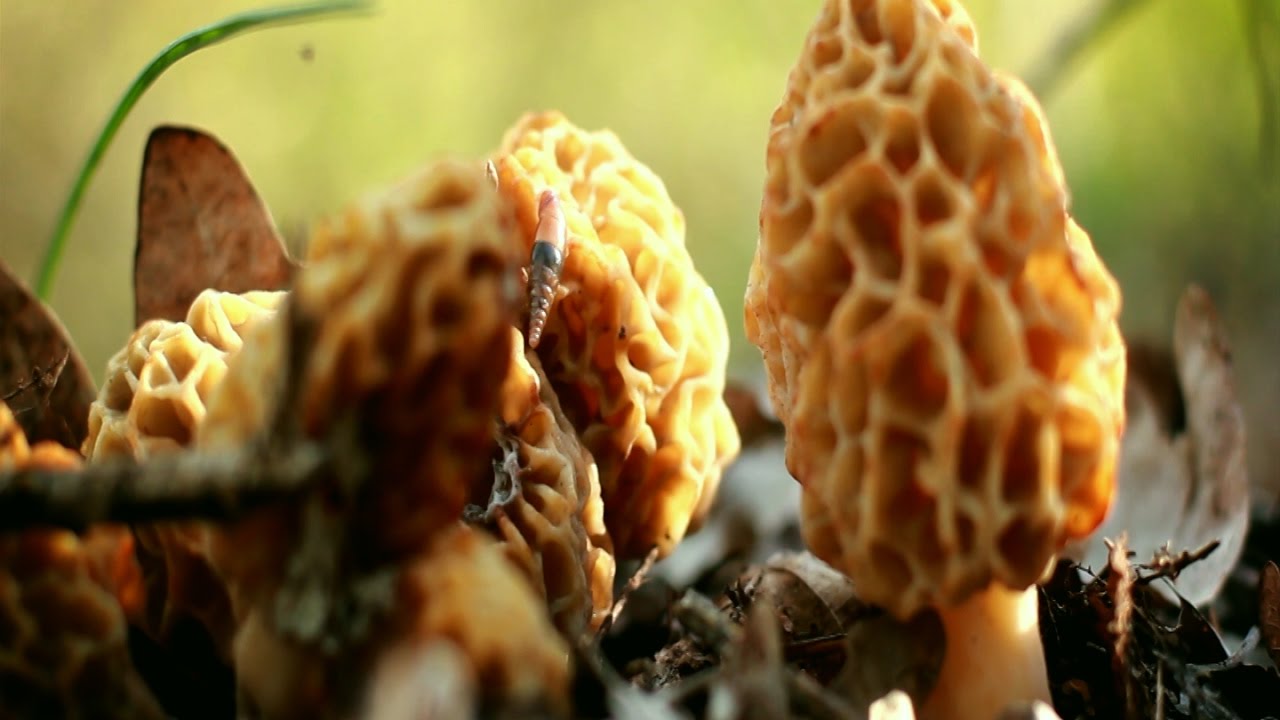
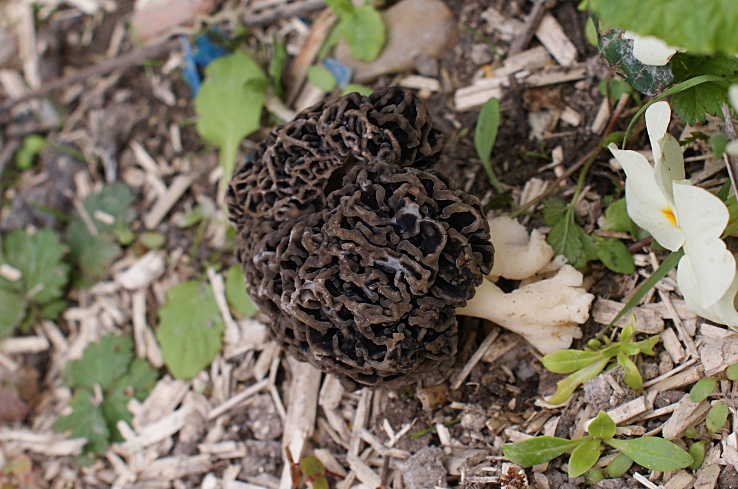
Botanical description
By their appearance, morels are very difficult to distinguish from each other. But the steppe can be identified by some distinctive features.
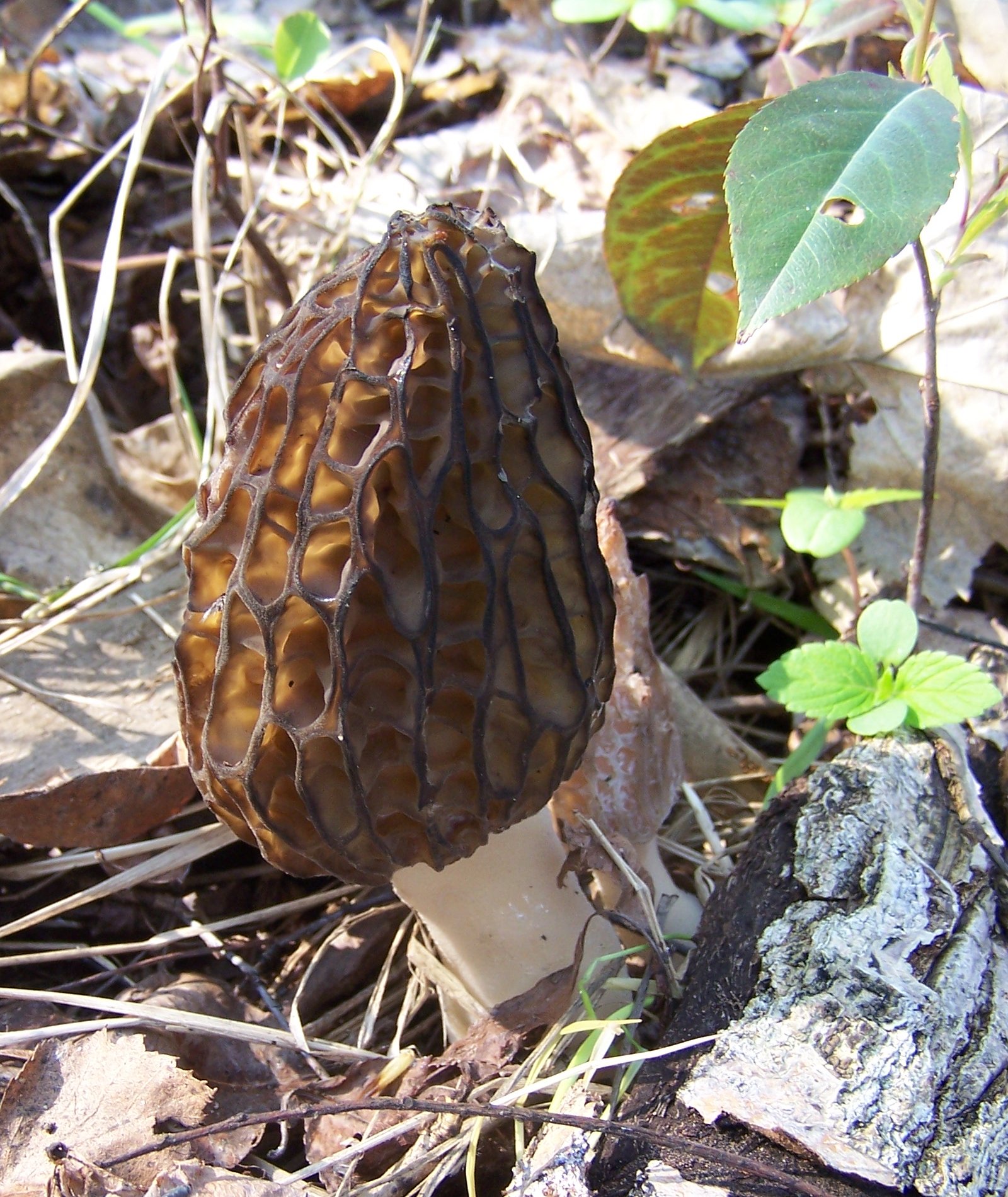
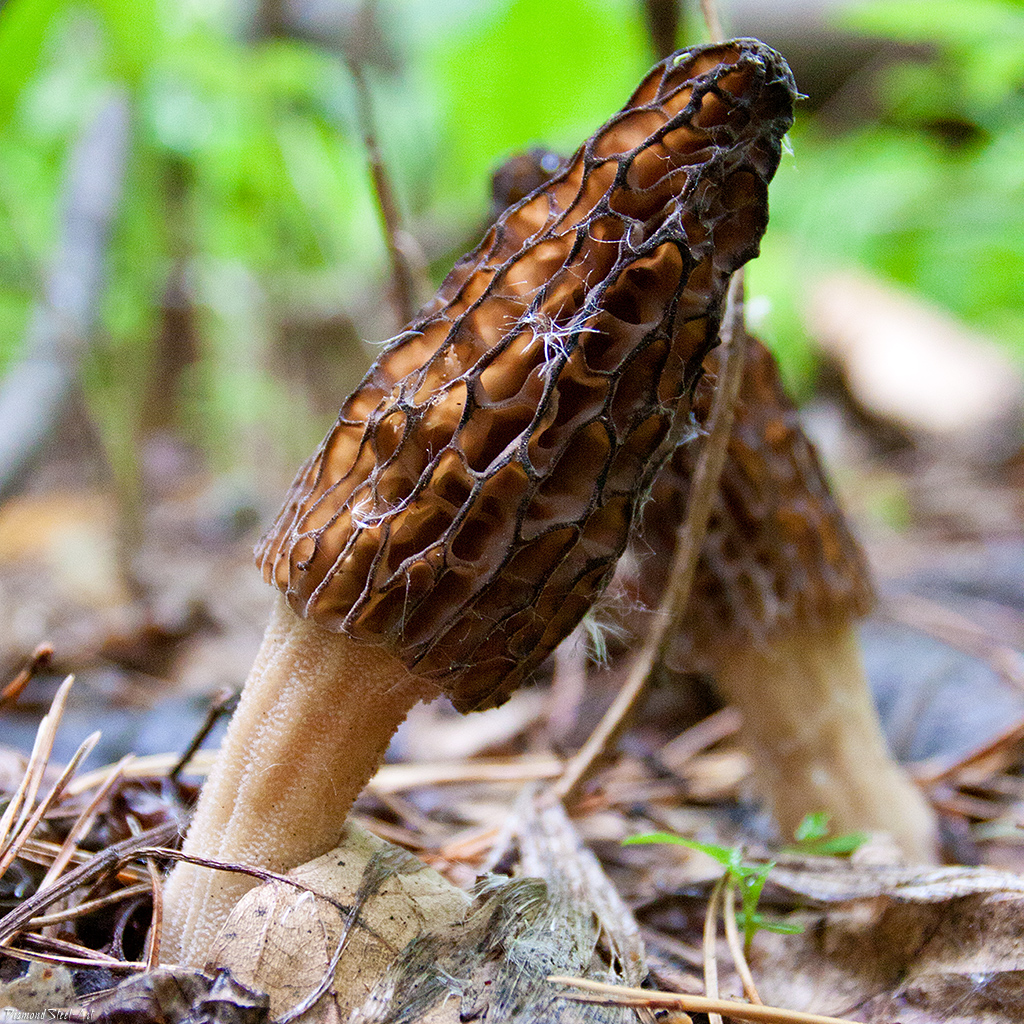
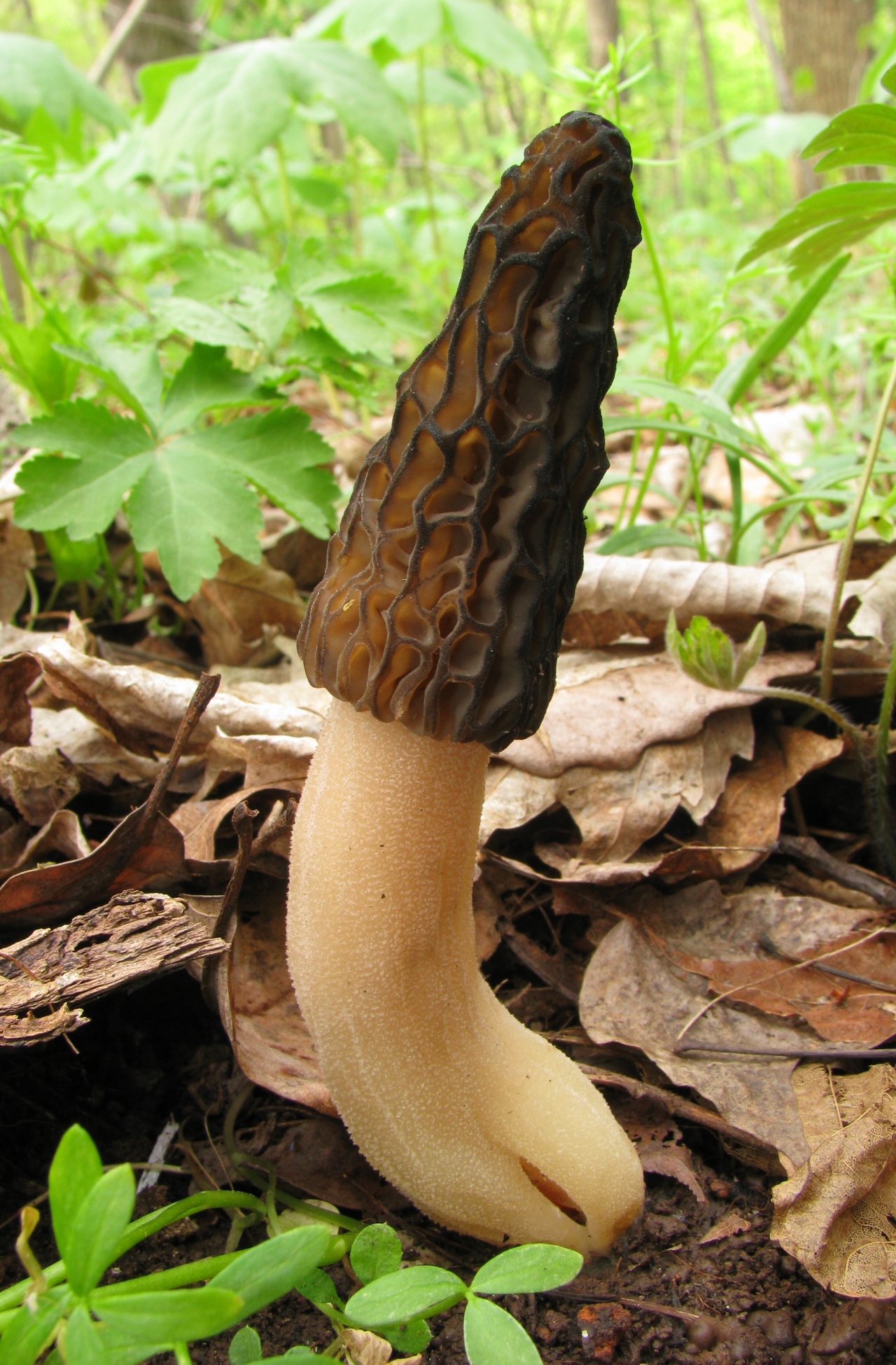
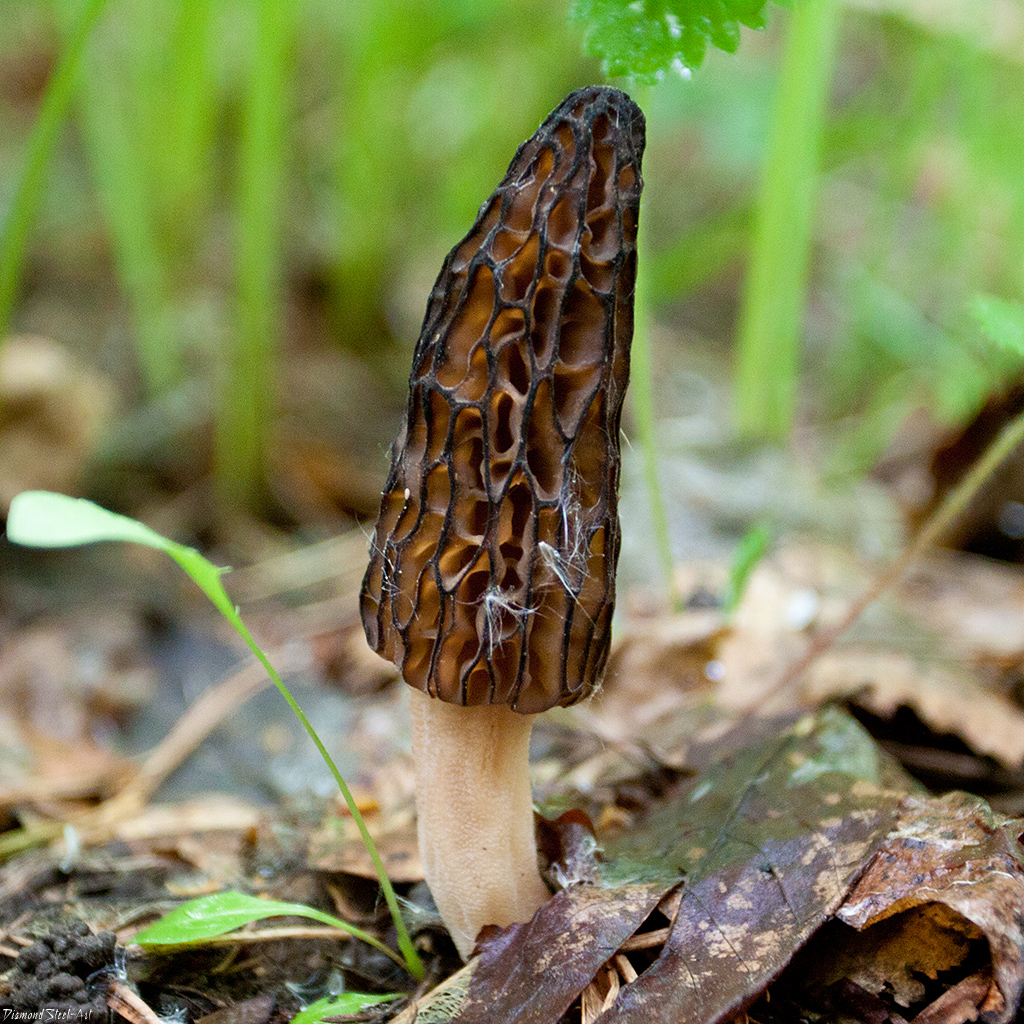
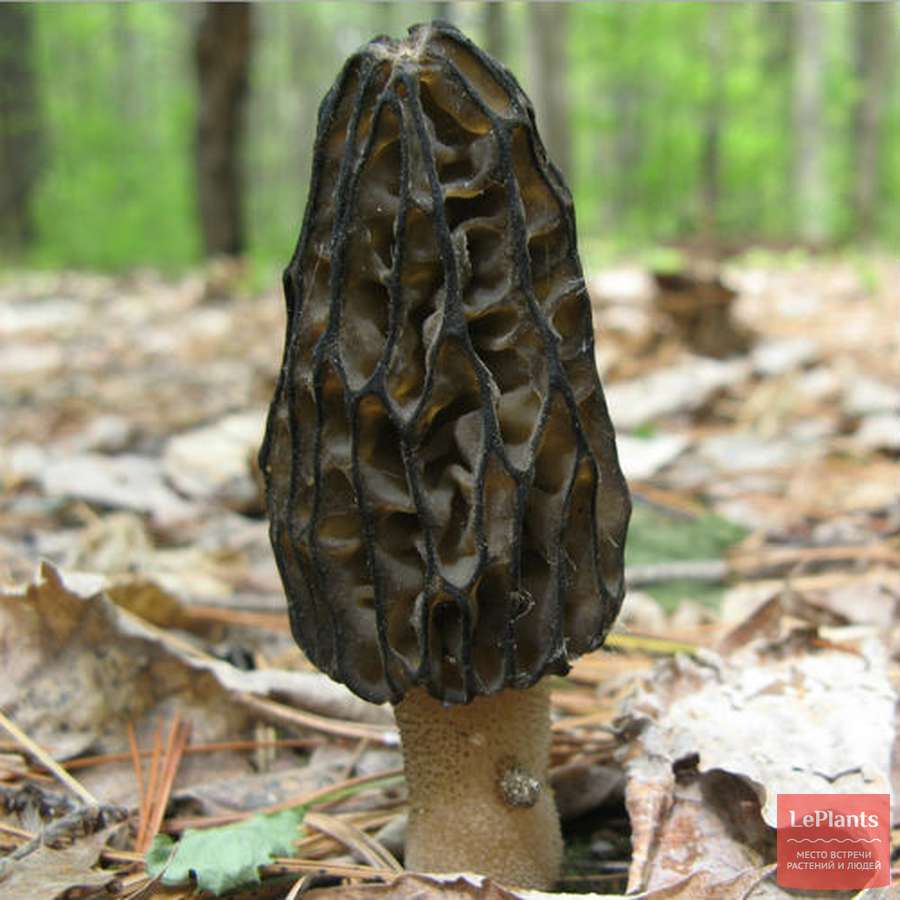
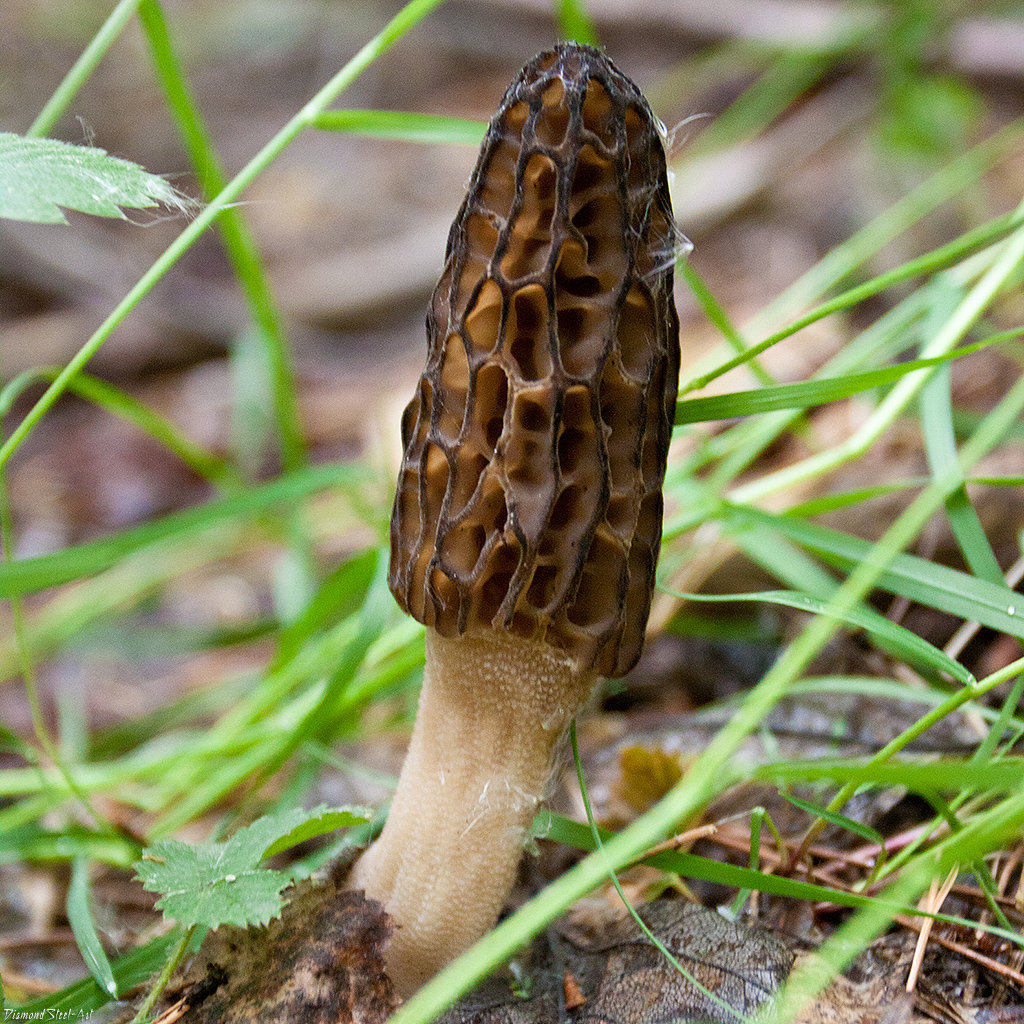
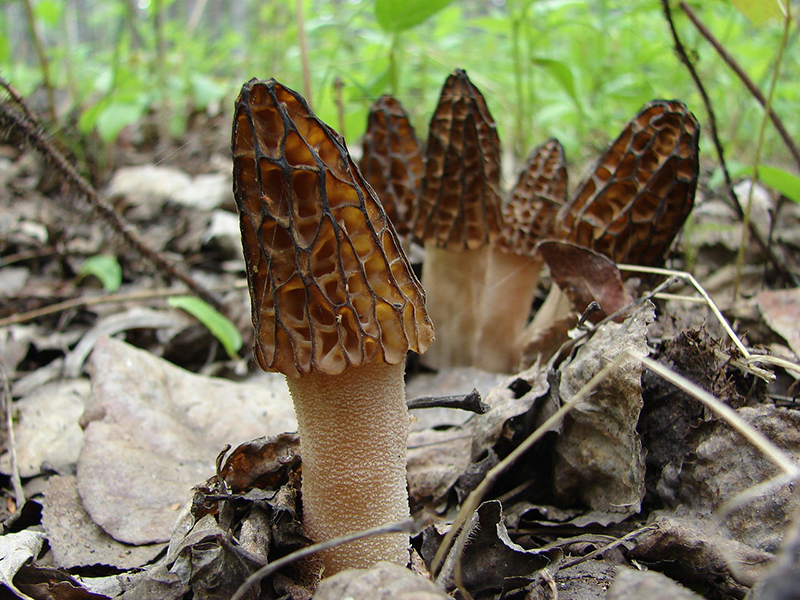
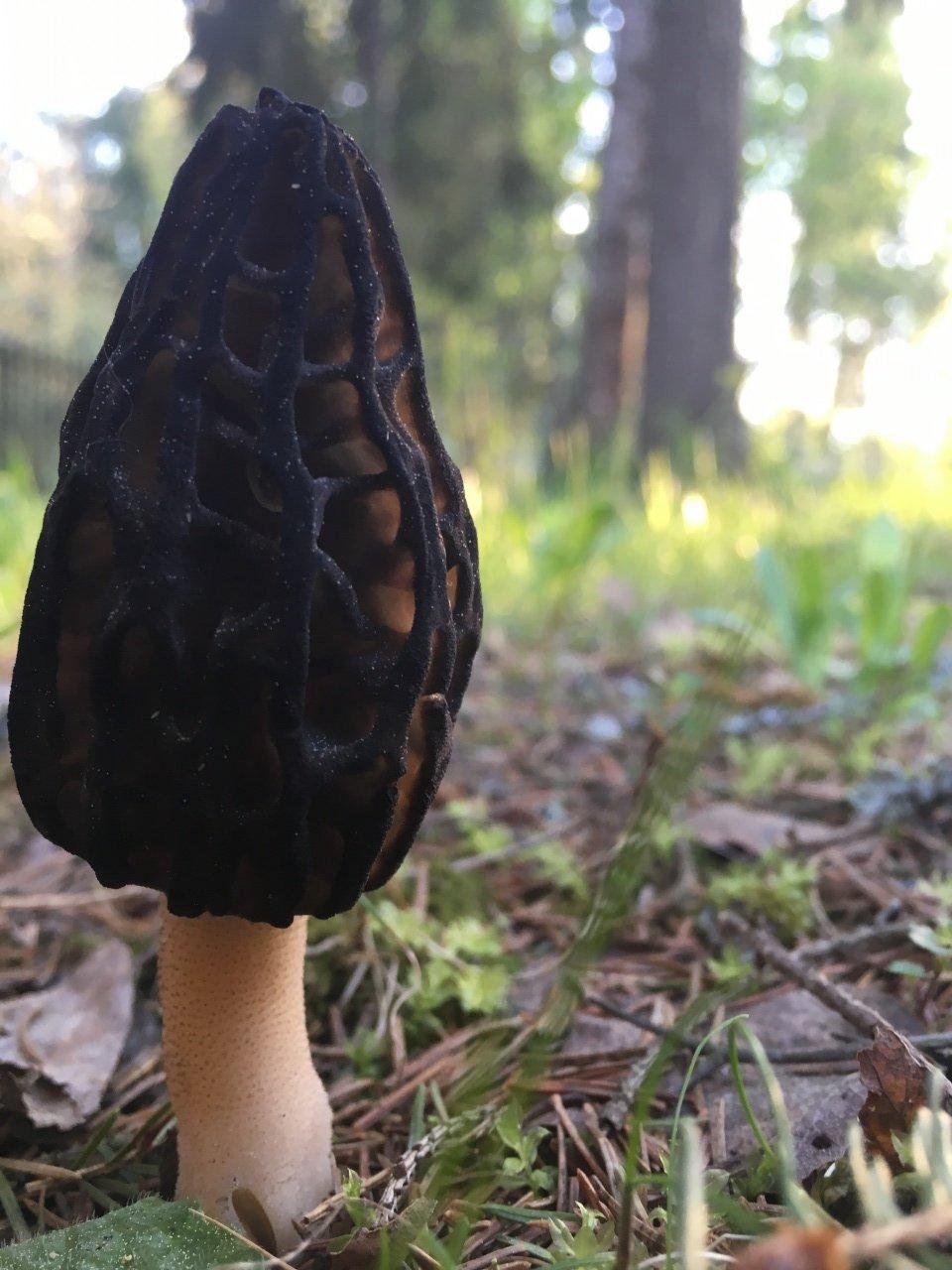
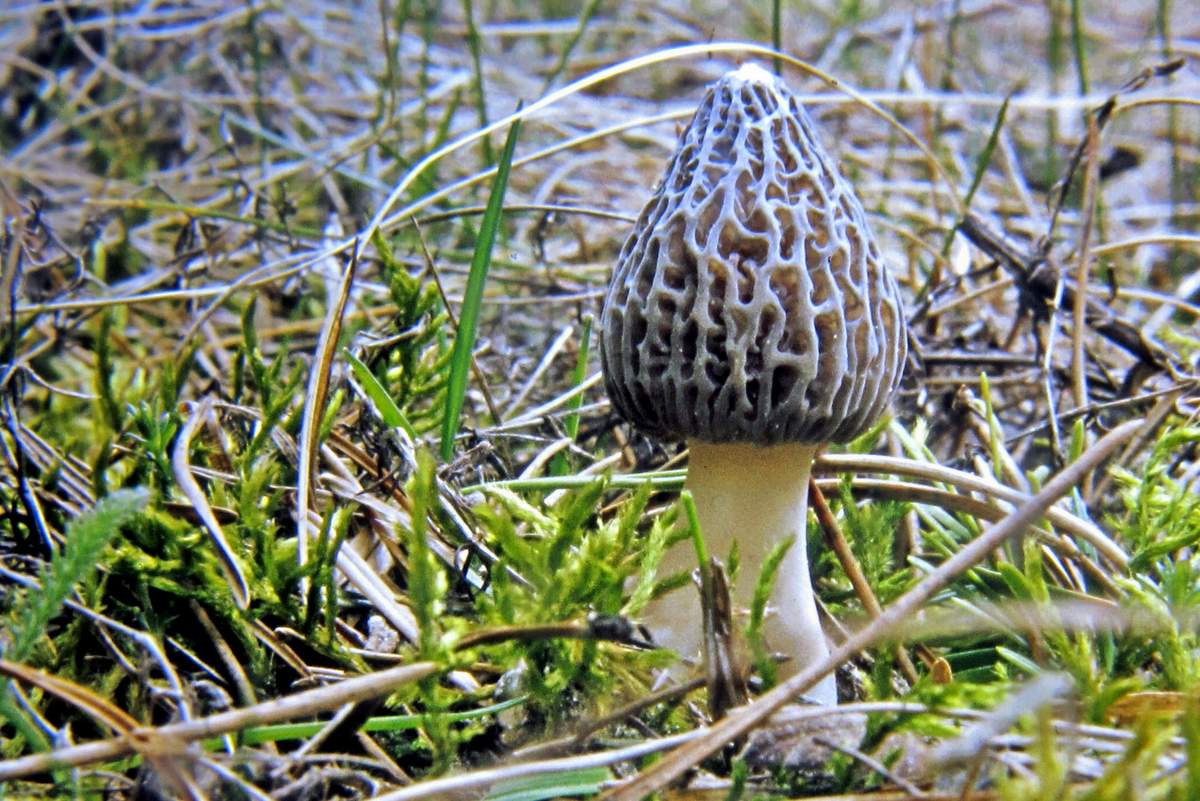
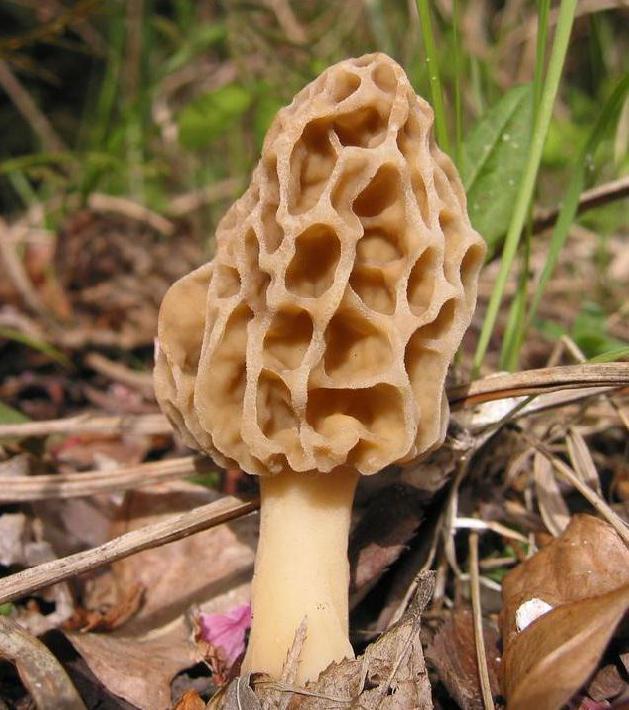
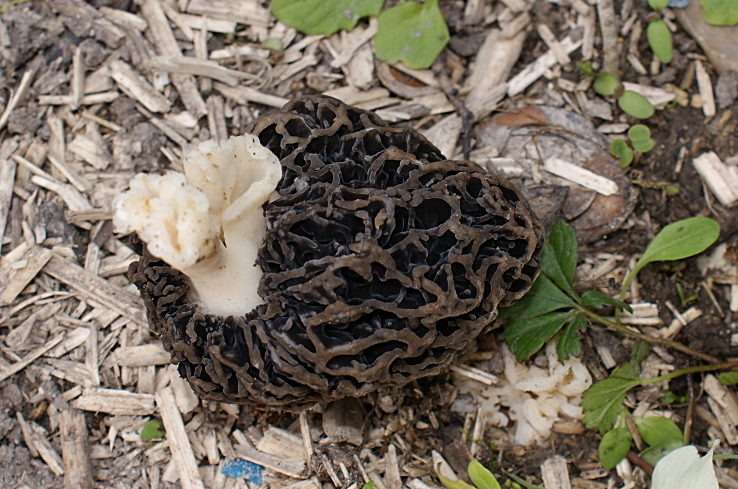
Morels of this species are much larger than their brothers. The fruit body reaches a height of 25 cm, and the weight can reach 2 kg.
The cap is spherical or ovoid, brain-shaped, with dense irregular grooves, yellowish-brown in color. The hat is 2-15 cm in diameter, the height corresponds to the diameter. The edge is adherent, inside it is hollow, it can be divided into sections.
The stem is short, cylindrical, wrinkled, about 1–2 cm long. The color is white with a cream shade. Young fruit bodies have a leg without voids, and with age, rare voids form in it. The pulp is elastic, white.
Spore powder of white, light brown or light gray color. Spores are ellipsoid, unicellular, arranged in one row. It has no pronounced smell, but it has a mushroom taste.
Edibility
Steppe morel is an edible and very tasty mushroom, considered a delicacy. It is used to prepare independent dishes, side dishes, sauces. Drying of these mushrooms is also popular. It is easy to do this, since this species is the most dense among its fellows. They have almost no internal cavities. The pulp is similar in density to the porcini mushroom.

