Sclerometer and its types
According to the principle of operation, the measuring devices are divided into mechanical and ultrasonic devices.
- The mechanical tool has a cylindrical body with an internal percussion mechanism, consisting of a scale with an indicator arrow and repulsive springs. Such a device is designed to determine the compressive strength of a concrete layer in the range from 5 to 50 MPa, and is widely used for examining concrete or reinforced concrete structures.
- The electronic device, depending on the model, can have an external or built-in electronic unit. The obtained measurements are shown on the display and remain in memory for a certain period. In addition, the instrument is equipped with a keyboard and connectors for connecting to a computer. Measurements are diagnosed in the range from 5 to 120 MPa with a methodical error of up to 5%, signals are given with an error of up to 0.2%. The results memory limit is designed to store up to 1000 versions in a 100-day period.
You can compare the two types of sclerometers using photos posted on the Internet. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the Hilti electric jackhammer and the Makita rotary hammer.
Operational service area
Moscow and the Moscow region: Eastern, South-Eastern and North-Eastern districts; Balashikha, Noginsk, Korolev, Reutov, Monino, Elektrougli, Drezna, Sergiev Posad, Kupavna, Krasnoarmeysk, Lyubertsy, Ramenskoye, Sofrino, Zhukovsky, Bronnitsy, Shchelkovo, Pushkino, Mytishchi, Ivanteevka, Elektrostal, Pavlovsky Posad, Zheleznodorozhny Elektrogorsk, Orekhovo-Zuevo and others.
Vladimir region: Vladimir, Pokrov, Petushki, Lakinsk, Sobinka, Stavrovo, Kirzhach, etc.
Krasnodar Territory: Krasnodar, Novorossiysk, Gelendzhik, Sochi, Abrau-Dyurso, Anapa, Krymsk, Slavyansk in the Kuban, Novomikhailovsky, Tuapse, Poltava, Novotitarovskaya, Timashevsk, etc.
What does a sclerometer consist of?

