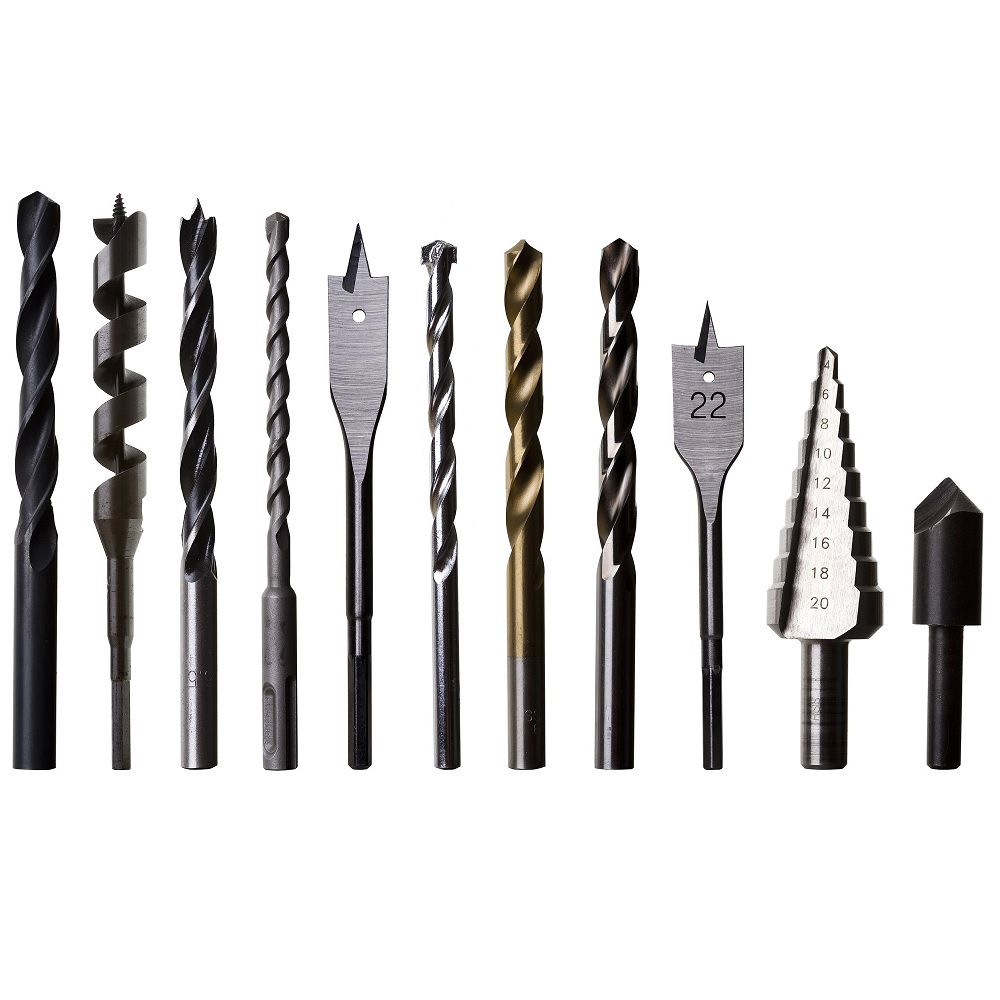
What are the types

There are many countersinks on the market, an inexperienced user may not understand why so much is needed, but each type has its own purpose and peculiarity in work. Some are suitable for increasing the diameter of the hole, and some will be most effective in working with the end part of the part. Most often, a basic set of nozzles is used when working with wood:
cylindrical;
one-piece conical,
one-piece shell-on.
Each countersink for wood designed for work of the corresponding holes, indicated in the title. But in some cases, in particularly laborious situations, you can resort to using a nozzle on an elongated mandrel. Such a tool has special legs that cut the end simultaneously with the countersinking process. Therefore, it is best to purchase a set where there will be several models at once by type and size, it will be more profitable and more effective.
Cooling and lubrication of carbide drills
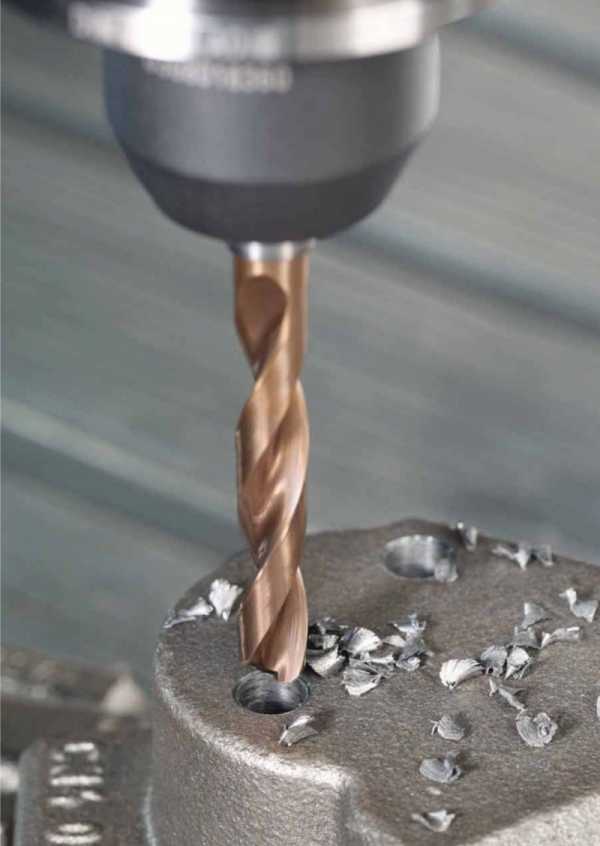
As mentioned above, in order to make machining with carbide drills more efficient, it is necessary to provide internal cooling of the tool. When using such drills, it is possible not to use a cooling lubricant in cases where the depth of the hole being formed does not exceed one tool diameter.