Before drying, the caps must be thoroughly rinsed and blown out, as there is a lot of dirt in them due to the large number of convolutions. Fine sand is very difficult to shake out, so they are first squeezed in the sun, then blown again, then dried.
When the dried mushroom is soaked for 10 hours, it will completely restore its original appearance, volume, shape. This type of morels does not require pre-boiling. They go well with poultry, meat, fish. Milled mushrooms make an excellent seasoning for sauces, broths, meat and vegetable dishes.
Where and when to look for morels
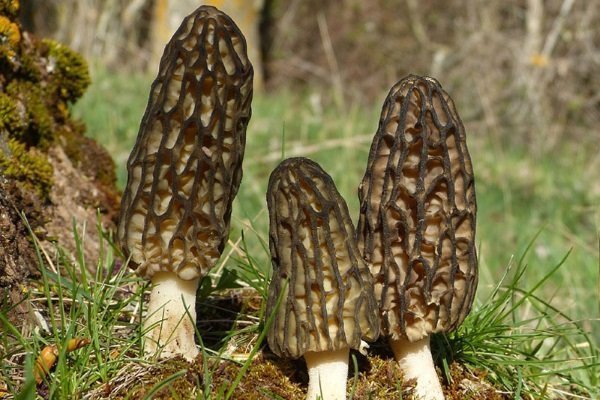
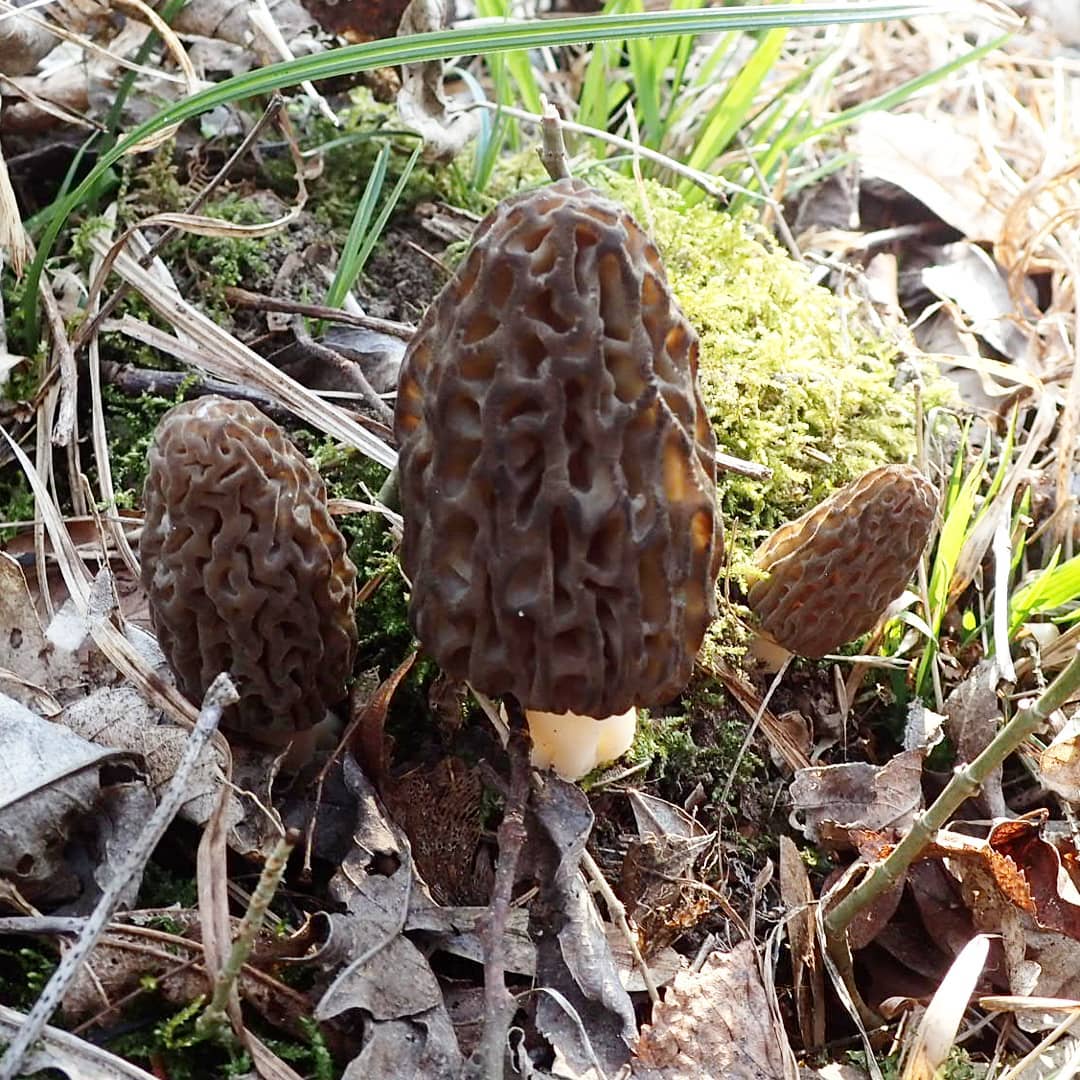
Morel mushrooms are common in the forest zone of the Northern Hemisphere with a temperate climate. As a rule, morels grow on calcareous soils, which distinguishes them from many other fungi, they need sunlight and moderate moisture. Morels usually hide in the grass, fallen leaves, or behind fallen tree trunks. Most often they grow under deciduous trees, can be found in orchards and parks, grow along streams and rivers. It is rare, but still possible, to find morels in coniferous or mixed forests. You can go in search of morels in early to mid-May, and usually the fruiting season ends in September. Provided a long and warm autumn, morels can be found until the end of October.
Reproduction of morels
Morels reproduce asexually or sexually.
- The asexual method includes reproduction by parts of the mycelium (the body of the fungus) or by conidia (motionless spores).
