Technology for growing mushrooms in the basement (in bags)
Before you start "mushroom business", you should find a room for growing mushrooms. A cellar, pantry or closet is almost ideal for breeding this culture. It is dark, damp, cool and there are no sudden changes in temperature.
Basement requirements:
- floor material - the floor in the cellar should be concrete, not earthen;
- lighting - one light bulb under the ceiling, installed for your convenience, is enough;
- ventilation - the ventilation system must be well tuned and actively function during the entire period of mushroom cultivation. Mushrooms grow poorly in musty rooms with minimal air movement. In addition, the nutrient substrate often emits carbon dioxide, so the mushrooms practically do not grow. Do not forget to avoid drafts;
- temperature and humidity - for the growth and distillation of mushrooms, you need to maintain the temperature at 15-17 ° C, for this you should use air conditioners or heating devices. And you can regulate the humidity by spraying the floor or racks from a spray bottle and airing.
Those who are seriously engaged in the cultivation of mushrooms usually divide the cellar into two parts - for the "distillation" of the fruit bodies and the incubation of the fruit bodies on the substrate. But more often than not, mushrooms are germinated on racks installed vertically one above the other.
When grown in a basement, you can harvest up to 6-8 waves of crops
For growing mushrooms indoors, you can prepare a substrate according to the following recipe:
- horse manure - 2000 kg;
- straw - 50 kg;
- urea - 5 kg;
- ammonium sulfate - 8 kg;
- superphosphate - 5 kg;
- chalk - 7.5 kg.
Soak the straw for a day in warm water in any convenient container. After that, lay it in layers, alternating with horse manure. You should have 6-8 layers. Sprinkle each layer generously with warm water. After 3-4 days, mix the resulting substrate and add a little urea and superphosphate to it. After 3-4 days, mix the mass again and add minerals again. Repeat this process 4-5 times, adding chalk one last time.
You can understand that the compost is “ripe” by light brown manure and the disappearance of the ammonia smell. This usually happens on the 25-30th day.
After that, you can start growing mushrooms in bags or on shelves. For 1 square meter of the prepared substrate, you need to add 500 g of compost mycelium or 400 g of champignon grain spores. Plant the mycelium in holes (up to 5 cm deep) at a distance of 20 cm from each other. Spores can simply be scattered over the surface. During this period, the humidity in the room should be 75-90%, and the temperature should not be lower than 27 ° C.
After 10-15 days, mushroom filaments will appear on the surface of the substrate. They need to be covered with a mixture of peat, limestone and earth (in a ratio of 5: 1: 4) and wait another 3-5 days. After that, you should lower the room temperature to 12-17 ° C and wait for the harvest.
The first mushrooms grow in 3-4 months. They need to be removed while the lower part of the cap is still covered with a whitish film, and the brown plates are not yet visible. Each mushroom, carefully twisting, remove from its place and sprinkle the hole with earth. Fruiting lasts for 1-2 weeks.
Planting mushrooms in the garden
In order for mushrooms in the country to become a familiar culture, you need not only to plant them correctly. The choice of the landing site is of great importance. Mushrooms do not need light, so you can choose shaded places for them. If there are no such zones, then the area with the mycelium will have to be specially shaded.
The principle of the arrangement of the place where the mycelium will develop is universal.In order to understand how to grow mushrooms in the country in the open field, it is enough to know that these mushrooms need to be provided with a large supply of dead organic matter, which must constantly decompose. For this, there is a mixture of manure and straw. Manure is an organic matter that will feed the mycelium in the first years of its development. Decaying straw (grass, leaves, sawdust, etc.) is food for mushrooms, which will be available to them in a few years.
In the beds
Placing crops in the beds is necessary to create specific conditions and fence this site with plantings. The beds are not only a separate area, but also a site raised above the main soil. This placement allows you to protect the planting from waterlogging and create special conditions.
Mushrooms in open ground beds are rarely planted. The expediency of such an arrangement arises in the case of constant waterlogging.
 If the bed is well shaded, then caring for the mushrooms will require little time and effort.
If the bed is well shaded, then caring for the mushrooms will require little time and effort.
