Varieties
Dielectric seamless gloves can be classified according to two criteria: the material of manufacture and the number of fingers. Personal protective equipment is produced from mixed rubber-based materials (sheet rubber or latex). Thanks to the use of natural raw materials, the products do not irritate the skin of the hands and do not cause allergies.
Latex and rubber dielectric gloves are available in different sizes. It is selected in such a way that it is comfortable to work with gloves.

This is done so that jerseys (for example, knitted leggings or warm mittens) can be worn under the gloves.
According to the number of fingers, products are traditional five-toed and two-toed. Options of the second type are less convenient, five-fingered ones do not limit the user's work. When choosing one or another option, one must not forget about the voltage level. Based on this, the products are divided into 2 groups: "Ev" and "En".
According to GOST 12.4.103-83, the "En" marking indicates that the product can be used as a means of protection against current at voltages up to 1000 V. 1 kV. At the same time, they are used with electrical insulating tongs and rods.

Universal remedy
Due to the design features and the benefits that the employee receives during the use of these gloves, the device has become quite popular and has been in demand for many years.

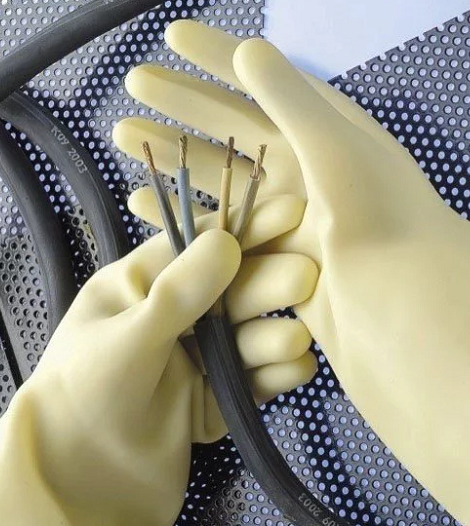
Without this means of protection, the employee would not be able to carry out so many operations, because any contact with cables or equipment under voltage is fatal, especially if work with high voltage is in progress.

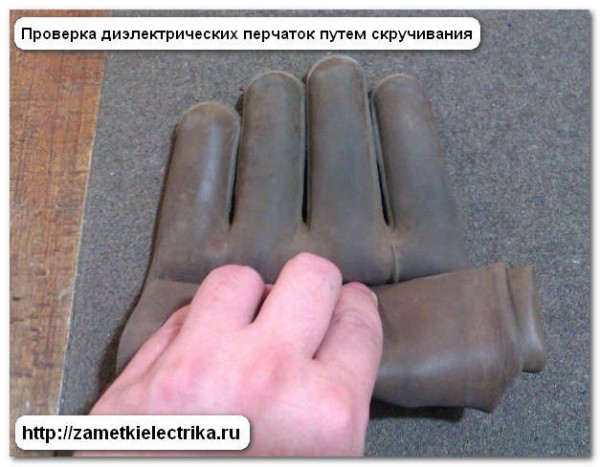
The versatility of this protective equipment and the relative ease of testing for suitability for work allows employees to go to work in those locations that would be inaccessible without special equipment, which is a key feature of protective gloves. There is no other such option on the market and it is not planned to appear in the near future, so you need to learn to work with what you have.

Types of gloves and their features
Despite the very high popularity of this accessory among electricians, the variety of models is not too great and for many years, tens of years, the assortment has not changed at all. Actually, this is due to the lack of need, because these types of dielectric gloves are not intended for beauty and attractiveness, but to protect against voltage, which they do well, decorative elements and, in general, design, few people care about. So, for decades, electricians have used almost identical protection options.


Let's take a step-by-step introduction to all types of gloves and discuss their advantages and disadvantages.

