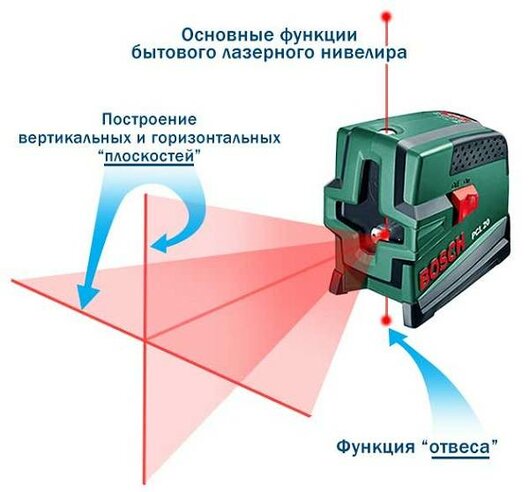
INTRODUCTION
Elevation surveys are surveys in which the elevation marks of points on the earth's surface are determined. The elevation of a point is its third coordinate - in addition to two plan coordinates, defined in a system of geographic or rectangular coordinates. As you know, maps give absolute heights of points, i.e. heights relative to the geoid surface (level surface). In practice, the heights of the points are determined relative to the points of the state geodetic network, the heights of which are determined in a single absolute system of heights.
Determining the height of a point is reduced to measuring the elevation between a point with a known height and a point whose height you want to determine. The desired absolute height of a point is determined as the algebraic sum of the height of the known point and the found elevation.
Popular models rating
Let's consider the most popular models of laser levels and their main characteristics. For ease of comparison, all parameters are combined in the table.
Table: Comparison of the characteristics of the models of laser levels
| Device brand | Accuracy, mm | Range of action, m | Number of beams | Self-alignment angles | Beam color | Price, rub |
| Condtrol QB | 0,5 | 10 | 2 | 4o | Red | 2 290 |
| Bosch GLL 2–10Professional | 0,3 | 10 | 2 | 5o | Red | 5 719 |
| Bosch PLL 360 Set | 0,4 | 20 | 2 | 4o | Red | 9 828 |
| Bosch PLL 360 | 0,4 | 20 | 2 | 4o | Red | 9 600 |
| ADA instrumentsTOPLINER 3 × 360 | 0,2 | 20 | 3 | 4.5o | Red | 14 390 |
| Bosch GCL 2-15Professional + RM 1 | 0,3 | 15 | 2 | 4o | Red | 7 520 |
| ADA instrumentsCUBE Professional | 0,2 | 20 | 2 | 3o | Red | 3 590 |
| ADA instrumentsCUBE MINI BasicEdition | 0,2 | 20 | 2 | 3o | Red | 2 490 |
| ADA instrumentsCUBE 360 Basic Edition | 0,3 | 20 | 2 | 4o | Red | 6 240 |
| Bosch GLL 3–80Professional | 0,2 | 15 | 3 | 4o | Red | 21 630 |
| ADA instruments2D Basic Level | 0,3 | 20 | 2 | 3o | Red | 4 990 |
The data in this table was taken from Yandex.Market, a selection by rating level was used. This includes the most attractive devices for buyers in terms of the general combination of parameters, hence some monotony of manufacturers.
The use of a laser level allows you to perform complex marking work with a high degree of accuracy, without the involvement of assistants and in a short time. There is a large selection of types and models of laser levels, allowing you to choose the most suitable device at an affordable price. When choosing a device, one should take into account the specifics of the upcoming work, clearly imagine the required level of accuracy, the capabilities of the device in order to get the best option.
Advantages and disadvantages
Automatic tilt angle compensators have significant advantages over cylindrical vials used for a long time:
- there is no need to constantly monitor the level of deviation of the device from the horizontal or vertical position;
- work becomes more stable;
- measurements are faster and provide more accurate and reliable readings.
Among the disadvantages are:
- the possibility of failure of the compensating system, the impossibility of troubleshooting on site;
- the presence of a blocker that will not allow measurements to be taken when the permissible deviations are exceeded;
- unstable operation and significant deviations in the readings of the device with a compensator with a magnetic damper near power lines: spurious electromagnetic interference has a serious impact.
Currently, levels with compensators are much more in demand and widespread than devices with cylindrical levels.
