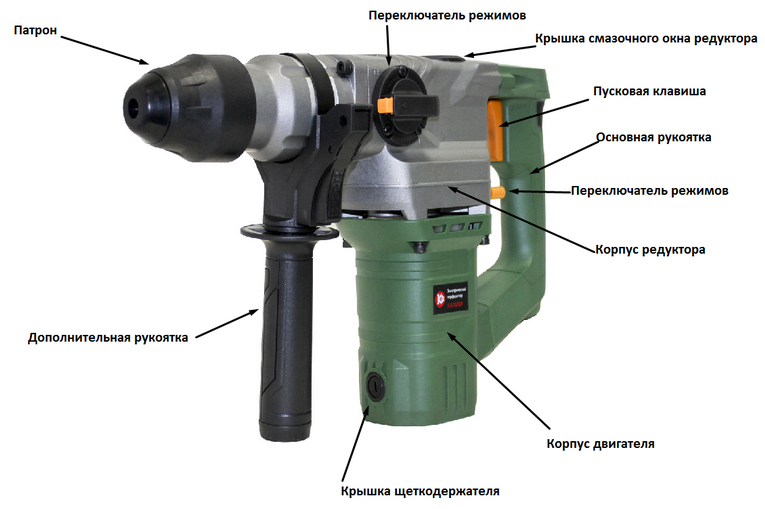
Varieties of the instrument
Pneumatic
The most common type of jackhammer. For the tool to move, it must be connected to a compressor. Crushing of the material occurs due to the compression of air molecules, which exert pressure on the chisel.
The equipment is used in a wide range of industries. Them:
- dismantle concrete buildings;
- destroy brick walls;
- create openings and recesses.
For a pneumatic jackhammer to work in everyday life, a power of at least 5 J. For industrial purposes, the impact force must be 10–100 J. Such tools are reliable and durable.
Classes of pneumatic equipment:
- Voluminous. There are rotary and piston. Their job is to expand the compressed air inside the piston system.
- Turbine. The mechanism of operation is simpler. The compressed air flow is supplied to the turbine blades through a flexible hose.
Important
The pneumatic hammer has an important advantage in comparison with other types of equipment - it is the absence of sparks during operation. He is not afraid of moisture, he can work in any weather .. The only drawback is the need to connect it to the compressor
Without the energy of compressed air, the tool will not be able to work
The only drawback is the need to connect it to the compressor. The tool will not be able to work without the energy of compressed air.
Electric
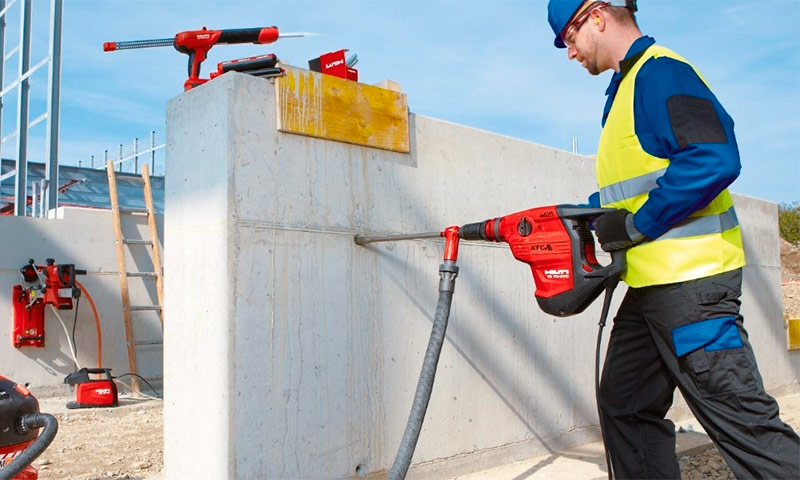
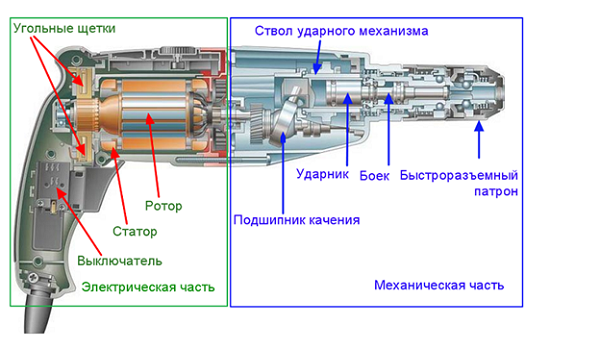
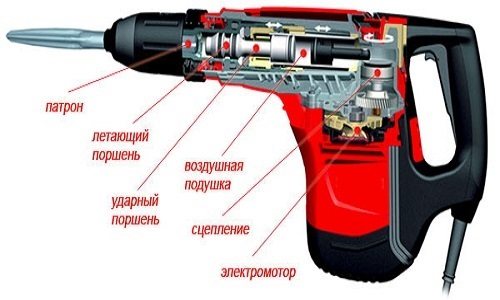
The principle of operation of the electric jackhammer is that the electrical potential is converted into mechanical potential. The work of the built-in electric motor consists in striking with a striker, which is built into the inside of the device. When the rotating tool is in operation, the process and rapid rotation of the hammer are activated. Due to this, high-quality breaking of walls and coatings occurs.
The design of the power tool is aimed at high impact power, it is not used for drilling and cutting materials. The fundamental characteristics of such an instrument are the force of impact, its power and frequency. Due to these values, the density of the surface for which the bumper is designed is determined. The equipment can have a power of up to 1700 W, impact energy - 45 J, the frequency of beats is 2000 times per minute.
