Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
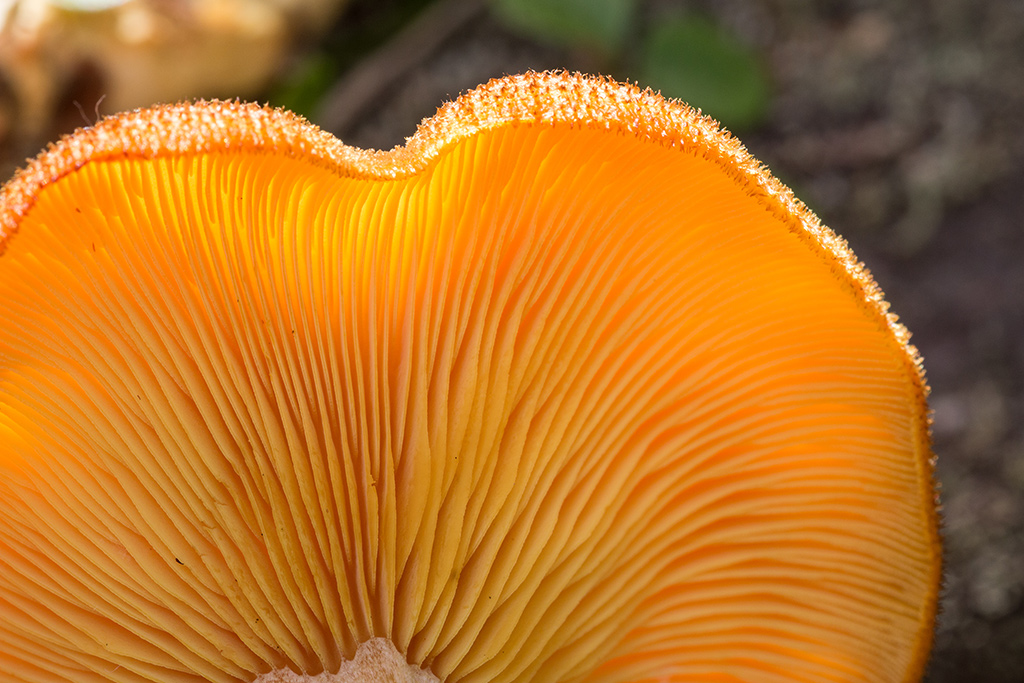
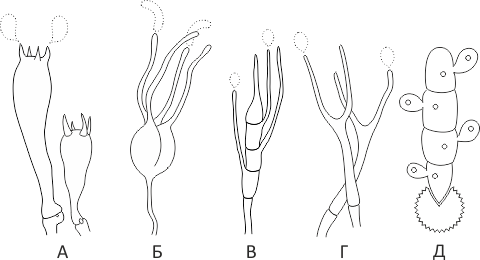
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
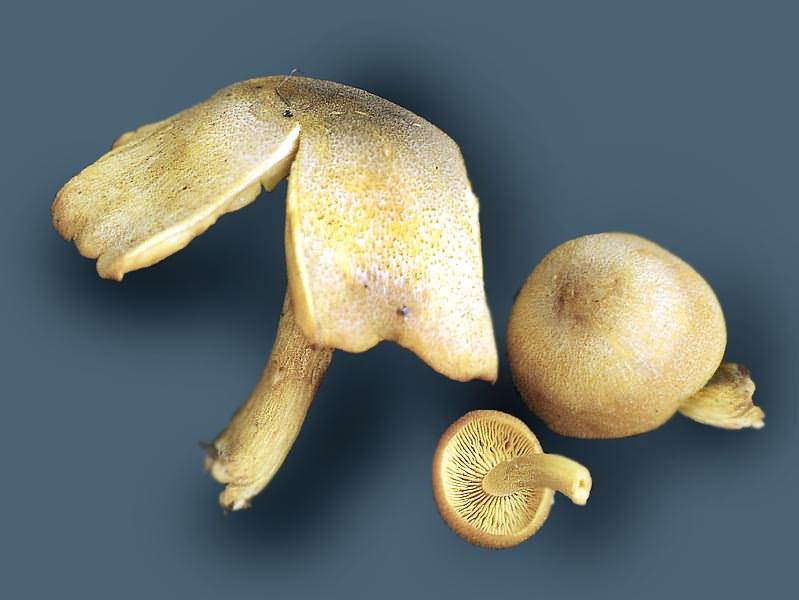
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Trichoderma (Trichoderma)
-
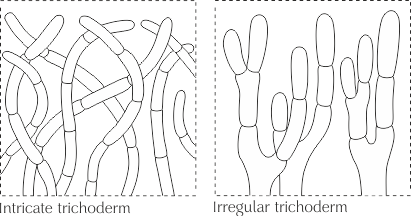
The type of cap skin, usually consists of straight, septate elements located more or less perpendicular to the surface and laid both at the same and at different levels; the ends of the hyphae can be morphologically modified and represent dermatocystids. The surface of the cap is velvety to almost felt.
Lat. Trichoderm.
Trichoderma, in turn, is subdivided into intertwined trichoderma and irregular trichoderma.
Intertwined trichoderm (Intricate trichoderm) - trichoderm, consisting of intertwined hyphae, located not parallel to each other and forming a tomentose pubescence.
Irregular trichoderm - Trichoderma, consisting of irregularly branching hyphae.
See Dermatotsistida, Hypha, Septa.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
Interesting Facts
The mushroom got its unusual name for its ability to grow in rows (ryadovka) or rings.
Pine honeydew can be grown in the country. To do this, it is enough to purchase mycelium in specialized stores. Its price is about 400 rubles / 100 grams. The substrate is placed in the ground and covered with foil to maintain optimal moisture content. The crop appears in waves within 3-4 months.
The calorie content of the mushroom is low, only 20 kcal / 100 grams.
The yellow-red medicinal raspberries are used to prepare antibiotics that are effective against tubercle bacillus. Alcoholic infusions on this forest fruit are used to treat skin inflammations.
The pine mushroom undoubtedly deserves the attention of lovers of quiet hunting. Collect this beautiful mushroom by carefully unscrewing its leg from the ground, properly process and prepare aromatic, tasty dishes
But first, pay attention to the differences between this species and similar poisonous counterparts, so as not to expose yourself and your family to mortal danger.
Recipes for cooking Ryadovki red
If you are still sure that it was the yellow-red ryadovka that got into the basket, and not its false counterpart, try to cook delicious, unusual dishes from it.
Primary processing
In order to pickle or pickle mushrooms, you will need to soak them in cool water for a long time. And for subsequent frying or use in other dishes, it will be enough to thoroughly rinse, remove forest debris and boil for 40 minutes in salted water with the addition of citric acid.
Cooking
Clean the caps and legs of the rows from the needles, rinse them well in running water. Place in a deep container, add 1 tbsp. salt (per 1 kg of mushrooms), a pinch of citric acid. Boil for 40 minutes from the moment the water boils. Then flip it in a colander to drain excess liquid. Cool and use as directed.