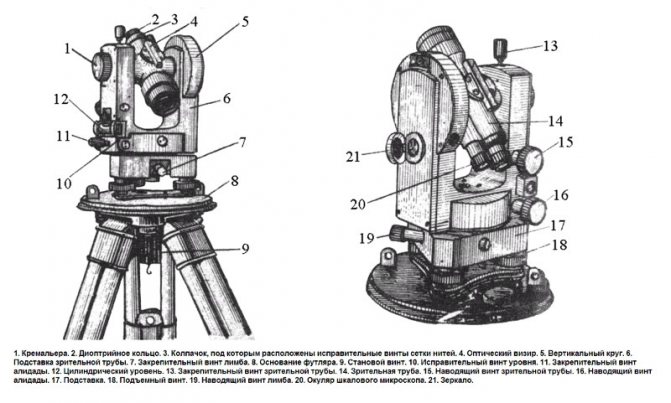
Errors when using an optical level
For beginners who are starting to work with the device for the first time, the following points should be taken into account:
- It is necessary to ensure the safety of the device. Although it is protected by various coatings, it is susceptible to impacts. To completely eliminate level errors, you should take care that each fastening element and components work properly.
- Use auxiliary tripods and brackets. This will make it possible to keep the device even during sharp gusts of wind.
- Do not blindly trust the information provided in the manual. It is better to check the functionality of the device yourself.
- It should be remembered that the help of an assistant is important while using the device.
- When mounting the rail, it must be exactly on the surface to avoid skewing.
- Do not allow the device to overheat, this may affect the accuracy of measurements.
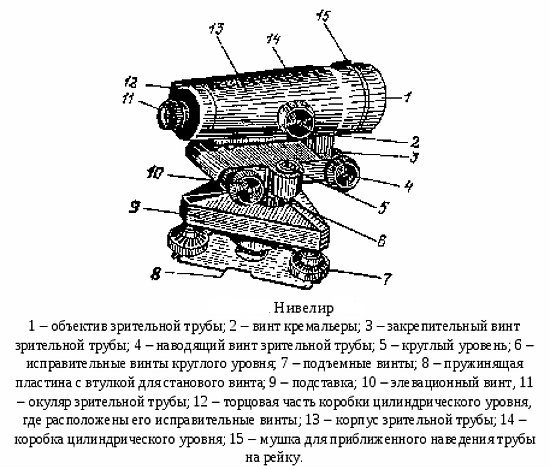
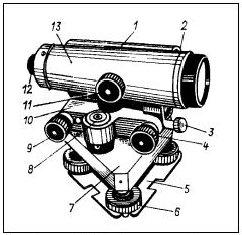
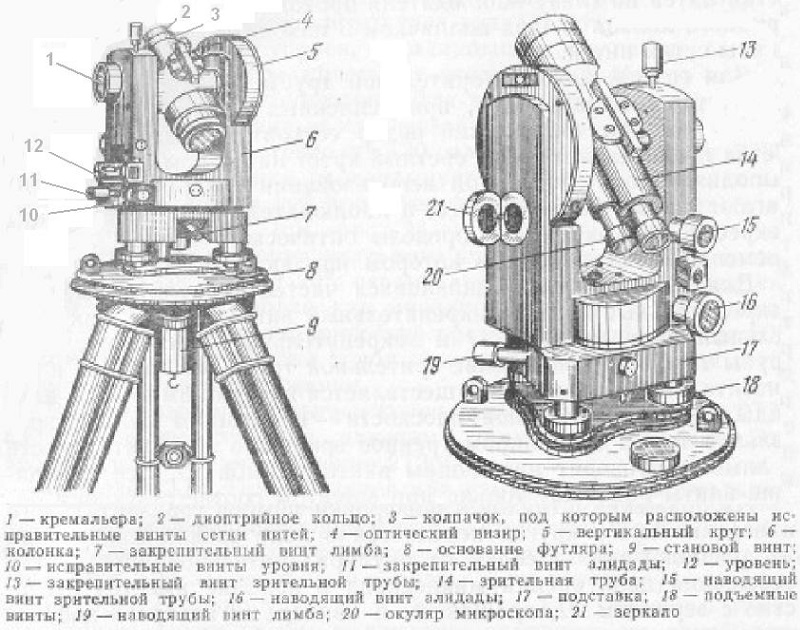
Leveling device with compensator
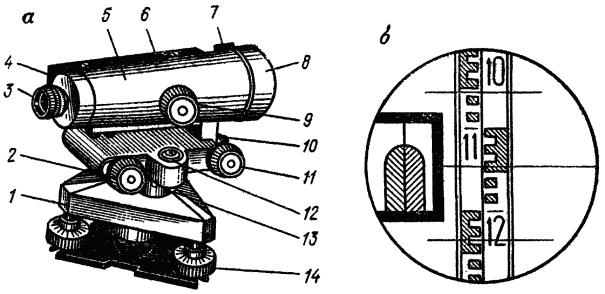
In a very simplified way, an optical level can be viewed as a telescope: a body, an operator's eyepiece and a lens. The system of optical-mechanical components allows you to see an enlarged image of the leveling rod against the background of a rigidly fixed mesh of threads.