Electric breakers can be plugged into regular outlets as they are double insulated. They can be used for finishing work indoors.
Replacing the cartridge
If you don't have a blueprint, take pictures of the disassembly process with your phone. This will save you a build error. To work, you will need the following tools: a flat screwdriver, pliers with long jaws, a hammer and an open-end wrench.
- Remove the rubber tip from the end.
- Using a screwdriver, remove the first retaining ring.
- Pull the plastic clutch cover down (as for changing the drill).
- Remove the second circlip in the same way as the first.
- Remove the clutch cover.
- Remove the spring, lock plates and balls.
- If you can do without replacing the entire assembly, then fold the steel parts into a suitable container and fill with kerosene.
The chuck is usually attached to the spindle using a thread. Clamp it with a vise or a gas wrench. And turn the spindle over the edges with an open-end wrench. If there are no faces, then disassemble the punch body, fix the spindle and rotate the chuck.
Installation and assembly of the unit is carried out in the reverse order.
General principles of the assembly process of Interskol rock drills
The assembly of Interskol perforators can be conditionally divided into several stages:
- Installation of rubber sealing rings.
- Assembly of individual units.
- Assembling blocks.
- Assembling the electrical part.
- Checking the performance of the power tool.
All Interskol rock drills consist of several large blocks:
- Impact unit mechanical block.
- Intermediate shaft block.
- Reducer block.
- Stator block.
- Control circuit block.
Selection of lubricants
Domestic manufacturers have developed special lubricants for the lubrication of rock drills. The lubricant is divided according to the operating conditions of the units. It is recommended to use lubricants specially formulated for these assemblies to lubricate the gearboxes, rolling bearing and clutch.
Lubricants are conventionally divided into three categories:
- For particularly loaded units, such as an impact mechanism, gearbox, intermediate shaft.
- For the lubrication of drill shanks.
- For lubricating rubber O-rings.
It is advisable to use Tsiatim-221 as a lubricant for rubber sealing rings, which does not destroy rubber.
Special lubricants are used for the gearboxes of Interskol rock drills.
