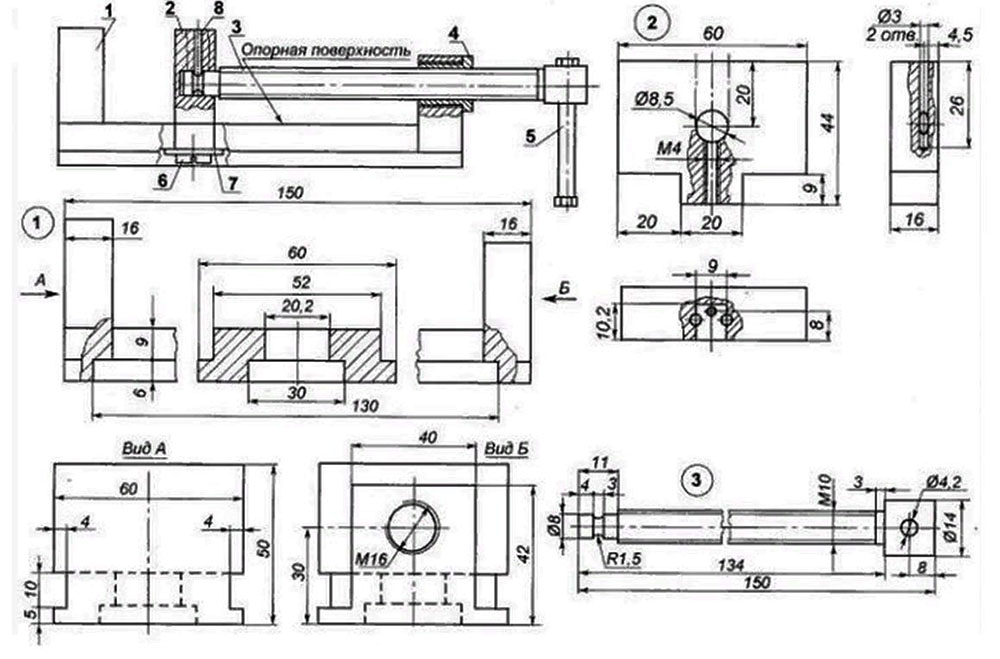
General tool characteristics
Structure
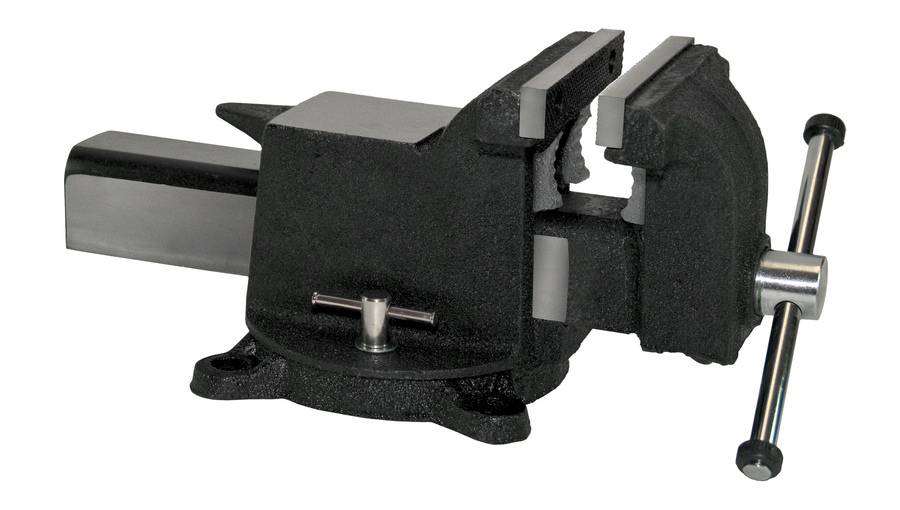
The pipe vise consists of two main parts. This is the base and the folding mechanism.
Both parts are made of durable cast iron, the other parts are made of alloy steel. The use of such materials ensures high reliability of the tool and its long service life.