For operation up to 1000 V and over 1000 V
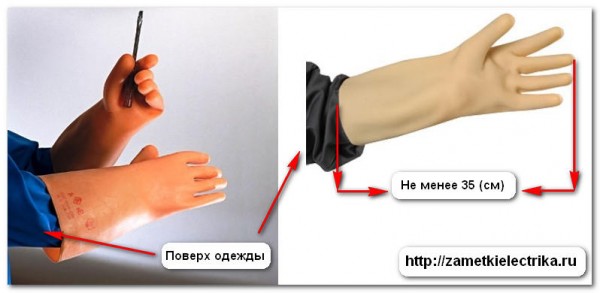
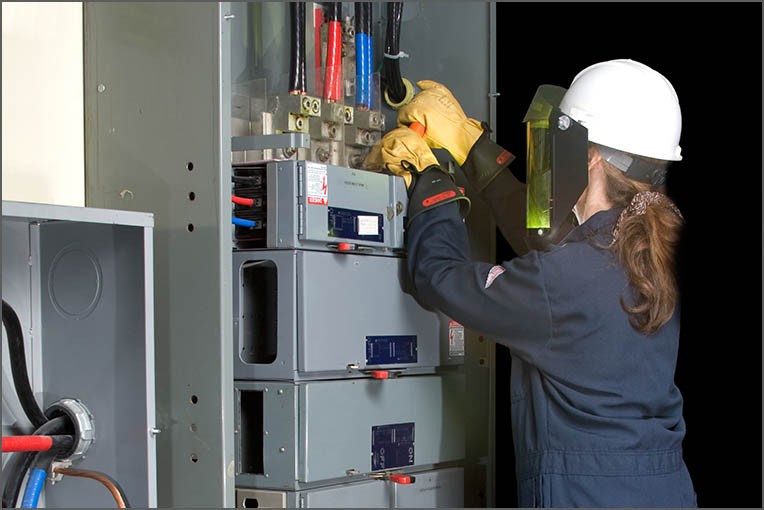
There is a third type of gloves called dielectric gloves up to 1000V and this model is used under certain circumstances and at very high voltages. It is worth noting that gloves are used only over outerwear, that is, put them on the hand and then wear protective overalls or work clothes on top, they are put on over.


Rarely enough gloves, the functions of which do not differ from previous models, only here you have the opportunity to work with a higher voltage without turning off the system. Such gloves are worn only by professionals who are able to repair the operation of transformers or other systems without turning off the power.

The process is quite dangerous and because of this, these gloves are also checked twice a year in order to be sure of protection from stress. There are a number of procedures for this, after which it will be possible to speak with confidence about whether the device can be used or not.

Peculiarities
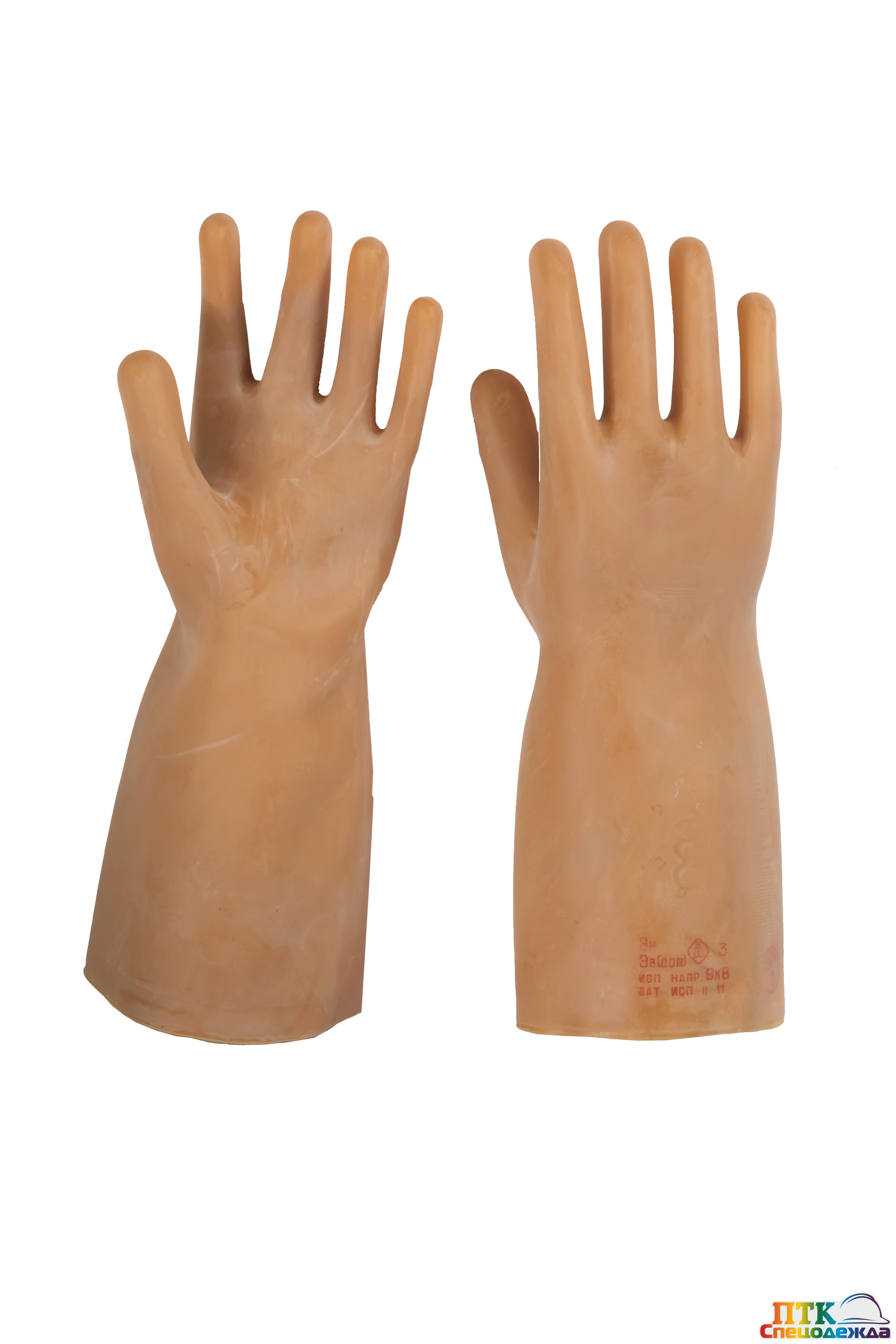
Their main feature is that they are made of materials that do not conduct electricity. They are made of latex and special dielectric rubber. You can use one pair of gloves for no more than a year, while all operating rules must be observed.
Another distinguishing feature of such gloves is that, unlike ordinary rubber gloves, they protect against cold and external influences on the skin of the hands. Wearing warm gloves from the bottom, the worker can work in them on the street even at sub-zero temperatures of 30 degrees. They will protect your hands from deep scratches, light burns and harmful impurities.