Pickling
In order to preserve the forest harvest for the winter, try pickling pine mushrooms.
Ingredients:
- rows - 1 kg;
- vinegar 9% - 3 tablespoons;
- salt - 1 tablespoon;
- sugar - 1.5 tablespoons;
- water - 250 ml;
- black and allspice - 5 peas;
- cloves, bay leaves - to taste;
- garlic - 3 cloves.
Cooking process:
- Discard the fruit bodies previously boiled in salted water in a colander, and then blanch to remove the bitterness. To do this, you need to lower them in boiling water for 5 minutes.
- Place the mushrooms in clean, dry jars.
- Prepare the marinade. Pour water into the container, add the rest of the ingredients: sugar, salt, vinegar, spices. Boil the brine for 5 minutes.
- Strain the broth and pour the boiling over the mushrooms in the jars.
- Seal with plastic lids, place containers in a cellar or other cool place.
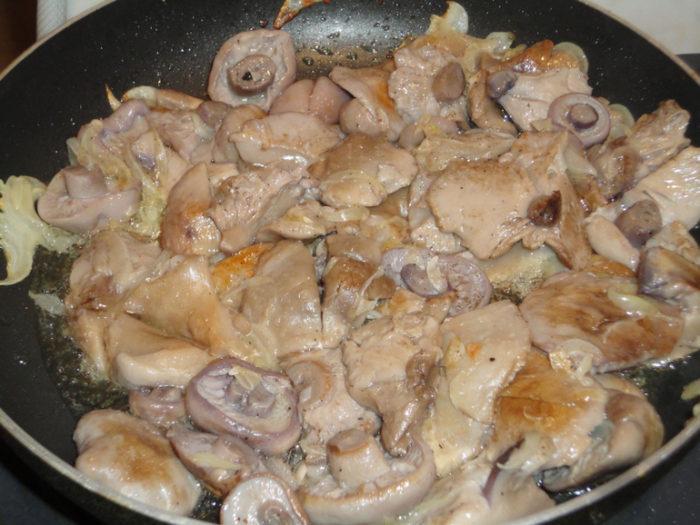 Frying
Frying
To prepare this delicious dish, you do not need expensive components, but after a while an unusual, aromatic addition to the side dish will appear on the table.