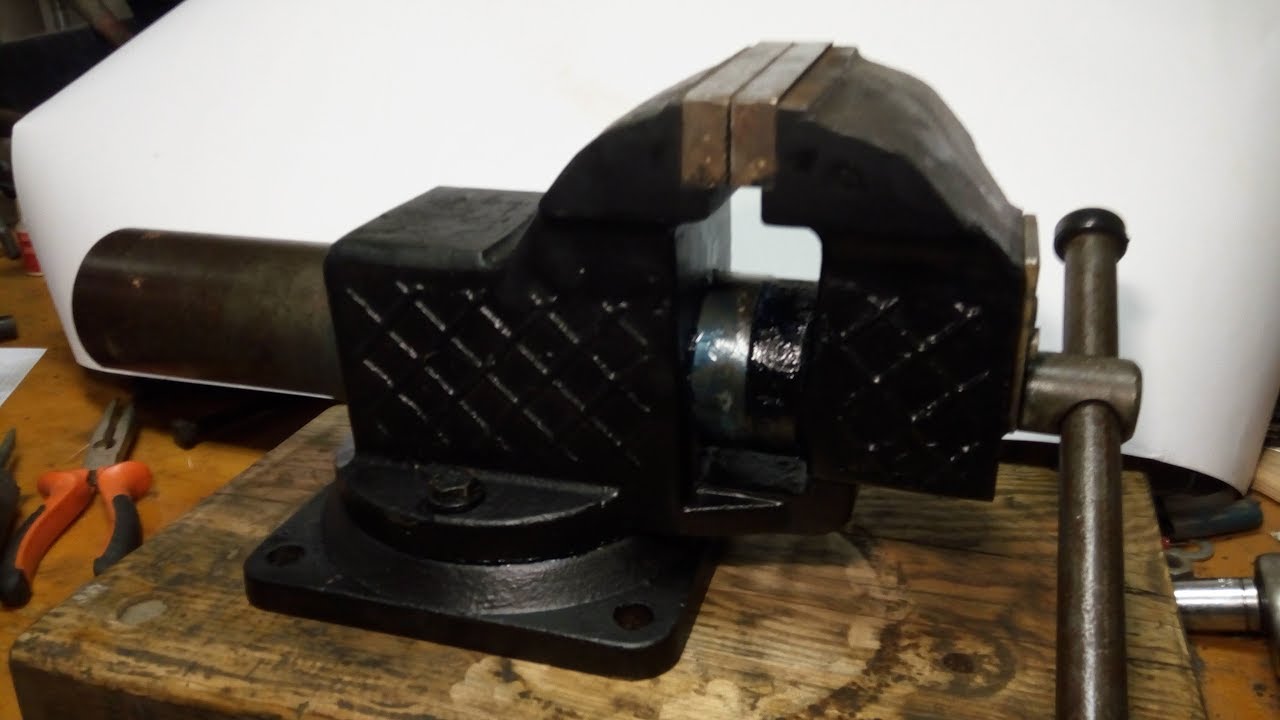
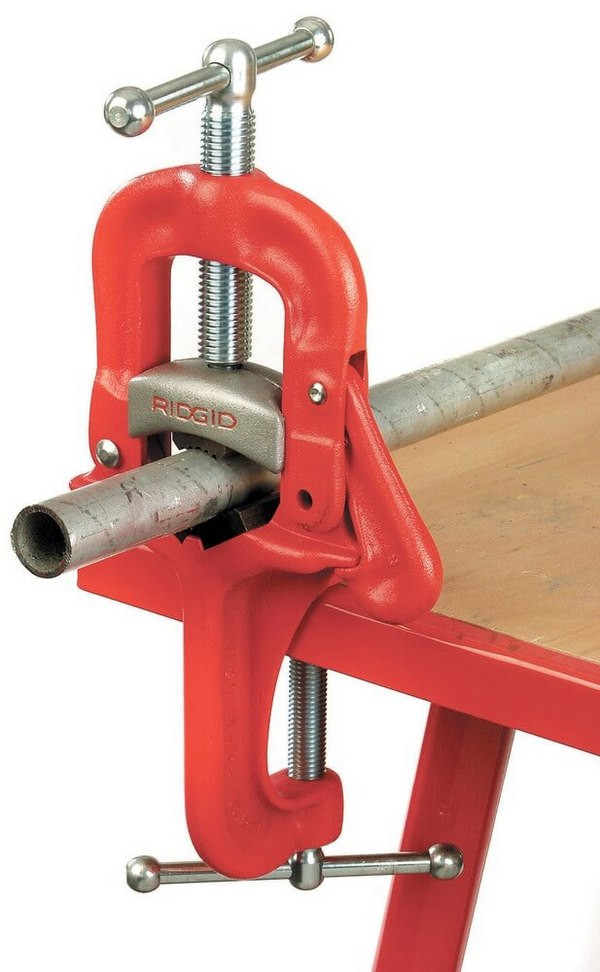
Pipe vise is used to process parts of the heat and water supply system
Desktop pipe vices TT 3 are additionally equipped with an automatic closing hook, an easy-moving bolt, a movable upper jaw, and a pipe support.
