Introduction
The machine consists of three main structural elements:
- base;
- sawing table;
- parallel stop.
The base and the sawing table itself are not very complex structural elements. Their design is obvious and not so complicated. Therefore, in this article we will consider the most difficult element - the parallel emphasis.
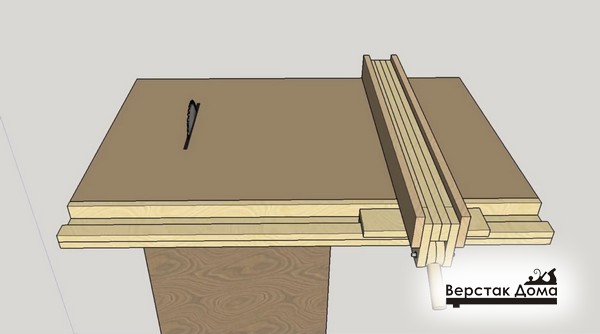
So, a parallel stop is a movable part of the machine, which is a guide for the workpiece, and it is along this part that the workpiece moves. Accordingly, the quality of the cut depends on the parallel stop due to the fact that if the stop is not parallel, then either the workpiece or the curve of the saws may jam.
In addition, the parallel stop of the circular saw must be a rather rigid structure, since the master applies forces, pressing the workpiece against the stop, and if the stop is displaced, this will lead to non-parallelism with the consequences indicated above.

There are various designs of parallel stops, depending on the methods of attaching it to the circular table. Here is a table with the characteristics of these options.
| Rip fence design | Advantages and disadvantages |
| Two-point fixing (front and back) | Advantages: · Quite rigid design; · Allows you to place the stop anywhere on the circular table (to the left or right of the saw blade); · Does not require the massiveness of the guide itself Disadvantage: · For fastening, the master needs to clamp one end in front of the machine, and also go around the machine and fix the opposite end of the stop. This is very inconvenient when choosing the required stop position and, with frequent changeovers, is a significant disadvantage. |
| One point mount (front) | Advantages: · Less rigid design than when fastening the stop at two points; · Allows you to place the stop anywhere on the circular table (to the left or right of the saw blade); · To change the position of the stop, it is enough to fix it on one side of the machine, where the master is located during the sawing process. Disadvantage: · The design of the stop must be massive to ensure the required rigidity of the structure. |
| Fastening in the slot of the circular table | Advantages: · Quick changeover. Disadvantage: · Complexity of the design, · Weakening of the design of the circular table, · Fixed position from the line of the saw blade, · Quite a complex design for self-production, especially from wood (made only of metal). |
In this article, we will analyze the option of creating a parallel stop design for a circular with one attachment point.
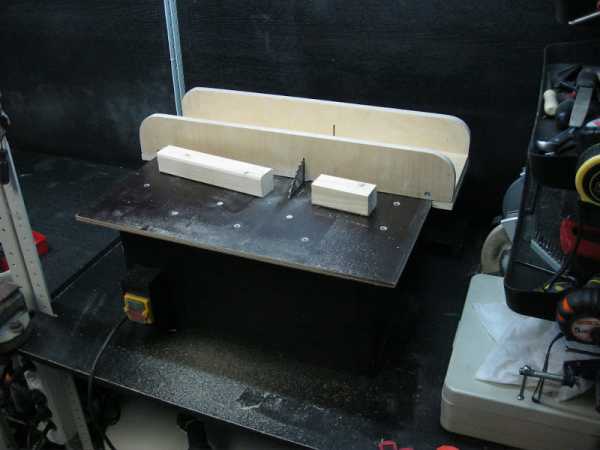
A straight edge is a simple and straightforward element
This type of tire as a stop ruler is the simplest, easiest to manufacture and use. When making it, it is necessary to remember, no matter how simple the design is, it must ensure reliability and safety. A well-made stop fence can be used for electric jigsaw, hand-held circular saw, simple hand saw. Manufacturing is carried out in the following sequence.
- Prepare a strip of wood or plywood. The width should exceed the width of the platform of the used circular saw by 20 centimeters.
- A ruler is made from this strip. The remaining plywood sheet is used to make the base.
- The finished structure is screwed to the base. For this purpose, wood screws are used.
- The protruding part of the ruler is carefully cut off. The edges should be milled.
Stop ruler
When starting to work with a ready-made tool, it is advisable to carry out several test cuts on secondary wood products. It is necessary to get used to the fact that moving the saw along the length of the ruler, you must apply different forces. Therefore, one should acquire some experience. Then proceed to the fine cut.
What are miter saw stops for?
All kinds of additional devices: stops, clamps, fasteners are used to securely fix the workpieces. The miter saw stop helps you make precise cuts across the grain of the wood. The factory stop has one drawback, which significantly reduces the area of application. The cut cannot be made more than the width set by the manufacturer. This parameter is individual. Sawing boards of wider width requires a rigid fixing of the stop.
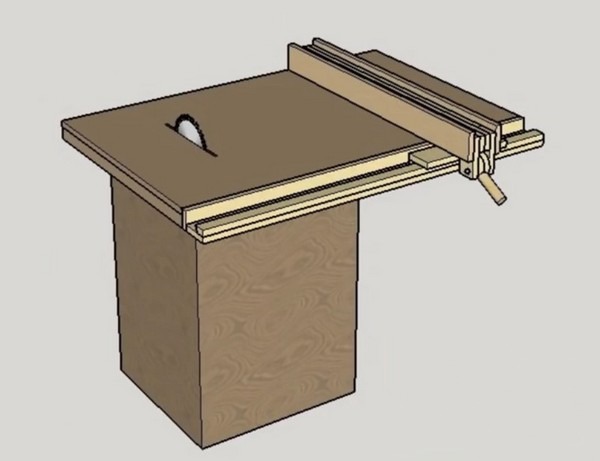
The design of the stop of the circular machine
The whole structure consists of two main parts - longitudinal and transverse (meaning - relative to the plane of the saw blade). Each of these parts is rigidly connected to the other and is a complex structure that includes a set of parts.
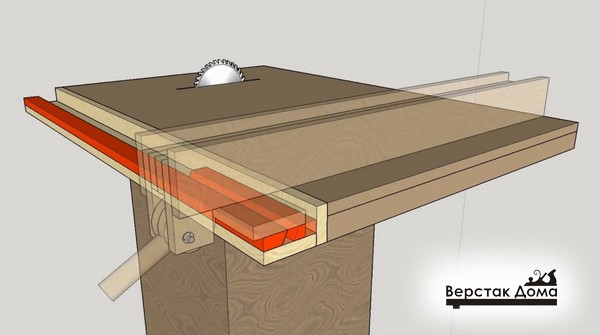
The main technological solution of this stop is the principle of jamming with the help of an eccentric and tight pressing of two transverse guides with an oblique end.
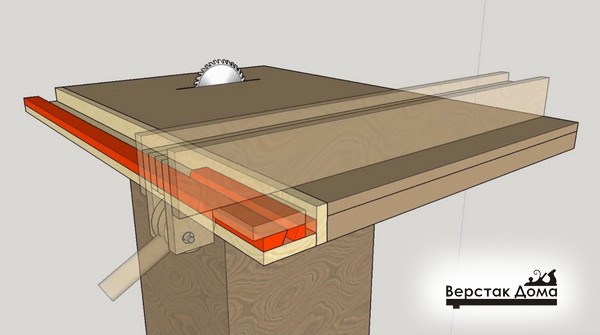
Fixation takes place by turning the eccentric mechanism.
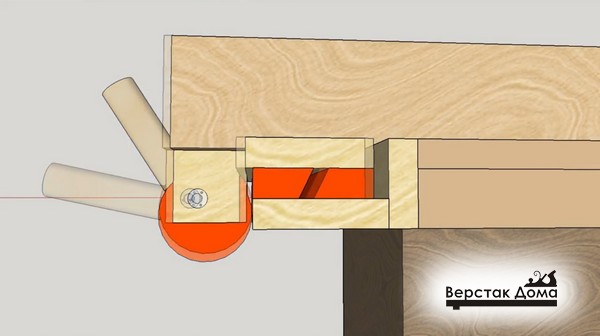
The clamping force is large enough to ensure structural strength and securely hold the entire rip fence.
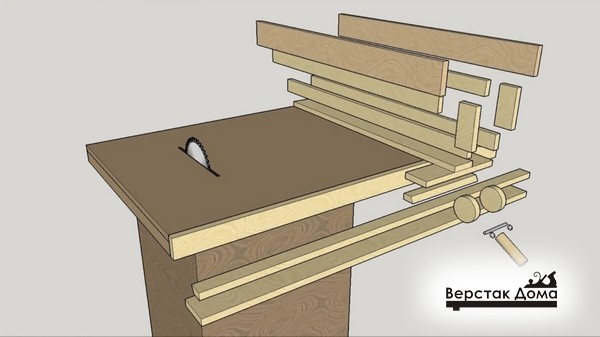
The whole design is not trivial and consists of a large number of different parts, each of which has its own purpose and size.