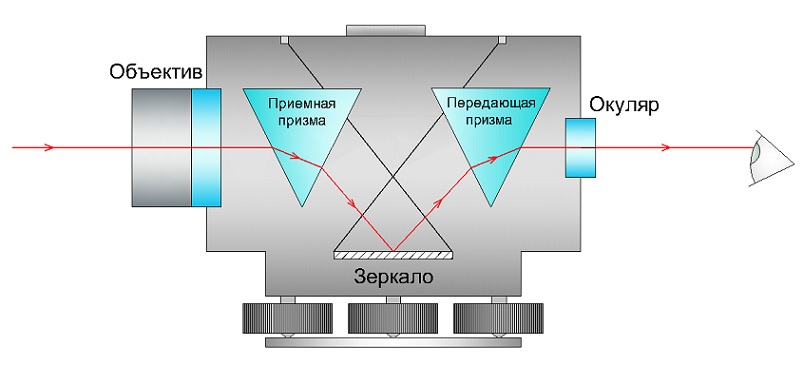
The line of sight of the device for the operator coincides with the center of the crosshair of the reticle and should always be perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the pipe.
Lasers with a compensator are fundamentally different from optical ones - they do not have a traditional optical system and are equipped with a self-leveling compensator:
- automatic magnetic - damping of oscillations is carried out due to the magnetic field of magnets fixed on the compensator;
- automatic electronic - equalization of the compensator is carried out by servo drives, in case of critical deviations, an alarm occurs and automatic adjustment of parameters.
The device of a level with compensators in case of problems requires repair and adjustment in specialized workshops and service centers.
How to work with a laser level, educational program for beginners
This device is quite simple to use, however, starting work, you should study the manual.
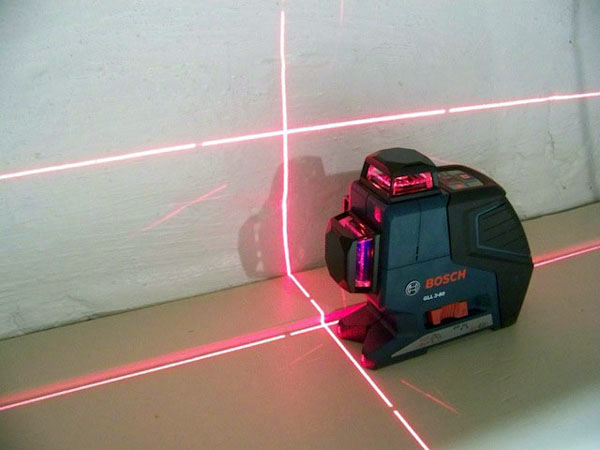 Working with laser levels
Working with laser levels
How to measure distance with a laser level
A number of devices have special rangefinders, which will make it possible to build a plane in auto mode, as well as calculate the distance. Otherwise, you will need to use ordinary tape measures.
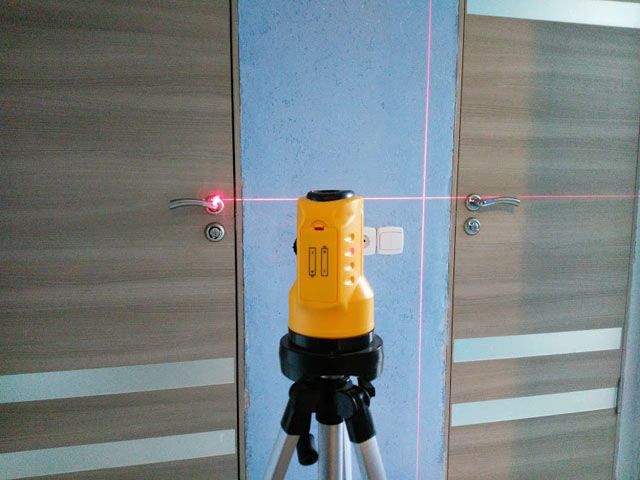 Distance measurement
Distance measurement
How to use a laser level for flooring
The level is irreplaceable during the arrangement of the floor logs. After starting the device, the so-called zero level appears around the perimeter.