 Pipe vise
Pipe vise
In some models, the handles are additionally modified to improve the comfort of working conditions.
The lower part of the case has special holes. They contribute to the reliable fastening of the tool to the workbench using bolts, which are additionally included in the package.
For ease of installation, some manufacturers make tripods for pipe vices. This allows parts to be machined away from the workbench. In addition, the protrusion of the vise body for the front legs makes it possible to work without hindrance with the element, welding bends, stubs.
Typically, in a vice on tripods, pipes with an inch from 1/8 to 2 1/2 and sizes from 10 to 76 mm are processed.
The tripod makes the work more maneuverable, allows you to process the part from different sides
The tripods are lightweight and compact. They move and carry over any distance.
Technical description
The vice is intended for locksmith work. They do not have a rotation function (those that are attached to the workbench). Working stroke up to 90 mm. The minimum diameter of the clamped pipe is 12 mm, the maximum is 90 mm. Weight does not exceed 10 kg. Producing countries: Russia, Spain, Germany, China.
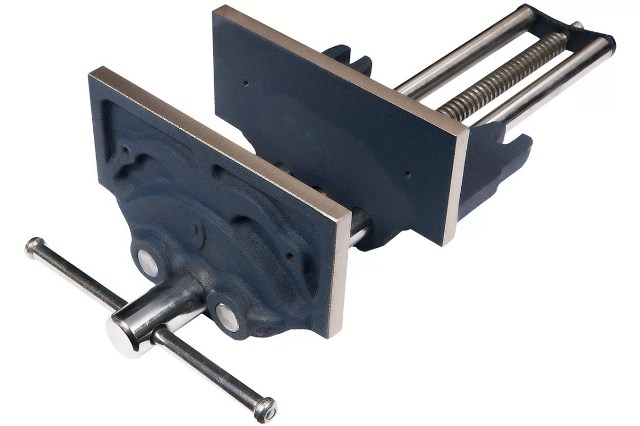
 Vise structure
Vise structure
To bring the folding pipe vise into working condition, perform the following actions:
- unscrew the screw by the amount that will be sufficient to install the workpiece;
- remove the axle from the base;
- turn the bracket to the working position, connecting it to the axis and the base;
- by rotating the screw, the clamp is lowered until it contacts the pipe and the required clamping force is created;
- start processing the pipe.
Pipe vise advantages
- For the manufacture of the vice, high-quality materials are used (metal of special casting).
- It can be used for locksmith work involving heavy loads.
- Pipe vices TT 3 have a long service life;
- Convenience in work and quick access to the desired section of the processed pipe.
- High-quality processing of pipes and rods.
- Fast positioning and fixing of the workpiece.
- Low probability of damage to parts and materials during installation.
- Low risk of injury at work.
- Wide range of applications (manufacturing, construction).
In order for the pipe assembly tool to serve for more than one year and in the future, it will allow you to work comfortably with parts, perform maintenance.
Machine oil lubricates all rubbing surfaces of the vice - the threaded part of the screw, axles, the joint of the screw with the clamp.
If the tool is used systematically, the parts are lubricated once a week, if from time to time, then before starting work.
How to do it yourself?
First, decide on the material. We have already talked about how to choose it correctly. You should not limit yourself, you can make several pairs of clamping bars "at a time" and change them as needed.
Next, dismantle the old pads. This work is very laborious, for sure the bolts are rusted, and it will not be possible to remove the linings just like that. Then they need to be cut down with a grinder with a cut-off wheel. But be prepared that you will not be able to unscrew the rest of the bolts. Then you need to grind them off, and then drill new holes and cut threads into them.
Next, we start manufacturing. Using simple tools, you can make good wood trims. In this case, they will be fixed not with screws, but with magnets, and you will not need to remove the old sponges.
The main idea is to make easily removable sponges. They are attached to the magnets with a bracket made of sheet metal 1–2 mm thick. The work consists in performing a certain sequence of steps.
