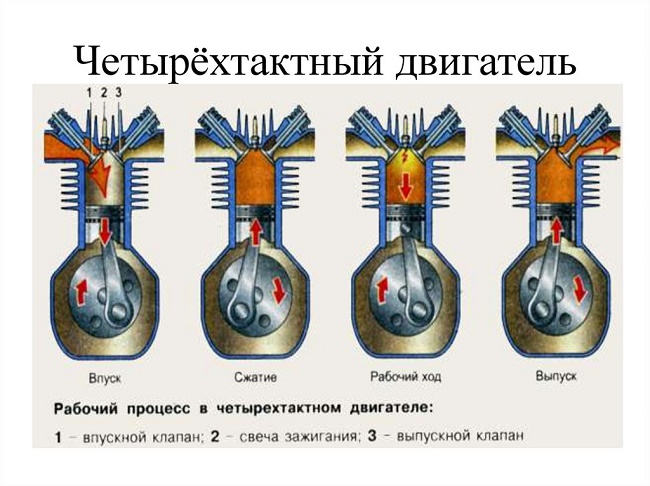
How to fill in correctly?
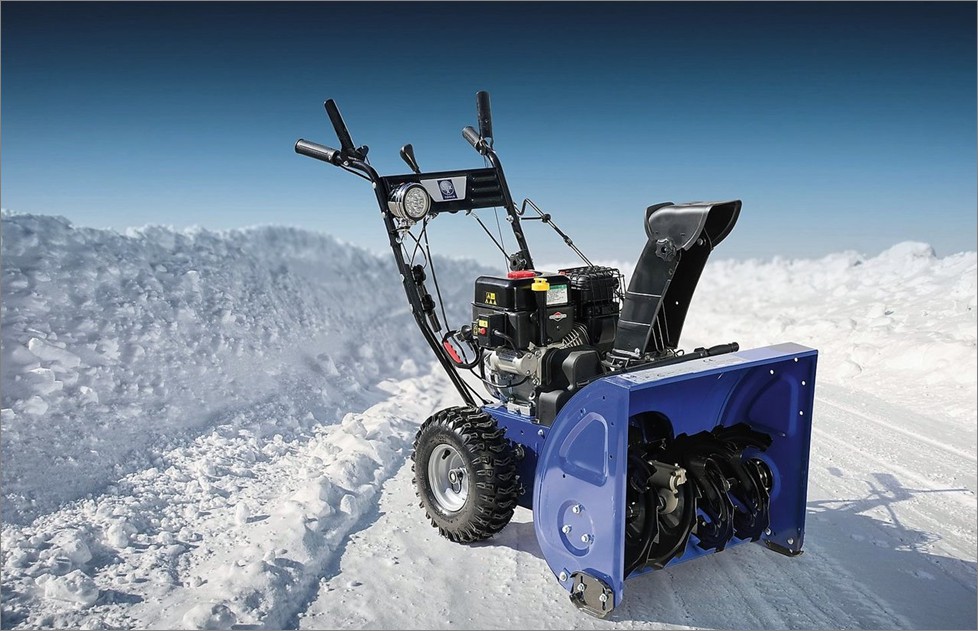
For the stable operation of the snow blower, it is necessary not only to repair and replace parts on time, but also to fill in oil in a timely manner. This procedure consists of a set of rules that are binding. Oil filling stages:
- placing the device on a flat horizontal surface;
- starting the engine for a few minutes to warm up the old fluid;
- disconnecting the device;
- preparation of a container for waste liquid;
- draining oil through an open hole in the tank;
- closing the drain hole;
- removing the cover and dipstick from the neck;
- infusion of new oil;
- starting the device for a few minutes;
- checking the level of the new lubricant.


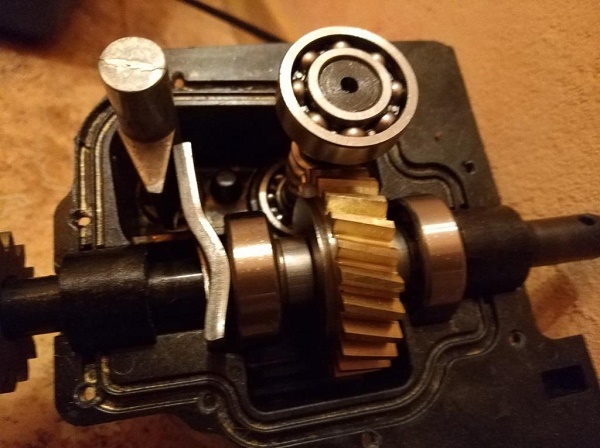
The oil change must be carried out not only in the engine, but also in the gearbox. Reducer - a part that is located between the moving mechanism and the auger. An oil change must be carried out every 60 hours of operation, as well as at the beginning and at the end of winter. Manufacturers produce two types of gearboxes:
- serviced - the device can be disassembled for revision;
- maintenance-free - a non-separable device that, in the event of a breakdown, needs to be completely replaced.