The quality of the hole being made, as well as the speed of its drilling, is influenced not only by the amount of coolant supplied to the inner cavity of the drill (not less than 12–15 l / min), but also by the amount of pressure (not less than 12–15 atm). The lubricating-cooling liquid supplied to the processing zone in such an amount and with such a pressure provides not only intensive cooling of the tool, but also an effective removal of chips and other drilling waste.

Drilling with external coolant supply
Species overview
In hardware stores, buyers will be able to find a huge number of models of such tools with these attachments. These include the following samples:
- conical one-piece;
- mounted one-piece;
- cylindrical.
Each of them is used depending on what kind of hole you want to make in the wooden structure. For particularly laborious work, you can use such a slightly elongated nozzle. The latter version has small legs designed for trimming the ends of products. The best option for users would be to purchase a whole set with several varieties of such tools.
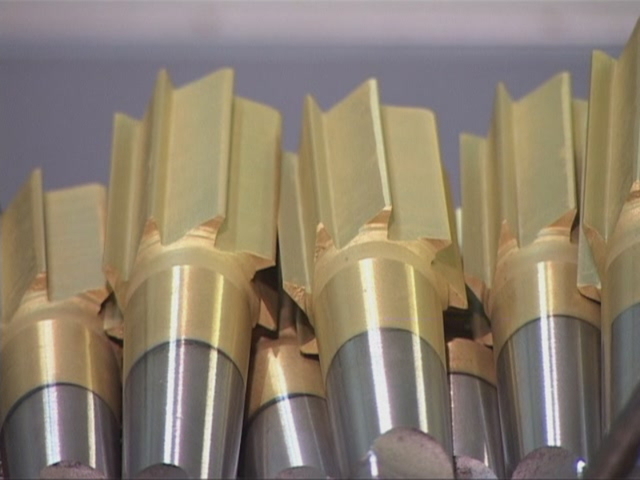
Cylindrical types of drills, as a rule, are covered with a special layer during the manufacturing process, which significantly increases the level of wear resistance of the product and its durability. The number of cutting parts can vary from 4 to 10. Externally, the design is similar to a conventional standard drill.
In addition, a special pin is placed at the end of the cylindrical models. This element is designed to fix the position of the tool itself during operation. Such products are equipped with limiters, they can be removable or act as a part of a whole structure.
Models with a removable drill depth stop are considered the most practical. They suggest the possibility of installing an additional cutting type attachment.
Removable varieties are attached to the structure itself using small hidden screws. These stops are sometimes attached with a hex wrench.
If it is necessary to make several holes at once on one wooden product, while they must have the same depth, then it is better to use such drills that will be equipped with special holders with movable or fixed drilling stops.
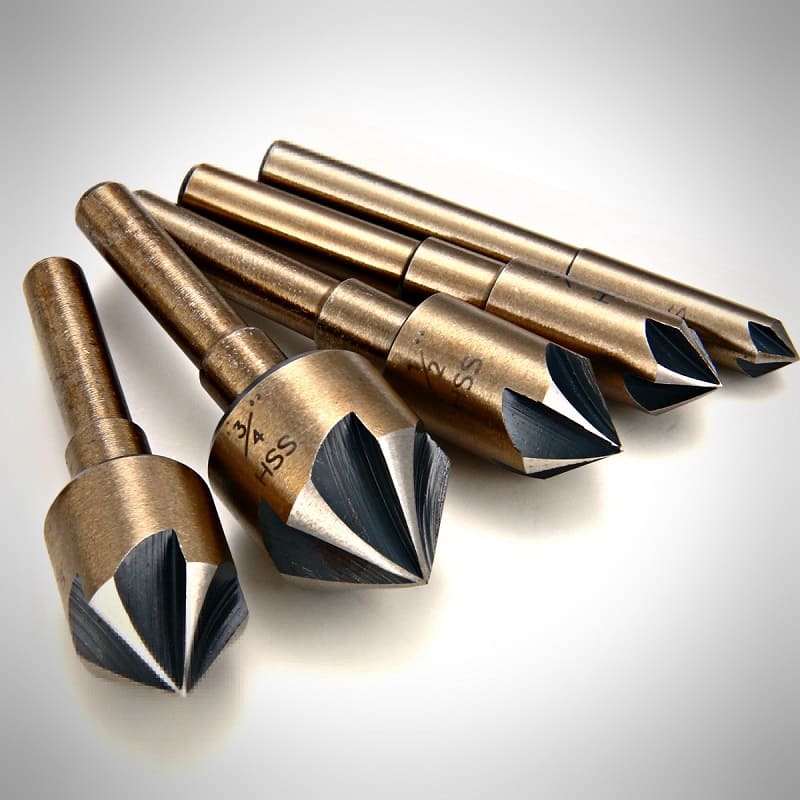
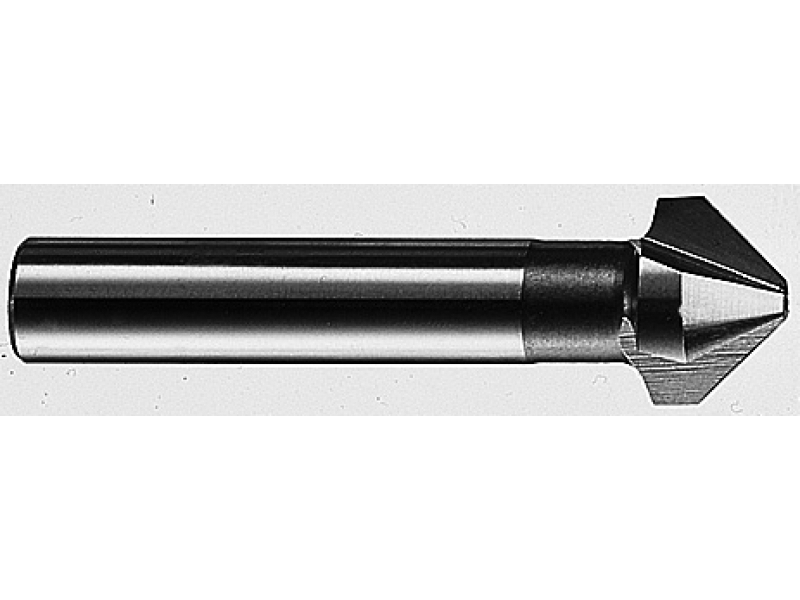
The mounted conical drill model is a structure that works at a certain angle, the value of which will depend on the purpose of this model. The angle can be between 60 and 120 degrees. The number of cutting elements can be from 6 to 12 pieces.