A trench 1 m wide is dug in a shaded lowland. The length of the trench is determined at will and in connection with the peculiarities of the place. The width of 1 m is determined by the convenience of caring for the garden and harvesting. The trench is filled with a nutrient substrate according to the scheme described above. Only the top layer of the soil in which the mycelium is located should rise 10-15 cm above the ground level. The edges of the beds should be strengthened with boards or bricks.
With such a device, the mycelium will be located in a zone of sufficient moisture, and rotting organic matter - in the area of waterlogging. If the bed is well shaded, then caring for the mushrooms will require little time and effort.
In the pit
A layer of compost is laid on the bottom of the pit. Cover it with fresh grass or leaves. Then a layer of soil is laid. After watering, mushrooms are sown on the soil in the form of spores or ready-made mycelium. From above, the seed is again covered with a thin layer of soil and leaves. After that, the pit can be covered with a lid. With such a device, moisture will not evaporate, and the temperature regime will be constant.
Sowing mycelium
At home, the purchased mycelium must be activated before planting. To do this, it is placed in a dark place with a temperature of about + 20 ° C. This should be done 2-3 days before planting. If in the warmth the mycelium begins to develop (a well-visible "web" of hyphae appears), the humidity inside the package rises and the mushroom smell increases, this means that it is time to start planting.
It is recommended, if possible, to disinfect the soil before sowing. This is done in order to control diseases and pests. Only the top layer of the soil, into which the mycelium is immersed, is subject to disinfection. This should be done only in the case of planting a purchased mycelium or sowing spores. If the soil is transferred from the forest, then it makes no sense to disinfect.
 Growing mushrooms in a box.
Growing mushrooms in a box.
Detailed instructions on how to grow mushrooms at home
Now let's get down to the point of how to grow mushrooms at home. Before that, consider how the planting of the mycelium itself occurs, the so-called. fungus embryos.
Step-by-step description of planting mycelium at home:
We need to purchase mycelium from a supplier. For 1 square meter, you will need 500 grams of champignon varieties. For one and a half kilograms, we will pay about 250 - 300 rubles.
The mycelium is grain and compost. Grain is stored for six months in a cold place at +4 degrees. Compost mycelium can be stored at room temperature about 20 days. Grain mycelium gives a high yield.
On the soil, we make dimples 5 cm deep, the distance between them is 20 cm. The box with mycelium indicates how many grains should be in each individual dimple.
In a few days, you will see the mushrooms sprout. White threads will be visible on the surface. Indoor humidity should be around 70-85%. If the soil is dry, pour water over it.
Greenery business
Mushrooms will actively grow 10-12 days after planting. During this period, the temperature in the cellar should be +20, maybe even +25 above Celsius.
Be sure to sprinkle the compost 3-5 cm with earth mixture. It is made from 1 part sand and a ninth part peat. For 3 square meters, you need 150 kilograms of cover.
After three days, lower the room temperature. It should be between 12-16 degrees above zero.
After 3 months, the first ripening wave will go. In total, there can be from 5 to 8. From one square meter, 6-10 kg can be collected. Take breaks of 5-7 days between harvesting mushrooms, and be sure to sprinkle the surface with earth mixture each time after harvesting.
Note! In no case should the mushroom be cut off, it is only twisted so that harmful bacteria and microbes do not get into the soil.
It is important that it matured. What are the signs you can understand this? The film between the leg and the cap should not be damaged, but firmly connect these 2 parts of the champignon
What are the signs you can understand this? The film between the stem and the cap should not be damaged, but firmly connect these 2 parts of the champignon.
Substrate preparation

Nutrient compost can be purchased ready-made. This is especially convenient when growing champignons in an apartment, for personal consumption and for beginners' initial experience. Large volumes are formed independently, observing the necessary conditions:
- A place. All work with the future substrate is carried out on a flat area with a hard surface, underlaying strong polyethylene, which insulates the mixture from the soil. There should be a canopy above the site, which will protect the maturing compost from waterlogging by rain and drying out by the sun. The width of the site is at least 3.5 m, and the length corresponds to the total volume of the mixture to be produced.
