Content
- 1 Choosing a future bonsai style
- 2 Choosing a cutting
- 3 Choosing a ceramic bowl
- 4 Soil preparation before planting
- 5 How to grow bonsai at home?
- 6 Bonsai care
- 7 How to grow bonsai at home: video
- 8 Where to begin
- 9 Where to get planting material
- 10 Yamadori
- 11 Toriki
- 12 Misho
- 13 Classification according to size
- 14 Classification by crown shape
- 15 Exclusive Styles
- 16 Growing rules
- 17 Landing
- 18 Transfer
- 19 Bonsai (plant): how to care
- 20 Bonsai formation
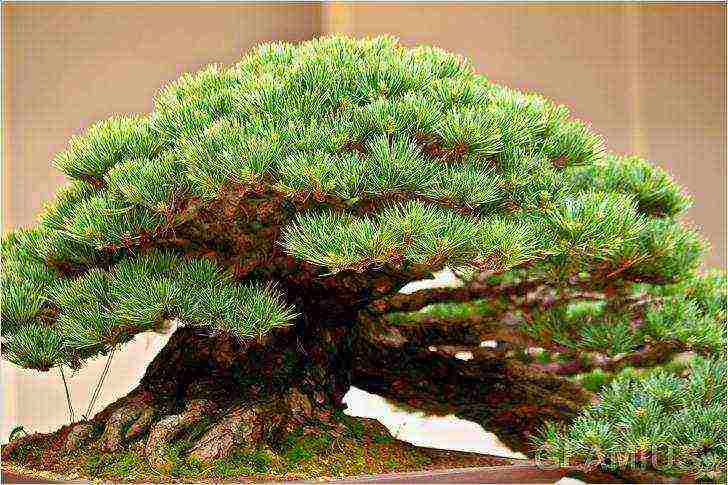

Not everyone can properly grow a bonsai at home, because this is a real art that requires creativity and special skill from a person.
As you know, bonsai is a copy of an ordinary tree, but only in smaller sizes. Such plants are very often used to create a unique and original interior in a home or office space. Before growing a bonsai, it will take a lot of time to study special literature on planting techniques and further care.
In order to create such a piece of art at home, you must take care of the following tools and working materials in advance:
- special ceramic bowl for bonsai;
- cutting of the future tree;
- expanded clay;
- granite chips of different colors;
- thick soft wire;
- sharp garden knife;
- secateurs;
- black soil;
- elements for decoration (beautiful stones, moss, etc.).
Bonsai: growing

Growing bonsai
In order to find out how to grow a bonsai on your own, consider the detailed instructions with which you can not only choose the right plant, but also create a unique work of art that will decorate your home for a long time.
Choosing a cutting

Bonsai stalk
To form a bonsai, it is necessary to acquire such a plant so that it has medium-sized, but beautiful foliage, a densely woody trunk, as well as quickly blooming flowers. Some of the cheapest cuttings are trees such as orange and lemon. Of course, you are unlikely to succeed in getting fruits from them, but bonsai from them will turn out to be perfect.
Choosing a future style
Bonsai style
Decide in advance how you want to see the bonsai that you plan to grow on your own. Draw on a piece of paper the approximate shape of the crown and trunk, and also think about its future decoration. It is worth noting that you will have to keep this sketch for a long time, since growing a beautiful and stylish tree can take you more than one year.
Buying a ceramic bowl

Ceramic bowl
Choosing a container for bonsai is no less a responsible matter than buying the cutting itself. After all, this is also part of the composition, which plays a huge role in decorating the room. The bonsai must be in harmony with the chosen plant, it is also recommended to give preference to natural materials (clay, ceramics, etc.). In order for the tree to grow quickly and not hurt, it is necessary to choose a bowl with a large number of drainage holes.
Correct soil preparation

Bonsai soil preparation
In order to avoid accelerated growth of bonsai, it is not recommended to use fertile land when planting it. If you live in a city, then such raw materials can be easily found in flower shops.And in the case of living in rural areas, it is advisable to prepare a suitable soil mixture yourself. To do this, you need regular garden soil and some coarse river sand. The prepared raw materials should be thoroughly mixed, and only then proceed to planting the plant.
Sapling processing

Bonsai seedling processing
Before planting the cutting in a ceramic bowl with soil, you will need to grow it for a long time in a regular pot (about two years). In addition, thin branches should be removed frequently during this preparation, leaving a sturdy trunk and strong shoots. This procedure is necessary in order for the plant to acquire a good root system, as well as the desired thickness and size. After the trunk of your tree gets stronger and acquires special hardness, you can safely start forming the crown.
Crown processing

Crown formation
In order to create a form of a house plant that would be no different from a real tree, you must selectively remove shoots that do not match your old drawing. To give the individual branches suitable lines, they should be secured in the desired position with a thick, but soft wire. This must be done carefully so as not to harm the entire plant. First, you need to process the lower shoots, and only then go up. Do not pull the wire too tightly, as it will easily stick into the trunk, and then form ugly scars on it. It is advisable to leave the fixing elements for several months, because the shaping is considered complete only after, having removed the wire, you note the safety of the necessary lines.
Transplanting a Bonsai into a Ceramic Bowl
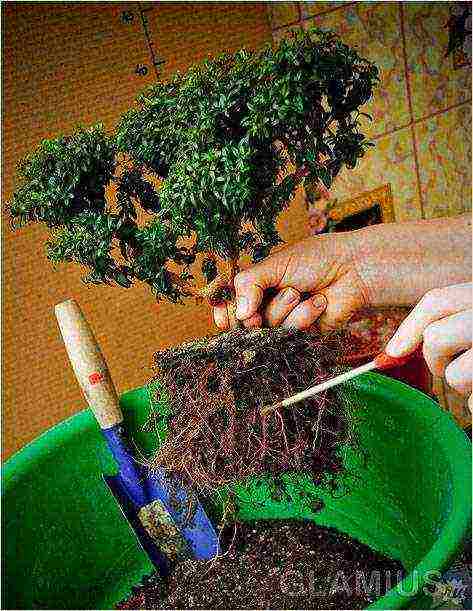

Bonsai transplant
For such a transplant, you should remove the plant from the container, and then clean the roots from the soil and remove unnecessary elements. Lay a dense netting at the bottom of the bonsai tree so that the soil is not washed out with the water during irrigation. Next, you should pour expanded clay, and then a little prepared soil. After that, it is necessary to place the plant evenly, straightening all its roots, and fill up the soil, securing the trunk well. The soil must be thoroughly watered, and, if desired, decorate it with decorative stones, ceramic chips, live moss, etc.
Video
To learn more about the art of growing bonsai at home, watch the following video:
Not only owners of private houses, but also residents of the most ordinary apartments can admire the beautiful trees. The ancient art of bonsai will allow you to place coniferous or deciduous plants in a small room. The first to grow shrubs and trees in small bowls were in ancient China, but the plants were selected not decorative, but suitable for food or necessary for the manufacture of medicines.