The solid drill bit also looks like a conventional screw bit. It is most often used specifically for processing holes made in wood.
Various materials can be used for the production of countersinks. Most often in stores you can see such building elements made of various types of steel. So, they can be made from tool, alloy, carbon, high speed or carbide steel base.
If you need a drill to process various metal products, then carbide models can become the best option, because it is this variety that differs from all the others in its special resistance to constant loads.
Also countersinks for wood processing can differ in the diameter of the holes to be machined. The following options are considered the most common:
- standard models - the diameter will be from 0.5 to 1.5 mm;
- models for holes with a diameter of 0.5 to 6 mm - such samples can be produced with a safety device that will allow you to control the drilling depth;
- products for holes from 8 to 12 mm - this group, as a rule, includes special countersink drills with a shank.
Metal countersinking rules
At home, for countersinking recesses (for example, for bolt heads or for changing the hole diameter upwards), a simple drill fixed to an electric or even a hand drill is also suitable. On a production scale, countersinking is an operation that requires considerable power and precision of the equipment used. That is why, in production conditions, to perform countersinking, as, in fact, countersinks, they use the equipment:
- turning (most often);
- drilling (no less often);
- boring (often as one of the secondary operations);
- aggregate (as a secondary operation of an automated line);
- vertical or horizontal milling (rare).
In the process of machining the hole obtained in the product during its casting, it is advisable to first bore it with a cutter about 5-10 millimeters in depth so that the countersink takes the correct initial direction.
When processing steel products, it is recommended to use cutting fluids. The process of countersinking cast iron and non-ferrous metals does not require cooling. The correct selection of metal cutting tools used for both countersinking and countersinking is a very important step.
To do this, pay attention to certain factors:
- The type of tool is selected depending on the material of the part, the nature of the processing being carried out. The location of the hole, the seriality of the processes performed should also be taken into account.
- Based on the specified depth, diameter, required processing accuracy, the size of the tool for countersinking and countersinking is selected.
- The design of the countersink and countersink is determined by the method of fastening the tool to the machine.
- The material of the tool for performing countersinking or countersinking operation depends on the material of the workpiece (for example, there are countersinks specifically for woodworking), the intensity of the operating mode and some other factors.

Countersinking on a CNC vertical drilling machine
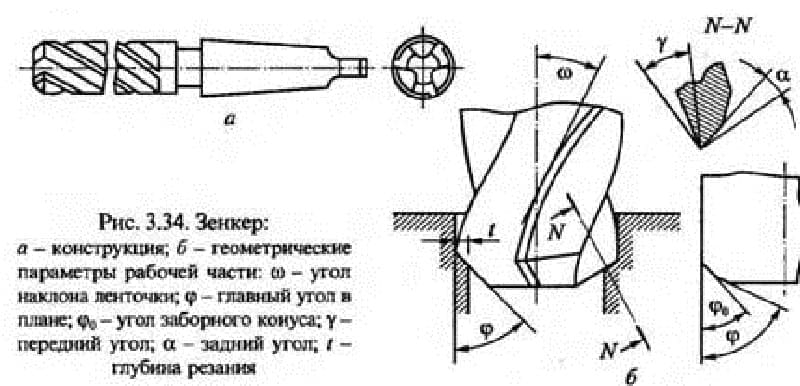
Zenker is chosen according to reference books or guided by such a regulatory document as GOST 12489-71. The tool must comply with certain technical conditions of use, which is also stipulated by GOST 12489-71.
- Products made of structural steel with holes up to 40 millimeters in diameter are processed with a countersink made of high-speed steel with a diameter of 10–40 millimeters and 3–4 teeth, respectively.
- For products made of difficult-to-machine and for boring, a tooling with hard-alloy plates with a diameter of 14-50 millimeters and having 3-4 teeth is used.
- In products made of structural steel, holes up to 80 millimeters in diameter are bored with a high-speed steel countersink using attachment heads with a diameter of 32–80 millimeters.
- In products made of non-ferrous metals and cast iron, a feather countersink is used for boring blind holes.