 Domestic grease for rotary hammer gearboxes
Domestic grease for rotary hammer gearboxes
Before installing the rubber sealing rings on the parts, the latter must be lubricated with an inert rubber grease that can withstand temperatures up to +120 ºС.
It is recommended to use not only a lubricant inert for rubber, but also providing a high seal during operation.
From domestic lubricants, pay attention to Tsiatim-221
 Domestic grease for rubber sealing rings in rock drills
Domestic grease for rubber sealing rings in rock drills
For a secure grip of the tool, easy removal at the end of the work, it is recommended to use a special bunch for shanks.
 Domestic grease for rock drills
Domestic grease for rock drills
Assembling the drum unit
In Interskol perforators, the percussion unit block consists of a barrel and parts of the percussion mechanism.
Let's consider the assembly of the impact unit using the example of the Interskol 26 / 800ER perforator barrel.

The percussion mechanism consists of an industrial mass, pos. 16, a barrel, pos. 37, a striker, pos. 45, and a piston, pos. 47.
The shock pulse is created due to the reciprocating movement of the piston, pos. 47, in the barrel, pos. 36. The striker, pos. 45, moves inside the piston and transmits an impulse to the industrial mass, pos. 16. And now the industrial mass transmits a shock impulse to the instrument receiver, pos. 12. In the given chain, there is one more device that smooths out the magnitude of the shock impulse from the striker to the industrial mass. The device is called a striker catcher pos. 42.
Barrel assembly
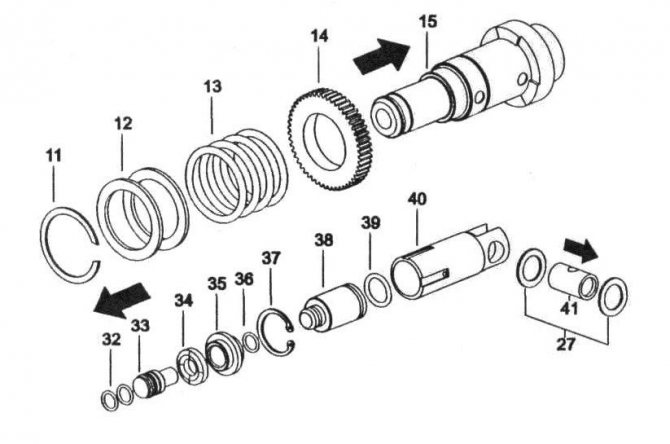
On the barrel poz.36 put on gear poz.35, on the other side the cam sleeve poz.38 and the connection gear-cam sleeve is fixed with needle rollers poz.37 and a retaining ring poz.34.
The gear is pressed by the spring, pos. 33, a washer is put on the barrel, pos. 32, and everything is fixed with a retaining ring, pos. 31.
The barrel is inserted into the body, pos. 18, into which the collar, pos. 19, is preliminarily inserted, the roller bearing, pos. 20, and the sleeve, pos. 21, are pressed in.
 Barrel, firing pin, catcher before assembly
Barrel, firing pin, catcher before assembly
The assembly of the barrel ends with the installation of the striker and the catcher inside after lubricating the inner surfaces. Installation of the catcher in the barrel body is fixed with a retaining ring.
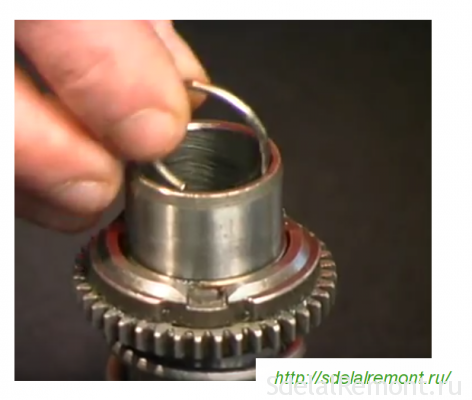

Piston assembly
Piston assembly pos. 47 begin by installing a finger on it, pos. 48, and two rings, pos. 49. The pin acts as a leash from the rolling bearing pos.60. A striker, pos. 45, with a pre-installed O-ring, pos. 46, is inserted into the piston.