- Sexual reproduction is carried out with the help of ascospores (cells with half a set of chromosomes), which mature in bags (asci). Mushroom sacs are formed in fruiting bodies (apothecia), the formation of which is preceded by a sexual process called somatogamy. At the same time, vegetative hyphae of different individuals merge.
Morels are not lamellar or tubular mushrooms. Their hymenophore is smooth. The spore-bearing layer (hymen) is located along the bottom and slopes of the ribs and consists of asci with 8 ascospores. Asci are large, cylindrical, rounded at the top. Ascospores are ellipsoidal or spherical, with an uneven surface or smooth, arranged in one row, multinucleated at maturity. Morel spores can be colorless or slightly yellowish. They can be seen under an electron microscope. The release of spores is regulated by solar radiation and occurs gradually.
The life cycle of morels begins with the germination of multinucleated ascospores.The sprout gives rise to the primary haploid multinucleated mycelium, which has existed for a very short time. Ascospores are able to germinate even after prolonged dormancy or storage, after 4-5 years. The hyphae of the primary mycelium of morel form anastomoses (connection of two hyphae of one mycelium) or merge with the hyphae of another primary mycelium. As a result of the fusion, a diploid multinucleated organism emerges. In the future, he is able to enter into symbiosis with higher plants, form conidial sporulation or sclerotia (dormancy stage). The main reason for the formation of sclerotia is the lack of nutrients in the soil. In the life cycle of morels, the asexual (vegetative) stage prevails.