From a different angle.
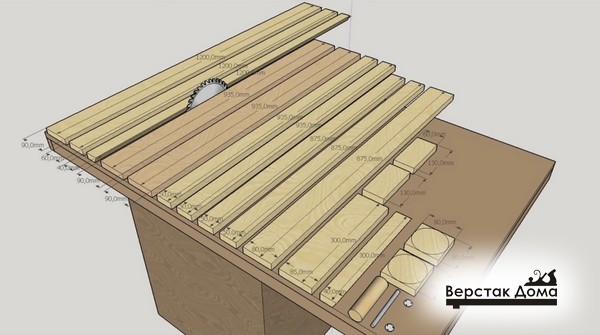
The general composition of all parts is as follows:
- Transverse part
- Base of the transverse part;
- Upper transverse clamping bar (with an oblique end);
- Lower transverse clamping bar (with an oblique end);
- End (fixing) strip of the transverse part.
- Longitudinal part
- Plane sliding element (laminated chipboard, 2 pcs.);
- The base of the longitudinal part;
- Clamp
- Eccentric
- Eccentric handle
Saddle stop
If you have to saw a lot of identical bars with a circular saw, then it is worth spending time making a simple saddle stop. Its application will more than return the spent minutes. The saddle bumper is especially effective when cutting thick beams that require two cuts on the disc from different sides.
The saddle stop has a U-shape. The base is a board 25 mm thick, its width is exactly equal to the thickness of the sawn timber.
The side surfaces of 10 mm plywood are attached to the base. The width of the sidewalls should be greater than the width of the bar to provide support for the circular platform until the saw blade comes into contact with the bar.
The saddle is put on the bar at a distance from the cut marking corresponding to the working distance to the saw blade, and through the sidewalls it is pressed against the bar with clamps. Using the sidewall as a stop for the saw platform, cutting is carried out. If the thickness of the bar is such that one cut is not enough, then turn it over and make another cut. The position of the stop does not change in any way.
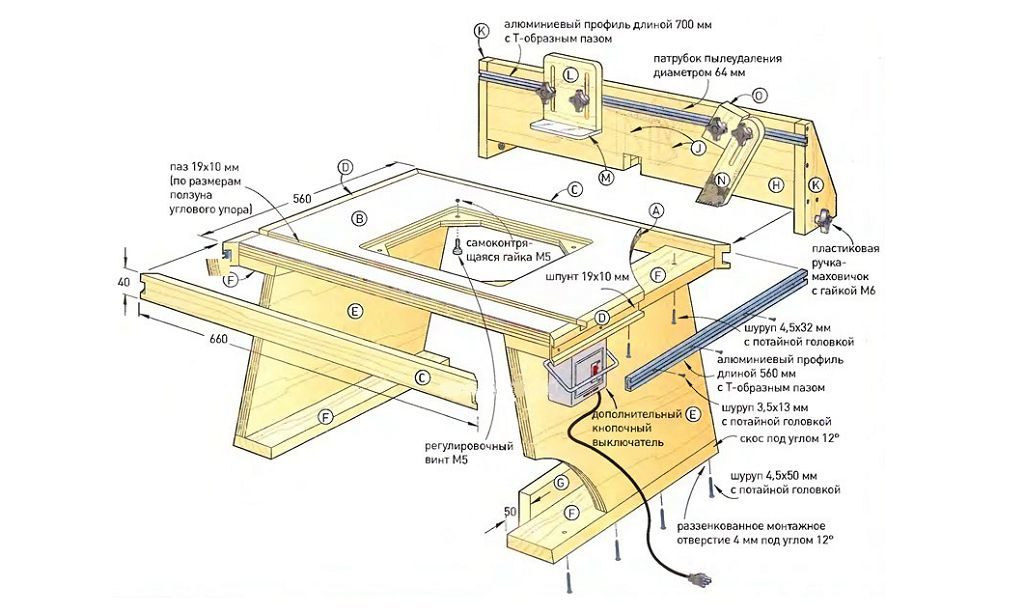
Circular carriage and installation of front and back stops:

- An additional rail (F) on the carriage, figure 1, is needed for working with long workpieces. (Note: The rail can be installed on the right side, the T-nuts for the bolts are inserted into the pot from the inside of the stop.)
- Next, drill through holes in the stop and additional rail, insert the nuts and tighten the bolts.
- Make a cut at the base of the slide, no more than 1/2 of the total length of the carriage, photo S.
- Switch off the saw. Using a square, set the rear stop perpendicular to the saw blade, photo C. Fix the stop firmly to the base using clamps.
- Use a wide piece of wood, scrapped and perfectly parallel, and make a test cross-cut, photo D.After the cut, flip one of the halves 180 degrees and attach the cut to the cut of the other half. The adjustment can be considered complete when there is no gap between the cuts, photo D, insert.
- After all the adjustments, it's time to fasten the backgauge (C) to the screws first, and then the frontgauge (B).
Installing the disc guard and sled stop block:
- Glue and secure the disc guard (E) to the stop (C), photo E.
- For safety reasons, the carriage for the circular saw should stop the moment the top of the saw blade touches the blade guard, Figure 1.
- Two pieces of wood rigidly fixed on the carriage and on the side of the circular table solve this problem, Figure 1.
- To avoid losing the handles, Photo G, reamer to fit the rubber o-rings on the inner surface of the extension rail, Photo H.
- Make a work stop block as shown in figure 2, it consists of three parts: a front stop block (G), a main stop block (H) and a stop block strip (I). Before gluing the three pieces of the block, make sure all the faces and edges are square to each other.
- The carriage for the circular carriage is waxed on the bottom of the slide and slider, this will allow the carriage to slide smoothly.
The preliminary dimensions of the carriage for the circular are shown in the table below:
How to make a device with your own hands
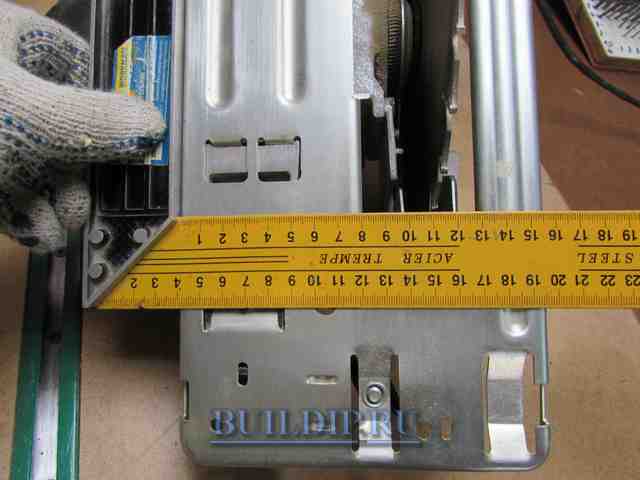
The cut-off device is made for a specific model of power tool. Measure the distance from the motor to the bottom of the sole on your circular saw and subtract 5 mm. The result obtained is the height of the guide stop.
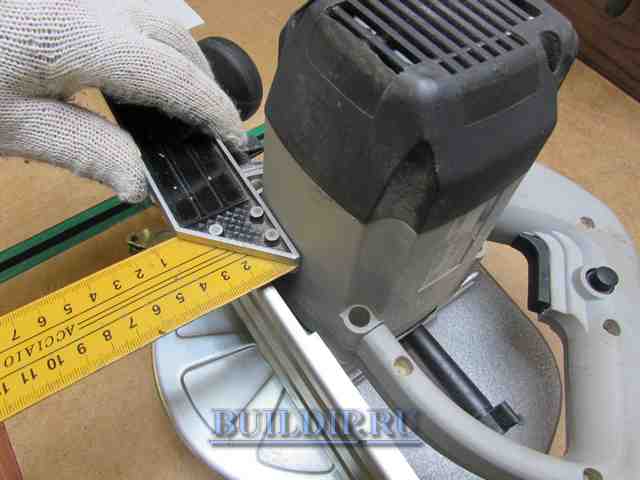

Removing the required dimensions of the circular saw.
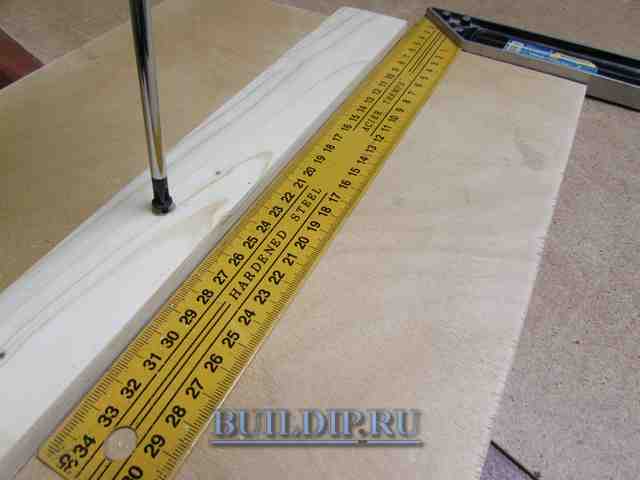
Prepare right-angled plywood base and parallel-edged wooden battens to measure.
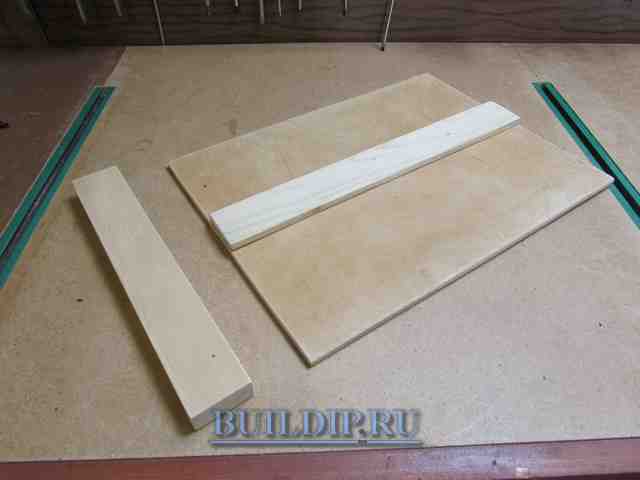

Blanks for assembling a cross-cut device with a circular saw.
Measure the distance from the blade to the edge of the sole.

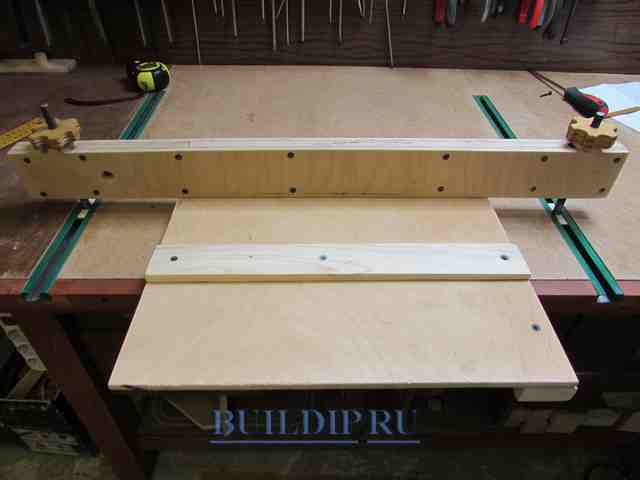
Add a 6-10 mm allowance and install a guide rail at this distance from the right end of the plywood. Fix the bar with countersunk screws, controlling its strictly perpendicular position.