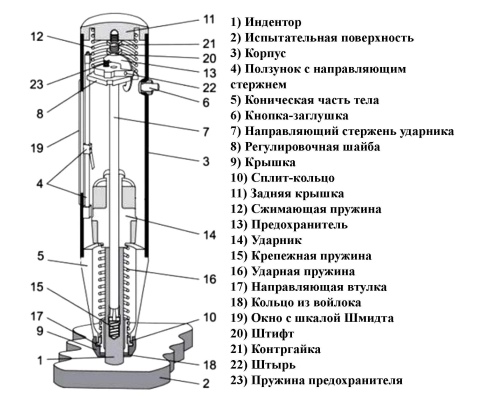
The term "sclerometer" means "hardness tester". Structurally, the device consists of 22 elements. In addition to the indenter (impact plug) and the body, the device includes:
- body cone;
- guide rods with a slider;
- a button performing the function of a corkscrew;
- firing pin with a given mass;
- guiding movements of the indenter - striker rod;
- washer for fixing the striker;
- cap;
- back cover of the sclerometer;
- felt ring.
Some models are supplemented with a fuse and a control nut, as well as 4 springs (compressing, impacting, protecting, fixing). There must be a coupling screw, a pin, a Schmidt scale, a display.
Instructions for use
Testing by the Kashkarov method does not depend on the force of impact and the speed that the moving parts of the device receive. Installation of any additional parts is also not required. Before testing, the rod must be cleaned of dirt and traces of grease.
The sequence for determining the strength of concrete is as follows. A series of blows are applied to the impact head with the help of a metalwork hammer (after each blow, the Kashkarov hammer is displaced by an amount slightly exceeding the diameter of the ball). If, after the first impact, a network of cracks appears on the concrete surface, then the test is continued in another place of the structure.
On impact, the hardened ball compresses the spring and acts on the rod, which moves and deforms the reference plate, which is inserted from the opposite side of the body before testing. An imprint remains on the plate, the diameter and depth of which characterize the specific force applied to the concrete.
The return of the head to its original position is provided by a spring, and the compression force is limited by a squeeze.The stroke of the rod can be adjusted by screwing or unscrewing the head in the body. Accuracy of direction is ensured by the fit of the lower part of the head on the inner surfaces of the glass and body.
The inevitable inaccuracies of the method are associated with the fact that, upon impact, the hardened ball leaves a dent in the concrete, the diameter of which, although a characteristic of the strength of concrete, at the same time worsens the appearance of the structure, which is not always acceptable. To minimize the error, it is recommended to hit the smoothest part of the concrete surface, and have a sheet of thick paper between the ball and the concrete.
The average ratio between the diameters of three to four indentations using a calibration table indicates the strength of the concrete. Using the calibration schedule, one obtains:
- With the compression limit from 3 to 18 MPa, the indentation diameter is 3.0 ... 1.7 mm;
- With the compression limit from 18 to 60 MPa, the indentation diameter is 1.6 ... 1.1 mm.
Detailed gradation is given in the instructions of the manufacturer of the Kashkarov hammer. To increase the accuracy, additional tables are also used (see, for example, VSN 02-69), taking into account the grade of concrete and the conditions for its hardening. For this, the inspector must have data on the reference footprint de obtained using stationary testing equipment.
Then the strength of concrete can be determined by the following data:
- d / de = 2.2 ... 2.7 - 15 ... 10 MPa;
- d / de = 1.9 ... 2.2 - 19 ... 15 MPa;
- d / de = 1.5 ... 1.9 - 26 ... 19 MPa;
- d / de = 1.3 ... 1.5 - 30 ... 26 MPa.
Here d is the average size of the indentation in the concrete product according to the test results, which were performed with the Kashkarov hammer.
What do I need to know about hammers? Key types of hammers, technical specifics
There are:
- locksmith;
- carpentry;
- hammer;
- mallet (wood hammer);
- sledgehammer;
- Fizdel's hammer;
- Kashkarov's hammer;
- rock hammer;
- jackhammer.
Photo 1 - Sledgehammer GRAPHITE ROUND Stanley 1-54-924