- Blind holes with a diameter of 15-25 millimeters are processed with a special tool for countersinking, in the body of which there is a channel through which the cutting fluid is supplied to the cutting zone.
A prerequisite for countersinking is the observance of the allowances. The diameter of the selected tool should eventually match the final hole diameter after machining. When the reaming of the hole is planned after countersinking, the tool diameter is reduced by 0.15–0.3 millimeters. If rough boring or drilling for countersinking is planned, it is necessary to leave an allowance on the side of 0.5 to 2 millimeters.
The difference between countersinking and related operations
Countersinking is similar to reaming holes, the cutting edges of the tool remove excess material from the wall, reduce roughness and increase the diameter. This is a semi-finishing operation, which means it is followed by another processing step. Deployment is the finishing procedure. During countersinking, drilling, punching and casting defects are eliminated. In the process, you can slightly adjust the alignment, achieve better alignment for the future connection. The accuracy can be increased to 5, and sometimes even to the 4th grade.
When setting the cutting mode, remember that the thickness of the metal removed during countersinking is equal to half the allowance for a given hole diameter. Compared to drilling, the feed can be increased by 1.5-2 times, and the speed can be left the same. Specific cutting parameters are calculated according to the formulas given in the regulatory literature.
Since the countersink has greater rigidity in comparison with the drill, due to the increased number of sharp protrusions, the accuracy of the direction of movement increases, as well as the quality of processing, smoothness and surface cleanliness. For comparison, drilling gives a roughness of 20 µm and grades 11–12, countersinking - roughness of 2.5 µm, grades 9–11, and reaming - roughness of 0.25–1.25 microns and grades of 6–9. Quality is the accuracy of manufacturing a part, with an increase in its value, tolerances increase, and accuracy decreases. If the technological process for processing a product requires both countersinking and reaming, then they are made in one installation and alignment of the workpiece on the machine.
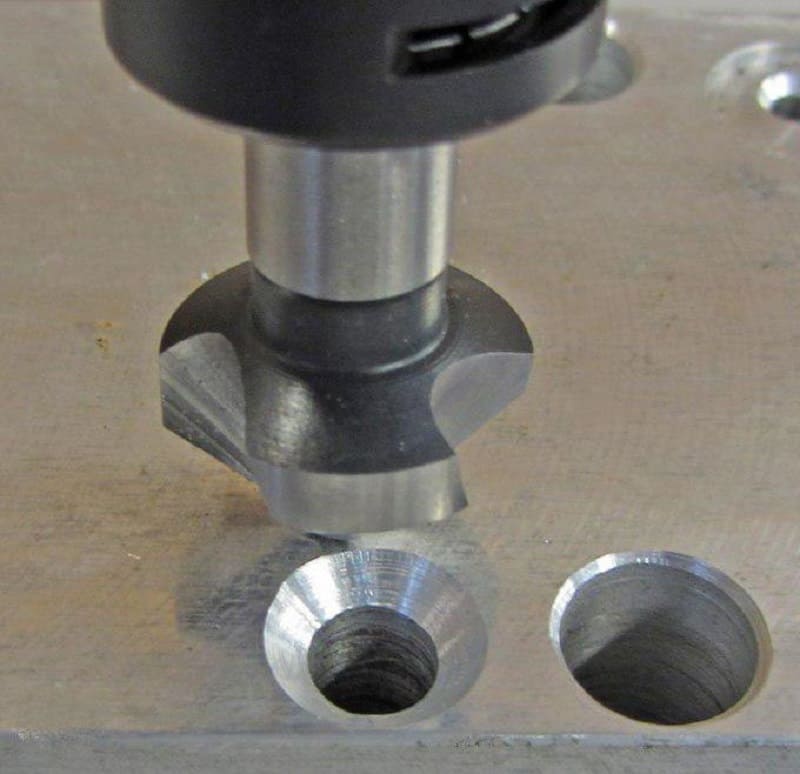
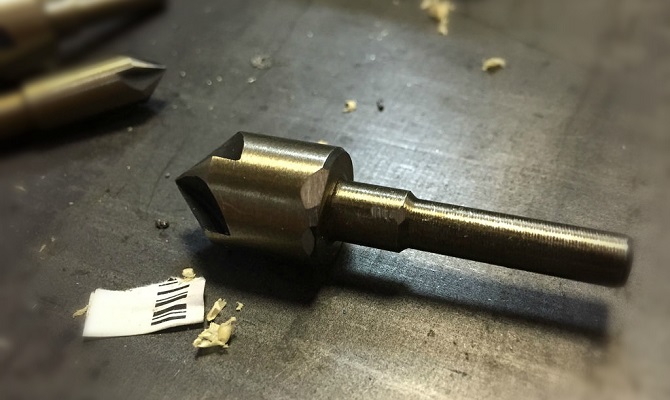
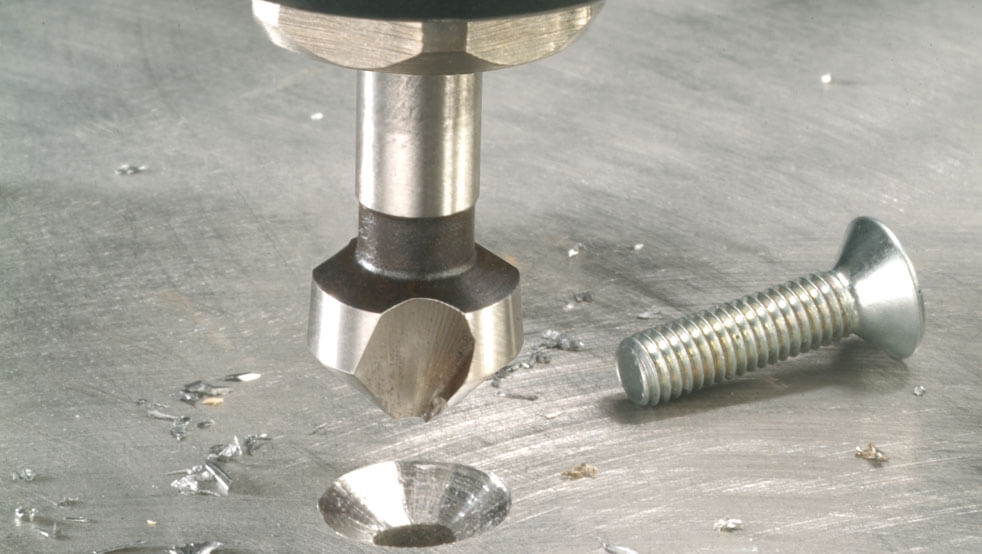
This type of machining creates recesses to position the fasteners flush with the surface of the part. In addition to chamfering, countersinks are used to cut conical depressions. Another purpose will be to clean and process the grooves before installing the fasteners, this is done using flat or end countersinks, also called counterbores, which is more competent.
