperate climate, preference is given to the cultivation of microalgae in greenhouses. In Japan, spirulina is grown in greenhouses on an area of 10 thousand hectares, in Italy - 2.5 thousand hectares, in France - 3 thousand hectares, in the Netherlands - 1 thousand hectares, in Ukraine - 12 hectares, Moldova - 0.1 ha.
Greenhouses for industrial cultivation of spirulina with photosynthetic blocks are located as close as possible to heat and sun. Photoblocks are filled with a nutrient medium of a strictly defined composition, repeating the composition of the water of Lake Chad. Usually, in this case, the purest artesian water is used from great depths, the optimal illumination and temperature of the nutrient medium are set at 26-28 ° C.
The grown spirulina is washed, filtered and dried at temperatures up to 65 ° C. At this temperature, it does not lose its valuable properties for a long time, it is easily transported.
The advantage of the closed type of spirulina cultivation over the open type is the ability to preserve pure cultures, high productivity of algae strains, and production automation.
Spirulina contains a balanced composition of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, amino acids, micro and macro elements, about 50 fatty acids. At the same time, spirulina contains only 5% fat and 8% cholesterol.
Huge opportunities are inherent in this microscopic plant!
Attention!
You must have complete information about the manufacturer. Nowadays, almost all spirulina, used as food or for medicinal purposes, is grown artificially. Conditions growing spirulina must comply with international standards. You can also grow it at home. But homemade spirulina does not contain enough nutrients. In addition, if not properly dried, putrefactive bacteria, mold and fungi can develop in it. And this dramatically reduces its nutritional and medicinal properties, and can also lead to poisoning. Doubt should be caused by spirulina, produced with the addition of food colors and preservatives. When purchasing, ask for the relevant quality certificates.
If you liked the article, share with your friends