- Composition. Nutrient soil is prepared on the basis of straw, wheat or rye, mixed with fresh manure - horse, cow, sheep, pork. The droppings of rabbits and poultry are also suitable for mushrooms. It is permissible to "dilute" the straw (maximum by one third) with fallen leaves, hay, potato tops, sunflower and corn stalks. You will definitely need chalk, as well as gypsum or alabaster.
Nutrient bases for growing mushrooms with manure and poultry droppings differ significantly in the number of components due to the different composition of organic matter.
| Compost with droppings | Manure compost |
|---|---|
| Straw 100 kg Bird droppings 80-100 kg Gypsum (alabaster) 6 kg |
Straw 100 kg Manure 100 kg Urea 2.5 kg Gypsum 8.5 kg Chalk 5 kg Superphosphate 2 kg |
The optimal compost mixture for mushrooms combines looseness, moisture and maturity, so its production takes place in the following sequence:
- Soak the straw for a day or two, pouring it with a hose or buckets, or immersing it in a tank with water.
- Divide the entire volume of moistened straw into 3-4 equal parts. Divide the manure in the same way.
- Lay the "layered" stack - cover the lowest straw bedding with a part of the manure, press the next part of the straw on top of it and then to the top in the same alternating order. In this case, the straw must be additionally moistened and sprinkled with additives, distributing them equally on each layer - in the case of a composition with bird droppings, only gypsum, and when using manure - urea, chalk, gypsum and superphosphate. Each layer is thoroughly tamped, watered with water.
- Watering is carried out daily, preventing the materials from drying out.
- After 5-6 days, perform the first slash, mixing the layers, pouring over them, sprinkling with plaster and stacking them again.
- After 4-5 days, stir again, moisturize and shape. In this case, sprinkle the mixture with manure with chalk and superphosphate.
- Make the third and fourth breaks at intervals of 3-4 days.
In general, the process of maturation of compost for growing mushrooms lasts from 22 to 26 days. The result is a dark brown, free-flowing and friable substrate without a pungent odor.
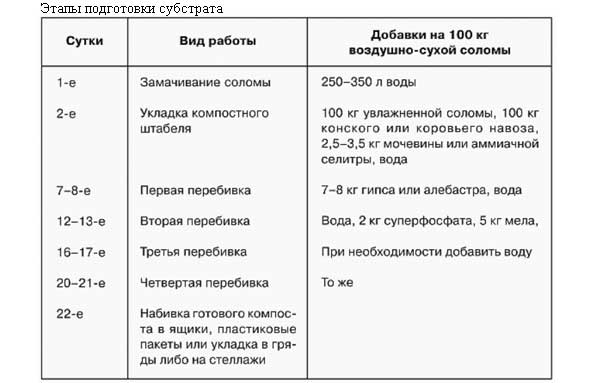
Humidity is controlled by the release of water during compression - it should only protrude, but not flow out in a stream. If the mass is waterlogged, add gypsum (up to 2 kg per centner of straw) and interrupt the compost 1-2 times with an interval of 1-2 days, spreading the mixture loosely. As a result, 250-300 kg of nutrient soil for a mushroom field of 2.5-3 m2 ripens.
Description of champignon mushrooms
Champignons belong to the Champignon family of the same name, of the Agaric order, which includes more than 60 different types of cap mushrooms. In nature, various types of champignons grow in the forest, in meadows among the grass, in open areas without grassy cover, and even in the desert.
By the nature of their nutrition, champignons are characteristic saprophytic mushrooms, therefore, representatives of the mushroom family prefer humus-rich soils for habitation, grow well on pastures manured by cattle, as well as in forests with thick vegetation rich in decaying organic compounds. In industrial mushroom growing, mainly 2 types of these mushrooms are bred: two-pore champignon and two-ring four-spore champignon; cultivation of field and meadow mushrooms is less common.

According to the description, the champignon is a hat mushroom with a pronounced central stem 4–6 cm high. The diameter of the cap of industrial champignons varies from 5 to 10 cm, but it can reach 30 cm or more.
Champignon is one of the few hat mushrooms that can be eaten raw. Raw mushrooms in Mediterranean cuisine are used in salads, for making sauces and as slices with various sour dressings.