The most widespread on the market are tapered countersinks with working angles of 90 and 120 degrees, which create indentations to hide the heads of bolts and screws. In the metalworking industry, countersinks with a flat tip are also used to clean out recesses for fasteners. Install countersinks in the same machines as the other tool for machining holes for fasteners.
Features of countersinking
Countersinking is the machining of holes to create various geometric recesses for the concealed placement of fasteners. It is also used for internal chamfering. For these purposes, there is a special tool - a countersink, which have a different shape. The choice of countersink depends on the desired end result.
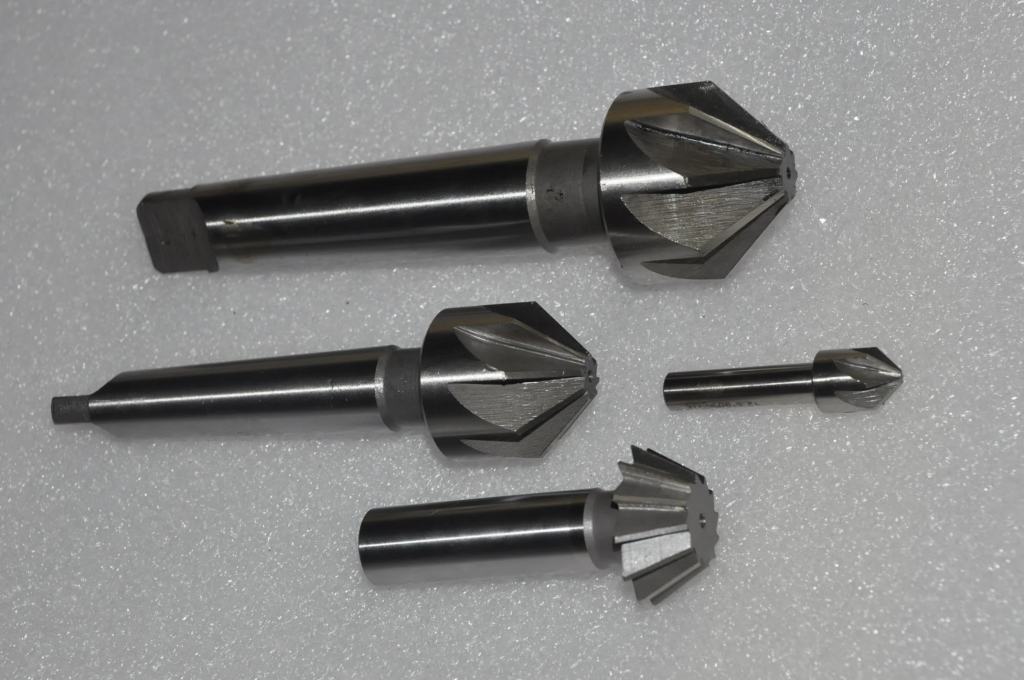
The main types of countersinks
-
Cylindrical countersinks. They are used to obtain cylindrical grooves in drilled holes for bolts and screws.
- Conical countersinks.Used for cutting tapered holes inside the part, as well as for cleaning sharp edges, chamfering and preparing recesses for fasteners. The most commonly used tools are 90 ° and 120 ° taper angles.
- Flat or end countersinks, you can also find the name counterbore. Mainly used for cleaning and processing grooves before installing fasteners.
The countersink consists of a working part and a shank with a special trunnion that acts as a guide belt. The trunnion is necessary to control the alignment in the process of cutting grooves.
How to choose the right step drill?
To choose the right step drill, you need to decide on the purposes for which the tool will be used. Thus, it is necessary to determine the holes of what dimensions need to be drilled.
The value of the smallest and largest diameters that are planned to be performed is especially important.
You should also decide on which hand tool or machine the drill will be used. This determines the type of shank that should be on the drill. Therefore, you should carefully study the connector of the drill chuck and clearly know the shape and dimensions of the shank. If the shank does not fit the existing connectors, you will have to purchase a special adapter separately.
It is important to decide on the manufacturer and the level of the tool. As already noted, the bright golden colored stepped conical drills are produced with admixtures of cobalt and titanium, with an abrasive coating and have a high hardness.
They will last longer and will allow you to work with thick rolled products, stainless and alloy steels.