Two methods can be used to lubricate the gearbox:
- pouring liquid with a medical syringe into a special hole;
- lubrication of the disassembled mechanism.

The main stages of disassembling the gearbox:
- disconnecting the cover and the drive cable;
- unscrewing the bolts, which are located behind the bell for pushing back the snow;
- removing the auger belt from the pulley;
- dismantling the drive shaft bolts;
- recess of the auger and impeller;
- unscrewing the middle auger bolts;
- division of the gearbox into two parts.
Selection recommendations

Snowplow oil is available in stores in assortment. Here are some examples that have proven themselves in Russian conditions:
- m-8 m is a mineral grease that is widely used in different countries of the world. Resistant to temperature changes and low wear of the units.
- mt-16 r is poured into diesel engines. Excellent wear resistance of parts and oxidation of metals.
- m-82 k - the most common type of mineral lubricant, designed for any engine. A pour point of -30 ° C is achieved using certain additives.

Nowadays, universal greases are very popular, as they are suitable for most types of engines. Representatives of such manufacturers are well-known domestic and foreign companies:
- RAVENOL Schneefraese 4-Takt 5W-30 is a well-known German brand that produces lubricants with such advantages as: low volatility and it is possible not even to warm up the engine.
- Oregon SAE 30 is an American semi-synthetic lubricant used in gasoline snow blowers.
- Craftsman SAE 5W-30 is a Russian oil suitable for all types of engines and is not inferior in quality to imported counterparts.
One significant drawback of this product is its high price, which is not suitable for everyone. But, there are less "seasoned" brands, their products are practically in no way inferior to the giants. One can single out manufacturers: "Patriot", "Champion", "Interskol".
On a note! You should not buy liquids that arouse suspicion, they are usually sold cheaply and by this they lure ordinary buyers.
ACEA classification
Divides oils into operating groups similar to API, helping to select the optimal one based on the year of manufacture and engine design features.It has class A / B - universal for gasoline and diesel engines, C for diesel and gasoline that meet the most modern environmental requirements Euro-4, E - oils for loaded diesel engines of heavy vehicles. In this classification, only some groups can replace others.
In the latest revision of 2012, three categories are distinguished:
ACEA AB - Lubricants for engines powered by gasoline and diesel. It combines all classes A and B developed before 2004, which in earlier revisions divided lubricants into two categories by fuel type. Now there are 4 classes in this category: A1 / B1, A3 / B3, A3 / B4, A5 / B5.
| Class | Application | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| A1 / B1 | For a certain category of light load engines where low viscosity oils can be used. | Has increased mileage, not recommended for hot climates. Energy saving. |
| A3 / B3 | For engines of passenger cars and light trucks with high power, turbocharged and without | Average replacement interval. Can be used in any season. |
| A3 / B4 | For units with turbine, direct injection and unit injectors or common rail system. | Almost completely identical to A3 / B3, but suitable for new injection systems. May replace the previous category. |
| A5 / B5 | For highly accelerated engines of light vehicles, where the use of low viscosity lubricants is allowed. | Low viscosity, suitable for winter months. Not suitable for some engine types. |
ACEA C - lubricants for gasoline and diesel fuel, suitable for the most stringent modern environmental requirements for the content of substances in the exhaust. It can be used in systems with catalysts and particulate filters, as they have a reduced ash content. There are 4 classes in this category: C1, C2, C3, C4.
| Class | Application | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Gasoline and diesel engines with injectors, powerful with a small clearance between internal parts. | Saves fuel and decomposes to neutral substances in the exhaust. It is not allowed to be used in outdated structures or engines in which more aggressive materials were previously poured. |
| C2 | Economical engines with exhaust cleaning systems. | The difference from the previous category is in the higher content of phosphates and sulfates. |
| C3 | Engines with exhaust aftertreatment systems, operating in difficult conditions, with or without turbocharging. | It differs from C2 in high viscosity, low and medium ash content. Suitable for extended drain intervals. |
| C4 | For systems equipped with DPF and TWC. | The composition is similar to C1, but the viscosity is higher. |
ACEA E are greases for heavy duty diesel engines and heavy vehicles. The category was introduced at the very beginning of the creation of the class in 1995. In the new edition there are 4 classes: E4, E6, E7, E9.
| Class | Application | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| E4 | State-of-the-art engines complying with Euro 1 to 5 standards and working in tough conditions. | Keeps parts clean and protects against wear, long drain intervals. Not suitable for systems with a particulate filter, not compatible with all exhaust aftertreatment systems. |
| E6 | For modern engines meeting Euro 1 to 5 requirements with an exhaust aftertreatment system, with or without a particulate filter, reducing nitrogen oxide emissions. | Provides cleanliness of internal parts, protects against wear, extended mileage interval. |
| E7 | Diesel engines operating at high revs Euro class from 1 to 5, equipped with an exhaust cleaning system. Not suitable for systems with particulate filter. | Increased antioxidant and detergent properties. Extended drain intervals. |
| E9 | The difference from the E7 is in compatibility with a particulate filter. | Ash content limitation. |
Understeer and pumpability
Pumpability refers to the ability of a lubricant to pass through passages under the influence of an oil pump. The term "cranking" refers to the ability of an electric starter to crank the engine crankshaft during start-up.
Since the liquid lubricant loses its viscosity with a decrease in the degree of heating of the environment, the resistance to rotation increases, and the supply of the substance to the rubbing surfaces decreases.
For the selection of lubricants, a table with the distribution of temperature ranges according to the SAE standard is used.