Ingredients:
- onion - 2 heads;
- rows - 1 kg;
- sunflower oil - 100 ml;
- sour cream - 100 g;
- paprika - a pinch;
- parsley greens - 20 g;
- salt to taste;
- ground black pepper - on the tip of a knife.
Cooking process:
- Clean the fruiting bodies, remove the tip of the stem. Wash and cut into equal pieces.
- Place the mushrooms in a container with salted water, boil for 15 minutes, constantly removing the resulting foam.
- Drain the liquid, refill the pot with cold water and cook for another half hour.
- Peel the onion, cut it into cubes or half rings and fry in vegetable oil until soft.
- Once the rows have been boiled again, fry them in another pan for half an hour.
- Combine mushroom slices with sautéed onions, spices, salt and paprika.
- Cook for another 10 minutes over medium heat. At the end, add sour cream, stew a little and serve with chopped herbs.
Salting
Try to prepare pine mushrooms this way - you will have a delicious, spicy treat for the winter!
Ingredients:
- false rows - 3 kg;
- salt - 4 tablespoons;
- garlic - 1 head;
- bay leaf - 2 pcs.;
- black peppercorns - 8 pcs.;
- dill - 2 umbrellas.
Cooking method:
- Clean the fruits from forest debris and needles, cut off the lower part of the leg. You can grind them, but it is better to leave them intact.
- Pour the mushrooms with cool water, add 2-3 tablespoons of salt and leave for 2-3 days, changing the water periodically so that the product does not sour.