Design features of the tool
Drills with carbide inserts are characterized by a number of design features. Let's list the most important ones.
- The working length of the drill, reduced by 20–35%, is explained by the fact that its regrinding is performed only on the carbide insert. The length of this type of drill, if used in conjunction with a jig, can be the same as that of a high-speed tool.
- The increase in the diameter of the core of the drill towards the shank is carried out in the range of 1.4–1.8 mm for every 100 mm of length, as with drilling tools of other categories.
- The angle of inclination of the helical groove of the tool depends on how deep the hole needs to be made.
- On the transverse edge of the drill, it is necessary to perform a sharpening with dimensions of 1.8–3.5 mm, which allows to reduce axial forces and reduce the load on the tool body.
- The taper shank, with which the drill is fixed in the spindle of the machine, must be precisely matched to the seating part, which will increase the rigidity of the drill and minimize the risk of vibration loads that can cause the carbide insert to chip and even break.
- To increase the reliability of the use of carbide drills for metal, a hole is often made in their inner part for supplying a cooling lubricant. This allows you to reduce the cutting temperature, reduce the intensity of tool wear, as well as facilitate the process of removing chips from the machining zone.

Drill device with removable plates
To give the working part of the drill the required hardness (56–62 units on the HRC scale), the tool is subjected to heat treatment, which, as a rule, is performed simultaneously with the brazing of carbide inserts.
High productivity of processing, as well as stability of drills of this category are provided by a number of parameters. This includes the shape of the carbide insert, the geometric parameters of its front surface, as well as the material from which such an insert is made.Currently, the most widespread tools are tools with carbide inserts of the correct three- and four-sided configuration, which allow drilling holes with a practically flat bottom.
Drills with such inserts, the cutting part of which is made in the form of a wave, allows machining using step-by-step plunge technology. The use of the latter not only ensures the stabilization of the position of the tool at the moment of its penetration into the processed material, but also minimizes the risk of its withdrawal during further processing. In addition, the corrugated drill can significantly reduce the cutting forces generated during the drilling process.

Drills with mechanical fastening of replaceable polyhedral plates (drills with MNP)
The design of drills, equipped with removable carbide inserts, allows them to perform not only drilling, but also such technological operations as boring pre-made holes, chamfering. In such cases, a peripheral carbide insert mounted on the tool is used.
Applications
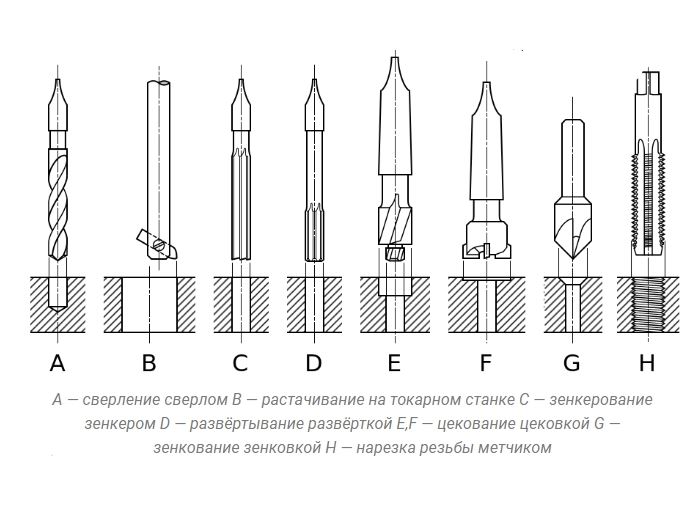
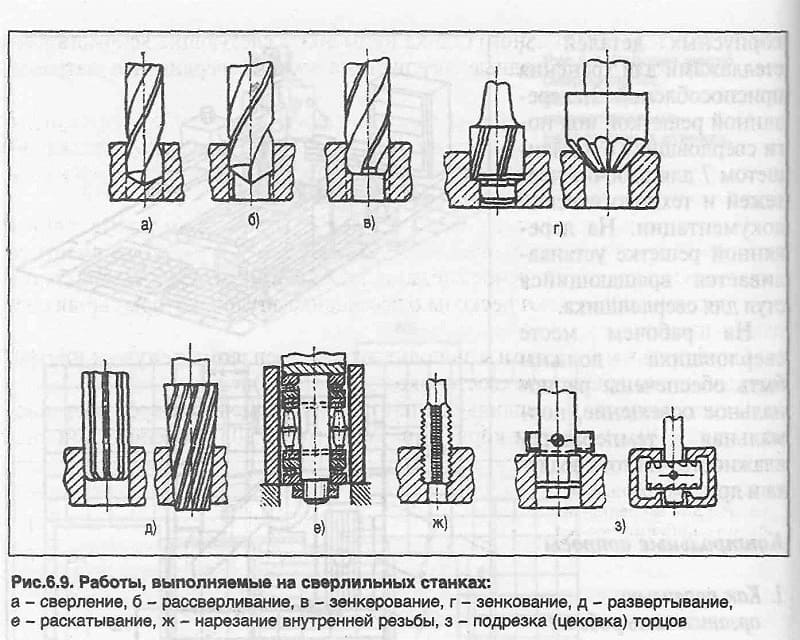
The areas of application of countersinks include the use on such machines as: - lathes; - drilling; - milling; - boring; - turning and revolving; - aggregate. According to the level of purity, the countersinking procedure, as a technological type process, is qualified as semi-finishing. It is usually used before reaming holes in blank elements made of various materials. Carrying out such a technological operation is necessarily performed at low machine speeds. Some types of countersinks are also used for processing and chamfering in holes that are located in hard-to-reach places - these are tools of the reverse type.