For example, the owner plans to fill a 2011 VAZ car with synthetic oil of the 10W-40 standard (according to SAE). The minimum pumpability for this grade of grease is achieved when cooled to -32 ° C, but the cranking falls to a minimum value already at -22 ° C.
Grease according to the SAE 0W-40 standard has improved characteristics, but due to its increased fluidity, the fluid is not suitable for all power plants. Information on the permissible grades of grease can be found in the operating instructions or service book (supplied with the machine by the manufacturer).
Which oil for a high-mileage engine is better to choose

If you carefully study the market for fuels and lubricants, then you will notice that there are products of the same specifications on sale, which at the same time differ in viscosity and oil base. In other words, for example, a product with the index 10W40 can be mineral or semi-synthetic, 5W40 will turn out to be semi-synthetic or hydrocracking oil, etc.
So, the difference in viscosity and the distinctive properties of a particular oil base in many cases allows you to get rid of the problems that are inherent in worn-out internal combustion engines. As an example, it can be noted that mineral water, which has an SAE index of 15W40, differs in terms of kinematic viscosity when heated to 100 degrees from synthetic analogs 5W40.
After refueling a running engine with such mineral oil, a thick lubricating film is created at operating temperatures, wear protection is improved, the oil pressure in the lubrication system increases, and there is less loss of lubricant for waste. As a result, the old motor starts to run quieter and smoother on mineral water than on semi-synthetic oils or synthetics.
However, it should be borne in mind that some ICE manufacturers separately recommend using exclusively synthetic-based lubricants in their engines. It turns out that you cannot use a lubricant on a different basis. There have been cases when problems began even after the use of semi-synthetics in such units, not like mineral water.
We also add that one should not forget about the fact that, with the same operational properties and characteristics, mineral water, semisynthetics and synthetics noticeably differ from each other in terms of antioxidant and thermal oxidative resistance.
This means that mineral oil oxidizes faster than others and loses its properties, that is, it simply ages. If we add to this a certain "fatigue" of the engine itself and its systems (leaking injectors, coking, etc.), the aging of the lubricant will occur even faster.
For this reason, it is separately taken into account that if a transition was made from semi-synthetics or synthetics to a mineral base, then it is necessary to further reduce the oil change interval. In simple words, you need to know when it is best to change the oil in the engine, depending on its type, properties and other factors. It is also necessary to correctly perform the replacement itself.
Choice
What kind of oil should I put in the snow blower to keep it working properly? Not many people know that the choice of oil should be based on the engine and its performance. As a rule, winter oil M8g2k and M8DM are used in diesel engines of naturally aspirated snow-blowing equipment.
The latter is good for turbocharged diesels.