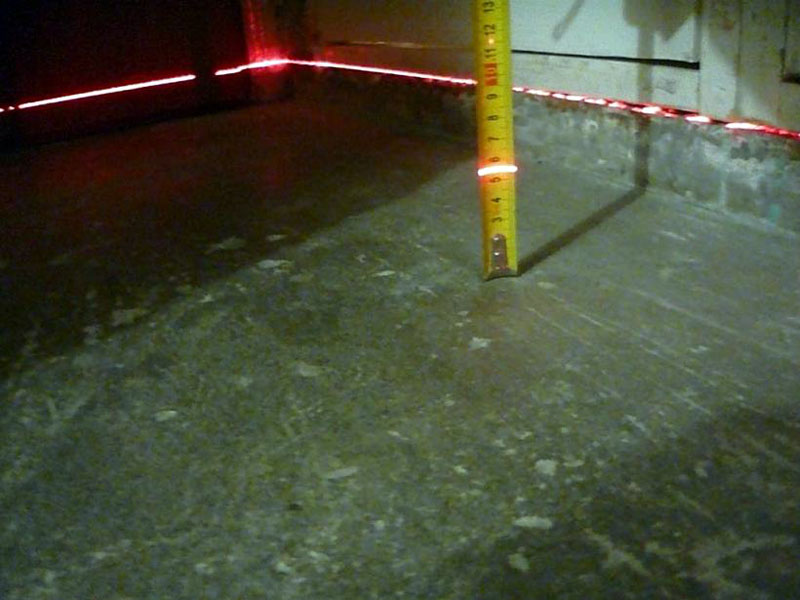 The use of the level during the arrangement of the floor
The use of the level during the arrangement of the floor
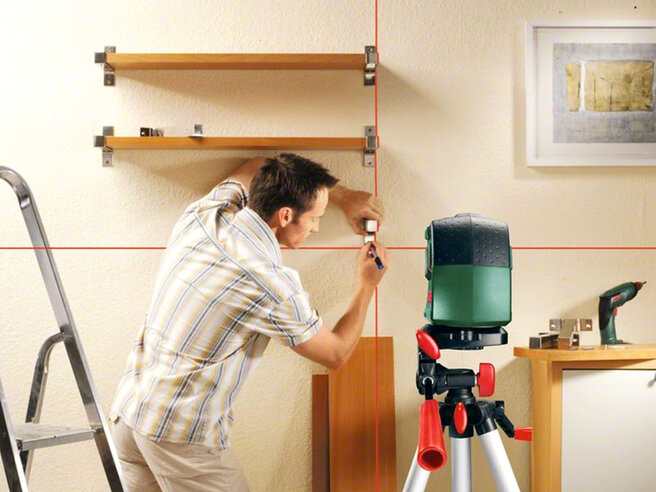
How to use when working with walls
The scope of the level is extensive. It can be used to control the laying of brickwork, install lighting fixtures and shelves, align handrails near stairs, lay panels, for other work where it is required to determine the exact position of an object in relation to any plane.
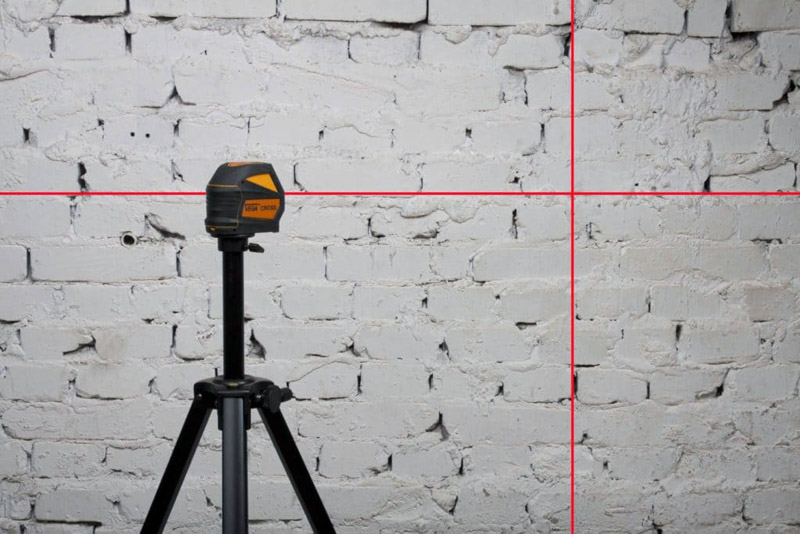 Applying a level when working with walls
Applying a level when working with walls
How to check the error of a laser level
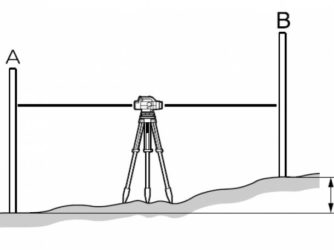
There are a large number of methods to test the accuracy of a device. The simplest is to check in a small room, which can be easily measured by yourself in order to refine the calculations. The device is installed exactly in the center of two walls, which are approximately 20 m apart. The level turns on and a point is marked on the wall, which is indicated by a laser cross. The plane builder is rotated 180 degrees and a mark is made on the opposite wall.