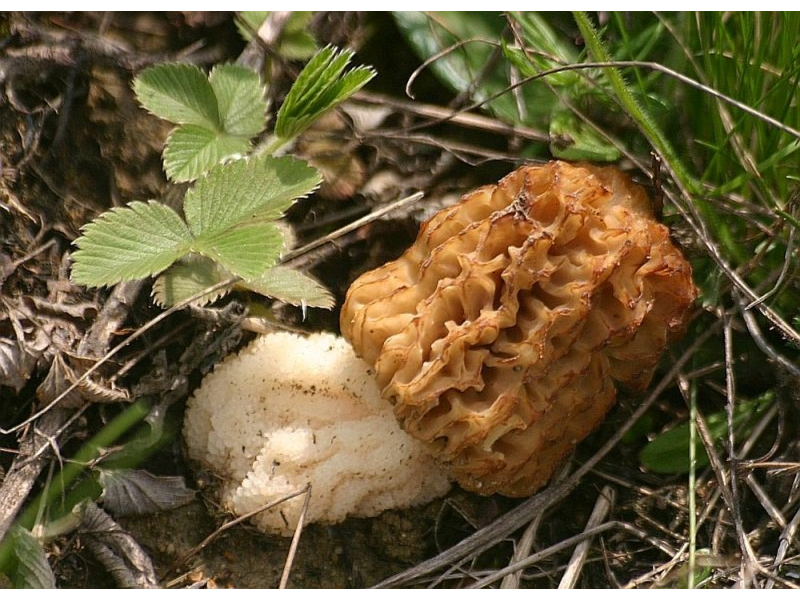
What is the difference between morels and lines?
Lines (Latin Gyromitra) are mushrooms that are often confused with morels. Both of them appear at approximately the same time. They are sold on the market under the general name "morels". But the lines are more poisonous, especially when raw, and in some countries they are even classified as inedible. Below are the differences between these mushrooms.
- The surface of the cap does not contain cells, it is sinuous-wavy (similar to the brain or a peeled walnut), asymmetrical and does not grow to the stem. In morels, this part of the mycelium has a more regular shape, it is covered with convex ribs of cells of different depths, and in almost all species it grows to the stem.
- The color of the cap line is yellow-brown, brown, less often brown or grayish, often with a reddish tint. In the morel, it is dirty grayish white or dark brown.
- You can also distinguish the morel from the stitching by the leg. The stitch leg is shorter (3-6 cm) and thicker (up to 5 cm in diameter). It is uneven and often swollen at the base. Sometimes it doesn't exist at all. The morel has a leg about the length of the cap. She is also more slender.
- The body of the line is not hollow inside: it is filled with septa and convolutions. On the cut, it is white with a purple tint. The cap and stem of the morel are usually empty inside, and the flesh of the mushroom is white, waxy and fragile.
Morel is the only edible morel

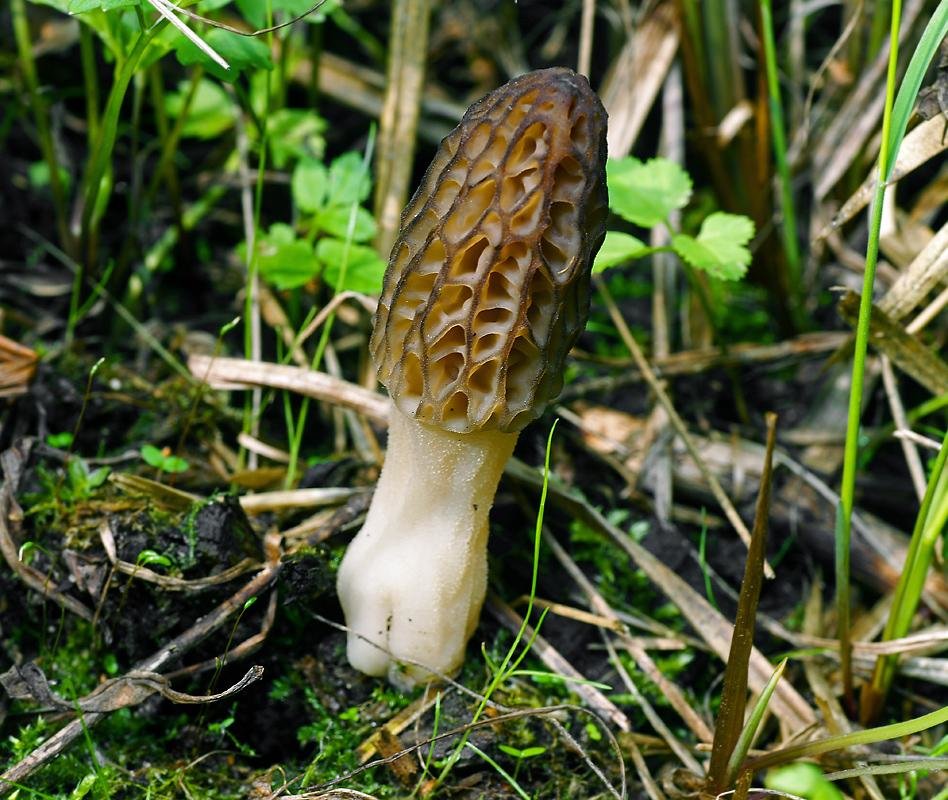
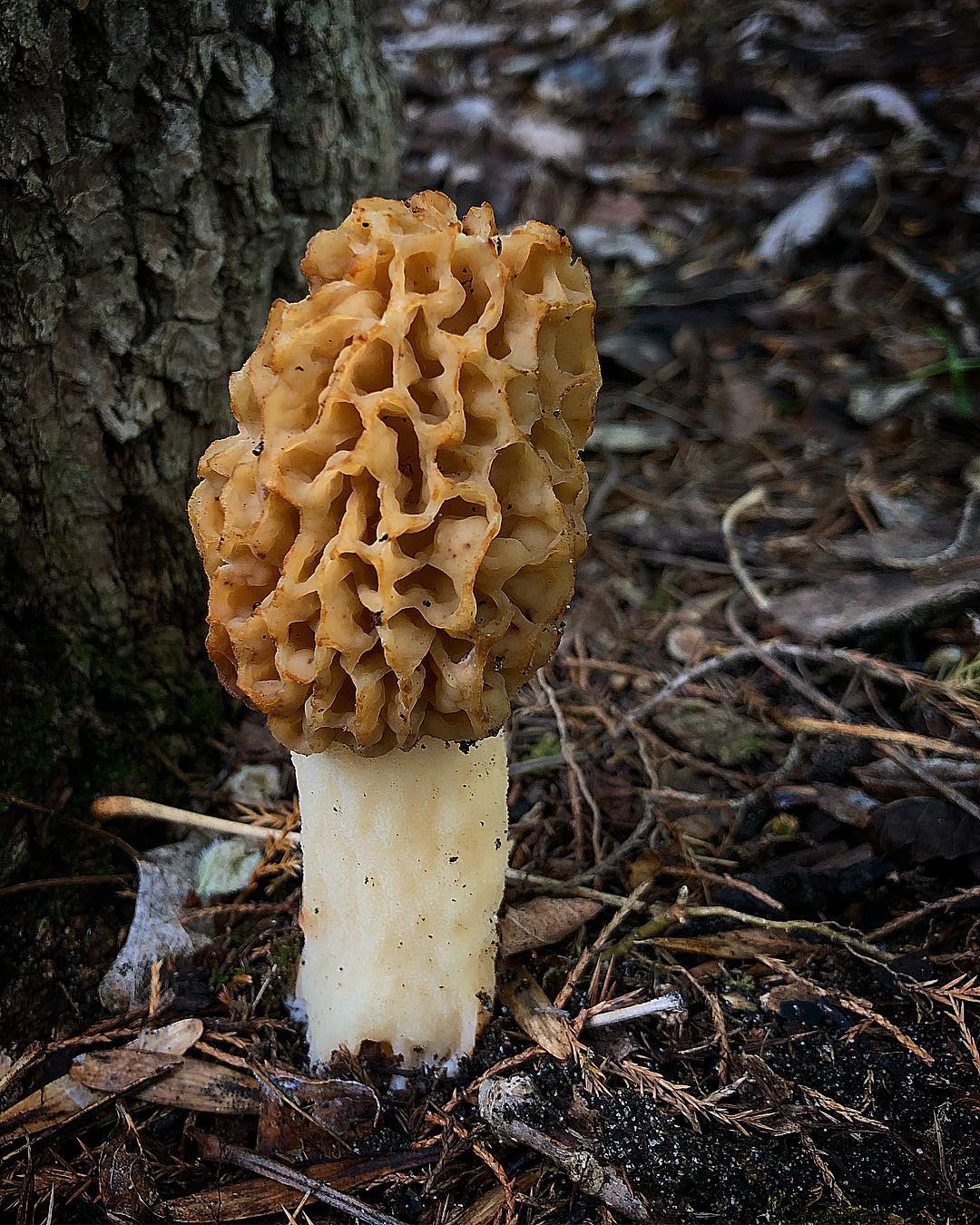
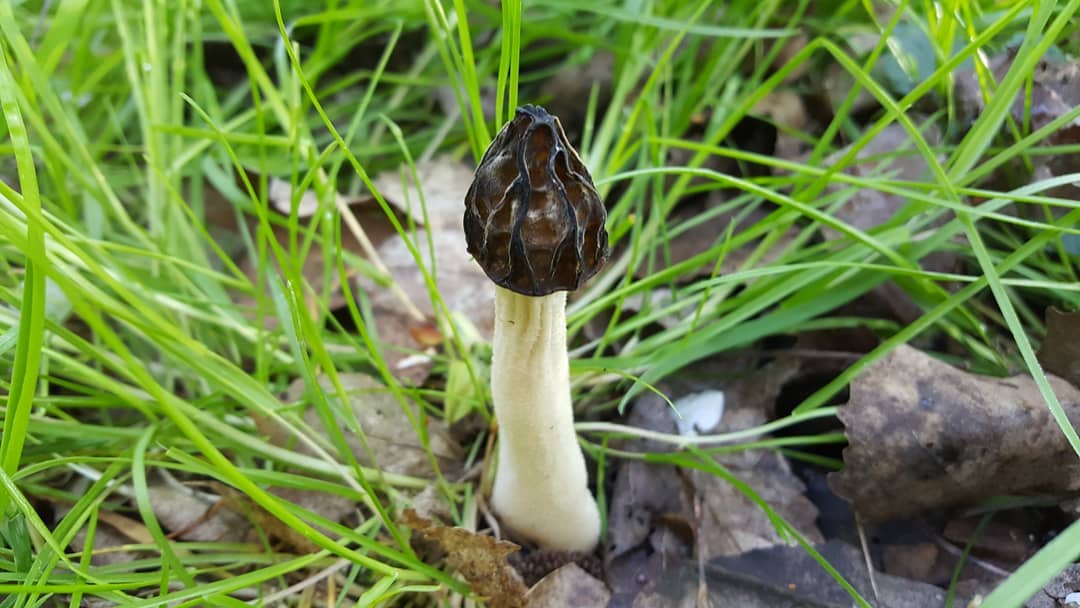
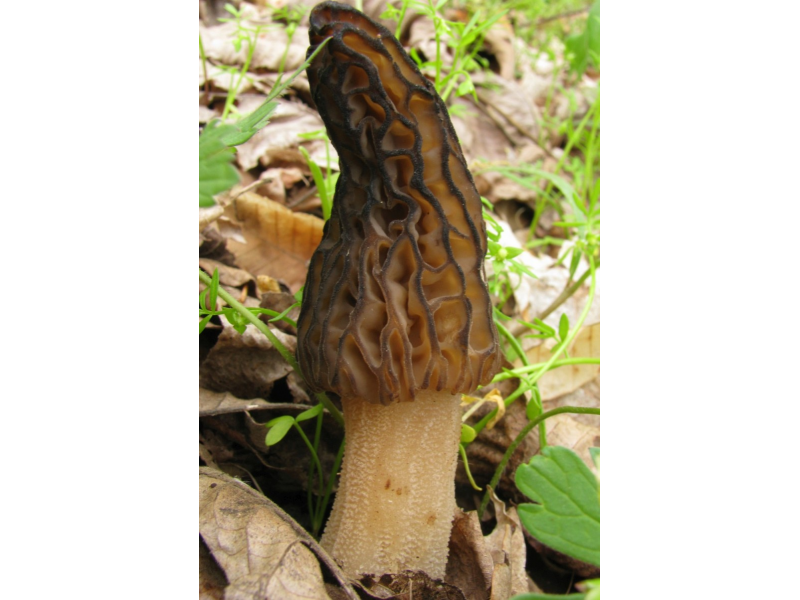
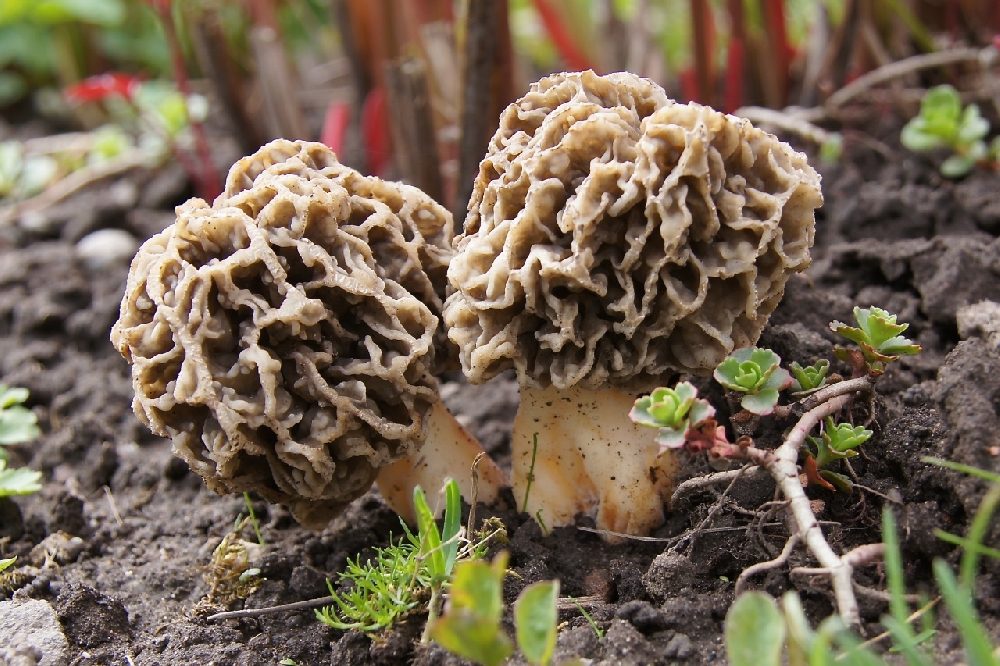
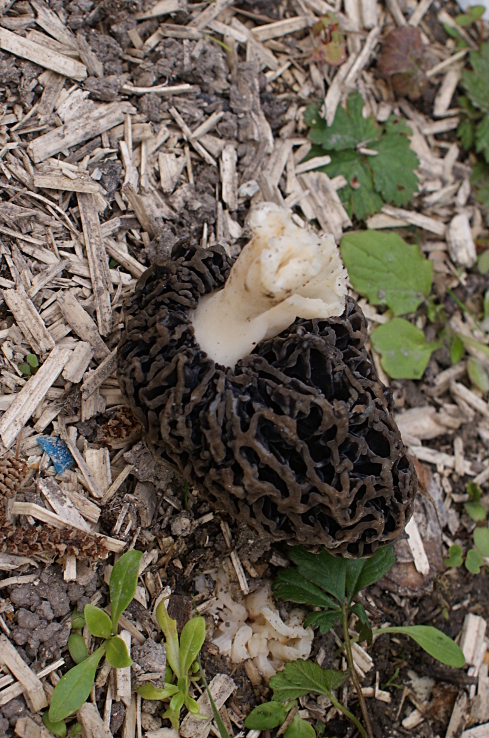
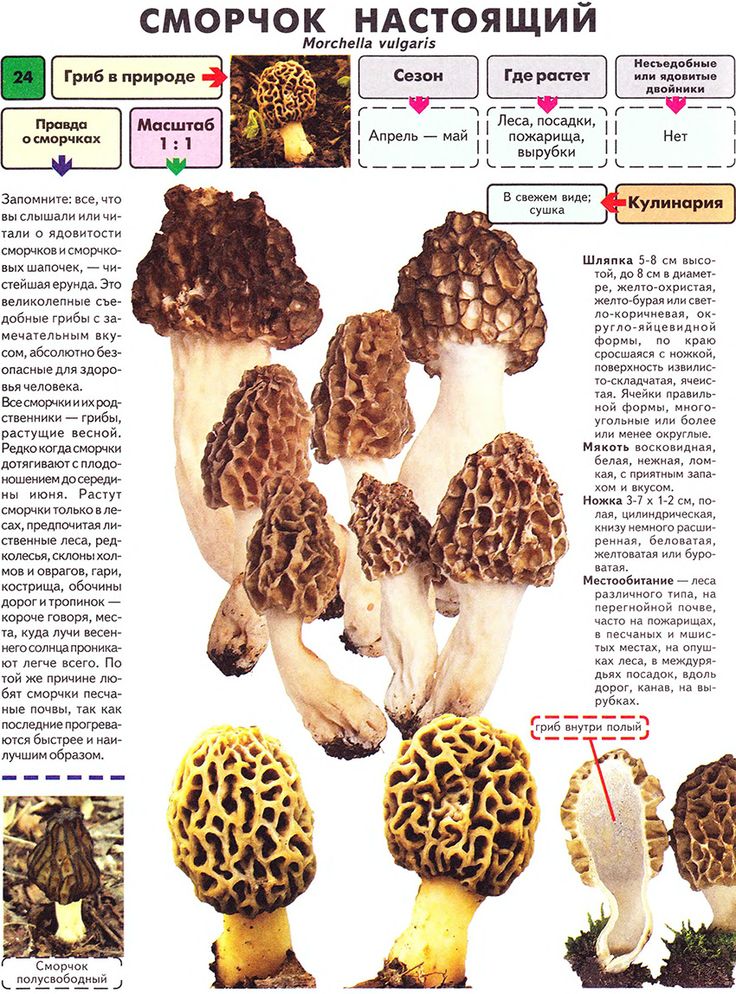
Morel is a conditionally edible mushroom of the Morel family. In another way, the common morel is called edible morel. From the morel family, this is the only representative that is suitable for human consumption.
