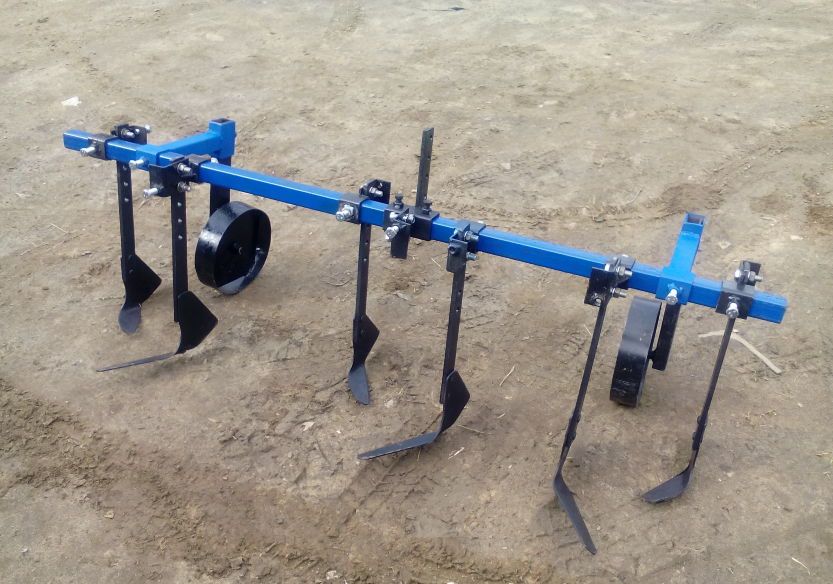
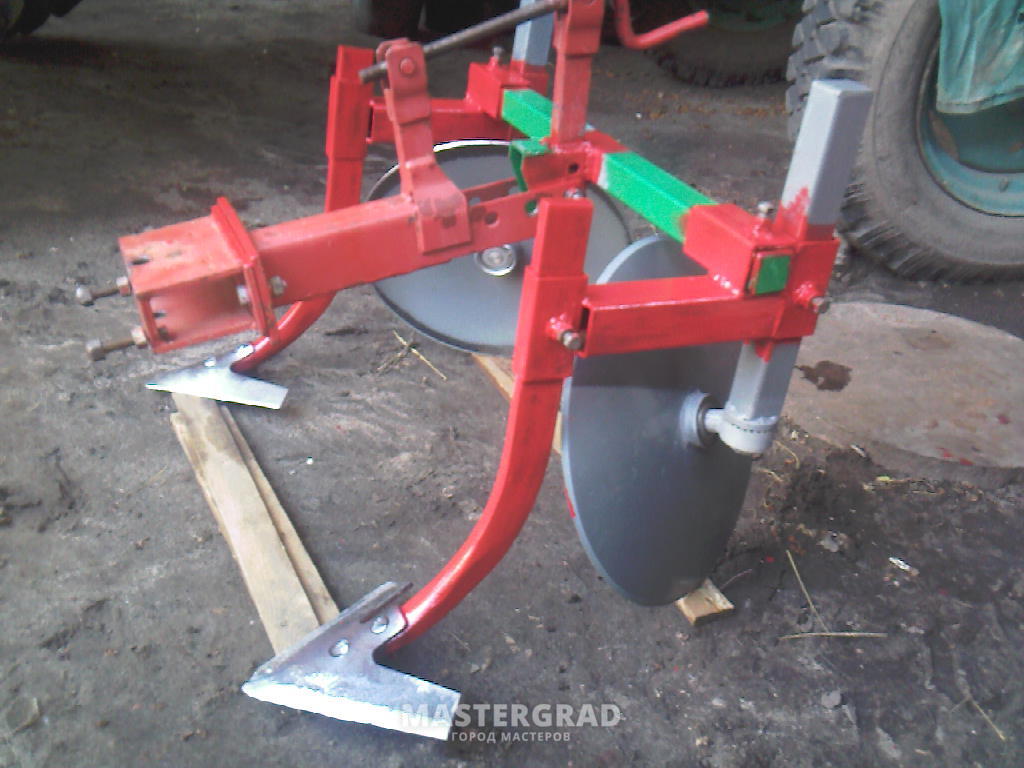
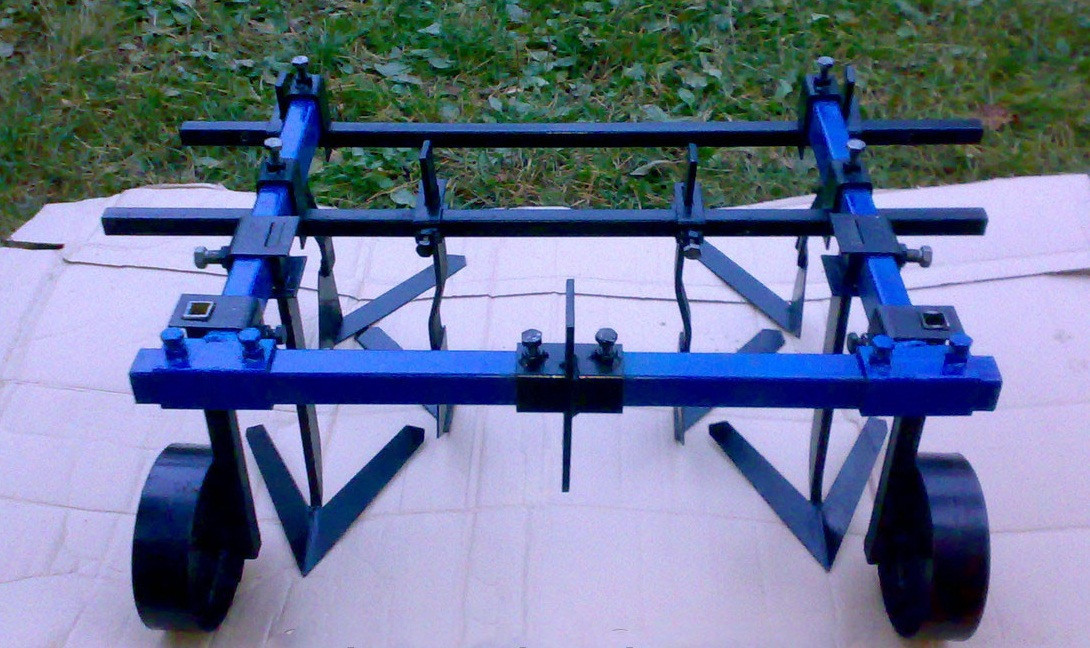
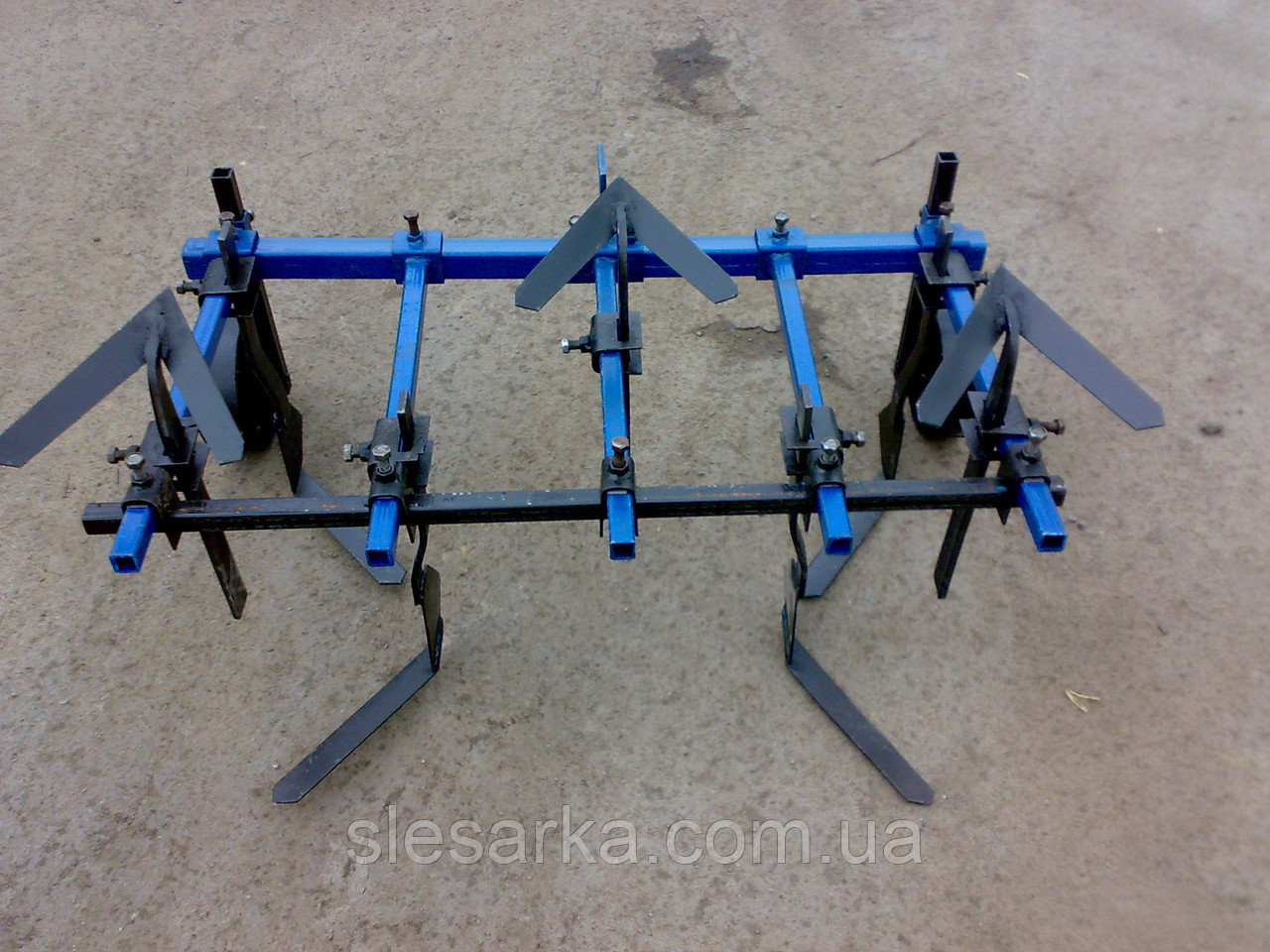
How to make a cultivator for a tractor with your own hands?
Modern cultivators for tractors are quite expensive, and therefore many farmers prefer to assemble small-sized equipment of this type with their own hands. To make a small structure, you need to prepare the following tools in advance:
- a small grinder;
- discs for cutting metal;
- welding machine with electrodes:
- double-sided sandpaper with different sizes of abrasive;
- drill with a set of drills.
From materials for work you will need:
- square steel plates, approximately 15 x 15 cm;
- flat rectangular plates - they will play the role of cutters. The width and length of these parts depends on the tractor model. Cutters with a width of 4 and a length of 25 cm are considered optimal;
- 16 pieces of nuts and bolts in pairs;
- long sturdy steel pipe.