In the initial phase of mushroom growth, the cap has the shape of a bell or hemisphere; as the mushroom matures, it takes on a convex-outstretched shape.

By the color of the cap, mushrooms are divided into 4 main groups: snow-white, milky, cream and light brown, which are often called royal. Sometimes white mushrooms and milk mushrooms are combined into one group. The plates of mushrooms change with the age of the fruiting body: in a young mushroom, they are light, white-pink, as they reach puberty, the plates darken to a red-brown color, and in old mushrooms they turn dark brown with a transition to burgundy-black.
The following is a detailed description of how to grow mushrooms in a basement or cellar.
What mycelium is needed?
The mycelium is also called mycelium. It is a vegetative body of fungi - a system of the finest branching filaments or hyphae.
The mycelium performs important functions, therefore, the process of growing mushrooms will not take place without it:
- participates in sporulation and is responsible for the preservation of the resulting disputes;
- helps organisms to attach to nutrient substrates;
- adapts well to the environment;
- with the help of enzymes, it processes cellulose, obtaining from it substances available for growth and development.
The mycelium is an important organ responsible for the vegetative reproduction of organisms.
Buying a finished product
For growing mushrooms at home, it is recommended to use grain mycelium, since it is not only convenient to sow, but it does not need additional processing
When buying a mycelium, pay attention to its appearance: the grains should be yellow with a slight orange tint
Be sure to pay attention to the manufacturer's company. It is advisable to choose mycelium from a well-known and large supplier
You should not buy a lot of mycelium right away, it is better to take it for a sample first. If there are no problems with germination, the formation of myceliums will be good, then buy a large batch.
Self-cultivation of mycelium
Before planting mushrooms, many gardeners and gardeners grow mycelium on their own, referring to the fact that this way they will be able to get a quality product. Mycelium, diluted at home, is compost and grain.
Grain mycelium is prepared according to the following scheme:
- Pour 10 kg of grains into a container, pour 15 liters of water.
- Put on low heat, bring to a boil and simmer for half an hour or an hour. The grains should not be soft, but should be soft.
- Drain the water, dry the grain, and then pour the finished material into liter jars. Make holes in the lids and grains.
- Close the holes on the lids with cotton swabs. Place the cans in an autoclave with a pressure of 1.5 atm. for 30 minutes.
- Place the mycelium in the chilled grain, or rather in its holes.
- Put the jars in a thermostat with a temperature of 24 degrees, do not take it out until the mycelium completely occupies the entire nutrient medium.
To obtain compost mycelium, the following procedures are performed:
- Take 3-liter jars and fill 2/3 of them with mushroom substrate. Seal well.
- Roll up the jars with lids, making 3-centimeter holes in them, covering them with cotton swabs.
- Heat the compost to 24 degrees, place the mycelium in it.
- Sealing the holes in the lids will help prevent mycelium contamination.

Making compost for champignons with your own hands
Unlike many mushrooms, champignons are undemanding to light and heat; they can actively grow in semi-dark basements. Optimal conditions for growing mushrooms are between 13 and 30 ° C. Moreover, these fungi do not need a host plant for nutrition and growth, since nutrition occurs due to the absorption of decaying organic matter. Therefore, compost (the so-called champignon compost), which is prepared on the basis of horse manure or chicken manure, with the obligatory addition of fresh rye or wheat straw and gypsum, is often used as a soil for growing mushrooms. Manure feeds mushrooms with nitrogenous compounds required for growth, straw provides mycelium with carbon and is an additional source of nitrogen, gypsum supplies mushrooms with calcium and at the same time structures the compost, preventing its caking. As additional additives, you can use chalk, complex mineral fertilizers, meat and bone meal.
Any mushroom farm, each mushroom grower develops his own formula for the best compost, as a basis for which you can practice the classic recipe for mushroom compost based on horse manure.
To prepare compost for champignons with your own hands, for every 200 kg of fresh horse manure, take 5 kg of straw, 0.5 kg of urea, superphosphate and ammonium sulfate, 750 g of chalk and 3 kg of gypsum.
With year-round cultivation of champignons, the composting technology is established in specialized rooms with a constant air temperature of at least 10 ° C. With seasonal mushroom cultivation, only in the warm season, compost can be laid under a canopy on a concrete area in the open air.