- Cut the garlic into thin slices.Place a small layer of salt, the rest of the spices and garlic on the bottom of clean, dry jars.
- Place the product in a container in layers until the jar is full. Moreover, each layer of rows should be no more than 5–6 cm, otherwise they will not be salted.
- Tamp the contents of the cans tightly. Cover with a layer of salt, cover with gauze, and top with a lid. After 30–35 days, the workpiece can be fed to the table.
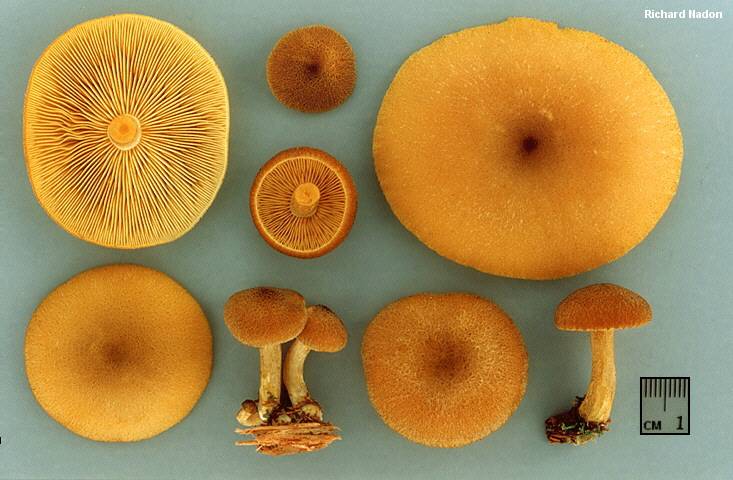