The Japanese, on the other hand, have always appreciated beauty and have been able to contemplate. They borrowed the practice of growing trees, but deprived them of any practical use. Bonsai is real the art of growing miniature treesthat anyone can master. What difficulties can a beginner florist face? And how to properly form the crown of a tree?
Choosing a future bonsai style
To get an unusual and spectacular plant, you need to decide what style of bonsai you are attracted to. Depending on the chosen direction, a specific type of plant is also selected. Beginners often make the mistake of acquiring the wrong trees and trying to give them the required shape.
So, there are several common bonsai styles that are easy to distinguish from each other.
Bonsai vertical style
This style has two subtypes: classic and free... In the first case, the tree trunk should be perfectly straight, have an ideal conical shape. The lower branches are distinguished by a large volume, towards the top of the branches they become thinner and thinner.
Free form implies the curvature of the tree trunk, which alternately "departs" to the right and then to the left. Yet the general direction of growth is upward.
Any plants are suitable for the vertical style, but the free subspecies is recommended for conifers.
Bifurcated trunk
This interesting shape can be obtained in one of two ways: by planting two different plants or from one root. It will be easier for beginners to get used to two different plants, and they need to be selected so that the pair has a pronounced leader. The weaker tree, however, should not be sick.
The composition can be either strictly vertical or with a slight slope.
Bonsai broom
This style of bonsai requires special attention to the tree as it is not easy to achieve perfect "equality" between all branches. The apical shoot is pinched at a height of about a third of the total size of the tree. From this point, skeletal branches begin to grow. Necessary keep equal proportions, the thickness of all branches must be equal. Thus, a beautiful and wide crown is formed.
Deciduous plants with spreading branches, which in nature form a large crown, are suitable for this style.
Platy bonsai
Such a plant is rare, since several trunks at a distance from each other are formed from one tree. How to achieve this unusual look? A seedling is selected, on one side of which the branches grow more actively than on the other. The "thick" part will become the basis for the bonsai. Excess branches from the other side are cut off, cuts are made on this side, and the tree itself is placed horizontally in a container with soil. Roots will begin to grow in the places of the notches. Thus, the branches of one side will turn into trunks over time.
Multi-stem bonsai
This style also has many stems from a single root. But the very shape of the tree can be almost any: vertical, curved and even inclined.
Bonsaz forest style
But in this case, the number of trunks determines the number of plants. Several trees are planted at once (always an odd number). The composition is formed rather compactly to emphasize the resemblance to a real forest. The central tree is usually taller than all the others, it is brought to the front, placing two more tall trees on the sides. Extra branches are removed from everyone, leaving bare trunks, the crown is thinned out. But the background is represented by smaller trees with dense branches.
Bonsai literary form
An interesting and unusual look of the plant is achieved by constant adjustments. The trunk of such a tree is constantly bending. It is quite simple to consider all the slopes, since the trunk is completely bare, leaving only the top with young shoots. The combination of a thick old trunk and young branches is especially appreciated in this style.
For the formation of bonsai, it is recommended to use densely branched coniferous plants.
Cascading bonsai
Such trees are a little more common because they look very impressive and immediately catch the eye. Cascading forms are typical for wildlife: rocky areas. A powerful root system is strengthened in the ground, and the plant itself hangs along the rock.
Separately highlighted and semi-cascade, which differs in the level of inclination. The lower branches of such a plant should be at the level of the base of the bowl.
Inclined barrel
Another common shape is a uniform slope on one side. The trunk can be either very thin or thick, but it is imperative that open roots remain on the surface. This view gives the impression of "tearing", as if a powerful hurricane was trying to uproot a tree.
Both deciduous and coniferous trees are suitable for formation.
Bent by the wind
The slope level in this bonsai style is close to critical. In nature, such forms are found on the coast, where the wind constantly blows only from one side.The trunk is formed in such difficult conditions and looks like it is constantly under pressure.
Choosing a cutting
There are many ways to grow bonsai. If you want to choose the style of the tree yourself and can wait, then do not purchase young plants, but give preference to cuttings or seeds. The last option is suitable for people who know how to wait.
The stalk is ideal for growing bonsai. It should be taken from a one-year (in some cases two-year) tree. The size of the shoot usually does not exceed 10 centimeters. In order for the root system to form quickly, special compounds are added to the soil, which accelerate root formation.
Make sure the cutting is from a healthy plant. The shoot should have no more than 6-8 leaves. The unfinished part is removed before planting in the pot.
Choosing a ceramic bowl
A very important part of preparation is choosing the right pot for growing your bonsai tree. The bowl should not only fit into the interior and be combined with the plant, but also meet many functional requirements. So, for example, notice the presence of wide drainage holes... Excess moisture can cause the development of diseases, rotting of the roots and cause the death of the plant.
The size of the pot must also match certain parameters. Experts recommend adhere to the following rules:
- the depth of the bowl is equal to the diameter of the trunk at the base,
- width - 2-3 centimeters less than the length of the branches,
- and the length is not more than two-thirds of the width or height of the tree.
However, you should not rush into choosing a suitable ceramic bowl, since the stalk is usually grown in a container, and transplanted into a beautiful pot only after a year or two.
Soil preparation before planting
Cuttings for the formation of shoots are planted in a mixture of peat and sand... The recommended depth for a 10 cm shoot is 3 cm. After watering, the plant is covered with polyethylene to protect it from temperature extremes, wind and sunlight.
Only after the tree gives its first shoots can it be taught to the sun and fresh air (if it is supposed to be grown on the balcony or outdoors).
It is recommended to transplant it into a ceramic bowl in a year or two, when the tree takes over and grows. At this moment, the most important phase begins - the formation of the trunk and crown.
To give the plant the desired look, you must first of all slow down its growth. And a properly selected soil will help with this. The characteristics of the soil, of course, depend on the specific type of tree. But it is still worth remembering that poor soil is the basis of bonsai... The composition usually includes peat, stones and sand, rotted leaves. The roots are pruned and the tree is transplanted into a prepared bowl.
How to grow bonsai at home?
The peculiarity of bonsai is that this art time is given daily... A good owner knows all the features of his plants, can remember all the branches and constantly monitors the condition of the trees.
First of all, it is worth taking care of growth, or rather, its slowdown. Even in sparse and rocky soil, a fairly large tree can grow if you don't artificially restrain it. For this, special nippers cut the trunk in several places... The juice will be used to heal wounds, not to grow quickly.
Pruning branches also slows down this process, but this method is rarely worth it. In addition, the branches should be clearly structured.
You also need to make sure that the tree takes the chosen shape. For this the trunk and branches are fixed with bandages or rings, even wrapped with wire.
