Features of the effect on the human body, what are useful and harmful
Vegetable protein increases the production of gastric juice. Plant enzymes involved in the breakdown of coarse fiber, glycogen and fats help to digest any food.

Mushrooms are digested in the stomach for up to 8 hours.
The pulp of the plant contains riboflavin, which improves the condition of hair, nails and skin. Boletus contains ergothioneine, which is involved in the processes of cell renewal, and the antioxidant glucan.
Healthy adult men and women can eat boletus in any form. It must be remembered that these products are heavy foods and difficult to digest.
The thermally processed pulp contains chitin, which is not degraded by enzymes. But dried porcini mushroom is absorbed by 80%.
Pregnant and lactating women should eat porcini mushrooms with caution. During pregnancy, portions of porcini mushrooms should be small.
It is advisable for a nursing woman to refuse such food until the baby is one year old.
At what age can children eat porcini mushrooms? Children under 12-14 years old should not eat porcini mushrooms (due to imperfection of the digestive system). The child may develop flatulence, colic, constipation, or diarrhea.
In old age, mushroom products should be eaten with caution. Elderly people often suffer from diseases of the internal organs.
The use of mushrooms can provoke an exacerbation of diseases.
Allergies are associated with the use of porcini mushrooms. It is caused not only by the dishes themselves, but also by getting into the lungs of mushroom spores.
In this case, boletus dishes are removed from the menu and refrain from any contact with fresh porcini mushrooms.
Athletes can eat boletus (up to 500 grams per day) if they do not have the above diseases.
This herb is good for building muscle mass for bodybuilders. It is recommended to increase the interval between meals and exercise.
With diabetes (types 1 and 2), porcini mushrooms can be eaten (after consulting a doctor). This plant has a low glycemic index, mushroom dishes do not increase blood sugar.
POSSIBLE HARMFUL AND MAIN CONTRAINDICATIONS TO USE
You should not conclude that the milk mushroom is a panacea for all diseases and has no contraindications for use. The harm from the use of the infusion of this culture can be noted in the following cases:
- the presence of individual intolerance to any dairy and lactic acid food;
- period of exacerbation and unstable remission of intestinal disorders;
- increased gas formation;
- a history of bronchial asthma;
- simultaneous use with any alcoholic beverages;
- simultaneous use with medications;
- hyperacidity and diarrhea;
- some diseases of a fungal nature;
- insulin-dependent forms of diabetes mellitus and simultaneous use with insulin.
Despite the fact that, in general, the Tibetan milk mushroom is able to have a beneficial effect, its use should be preceded by a consultation with the attending physician, which will allow you to get all the necessary recommendations related to this remedy.

HOW TO CARE FOR MILK MUSHROOM
Anyone can properly grow a milk mushroom, but, like all living things, this culture should be provided with competent, constant care, which consists in observing the basic recommendations:
- the Tibetan mushroom must not be covered with a lid, as the culture must "breathe" for growth and development;
- you can not keep the milk mushroom in a place that is too lit, where direct sunlight is possible;
- temperature conditions below 15-17 ° C often cause mold damage to the fungus;
- the Tibetan mushroom should be stored and grown exclusively in three-liter glass jars, which are washed not with aggressive chemical detergents, but only with a solution based on baking soda;
- daily, the milk mushroom needs to be carefully but thoroughly washed and a portion of fresh milk is poured in, which contributes to the active, full-fledged reproduction and growth of the cultured milk culture;
- if it is impossible to rinse the mushroom for a couple of days, pour milk and water in a 1: 1 ratio into a three-liter jar, then put the jar with the mushroom in a warm place.
For the first couple of weeks, when drinking milk mushroom infusion, there is a sharp increase in the activity of the intestinal tract, which is expressed by increased gas production and increased stool frequency. This process is natural. Patients with urolithiasis may notice the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the area of internal organs. After a couple of weeks of daily use, such symptoms disappear, after which there is a marked improvement in the general condition and an increase in tone.

Composition, calorie content per 100 g (fresh, fried, boiled, pickled, dried), nutritional value and glycemic index
Borovik is the leader in nutritional value among mushrooms in the Northern Hemisphere.
One hundred grams of pulp contains:
- protein - 3.7 grams;
carbohydrates - 1.1 grams;
fat - 1.7 grams.