In Latin, the name sounds - Morchella esculenta.
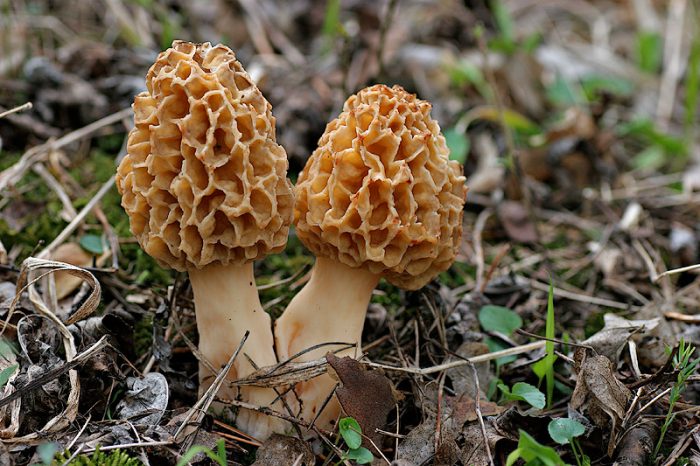
Description of morel edible
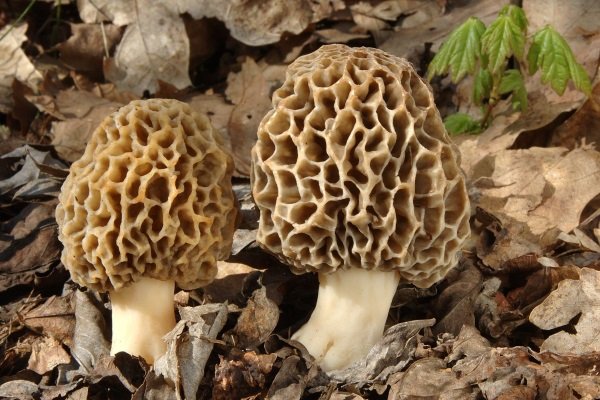
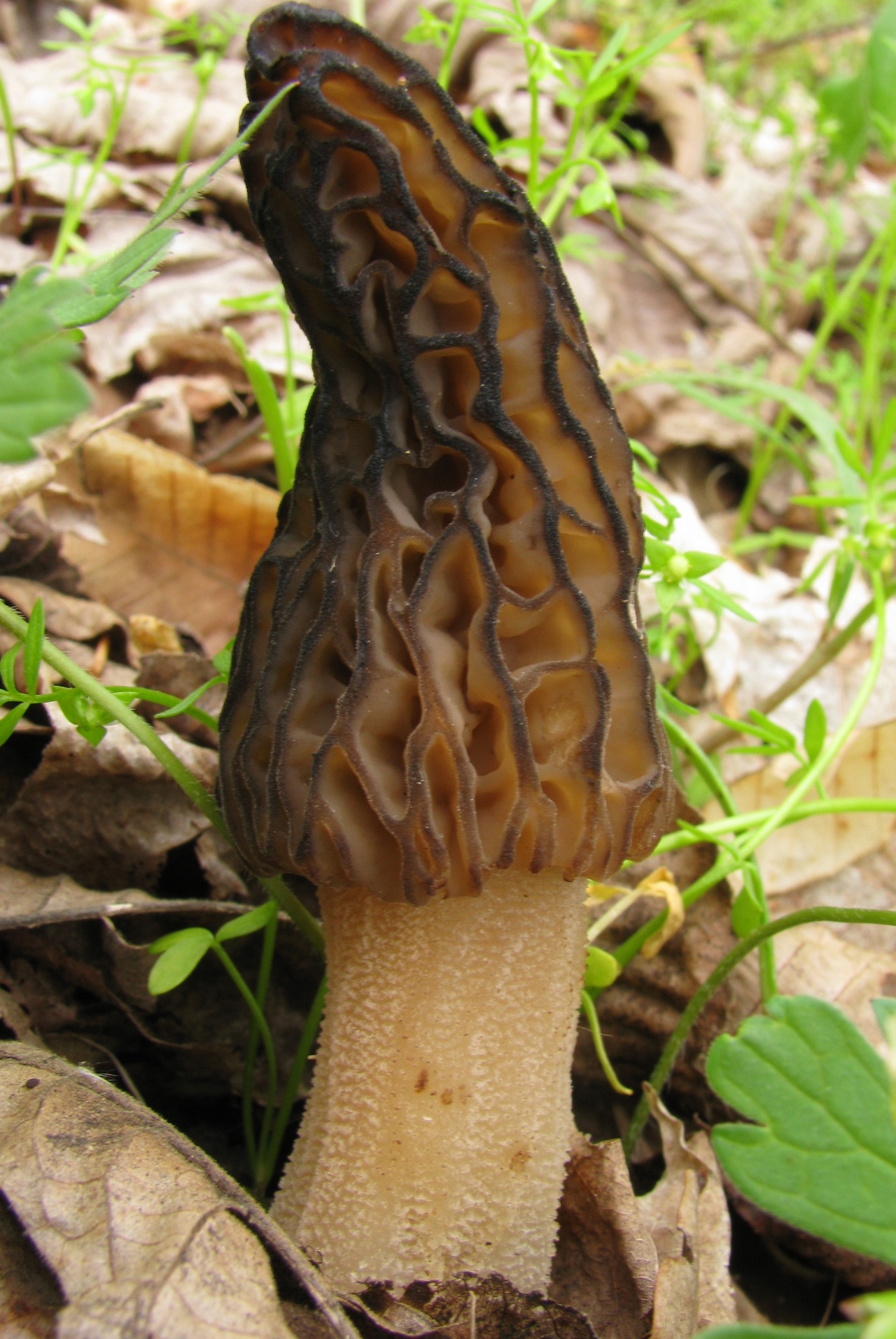
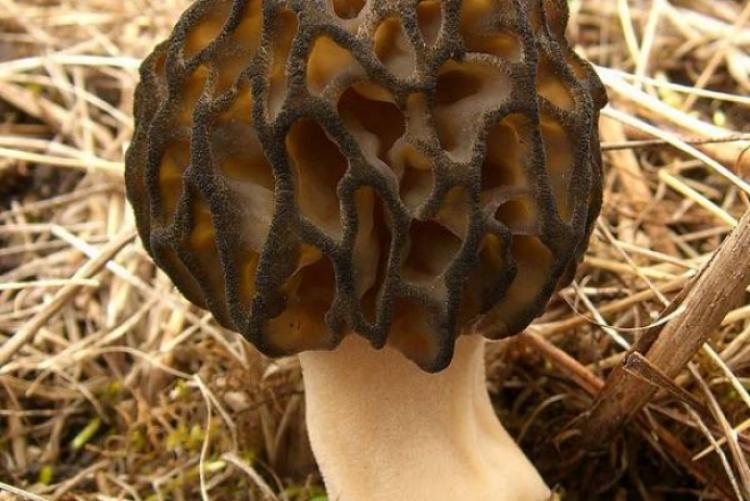
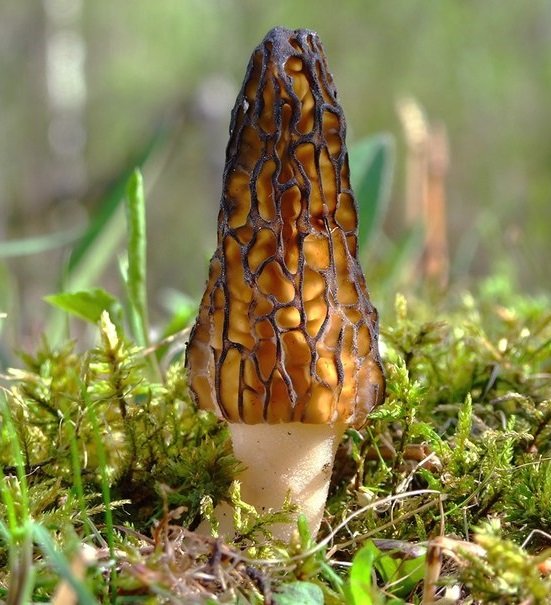
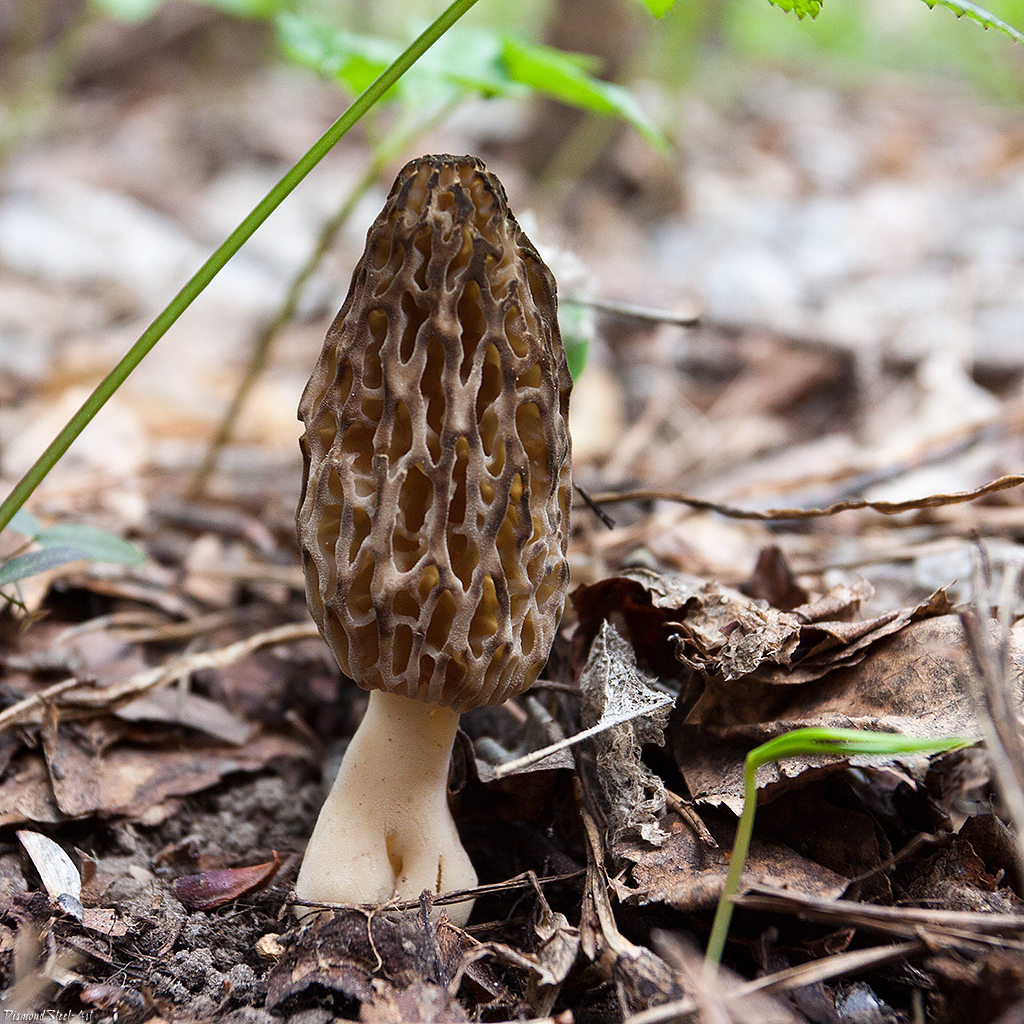
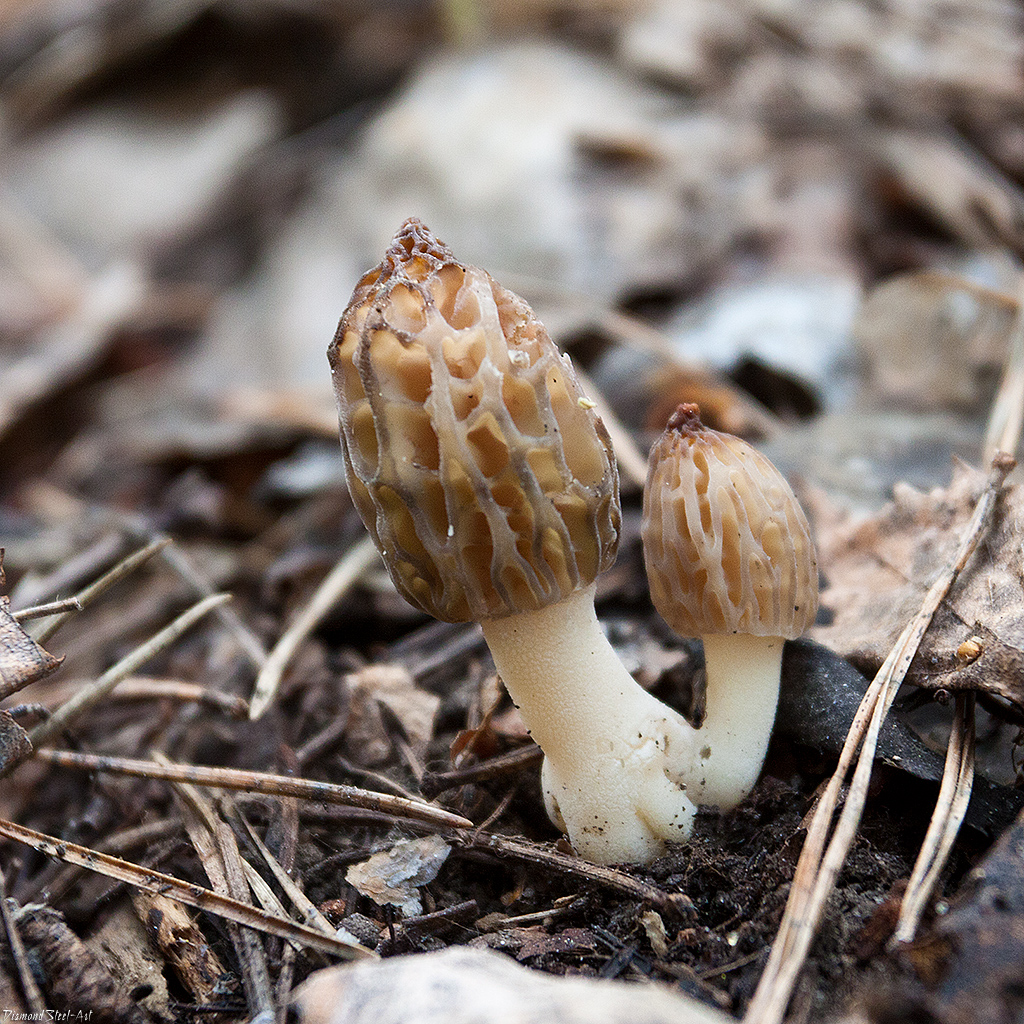
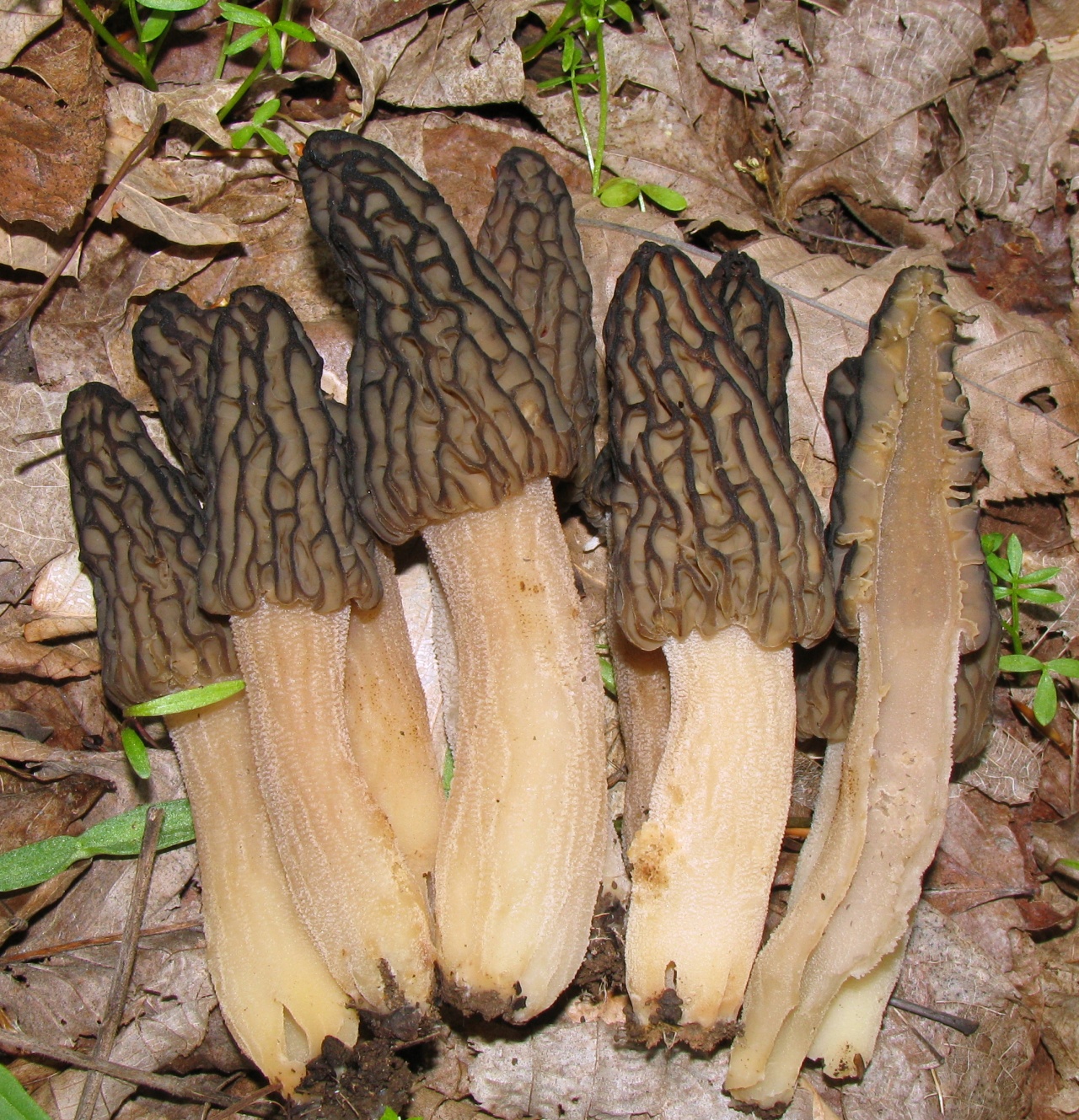
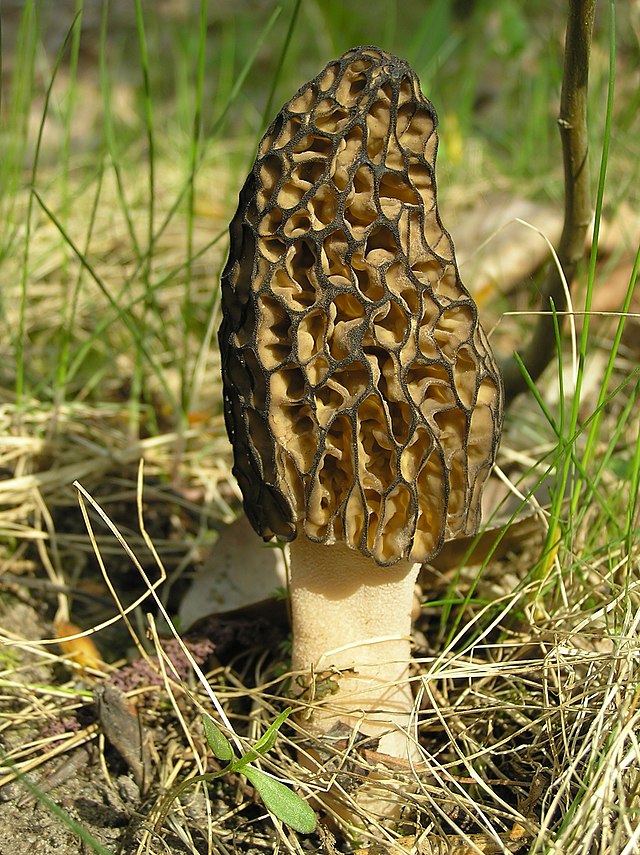
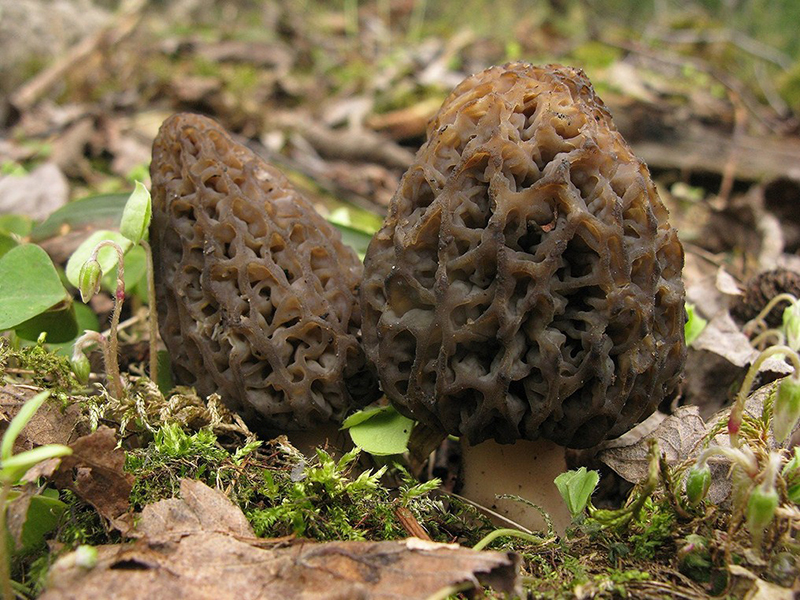
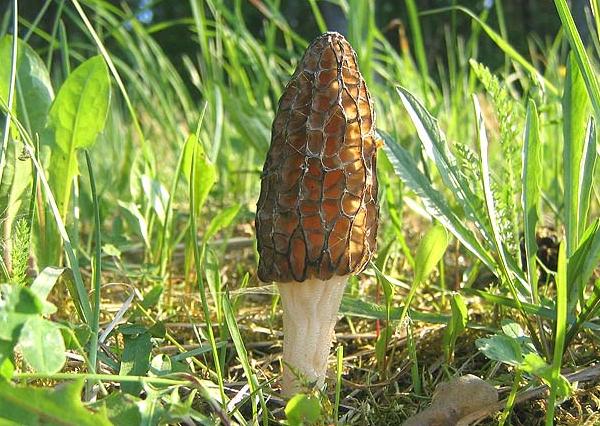
The inside of the mushroom is hollow, so its weight is small. The hat is round in shape, resembling an egg, sometimes morels are found with spherical or flattened caps.
The color of the cap varies greatly depending on various external factors, for example, the age of the mushrooms or where they grow. The longer the edible morels grow, the darker they become.