Screw the stop block on the back and fix the fixture to the workbench.

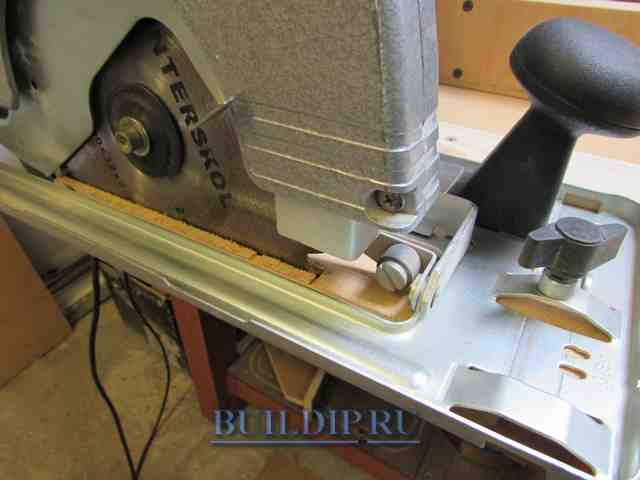
Saw the plywood with the circular saw to the final width, creating a reference end to accurately position the fixture along the lines.

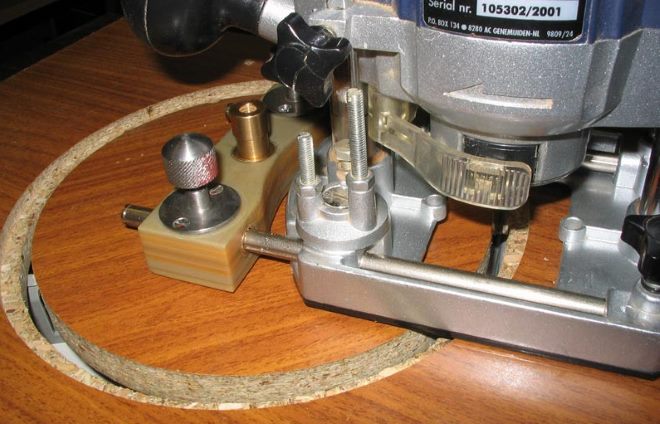
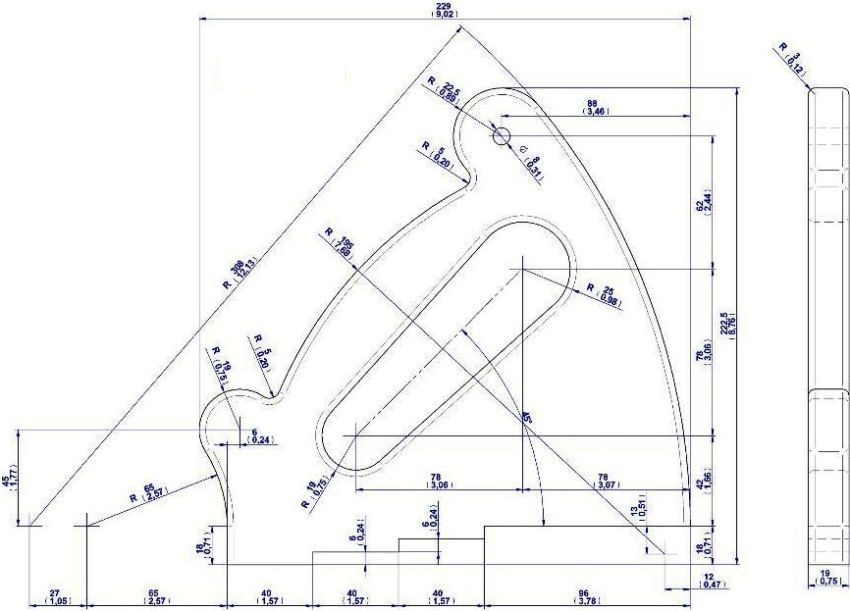
Draw the eccentric cam pattern on the paper.
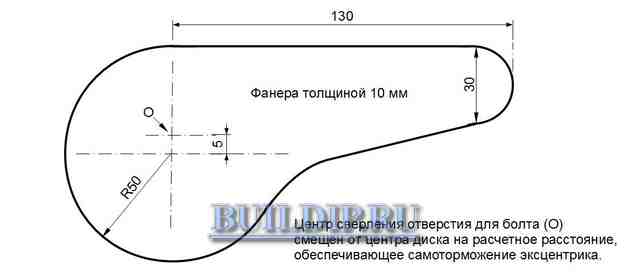
Eccentric clamp drawing.
Mark the part on 10mm plywood and mark the center of the bolt hole with an awl.

Saw out the workpiece with a jigsaw.
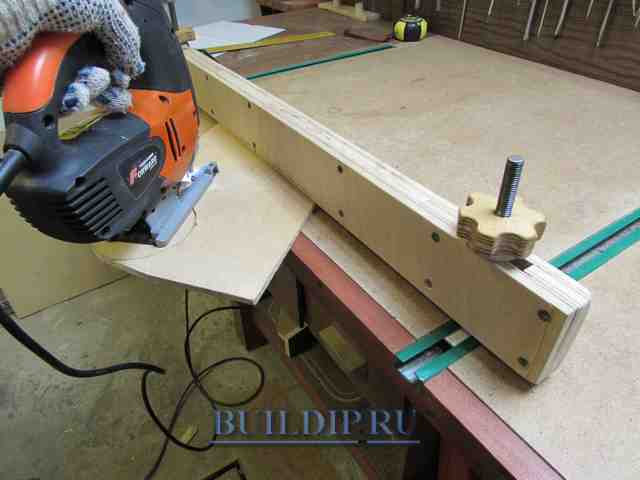

Make a 50mm washer out of the same plywood using the drill for wood "Ballerina".