Bonsai care
In order for the tree to delight you with its appearance for many years, try to observe simple rules:
- regular watering should not be done from above, but at the roots of the tree;
- branches and leaves need to be sprayed with water to nourish them and remove dust, but this procedure can only be carried out in the morning;
- the bonsai bowl should not be in direct sunlight;
- the plant should be protected from frost and protected from high temperatures;
- Regular pruning of branches and roots will allow you to form a tree of the desired size and shape.
How to grow bonsai at home: video
Some are convinced that bonsai is a variety of dwarf tree-like plants that are grown in standard pots. Others believe that bonsai is an art form or trend in Eastern philosophy that a tiny Japanese tree seems to complement. In fact, bonsai are really tiny trees, which are the most accurate copy of their tall relatives. They receive them - having comprehended all the subtleties of a special kind of art, and for years they successfully keep them in their home - only after understanding all the subtleties of Eastern philosophy based on contemplation, admiration and reflection. Previously, a unique Japanese tree as tall as an ordinary indoor flower could only be seen at exhibitions. Now bonsai has become incredibly popular and spread throughout the world. Many Russians have also begun to master the technique of its cultivation. It is simple only at first glance, but it contains many secrets and features.
Where to begin
If you have firmly decided that you need a tiny tree in a pot, the question arises of how to get it. To make the task easier, you can buy ready-made bonsai in the store. Then the duration of his life in the apartment will depend on knowledge and compliance with the rules of care. But many adherents of oriental culture certainly want to grow an exotic plant on their own from scratch. There are different types of bonsai, depending on the type of plant that will be converted into a dwarf. Almost any tree from the garden or from the nearest forest belt can become a candidate. The art of bonsai became famous thanks to Japan, but was born in China during the reign of the Tang Dynasty, when one of its rulers wanted to create a miniature copy of his empire. It was then that the clever ancient Chinese came up with the idea of making the same trees out of ordinary trees, only dozens of times smaller. The new agricultural technique was called "cultivated on a tray" or bonsai. Thus, observing certain techniques, any plant can be turned into a dwarf. But in practice, success often comes with trees that can withstand extreme conditions of existence, namely, develop in a miniature volume of soil, not get sick from changes in natural lighting conditions, changes in annual temperatures and watering. Therefore, no matter what types of bonsai you choose, it is important to take into account the natural living conditions of your pets and strive to get as close to them as possible.
There are different types of bonsai, depending on the type of plant that will be converted into a dwarf. Almost any tree from the garden or from the nearest forest belt can become a candidate. The art of bonsai became famous thanks to Japan, but was born in China during the reign of the Tang Dynasty, when one of its rulers wanted to create a miniature copy of his empire. It was then that the clever ancient Chinese came up with the idea of making the same trees out of ordinary trees, only dozens of times smaller. The new agricultural technique was called "cultivated on a tray" or bonsai. Thus, observing certain techniques, any plant can be turned into a dwarf. But in practice, success often comes with trees that can withstand extreme conditions of existence, namely, develop in a miniature volume of soil, not get sick from changes in natural lighting conditions, changes in annual temperatures and watering. Therefore, no matter what types of bonsai you choose, it is important to take into account the natural living conditions of your pets and strive to get as close to them as possible.
Where to get planting material
As mentioned above, different plants, both conifers and deciduous, are suitable for bonsai. When choosing, you need to pay attention to the size of their leaf blade. Since the potted plant will be miniature, it is desirable that the leaf blades of its prototype are not too large. Otherwise, the small trunk simply will not be able to hold them on itself. The second condition is that the species of plants from which different types of bonsai are created have a genetic tendency to form a dense crown. Having decided on the candidate, it is imperative to take into account in what soil your future bonsai grows in the wild, with what illumination, with what humidity. All this will exactly need to be recreated at home in a pot. In practice, success is achieved with fruit trees, citrus fruits, myrtle, maple, rhododendron, ficus and many others.
Yamadori
There are not only different types of bonsai, but different technologies for its propagation, or, more correctly, the starting operation of growing. Yamadori is considered to be the simplest technology.It consists in the fact that in its natural habitat the necessary young tree is looking closely. It is dug in a circle, too powerful roots (if any), truncated and left alone for three months. Then it is removed with a lump of earth and placed in a selected flower pot (bonsai). For early adaptation, the plant is shaded, sprayed, and a temperature regime similar to the natural one is created.
Toriki
This technology in Russian means trivial cuttings. It is important to respect the timing of this process. For example, in Russia, it is desirable to cut hardwoods by cuttings at the end of spring, and conifers, on the contrary, at the beginning. Plants from which cuttings are harvested must be five to ten years old. If you strictly follow the rules for harvesting planting material for your bonsai, caring for it in the future will not bring disappointment. Cuttings need to be cut only in cloudy weather, cutting off the still not stiff shoots. Their length can vary, depending on the number of internodes. There should be no less than three of them and it is not desirable that there should be more than five. The upper edge of the cutting is made even, and the lower edge is beveled, placed in water, covered with a damp cloth. Another practiced toriki method is to carefully remove a strip of bark no more than 2 cm wide on a branch that you like, or an incision is made on the branch, into which a pebble is inserted. This place is abundantly moistened with epin, wrapped in sphagnum, polyethylene on top, secured and wrapped on both sides to stop the air supply. This compress is regularly injected with a syringe. The sprig should take root in about 60 days.
Misho
This method is ideal for beginners and means seed reproduction. Maples, oaks, myrtle, pomegranate, citrus fruits are suitable for this. You can collect ripe seeds from selected trees, from which bonsai should be obtained without any problems. For this alone, the seeds must go through all phases of stratification. To facilitate the task, you can carefully remove the already sprouted seeds from the ground in the spring and place the ready-made sprouts for the future bonsai in prepared bowls.
Classification according to size
There are not only different types, but also styles of bonsai that differ in size. It is surprising that the world of miniature plants has its own tiny giants and midgets. The international classification distinguishes:
1. Mame. This group is made up of trees up to 20 cm high. Among them:
-Keshi-tsubu (Lilliputians in the country of Lilliputians, up to only 2.5 cm high).
- Sieve (up to 7.5 cm high, maximum 8 cm).
-Gafu (up to 20 cm high).
2. Syokhin. This group is made up of plants of intermediate sizes between very small and just small. There are two subgroups here too:
-Komono (about 20 cm tall).
-Mabi (up to 25 cm).
3. Kifu. The group is in the middle position. The plant included in it can grow up to 40 cm.
4. Ty. Plants in this group are almost giants and reach one meter in height. Subgroups:
-Tyukhin (up to 60 cm).
-Omono (up to 100 cm).