This amounts to 4.51, 0.86 and 2.62 percent, respectively, of the daily nutritional requirement for these substances. One hundred grams of products contains 16% of the daily value of plant fiber.
Mushroom pulp consists of 85-90% water (on average - 89.4%). This product contains vitamins A, C, D, E, K, PP, B vitamins.
The plant contains trace elements - calcium, sodium, chlorine, iron, sulfur, manganese, cobalt, fluorine, chromium, zinc, traces of selenium, silicon, copper and molybdenum.
The glycemic index of porcini mushrooms is 15 units.
One hundred grams of fresh boletus contains 34 kilocalories (according to other sources - 22), which is 2.39% of the consumption rate. The calorie content of boiled and stewed dishes is reduced, as fats and carbohydrates pass into the broth.
The energy value of 100 grams of pickled and salted products is 24 kcal, dried - 286.
The calorie content of fried foods increases due to the absorption of oil and fat and reaches 160-200 kcal per hundred grams of food.
Cooking Applications - Recipes
Porcini mushrooms are boiled, stewed, pickled, salted, fried, dried for the winter. In Italian cuisine, there are recipes for salads with fresh boletus, which are not processed in any way.
Mushroom pate
Boletus (1.5 kg) is cut into pieces, boiled until tender and put on a sieve. In a frying pan in vegetable oil, fry two large chopped onions and a large grated carrot.
The ingredients are fried together, then the mixture is scrolled in a meat grinder, ground black pepper, a clove of grated garlic are added. Mix the mass, put it in clean jars.
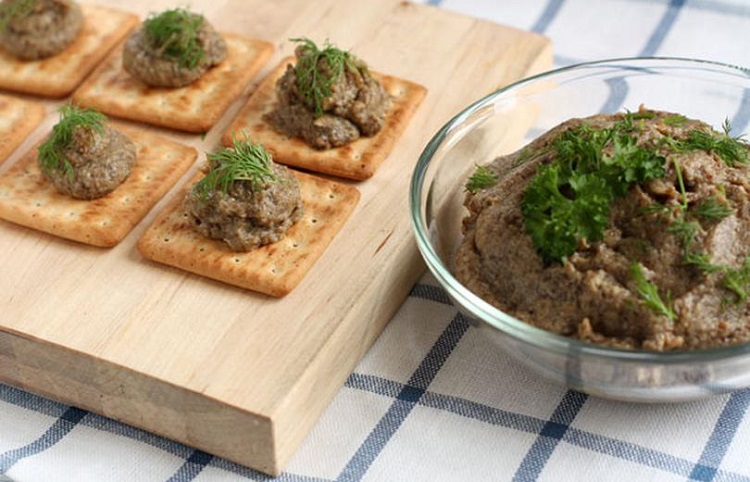

The pate can be eaten for a few days or frozen in the freezer for the winter.
With Worcestershire sauce and white wine
Boletus (0.7 kg) is cut and poured with cold water for an hour, after which they are thrown onto a sieve and dried. Flour is fried in a frying pan in butter.
Add a large shredded onion and grated garlic (2 prongs), fry until transparent. Spread mushrooms in a pan, mix the ingredients and stew under a lid for 2 minutes.
Then add a glass of dry wine and stew until the liquid is reduced by 2 times. Add a teaspoon of Worcestershire sauce and half a glass of warm vegetable broth.
The mixture is brought to a boil, stewed for about 40 minutes. Sprinkle portions of the finished dish with fresh herbs to taste.
In this video clip, a recipe for fried porcini mushrooms with sour cream:
Recommendations for use
Processing before meals: the mushrooms are sorted out and washed. Remove the wormy areas and cut the pulp into pieces.

Cooking time varies depending on the cooking method and ranges from 20 to 40 minutes.
Dried boletus can be eaten unprocessed (like chips or croutons).
How often can you eat porcini mushrooms? Healthy adults can eat mushroom dishes every day. The optimal time to consume is the middle of the day.
The daily intake of dried mushrooms by adults is up to 15-20 grams, fresh - up to 150-200 grams per day (according to the data of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the Russian Academy of Sciences of the Soviet era).
For pregnant women, lactating women, diabetics and children, the norm is 100-350 grams per week.
These gifts of the forest are included in the dietary menu, their beneficial properties are recognized by official medicine, folk medicine and cosmetology.