Motor 1D12VMS 1
Many cars are equipped with 1D12BMC1 motors, in which the use of low-viscosity oils is contraindicated. In order to lubricate engines of this type, it is necessary to use the M-14G2k, in rare cases the MT-16p. Cold start with M-14G2k and MT-16p can be applied only if outside the window is not more than five degrees.
If the snowplow has been standing in the cold for a long time or stored outside, then it must be warmed up before starting. During summer storage of the snow blower, care must be taken to protect the motor from corrosion.
For this purpose, often take used oil - its conservation values are much higher than that of what is placed in the barrel.
When choosing an oil for a diesel engine, one of the main values is its brand:
- Motor brand: D-242; oil for him: M-8G2k. Not at all like the M-8G2 and M-10G2. It differs from them in effective additive compositions, which make it possible to increase the time required to change the oil. M-8G2k is successfully used in domestic cars.
- Engine brand: YaMZ-236M2-4; oil for him: M-8G2k, M-8DM. M-8G2k differs from types M-8G2 and M-10G2 in more effective additive compositions, while it is possible to increase the period specified for oil change. M-8G2k and M-10G2k are used in KamAZ, ZIL, Ikarus.
- M-8DM. Contains a mixture of distillate and residual components, which are produced from sulphurous oil and new composite additives, which improve properties, which fight against corrosion and wear of parts. M-8DM is used during winter or summer operation of high performance turbocharged diesels

Oil M-8DM
It can be used in naturally aspirated diesel engines in which oil changes are infrequent.
It is poured into both domestic and foreign equipment:
- Motor brand: 1D12BMC1; oil for him: MT-16p, M-14G2k.
- MT-16p oil - used to lubricate naturally aspirated engine diesel engines. Certified in Russia. The oil has the following properties: detergent, antioxidant, anticorrosive and antiwear.
- M-14G2k. The composition with G2k oil is identical. Scope of M-14G2k:
It is used for transport diesel engines of the four-stroke type.
Can be used instead of M-10 G2k oil during summer operation of diesel engines, in regions where summer is long and very hot:
- Motor brand: Y-2D6-TK-C5; oil for him: MT-16p, M-14G2k.
- Motor brand: YAMZ-238BE; engine oil: M-8DM.
- Motor type: YAMZ-238M2; oil for him: M-8G2k, M-8DM.
- Motor type: YAMZ-238M2-1; oil for him: M-8G2k, M-8DM.
- Motor type: KamAZ-740.55-360; oil for him: M-8DM.
- Motor type: YAMZ-7511; oil for him: M-8DM.
You can also choose oil for the Revenol motor, which is used for 4-stroke engines of snow plowing equipment. The best selling oils are: Ravenol Schnefrase 4T SAE OW-30 Wollsink and Ravenol M 4T SAE 5W-30 Sinf. The latter is one of the highest quality synthetic engine oils.

Ravenol M 4T
For more details, see the video:
The oil has a light green color and can be used for small-sized 4-stroke vehicles, which are operated in the winter months. The oil prevents wear during high performance and protects the entire machine from rust.
During its use, the technique consumes less hot. This happens due to a decrease in the emission of harmful substances into the environment.
Ravenol m 4T SAE 5W-30 Sinf ensures uninterrupted start in February frosts at temperatures down to -30 ° C, Ravenol Schnefrase 4T SAE OW-30 Wollsink - up to -50 ° C.
The use of these engine oils reliably protects the motor during operation in extreme conditions, protecting the device under heavy load at maximum motor performance.
The Husqvarna snow blower oil is ideal for the snow blower of the same name.
One of the main characteristics is low viscosity.
The viscosity should correspond to the air temperature. If the temperature is between zero and eighteen degrees, use an SAE 5W-30 oil, but if the temperature is below eighteen degrees, use SAE 0W-30.
Experimental results with oils
Specialists of the well-known automobile magazine "Za Rulem" carried out six-month studies of several types of synthetic oils under conditions of operation of cars in city traffic jams (at idle speed). For this, the engines worked for 120 hours (analogous to the run of 10 thousand kilometers on the highway) at 800 rpm without cooling. As a result, interesting facts were obtained ...
First, the viscosity of all engine oils during continuous operation at idle up to a certain (critical) moment is significantly less than when driving “on the highway”. This is due to the fact that at idle there is a passage of exhaust gases and unburned fuel into the crankcase, where it all mixes with oil. In this case, there may be some (small) amount of oil in the fuel.
The drop in the viscosity of the engine oil is about 0.4 ... 0.6 cSt (centistokes). This value is within 5 ... 6% of the average level. That is, the viscosity is within the normal range. However, this only happens up to a certain point.
Clean and used engine oils
Approximately at 70 ... 100 operating hours (each oil is different, but the tendency is the same for all), the viscosity begins to increase sharply. And much faster than when working in the "track" mode. The reasons for this are as follows. The oil is constantly in contact with the products of incomplete combustion (as described above), and reaches its critical saturation. These products have a certain acidity, which is transferred to the oil. The lack of ventilation and low turbulence of the air-fuel mixture due to the fact that the piston moves relatively slowly are also affected. Because of this, the fuel combustion rate is below average, and the ingress of exhaust gases into the crankcase is maximized.
The widespread opinion that a large amount of dirt is formed in the engine at idle has not been experimentally confirmed. However, the amount of high-temperature deposits was small, and the amount of low-temperature deposits was large.
As for the products of wear, their quantity is much higher in the oil used in the "plug" mode than in the one that was on the "highway". The reason for this is the low piston speed and the high operating temperature of the oil (no ventilation). With regard to waste, each oil behaves in its own way. However, it can be argued that due to high operating temperatures and an increase in density, waste will also increase.
Based on the information provided, we will try to systematize the data and answer the question after how many kilometers to change the oil in the engine.
Types of oils and their features
Oils are divided into three types:
- synthetic;
- semi-synthetic;
- mineral.
Mineral oils are a product of the distillation of petroleum. Due to the fact that they contain sulfur, these oils increase the oxidizing properties of the metal. Therefore, the final sulfur composition should be no more than 1 percent. To improve the useful qualities, various additives are added. The cost of such oils is the lowest.