5. Bonju. In the world of midget plants, these are already giants, capable of stretching up to 120 cm and higher.
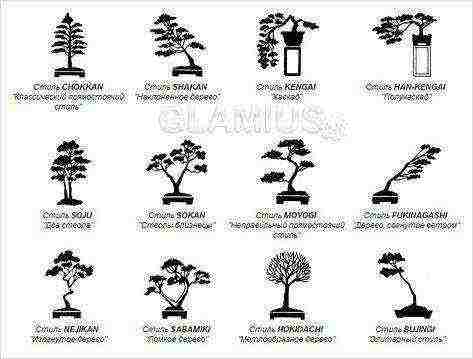
Classification by crown shape
It turns out that there are also different styles of bonsai based on how the crown looks. The traditional ones include:
-Tyokkan (erect trunk, thickening towards the base).
-Moyogi (base and top of the stem are perpendicular to the ground, and the middle is curved).
-Sokan (the tree has two stems, each with its own crown, forming something whole).
-Syakan (trunk without curvature, but growing towards the ground at an angle).
-Kengai (trees resemble classic weeping ones, that is, they grow with trunks inclined below the pot, as if falling).
- Khan Kengai (the stem of the tree is also falling, but the top is always in line with the ground of the bowl, and the outgoing branches resemble independent plants).
-Bundzings (the tree grows with an erect stem, but with a minimum number of branches).
-Sekijёju (there are stones in the bowl on the ground, and the roots of the tree seem to be entwining them).
-Ishitsuki (a composition of curly stones is created in a bowl, and plants grow in their crevices).
-Hokidachi (the stem of the plant is straight, and the twigs form a beautiful spherical crown).
-Yose ue (several trees grow in the pot, not a multiple of 4, different in height and age).
-Ikadabuki (imitation of a tree, as if falling to the ground, from the trunk of which individual branches grow upward).
Exclusive Styles
In addition to the classical ones, which are considered simpler, in the art of bonsai there are very complex ones that require high skill. It:
-Netsuranari (a tree from one root grows several trunks, which are intricately intertwined with each other).
-Fukinagashi (a complex composition in which the bonsai grows not just at an angle, but in such a way that its twigs and leaves are arranged like a tree is tending to the wind).
-Sakei (an imitation of a whole corner of nature is created in a bowl - a forest or a mountain area, and bonsai plants make this imitation more natural).
Growing rules
It is not very difficult to maintain a bonsai at home, the care of which is based on strict adherence to the rules. Those who believe that dwarf trees should grow only in the house, as an element of decor, are mistaken. Very often, bonsai compositions are placed in the fresh air, and they are brought into the house only with the onset of cold weather. If the winters are not harsh, the bonsai can be left outside, but the bowls must be placed in a container with a large diameter, and covered with a thick layer of moss from above to the very branches of the tree.
It is very important that deciduous bonsai in winter, as well as in natural conditions, shed their foliage and remain dormant for some time. To do this, they are taken out into a cool room. The third condition for success is strict adherence to lighting and humidity standards. If the bonsai lacks natural light, they additionally turn on the lamps, but at the same time take into account the heat generated by them. You can maintain optimal humidity with an electric humidifier. If there is none, the pot with the plant can be placed in a tray lined with pebbles and half filled with water. The simplest, but also the most ineffective way is to spray the plant crowns.
Landing
When the planting material is prepared - cuttings or seeds - the bonsai needs to be placed in his house. The Japanese and Chinese use bowls and low flower pots for this, covered with glaze or matte, but always having several drainage holes. So that the soil does not wash out of them, the holes are covered with a piece of tile. The shape of the pot can be any. It is best to take the soil for indoor bonsai the same as that of its outdoor relative. Some masters prepare the soil separately. Everyone has their own recipes. The most common ones are:
- a mixture of equal parts of clay, fine gravel, humus, stone chips or sand;
-clay, humus and gravel in the ratio (3: 5: 2);
-clay humus, gravel (1: 5: 3);
- leafy earth, coke, sand, crust, volcanic soil.
In any case, the soil should be easy to pass water in order to avoid stagnation. In addition, experienced craftsmen advise disinfecting the pot and soil before planting. The stratified seeds are placed in the ground, covered with glass, the whole period of germination is maintained at a warm temperature and moderate humidity. The plants that hatch and have reached the stage of 2-4 leaves dive. In order for the root system to develop, the picking operation must be carried out several more times. Cuttings and seedlings are planted in the same soil as the seeds. For better rooting, the cuttings are covered with foil.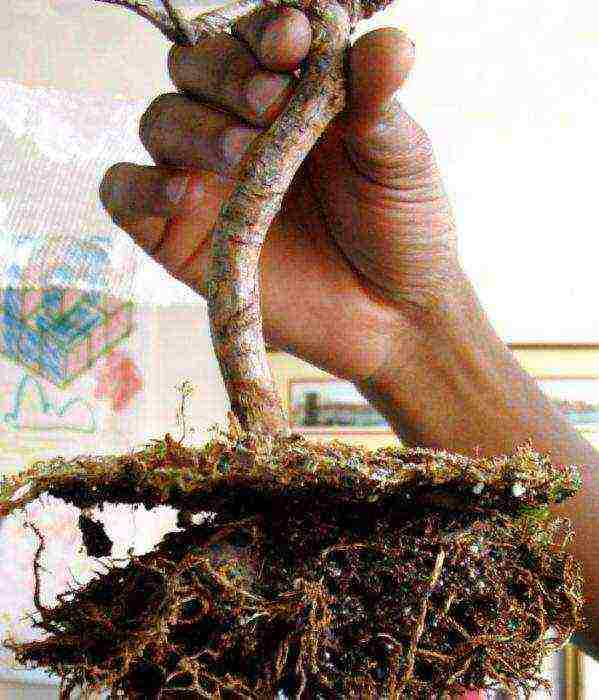
Transfer
Growing bonsai is unthinkable without a transplant, which must be performed every two, maximum three, years before the start of sap flow.This operation is also carried out if there is a suspicion of decay of the root system. Before transplanting, the plant is left without watering for a couple of days. Remove from the pot with a knife. The soil is carefully removed from the roots, all suspicious roots, and large roots are also removed. The pot is disinfected, filled with a couple of centimeters with new soil, the roots remaining after pruning are straightened with a wooden stick, laid out on the ground, sprinkled with earth, compacted and watered. The plant can be fixed with a wire inserted into the drainage hole.
Bonsai (plant): how to care
Keeping small trees is not very difficult. They need to be regularly watered with cold water, making sure that the soil in the pot does not remain dry or too waterlogged. During the dormant period, the plants are watered less often, during the growing season more often. Bonsai feeding is mandatory. Do this from the beginning of the growing season every week, adding sapropel or urea. You can also use mineral fertilizers in the form of granules or solutions. Fertilizers containing a lot of nitrogen are applied after the end of the first wave of growth. With the onset of a dormant period, feeding is stopped. Coniferous bonsai also do not feed in winter. You cannot fertilize sick and recently transplanted plants.