Next, you should move the device to any of the walls, set it at a distance of 60–70 cm from the wall and make similar marks as indicated above.
The distance is measured between points a1 and a2, between points b1 and b2. The distance is subtracted from the other (a1 and a2) - (b1 and b2), the finished indicator is compared with the specified accuracy. When the data does not exceed the accuracy of the manual, therefore, the level is functioning properly.
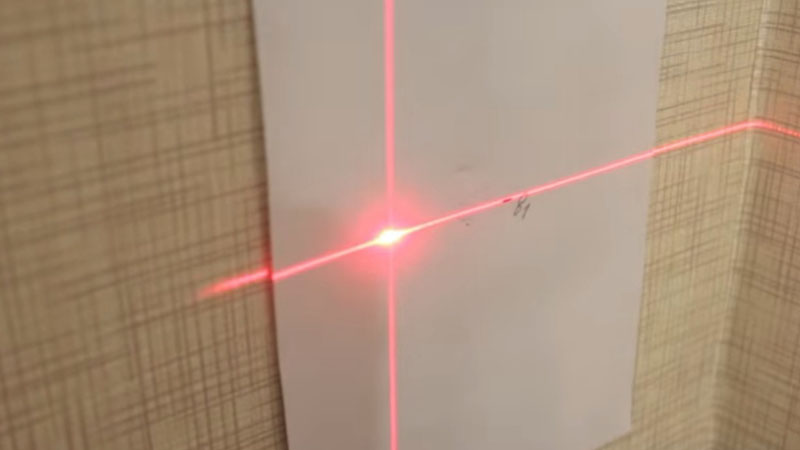 Point elevation A1 and A2
Point elevation A1 and A2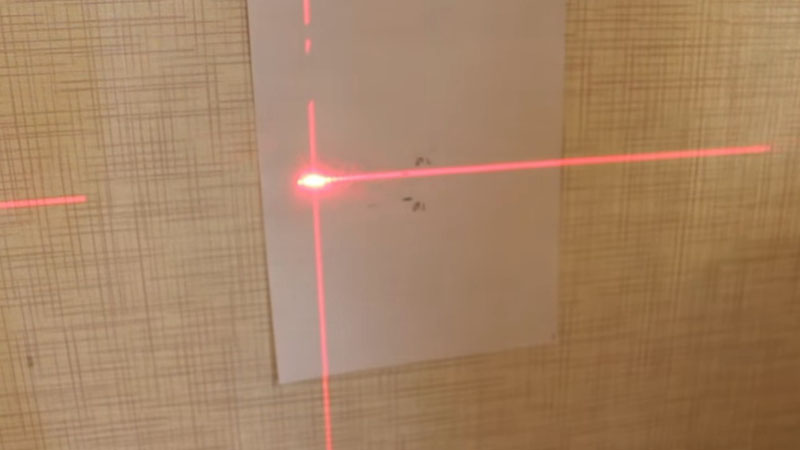  Elevation of points B1 and B2
Elevation of points B1 and B2  Distance comparison
Distance comparison
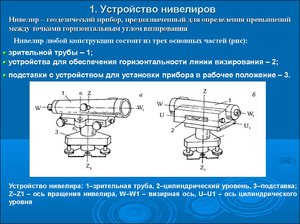
Fundamentals of geometric leveling
When working with a level, there are a number of methods that allow you to effectively achieve an accurate result:
- By leveling from the middle
- Forward leveling method
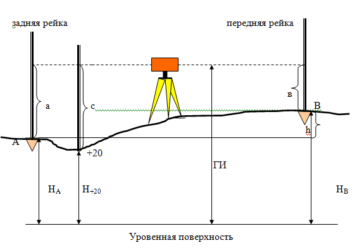
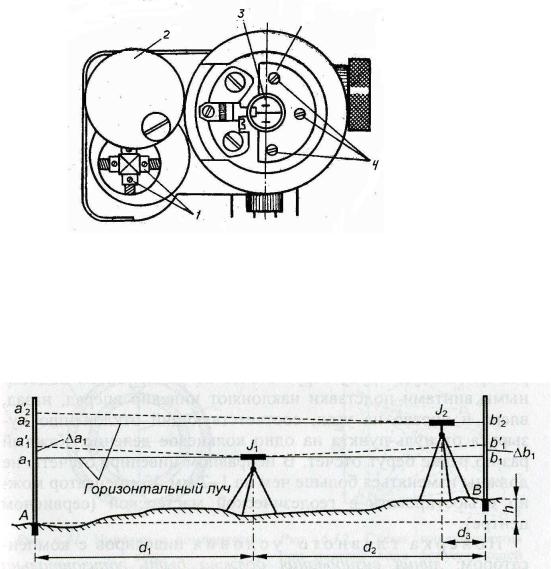
Each of them is based on its own operating principle. So the first method involves reading the readings on geodetic rods, which are installed at the standing points, behind and in front of the level. The excess difference data is then taken and recorded in the log.The method of positioning the level in relation to the laths was called the “method of leveling from the middle”, which is the main method in construction.
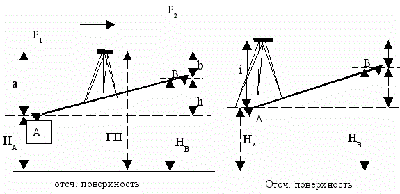
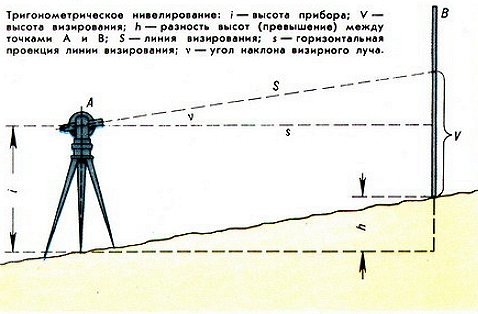
This method is based on the principle of counting, by analogy with the theodolite traverse, which is conducted from previously known heights, called benchmarks. The principle is well illustrated by the picture where there are points A and B. Naturally, the difference between the points along the rivers is the excess, which can be either negative or positive. The data of one elevation on the ground, in practice, cannot be considered final, since for an objective picture of its relief, it is necessary to remove as many such elevations as possible.