When choosing the materials required for work, it is necessary to take into account that all of them must be not only as strong as possible, but also resistant to corrosion. This need is due to the fact that a cultivator for a tractor is often used in conditions of high humidity, which is a strong oxidizing agent, and leads to the appearance of rust on metal parts of the structure.
For work, you also need to study the drawings with dimensions and methods of fastening parts to the structure. The final result largely depends on the correctness of the schemes, therefore, their choice should be treated with special care.
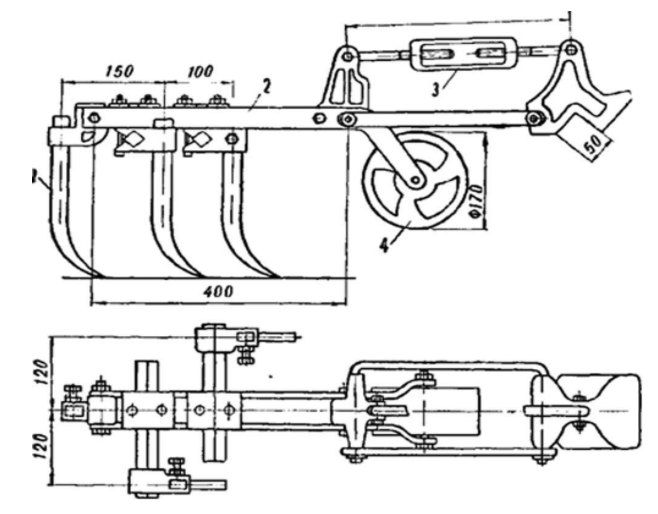
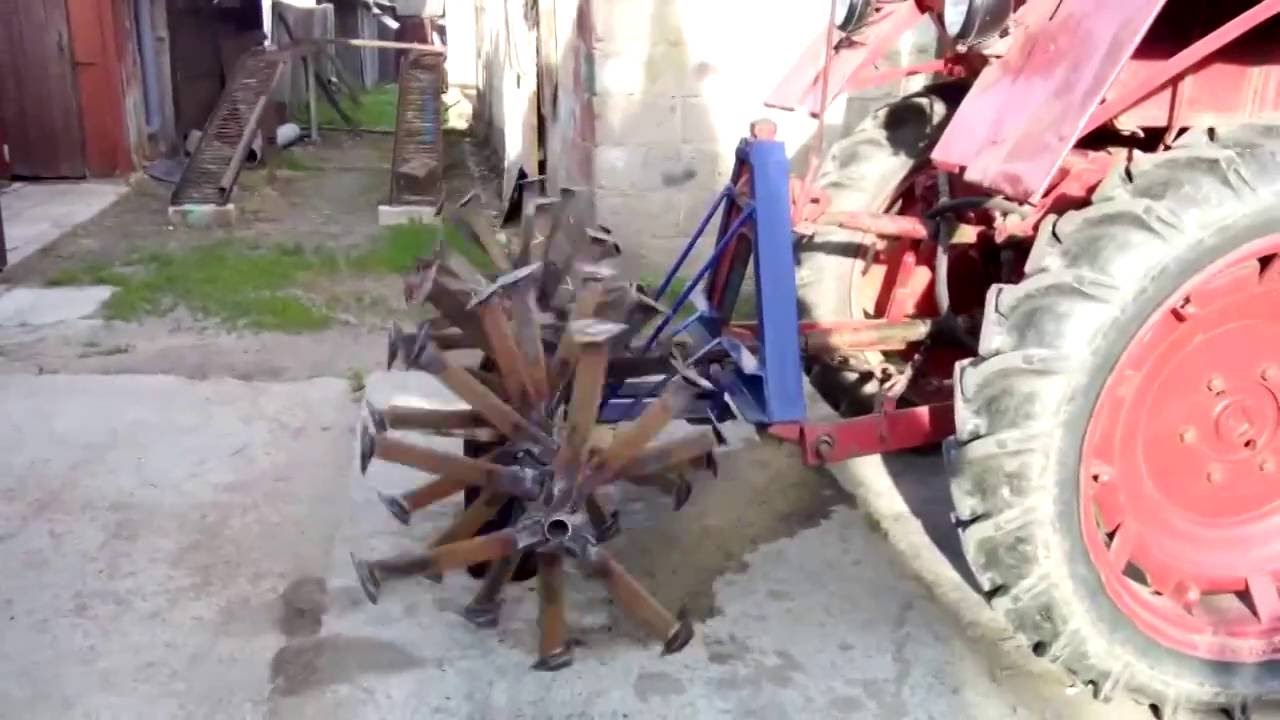
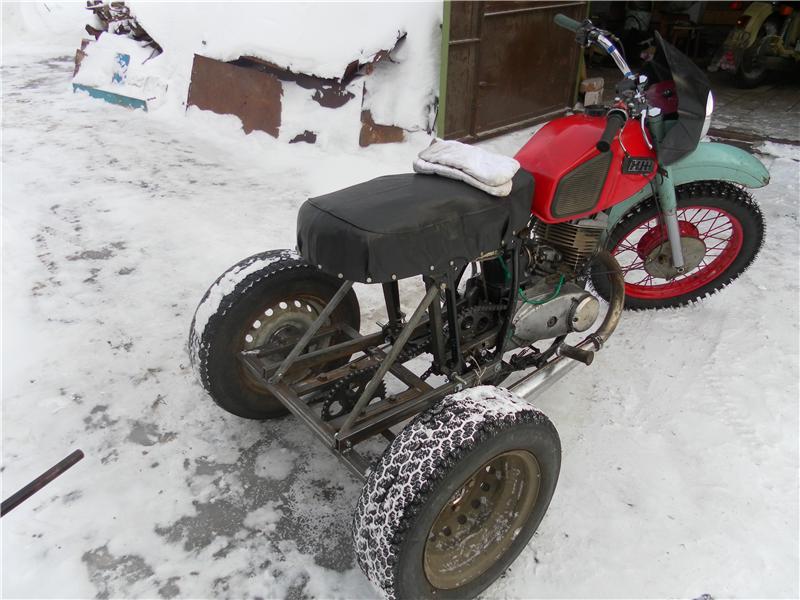
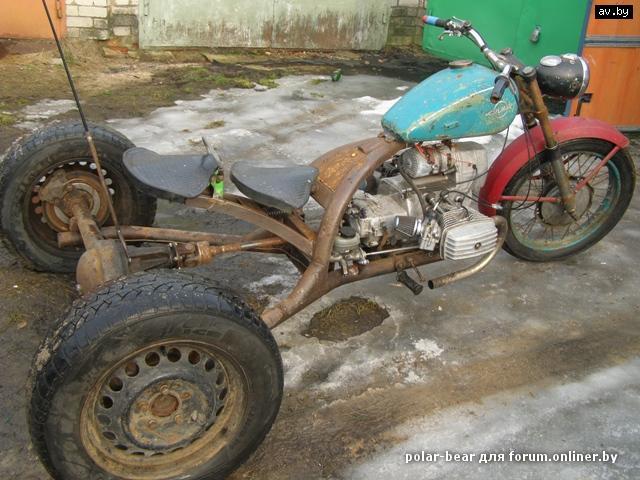
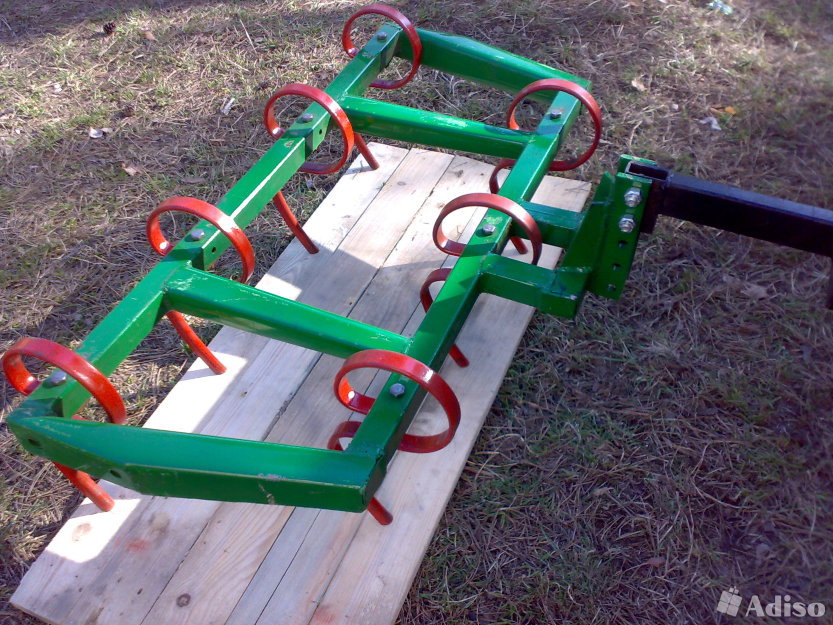
After preparation, you can proceed directly to the assembly of the cultivator for the garden. The algorithm for its manufacture is as follows:
- At the very beginning of the assembly, one hole will need to be drilled in each rectangular and square metal plate;
- Next, the plates must be aligned so that one cutter is located on each side of the square. They can be attached to the base with suitable bolts;
- If there are no bolts, then the parts can be welded to each other. This kind of connection will be less reliable, due to which the cultivation of the land with a tractor will only be possible in areas with loose soil. Nevertheless, the mounted cultivator must have maximum strength, since it is often used for plowing hard soils, during which the cutter and the base of the structure lend themselves to the greatest loads;
- After aligning the plates, you will need to make a hole in the center of the equipment through which you need to push a metal tube;
- The tube must be cut into two identical parts, on each of which you will need to put on a platform with cutters. The latter can be bolted or welded;
- Next, it is necessary to connect both parts of the cultivator to the power take-off shaft of the tractor. To do this, it is best to use a drill and a few suitable bolts;
- The tractor shaft and cutter tube will need to be drilled through. The drilling area depends on the tractor model. For example, if the farm uses a Zetor tractor or other large-sized machines, then you will need to drill a hole closer to the center of the PTO of the unit. After that, all the holes must be aligned, and a bolt must be inserted through them, on which you need to put on a nut and a locknut. A video will tell you in detail about the manufacture of a cultivator for a tractor.
Popular models
The T-25 is a rear wheel drive light tractor with smaller front wheels than the rear.The vehicle is equipped with a two-cylinder, four-stroke air-cooled diesel engine. The reversible manual transmission has the ability to compile with attachments. Thanks to this, cultivators and other devices are hung on the T-25 to facilitate the worker's work.
For hitching to the T-25, the cultivator-hiller with duckfoot or loosening tines is ideal. The device can be supplemented with a weeder suitable for removing weeds. The machine can process row spacings from 62 to 75 cm wide.