The gloves in question can be of two types.
- For electrical equipment up to 1000 V. They are used as the main means of protection when working with electricity. In no case should they be used at voltages above 1000 V. During their production, the value "Ev" is set.
- For installations over 1 kV. They belong to additional protective equipment. They are used when working with electrical installations over 1000 V. In such cases, the main means of protection are: insulating tongs, high voltage plates, instruments for measuring voltage and current, etc. These gloves are marked with "En".


Testing
It is imperative to check dielectric gloves (GOST is given above) and imported ones before use. But according to the rules, such personal protective equipment must also be tested every six months. Such activities are carried out to protect workers in the laboratory. Here the gloves are subjected to a special test.
During tests, an electric current of 6 kV is passed through the products. Only gloves that conduct less than 6 mA are suitable for use in production. Otherwise, the products are discarded.
For dielectric gloves, the current GOST 12.4.183-91 is the main document governing their production and operation. However, the procedure for testing such protective equipment is still determined by a special instruction GOST 12.4.252-2013.
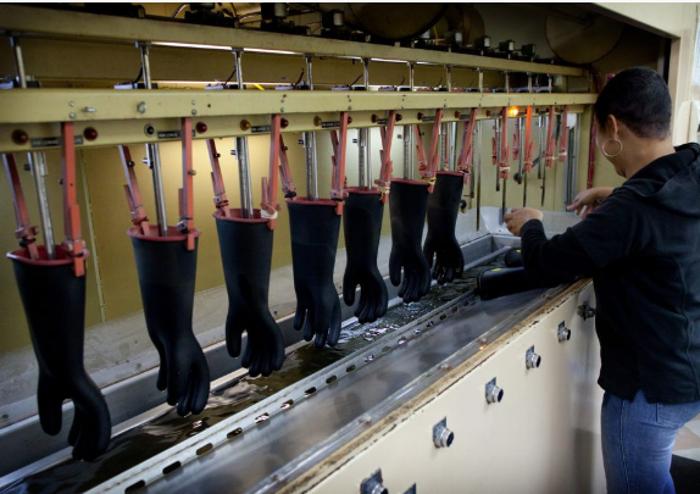

Inspection procedure for dielectric gloves?
A metal container is used for testing. As a rule, this is a rectangular bathtub filled with water, the temperature of which should not be lower than 25 ° C. Gloves are immersed in a water tank in an upright position, leggings up. They also need to be filled with water. The distance from the edge of the glove to the water level should not exceed 55 millimeters. The edges of the arms and the container must remain dry. One terminal of the transformer is connected to the container body with mandatory grounding, and the other is attached to the electrode connected through a milliammeter. During the test, the electrode is immersed inside the glove.

Circuit connection diagram for testing PPE against electric shock
At the beginning of the test, the switch (marked “2” in the diagram) must be in position “A”. When applying an electric current with a voltage not less than 6 kV, the signal indicators determine the presence or absence of physical breakdowns or cracks in the gloves. If the warning lights show breakdowns, the test is terminated. Gloves recognized as defective... If the breakdown test is successful, the switch is set to position “B”.
With this switch position, the throughput properties of the gloves are checked. The check is considered successful, and the gloves are fit for further use, if within 60 seconds the readings on the milliammeter did not exceed 6 mA and there were no sharp fluctuations of the ammeter needle.
Gloves that have successfully passed the test are sent for drying, after which a stamp with information is applied to them, and the test results are recorded in the test log, in accordance with Appendix 2 "Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations SO 153-34.03.603- 2003 "
Sample PPE Inspection Log
In addition to the above procedures, the organization that conducted the test is obliged to draw up and issue a test report drawn up in accordance with the requirements of GOST R 51000.3-96.

PPE test report form