The system for comparing heights used in topographic plans is called "Baltic". It has the starting point of zero of the Kronstadt footstock, which in turn is located on the Baltic coast. In this case, in the picture, the absolute height (point B) is calculated as h = A + a - b. Point A is the mark of the state system of heights, and reading from the rails is carried out along the segments a, b.
Forward leveling is based on the use of the device and one staff installed in front of it. The level itself is set to a predetermined point, and the formula by which the excess is calculated looks like:
h = A + i - b, where i is the height of the level measured with a tape measure. This method is used less often, since it has difficulties in installing the device on the vertical surface of the walls. In addition, remote work is much easier and allows you to stay away from objects.
Here, as the starting point of reference, it is conventionally accepted to take the water edge of reservoirs communicating with any world ocean. But in this case, we will be dealing with a conditional system of heights, the accuracy of which will not be enough for carrying out large-scale construction work. And yet, this principle of geometric leveling is perfect for local construction sites, where alignment of building heights with regional systems is not required.
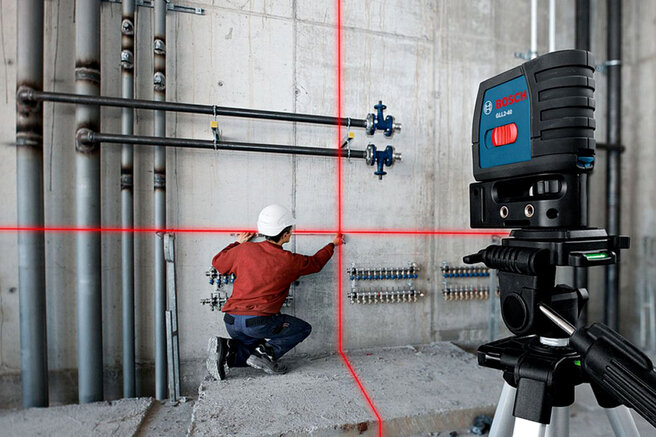
How are rotary lasers used in open areas
Such levels are considered one of those that, due to the high-speed rotation of the laser head, will project a beam (it will become noticeable even in bright sunlight).