A carpenter's hammer is a tool with a bifurcated protrusion-tooth, which is convenient for pulling out nails.
The chisel is used for facing edges and corners in masonry work. They beat him with a mallet. It is made of wood and has strikers on both sides.
Sometimes the striking part of the instrument is made of soft material - copper, rubber, lead. They are used for a gentle blow so as not to damage the part.
In zero gravity, a tool is used that does not bounce on impact. Its hollow firing pin is filled with heavy metal shot.
They make tools of different types, shapes, sizes, specified in GOST 11042-90.
| The weight | Hammer |
|---|---|
|
400 g and 500 g |
Locksmiths |
|
600 g and 800 g |
Construction |
|
4-16 kg |
Sledgehammers |
Tool design
The main part is a solid piece of steel with a carbon content.
The handle is wood, mainly of beech, birch, ash, oak, hornbeam, maple or mountain ash.
The main thing! Pine, aspen, spruce and alder are not suitable for the handle.
Models with a fiberglass handle are considered good - sturdy, not afraid of dampness, excellent shock absorption, they never jump off the handle. Fiberglass grips are beautiful on the outside and more comfortable to hold in the hand.
Photo 2 - Solid-forged bison, with a fiberglass handle, 500 g
The model with a solid metal handle is comfortable, but it should be verified when purchasing: hitting the surface with the same hammer is a good tool and the handle does not leave marks.
Question # 1: how to choose a hammer and which one is preferable?
Answer: You need to follow the goals and scope of use.
| Name | Dimensions (edit) | Average weight | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hammer | The height of the hammer in mm depends on the weight of the woman and can be from 1830 mm to 3500 mm | From 0.5 kg to nine kilograms, in large forges - from 40 to 100 kg, in steel and metal factories up to 50 tons | For striking when breaking stones, forged metal products |
| Locksmith hammer | Weight in grams | 300-500 g - for home and household use, larger - 2 kg | Work with metal products, production of blows on a chopping tool or on a core |
| Carpenter's hammer | Handle length - from 20-30 cm | 250-450 g | For hammering or removing nails in joinery or carpentry |
| Mallet (wood hammer) | 130x90x60mm | 300 g | Installation, dismantling, molding of materials and structures |
| Sledgehammer | Weight in kg | 3 to 15 kg | Dismantling and installation work (breaking walls, driving posts and pipes into the ground) |
| Fizdel's Hammer | The impact part of the hammer ends with a steel ball O17.5 mm | 250 g | Testing the strength of concrete |
| Kashkarov's hammer | 253x40x53mm | 1.5KG | Shock test of concrete compressive strength |
| Rock hammer | 290 mm | 600 g | In rock climbing, mountaineering, caving, for stuffing and removing rocky hooks, finishing the edges of rocky ledges, punching bolts |
| Jackhammer | Average shank size O 24 mm, length 70 mm | 3 to thirty kilograms | Cutting down in the walls of openings and niches, dismantling of brick-concrete structures of the capital type, destruction of frozen or heavy soil, removal of the old road bed |
| Roofing hammers | MKR-1 - 300x118x50 mm MKR-2 - 340x160x67 mm | Not more than 0.6 - 0.75 kg | For works related to roofing, leveling and sealing of folds |
Description
The most common method for controlling the strength of concrete
 The Schmidt hammer MSh-225 is a device that uses the world's most popular method for measuring the strength of building materials, primarily concrete. The principle of the method is based on measuring the height to which the device striker bounces after hitting concrete. The design of the device provides fixation of the maximum rebound value and indication of this chill on the scale of the device. This measurement method is called the Schmidt method, and the device is called the sclerometer.