Before inserting the firing pin inside the piston, the inner surface of the piston must be checked for roughness. There should be no scratch marks on the surface.
After lubricating the inner surface of the piston with a thin layer of Ciatim-221, insert the firing pin inside.
Types and scopes of SDS cartridges
Depending on the shank diameter with which the tool or adapter is equipped for fixing it to the hammer drill, SDS chucks are divided into five main types: conventional SDS chucks, models of the SDS-top, SDS-quick categories, as well as SDS-plus and SDS- chucks. max. The most popular chucks are the SDS-plus category, which are designed to hold tools with a shank diameter of 10 mm.The shank of the tool, adapted for fixing devices of the SDS-plus category, goes into them to a depth of 40 mm. In this case, the diameter of the working part of the tool, which is fixed in SDS-plus chucks, can be in the range of 4–26 mm.
The maximum tool length that can be clamped in SDS-plus chucks is 1 meter, and its most common working diameters range from 6–12 mm. Devices designed for fixing SDS-plus shanks and corresponding adapters for rotary hammers in them are used to equip equipment of light and medium category, the mass of which, excluding the weight of the tool, ranges from 3 to 5 kg. It is these punches, which are designed for an impact load of up to 5 J, that are most popular with DIYers and small repair crews.
Common types of SDS shank
The SDS-max chuck, with a bore diameter of 18 mm, is used to equip heavy professional rock drills starting from 5 kg. These rotary hammers, which can be used with tools up to 6 mm in working diameter, are capable of generating shock loads of up to 30 J. To ensure accurate and secure tool fixation in such serious equipment, an additional guide slot is provided on SDS-max shanks. ...
The SDS-top and SDS-quick chucks are intermediate rock drill options and are used much less frequently than the models described above. Meanwhile, the design of the SDS-quick devices, which were developed by Bosch engineers in 2008, is worth taking a closer look at. The tool is not inserted into SDS-quick chucks by means of grooves, but by means of protrusions on the shank. The design of SDS-quick chucks allows you to lock tools with a hex shank and a quarter inch size.
The SDS-quick system is used in the Bosch UNEO cordless rotary hammer
Punch chuck device
Almost any construction tool is versatile, and the hammer drill is no exception. There are many different attachments, cartridges, adapters for them. The basis for any work is the patron. The hammer drill adapter is used to mount a drill directly removed from a conventional drill. Both bits and drills have a huge variety and are selected in accordance with the tasks at hand.
At home, you must always keep a replaceable chuck for a perforator, since at any time one may well fail. It should be noted that for each type of work it is better to use different cartridges. The main types of cartridges:
- quick-release: perfect for frequent change of attachments during operation;
- key: intended for large drills.
To know how to repair a hammer drill cartridge, you need to study its direct structure. At one time, the drill was mounted using movable cams, but progress does not stand still. In SDS, the drills are held in place with 2 guide wedges and 2 locking balls. The difference between SDS-plus and SDS-max is only in the number of guide wedges. So, the fastening is reliable and fast.
The fixing of the nozzle itself has been simplified: it is necessary to insert the selected nozzle into the socket of the cartridge, slightly press, wait for a click. This will ensure that the attachment is secured well. And removing the drill is not particularly difficult: you need to press the movable cover, as a result of which the drill will be removed.
Additionally, the punch can include components in the form of:
- speed regulator;
- electronic reverse;
- brush reverse;
- quick change systems;
- immobilizer;
- indicators;
- anti-vibration system;
- friction clutch.
Daily care and storage of the rotary hammer
In order for the tool to serve for a long time and properly, you need to follow simple rules.
- Before starting work, conduct a cursory inspection of the technical condition of the tool. In no case should you ignore the symptoms of a malfunction, if any.