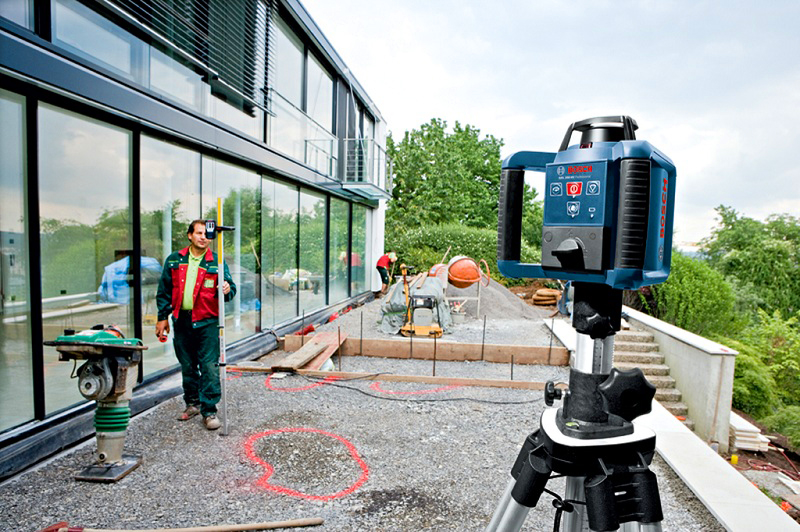 Directly laser levels, in combination with optical devices, are often used by specialists on an open construction site
Directly laser levels, in combination with optical devices, are often used by specialists on an open construction site
A characteristic feature of the functioning of such products will be that they work perfectly on planes in 360 ° and pointwise. For example, the scan option will allow you to select only the place where you want to align the door opening or window.
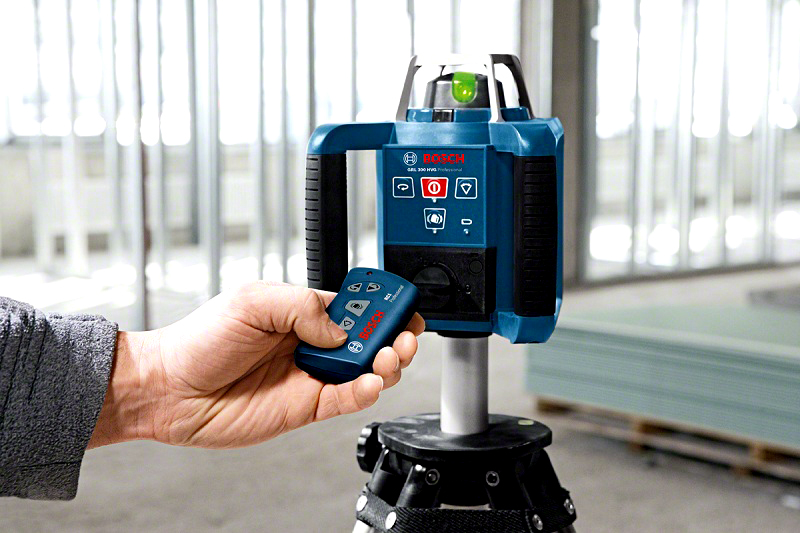 When using this option, the device will display the laser beam only in certain areas of the PHOTO:
When using this option, the device will display the laser beam only in certain areas of the PHOTO:
The level is equally necessary when taking measurements in open spaces, in the process of erecting large-scale objects, as well as during repair work. If you liked our article, be sure to rate it. In addition, we are always happy to answer your questions, which can be left in the feedback form.

Previous Household appliancesUltrasonic air humidifier: features, selection rules and prices
The next Household appliances
18.4. DIGITAL AND LASER LEVELS. BARCODE RACKS
In connection with the increasing requirements for the quality and accuracy of geodetic works, digital and laser levels are now widely used. Digital level.