In addition to the hiller, on the T-25 it is possible to adapt a continuous and presowing cultivator for soil cultivation, which will provide simultaneous harrowing. The KON-1.4 product is equipped with tooth (spring) harrows, which provide high-quality loosening to the selected depth while simultaneously getting rid of weeds.
The attachment is compiled with a hydraulic frame, which allows the transport width to be reduced to four meters - this eliminates the need for additional equipment to transport the coupler from several cultivators.
Other popular cultivator models:
- KPS-4 - steam;
- KRN-5,6 - inter-row;
- KPM-8 - pre-sowing;
- KRG-3,6 - hydraulic.
The devices are designed to handle areas from 4 to 10 hectares.
T-40 is a wheeled tractor that rolled off the assembly line of the Lipetsk plant in 1961. The reliability and improved characteristics of the product made it the bestseller in the Soviet engineering industry.
A rotary cultivator or a rotary tiller will work successfully in conjunction with the T-40. The unit is used to cultivate virgin lands. The T-40 with a rotary cultivator copes with corn fields. This culture is considered a good green manure. The rotary cultivator will not only efficiently crumble plant residues, but also guarantee their mixing with the soil.
Types of replaceable cultivator nozzles
The cultivator for a motor-tractor can be equipped with various attachments.
They are divided into several types:
paws - necessary for plowing the soil while removing weeds. There are several types of these attachments. Chisel attachments are designed to loosen the soil to a depth of 15 cm. Pointed universal shares are used for continuous or inter-row plowing of the soil to a depth of 14 cm. Attachments of this type do a good job with crushing the earth and cutting weeds. One-sided flat-cut tines are designed exclusively for cutting large weeds;
- harrows - nozzles of this type are used for soil cultivation between rows and in protective zones;
- feeding knives - used for loosening the soil in the aisles and simultaneously embedding fertilizers in the soil. The maximum working depth is 16 cm;
- needle discs - designed to break up the earth crust and kill weeds. The working depth is 4 cm, and the ground shift is 1–2 cm;
- hillers - these attachments are used to cut ridges and destroy weeds in the aisles. Maximum processing depth - 16 cm:
- irrigation irrigation ditches - used to prepare furrows for further irrigation. The furrow depth does not exceed 20 cm.
All replaceable attachments are fixed to the cultivator racks by means of a bolt connection. To prolong the life of the equipment, you should regularly clean it of weeds and avoid contact with too wet soil.
It is interesting: Features and characteristics of the italian tractor lamborghini r2 (lamborghini r2)
Popular models
The modern market offers a large number of cultivators that can be aggregated with MTZ tractors. Among them there are both models of Russian and Belarusian production, as well as guns of well-known European and American manufacturers. Below are some of the popular samples, reviews of which are most common.
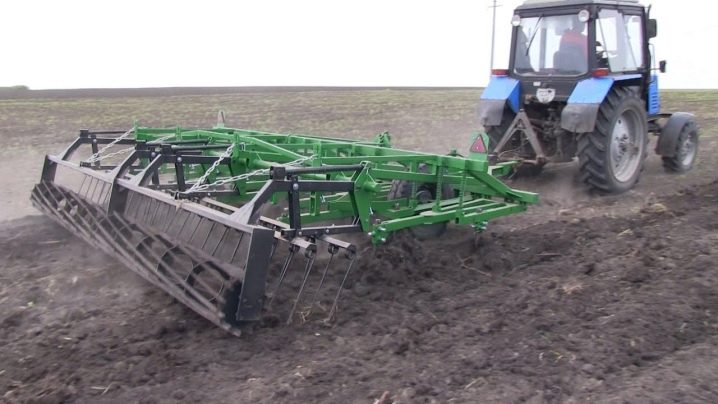

KPS-4
The model is an indispensable assistant for high-speed processing of vapors, it allows pre-sowing soil preparation without crushing plant residues. The gun belongs to the lancet type, capable of operating at speeds up to 12 km / h. The productivity of the device is 4.5 hectares / h, the width of the working surface reaches 4 m.The model is equipped with knives with a width of 20, 27 and 30 cm, capable of cutting into the soil to a depth of 12 cm.
The implement can be aggregated with MTZ 1.4 tractors. It is available in both mounted and trailed versions. The weight of the structure is 950 kg. The transfer to the transport position is carried out hydraulically. The ground clearance is 25 cm, the recommended speed on public highways is 20 km / h.


KPS-5U
This cultivator is designed for continuous cultivation of the land. It is capable of being aggregated with MTZ 1.4-2 level tractors. The model is used for grooming couples. It is able to effectively carry out pre-sowing soil cultivation with simultaneous harrowing.
The design of the tool is represented by a reinforced all-welded frame, for the manufacture of which a metal profile with a thickness of 0.5 cm and a section size of 8x8 cm is used. Ridge strips with a thickness of 1.4 cm have a reinforced design, and thanks to the extended surface of the bypass ridge, the possibility of clogging the wheels with plant residues and earth clods is excluded.
The working width of the unit reaches 4.9 m, the productivity is 5.73 ha / h, the processing depth is 12 cm. The implement weighs 1 ton, the recommended transport speed is 15 km / h. The model is equipped with ten 27 cm wide cutting elements and the same number of tines with a 33 cm cutting edge.


Bomet and Unia
From foreign models, one cannot fail to note the Polish cultivators Bomet and Unia. The first is a traditional soil cutter capable of breaking up earth blocks, loosening and mixing the soil, as well as cutting off the stems and rhizomes of the grass stand. The tool is aggregated with the MTZ-80 tractor, has a working width of 1.8 m, and can be used not only for field work, but also for garden work.