Synthetic oils are obtained by the synthesis of various substances, initially have protective properties, are characterized by lower consumption and resistance to extreme loads and temperatures. Due to the costly production, the output is a high price tag. However, the quality of these oils is much higher.

Semi-synthetic - an intermediate that is obtained by mixing mineral and synthetic oils in a ratio of 70 to 30. They have better characteristics and properties than mineral oils, but are inferior to synthetics. Accordingly, the price tag is average here.

The table below shows the recommended types of lubricants for various engines, as well as their characteristics and costs.
| engine's type | Oil type | Specifications | Price |
| D-242 | M-8G2k | Mineral oil is widely used in Russian cars, has a large number of useful additives, which increases the time until the next oil change. Suitable for diesel engines. The pour point is from -30 degrees. | 570 rubles for 5 liters |
| YaMZ-236M2-4, YaMZ-238M2, YaMZ-238M2-1 | M-8G2k, M-8DM | Universal mineral oil, suitable for equipment assembled in Russia and abroad, has excellent anti-corrosion properties, has high resistance to extreme temperatures, which makes the replacement period very long. Viscosity change temperature from - 30 degrees. Suitable for gasoline and diesel. | 1500 rubles for 18 liters |
| 1D12BMC1 | MT-16p, M-14G2k | MT-16p is a mineral oil for diesel engines. Protects against corrosion, oxidation and wear. Certified on the territory of the Russian Federation. M-14G2k - properties are completely similar. | 1800 rubles for 30 liters (MT-16p) 1650 rubles for 20 liters (M-14G2k) |
In addition, there are universal lubricants for all types of engines.
- RAVENOL Schneefraese 4-Takt 5W-30 is a synthetic four-stroke oil. Low evaporation rate ensures low consumption. Protects against corrosion, wear, carbon deposits. Has a high resistance to oxidation. It can be used in conditions of "cold start", that is, it quickly and efficiently lubricates all parts of the mechanism in conditions of cold temperature and an unheated engine. Price for 1 liter 550 rubles. Production - Germany.
-
Oregon SAE 30 is a semi-synthetic oil for gasoline engines with high cleaning properties and low consumption. Manufactured in the USA. Price for 1 liter 420 rubles.
- MTD SAE 5W-30 is a 4-stroke mineral oil. Provides a "cold start", well protects against wear and corrosion. Differs in low consumption. Made in Germany. Price per liter - 600 rubles.
- Craftsman SAE 5W-30 is a mineral oil for gasoline and diesel engines. Provides a "cold start", reduces operating noise, provides fuel economy, protects against corrosion and wear. Production - Russia. The price for 1 liter is 390 rubles.
Two-stroke and four-stroke engines
Internal combustion engines are divided into two types:
- two-stroke;
- four-stroke.
One stroke is the movement of the piston up or down. One revolution of the shaft requires two strokes. Engines in which one shaft revolution occurs during a working cycle are called two-stroke engines. Two-speed models are four-stroke. The differences between these engines lie not only in design, but also in some other indicators. In particular, there is a difference in the method of lubrication.