Bonsai formation
How to make unusual out of ordinary wood is perhaps the main question. The technologies are different here. In our conditions, even novice bonsai maple is good at it. Having chosen the desired variety, according to the general rules, seeds or cuttings are planted, the first year the plant is allowed to grow stronger. In the future, they change the appearance of the trunk, gently wrapping it with soft (copper or aluminum) wire. But with maples, this does not always work. Most often they are formed by pruning. To stop the growth of the top, new shoots are regularly removed on it. Maple has a rather large leaf blade. To reduce it, around the middle of summer, the grown leaves are removed, leaving the petiole. For this period, the tree is moved to a shaded place. In order for the maple bonsai to grow lush, when pruning, you can truncate a too elongated trunk (cover the wound with an antiseptic), remove skeletal branches, and pinch young shoots. To give the trunk a slope or bends, a weight can be tied to it during the period of active growth, or it can be gently bent in the desired direction and secured with copper wire, placing a cloth under it. Several methods can be used to achieve the desired barrel thickness. In some plants, young stems are spliced, planting them next to each other and fastening them together. For maple, this method is not very successful. The thickness of the trunk in this case is achieved by truncation.
Bonsai cultivation is a constant discovery, discovery and creative work that makes a person truly happy. And in order to achieve this effect, you need to know the methods and some features of growing bonsai. In order to grow bonsai according to all the rules, you need special dishes, tools, special care, etc. etc. In this article I will talk directly about the growing process.
Bonsai from Sargent Juniper. Age 15. Han-Kengai style
Content:
- Choosing plants for bonsai in the nursery
- Bonsai taken from nature - Yamadori
- Bonsai from native tree species and their benefits
- Bonsai grown from cuttings
- Bonsai grown from seed
- Bonsai sizes
- Features of growing bonsai
- Artificial aging bonsai
- Keeping the needles and shoots small in pines and spruces
- Air layering in bonsai
Choosing plants for bonsai in the nursery
Young plants purchased from the nursery can be used to form beautiful bonsai relatively quickly. Most of the plants sold in nurseries have been container grown for many years.As a result, they tend to develop a well-formed and dense root system, which is ideal for bonsai formation.
The plant is removed from the container, the old soil is removed and the first root pruning is carried out to obtain a flat root system. The plant is then transplanted into a regular container, now filled with potting soil for bonsai. Very soon, such plants can already be transplanted into low special containers (bowls).
The only thing that needs to be remembered when carrying out a strong pruning of roots is the observance of the correct timing of planting plants, in other words, all these activities are carried out at the end of winter, while the period of active growth has not yet begun.
The assortment of plants sold in nurseries is very large and it is easy to get confused in it. That is why it is best to thoroughly review all available plants in the nursery and try to find the most suitable specimens for the formation of bonsai. In addition, you should regularly visit horticultural centers and nurseries and look there into the farthest corners, where prematurely aged dwarf trees may be located.
True, beginners are advised to select younger plants, from which it is easier to form bonsai. The choice of plants must be very critical. Bonsai trees should be densely branched to the ground so that after pruning, branches suitable for different styles can be left.
When inspecting the plants, the soil around the trunk should be slightly excavated in order to be able to get a good look at the base of the trunk. The grafted plants should be grafted in such a way that the grafted bonsai do not show the graft site.
Special care is needed when buying plants with a very dense crown, the inside of which is usually completely bare. It takes such plants a very long time for new shoots to appear on the inside of the branches. This applies mainly to large specimens of common spruce (Picea abies) "Pumila Glauca" and gray spruce (Picea glauca) "Conica".
Rhododendrons with a spherical crown shape are more suitable, since they relatively quickly give young shoots from old wood. For the formation of bonsai, you can safely recommend all low-growing forms and varieties of pine, not grafted fan maples, field maple, all types of barberry, local species of elms, not grafted hornbeam, cedar elfin (dwarf pine), juniper, hawthorn and many others.
Bonsai. Composition of several trees
Collectors who have the necessary experience and prefer difficult to form and expensive plants can only be advised to look for suitable starting material in nurseries. Since bonsai became famous in Germany, the first nurseries have also appeared, which, along with the usual assortment, began to grow trees intended for bonsai formation.
They now have a good selection of suitable and very inexpensive plants that can make very beautiful and very valuable bonsai in a couple of years. Therefore, nursery plants are the best way to learn how to form bonsai.
Bonsai taken from nature - Yamadori
There are beautiful trees in nature, which, despite their age, are excellent for the formation of bonsai. Mainly, high in the mountains, on the border of forests, you can find century-old trees that do not exceed 50 cm in height. A very short growing season allows plants to grow only a few millimeters per year. Due to constant strong winds, ice and snow storms, they remain dwarf and acquire a bizarre, often very curved shape.
In order to dig up plants in nature, you must obtain permission from the landowner.When digging up a plant, a seedling is planted in its place, if possible. In order to form a harmonious bonsai from such a source material, it is necessary to have the appropriate experience. First of all, it can be very difficult for novice bonsai lovers to make something decent out of this intertwined, intricate and abstractly shaped material. That is why they are encouraged to look for younger specimens with a compact root system.
80-year-old trees 50-60 cm in height often have roots of 5 m or more. Such plants are found on rocky soils, as their roots, in search of moisture and nutrition, grow deep into cracks and crevices of rocks. In order to dig up such plants, it is necessary to skillfully cut their long roots. In some particularly unfavorable cases, this procedure is stretched for years, so that during this time new roots form at the base of the trunk, thanks to which the dug plant can survive.
The best time to dig up plants is in early spring, when the soil has thawed and plant growth has not yet begun. From the tool, you must have a folding shovel, a climbing pick, pruning shears, a folding saw, a hammer and a chisel.
The roots of the excavated plants are placed in plastic bags with damp moss to withstand transportation. At home, these plants are first planted in large plastic containers.
The soil used is Japanese clay granulate (Akadama), as large as possible, 6-12 mm. After planting, the plants are placed in a shaded place protected from strong winds. After about 3 years, they can be transplanted into a smaller container. Typically, it takes 5 to 10 years for the excavated plants to produce powerful and impressive bonsai. Older yamadori take even longer for them to take root well in the container.
Nursery plants, on the other hand, root perfectly, most often in the same year. If strong leaves or needles have begun to form on the tips of the shoots, this is a sure sign that the plant is well-rooted. Only after that it is necessary to start fertilizing with fertilizer. When transplanting, deciduous trees take root much faster than conifers. Juniper dug out in nature takes root especially slowly in the container.
That is why it is advisable to dig up the plants not in one step, but to gradually chop off long roots year after year. After a few years, such a plant can be painlessly dug up.
For a beginner who has yet to learn how to recognize shapes in the original plant material and who still feels insecure about the techniques of forming a bonsai, the use of yamadori is not recommended.
Younger, densely branched deciduous trees with finger-thick trunks are fine for beginners, although they are not typical yamadori. For experienced bonsai collectors, there is also the option to take plants from their garden.
Over time, it is often necessary to remove some trees in the garden, because they were planted too often, or the question of redeveloping the garden is on the agenda. These plants are the ideal starting material for the bonsai collector. Very often it (material) is distinguished by trunks as thick as an arm, powerful root bases and strong long branches.