- At the end of the work, clean the rotary hammer from dust and debris. It is advisable to blow with a jet of air from a vacuum cleaner.
- When transporting in a cold season, before starting work, give the device at least 20 minutes to "acclimatize" the device. The grease should thaw and become elastic.
- Work in compliance with the operating standards described in the technical data sheet of the tool.
The punch should be stored in a dry and warm place. For long-term storage, it is recommended to pack in a plastic bag and cardboard box. Do not allow moisture to enter electrical parts, including condensation from the air.
The case is the best place to store the hammer drill
Aware means armed. Knowing the intricacies of the structure of the hammer drill mechanism, you can repair the tool yourself and in the shortest possible time. However, if you look under the puncher casing in a timely manner, clean and lubricate the mechanisms, then it is quite possible that you will not have to resort to repairs at all. Regular maintenance of the appliance will help extend its life.
Tool chucks
There are several ways to secure the drilling or slotting equipment to the tool. They have a different method of application and design. The frequency of use in various models is also different for them.
Self-clamping device
The name of the patron speaks for itself. To clamp the drill or drill, a special wrench or any additional tools are not required. The tooling is changed at a high speed. Press on the spring-loaded body by hand and take out an unnecessary drill, and install a new one in its place.
Such devices are of two types: with one coupling and with two. If a double-sleeve clamp is installed, hold the lower part of it with the other hand. The disadvantage is the unreliability of the fastening. When pressed hard or biting, the drill rotates. Despite this, such a device is used in everyday life and in production - where in the process of drilling it is necessary to change the equipment many times.
Impact drill adapter
This device will help out when there is no drill at hand, and it is simply necessary to make a hole with an ordinary drill. Such an adapter for a hammer drill is inexpensive and is a conventional collet chuck with a shank. In this case, the capabilities of the drilling device itself are expanded. Almost any modern model allows you to install such an adapter.
However, there are some minor caveats. When drilling with such an adapter, accuracy will suffer slightly due to the fact that the rotational speed is quite high, and the bit will reel. In addition, the size of the adapter must be calculated based on the strength of the hammer drill. If you put a more powerful adapter on a weak tool, then you can disable the drill.
Installing the drill with a key
Such a chuck is also called a toothed chuck due to its toothed appearance, or a cam chuck because the locking process is similar to clenching a fist. Clamping takes place using a special key. The method is quite time consuming, not only in terms of tool replacement. The cartridge itself cannot be quickly changed either, because a special cartridge key is needed here. However, the clamp turns out to be the strongest and most reliable, it supports the installation of drills of the maximum size. Any shank will work too.
Varieties of quick-detachable cartridges
Such equipment was developed in Germany by engineers of the Bosch company, and since 1980 they have been equipped with their hammer drills. At the moment, most models of such power tools are equipped with them. Steck-Dreh-Sitzt in translation means "inserted, turned, village."From these German words the name of the whole class of keyless chucks for the SDS rock drill comes from.
They, in turn, are divided into subclasses - depending on what their diameter is.
The most widely used products are of the SDS-plus type. Drills with a shank of 10 millimeters and a diameter of 40 mm enter them. The drill itself for the chuck has dimensions from 4 to 26 mm and a maximum length of up to 1 meter. This type of quick release tool holder is suitable for light to medium rock drills designed for a 5 joule shock. This will be enough for both household chores and the needs of the construction team.
The 18 mm bore hole characterizes the SDS-max category keyless chucks used on heavy-duty tools weighing more than 5 kilograms. The working diameter reaches 60 mm, the depth of the head is 90 mm. The technique of using such a tool is more powerful - the impact force rises to 30 joules. The presence of an additional groove guarantees a firm fixation of the equipment.
Less commonly used are the SDS-top and SDS-quick hammer chuck. The first is designed for drilling holes with a diameter of 16-25 millimeters and a fit of 40 mm. The shank has a diameter of 10 millimeters. This type of quick-change cartridge was considered as a transitional one between classes.