THE BENEFITS OF MILK MUSHROOM
Live milk mushroom is widely used today. The main beneficial properties of this culture are due to the chemical composition, therefore, it is recommended to use it in the following cases:
- Choleretic agent;
- Antispasmodic;
- Reduction of benign tumors represented by fibromas, fibroids, polyps, prostate adenoma;
- Increased sexual activity;
- Rejuvenating the body;
- Reducing the side effects of drugs, including broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- Decrease in blood sugar levels;
- Improving overall tone;
- Getting rid of depression and insomnia;
-
Getting rid of diaper rash and cracks in the skin.

There have been cases of positive effects in inflammatory processes in the lungs, as well as malfunctions of the liver, kidneys and gallbladder. You can drink the infusion while following a weight loss diet, which is due to the ability of the Tibetan mushroom to very actively break down accumulated fats. Also, the infusion can be used as a highly effective cosmetic product, and milk mushroom can be used to prepare tonic and masks at home.
In cosmetology
Masks made from the pulp of a young boletus soften the skin and give it elasticity. Mushroom broth is used to rinse hair and to strengthen nails.

Mask for the face:
- young fungus is peeled, crushed and measured out 20 grams;
the gruel is mixed with a spoonful of sour cream and applied to the face;
after 20-25 minutes, the mixture is washed off with warm water, after which a nourishing cream suitable for the skin is applied.
Acne compress:
- the pulp of the mushroom is crushed and mixed with 2 teaspoons of olive oil;
the mixture is applied to the face, covered with a clean cloth with slits for the lips, nose and eyes;
the compress is kept for 20 minutes, then washed off with warm water.
Porcini mushrooms have firmly taken their place in the cuisines of many peoples of the world. Dozens of simple and complex dishes are prepared from this product, preparations are made for the winter.
Mushroom products allow you to get an additional portion of vitamins, amino acids and beneficial trace elements.
Healing properties

Boletus is recommended to be consumed in the treatment of chronic fatigue, inflammatory diseases, to activate metabolism.
It is recommended to eat them in the treatment of tuberculosis, anemia, to improve the functions of the pancreas, to strengthen the immune system.
When dried, hercedine is formed in the pulp - an alkaloid used in the treatment of angina pectoris, atherosclerosis.
On the Internet, you can read the information that this product should be eaten for cancer.
Traditional healers prepare an alcoholic infusion on boletus for the prevention of oncology, the development of atherosclerosis, a decrease in blood viscosity and the prevention of stroke.
Alcohol tincture treat angina pectoris.
Alcohol infusion
The mushroom caps are broken, placed in a jar (almost to the top), poured with vodka or alcohol (40%). The vessel is hermetically closed, placed in a dark place for 2 weeks.
After that, the raw material is squeezed out and discarded, and the alcohol is filtered into another container and stored in a dark place.
Take the remedy for 10 days.A teaspoon of the infusion is diluted in a small amount of water and drunk twice a day, half an hour before meals.
Tincture on water
Three teaspoons of crushed peeled caps are boiled in 100 ml of water. The solution is boiled in half, cooled and stored in the refrigerator.
Boletus tincture on water heals skin diseases, wounds, poorly healing ulcers, joint pain, cramps, numbness of the limbs.
The product is used for compresses and rubdowns. The skin is rubbed with a cotton swab three times a day.
GROWING FROM ZERO
Growing a Tibetan Milk Mushroom yourself from scratch isn't too difficult. However, you should definitely adhere to the following recommendations:
pour a couple of tablespoons of the dairy product with milk and remove the jar with the culture in a dark place, where the active fermentation process takes about a day; strain the kefir liquid obtained as a result of fermentation with a sieve and a wooden spoon; thoroughly enough, but very carefully, rinse the mushroom with water at room temperature, carefully removing pieces of mucus and remaining fragments of kefir; transfer the mushroom to a clean and dry three-liter jar, then pour the milk; remove all floating fractions. To prevent overheating, cover the jar with gauze and store at a comfortable room temperature.
Gauze will also prevent small debris and dust particles from getting into the infusion.
To prevent overheating, cover the jar with gauze and store at a comfortable room temperature. The gauze will also prevent small debris and dust particles from getting into the infusion.