These plants also take a while to root well, so they are first planted in large plastic containers. After about three years, depending on the size of the plant, they can be transplanted into smaller containers. Already in the plastic container, you can begin to roughly shape the plant until after three years it is transplanted into a suitable bonsai container. For such plants, the roughing phase lasts about 46 years.But later you get a bonsai at the age of about 50 years, looking very impressive and powerful.
Bonsai shaped rhododendron. The plant is 22 years old
There are a number of tree species native to Europe that are well suited for bonsai formation. Often, local breeds are even much more resilient than exotic species. To this it should be added that we know better their needs in terms of location, quality composition and structure of the soil, as well as possible pests and diseases. The trees growing in our forests are frost-resistant, and therefore, they do not need to overwinter indoors.
You can find out many questions for yourself at the place of natural growth of the selected trees. In principle, bonsai can be grown from any European tree species that has never been used as a bonsai before. There are many possibilities for this.
Firstly, you can simply experiment on the plant with soil, light and water for irrigation, which, in general, is hardly worth recommending, or you can give preference to a more acceptable solution, which consists in learning about the growing conditions of this or that species in nature.
When growing bonsai from local tree species, you can get a clear idea of the growing conditions of a particular tree if you carefully observe it in its natural habitat and ask yourself the following questions:
- What soil does the tree grow on?
- How much light does it need?
- Is the location of the tree shaded or light?
- Does the tree only grow in a protected forest or ravine?
- Which places does it prefer: dry or wet?
Example: it is necessary to form a bonsai from black pine. In search of old trees, they usually go to tall sparse forests. The tops of the black pine are densely covered with needles. The rest of the crown, primarily its lower part, remains transparent. This is because the black pine is a very light-loving plant and develops lush needles only at the tops of the crown.
From this it should be assumed: black pine bonsai need very bright lighting, therefore, the place for them should be several meters away from walls and buildings and slightly raised above the ground, so that the bonsai also receive a little light from below.
In natural conditions, pines grow on well-drained calcareous-sandy or karst foundations. Therefore, for bonsai, a soil mixture of coarse sand or crushed stone with a small addition of humus is chosen. When forming a bonsai from black pine, it is not at all necessary to accurately copy the natural shape of the tree, traditional Japanese forms are also possible.
Thus, the natural forms of trees of any species growing in our country can be used as a sample for their subsequent transfer to bonsai. For those who want to engage in the art of growing bonsai more intensively and purposefully, it is necessary to make it a rule to pay attention to the beautiful trees on the street and study them closely, especially those that you pass by every day.
When forming bonsai, it is not at all necessary to be guided by the classical Japanese or Chinese forms. When working with local species, it is even much more reasonable to take the shape of the trees growing in our forests as a reference. We have some very beautiful trees that deserve to be modeled on bonsai.
In addition, it is much easier to carefully examine and study trees in nature and then transfer their shape to bonsai. Isn't it interesting to imagine that an oak, only a meter high, together with twigs and branches, can look like an old adult tree. Among the tree species growing in our latitudes, there are at least a dozen that can certainly serve as a good starting material.
Anyone who from time to time makes attempts to use tree species that are almost unknown in this capacity to form bonsai, very soon comes to the conclusion that not every tree is suitable for forming bonsai from it. So, for example, the chestnut has amazingly beautiful flowers and leaves, and besides, it also has a magnificent crown in shape, however, because of its huge inflorescences and leaves, this tree is not suitable for the formation of bonsai.
In contrast, hawthorn bushes are not very attractive in nature and do not have much charm, however, for use as a bonsai, they are an excellent source material.
Therefore, when choosing local tree species, you need to mentally answer yourself the following questions:
- Does this tree species have small leaves?
- Does it give young shoots from old wood?
- Does it form many ramifications?
- Do his shoots grow strongly?
- Does it grow well in a small pot?
- Is the base of the roots beautifully formed?
However, in addition to the type of wood, the appearance and condition of the individual plant are also decisive when choosing the starting material.
Bonsai. Youse-Ue Style
Growing bonsai from cuttings is also time consuming and requires patience. True, growing plants in this way gives a gain per year compared to seedlings.
Cuttings are cut pieces of branches (lignified shoots) without roots, which are cut from healthy mother plants and inserted into the soil for rooting. The right time for grafting conifers is early September or April.
Cuttings in deciduous trees are best cut from early to late June. To stimulate root formation, cuttings can be treated with a special growth stimulator (phytohormone). Deciduous tree cuttings take root after a few weeks.
In conifers, the rooting process can take more than a year. It is best to use plastic mini-greenhouses as utensils for rooting cuttings. Its lower part is two-thirds filled with a mixture of sand and peat, and the cuttings are stuck into the soil at an equal distance from each other.
Then the cuttings are carefully watered and covered with a transparent lid on top of the greenhouse. To place a greenhouse with cuttings, a darkened place is chosen and the soil moisture is monitored daily, if necessary, the soil in the greenhouse is watered.
When young leaves appear on the cuttings, which is possible in a couple of weeks, this means that roots have already formed. Now the transparent cover of the mini-greenhouse can be lifted from time to time for airing in order to harden young plants and gradually accustom them to the usual climate. After a few months, the cuttings are already well rooted and can be planted in separate containers.
For this, a loose, clay-containing soil mixture for plants is used. This year, young plants do not need to be fed with fertilizers, since fresh soil contains a sufficient amount of nutrients. To overwinter such plants, it is necessary to take care of a special shelter, since their delicate roots are not yet able to withstand prolonged frosts. Containers with young plants should be well dug into the soil and covered with a film folded in several layers on top to protect from the wind.
Not all trees reproduce by cuttings. For example, cedars and pines cannot be propagated in this way. They are propagated exclusively by seeds. Elms, on the other hand, can be grown very quickly from cuttings, like most trees and shrubs used for hedges such as privet, hornbeam, field maple, barberry and dwarf elm.
Bonsai from Lanta Camara, the plant is 3 years old. Sekijoju Style
Growing from seed is the longest-lasting way to form bonsai.It takes 12 to 15 years to get approximately bonsai-like plants from seeds. Most of the plants sold in horticultural centers and nurseries are of this age. What is such a long journey for?
There are some types of trees in which the optimal shape can be achieved only if you begin to form the plant from the very first days of its life. This applies, for example, to elm trees, from which it is planned to form a bonsai in a strictly vertical style. In such plants, it is necessary to cut out part of the roots already in the first year and regulate the growth of young stems by pruning.
After about 20 years, it will already be clearly noticeable that these plants were formed at an early stage of their development. This can be determined primarily by the base of the roots. All the roots protruding on the surface of the soil diverge from the trunk in the form of a star, and the trunks themselves are beautifully shaped. When looking at the base of the branches, their harmonious distribution is striking.