The second was developed in 2008 and is designed to support ¼ ”drills.
How to disassemble and replace the chuck at the hammer drill
Punch chuck breakage is rare, but always out of place. It is good that the malfunction of this unit can be easily eliminated on its own. But for this you need to know its structure.
Cartridge
All electric rock drills are equipped with simple and reliable SDS chucks. Their prototype was designed by engineers from the West German firm Bosch. Therefore, the abbreviation in the name is derived from the German words: Steck, Dreh, Sitzt. Which in this case mean - "insert", "turn", "sits". Five modifications of this design are currently being produced:
- SDS. For bits with a Ø 10 mm shank with 2 longitudinal grooves to secure against twisting. Shank insertion depth - 40 mm. This design works well with SDS-plus shanks.
- SDS-plus. The leader in frequency of use among hammer drill chucks. Designed for bits with Ø 10 mm shank, which has four slots (two long ones to prevent twisting and two short ones to secure them against falling out). The insertion depth is 40 mm. This type is used on light rock drills. It can work with attachments Ø 4–32 mm, lengths from 11 cm to 1 m.
- SDS-top. A rare species. Fits on medium rock drills. The nozzle for it has a Ø 14 mm shank equipped with two long and two short grooves. The depth of alignment is 70 mm, with a drill diameter not exceeding 32 mm.
- SDS-max. It is found on punchers only slightly less often than the leader. Designed for drills larger than 2 cm in diameter. Used primarily with heavy rock drills. The shank for it Ø 18 mm is inserted 9 cm, has three long and two short grooves.
- SDS-quick. This type is for a quarter-inch hex shank instead of a slotted shank. It can even hold drills and bits. Until 2009 inclusively installed exclusively on Bosch Uneo. Boers do not make it thicker than 1 cm.
- SDS-hex. Only lances and chisels have shanks for working with it. And they only complete jackhammers.
The designs of hammer drill cartridges and electric drills have nothing in common. The drill chuck grips the drill with movable jaws. In the hammer drill, the drill is fixed against turning by guides entering the grooves of the shank. The latches of the spring-loaded balls do not allow it to fall out. To fix the drill, you need to insert the shank into the hole of the chuck. And by pressing on the nozzle, insert it inside until it clicks. To remove the drill, pull the plastic skirt towards you.
Replacing the cartridge
Procedure:
- Remove the rubber tip from the end.
- Using a screwdriver, remove the first retaining ring.
- Pull the plastic clutch cover down (as for changing the drill).
- Remove the second circlip in the same way as the first.
- Remove the clutch cover.
- Remove the spring, lock plates and balls.
- If you can do without replacing the entire assembly, then fold the steel parts into a suitable container and fill with kerosene.
The chuck is usually attached to the spindle using a thread. Clamp it with a vise or a gas wrench. And turn the spindle over the edges with an open-end wrench. If there are no faces, then disassemble the punch body, fix the spindle and rotate the chuck.
Carefully. Do not put in the kerosene tip
Since its rubber is not oil resistant, it will not withstand prolonged contact with it.
Installation and assembly of the unit is carried out in the reverse order.
The drill is not fixed
There may be several reasons why the chuck does not hold the drill shank. Below are the most likely ones.
- Body, lock plates or balls worn.
- Loose or broken retainer spring.
- Dried out or thickened grease from dirt that impedes the movement of the locator balls.
Important. During assembly, do not lubricate the parts with petroleum jelly.
It is only used for conservation. Of the greases, lithol is best suited.
Repair or replacement
If you don't have spare parts, repairing a cartridge is easy in just two cases:
- When the balls are worn.
- And when the lubricant, having lost its plasticity, impedes the movement of parts. In other cases, it is easier to find a replacement than to repair it.
What is a hammer drill chuck?