The cap of the common morel has a rather specific structure: the surface is uneven, wrinkled, with dimples. The pits can be of different sizes, they are lined with hymenium. The cells are irregular, slightly rounded. In addition to the cells, the mushroom has light ribs, which are rather narrow in shape.
The leg is shaped like a cylinder; there is a thickening at its base. The leg breaks easily. The pulp of the mushroom is very fragile, tender and easily crumbles. The color of the pulp is light, close to ocher. Over time, the leg becomes darker. The pulp does not have a pronounced mushroom smell, but it tastes good.
Areas of growth of common morels
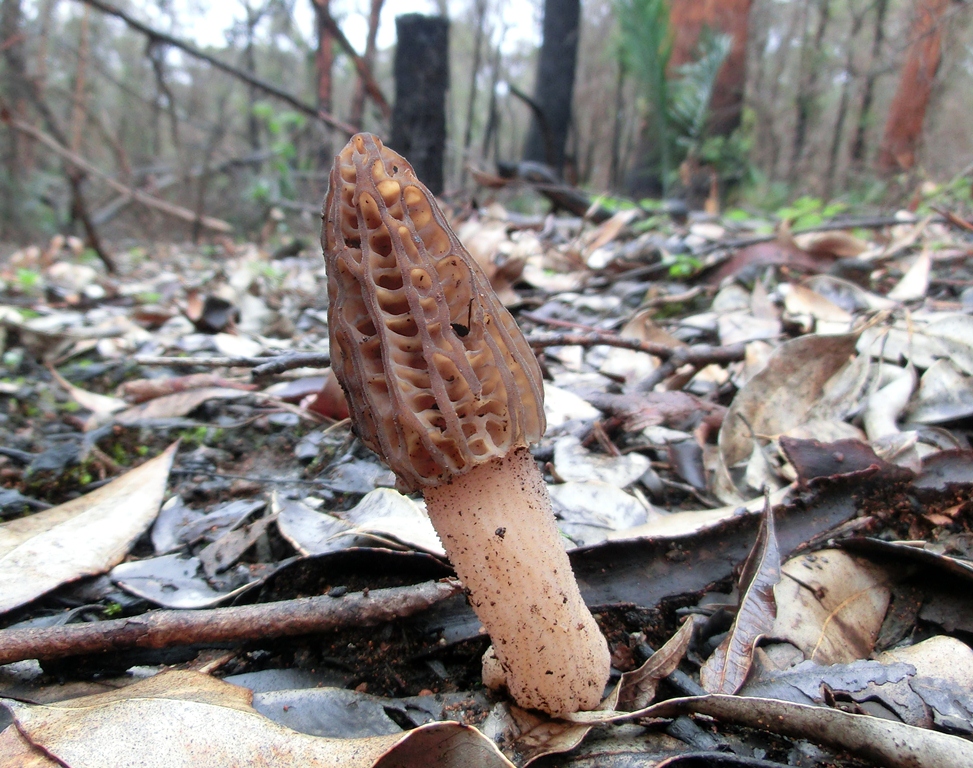
Edible morels prefer warm and bright places. These mushrooms grow on soils saturated with lime. Alder, birch, ash and oak forests are perfect for them, in addition, they grow in forests mixed with needles.