The Unia model is fully adapted to the harsh Russian climate. It is one of the most demanded in the domestic market. The tool is used for loosening, plowing and mixing the soil, has a working width of up to 6 m, is able to go deep into the soil by 12 cm. The company's assortment includes disc and stubble models, as well as tools for continuous soil cultivation.


For a detailed review of the KPS-4 cultivator, see the next video.
Geometric parameters of development
If you want to make a plow with your own hands, pay attention to such important indicators as the size and shape of the cutting part. It is they who determine the efficiency of immersion of the unit in the soil and the volume of cultivated land.
If plowing is in progress, the plow should not protrude or burrow too deep into the ground, sideways and deviate from the desired path. Key design properties that require increased attention are the following:
- the corner of the edge that enters the ground;
- the angle of the bending of the blades.
 Good edge angle ensures easy entry of the implement into the soil and fixation of the set position. In most cases, it is kept at around 40 degrees. If the angle is too sharp, the plow slips out, and if the angle is large, it simply cannot solve the assigned tasks. As a result, the ground will start to get stuck. The curvature of the blade affects the turning table, or blade angle. It is easy to guess that the larger the blade, the more land it can handle at a time. True, in this case, the load on the mini tractor increases. The best tilt angles are degrees from 25 to 130.
Good edge angle ensures easy entry of the implement into the soil and fixation of the set position. In most cases, it is kept at around 40 degrees. If the angle is too sharp, the plow slips out, and if the angle is large, it simply cannot solve the assigned tasks. As a result, the ground will start to get stuck. The curvature of the blade affects the turning table, or blade angle. It is easy to guess that the larger the blade, the more land it can handle at a time. True, in this case, the load on the mini tractor increases. The best tilt angles are degrees from 25 to 130.
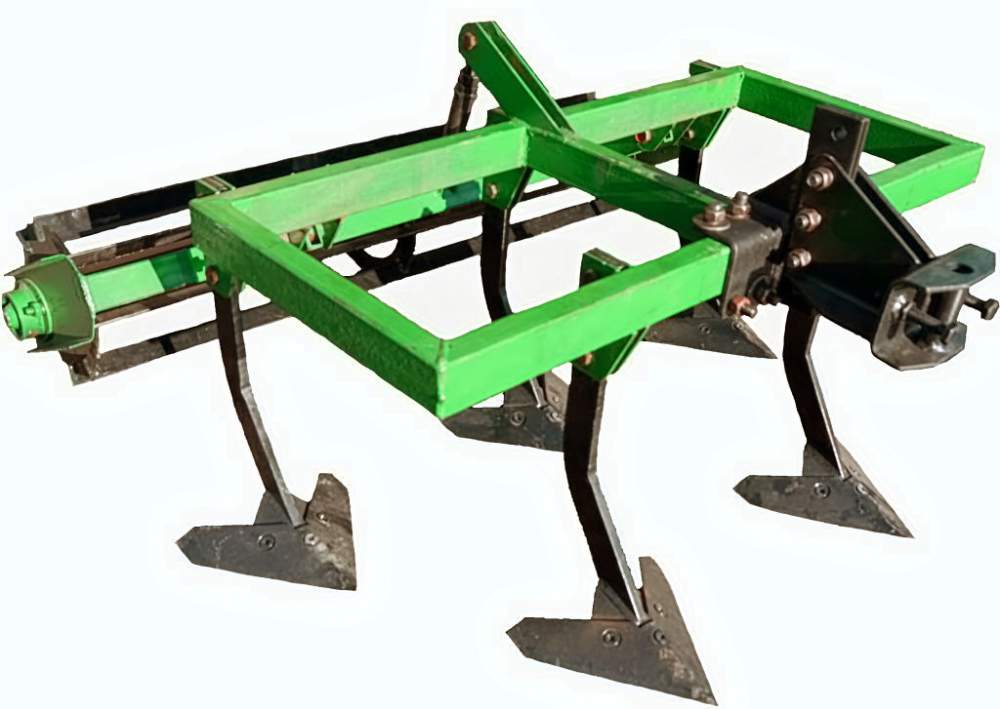
As for the working part of the plow, it uses a share that can take on the main load. It is made of durable heavy-gauge steel. As for the shape, it can be cylindrical, semi-cylindrical or screw. The bending angles correspond to the angles of inclination of the blade. A holder mount is attached to the ploughshare.
Cultivator location
To do this, use a marking plate or a flat area with a hard surface. The width of the slab should be 0.5−1 m larger than the working grip of the cultivator. The longitudinal center line of the ON unit is drawn on the plate. With chalk mark the axial lines mm of the rows of plants and the boundaries of the protective zones, (shaded) at a distance A from the axis of the row. If the cultivator in one pass will process an even number of rows, then from the ON axis to the right and left, draw lines mm at a distance equal to half the row spacing b / 2, and then at a distance b. With an odd number of rows from the center line ON of the cultivator, draw lines mm at a distance equal to the row spacing b.
The unit, on the marking plate, is installed so that the middle of the cultivator bar, point C, is located above the middle of the plate, point N. The bar is placed parallel to the platform with the hitch of the tractor, and the hinge rack is placed vertically.

The arrangement of the working bodies on the cultivator: I - for cutting weeds; II - for loosening and cutting weeds; III - for deep loosening; IV - for hilling plants; V - for feeding and hilling; 1 - one-sided pollen paws; 2 - lancet lindens; 3 - loosening paws; 4 - hilling hulls; 5 feeding knives.