The proportion of trunk height to crown height forms a balanced spatial relationship. All these benefits come from growing plants from seeds. In one-year and two-year-old seedlings of coniferous trees, the trunks can be very strongly bent, giving them any complex shape.
In all conifers with rough bark, the wire applied to the trunks and branches should grow into the wood to a depth of bark thickness. Thanks to this, the bent and uneven trunk additionally gains the effect of healing wounds, which quickly heal in young plants.
Two-year-old black pine trees, for example, can be very strongly bent in winter, which is possible only with seedlings. The overlaid wire is allowed to grow into the bark and is removed only after 3 years, without fear of damage to the plant.
Later, the wire can be applied again to get the effect of scarring again. When the plant grows to such an extent that it is ready for display as a bonsai in the next 45 years, in no case should the wire be allowed to grow into the trunk. Since the trunk of plants grows in thickness much more slowly with age, wounds from wire that have grown into the bark grow much worse and it will take more than a dozen years for the last traces of the wire to become invisible.
Collecting tree seeds on your own is very exciting and full of surprises. While walking in the park or in the forest, you can constantly find more and more seeds of trees and shrubs. If bonsai seeds are harvested in the fall, they can be sown directly into seed bins or bonsai containers.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the following: there are seeds that need cold (freezing) for germination.
These are hard-shell seeds such as cherry, blackthorn, hawthorn, hazel, juniper seeds. The seeds of these trees are sown in a flat container with wet sand and covered with a layer of sand on top. Then the container is covered with foil so that the crops do not dry out. After that, the container with the sown seeds is taken out into the street in a place darkened from direct sunlight and left there for the whole winter so that the hard shell of the seeds will crack under the influence of frost. The first shoots appear in the spring.
Usually, not all seeds germinate. In this case, such seeds are not thrown away, but they are trying to get seedlings from them for the next year. You can also artificially freeze the seeds in the fridge freezer. Soft-shelled bonsai seeds can be partially sown as early as fall, immediately after harvest. Mountain pine seeds are harvested in August and sown immediately. They germinate after 34 weeks.
The container with the emerging seedlings is dropped in a place protected from the weather so that tender seedlings do not die in winter from drying out the soil. The seeds of most maple trees found in Germany also germinate in the year they are harvested.
To do this, proceed as follows: the seeds are scattered into a flat container with wet sand, after which they are sprayed with water from a spray bottle. A newspaper is then placed on the seeds to keep them moist and to allow some light to pass through the newspaper, since maple seeds need light to germinate. If the winter is mild, then the first shoots appear already in the winter. A year later, next spring, when the seedlings are a little lignified, they can be carefully planted in small pots and form-forming pruning carried out during the summer.
Bonsai from Sargent Juniper. Grown since 1905. Han-Kengai style
Bonsai can vary greatly in size. The smallest of them barely reach a height of 8 cm, however, there are also trees of impressive size with a height of 130 cm. At the same time, it is not at all the case that small bonsai are young, and large ones are old, grown over the years.
The future size of the bonsai is approximately established at the very beginning of formation. More often than not, the main skeletal branches, at least their rudiments, are already on the plant, and they largely determine in what style a bonsai can be formed. And although over the years bonsai grows several centimeters in height, the growth of the tree is limited mainly to the development of the ideal shape, which the amateur seeks.
The ideal size of a bonsai depends primarily on the size of the leaves. Bonsai trees of any size can be formed from trees with small leaves.
For trees with large leaves or long needles, a minimum size must be set at which they can be represented in the correct proportion (the ratio of the size of the leaves to the size of the tree itself). For example, a chestnut must be between 1.20 and 1.50 m in height to look harmonious.
Suitable trees for different bonsai sizes:
- 8-20 cm: juniper, irga, rhododendron, spruce;
- 20-30 cm: barberry, field maple, rock maple, privet, mountain pine with small needles;
- 30-70 cm: birch, hazel, pine, ash-leaved maple (American), elm;
- 60-100 cm: beech, oak, elderberry, false-sycamore maple (sycamore), sycamore maple, black pine, larch, linden, ash, ash-leaved maple;
- 100-130 cm: plane tree, chestnut, black pine, elderberry, acacia, wisteria.
Features of growing bonsai
For the formation of a certain shape of the branches and trunk of the bonsai, usually, you cannot do without the use of wire. It does not matter at all whether you put wire on the branches or change their direction with the help of tensioning devices, any technique of working with wire is very important for the formation of bonsai.
Wire-laying is the most time-consuming bonsai shaping technique, especially in conifers. Here it is necessary to fix with wire all branches, without exception, to the very top of the shoots. In deciduous trees, the shape can often be perfectly adjusted only by pruning the branches, and the need to apply wire to the branches is relatively rare.
In trees with smooth bark, such as beech, elm, maple, linden, the wire should remain on the plants only for a short time, since the ugly marks from the wire ingrown into the trunk remain visible for decades. Things are quite different with junipers or pines.
These trees have a rough bark and wire marks grow overgrowth relatively quickly. However, even in such trees, the superimposed wire should not be allowed to grow into the bark, since otherwise spiral scars on the trunk will form here too.
Wire is best done in winter or early spring when bonsai pruning is also done. Deciduous trees still have no leaves at this time of year and all branches are easily accessible.
With the beginning of sap flow and the growth of young shoots in spring, the branches quickly become thicker, so the wire must be applied very weakly and subsequently regularly checked so that it does not cut into the bark or grow into the wood.
After about three months, the desired shape is usually stabilized and the wire can be removed. It is carefully bitten off with wire cutters, and not untwisted, as this can easily break off the branches.
Correct wire placement requires skill and dexterity. Therefore, before starting to wire the fragile bonsai branches, you can practice applying wire to tree branches from a garden or forest.
The wire used is copper-plated aluminum bonsai wire of various thicknesses, from 0.7 to 7 mm, sold in specialized stores. To determine the correct thickness of the wire, there is a basic rule: wire thickness = 1/3 of the thickness of the branch it fixes. Thus, with a branch thickness of 1 cm, a wire with a thickness of about 3 mm should be used.
Iron wire or wire used in floristry is not suitable for the formation of bonsai, because it is not flexible enough and rusts. When the bonsai is first formed from the original plant, the wire is applied entirely to all branches, including their thinnest parts.
In this case, no one branch should intersect with another. In conclusion, each branch is individually given the desired direction and shape. Bonsai wire is not done to decorate the tree, but only to improve and change its shape.
Bonsai with wire applied to the trunk and branches should not be displayed or displayed at exhibitions. Wire staples are used wherever it is no longer possible to achieve the desired result using wire overlay, for example when changing the direction of growth of thick branches and trunks.
In multi-stemmed bonsai, wire staples can be used to correct or correct the growth direction and shape of individual stems.
This work requires the application of a certain amount of force. In this case, it is necessary to regularly check whether the wire has grown into the wood, and from time to time rearrange the brackets.