Among the fallen leaves, it is not easy to notice the common morel, since its masking color allows it to remain invisible. Most often, these mushrooms grow alone.
Where and when are edible morels harvested?
Common morels are quite rare mushrooms, although they are the most common among other morels. They are collected on lawns and forest edges with grass cover. In the south of Russia, they can be found directly in the garden or vegetable garden.
You can go in search of morels at the end of April, but the early morels are more watery and have a vague smell. In May, they become stronger and take on a real mushroom aroma with a light fruity note. In the middle lane, there are much less April morels than May morels. Some specimens can be found even at the beginning of June.
Also edible morels appear in parks and gardens of large cities. These mushrooms even grow in Australia. In the United States, they are expensive, there is even a Society of Morel Lovers, whose representatives call morels "kings of mushrooms."
How dangerous can morels be?
Morels, like stitches, contain a dangerous substance called gyromitrin. But there is much more of this substance in the lines than in morels or morels. Some researchers are confident that morels grow in many areas, which do not contain the toxin.
In any case, it is recommended to pre-scald, but it is better to boil morels, and then drain the water. In this case, the mushroom will delight you with its taste and will not cause any harm.
A dangerous resemblance, or how to distinguish an edible morel from a line?
Some mushroom pickers confuse morels with their poisonous cousins.
Indeed, related species are very similar, but they can be distinguished due to the shape, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the cap of the edible morel is round, in addition, its size is larger than that of poisonous species
In the morel, the length of the cap and the legs are almost the same, and in the stitching, the leg is often shortened, sometimes it is not visible at all.
In morels, both the cap and the leg are hollow inside, and the lines are filled with sinuous pulp. There are sinuous cells on the surface of the morel.
Edibility of common morels
In our country, these mushrooms are allowed for harvesting. These are conditionally edible mushrooms, they must be boiled beforehand. You can also dry morels.
We treat these mushrooms with caution, since from time to time there is information about cases of poisoning with morels.
But this is due to improper preparation of mushrooms or the fact that poisonous lines are often sold in the markets instead of morels.
Edible morels in any form are a great treat.
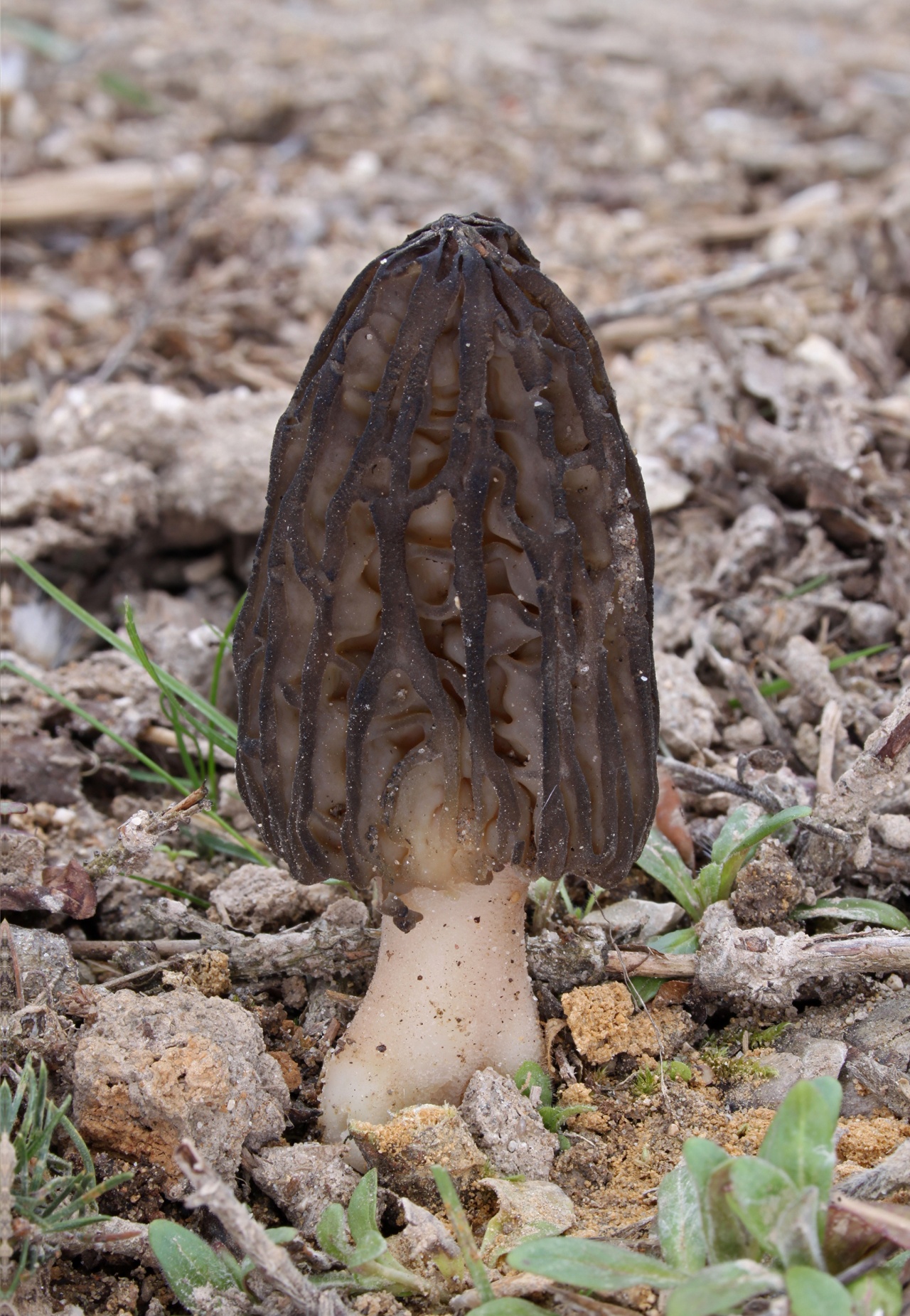
Giant stitching (Gyromitra gigas)
Synonyms:
Giant stitch (lat.Gyromitra gigas) is a species of marsupial mushroom of the genus Strochka (Gyromitra), which is often confused with edible morels (Morchella spp.). In its raw form, all the lines are deadly poisonous, although there is an opinion that the giant lines are less poisonous than other species of the Strochkov genus. It is widely believed that the lines can be eaten after cooking, however, gyromitrin is not completely destroyed even after prolonged boiling, therefore, in many countries, the lines are classified as definitely poisonous mushrooms. Known in the USA as snow morel, snow false morel, calf brain and bull nose.
Giant's hat stitch:
Shapeless, wavy-folded, adherent to the stem, in youth - chocolate brown, then, as the spores mature, gradually repainted in ocher color. The width of the cap is 7-12 cm, although absolutely gigantic specimens with a cap span of up to 30 cm are often found.
Foot stitching giant:
Short, 3-6 cm high, white, hollow, wide. It is often not visible behind the hat.
Spreading:
The giant line grows from mid-April to mid or late May in birch forests or forests with an admixture of birch. Prefers sandy soil, in good years and in good places occurs in large groups.
Similar species: The common line (Gyromitra esculenta) grows in pine forests, its size is smaller and its color is darker.
Edible: Incomprehensible. In all Western literature, the lines are notoriously poisonous: the defenseless bunnies running past fall dead, unable to withstand the poisonous fumes of the line. There is no unity among our authors. But all more or less agree that the giant line is relatively less poisonous than the ordinary one (Gyromitra esculenta). The end consumer decided everything for himself long ago: in the markets, giant and ordinary lines are sold under the guise of morels.
Video about a mushroom Giant lines:
Initially, there was little that connected me with the line and the morel. And as I saw, it became uninteresting. Some kind of fake mushroom. Illusory. And he has some kind of imaginary poisonousness. Gelvelic acid, which the Enlightenment publishing house scared several generations of our mushroom pickers, no longer exists. They are looking for some other poison, find and refute what they have found. Not serious somehow.
However, every mushroom is valuable in spring. This means that each new copy is capable of evoking at least some, but emotions. So, a long and lengthy search in early May 2002 led to the finding of three copies of the giant line. The points of location, equidistant from each other, were the vertices of a triangle with a side of about two kilometers. This is the question of accuracy. The following years have passed, one might say, in vain: it was only in the spring of 2005 that one neat specimen of Gyromitra gigas was found on a forest road, very close to the anthill.
Precautionary measures
When collecting morels, it is important to remember only the basic safety rules - to avoid polluted forests located close to industrial enterprises or highways. But there are no dangerous morel doubles in nature.
Even similar, but poisonous species belonging to the genus of morels do not have similar characteristics and radically differ in the shape and size of the caps.
But, dangerous twins of the morel do not exist in nature. Even similar, but poisonous species belonging to the genus of morels do not have similar characteristics and radically differ in the shape and size of the caps.
Toxicity
It was known more than 100 years ago which mushrooms are dangerous lines. Although at first such poisoning was attributed to the individual allergic reaction of people or it was mistakenly believed that the poisoning was caused by other products. Cases of joint use of mushrooms by several people are described. At the same time, some suffered from severe intoxication, others felt absolutely normal. Many experienced mushroom pickers consider the line mushrooms edible, for many years they have been collected and eaten without any consequences.
The study of toxins contained in ordinary lines began in the middle of the last century. Recent biochemical studies have shown that these mushrooms are poisonous and deadly. It is curious that the degree of toxicity of the fungus depends on the growing zone, the warmer the climate, the higher the level of toxins. Poisoning is provoked by gyromitrin, its lethal dose is:
- children - 10-30 mg per 1 kg of body weight;
- adults - 20-50 mg.
This dose can be obtained from the use of 200 gram up to 1 kg fresh mushrooms (depending on the climatic zone). The individual body's resistance to the toxin can dramatically increase or, conversely, reduce the risk of using lines. Statistics of recent years show that in North America and Europe there are extremely rare cases of gyromitrin poisoning. They are more common in Eastern Europe and Scandinavia. Polish scientists have found that in relation to the total number of mushroom poisoning in the country, 23% of cases fall on the line. Fatal poisoning has dropped significantly in recent years, due to the correct handling of the mushrooms. The average European mortality rate is still high - up to 25%.

Poisoning symptoms are divided into gastrointestinal and neurological. Signs may appear on average after 6-12 hours. There are known cases of their manifestation after two hours. First signs:
- redness of the face;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- stomach pains.
When the situation worsens, tremors, lethargy, convulsions, ataxia, severe headaches and dizziness appear. Fever is not a characteristic symptom of poisoning with other types of mushrooms, it manifests itself exclusively as a symptom of intoxication with lines. In the vast majority of cases, such manifestations disappear after a couple of days or within a week. Particularly severe cases are accompanied by destruction of the liver and kidneys, neurological dysfunction may occur, up to coma. Serious damage to internal organs can lead to death 5-7 days after the first signs of poisoning appear.

Morel traditional medicine recipes
Research results have shown that polysaccharides from morel fruit bodies have many healing properties, including antitumor, immunoregulatory, and antiviral effects. Extracts from them have, among other things, antioxidant properties.
Morels are used in folk medicine to treat indigestion, excessive sweating, and shortness of breath. For this purpose, a decoction or tincture of mushrooms is used for a long time, the beneficial properties of which are obvious.
Morel juice
It is believed that morel juice is able to benefit the body, providing a healing and tonic effect. You can get it by preparing a concentrated mushroom broth. This is done simply. The proportion is calculated as follows: for each glass of water there should be a tablespoon of chopped mushrooms. The mixture is boiled for half an hour, after which it is left for several hours. The finished broth should be filtered and taken in small quantities (no more than 50 ml at a time).
Alcohol tincture on morels
The tincture is used externally for medicinal purposes. To prepare it, you will need the following:
- dried chopped mushrooms;
- absolute alcohol;
- purified water;
- glycerin of vegetable origin.
The dried chopped mushrooms are divided into two equal portions. Then cover half of the mushrooms with a mixture of 70% alcohol, 20% glycerin and 10% water. Insist 4-6 weeks.
Then a decoction is prepared by mixing the second half of the mushrooms with a volume of water twice as large as that used in the previous step. Boil it for at least one, preferably two or more hours, adding water as needed during cooking. After that, you need to continue boiling until the liquid begins to evaporate. It should remain exactly the same as the alcohol solution. After that, the broth is removed from the heat and completely cooled.
It is necessary to mix the liquids from the decoction and the tincture, while the final product should contain about 25% alcohol. A useful traditional medicine is ready!
Application and processing
Dried morels are used to make mushroom powder, which is a natural flavoring agent. It is added to various dishes. Dried mushrooms absorb moisture quickly, so they are stored in paper bags or cardboard boxes in a dry place, otherwise they will become moldy. They are not salted or pickled.
Morels processing:
- mushrooms are cleaned, washed thoroughly;
- soaked in water for 1 hour;
- boil in water - 30 minutes;
- washed with hot water;
- the mushroom is ready to use or eat.
Morels are the first spring mushrooms, which, despite their low nutritional value, are very tasty. They should not be used by people who have individual intolerance, children under 12 years old, pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with severe cardiovascular diseases.
What is the difference between morels and stitches? Difference photo
Distinctive features help to remember not only the names of mushrooms, but also to preserve life after collection.Eating edible fruits and avoiding poisonous ones will allow you to collect a full basket of healthy forest harvest, containing a lot of usefulness necessary for the full functioning of internal organs.
There are many tables on the Internet that demonstrate the distinguishing features. In today's article, we will try to assess the difference without it, resorting not only to the features of each species, but also to a photo example.