On the bar of the cultivator, chalk marks out the attachment points of the sections. With an even number of rows to be processed, the middle section is fixed at point C, and the next ones - at a distance B equal to the row spacing. The axes of symmetry of the beams and section wheels pass in the middle of the row spacings, along the center lines of the OO.
Classification of cultivators for MTZ 82 (80)
Tillage devices are divided into groups, taking into account the method of aggregation and the type of operations performed.
According to the method of connection to the tractor, the processing machines are subdivided:
- Trailed - connected through the hitch of the rear hitch of the tractor. The lifting and lowering of the working bodies is carried out by a remote hydraulic cylinder as part of a trailed cultivator. Due to the presence of a running gear in the cultivator design, the advantage of the trailed unit is the balanced load on the tractor axles.
- Mounted - rigidly connected to the three-point hitch of the tractor. The position of the unit is translated by the hydraulic cylinder of the rear hitch of the tractor. The attachment has a much smaller size, which increases its maneuverability.
As a rule, manufacturers of agricultural machinery produce analogs of mounted machines in a trailed version in case of justified consumer demand.
According to the intended use, the equipment is subdivided into:
- Cultivators for continuous tillage are used for pre-sowing soil preparation, steam treatment and post-harvest stubble plowing. They can be connected to the tractor, depending on the design of the device, both in mounted and trailed versions.
- Cultivators for inter-row cultivation of crops are used for row crops with the possibility of simultaneous feeding of crops with mineral fertilizers. The devices are distinguished by hinged aggregation, since the rigid connection with the tractor ensures a strict course of the working bodies in the cultivated inter-row area.
- The group of special-purpose cultivators includes devices used in certain types of work, such as soda and vineyard cultivators. The devices are distinguished by reinforced working bodies capable of processing soddy and overgrown soils with woody growth.Additionally, cultivators can be equipped with cutting active organs for mulching branches and weeds.
Principle of operation
The transverse frame bar rests on the wheels; five working compartments and seeding devices of the fertilizer configuration are fixed on it. To interact with the tractor, an automatic coupler lock is used, which is welded to the frame beam. The working section is a parallelogram mechanism with four links. It consists of a front bracket, a link in the form of the letter "P", an upper adjustable analogue, a beam. The last element contains: a working holder, a support wheel frame, two side elements.

The sections are rearranged along the frame, which allows processing row spacings with a width of 0.6-0.7 m. The main parallelogram mechanism on the ups and downs of the wheel, on uneven ground, guarantees uniform movement of the bead, maintaining constant angles of the working bodies in depth and inclination.
What is a "mini tractor" and what are its differences from the classic one?
 The power of the mini tractor is enough for a dacha or a medium-sized vegetable garden. It is ideal for farms and small private farms.
The power of the mini tractor is enough for a dacha or a medium-sized vegetable garden. It is ideal for farms and small private farms.
The difference is not only in size, but primarily in the traction class. Mini tractors are inferior to traditional models in weight and, accordingly, power. Therefore, their cost is much lower, and they also consume less fuel and have less expensive parts.
Using a mini tractor, you can:
- Remove snow, debris, branches, leaves, etc.
- Uproot the stumps.
- Plow the land.
- Clear outbuildings.
- Straighten the road level.
- Patch the asphalt.
- Cover the lawn.
- Mow the lawn.
- Irrigate the ground.
- Spread deicing agents or fertilizers.
- And much more.
Popular models
Cultivator "Texas"
There are a number of models that are very popular:
- The KPS-4 model is a steam cultivator that is used by tractors of class 1.4. Designed to move at a speed of 12 km per hour. It can be used on an area of up to 4.5 hectares.
- The cultivator KRN-5,6 is an inter-row device. Suitable for work with tractors of class 1, 4 or 2. The cultivator is adapted to work with long-stemmed crops, as well as with essential oil crops.
- KPM-8 - designed for pre-sowing processing. Works at high speed: in one hour it is able to process a field occupying 10 hectares.
- KRG-3,6 is a device with lancet paws, which is hydraulic. It is usually used in areas that have a small area.
- KOH-2.8. This cultivator model has a hilling function. It can be used when planting potatoes. At the same time, he can additionally carry out fertilizing with fertilizers.
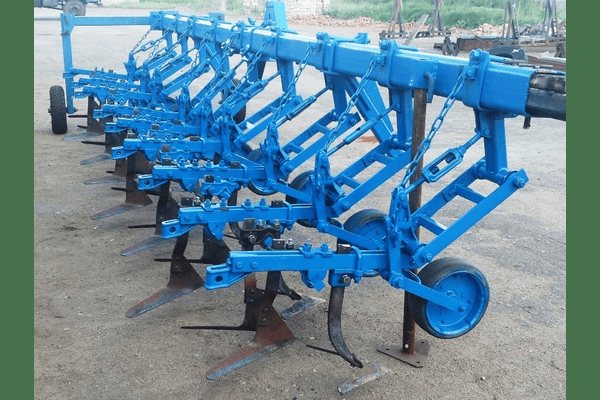

Cultivator KRN
Other models are widely known, for example: Will Rich, KNK, Salford, KPSh, Champion, Cayman.
About this device
Cultivators of different designs, and different specifics of work, this is exactly the equipment that is rarely used, but brings great benefit.
It's not for nothing that the most popular product drawings are a home-made cultivator for a walk-behind tractor and a home-made hiller cultivator. They are relatively easy to make on your own, at home, so there are a lot of variations of schemes on this topic.
The principle of operation and purpose of home-made cultivators is the same as that of cultivators Patriot, Champion, Strizh, Texas, Viking, Cayman of industrial production.