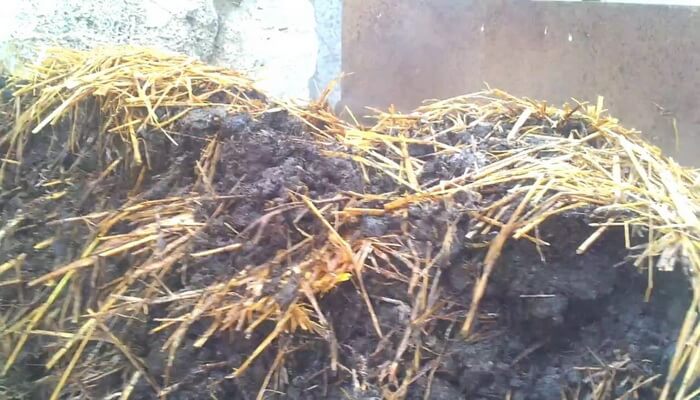

The main conditions for preparing compost for growing champignon mushrooms is to prevent contact of its constituent parts with the ground, since natural pests can get into the mushroom compost from the soil.

At the first stage of composting, the straw is crushed and abundantly moistened with water until completely moistened. After two days, it is combined with manure, laying it in successive layers. In the process of laying, the straw is watered with mineral fertilizers diluted in water. The formed roll-shaped pile with dimensions of 1.5 m in height and width is left to warm up. The folded pile must contain from 100 kg or more of straw, otherwise the fermentation process will either be too slow or will not start at all due to the low heating temperature. After 5 days, it is necessary to make a break of the formed heap, while adding water. The re-mixing helps to align the fermentation processes that are running at different rates in different parts of the compost heap. On average, composting requires 4 cuttings, and the full compost production cycle takes 20 to 23 days. 3 days after the final cut, subject to the compost preparation technology for growing compost, ammonia will gradually cease to be released from the heap, the characteristic odor will disappear, and the mass itself will take on a dark brown color. After that, the finished compost is placed in special containers or beds are created from it for sowing mushrooms.
How to prepare compost for growing mushrooms is shown in this video:
Features of growing in a greenhouse
Growing in a greenhouse can be carried out all year round or only during the period of freezing temperatures. Myceliums can be planted in beds or racks. It is impossible to leave the soil with mycelium on the shelves for the winter - the hyphae will freeze and dry out. Only myceliums immersed in a thick layer of earth and covered with leaves, sawdust and grass can hibernate.
Even unheated greenhouses save mycelium from thermal damage, since there is no wind or sudden temperature changes in a closed room. However, there is no snow there either. To compensate for its insulating role, a shelter made of leaves or plastic wrap is needed.
Growing mushrooms in bags

For growing champignons in large volumes for sale through retail chains I use polymer bags. This method has received its recognition in many countries. With its help, a large harvest is obtained.
- For the manufacture of the bag, a polymer film is used. The capacity of each bag varies from 25 to 35 kg.
- The bags should be of just such a volume so that it is convenient to work with them. In addition, the correct arrangement of the bags affects the number of mushrooms grown. Usually they are arranged in a checkerboard or parallel order.
- So when installing bags with a diameter of about 0.4 m in a staggered arrangement, only 10% of the usable area will be lost, while their arbitrary installation gives losses of up to 20%.
- The height and width of the bags may vary. You need to proceed from their conditions and convenience of work, as well as the physical capabilities of the basement (cellar).
The method of growing mushrooms in bags is less costly, since they do not require specially mounted shelves or containers to place them. If it becomes necessary to use the area of the room as efficiently as possible, then a multi-tiered system can be created for the location of the bags. The advantage of this method also lies in the speed of dealing with emerging diseases or pests. The infected bag can be easily removed from healthy neighbors and destroyed, while if the mycelium is infected, it will have to remove its entire area entirely.
It is important to remember that growing mushrooms is a rather laborious process. If champignons are grown for sale, then it is impossible to do without the use of agricultural machinery to facilitate the work of the workers.