Sand the workpieces and pick up an M6 or M8 furniture bolt with a mustache (or with a square headrest), a handwheel nut, washer and bushing. The latter can be made from a tube of a suitable diameter. The bushing length is the total thickness of the base, arm, and plywood washer.
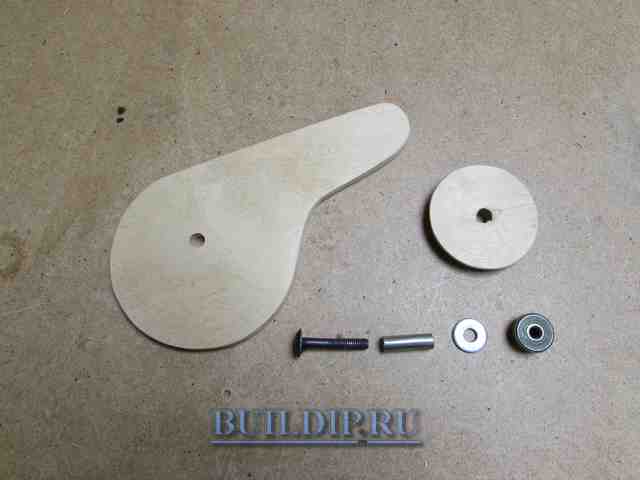

Ready-made eccentric made of plywood.
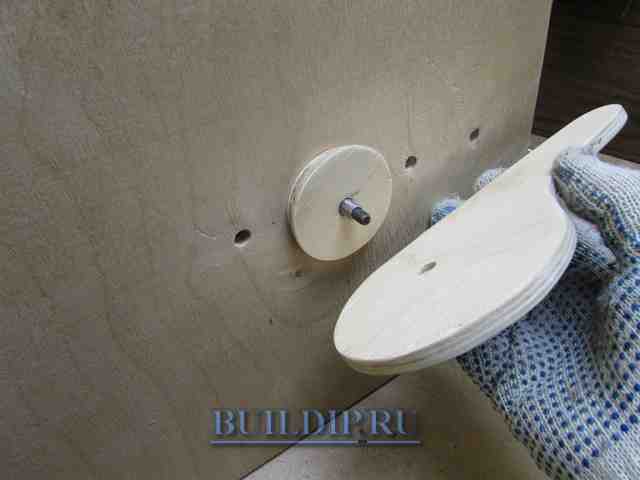
Make holes in the base with a drill according to the diameter of the sleeve, which serve to rearrange the eccentric clamp according to the width of the board to be cut.
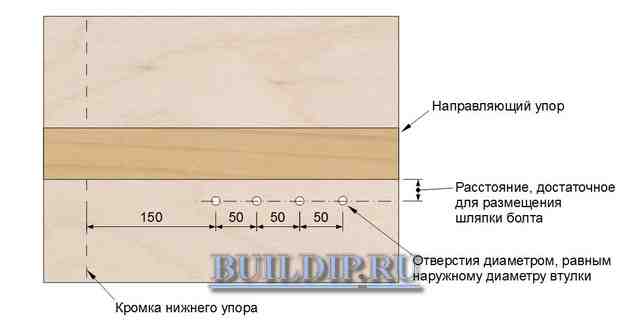
Hole drilling pattern.
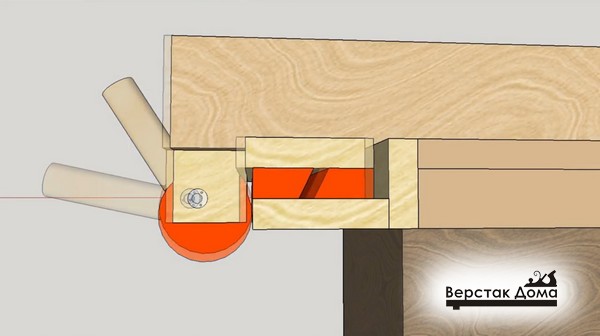
Assemble the eccentric mechanism: insert the bolt with the sleeve from above, and from the bottom insert the wooden washer, the cam itself and the steel washer. Tighten the parts with a nut.

Stick a strip on the inside of the stop sandpaper for prevention of slippage at the moment of locking of the eccentric, which can occur in the case of fixing the device on a smoothly planed workpiece.
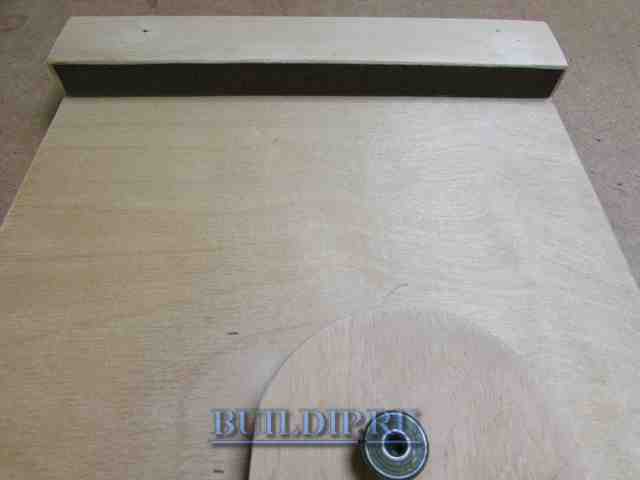

The clamping system of this device has a stroke that ensures fastening on the boards with a take-off in width of about 10 mm. If you need to cut or trim different sizes of workpieces, simply place a piece of wood in front of the stop bar.

An example of using a device for a cross-cut with a hand-held circular saw of a board of smaller width.
If desired, the potential of the considered device can be expanded by adding a cutting angle of 45 °. To do this, you will need to slightly increase the dimensions of the support platform and install the second thrust bar at this angle.
Let's discuss how to work with a dust-free rock drill. And also: disadvantages when using a vacuum cleaner, how to avoid dust when drilling a wall and drilling a ceiling.
The article discusses the process of making simple holders, stands and shelves for hand tools in a home workshop.
Variants of homemade side stops for a joiner's workbench are considered. A drawing is presented and the procedure for making one of them is shown in detail.
Master class on replacing a failed one nickel cadmium battery screwdriver to a modern lithium polymer.
A step-by-step instruction with a photo examines the process of making a simple tap wrench with your own hands.


Execution first
A rail is taken from the above-mentioned corner with a length of 450 mm. For correct marking, this workpiece is placed on the working table of the circular so that the wide bar is parallel to the saw blade. The narrow strip should be on the opposite side of the drive from the work table, as shown in the figure. In the narrow shelf (41 mm wide) of the corner distance 20 mm from of the end face, the centers of three through holes with a diameter of 8 mm are marked, the distances between them must be the same. From the line of location of the marked centers, at a distance of 268 mm, the line of the location of the centers of three more through holes with a diameter of 8 mm (with the same distance between them) is marked. This completes the markup.
After that, you can proceed directly to the assembly.
- 6 marked holes with a diameter of 8 mm are drilled, burrs, which inevitably arise during drilling, are processed with a file or emery paper.
- Two pins 8x18 mm are pressed into the extreme holes of each triplet.
- The resulting structure is placed on the working table in such a way that the pins enter the grooves provided for by the design of the circular saw table, on both sides of the saw blade perpendicular to its plane, the narrow angle bar is located on the plane of the working table. The entire device moves freely along the surface of the table parallel to the plane of the saw blade, the pins act as guides, prevent skewing of the stop and violation of the parallelism of the planes of the circular disk and the vertical surface of the stop.
- From the bottom of the desktop, M8 bolts are inserted into the grooves and middle holes between the pins of the stop so that their threaded part enters the slot of the table and the holes of the rail, and the bolt heads rested against the bottom surface of the table and ended up between the pins.
- On each side, over the rail, which is a parallel stop, a wing nut or ordinary M8 nut is screwed onto the M8 bolt. Thus, a rigid attachment of the entire structure to the work table is achieved.