In a two-stroke engine, lubrication is carried out using a mixture that is obtained by combining oil and gasoline in a ratio of 1:25 or 1:50. The mixture circulates in the system and lubricates all the necessary components. After its ignition, the oil is eliminated in the form of combustion products. There are two ways to get the mixture. In the first case, this is carried out directly by the operator, that is, a ready-made version is filled in. In the second, the technique does everything by itself. In this case, the engine is equipped with a special oil tank, from which, with the help of a pump, oil in a strictly specified amount enters the branch pipe, where mixing is carried out.
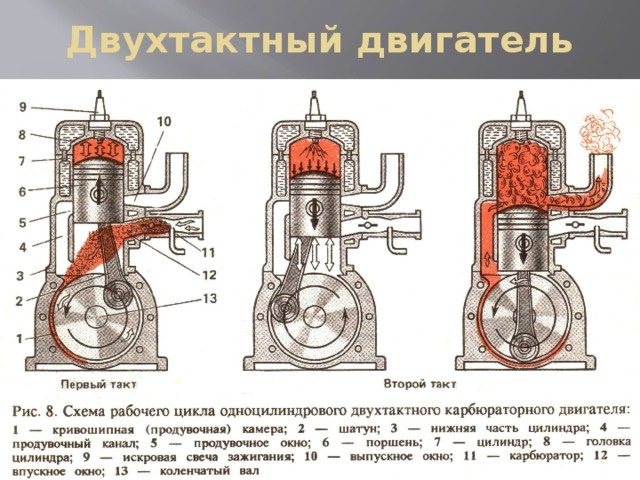
In four-stroke engines, no mixture is needed. Oil and fuel enter the system separately. In this case, the engine has a special lubrication system that includes a pump, filters, valve and oil supply line.
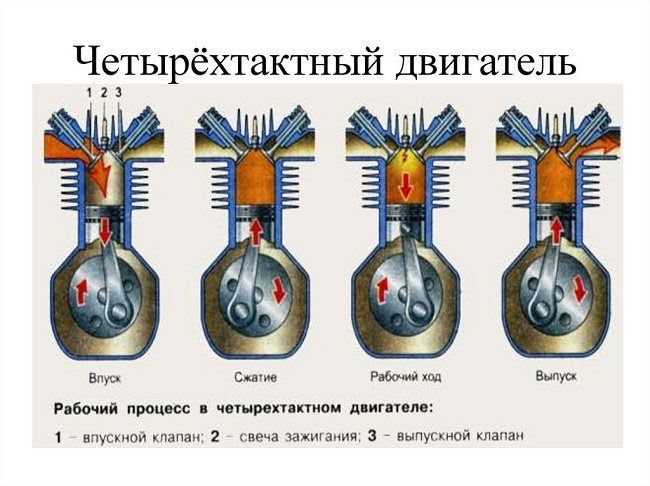
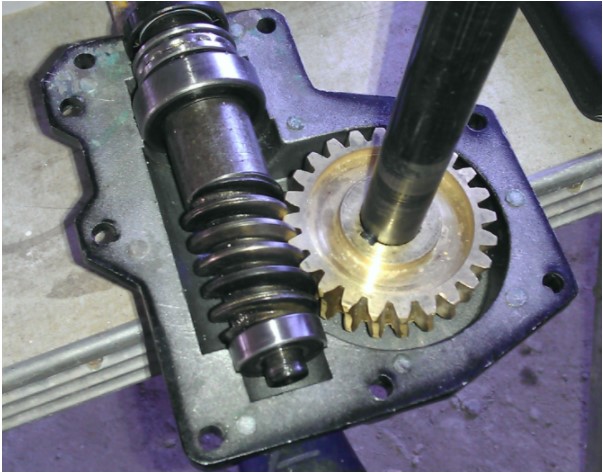
Snow blower gear oil - how to replace it yourself?