- Take 2 identical wooden blocks. Their thickness must be sufficient so that a screw can be screwed into the end. The length and width are determined by the dimensions of the vise.
- Attach a magnet to the top of each sponge. Find a position where they hold with the greatest strength.
- Clamp both of our new pads in a vice.
- Make a template out of paper by attaching it to the pad and magnet. Make the necessary folds. Next, cut out the resulting shape, straighten and transfer the contours to the metal.
- Shape the metal into the desired shape. To do this, attach it to the pad and magnet and make bends. Then remove any burrs and sharp edges.
- Fasten the brackets to our wooden cover with 2 screws. To do this, you need to drill holes.
- Do the same to make another sponge.
The magnet does not need to be attached to the bracket at all - it will hold on by itself. But if you need more reliability, then it can be attached with screws or glue. Great strength is not required since the fastening forces do not act on the joint.
The main requirement is that the overlays must be strictly parallel.
You can make metal sponges yourself, but you can't do without a snap. Use standard mounts. But make sure the mounting slots are straight. If this is not the case, they need to be leveled with a router, dremel or sanding.
- Determine the required dimensions with a caliper or internal gauge.
- Use them to make 2 metal bars. These will be the sponges.
- Drill 2 holes each. They must clearly coincide with the installation ones and lie strictly perpendicular to the clamping surface. This is the most crucial moment. To ensure their diameter can be made slightly larger.
- Make indentations in the holes for countersunk bolts. Better counterbore so that the bottom turns out flat rather than tapered.
- Apply risks with a dremel or grinder with a thin circle.
- Temper the sponges and then release them. The temperature depends on the grade of the material.
- Fasten the pads in a vise. If they "sit" unevenly, adjust the dimensions as needed. After hardening, this can only be done by grinding.
Pyramidal jaws can be made from a flat file. Before work, annealing must be carried out to make the material softer. Further, the technique is no different.
In the next video, you can watch the process of creating do-it-yourself vise jaws.
Description
The hand vise is a pliers tool that does not require attachment to the surface and has a quick fixation. The main function of the hand vise is to securely hold finished parts or workpieces for machining.
The design of the tool is very simple and looks like pliers. The parts are fixed between two jaws, which are clamped using a wing nut. During operation, the vice is held with one hand, while the other hand is processing the part.
The scope of the manual vise is quite wide.
- They are actively used when performing small welding works in automotive service and in industrial production.
- In addition to welding, a vice is used instead of a wrench and adjustable wrench, if necessary, to unscrew the threaded connection, and also use them to unscrew nuts and bolts with knocked down edges.
Device and application
It is correct to note that joiners and locksmiths are not the only ones using them. They really most often resort to their help, however, they can use a vice in electrical work, and in woodworking in general, and in any other craft. Despite this, their structure does not fundamentally change. Any vise consists of a body and two plates in parallel. The first is securely fixed, and the second can move. The workpiece is placed between them, after which it is fixed there with the help of clamps. At the same time, the second plate should fit tightly enough to avoid unpleasant situations, but also not damage such material as, for example, wood.
Modern technologies and tools are widely used in large industries. There they can use not only fixed vices, but rotary ones. For processing some non-standard parts, they need to be fixed in an upright position. There are clamps for such cases - specially modernized. This vise has an enlarged anvil with a base that rotates 360 degrees. Round workpieces are processed using equipment with a prismatic body.
In especially rare cases, if it is necessary to deal with a non-standard part, sinus and double vices are used. The former allow you to fix the workpiece in two or three different, mutually perpendicular planes. And the second is to simultaneously process two parts at once.
Machine yews
Design and principle of operation of rotary yews
The base of the vice is a bar to which clamps and transmission mechanisms are attached. The jaws are placed on metal bearings, a clamping screw is attached to one of them. In homemade devices, this can be a threaded steel pin. Factory counterparts have rectangular or bevel gears on the bolt. The clamp movement system can be any. The simplest solution is that the bolt turns in the thread of the bed and moves the clamp at one end. In other words, during the twisting of the screw to the right, the jaws are connected, and to the left, they move away from each other.
One of the main features of rotary yews is the presence of clamping strips that securely grip the workpiece to be processed, and then are fixed on the base. The legs are made in different shapes: in the form of flat plates, a horseshoe, a cross, etc. The slats with a special spring mechanism are installed on modern designs, which allows to handle the part as comfortably and efficiently as possible.