The Schmidt hammer MSh-225 is a device that uses the world's most popular method for measuring the strength of building materials, primarily concrete. The principle of the method is based on measuring the height to which the device striker bounces after hitting concrete. The design of the device provides fixation of the maximum rebound value and indication of this chill on the scale of the device. This measurement method is called the Schmidt method, and the device is called the sclerometer.
Determination of strength in units of MPa is carried out using the table supplied with the device.
The sclerometer is highly accurate, robust and very easy to use. The measuring method of the device complies with GOST 53231-2008, GOST 22690, ISO / DIS 8045, EN 12 504-2, ENV 206, DIN 1048, ASTM D 5873 (rocks), ASTM C 805.
This test method is non-destructive, since it practically does not leave marks on the surface of the structure after measurement.
The accuracy of the readings of the Schmidt hammer MSh-225 can always be checked
It is recommended to use a special test anvil to check the functionality of the device. After hitting such an anvil, Schmidt's hammer should display a certain number. Thus, the user can independently check the operability of the device and determine the measurement error.
How to conduct research correctly?
Each Kashkarov hammer is sold complete with instructions for use, which clearly describe how to use this measuring tool correctly. To test the strength of concrete with a Kashkarov hammer, you need to select a 10x10 cm section of a concrete object. It must be flat, without grooves and bumps, and there must be no visible pores. The distance from the edge of the product should be more than 5 cm.
You need to take Kashkarov's hammer, insert the reference rod into the corresponding groove with the sharp end inward. A clean sheet of paper and a piece of carbon copy should be laid on the selected area of concrete. Then you need to hit the workpiece with a hammer, as described above. After each impact, the standard should be advanced to a new area and the sheet of paper should be replaced. The next blow should fall on a new place (at a distance of more than 3 cm from the previous one).
The next step is to measure the prints. If the difference in the obtained indicators is more than 12%, all studies should be repeated anew. Based on the obtained indicators, the class of concrete is determined, while the smallest of the resulting indicators is selected.
Low air temperatures have practically no effect on the result of the study. Therefore, it is allowed to use this measuring tool at ambient temperatures down to -20 degrees.However, in this case, the temperature indicators of concrete and reference rods must be the same. This means that the reference rods must be left outside for at least 12 hours before testing in freezing temperatures.
Characteristics of modern models and tips for choosing
Any modern model of a tester for the strength of solid materials facilitates the processes of all areas of construction work. With the help of a small device, quality control of even masonry can be easily carried out without serious damage.
The main characteristics of all types of sclerometers include several parameters.
- Measurement error. The largest error in mechanical models. It is usually not indicated, but often reaches 20%. And also mechanical models have the highest frequency of breakdowns. For electronic equipment, this figure is 5%, and the smallest for ultrasonic equipment: 1%.
- Working range of strength. In mechanical devices it is 60 MPa, in electronic - 100. In ultrasonic devices, the interval varies in time and speed.
- Comfort of use. It is less convenient to use a mechanical device due to the lack of preservation of results and a large weight (1 kg).
- Price. In this indicator, the opposite is true: the most expensive is an ultrasonic device.