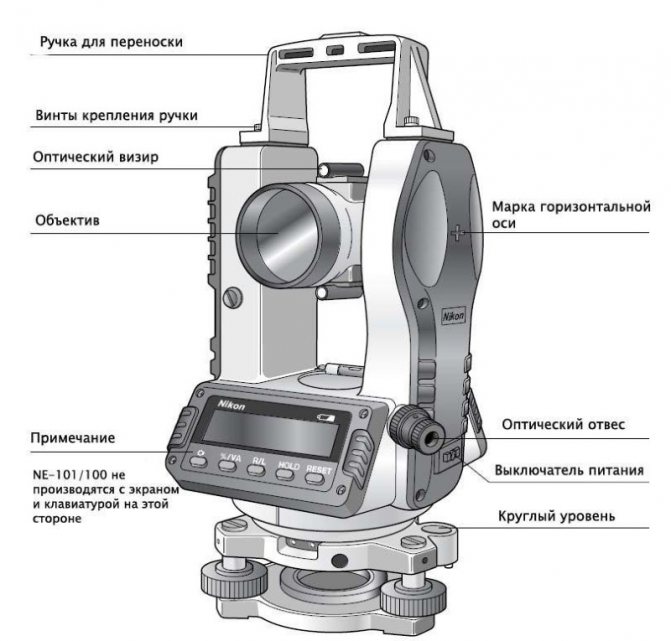
A digital level is a high-precision optical level, but with automatic collection, storage and processing of the information received (Figure 18.10). This means that all the basic conditions necessary for making high-precision measurements with optical levels must be met for digital levels as well.

 Rice. 18.10.Leica Sprinter 50 digital level and double-sided leveling staff for optical / electronic reading
Rice. 18.10.Leica Sprinter 50 digital level and double-sided leveling staff for optical / electronic reading
Geodetic measurements are performed in a set with a rail with a scale with a barcode pattern. The front side of the barcode strip has a raster scale of alternating black stripes and white gaps. Their width in height is coded. Light waves from the barcode pattern act on the level's decoding sensors.
The leveling line is installed horizontally using a compensator.
The decoding device decodes the height of the level relative to the staff according to the ratio of the light influences from the dark and light strip stripes received into the lens.
The level processor counts the measured elevations and their sums with an accuracy of 0.1 mm, and also determines the distance to the rails and the inequality of the leveling arms. The time for taking readings on the staff is 2–4 s. The electronics of the device automatically introduces corrections for the curvature of the Earth, refraction and error in the deviation of the sighting beam from the horizon.
The results of measurements with already entered corrections are tracked on the display and, at the request of the operator, can be sent to the level memory. The program implements the sequential calculation and display of the heights of the points of installation of the staff. Laser levels are designed to measure elevations and transfer heights. The level emits a visible beam of light, relative to which the excess is measured. In laser geodetic instruments, optical quantum generators (lasers) are used as the emitter of the luminous flux.

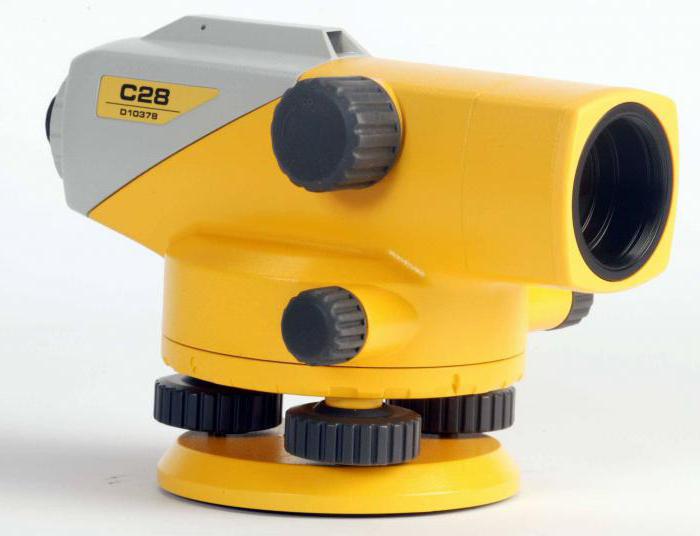
Rice. 18.11. Laser levels

Rice. 18.12. Rail count
Currently, laser levels are produced mainly with an automatically leveling beam of radiation, a rotating laser beam, which makes it possible to form light lines and planes in space. The position of this plane is fixed on a special rail or walls of buildings.
The device is mounted on a tripod and is brought to a vertical position by means of three lifting screws. The light plane is fixed visually or using a photodetector. The level can be installed so that a vertical plane is formed. It is equipped with a computing device that allows the automatic calculation of elevations, heights and distances.