Operating procedure:
- both wing nuts are released;
- the rail moves to the required distance from the disc;
- fix the rail with nuts.


The rail moves parallel to the working disc, since the pins, acting as guides, prevent the parallel stop from skewing relative to the saw blade.
Preparation for work
Before starting work, you need to decide on the necessary set of tools and materials that will be needed in the process of work.
The following tools will be used for work:
- A circular saw or a jigsaw saw can be used.
- Screwdriver.
- Grinding machine.
- Bulgarian (Angle grinder).
- Jigsaw.
- Hand tools: hammer, pencil, square.
In the process of work, you will also need the following materials:
- Chipboard.
- Plywood.
- Solid pine.
- Steel tube with an inner diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Steel bar with an outer diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Two washers with an increased area and an inner diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Self-tapping screws.
- Joiner's glue.
Manufactured carriage for circular in parts.

- The size of the base of the slide (A) corresponds to the size of the circular table in the workshop, figure 1.
- For back (C) and front (B) woods with straight grains, moderately dense, such as cherry, maple, are used. Make sure the stops have absolutely perpendicular edges. The lengths of the stops correspond in size to the width of the base (A).
- As shown in figure 1, the front and back stops (B) and (C) have a significant increase in stop at the passage of the saw blade. Use a band saw or jigsaw to round off the sides of the stops to reduce weight and convenience.
- Use dense hardwood to make the guide bar (D), the size of the bar (slider) matches the size of the slot in the circular table.
- Based on the dimensions of the saw blade, make a guard (E) and then round the near top corner. (Warning: the guard is not a handle. Do not use it while the sled is moving!)
ASSEMBLY OF BASE, SUPPORTS AND GUIDE.

- Secure the back stop (C) to the base (A). Drill and unfold flat head screw holes at the bottom of the base to adjust the stop later.
- Insert the guide bar (slider) (D) lubricated with a small layer of glue into the groove of the circular table. Place the base (A) perpendicular to the saw blade on the circular table and on the guide bar (slider) and leave until the adhesive is completely dry.
- Then take a few screws and fix the guide bar first from the outside and then from the inside of the slide, as shown in Photo B.
- Turn the base over and check that it fits in the grooves on the circular table, if necessary, use a scraper or sandpaper to remove any excess wood on the slider. (Note: You can use a graphite pencil to identify tight spots. Rub the inside edges of the slots on the circular table with a pencil, and then insert the slide into the guide and move them back and forth. The graphite mark on the slider will indicate where you need to trim.)
Plywood

Necessary materials
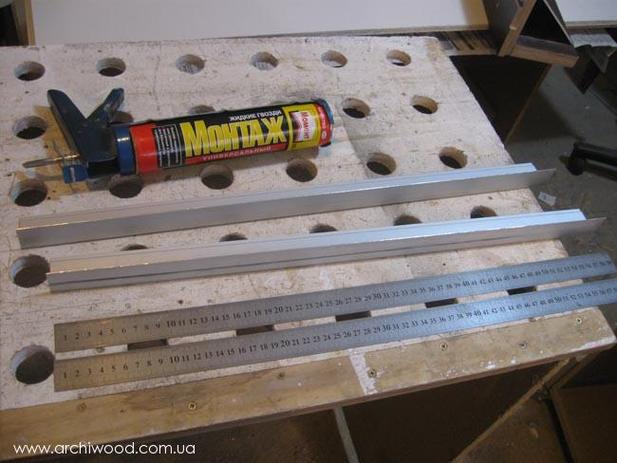
To make such a tire, you will need three pieces of plywood with a thickness of 10 mm. Their length should be the same and usually equal to the length of the workbench on which the work will be done. One of the segments should be 25-35 cm wide (it will serve as the base), the width of the other two will be determined during tire manufacture. Also prepare self-tapping screws for wood with a size of 16 mm.
Dimensional drawing:

Manufacturing instruction
When creating a guide, you need to be very precise with all dimensions. Small deviations can lead to a sharp deterioration in the result. If desired, laminate can be used instead of plywood.
The plywood guide bar is made in several steps:
- measure the distance from the inner edge of the saw blade to the rip guide slot located on the tool support platform.
- Cut one of the plywood strips so that its width is 0.2-0.5 mm less than the distance obtained in step 1. The fibers of the top veneer layer on the plywood should be directed longitudinally.
- Using self-tapping screws, screw the resulting strip to a wide piece of plywood (base), precisely aligning their ends. This will be the rim of the tire.
- Use a vernier caliper to measure the width of the rip guide slot.
- Screw the remaining strip of plywood to the base parallel to the first strip. There should be a gap between them, the size of which should be 0.2-0.5 mm less than the width of the groove measured in the previous paragraph.
- In order not to damage the material to be cut, a layer of soft cloth is glued to the finished guide from the bottom side.
The homemade guide is ready, it remains to prepare the hand saw. To do this, saw off a narrow strip thick plywood or other sufficiently durable material.The height of this strip should be 8-9 mm greater than the depth of the guide groove on the saw blade. The width corresponds to the width of this groove. The length is several centimeters longer than the sole.
The resulting stop strip should be fixed in the guide groove so that it protrudes beyond both edges of the sole.
How to use a plywood tire?
To make a cut, you will need two clamps and two flat pieces of wood that are slightly thicker than the workpiece. The guide rail is installed with its ends on these bars so that its working edge protrudes slightly beyond the edge of the workbench tabletop. In places where the tire rests on the bars, it is tightly fastened with clamps to the workbench.
The workpiece to be cut with the cutting line marked in advance with a pencil is placed under the tire, and the cutting line is aligned with its working edge. Finally, the circular with the bounding strip fixed on it is installed on the tire so that the stop on the sole fits exactly into the prepared gap. You can now cut by holding the workpiece with your free hand and lightly pressing the saw towards the workbench.
Nuances at work
In conclusion, we will give a few subtleties that are useful to know if you want to make a homemade carriage for a circular saw:
- It is recommended to install a thick block on the support wall in the place where the disc passes through it, which will prevent the saw from jumping out of the edge of the wall, which can lead to injury.
- In order to give the structure more sliding, it is recommended to clean the runners with sandpaper, and periodically lubricate the grooves with a candle stub (from paraffin or stearin). Sometimes wax is taken, but it is not recommended to use it, since melting during operation, it sticks to the runners.
- Before applying glue to parts, blow out wood dust and shavings from the structure to avoid unevenness after gluing.
- After sawing through the walls, make sure the saw goes through them freely. To do this, you can make a sawn hole slightly larger than the thickness of the disc.
Having made an end carriage in such a simple way in a home workshop, the master will have an easy-to-use, universal tool at hand that can be used in most types of carpentry work.
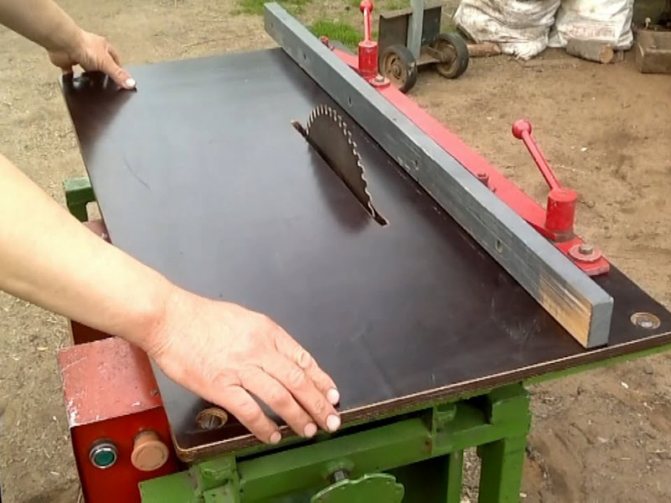
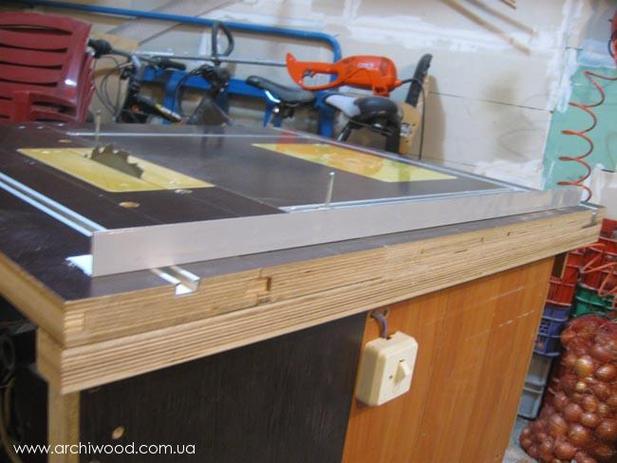
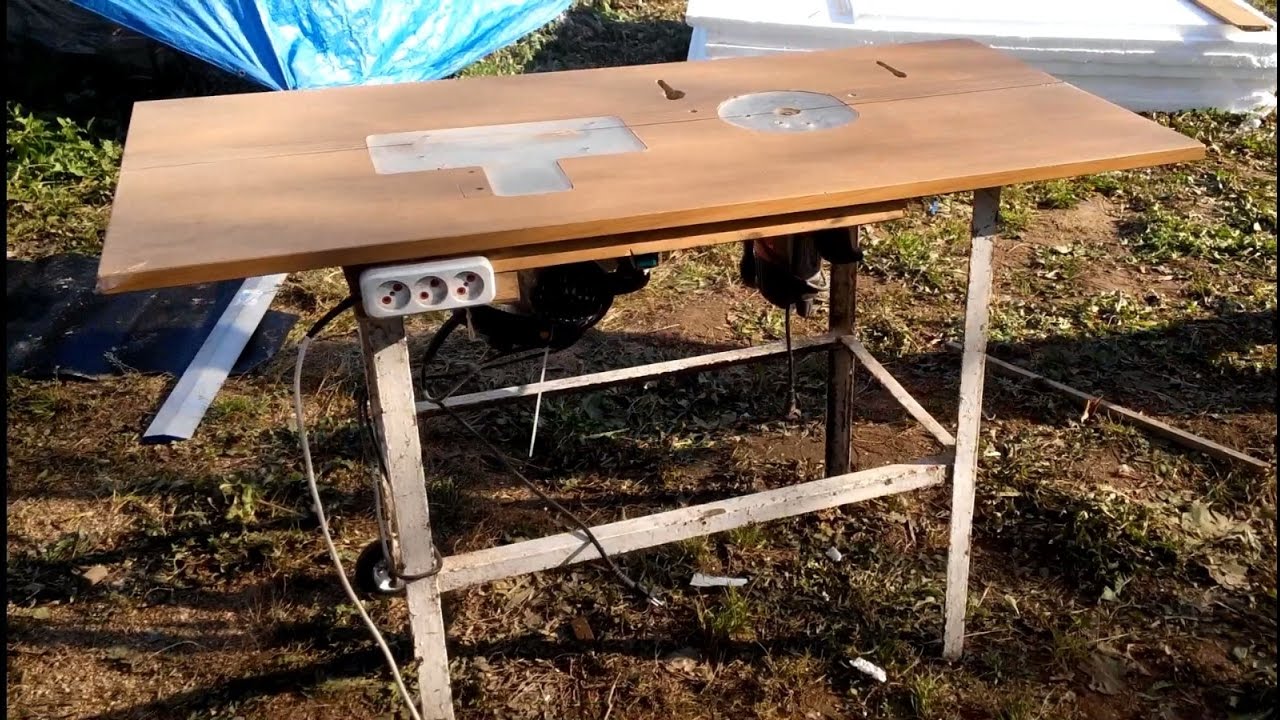
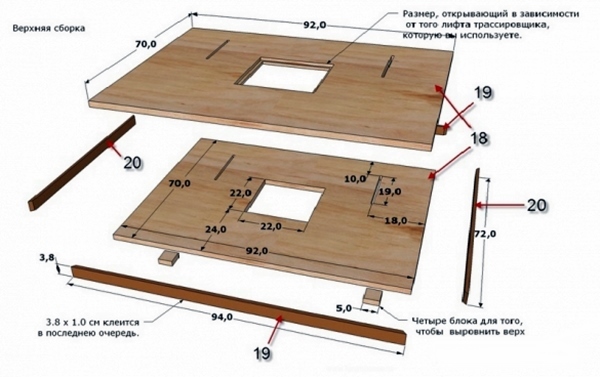
Making a workbench
- Mark and cut out the desired size tabletop from plywood. Sand the surface with sandpaper.
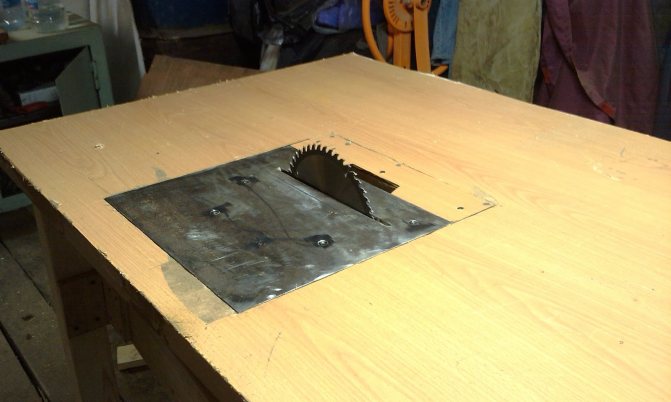
- In the lower part on the tabletop we mark the places for the holes for fixing the saw. To do this, you need to remove the blade and set the saw in the desired place, making notes. On the surface of the hole for the bolts we countersink, and the caps of the bolts need to be sanded.
- If the material will be cut at different angles, the hole for the disc must be made in the form of an inverted trapezoid.
- Apply the stiffener attachment points on the worktop (from below, at a distance of about 8 cm from the edge). The legs need to be fixed to the ribs. The ribs are screwed on with self-tapping screws at intervals of 25 cm and glued with PVA.
- The legs are made from a bar 100 cm long. Then a screed is made from a bar for additional strength.
- To be able to adjust the height of the table legs, nuts with M14 bolts are attached from below.
- We fix the saw from below.
- We fix the socket on the inside of the table. We pull the wire from it to the switch.
- We make a parallel emphasis. Cut off two strips of plywood, the same length as the width of the table. The width of the strips is 10 cm. We make the corners round. Grind and fasten both strips with self-tapping screws. Then we cut two strips of the same length, but three times wider. We fasten them. This will be the guide. We fasten the stop and the guide. We expose a right angle relative to the disc. We fix the rollers.
Table circular saw
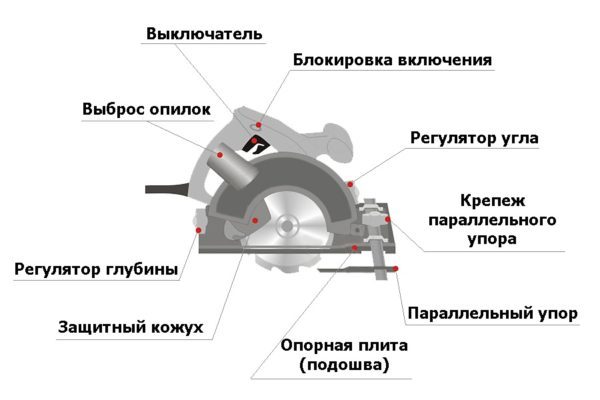
When choosing a circular saw, you need to be guided by the following characteristics:
- Saw power. If the volume of work is quite large, it is advisable to take a tool with a power of at least 1.2 kW.
- Cutting depth. The thickness of the material to be processed depends on this parameter. For hand saws it is 40–70 mm.But when it is installed in the table, there will be a decrease in the region of 10 mm.
- Placement of buttons. The design of the sawing table must provide free and safe access to all control buttons, otherwise it will be necessary to modify the control system yourself.
- Rotational speed. For cutting wood, high rotation speed is a priority. This affects the quality of the cut. For plastic, for example, this is not very good. The plastic heats up from the high speed of the wheel. You need to choose average characteristics. 3-4 thousand revolutions per minute will be enough.
Circular and rip fence step by step production:
Step 1: Making a stop.
Cut three strips of laminated chipboard, 1.1 m long and 8 cm wide, and then assemble them together to make a U-profile. According to the internal dimensions of the profile, make five blanks-inserts for stiffness and insert into the inside of the profile, they will create a square section required for the stop. The advantage of this stop is the possibility of using it on both sides of the saw blade (photo on the left).
Step 2: Making a liner for the stop.
Step 3: Assembling the Stop - Part 1
So, the circular and the parallel stop now have a guide channel. Putting it all together, using a small piece of MDF in the shape of an inverted "T", it will be screwed on the back of the stop and inserted into the guide channel. The channel width directly depends on the thickness of the T-shaped MDF blank, which will ensure tight placement of the T-shape in the channel.
Step 4: Assembling the Stop - Part 2
Step 5: Stop locking mechanism.
In fixing the stop, slots for the original stop are used. The locking mechanism is simple: a threaded bolt with a nut, a hole in the lower strip of the parallel stop, a wooden washer. By tightening the bolt, the block pulls the stop down towards the tabletop and clamps very tightly.
There is no emphasis on the prize of the most beautiful project, but it is made of waste wood and laminate, and bolts and nuts that were not used from factory devices also came in. Changing the dimensions of the cuts is now quick and much easier than with the original stop system. I use the resulting niches in the “pockets” to store pencils, tape measure, ruler and other necessary tools, as they say, they are “always at hand”.
Edge stop
This is already a rather complex device that requires time and precision in manufacturing. It allows you to cut parallel to the edge of the material being cut. It will be useful to make a drawing of it before starting work so as not to overshoot in size. In fact, such an emphasis is included in the set of a circular saw, but its small length does not always ensure an even cut. The large size and the desired strength require the base of the stop to be made of plywood with a thickness of at least 15 mm. You can also make a stop bar from it.