The main feature of the rotary vise is that they are mounted on a tabletop, which can be moved in a circle or rectilinearly, this allows the workpiece to be twisted relative to a horizontal plane by 360 ° or moved through an angle from -15 to 90 °, fixed in the desired position. Moreover, many rotary structures have a removable base. An important requirement of machine yews is their rigidity, they are installed in the keyway and firmly fixed with screws.
Manufacturing
welding
- A clamp is made, thanks to which the yews can be held on the work table.
- 2 metal plates are cut out, three holes are drilled in them for the guides. The carriage is welded. The swivel structure is assembled as follows: a threaded pin is inserted into the middle hole, and the rails for the clamping bar are inserted into the outer ones. A handle is attached to the end of the pin for comfortable control.
- A static sponge is screwed onto the screws, the heads are recessed into the surface, and the nuts are located on the outside. The clamping jaw holder is welded.By design, it is a metal corner with three stiffeners. Its horizontal part is bolted to the carriage. The sponge is also fixed with screws, which allows you to change the legs if necessary - for example, to install a homemade pipe fastening structure.
- A hinge is being prepared that changes the position of the blank. It is made in a welded way.
The video presented shows how to assemble a rotary mechanism and a vice with your own hands:
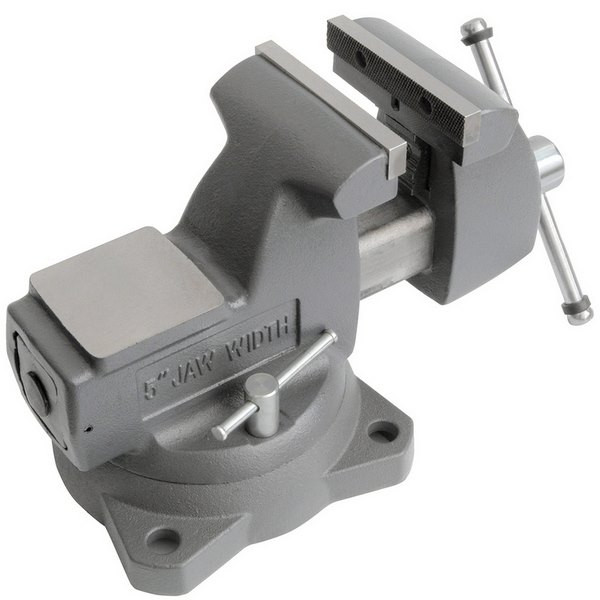
What is a locksmith vise?
Any craftsman knows that a locksmith's vice is a device that ensures the immobility of a metal workpiece during its processing manually or mechanically. Depending on the type and structure, they are able to tightly fix everything: from the smallest golden curl of a future jewelry piece to a large auto part. The main parameters, design and requirements for locksmith vices are fixed in the state standard 4045-75.
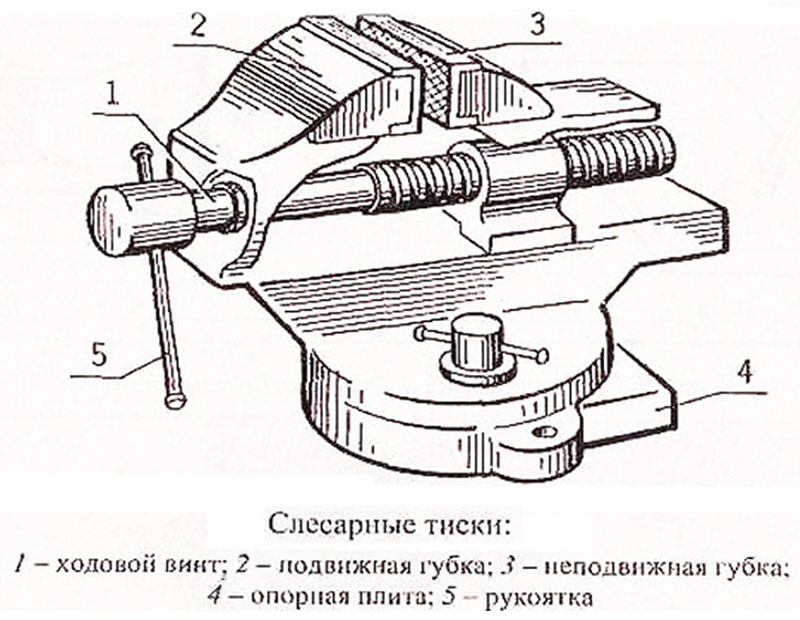
Locksmith vice device
Modern manufacturers have provided us with the widest range of options for the appearance of the vice. However, any model basically has the same elements of the internal structure:
- Sturdy support base with a fastening mechanism that holds the locksmith's tool tightly to the surface.