It is best to choose the latest models of popular manufacturers of measuring instruments for purchase. The top companies producing quality products include Interpribor with Onyx devices, Condtrol with the same name, as well as Schmidt Hammer and RGK.
For an overview of the IPS-MG4 sclerometer, see below.
Device and principle of operation
Most sclerometers are constructed of the following elements:
- impact plunger, indenter;
- frame;
- sliders that are equipped with rods for guiding;
- cone at the base;
- stopper buttons;
- rods, which ensures the directionality of the hammer;
- caps;
- connector rings;
- back cover of the device;
- spring with compressive properties;
- protective elements of structures;

- strikers with a certain weight;
- springs with fixing properties;
- striking elements of springs;
- a sleeve that directs the functioning of the sclerometer;
- felt rings;
- scale indicators;
- screws that carry out the coupling process;
- control nuts;
- pins;
- protection springs.
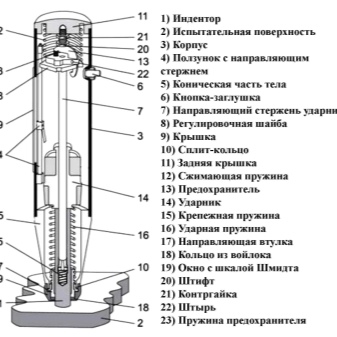

The functioning of the sclerometer has a basis in the form of a rebound, characterized by elasticity, which is formed when measuring the impact impulse that occurs in structures under their load. The device of the meter is made in such a way that after impacting the concrete, the spring system gives the striker the opportunity to make a free rebound. The graduated scale, mounted on the device, calculates the desired indicator.

Advantages and disadvantages
Kashkarov's hammer has both pros and cons. The advantages of using this tool include, first of all, the ease of measurement. Even a beginner in the construction business can cope with such a study.

There is no need to destroy the sample for testing, that is, the study can be carried out directly on the finished product
This is especially important if the research items are large. Also, the pluses include the cost of the device.
Such a tool can be purchased for use in everyday life, for example, building a monolithic house for yourself.

But Kashkarov's hammer also has significant drawbacks. The error of the device is 12 to 20 percent, which is quite a lot. Modern electrical sclerometers provide more accurate results. The strength of concrete is determined only in the surface layers (1 cm deep). As you know, these layers are often susceptible to destruction due to carbonization. In addition, the device is practically insensitive to the strength of the coarse aggregate and its grain size composition.

Types of sclerometers
The compressive strength of the concrete is shown on a digital scale. The figure characterizes the rebound of the striker to a certain height.The stronger the rebound, the harder the concrete.