How to countersink metal correctly
If an amateur master can take a drill and a drill for countersinking, then in industrial conditions the following machines can be used for this:
- drilling;
- turning;
- boring;
- milling;
- aggregate.
The countersinking process takes place in strict accordance with the technology, the general points in which can be described in the form of the following recommendations:
- In cast parts with an uneven margin for subsequent metalworking, it is necessary to bore a hole to a depth of 5–10 mm for the correct direction of movement of the cutting tool.
- For the operation of countersinking holes, an allowance of 1–3 mm is left, depending on the final diameter.
- Countersinking of steel products is not complete without cooling with special oil solutions. When working with cast iron, as well as non-ferrous metal, it is optional.
- The optimal version of the countersink and the mode of operation are selected taking into account the required hole diameter, processing accuracy, its depth, metal of the part and the options of the production machine.
- The cutter attachment must mate with the slot on the workstation.
- In the case when finishing with a reamer is assumed, then during countersinking, a part of the allowance, from 0.15 to 0.3 mm, is left for further work.
- For processing products made of hardened and alloyed steels, countersinks with carbide inserts with a diameter of 14-50 mm and 3-4 teeth are used.
- When processing non-ferrous metals and iron alloys with a high carbon content, feather countersinks are used.
- High-speed steel tools are used to process products made of ordinary structural steel. For holes of more than 40 mm, the tooling is supplemented with nozzles with a diameter of 32–80 mm.
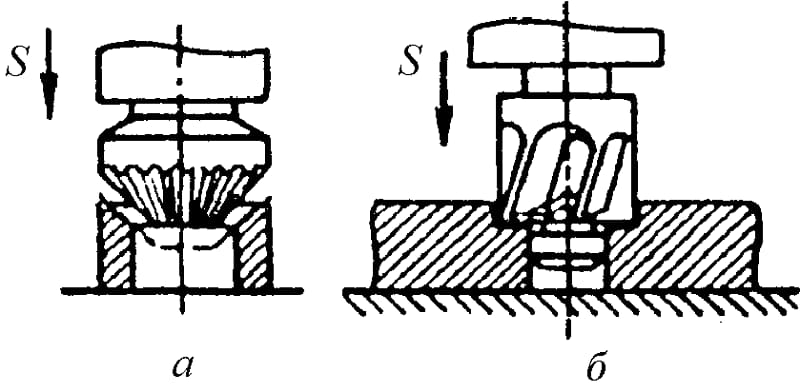
Inconsistency of the process with the established technology is often the cause of marriage. With a lot of tool wear, the resulting hole will be smaller than according to the project. When the technician overshoots the feed, or debris sticks to the countersink teeth, the cleanliness may not be satisfactory.Other defects: part of the surface is not machined, the resulting diameter is larger than the required one, are the result of an incorrect choice of a countersink or its incorrect installation.
Countersinking for metal and wood. Peculiarities
First, the design of the countersink is selected. For example, workpieces made of non-ferrous metals and alloys can be machined with an ordinary feather countersink, and for countersinking high-carbon steels, a metal tool with 3 ... 4 teeth is suitable, while the angle of the truncated cone can vary in the range of 60 ... 90º.

The production technology of these operations includes:
- Checking the straightness of the axis of the pre-drilled hole. For this, an internal gauge is used, and the part is laid on a flat rigid plane.
- For workpieces from cast alloys - test boring to a depth of 5 ... 10 mm. This makes it possible to exclude the influence of a possible discontinuity of the cast structure of the workpiece on the runout of the countersink.
- Wetting with coolant of the leading edge of the hole (for cast iron blanks, as well as for non-ferrous metal products, this is optional). Subsequently, the supply of coolant is performed along the existing helical grooves.
- Power supply of the countersink as it penetrates into the metal (the force will increase 2.5 ... 3 times, but this is not the cause of the malfunction).
- A gradual decrease in feed as it approaches the opposite end of the hole.
After processing the workpiece with a countersink with a developed guide part, the subsequent passage of the tool through the hole is not needed.
Of particular interest to home craftsmen is the combined drill-countersink tool. It is a stepped drill, at the end of which a countersink part is formed. To reduce wear and longitudinal feed force, this part is equipped with hemispherical grooves, where coolant is periodically supplied, and the resulting chips are removed.
Since the countersink drill, as it deepens into the metal, works under different conditions, a number of additional requirements are imposed on its performance:
- The greatest durability will have a working tool with a surface highly resistant coating of titanium or tungsten nitride. A blued tool (black) will have a slightly lower durability;
- Sets of several standard sizes of countersink drills help to form a conical transition part for fasteners of the required dimensions at the end of the hole;
- The working part of the drill should be the minimum permissible, at which stable processing is ensured: long tools sharply lose their stability from buckling, which, given the increased hardness, will instantly lead to breakage.