In order not to damage the bark of the tree with wire braces, pieces of leather are placed under them. Changing the direction of growth of branches with the help of tension wire devices is appropriate where it is no longer possible to overlay wire on too thick and powerful branches.
Pulling the branches down, of course, is not such a laborious process as laying the wire. The disadvantage of wire tensioners is that this method allows you to change the direction of growth of the branch in only one specific direction. This bonsai shaping technique is used primarily where branches grow upward and need to be pulled downward.
Learning how to accurately and accurately shape a bonsai with wire takes time and training. That is why it is advisable as an exercise to often put wire on trees and give the branches a different shape. Only with the help of regular training can you constantly improve your skill in the formation of bonsai.
Indian rhododendron in the form of bonsai
Various techniques and techniques are used to give a relatively young bonsai the appearance of an old tree. One of them is the removal of bark from branches and trunk using a knife or nippers. The job will be more difficult when the trunk needs to be cut or split. To practice these techniques, you need a certain theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
In addition, you need to know that you cannot remove the entire bark from those branches or trunks that are supposed to be left alive.It is necessary to leave thin strips of bark leading to the top of the branch or trunk, through which water and nutrients will flow to the needles.
The situation is different with parts of branches and trunks that should be dead on the bonsai. From them, the bark can be removed entirely and the bare wood can be processed with a wood carving knife. Removing bark from branches and trunk is not particularly difficult, but processing bare wood with a wood carving knife (chisel) requires a certain skill.
Therefore, before starting to work with bonsai, you need to practice on a piece of wood. Conifers such as juniper, yew, spruce and pines are ideal materials for artificial aging among bonsai trees, as their wood is not attacked by fungus and does not rot. However, deciduous trees can also be artificially aged.
To confidently master these special techniques, it is imperative to observe plants in nature. Trees in "war zones", that is, in particularly open and unprotected places, are the best examples.
Particular attention should be paid to trees marked by lightning, windbreak or drought. Before starting work, it is necessary to prepare a suitable tool and aids. Among them there must be a set of knives for wood carving, pliers for removing bark, nippers of a concave shape, skin, a special bleaching agent with dye for impregnating bare wood.
There are also many electrical tools that make the job much easier. However, they are more difficult to handle. That is why, at the very beginning of mastering the techniques of aging bonsai, it is necessary to use a conventional tool. Those who are constantly engaged in this craft, using the appropriate tools, will quickly find out which power tool for wood carving can be used.
Sharimiki - a technique of artificial aging, in which the bark is removed from a significant part of the bonsai branches, after which the bare wood is processed with a knife or a special cutter. Beginners should not use expensive plants for this, because it takes a while for the necessary sense of form to develop.
Sabamiki is called a bonsai with a split trunk. Outwardly, they look like trees hit by lightning. Very often they no longer represent whole trees, but they are very expressive. In bonsai, this effect can be achieved by splitting the trunk with nippers and wedges. Thanks to this, the tree itself becomes more powerful and strong.
Plants found in nature suitable for sabamika, which have the desired trunk thickness, often exceed 2 m in height. as if it had been struck by lightning. The top of the trunk needs to be tapered to make the tree look natural. Balls can be used in such places of the trunk.
Red Maple Bonsai
Pines growing in the forests of Germany often have very long needles, especially black pine. The size of the needles in these trees can be slightly reduced by watering the plant less and using a leaner potting mix. It is also desirable to apply fertilizers less frequently.
In order to keep the general shape of pines and spruces compact and harmonious, the tops of young shoots are broken from the pines from April to early May. In spruce trees, young shoots are allowed to grow a little, and then they are shortened by half or two-thirds.
Thanks to radical breaking out or cutting off the tops of young shoots with the tips of scissors during the summer, new tender buds are formed on the part of the branches covered with needles, which bloom the next year. A year later, new apical shoots are formed.
They are allowed to grow long enough and then shortened by one third or one quarter of their length. From September to the end of October, two or three-year-old needles are plucked or trimmed.
Bonsai from Rhododendron
Air layering in bonsai is obtained in cases where a too high trunk disturbs the harmony of the tree, in addition, with ugly or unevenly diverging roots or when the trunk of the tree rejuvenates downward.
Air layers can also be obtained from beautiful tree branches growing in natural conditions. Bonsai hobbyists and collectors in Germany do not use layering as often as, for example, in Japan. However, this technique is necessary for many bonsai to improve the shape of the tree or get a new bonsai from a beautiful bonsai-like branch. The very technique of obtaining air layering is not particularly difficult. It takes longer for conifers than for deciduous trees.
Technique for obtaining air layers in deciduous trees
Suppose you want to get an air cut from a bonsai with a poorly formed stem. To do this, a circular incision is made on the trunk or branch above the ugly formed place and a strip of bark is removed. Then a small amount of wet sphagnum moss is tied to the cut site. On top of the moss, a kind of larger casing of a metal mosquito net is fixed, which is filled with soil mixture for bonsai.
Then the plant is watered as usual. In late autumn, the cut site is checked. To do this, open the metal mesh and carefully remove the soil and moss. If the roots are formed evenly along the entire circumference of the cut, then the metal mesh is fixed in the same place and its inner part is again filled with soil. Now you need to wait until stronger and more powerful roots are formed. The trunk can then be cut slightly below the new roots and the resulting new bonsai can be planted in a container.
Sokan style bonsai, Sokan
Technique for obtaining air layers in conifers
The technique here is slightly different. On the trunk of the tree, not a circular cut is made, but a loop of wire is applied, after which it is pulled tightly and turned so that the wire cuts a little into the bark. Then, with a small hammer, gently tap the wire around the trunk so that small wounds form on the bark. In this way, root formation can be stimulated. A small part of the trunk or branch on top of the wire is treated with a growth stimulator (phytohormone).
Then a handful of wet sphagnum moss is applied to this place and fixed with bast or twine. After that, a metal mesh is applied around the trunk, as in the first case, and filled with soil mixture for bonsai. After a year or two, new roots are formed. When they are strong enough to feed the tree with water and minerals, the trunk of the bonsai can be cut between the old and new roots and planted in a container.
In deciduous trees, air cuttings are obtained from mid to late April. You can carry out a similar procedure for conifers a little later. In this case, the air temperature should be in the range of 18-22oС. Caring for plants is the same as for freshly planted bonsai, namely, you need to put the plants in a slightly shaded place and rotate them every 14 days, since the roots grow faster in shaded areas.
Plants are not pruned during the production of air layers, since the strong growth of branches and shoots contributes to a more powerful root formation.Plants from which air layers are obtained must be healthy and vigorous in growth. Young plants produce air layers faster than old ones. In deciduous trees, roots are often formed after 3-4 months.
Conifers take root very slowly. In pine trees, the process of root formation can take 4-5 years. For beginners, it is much wiser to obtain air layers from young and low-value plant material in order to test the reaction of plants to this method of vegetative propagation.