There are several types of Schmidt hammer - they differ in the principle of operation (mechanical or ultrasonic action on the test object). The second common classification is based on the use of impact energy, measured in J.
Mechanical and ultrasonic devices
A mechanical-type device designed for the study of reinforced concrete or concrete structures looks like a cylinder with an impact mechanism placed inside from a repulsive spring, an indicator scale, and a striker.
The sensitivity of the device is from 5 to 50 MPa.
The electronic Schmidt hammer of ultrasonic action is equipped with electronic units of two types:

This device design is preferable. First, the results do not need to be recorded - they are stored in the block memory for 100 days. The maximum memory reserve is 1000 readings. The hammer is suitable for connecting to a computer through special ports and connectors.
The sensitivity of the electronic modification is much higher than that of the mechanical analogue. The device recognizes strength in the range from 5 MPa to 120 MPa.
Impact energy classification
According to the force of the blow, there are 4 main modifications of the sclerometer:
- 1 modification - the least "powerful" MSH 20. Impact energy value does not exceed 196 KJ.
- 2 modification - pendulum type RT, operating in 2 planes. Impact power - from 200 to 500 KJ;
- 3 modification - MSh 75 (type L). The impact force is 735 KJ;
- 4 modification - MSh-225 (type N). The most powerful option of all - with impact energy up to 2207 J and sensitivity from 10 to 70 MPa.

Devices of different power and purpose have different. MSh 20 measures the strength of a mortar for masonry, RT is necessary for measuring the strength of a newly laid cement-sand screed. MSh-225 (type N) is intended for measuring the strength of brick and concrete up to 100 mm thick. The purpose of using MSh 75 (type L) is to determine the reliability of walls with a thickness of at least 70 mm.
Testing of concrete by the method of non-destructive testing GOST 17624-2012
An ultrasonic method for checking the strength of concrete is to register the speed of waves passing through the monolith. There is end-to-end ultrasonic sounding with the installation of sensors from different sides relative to the tested sample, as well as surface sounding with the fastening of sensors on one side. The through method makes it possible to control the strength of not only the surface, but also the deep layers of the structure.
Ultrasonic control devices are used for flaw detection, quality control of concreting, detection of the depth of reinforcement in concrete and the monolith itself. The devices make it possible to repeatedly investigate different forms, to continuously monitor the decrease / increase in strength.
The relationship between the grade strength of concrete and the speed of ultrasound transmission is influenced by the composition and volume of the filler, the consumption of the binder, the method of preparing the concrete solution, and the degree of its compaction. The main disadvantage of the method is a significant error in the research results.
Taking into account the high speed of passage of ultrasound in the monolith of the material (about 4500 m / s), the calibration dependence of the wave speed and concrete strength is calculated for each tested composition in advance. Using two graded dependencies for a specific concrete and an incomprehensible composition can give a big error.
The main feature of testing the strength of concrete by a non-destructive ultrasonic method is the ability to carry out mass studies of products of any shape repeatedly, effectively conduct continuous monitoring of the increase / decrease in the strength of a structure online.

Schmidt's hammer instructions for use.
| Schmidt's hammer - we test concrete for strength without a laboratory. |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Schmidt hammer 225A for measuring the strength of concrete. Sclerometer - quick guide |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Automatic concrete strength meter ONIKS-1.OS.060E |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Concrete strength meter ONIKS-1.OS |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Video report No. 8. Schmidt's hammer OMSh-1E |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Concrete strength test, sclerometer. Schmidt's hammer |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Application of the concrete strength meter (sclerometer) IPS-MG4.04 |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| For control of concrete strength gain in PSK ENERGY use Kashkarov's Hammer |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Application of the concrete strength meter POS-50MG4 |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| How to measure the strength of concrete? How to check the strength of the concrete foundations? Schmidt's hammer |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Sclerometer RGK SK 60 |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Schmidt Hammer Original SCHMIDT Type L |
| BM: Grade and grade of concrete - what's the difference? |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| How to check the quality of concrete? |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Concrete Test Hammers: Schmidt Rebound Hammer Portfolio from Proceq |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Original Schmidt Live Concrete Test Hammer Review Reviews |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Sclerometer RGK SK-60 (review) |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Impact-impulse concrete strength meter (sclerometer) ONIKS-2 |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| SilverSchmidt concrete test hammer / Schmidt hammer |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Kashkarov's hammer at students |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Measuring the strength of concrete. Schmidt's hammer. Concrete strength meter Checking concrete. Russian Dvor. |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Checking concrete for a set of strength with a device |
|
Click to view |
|
||||||||||
| Schmidt's hammer SilverSchmidt PC N for testing concrete |
Instructions for use
The Schmidt walk-behind tractor operates on the calculation of shock impulses that occur during loads. Impacts are made on hard surfaces that do not have metal reinforcement. The meter must be used according to the following scheme:
- attach the percussion mechanism to the surface to be investigated;
- using both hands, it is worthwhile to smoothly press the sclerometer towards the concrete surface until the impact of the striker appears;
- on the scale of indications, you can see the indications that are highlighted after the above actions;
- for the readings to be absolutely accurate, the strength test with the Schmidt hammer must be carried out 9 times.
It is necessary to take measurements in areas with small dimensions. They are preliminarily drawn into squares and then examined one by one.Each of the strength readings must be recorded, and then compared with the previous ones. During the process, it is worth adhering to the distance between the beats of 0.25 cm. In some situations, the data obtained may differ from each other or be identical. From the results obtained, the arithmetic mean is calculated, while a slight error is possible.