Experienced mushroom pickers can list a large number of methods they have tested for growing mushrooms on their own in a basement (cellar). Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The main thing is adherence to the cultivation technology, strict adherence to all instructions and requirements. The result is the achievement of the desired result and obtaining a rich harvest of mushrooms.
Care of the developing mycelium

To ensure the rapid growth of a full-fledged mushroom mycelium, it is necessary to maintain an optimal temperature and humidity regime for it. In the first two weeks, the soil temperature should be 24-27 ºС, and the air temperature - 21-25 ºС. If the substrate is overheated, the plantation must be ventilated. If too cold, the compost layer should be covered with compressed straw or burlap.
Air humidity must be maintained at 90-95%. The compost should be moistened regularly, enough, but not too much. A drop in temperature in combination with waterlogging is especially dangerous. In such an environment, the processes of decay begin and the mushroom mycelium dies.
Under optimal conditions, after two weeks, the whitish hyphae of the overgrown mycelium come to the surface.
What diseases and pests can you expect harm from?
Basic disinfection of the premises with the help of smoke bombs, spraying and liming will help to fight pests and diseases. But occasionally there are situations when mushrooms are exposed to various diseases and pests. The most common are:
| Name | Causes | Control methods |
| Mushroom mite | A small yellow parasite that eats the legs of mushrooms. | Eliminate the problem by spraying mushrooms and compost with a 0.1% metaphos solution. |
| Mummies | A disease that occurs due to a lack of light. The caps of the mushrooms become dark gray, and the flesh is brown. | The infected mycelium is removed along with the substrate. |
| Mushroom midge | Fly larvae entering the compost with manure. Over time, the mycelium is affected, which is fraught with termination of fruiting and death. | The compost is treated with chlorophos 0.5%. |
| Rotting mushrooms | The development of the disease takes place with direct penetration of moisture into the already formed mycelium. This leads to instant infection of other fungi. | The spoiled myceliums are removed, those that remain are treated with a formalin solution with a concentration of 0.2%. |
| Mold | Wet brown spots form on the surface of the mushrooms, increasing in size. | Diseased mushrooms are removed, the substrate is sprinkled with superphosphate and table salt. |
Fruiting and harvesting
With the formation of the primary rudiments of fruiting bodies, the air temperature should be gradually, in 4-5 days, reduced to 14-16 ºС, the room should be regularly ventilated. With the appearance of the first mushrooms, water it daily, in moderation, consuming up to 1.5 liters of water per 1 m2. The crop appears in waves for 2-4 months - up to five waves of champignons at weekly intervals. Before the next fruiting, it is useful to water the plantation with a solution of epin - 0.005 ml per 0.8-1 l of water. This volume is sufficient for 1 m2 of substrate area.

It is necessary to collect champignons at the stage of maximum size, at which the membrane at the bottom of the cap is completely preserved. Mushrooms are unscrewed from the substrate, but not cut, so that the "hemp" left in the soil does not become sources of putrefactive infections and breeding grounds for insect pests. Champignons with dark plates and a destroyed film do not correspond to the marketable condition, and old mushrooms can cause food poisoning.
The used nutrient soil is an excellent organic fertilizer, which, moreover, significantly improves the structure of the soil.
Growing champignons is a well-established process. With its observance, fruitful "waves" of snow-white gourmet mushrooms with excellent taste and aroma can be obtained three times a year.
Champignon plantation care
After you have landed, the room temperature is kept high. This is a prerequisite - the germination of mycelium will not begin at below + 24 ° C and above + 26 ° C. At this time, at the initial phase of mycelium growth, do not expect immediate "shoots". Champignons are not vegetables. They grow deeper into the soil, gaining ground and forming the future harvest. At low temperatures insufficient growth, at high - weak formation of the fruiting body.
The moisture content of the compost must be constantly maintained in the range of 55-60%. As soon as it dries up, the mycelium "freezes" and stops growing. The compost is moistened superficially, from a sprayer, so that the water does not flood the mycelium, otherwise it will become moldy and die
It will take 12 days to grow deep into the mycelium. After that, the temperature in the room will definitely decrease. Either the heating is turned off, or the transoms and ventilation openings are opened - all methods are good to reduce the temperature to + 18 ° С… 20 ° С.