Next, we will consider the most successful and simple options for homemade cultivators. Also see the articles "harrow for a walk-behind tractor with your own hands drawings" and disc hillers for do-it-yourself walk-behind tractor.
For more information about the work of the cultivator, see the video:
It is interesting: Review of mini tractors kubota
Location of working bodies
When preparing the cultivator for work, the working bodies are placed in the designated rows so that the edges of the blades closest to the row of paws pass from the row axis at a distance equal to the width of the protective zone A.
For complete cutting of weeds, lancet paws and razors are installed in row spacings with an overlap of 3-7 cm. Chisel-shaped paws, loosening a strip of soil wider than their grip, are placed without overlap.
When installed on a section of several working bodies, they are distributed in a checkerboard pattern along the length of the ridge so that the gaps between the ends of the wings of adjacent paws are at least 3 cm, for the passage of soil and plant residues. Chisel paws are fixed on the beam at the maximum distance between them. On the beam, closer to the section wheel, a hilling body is installed, which improves good copying of the row-spacing relief. On the last sections, one or two paws are mounted, since the butt aisle is processed in two passes.
In order to set the working bodies at a given working depth, bars of the same thickness are placed under the wheels of the sections as under the wheels of the frame. The length of the upper link of the parallelogram mechanism, the section bead, should be parallel to the platform. The working bodies are arranged and fixed so that the cutting edges of the duckfoot paws and razors are in contact with the plate, and the chisel paws rest on it with their toes. In an overly short link, the feet will rest on the toes.
Accordingly, the mixing of the loosened layer will increase, the cutting of weeds will worsen, the filling of plants with soil will increase, the bottom of the furrow will be wavy. If the link is too lengthened, the paws will move "on the heels" and will not go deep enough.
In the event that working bodies are installed on the sections, for working at a large or small depth, then the height of the pads under the support wheels of the bar and the wheels of the sections will be the maximum processing depth, reduced by 2-3 cm, to the depth of immersion of the wheels in the soil. Working bodies, when working with the greatest depth, are placed on the site. Under the working bodies working at a shallower depth, shims are installed with a height equal to the difference in the depth of processing by the first and second paws.
Varieties
Cultivators for MTZ are classified according to four criteria. These are the specialization of equipment, the design of working elements, the principle of operation and the method of aggregation.
On the first basis, there are three types of tools: steam, row-crop and specialized. The former are used for the complete destruction of grass stand and leveling the soil in preparation for sowing. The latter are intended for processing row spacing of agricultural crops with simultaneous weeding and hilling.
The second criterion for classification is the type of construction of the work items. On this basis, several subspecies are distinguished.
- The disc cultivator is the most common type of implement that allows you to cut the soil in even layers. This helps to retain significant amounts of moisture inside the earth. This procedure is part of the mandatory agrotechnical measures carried out in regions with an arid climate. The size of the disks and the range of their location from each other are selected depending on the specific tasks and external conditions.
- The model with duckfoot paws is aggregated with all types of MTZ tractors. It allows you to quickly and efficiently separate the top sod layer from the main soil layer. This technology leaves no chance for weeds and contributes to the retention of a large amount of moisture in the soil. The object of processing lancet tools are heavy loamy soils, as well as silty black sandy loam soils.
- The stubble cultivator combines two functions at once: weed control and deep loosening. The soil treated with such a tool acquires an amorphous aerated structure and becomes completely ready for sowing.
- The share model looks like a plow, but it is equipped with much smaller shares and does not overturn the soil layers. As a result, it is possible to achieve a gentle impact on the ground with simultaneous breakdown of large fragments. The tool is characterized by a large working width, which allows processing large areas in a short time.
- The milling cultivator is used to cultivate fields before planting seedlings on them using a cassette harvester. The implement is able to go 30-35 centimeters deep into the soil and thoroughly mix the top soil layer with weeds and small debris. The soil treated in this way acquires the ability to quickly absorb water and ventilate.
- The chisel cultivator is intended for deep soil broaching using thin plowshares that do not violate the natural structure of the soil. As a result of this impact, the earth acquires a porous structure, which is necessary for the normalization of air exchange and fertilization. It should be noted that this type of cultivator is not often used in our country. One of the few implements compatible with MTZ tractors is the Argo chisel model.
- The forest cultivator is designed for soil reclamation after tree felling. It is capable of being aggregated exclusively with the MTZ-80 forest modification. Moving behind the tractor with a permissible speed of 2-3 km / h, the tool lifts the layers of earth and shifts them to the side. This helps the soil to renew itself and quickly restore the damaged fertile layer.
According to the third criterion (principle of operation), two types of equipment are distinguished: passive and active. The first type is represented by trailed devices operating due to the traction force of the tractor. The rotating elements of the active samples are driven by the power take-off shaft. They are distinguished by high efficiency of soil processing and a wider spectrum of action.
According to the method of aggregation with a tractor, implements are divided into mounted and trailed. The cultivator is attached to the tractor using a two- and three-point hitch, which allows the operator to adjust the depth of soil cultivation and work with almost any type of soil, including sandy loam, silty and stony.
The most common is the three-point canopy. In this case, the implement can rest on the tractor frame at three points, while gaining maximum stability. In addition, this type of attachment makes it possible to hold the cultivator hydraulically in an upright position. This greatly simplifies its transportation to the place of work.
With a two-point attachment, the implement can turn in the transverse direction relative to the tractor, which leads to an uneven distribution of the traction load and reduces the controllability of the unit. This, in turn, entails a drop in productivity and negatively affects the quality of processing of heavy soils.