The gearbox is another mechanism that needs a timely oil change. As with the snow blower motor, proper gearbox performance is highly dependent on the correct lubricant. There are two types of oils that are suitable for the gearbox of snowplow equipment - thick oils and liquid oils.
Determining which lubricant is suitable for a snow blower gearbox is quite simple. If an oiler is provided in the mechanism, then the gearbox must be lubricated with a thick compound. If there is no oiler, but there is a filler bolt, then only liquid lubricant should be poured into the gearbox.
The algorithm for changing the oil is as follows:
- Place the snow blower in a stationary position;
- Unhook the protective plastic cover that prevents damage to the belts, then remove the auger drive cable;
- Then unscrew the screws that are located behind the snail, from which the snow masses are thrown;
- Remove the auger drive belt from the snow blower pulley;
- Remove the screws holding the auger shaft;
- Move the snow blower snail to its natural position and pull out the auger mechanism together with the impeller;
- Remove the shear bolts that secure the auger to the shaft and disassemble the auger;
- Disassemble the gearbox in two. To do this, clamp the part of the shaft on which the gearbox is located in a vise in a stationary position. Then unscrew the 6 bolts holding the two parts of the mechanism together. Then, using a hammer, disconnect one part of the gearbox from the other;
- After disassembling the gearbox, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse its elements from the remnants of the old lubricant. To do this, it is best to place them in a container with gasoline and wait about 30 minutes;
- Next, unscrew the fitting, clean it from the remnants of dirt and fill it with new grease;
- Then screw the union back and assemble the gearbox in the reverse order.
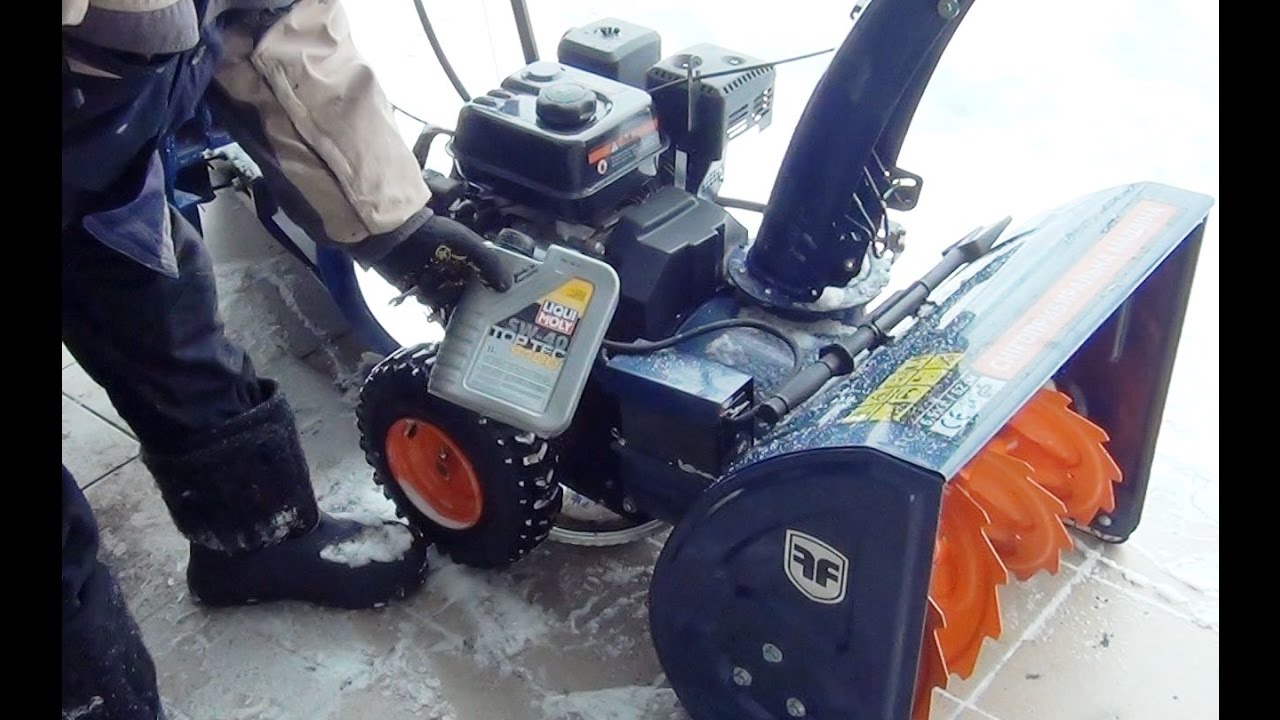
How to change engine oil on a snow blower, where to fill