By this time, it is necessary to prepare the soil for backfill. The mycelium will grow upwards not on compost, but from nutrient soil of the following composition:
- sod land;
- loam;
- sandy loam;
- fine-structured peat soil.
Any of the listed structural types will do.The main thing is that the soil is not heavy. To add "airiness" and to ensure the penetration of air to the spores of the fungus, the soil is sieved on a coarse sieve.

Before backfilling, the soil is moderately moistened. And cover them with a layer of compost 3-4 cm.
Further, caring for the mushrooms is simple.
Maintaining the temperature within the specified limits. - + 16 ° С ... 18 ° С, plus - minus two more permissible degrees.
Maintaining humidity in the range of 65-85% (air) and not higher than 60% - of the earth layer.
Daily intensive ventilation of the room to remove accumulated carbon dioxide.
You can collect the first homemade mushrooms from your own plantation already on the 35-40th day. One fruiting cycle lasts about two months.

Despite all the seeming difficulties and conventions, the cultivation process, starting from the moment the compost is prepared, takes no more than four months. For two months of fruiting, the crop can be harvested 6-7 times. From 5 to 10 kg of mushrooms are collected from a meter of a square ridge. The next crop ripens after 5 days.
The champignons are not cut with a knife during collection. The mushrooms are twisted with a gentle movement of the hand. The holes formed after collecting are sprinkled with soil
Growing conditions
Obtaining a rich harvest requires a certain environment, the parameters of which change depending on the stage of growth of the mushrooms.
Temperature regimes
Champignon spores can germinate in the range of 15-30 ºС, while the optimal temperature is from 22 to 25 ºС, and the best season is spring-summer. The mycelium takes root most quickly in an environment warmed up to 25-28 ºС - “ingrowth” takes no more than 2 weeks. An increase in the temperature of the substrate to 29-30 ºС reduces yields, and at 32 ºС the death of the mushroom mycelium begins. If the soil cools down to 18-20 ºС, the development of mycelium slows down significantly, so that the overgrowth of the soil layer takes from 18 to 25 days.

During the period of mycelium growing, the soil should be 2-3 ° C warmer than the air. During ripening of mushroom fruiting bodies, the ideal ratio of these temperatures is as follows: substrate - from 16 to 18 ºС, air - from 15 to 17 ºС. If the air is warmed up to 18-20 ºС, mushrooms grow quickly, but lose their commercial quality. At 12-14 ° C, the crop will take more than 2 months to grow.
Humidity
Champignon is a moisture-capacious mushroom, as its mycelium and fruiting bodies consist mainly of water. Therefore, at all stages of growing a mushroom plantation, air humidity is required in the range of 85-95%, and the soil must be saturated with moisture by 64-68%. Such conditions ensure the formation of dense, weighty mushrooms with smooth skin and impeccable color.
Gas environment
Developing champignons "exhale" a noticeable amount of carbon dioxide and ammonia vapors. At the stage of mycelium growth, the increased content of these gases does not harm the process, therefore, closed rooms do not need to be ventilated. At the stage of growing fruit bodies, the atmosphere saturated with carbon dioxide slows down the growth of mushrooms and degrades their quality. During this period, the mushroom plantation requires intensive ventilation with an influx of fresh air. Indoors, appropriate equipment will be required.
Chemical parameters of the substrate
Mycelium hyphae absorb well the ready source of carbon - organic matter, in particular, containing glucose, xylose, starch, cellulose, lignin and glycerin. Developing champignons get nitrogen from organic residues and inorganic substances - mainly ammonium salts. The carbon and nitrogen component during cultivation must be balanced, since with an excess of nitrogen, the fruiting of mushrooms stops.
Lighting
At all stages of development, mushroom plantations practically do not require lighting. These mushrooms grow successfully in dark rooms. In open areas, in the country and in the garden, mushrooms are planted in the most shaded places, on the north side of the house.
The correct technology for growing champignons is a guarantee of an abundant harvest and, at the same time, the best prevention of bacterial and fungal diseases.
























