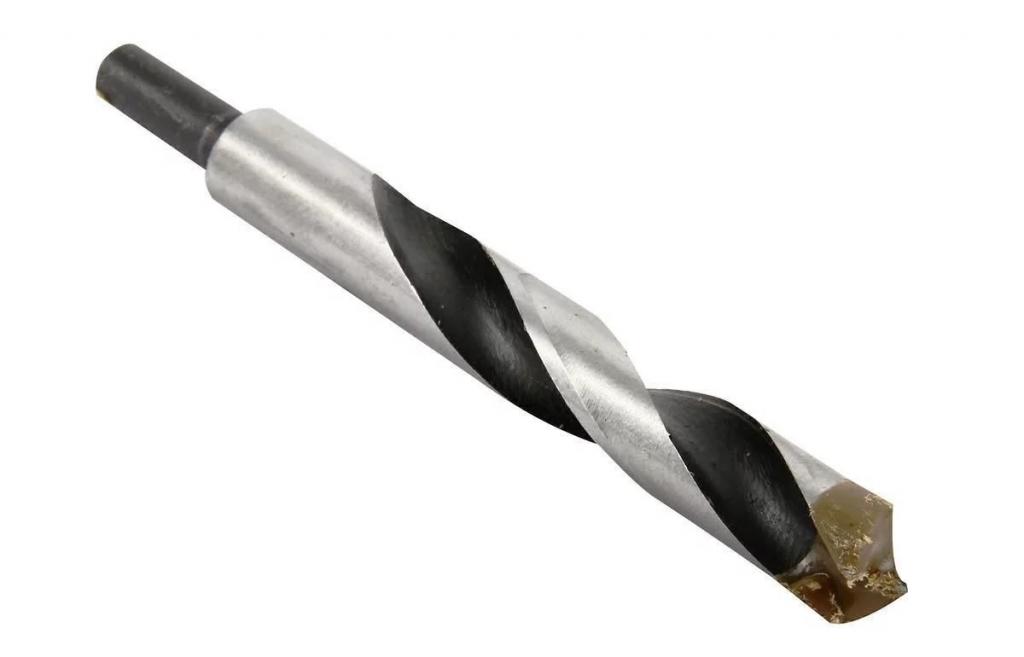
Countersinks for wood differ not only in material, but also in the shape of the end of the working part. It is also convenient to use a special countersink bit, which is put on top of a conventional drill and attached to it with a screw. At the same time, the quality of drilling is ensured by the correct sharpening of the drill and the optimal choice of its material. For deep workpieces (sizes above 40 ... 50 mm), it is more rational to use drills made of blued tool steel, while for less thick products, carbide countersinks show better durability.
The countersink bit for the main tool has one more operational advantage: it is double-sided, therefore, being mounted on the drill with its opposite part, it can be effectively used as a depth limiter for the machining of a cavity.
Main features of wood countersinks:
- Working end shape made at an angle of 90 °.
- The number of teeth increased to 5.
- Can also be used for countersinking a hole without changing its diameter.
- Dependence of the number of cutting edges on the material to be processed: for soft woods - pine or linden - usually one cutting edge is sufficient.At the same time, if it is necessary to process wood along the grain, due to the danger of chipping, the number of cutting edges is two or more.
Center drills: what they are, their characteristics
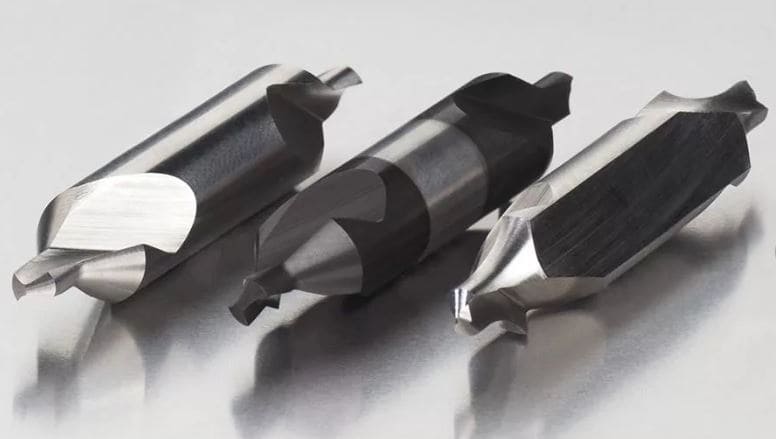

Anyone who has come across hole drilling knows how important it is that these holes are straight and made exactly where you need them. After all, usually, if the hole is uneven, made at an angle or a little in the wrong place, the part or material has to be thrown away
Therefore, they came up with a special tool called centering drills.
Let's figure out what this tool is. Center drills for metal (or, as they are also called, centering drills) are special multifunctional (they have several working areas for performing various operations) tools for cutting metal.
Center drill appearance
They are usually quite short, with a thin cutting area, tapered cutting edges and a thicker tail (a couple of times thicker than the tip), which provides improved tool rigidity.
The essence of the countersinking process
Countersinking and drilling are closely related. Usually countersinking is carried out on the finished hole, but there are times when it is necessary to make a recess without preliminary drilling. And in that, and in other versions, a countersink tool of different designs is used.
The countersinking process itself is very simple: a special cutter is used to chamfer the hole. The more metal is removed, the larger the indentation is. The countersink shape is usually conical. The main thing here is to observe strict alignment of the cutting element and the hole: there must be perfect alignment. Otherwise, the recess will be displaced relative to the hole, and the screw head will not be able to enter it.
To perform the countersinking operation for chamfering and for grooves, it is necessary to go through the following stages of the technological process:
- Measure the head of the threaded hardware for which the recess will be made (meaning both the diameter, height, and the angle of the bevel, if the head has a design for a sweep).
- Select the appropriate countersink and attach it to the drilling or turning equipment.
- Strictly observing the ratio of the axes, fix the workpiece with the hole opposite the cutter.
- Turn on the drilling equipment and set the required number of revolutions (if the circuitry of the machine allows it) or knowingly select the necessary tool for the parameters of the equipment.
- Countersink the hole.