Stages of stop manufacturing:
- longitudinal grooves are made at the base for dowels;
- hardwood dowels are attached to a stop bar;
- another through groove is made between the longitudinal grooves to secure the thrust bar during operation;
- a hole is cut at the base for the circular saw blade;
- on the sides of the base, limit strips are placed for installing the circular and clamps are provided for its reliable fastening.
When placing the stop on the material to be processed, the stop bar moves in the grooves of the base to the required distance and is fixed through the through slot with a clamping thumbscrew. In order not to suffer every time with a ruler, you can fix it (or a piece of tape measure) on the basis of a stop along the guide grooves.
A persistent ruler is a simple and straightforward element
Before proceeding with the description of the process, we remind you that working with a circular saw is associated with a certain risk, therefore, the independent production of related accessories for circulars requires strict adherence to safety rules.Now let's return to the cutting stop, which is often used when processing material with an electric jigsaw and can be useful when working with a circular saw, albeit with some caveat. The thing is that the assembled stop for a circular saw with your own hands is effective precisely in the case of a jigsaw, but with a cut, certain inconveniences may arise due to the fact that in this case the tire is pressed against the workpiece with a clamp.
If you are familiar with such a tool, you can easily imagine how its bracket protrudes from the lower and upper sides of the machine tabletop. As a result, we get a limiter along the length of the cut, but the saw motor will inevitably rest against the clamp, and the cut can be performed exclusively in two stages. Based on such realities, it becomes clear that the quality of the edge will be questionable, and besides, there is a high probability of the formation of a characteristic unwanted step. This is not surprising, because to ensure a perfect cut, continuous movement of the cutting blade is necessary from the beginning to the end of the lumber. Unlike handicrafts, in factory models, the fastener is moved out of the range for the circular saw. therefore does not interfere with comfortable work.