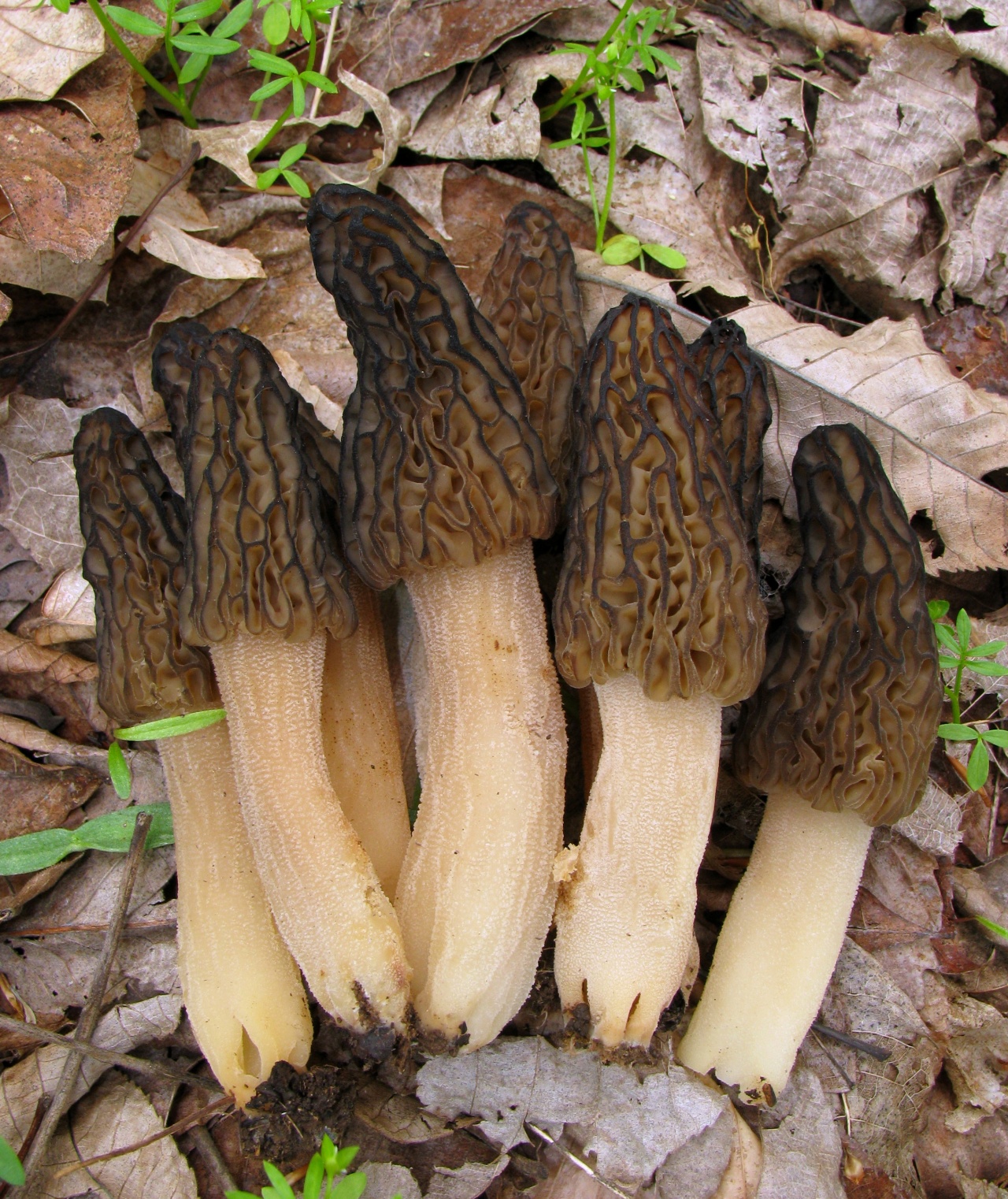
Many novice hunters, having seen the hat of both families, stop wondering what it looks like. In morels, it is more elongated, resembling the shape of a cone. Has holes, visually comparable to a dried, wrinkled sponge. Stitching hats are more unusual, comparable to oriental hats, which have rounded, slightly stretched outlines. In comparison with the leg, the cap has a dominant size.
Considering the size of the cap, we can say that both mushrooms do not differ in giant diameter. However, the size of the morels' cap is several times inferior to the lines reaching 20 cm.
The fruit body of morels is hollow or, one might say, whole. The pulp is snow-white, less often milk, it is fragile. The lines have separate cavities and unevenly growing pulp. When pressed, the mushroom breaks easily.

Leg of morels is white, cream-colored cut, belonging to the fine-grained variety. The height does not exceed 11-12 cm. In circumference, it can reach 6-7 cm. It is fully visible on the surface. It grows exclusively on damp surfaces: needles, damp soil or moss. The lines are opposite, the leg is short. Often, the hat practically hides it. It grows normally on moist soil.
The pattern on the cap, despite the similarity, is different. The first ones are covered with deep cells that differ in size. The second ones resemble uneven strips connected together. If you look at the mushroom for the first time from afar, the lines will resemble the structure of the brain or the core of a pine nut.
The color range of the cap is variable. Morels, unlike stitches, can be painted in light shades of yellow and brown, or to resemble a shade of wet asphalt. The lines are brighter, usually in brown or brown colors.
Morels aroma is associated with edibility. Mushroom notes are felt both raw and cooked. The lines are more likely to repel from the use. The aroma of dampness, reminiscent of a swamp, can hardly be tasty and attractive.
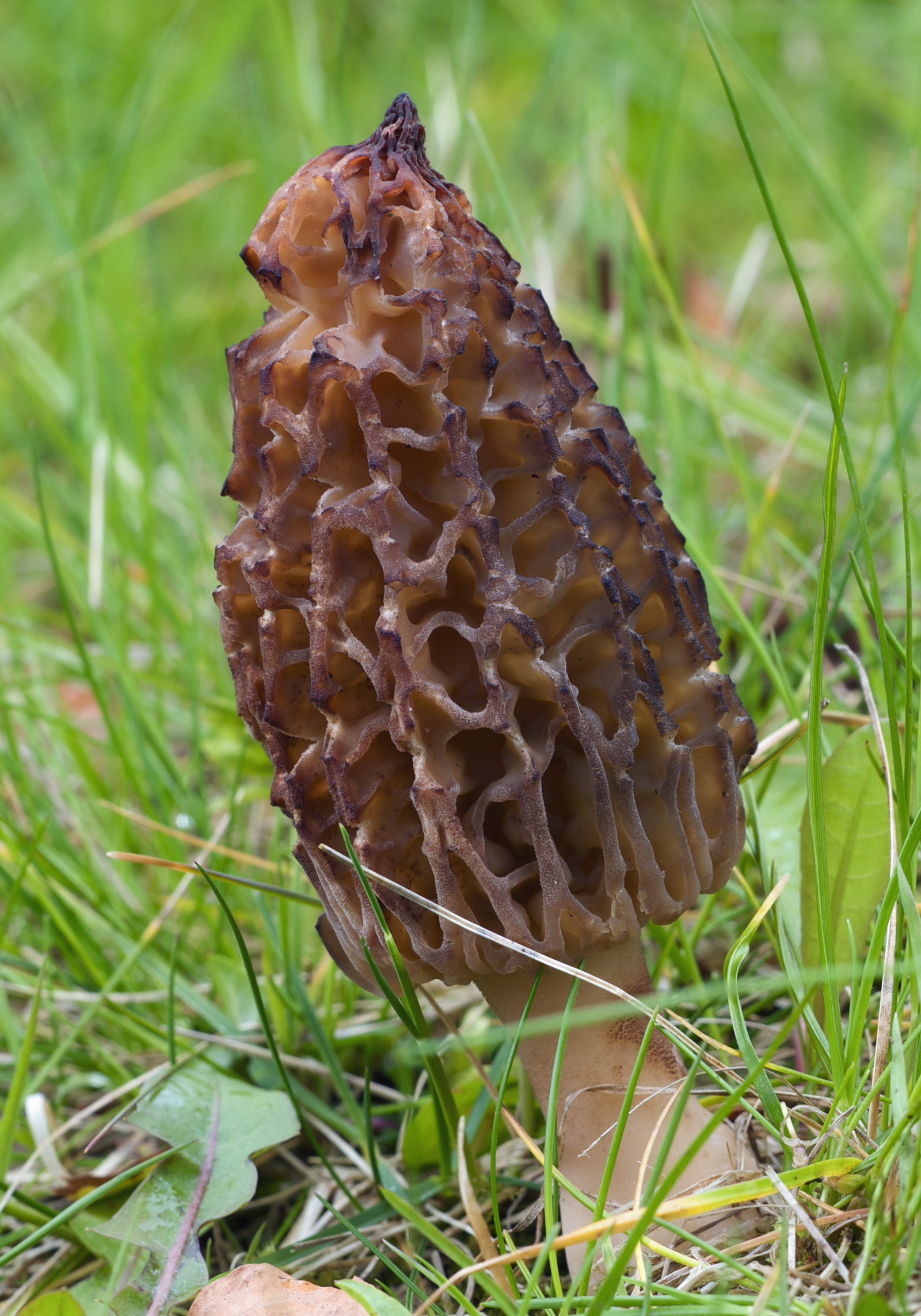
Description of steppe morel
Steppe morel is the largest among Russian morels. His hat is spherical or egg-shaped, its diameter is 2-10 centimeters, and sometimes it reaches 15 centimeters, while the height corresponds to the diameter. The edge of the cap is adherent, it is hollow inside, it can be divided into sections.
The leg to which the cap is attached is very dense and short - its length does not exceed 1-2 centimeters, sometimes the leg may be absent altogether. The color of the leg is white with a cream shade. There are rare voids inside the leg. The pulp is quite elastic, whitish in color. Spore powder is white or light gray.
Growing places of steppe morels
Steppe morels grow in the European part of our country and in Central Asia. These mushrooms settle in the wormwood steppes. They bear fruit from April to June. When collecting, it is recommended to cut the morels with a knife so that a whole mycelium remains. To find these mushrooms, you have to visit the harvesting sites every day at the beginning of March, otherwise you can skip the beginning of the harvest, and after 3-4 days the season will end altogether.
Fruit bodies in steppe morels develop very quickly, and their lifespan is only 5-7 days, in comparison with ordinary "long-playing" morels, this is extremely small.
In years with humid winters, steppe morels can form "witch circles", consisting of about 20 fruiting bodies, and the diameters of such circles reach 7-8 meters. In dry springs, mushrooms may not appear for several years in a row.
Edibility of steppe morels
Steppe morels are delicious edible mushrooms. They are mushroom delicacies, from which you can prepare independent dishes, as well as sauces and side dishes.
Drying steppe morels is not difficult at all, since they are the densest among other morels. These fungi have practically no internal cavities. The pulp of the steppe morels is similar in consistency to the pulp of the porcini mushroom. Before drying, these mushrooms must be blown out, since there are too many folds and convolutions in their caps, into which sand and dirt are clogged. The sand from the mushrooms simply cannot be shaken out, they are first dried a little in the sun, then they are blown out, and only then they are dried.
Also, these mushrooms can be dried in a special electric dryer, but in the sun they will have a more pronounced mushroom aroma.
If the dried morel is soaked for 8-10 hours, it will completely restore its structure, volume and shape. Steppe morels do not need preliminary boiling. They go well with meat, poultry and fish. Steppe morel powder makes an excellent seasoning for broths, sauces, vegetable and meat dishes. In addition, very tasty mushroom kebabs are obtained from steppe morels.
Other morels
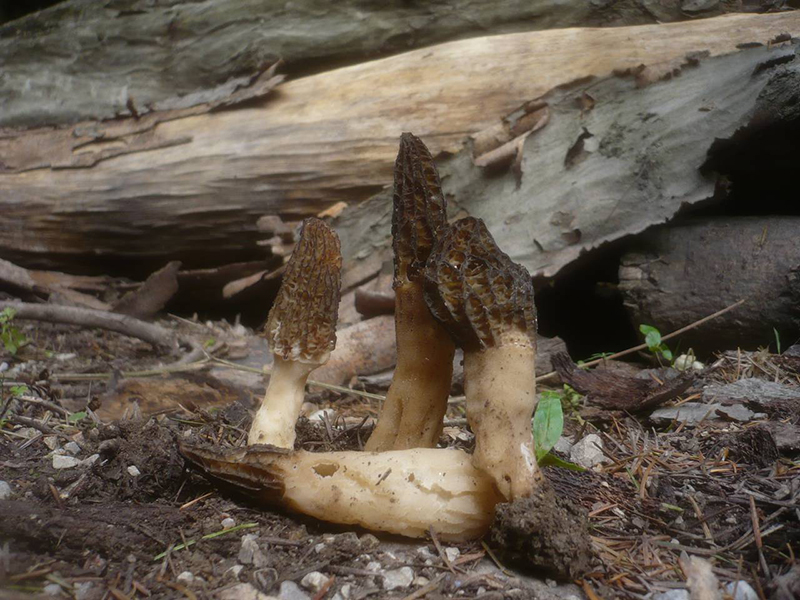
Morel conical - conditionally edible mushroom. His hat is elongated and conical. Its diameter does not exceed 3 centimeters, and its height reaches 10 centimeters. The color of the cap is reddish-brown with a gray or green tint, sometimes the cap may be black. Its surface is cellular, outwardly it looks like a honeycomb. The leg is straight, hollow, white or yellowish.
Conical morels grow on well-heated soils, in clearings and forest fires. Often these mushrooms settle in aspen forests. They bear fruit from April to May. The flesh of conical morels is tasty and soft, but it requires preliminary boiling for 15 minutes.
Morel cap, or cap, or tender morel is a conditionally edible mushroom. A small cap has the shape of a cap, its diameter is 2-4 centimeters, and its height is 2-5 centimeters. The color of the cap at a young age is chocolate brown, and in mature it becomes ocher yellow. The leg is smooth, most often curved, its length is 6-10 centimeters, and its thickness reaches 2.5 centimeters. The leg is often flattened on the sides. With age, an enlarged cavity forms in the leg. The cap and the leg are not firmly connected. The color of the leg is cream or white.
The morel cap is the smallest species in the morel family. These mushrooms bear fruit in mid-May. They often grow among young aspens and lindens. They give preference to poor soils. Under favorable conditions, morel caps are found in large numbers.
Morel hats are eaten only after preliminary boiling, then they can be fried, boiled and cooked in any way. It takes at least a month to dry a morel cap.
Medicinal properties and contraindications
The benefits of morels are due to the presence in their structure of rare polysaccharide substances (galactomannans, glucose, rhamnose, n-acetyl-glucosamines). These compounds improve metabolic processes in the visual apparatus, strengthen the eye muscle, and prevent "clouding" of the lens. In view of this, morel extract is used to combat cataracts, glaucoma, myopia and hyperopia. In addition, drugs based on them are shown to people whose work is associated with increased load on the visual apparatus.
Useful properties of morels:
- Strengthen the secretion of gastric juice, accelerate metabolism.
- They activate the production of insulin.
- Stabilize pressure.
- Improves metabolic processes in cells and tissues.
- Strengthen blood circulation, elimination of toxins and toxins, increase the production of red blood cells.
- Prevents the development of varicose veins.
- Increases the production of breast milk.
- They restore the work of the vestibular apparatus.
- They normalize the water-salt balance.
- Reduces the manifestation of toxicosis in pregnant women.
- Improves the functional state of the brain.
- Reduces inflammation in muscle and cartilage tissue (after sprains).
- Increase sputum discharge.
Contraindications to use:
- pancreatic diseases (pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis, cyst);
- acute pathologies of the digestive tract (ulcer, gastritis, duodenitis);
- kidney disease (hepatitis, renal failure);
- decreased blood clotting;
- children's age (up to 5 years);
- individual intolerance.






















