How to change the oil
To calculate how much oil you need to pour into the engine, read the manufacturer's recommendations and instructions for using the technique. If the oil is underfilled, the engine will quickly fail, and with an arrogant amount of it, the spark plugs will stop working properly.
The four-stroke type motors are powered by gasoline (oil is poured into the engine crankcase). Such models can last longer and they start much faster. Fuel is used economically, while the noise level during operation is reduced.
The oil can only be changed if the engine is well warmed up. If the device has been idle for a long time, the engine must first be turned on so that it runs for 5-7 minutes.
- The crankcase has an oil filler neck, the cap of which must be unscrewed. If this is your first time doing this, it is usually located on the left side of the car.
- Before filling with new oil, drain the used one. To do this, unscrew the drain plug and drain whatever is left there.
- Replace the drain plug and make sure it is tightened securely.
- Now it is time to pour new oil into the oil filler neck. Make sure that the oil level does not exceed the permissible limits.
- After making sure you have done everything correctly, insert and screw back the oil filler cap.
Do not dispose of containers of oil that has been drained from the snow thrower into places that are not specifically designated for this.
You should also be aware that when buying a snow blower, it comes without oil in the engine crankcase.

Carter
Therefore, before starting work:
- Fill the crankcase with oil.
- Adjust the auger and wheel drive system.
- Check the tire pressure because it may exceed the required values.
- Check the correct assembly of the entire machine.
- To make it convenient to fill in oil, use a special device for this, a funnel is ideal.
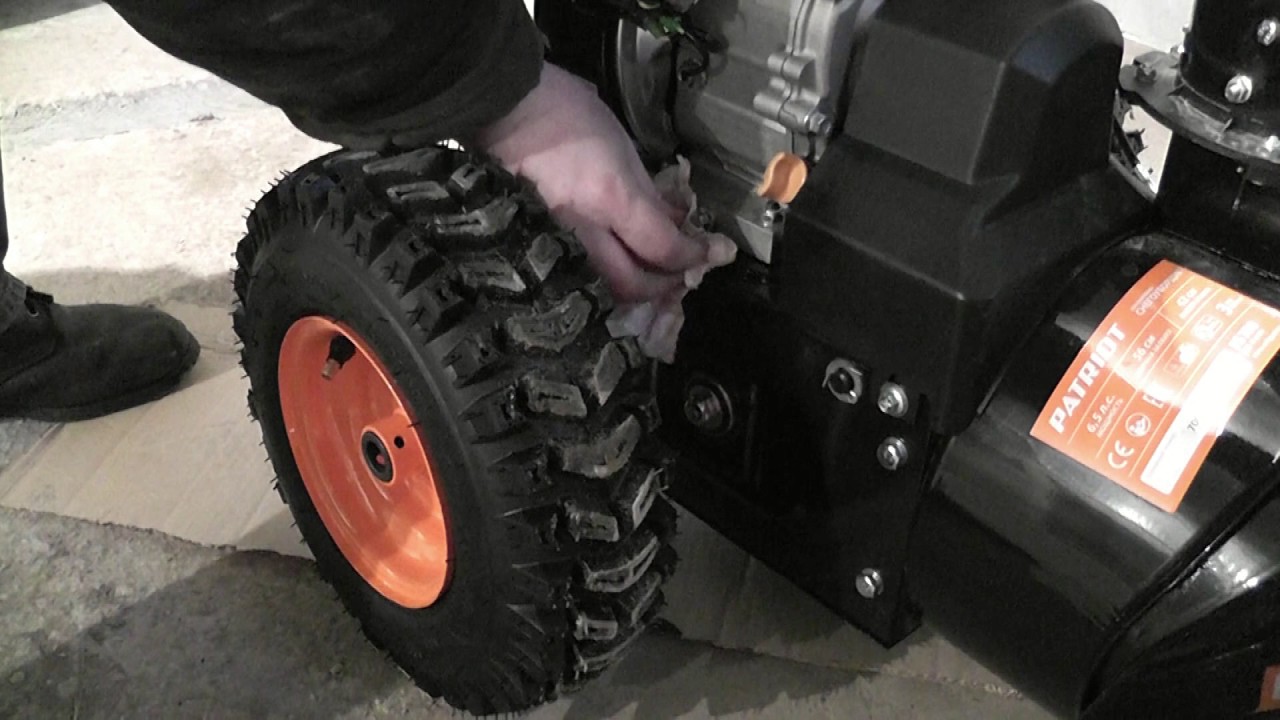
The next step is to check the oil level. To check it, turn off the engine.
- There is an oily neck on the motor crankcase, unscrew it and take the dipstick.
- Wipe the dipstick with a rag.
- Insert the dipstick into the oil filler neck to the very end and take it abruptly.
- Thus, you check the oil level, if necessary, you can add it or, on the contrary, drain the excess.
- Screw in the oily neck.
On the oily dipstick, the oil level will be in the area near the top edge.