For the first time, an electric hammer drill was made in the 30s of the last century. The first electric drill was produced by Bosch, which specializes in the production of household and industrial appliances. The torque combined with the cyclical chiseling is expected to please all consumers. From that moment on, the power tool has never disappeared from the windows of hardware stores.
Diagram of the percussion mechanism of the drill.
But after the production of the first piece of equipment, most consumers ran into some trouble. The main problem was the hammer cartridge. This was due to the fact that the simultaneous chiselling and drilling severely damaged the structure of the socket for the nozzles.
Industrial equipment manufacturers have found an easy solution to this problem - they have simplified the design of the cartridge, thereby strengthening its structure.
At the moment there are 2 different types of hammer drill cartridges:
Each of them, in turn, is subdivided into several types.
The key type of chuck is a nozzle that is clamped with a special key that fixes the chuck from the inside using a crimp rod. It is also called gear or cam. The main advantage of this type of cartridge is the increased level of reliability when fastening. But often replacing the cartridge takes a certain amount of time when compared with other types of attachments.
The quick-release type of the chuck is secured by clamping the nozzle with light force, this allows manual replacement. This mechanism is divided into 2 types: one- and two-clutch. The first type is one-handed, but is only used in self-locking tools. The second type involves holding the rear sleeve with one hand and unscrewing the front sleeve with the other.
Video: How to Disassemble the Pit Hammer
Video: how to remove a drill stuck in a chuck
Removing the mode switch
To remove the mode switch, you must:
- Turn the switch to the “impact” position (hammer icon) and rotate it about 1 cm lower.
- Release the lever from the socket.
- Pull the lever towards you.
How to check the start button and brushes
To get to the collection of brushes and the launch control button, you need to remove the back cover. To do this, unscrew two or three screws from the plastic case (depending on the model).
The start button is checked with a multimeter. Keep in mind that the engine speed control system is also located inside the triggers.If molten plastic is visible on the button body, it should be completely replaced as it will no longer work properly.
After replacing the button, you need to replace the housing cover, be sure to tighten the screws securely. Only then can the hammer drill work.
How to disassemble an electric motor
To disassemble the engine, disconnect the engine housing from the transmission. They are held together with four screws. If they are unscrewed, the mechanical part is easily separated from the plastic shell. When dismantling, the engine rotor is removed from the guide sleeve, freeing access to the gearbox. Accordingly, it becomes possible to inspect the electrical components of the engine.
The motor consists of a movable rotor and a rigidly fixed stator. The rotor rotates under the action of the force generated on the windings, which consist of turns of a copper conductor. Checking the windings is to determine the integrity of the insulation, the absence of a short circuit between the turns. This is done with a multimeter by sequentially measuring the resistance on the rails. If a short circuit is found on a corner, the armature must be replaced or repaired. The stator windings at home can be rewound using a special template.
The anchor is usually replaced completely together with the bearings and air intake plates.
To determine if the transmission is faulty, it must be completely disassembled. For this, the plastic case is removed, the gearbox is thoroughly cleaned of old oil. The following are disconnected from the transmission:
- Floating bearing;
- Transfer shaft;
- Raster sleeve;
- Sleeve with a piston.
The floating bearing, also called "drunken bearing", is mounted in an aluminum gear housing with a bracket that must be pressed down with a flat-blade screwdriver. The released bearing is removed and replaced if necessary
Also note that inside the "drunken bearing" is the needle bearing on which the drive spins. When the hammer is in impact mode, it is subjected to heavy loads and therefore often fails.
A new bearing is purchased separately or assembled with a gap.
The raster sleeve contains an impact bolt, which is secured internally by a metal retaining ring. On the sides of the sleeve there are two technological openings through which access to the locking mechanism is provided. After unscrewing the ring, the impact bolt falls freely out of the bushing. Inside there is a high-alloy steel drum.
When repairing or replacing the impact bolt, it is also necessary to replace the rubber grommets that ensure the tightness of the mechanism. All parts of the hammer are heavily lubricated with special grease.