October 11, 2013
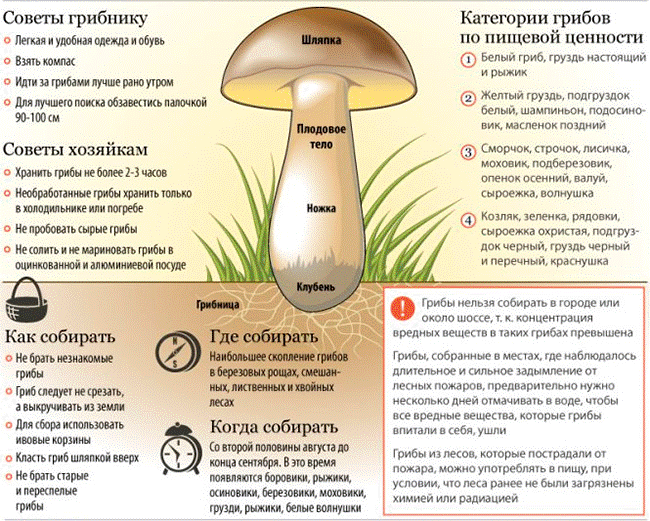
Recommendations for the collection and consumption of wild mushrooms
mushrooms
In autumn, the number of cases of mushroom poisoning increases. Among the main reasons are the use of inedible mushrooms or improperly prepared conditionally edible ones; old or spoiled edibles; eating mushrooms that have twins or have changed due to mutation.
To prevent mushroom poisoning:
- Buy mushrooms only in places designated for their sale (shops, greenhouses, specialized kiosks).
- Collect and buy only edible mushrooms you know.
- Do not pick mushrooms that grow near highways, in industrial wastelands, former dumps, in chemically and radiation-hazardous areas.
- Avoid unknown fungi, especially those with a cylindrical stem, at the base of which there is a thickening "tuber", surrounded by a shell of damaged surface, old, flabby, wormy or slimy: do not collect lamellar species, as poisonous mushrooms are masked by them; avoid "champignons" and "pastries", in which the plates of the lower surface of the cap are white.
- Don't taste raw mushrooms.
- Throw away the soiled bottom of the stem of the mushroom. Rinse the mushrooms, remove the slippery film from the caps.
- Wild mushrooms must be cooked on the day of harvest, otherwise cadaveric poison is formed in them.
- At the initial stage of processing, boil the mushrooms in water for 7-10 minutes, then drain the broth. Only then can the mushrooms be boiled or fried.
- Be sure to soak or boil conditionally edible mushrooms that are going to be salted (milk mushrooms, volnushki and others containing milky juice) in order to get rid of the bitter substances that affect the gastric mucosa.
- Avoid giving mushrooms to children, the elderly, and pregnant women.
- Some mushrooms (greenfinch, bruise - oak tree, etc.) contain toxic substances that do not dissolve in the stomach. The poison dissolves in interaction with alcohol, which leads to severe poisoning.
- A significant number of mushrooms, which until now were considered edible, contain micro doses of toxic substances. If consumed several days in a row, poisoning can also occur.
- Canned mushrooms, improperly cooked, can lead to a very serious disease - botulism.
- Mushrooms that have been stored for a long time must be boiled for 10-15 minutes.
Symptoms of poisoning are nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, increased sweating, convulsions, decreased blood pressure, involuntary urination, diarrhea, and the development of symptoms of cardiovascular insufficiency.
The primary signs of poisoning appear 1 to 4 hours after eating the mushrooms. Pain and nausea are repeated several times after 6 to 48 hours, and death occurs 5 to 10 days after poisoning.
First aid for mushroom poisoning:
- Call an ambulance. Do not hesitate while waiting for doctors - flush your stomach: drink 5-6 glasses of boiled water or a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate, induce vomiting by pressing the root of your tongue with your fingers, and when the water is clear, take 4-5 tablets of activated charcoal.
- Drink strong tea, coffee, or lightly salted water to restore the water-salt balance.
- Find out who else was taking the mushroom dish that led to the poisoning and take preventive measures.
It is forbidden to use any medicine and food in case of poisoning, this can accelerate the absorption of toxins in the intestines. Compliance with these rules can save your health, and even life, because mushroom poisoning is very difficult to treat.
According to the Main Directorate of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Ukraine in the Donetsk region.