- Two jaws - static and moving, directly clamping the product.
- Plates on the jaw planes, as a rule, are replaceable, with a notched surface for better adhesion to the part.
- Lead screw, which regulates the movement of the movable jaw;
- Guide rods along which the screw "runs".
- It is rotary, fixing the desired turn of the tool.
The configuration of this device is widespread, in which its base plays the role of a stationary sponge, that is, the moving element presses the product against the surface on which the locksmith's vice is fixed. Since the tool often serves as an anvil, they prefer to make it from steel, other materials (for example, cast iron) are not able to withstand a heavy load.
Disadvantages of using
The least durable in comparison with steel products are vices made of cast iron. Their wear resistance is much lower.
Other possible disadvantages are associated with the individual design and functional features of different vices:
- usually have a slight backlash;
- during operation, the plates can be displaced and they can be aligned only using special tools;
- lock washers, which are part of the vise design, wear out quickly and require frequent replacement;
- it is difficult to hold large parts between the plates.
Disadvantages of a chair vise:
- insufficient strength of the vise fastening on the workbench;
- Due to the fact that the working surfaces of the plates are not parallel to each other in all positions, narrow workpieces can be clamped during clamping only with the upper jaws. Holding wide objects is possible only by means of the lower plates;
- dents may remain on parts if the pressure when fixing them is too strong;
- Due to the open screw, its rotating part is very quickly subject to contamination, and the vice can quickly fail.
Disadvantages of manual models:
- due to the small take-off and width of the plates, such sheets cannot hold and process large parts;
- Clamping most hand vices can damage parts, leaving dents and scratches on them;
- restricts freedom of movement. You have to hold the vise in your hands, manipulating the parts with your free hand;
- without the use of special devices, it is impossible to work at an angle;
- it is almost impossible to hold a large workpiece in a stationary position.
Vise qualities and functions for which we need them
We are sure that the article is read by experienced craftsmen, so we will not dwell on defining what a vice is, on their structure and types.Even the poor knowledge of the average student will help the boy understand the structure of the clamping tool.
Let us recall the privileges that the use of a vice gives us:
- Safe and convenient work with inconvenient parts (large, small, sharp, thin, rounded);
- Precision in work (when sawing, notching, drilling, threading, etc.);
- Free hands.
In other words, a vice is an apprentice for any craftsman who lacks the human factor in functionality. The tool will not let you down as a person can. A vice does not care what to clamp, you will not be frightened by either the weight, volume, or shape of the object.

Types of locksmith vices
Locksmith vices have the following most common types, produced in accordance with GOSTs:
- Stools. Their feature is the way of spreading the jaws. Movable - moves away from the stationary not in a straight line, but in an arc with a large circle radius. The disadvantage of this design is that the workpiece is not held by the entire plane of the cheeks: the narrow one is clamped by the upper edge of the pads, and the wide one, requiring a strong spreading of the jaws, is the lower edge. Another distinctive feature of the device is the ability to mount only on the edge of the workbench.
- Manual. It is a small device designed to be held in the hands of a locksmith. Very convenient for fastening small workpieces when processing them in drilling machines or manually with frequent turning. There are several types: spring, hinged, tapered.
- Parallel. Their release is regulated by GOST 4045-75. The peculiarity and convenience of this mechanism lies in the method of spreading the jaws. Movable - moves away from the stationary evenly (in parallel, hence the name). The size of the workpiece does not affect which part of the cheeks will hold it. In addition, this type of device allows you to install it anywhere on the workbench (and in the middle too) and even on the floor. It has several types of construction: swivel, non-swivel, free-wheeling. Swivel ones differ from non-swivel ones only in the ability of rotational displacement at an arbitrary angle relative to the base. This makes them more convenient to use. The free-running locksmith vice provides a very quick and convenient clamping of the workpiece. One turn of the handle releases the toothed nut from its engagement with the sawtooth racks; moving towards yourself - the movable jaw is released, which sets the working gap between the cheeks; the workpiece is fixed by movement from itself; it is clamped by turning the handle.