How the Schmidt hammer works
A working Schmidt sclerometer shows the strength of concrete when an impact is made on its surface, followed by an elastic rebound. How much the tested concrete is resistant to destructive mechanical stress is known from statistical data.
The device measures the shock pulse that occurs when a mechanical load is applied to the solid surface of the test object. Simplified, the algorithm of the device looks like this:
- the impact plow (indenter) is pressed against the concrete surface, where there are no metal parts (reinforcement);
- due to the spring, the indenter strikes the tested surface;
- a system of four springs returns the striker (plow) to its original position by means of a free rebound.
Types and principles of work
The modern construction market produces three types of sclerometers: mechanical, electronic and ultrasonic. The first two types perform measurements according to the shock-impulse method standardized by GOST. It consists in determining the length of the bounce of the built-in mechanism, which transmits the impact to a hard surface.
The mechanical device has an elongated shape, similar to an enlarged ballpoint pen. An impact firing pin with a spring is mounted inside it, and outside there is a scale that displays the pressure withstand by the surface. This is the simplest of the existing devices, which has a significant error and a small range of applications.
The electronic device looks like a mechanical one, but it has a much smaller size and is additionally equipped with an electronic device. This device displays the measured values taking into account the temperature error, and operates on only two batteries. The electronic device has a smaller error and can be used not only on concrete, but also on composite, metal, brick and marble surfaces.
The ultrasonic type calculates the strength of materials by the time and speed of the emitted wave. The body of the tool is made of plastic, on the front part there are keys and a display, and on the side there are two contacts. Like the electronic one, this device has the function of saving the measurements taken and runs on batteries.
7. CALIBRATION AND MAINTENANCE.
Periodic calibration should be performed at least once a year or after every 1000 impacts.
External conditions:
Ambient air temperature 20 ± 2 ° С;
Relative air humidity 60 ± 20%;
Atmospheric pressure 84.0 kPa… 106.7 kPa.
Visual inspection:
An external examination should establish the presence of marking and the absence of external damage affecting the operation of the hammer.
Determination of metrological characteristics.
Clean the anvil and plug contact surfaces.
Apply approximately 10 hits with the concrete test hammer and check the result against the calibration value printed on the test anvil.
If the Rm value corresponds to the value of the test anvil within the accuracy of the technical characteristics of the hammer, the device does not require calibration.
Otherwise, carry out the maintenance of the hammer according to the diagram of the Schmidt hammer device in clause 5:
Dismantling.
Attention! It is forbidden to dismantle, adjust or clean the slider with the guide rod 4, otherwise the friction force of the pointer may change, and then special tools will be required to re-adjust it. Position the concrete test hammer perpendicular to the test surface
Position the concrete test hammer perpendicular to the test surface.
Dangerous! When the impact plunger 1 is triggered, a rebound occurs. Therefore, always hold the concrete test hammer with both hands! Always aim the indenter 1 at a hard surface!
Press the concrete test hammer against the test surface until the impact plunger trigger 6 is activated.
Unscrew the cap 9 and remove the split ring 10.
Unscrew the back cover 11 and remove the compression spring 12.
Press on the safety catch 13 and pull the entire assembly straight up and out of the housing 3.
Lightly hit the plunger 1 with the mass of the striker 14 so that it 1 works and comes out of the guide rod of the hammer 7.
The fixing spring 15 is released.
Pull the firing pin 14 off the hammer guide rod together with the impact spring 16 and the guide sleeve 17.
Remove the felt ring 18 from the cap 9.
Cleaning.
Immerse all parts except body 3 in kerosene and clean with a brush.
Use a round brush (with copper bristles) to thoroughly clean the inside of the plunger 1 and striker 14.
Allow the liquid to drain from the parts, then wipe dry with a clean, dry cloth.
Clean the inside and outside of the cabinet with a clean, dry cloth 3.
Mounting.
Before assembling the guide rod of the hammer 7, slightly lubricate it with low viscosity oil (1-2 drops are enough;
viscosity ISO 22, e.g. Shell Tellus Oil 22).
Place a new felt ring 18 over cap 9.
Apply a small amount of grease to the cap of the fastening screw 20.
Pass the guide rod of the hammer 7 through the firing pin 14.
Insert the retaining spring 15 into the indenter 1.
Insert the guide rod of the hammer 7 into the indenter 1 and push it inward until it stops.
Before and during installation of this unit in body 3, make sure that the firing pin 14 is not held in place by the fuse 13. Advice:
to do this, press the safety catch 13 sharply.
Install the assembly straight down into the body 3.
Insert the compression spring 12 and screw the back cover 11 to the body 3.
Insert the split ring 10 into the groove of the guide bush 17 and screw on the cap 9.
Perform a performance check.
If, after the performed maintenance, the hammer does not work correctly or does not reach the calibration values indicated on the test anvil, send the device for repair and draw up a conclusion about the removal of the hammer from circulation.
8. CLEANING, STORAGE AND TRANSPORTATION.
8.1
Cleaning To prevent damage to the device, handle it with care, keep it away from dust, dropping and contamination with oily substances.
Attention! Do not immerse the device in water or rinse it under running water!
Wipe plunger 1 and body 3 with a clean piece of cloth. Do not use abrasive substances and solvents for cleaning!
8.2. Storage.
Attention! During storage, the shock spring must be unloaded! To do this, before removing the concrete test hammer into the instrument box, move the indenter to the retracted position and lock it by pressing the stop button 6 as in the measurement. Additionally secure the button with adhesive tape
8.3. Transportation The hammer can be transported by any means of transport, protected from direct ingress of dripping moisture on a wooden instrument box.
10. WARRANTY. MANUFACTURER.
Peculiarities
Each type of apparatus has its own characteristic features.
For ultrasound models, these are:
- the ability to exchange data with a computer;
- convenient control and configuration of the device using buttons and interface;
- shutdown with a long break in use;
- memory for saving measurements;
- sounding the process of work;
- automatic change of waves;
- the ability to search for defects and cracks.


Distinctive features of electronic models are:
- ability to record measurements;
- the ability to transfer indicators to a PC;
- sorting function of measured data;
- changing the direction of the impact.


The specificity of mechanical models is as follows:
- the ability to work at a temperature - 40 °;
- low cost;
- high error;
- great weight.

Few numbers
Concrete structures after 28 days after pouring show different compressive hardness (maximum error does not exceed 13.5%). Hardness depends on the class and grade of the building material:
Table.1 The average value of the compressive strength of an experimental concrete sample in the form of a cube with a side of 15 cm, depending on the brand and class.

Schmidt's hammer was invented back in 1948, thanks to the work of a scientist from Switzerland - Ernest Schmidt. The advent of this invention made it possible to measure the strength of concrete structures in the area where construction is being carried out.