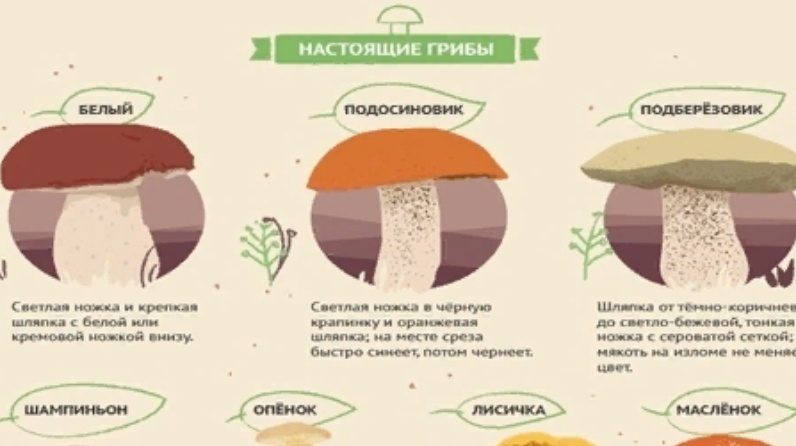
How to choose and check the quality
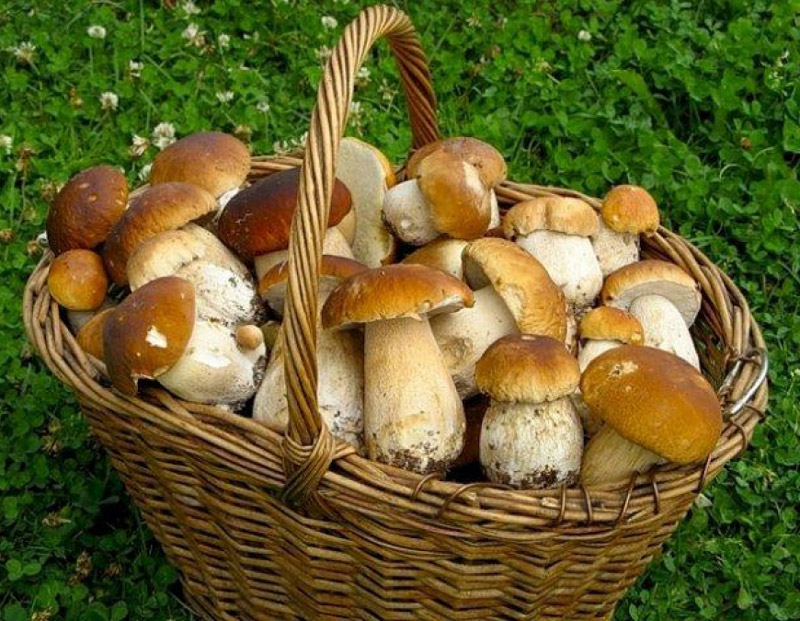
How do you pick a good product on the market or during a mushroom hunt? I want to bring home a basket full of clean, strong mushrooms and use them all.

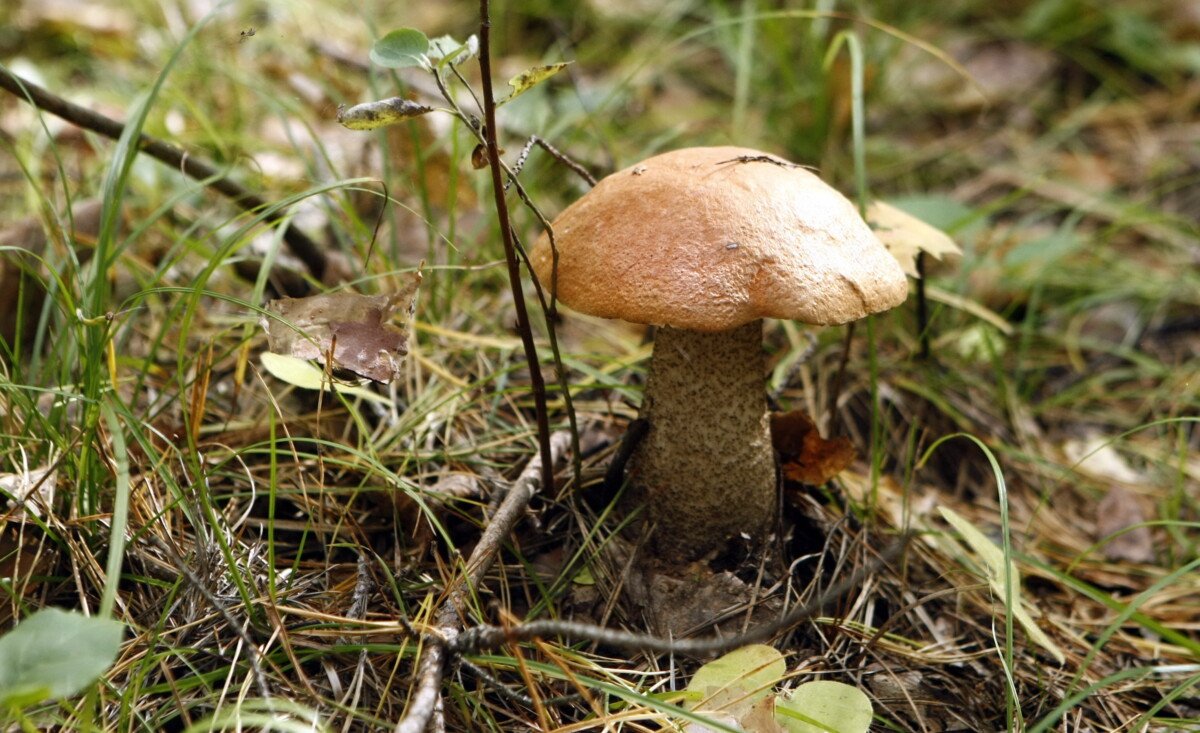
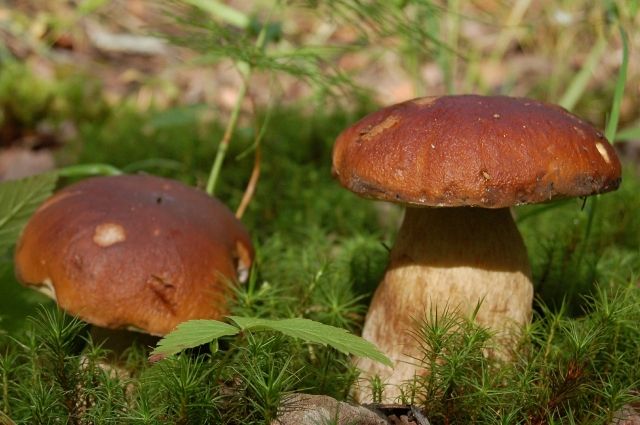
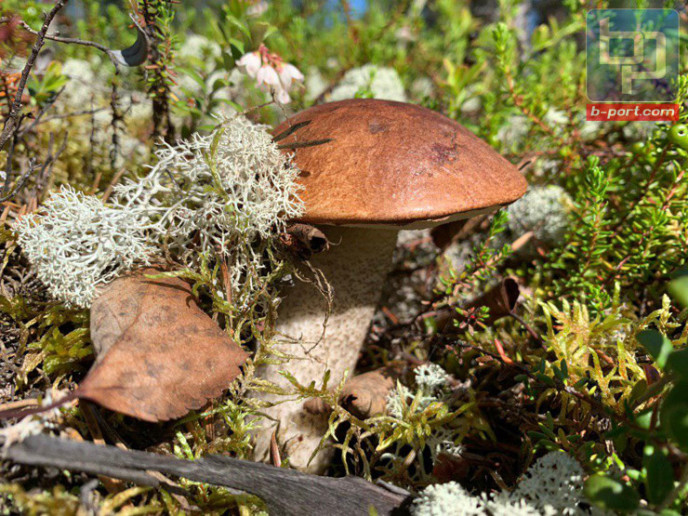
The mushroom cap is dry in sunny weather. If it has rained, it can be slippery.
The pulp of a young mushroom is dense, juicy, white, mature - fibrous, yellowish, light beige. The leg is firm and strong. During processing and drying, the cut does not darken.
Do not collect wormy specimens. If the plant smell seems unnatural, the product will not be edible.
On the market, the product should be taken only from trusted suppliers who collect forest gifts in an ecologically clean forest.
How do you pick a good product in a store? It is better to buy mushroom products in a specialized department.
When buying, pay attention to the storage temperature, the tightness of the bags, the shelf life.