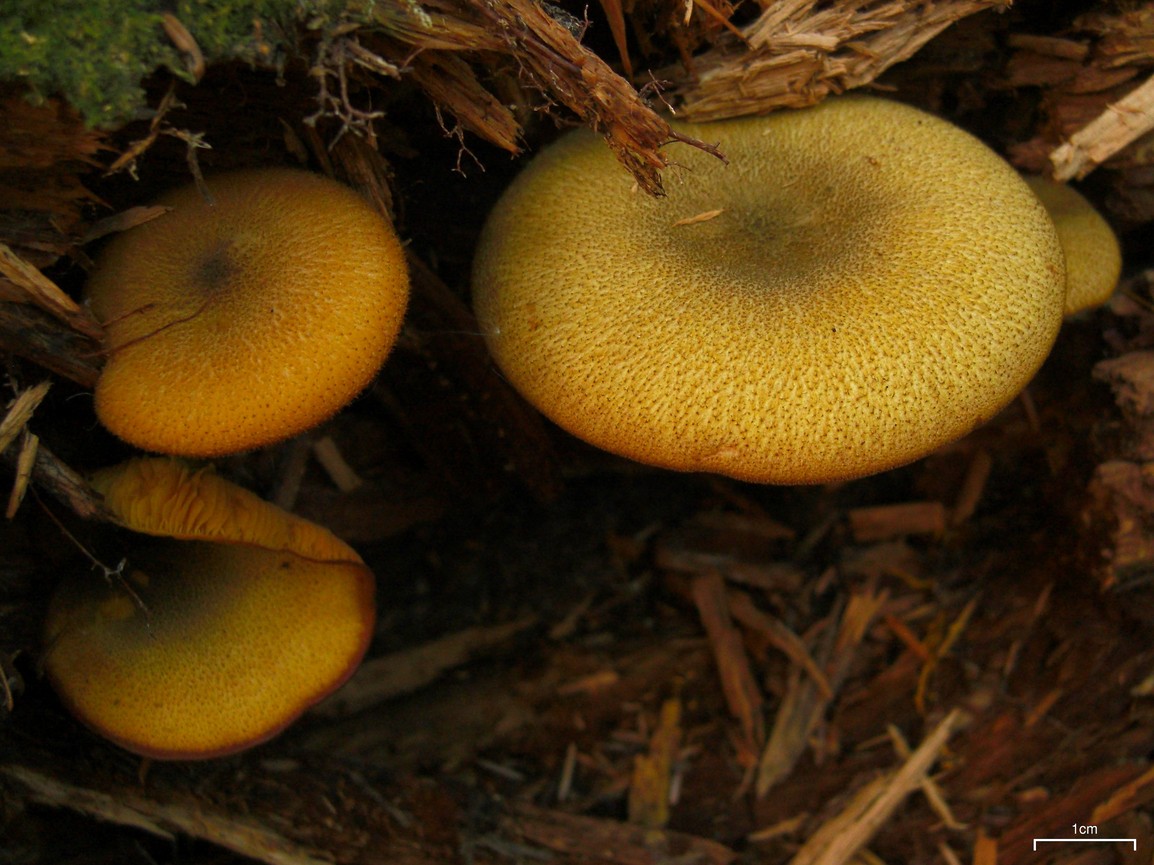
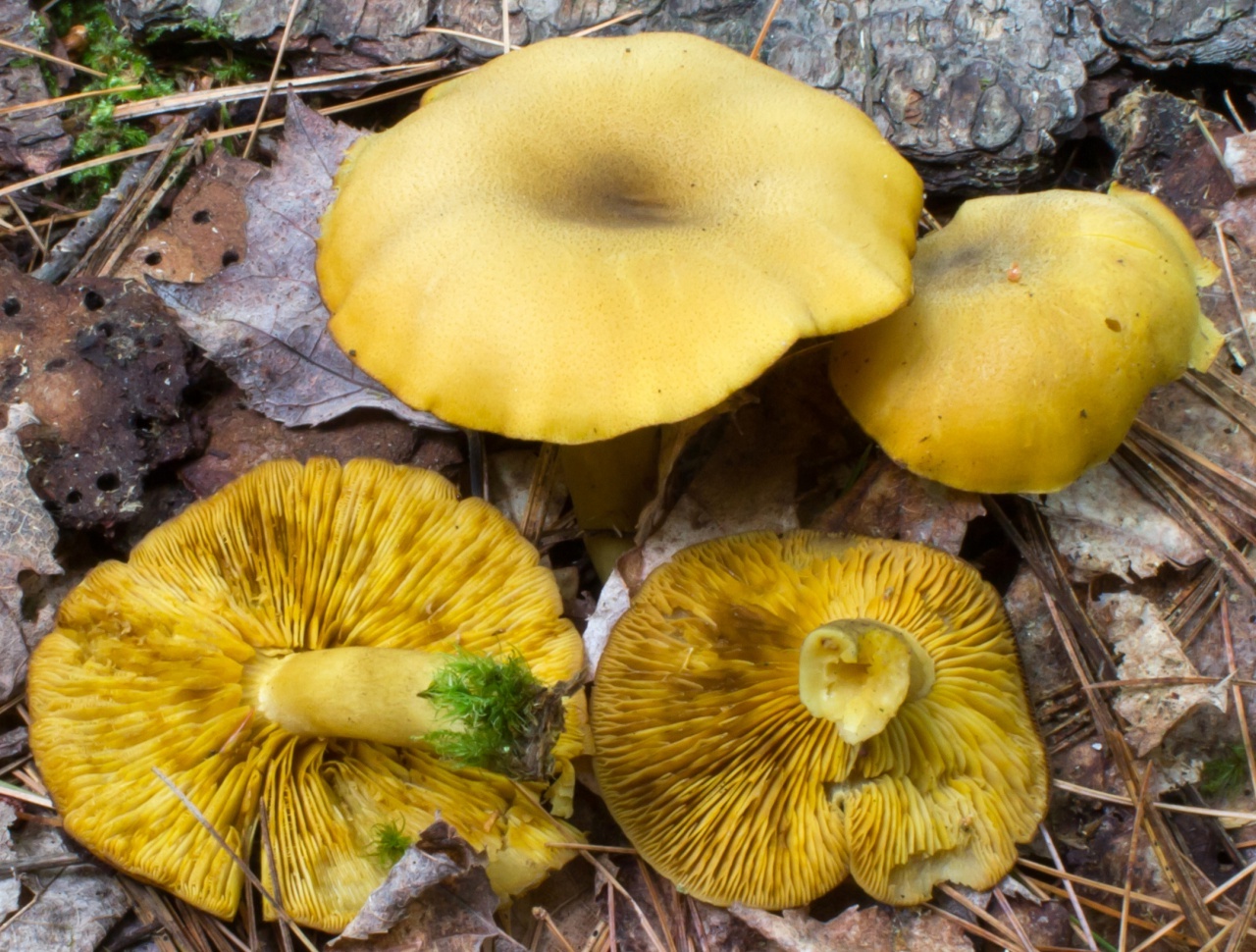
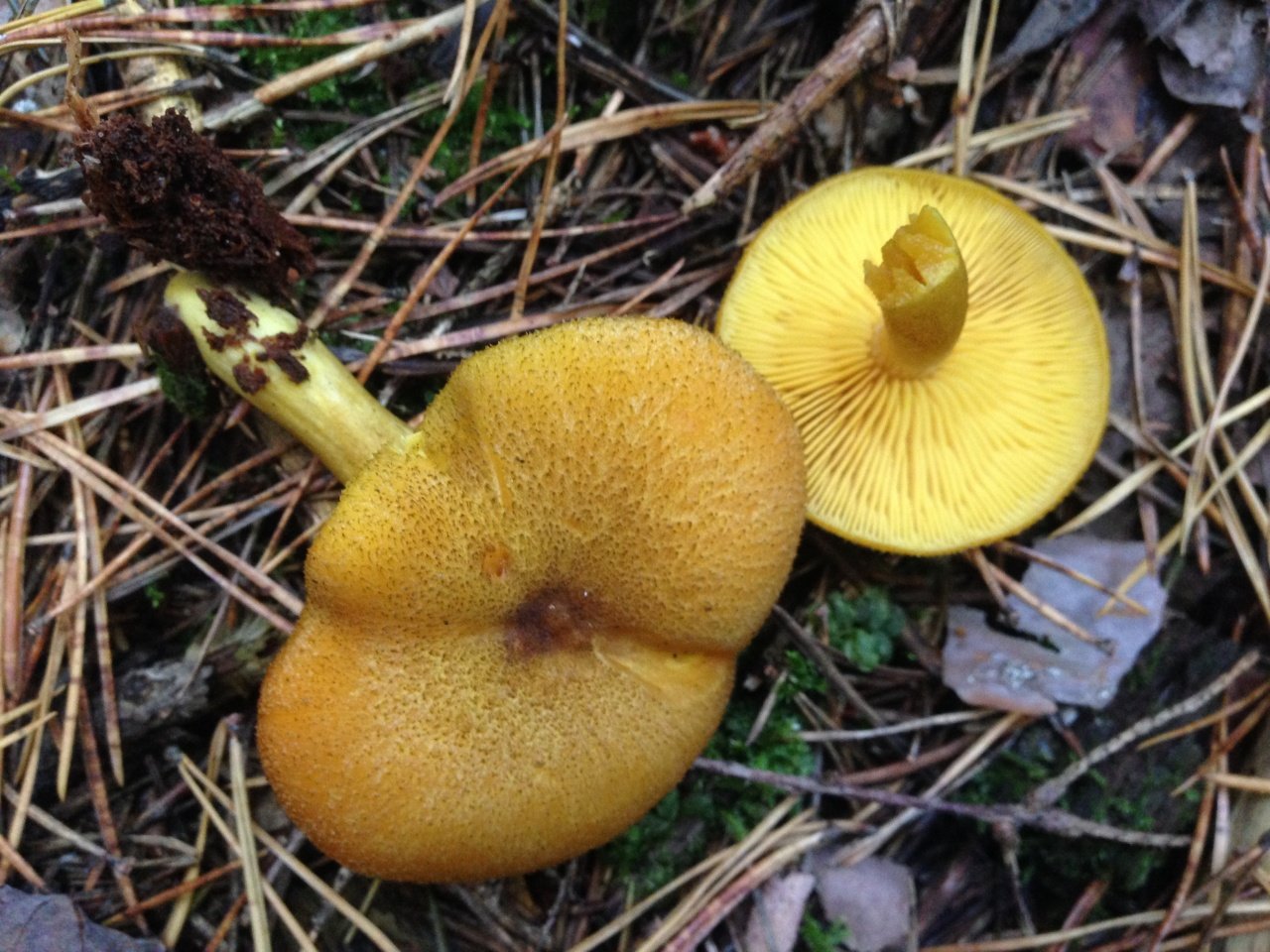
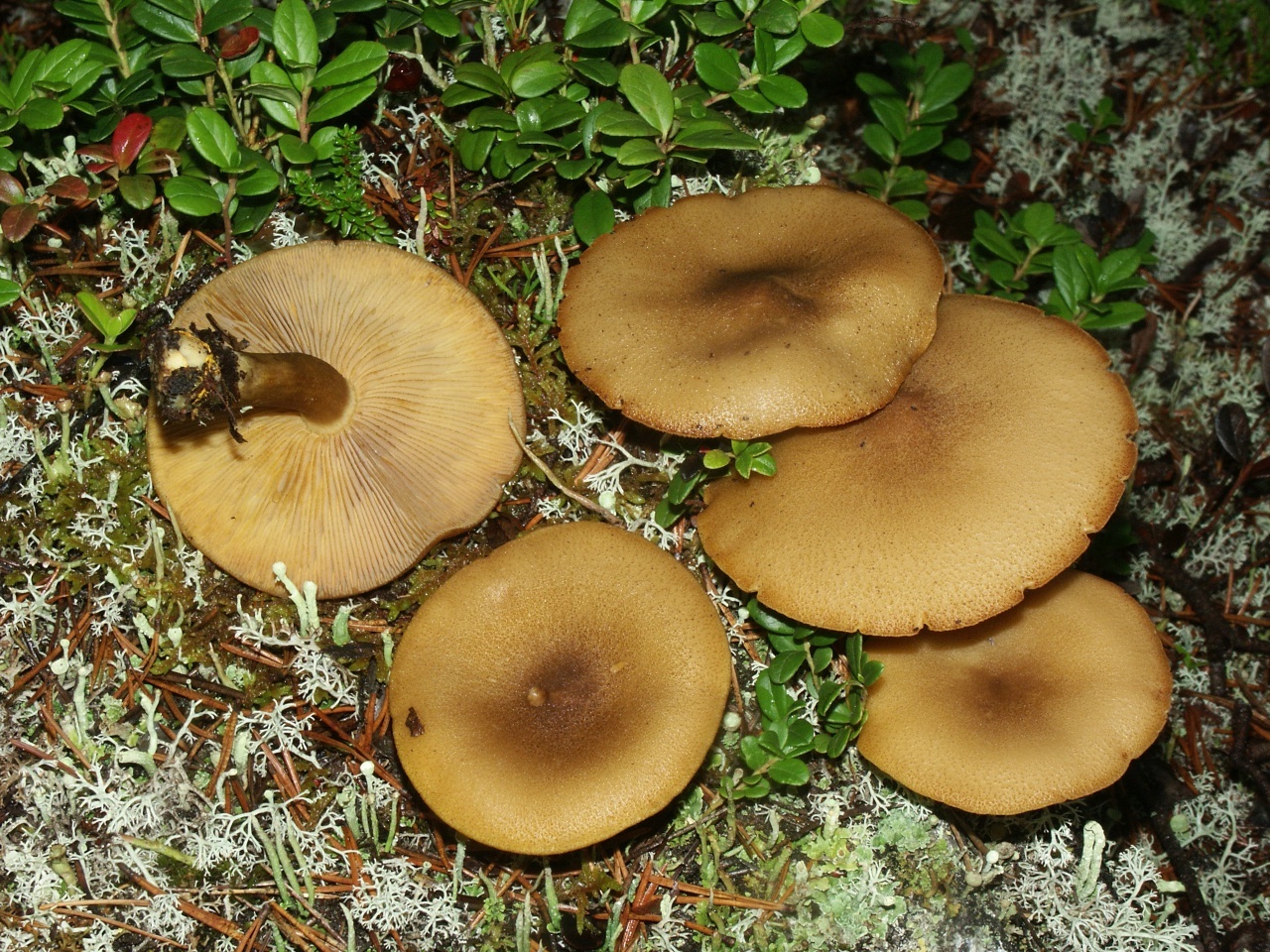
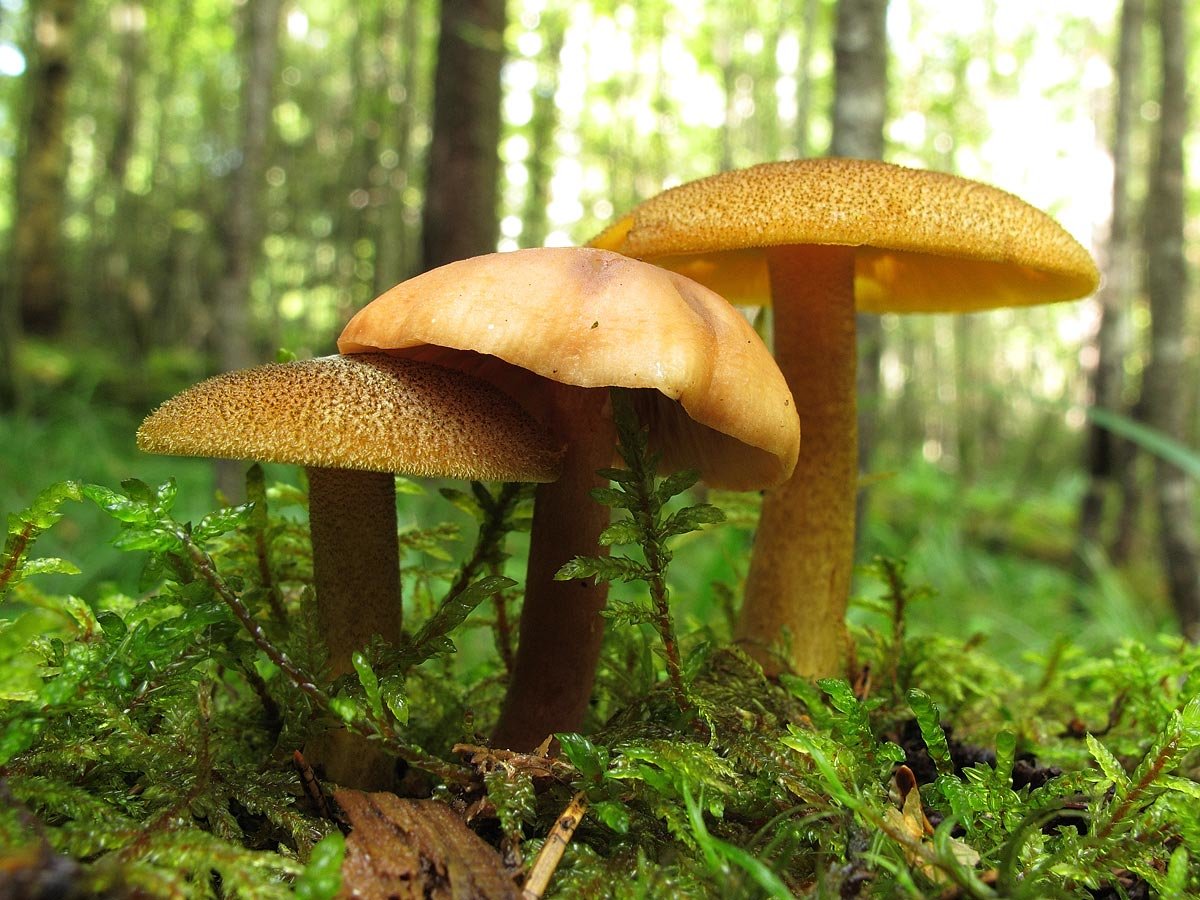
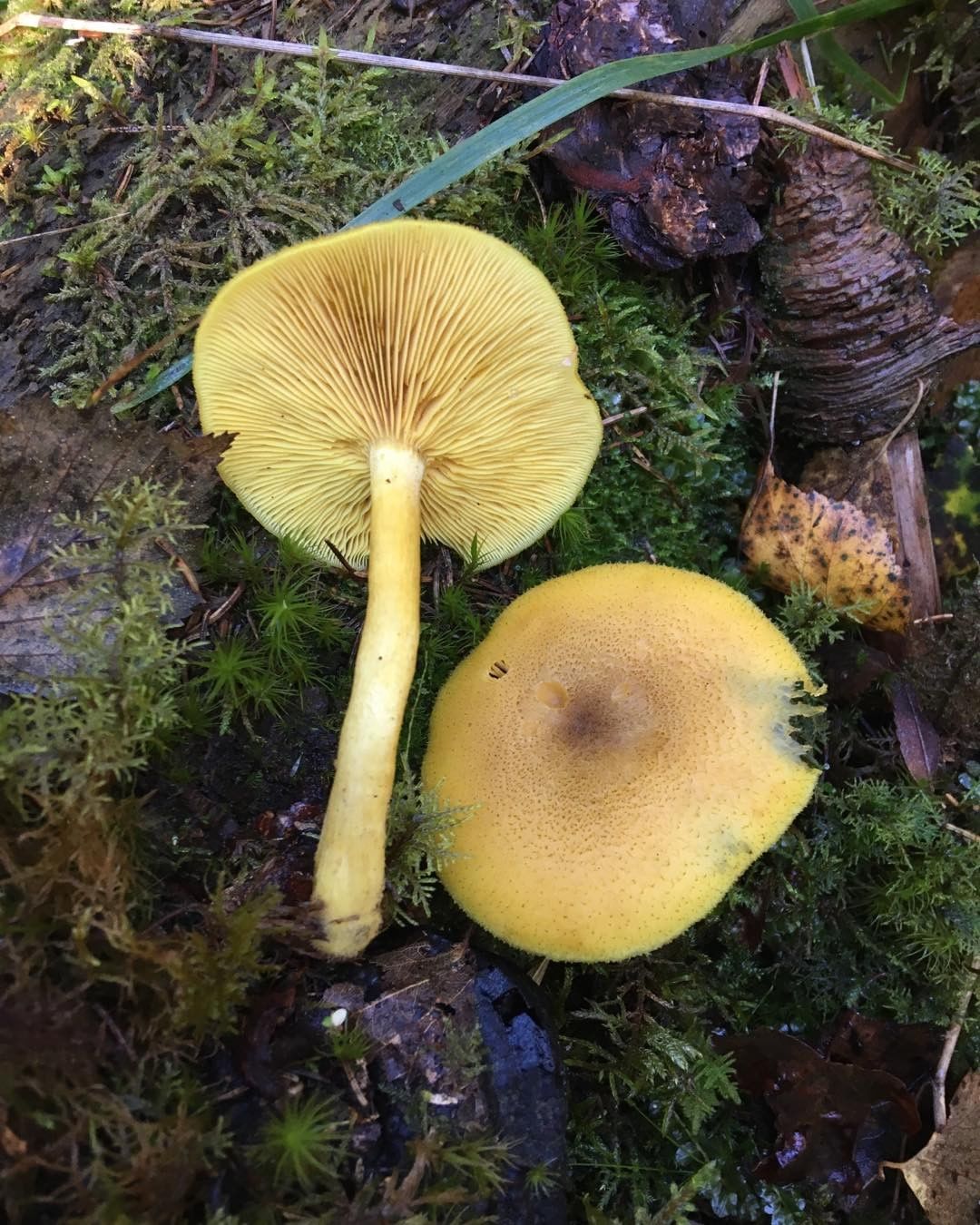
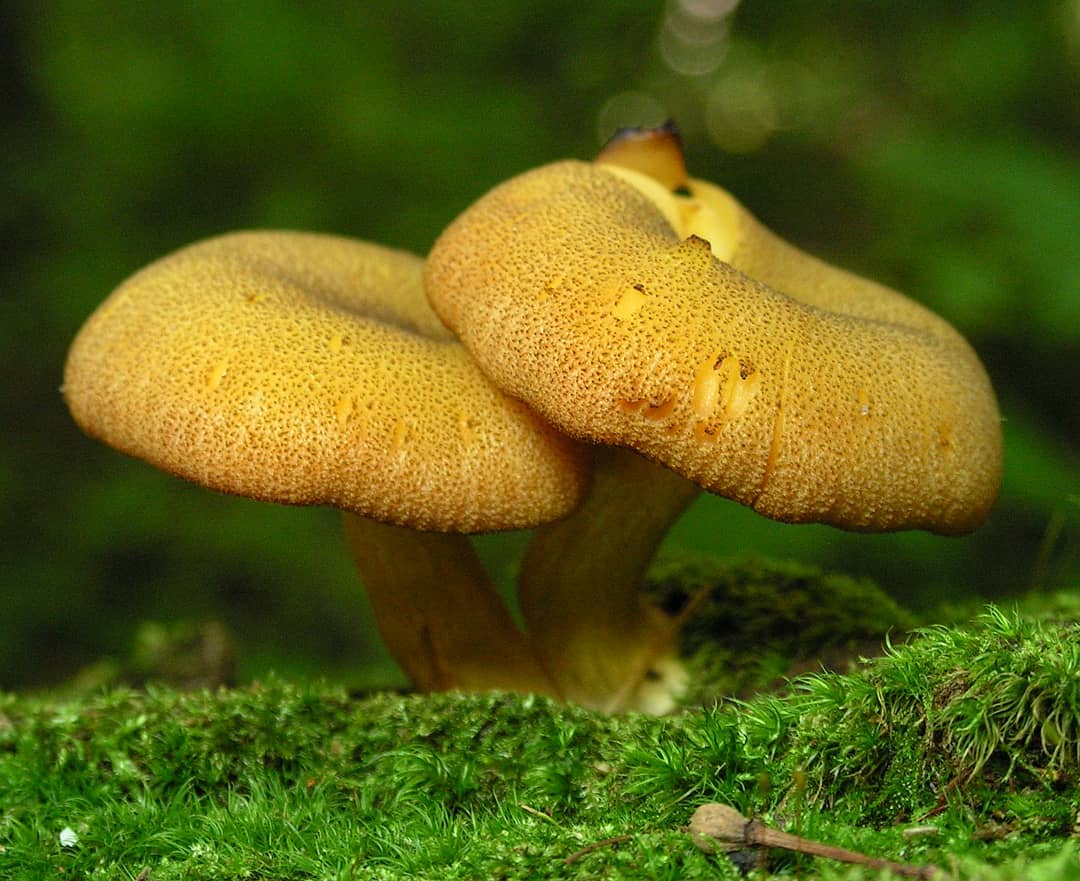
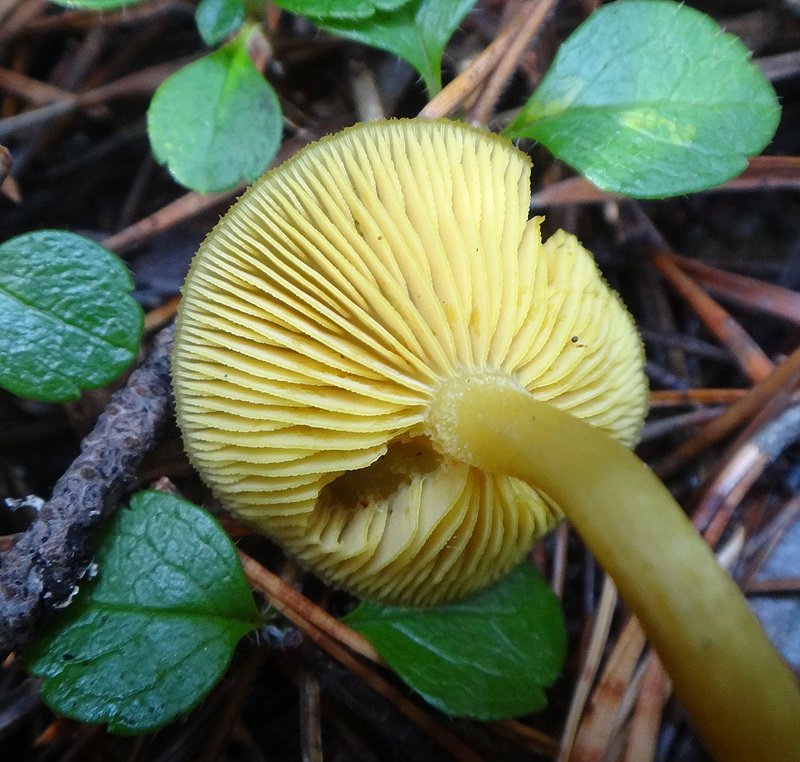
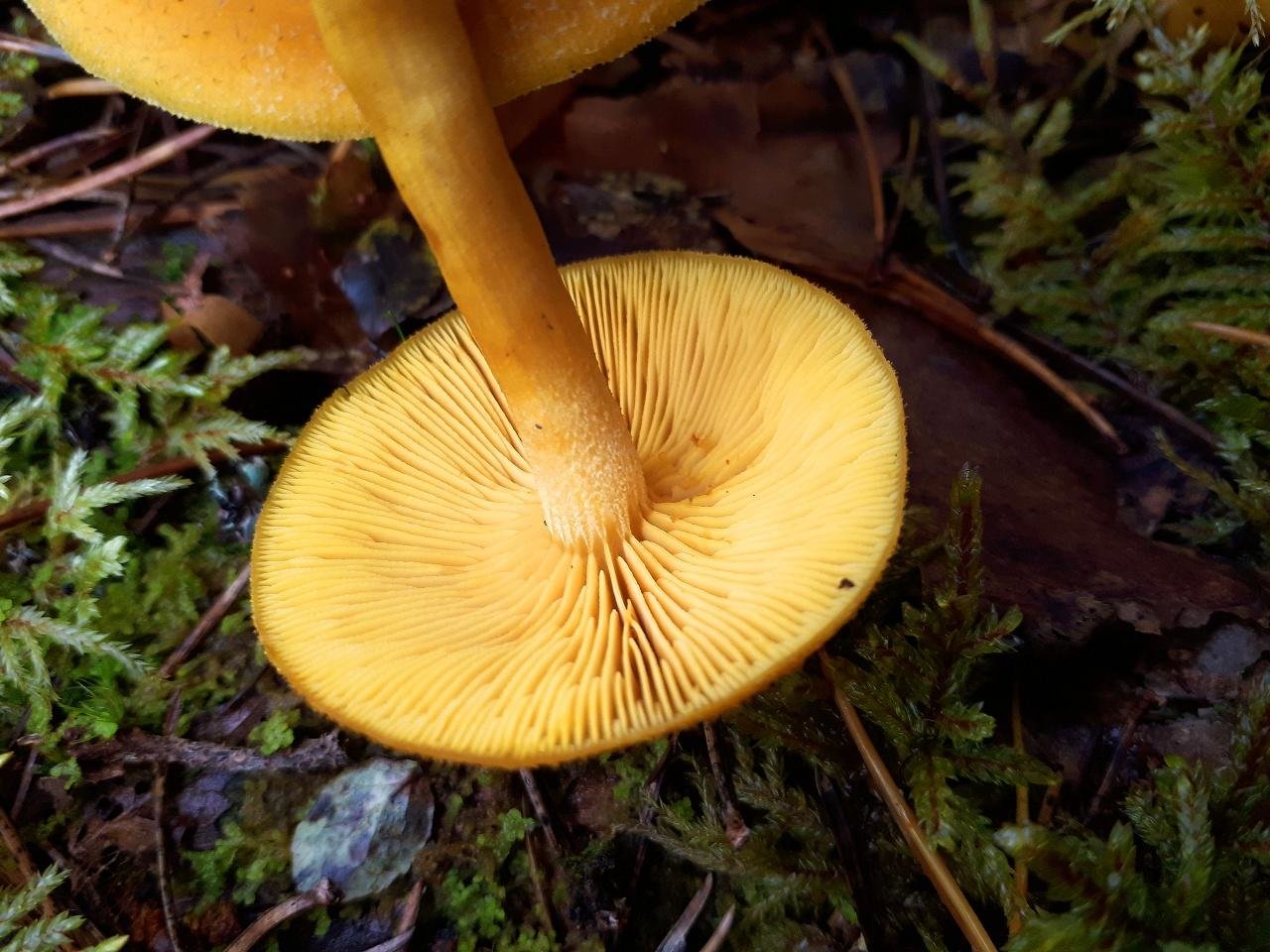
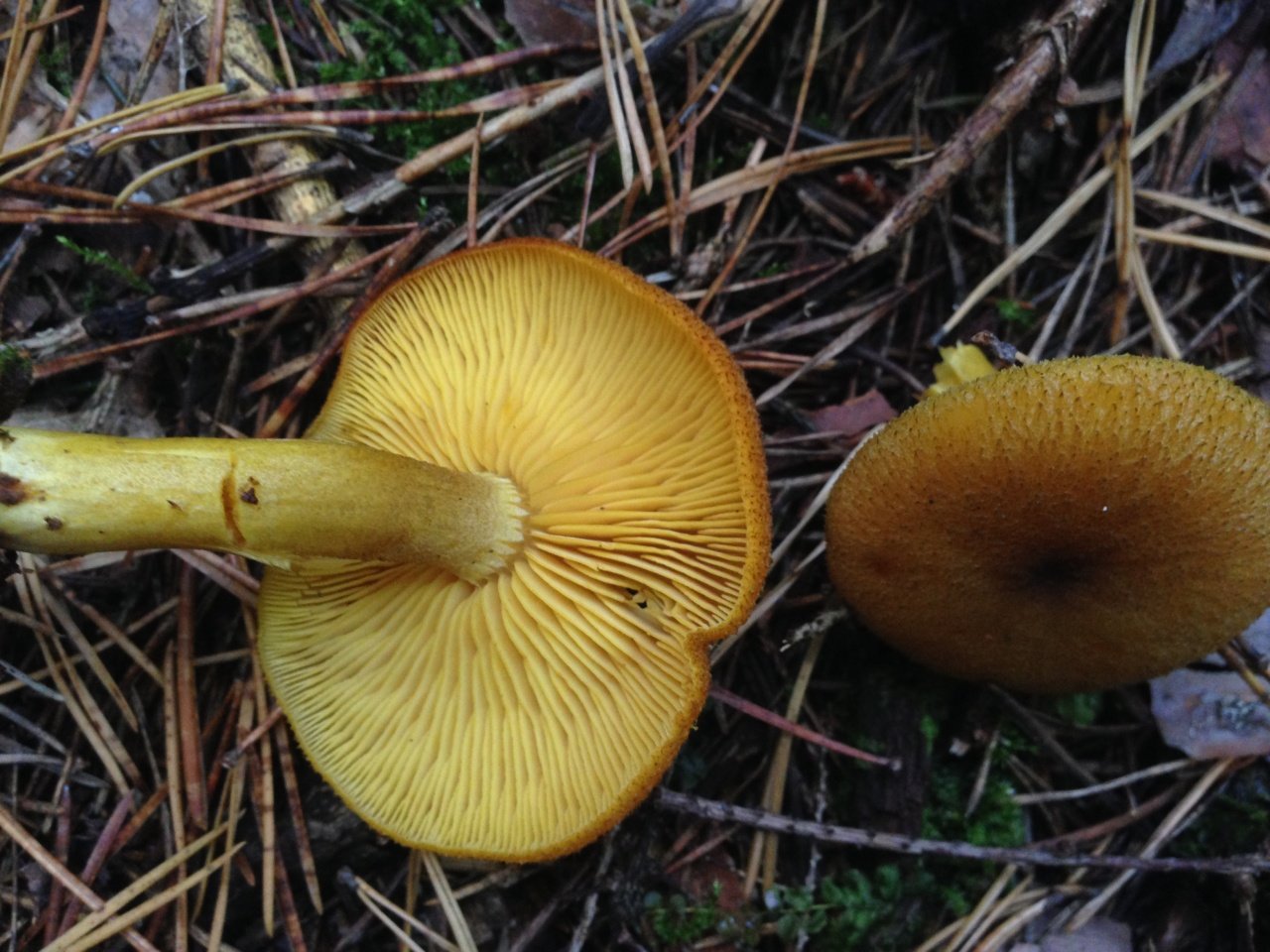
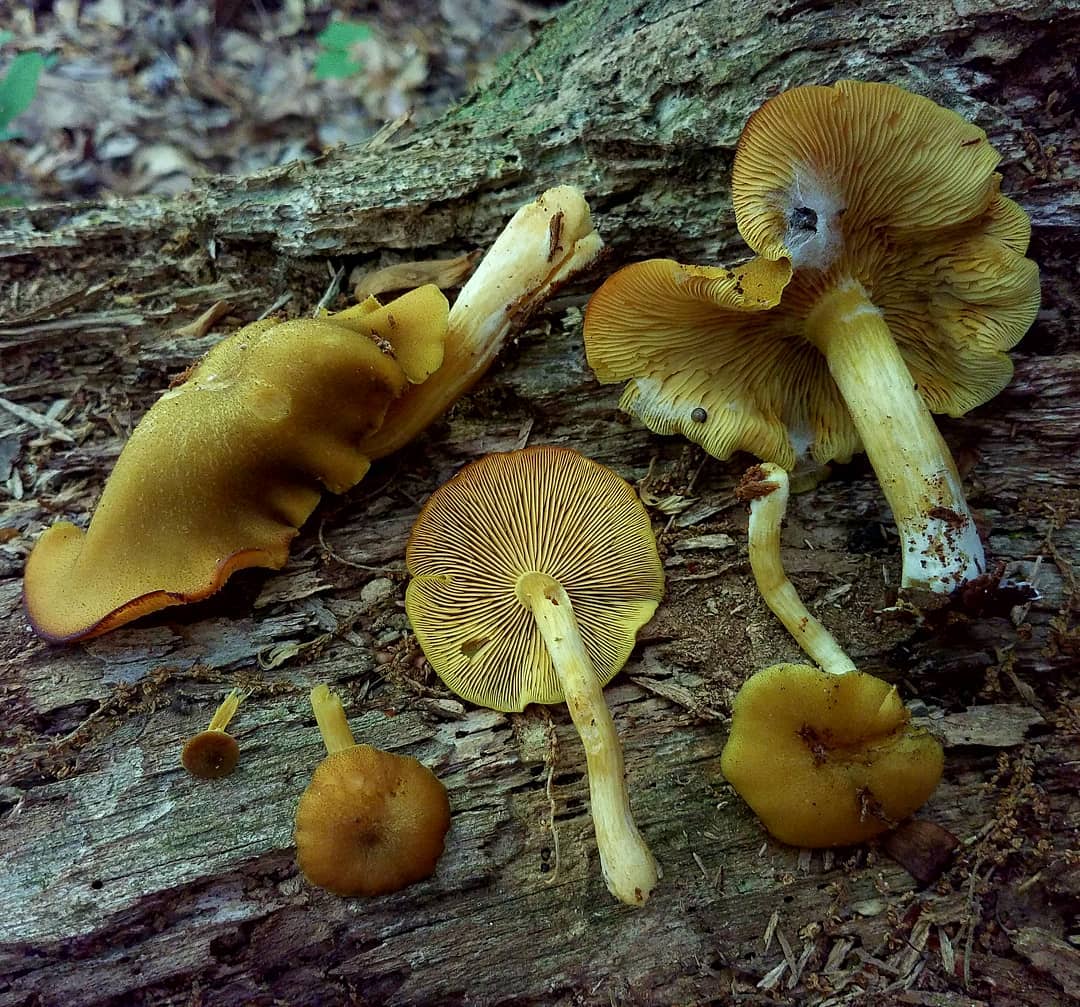
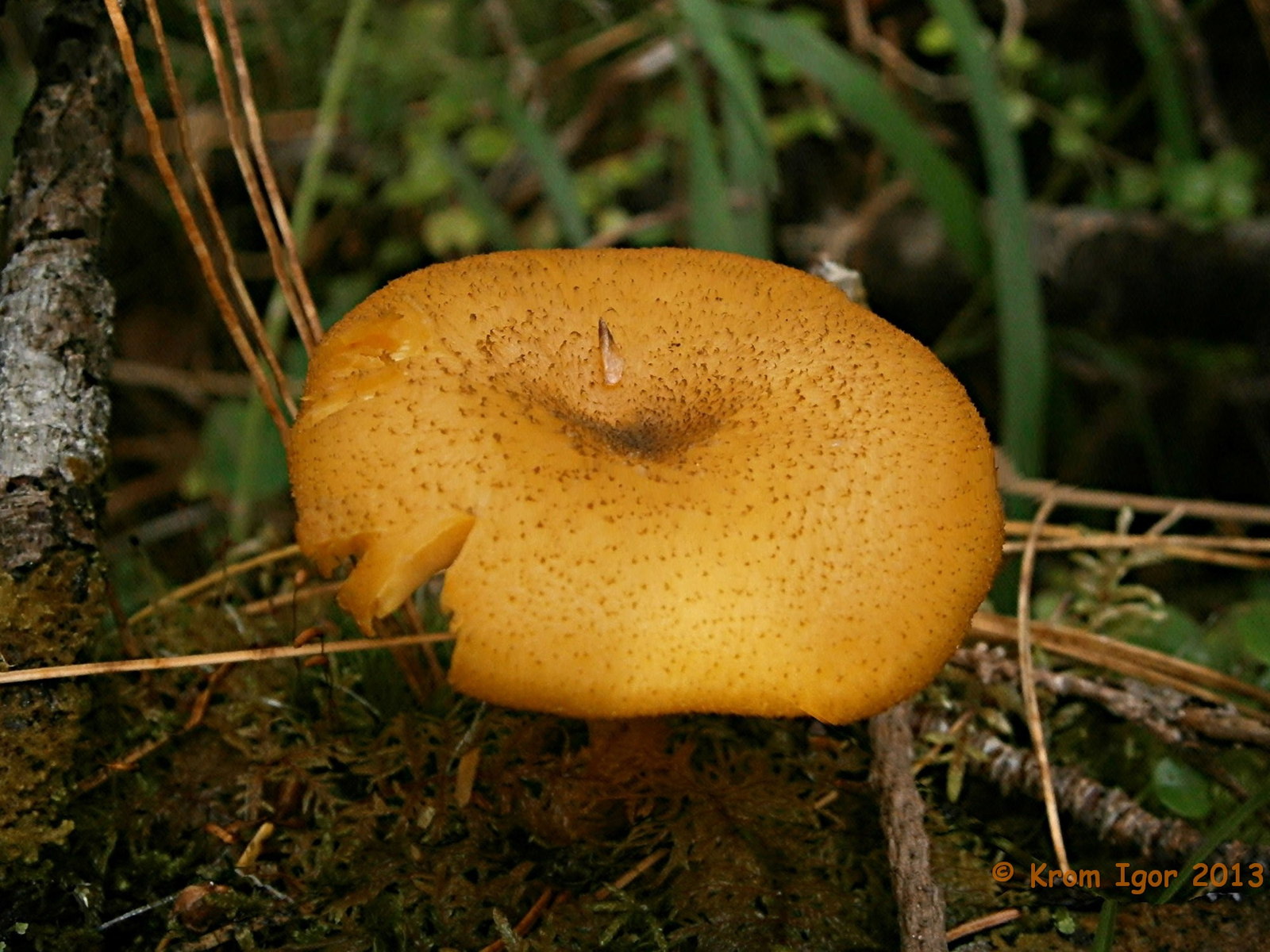
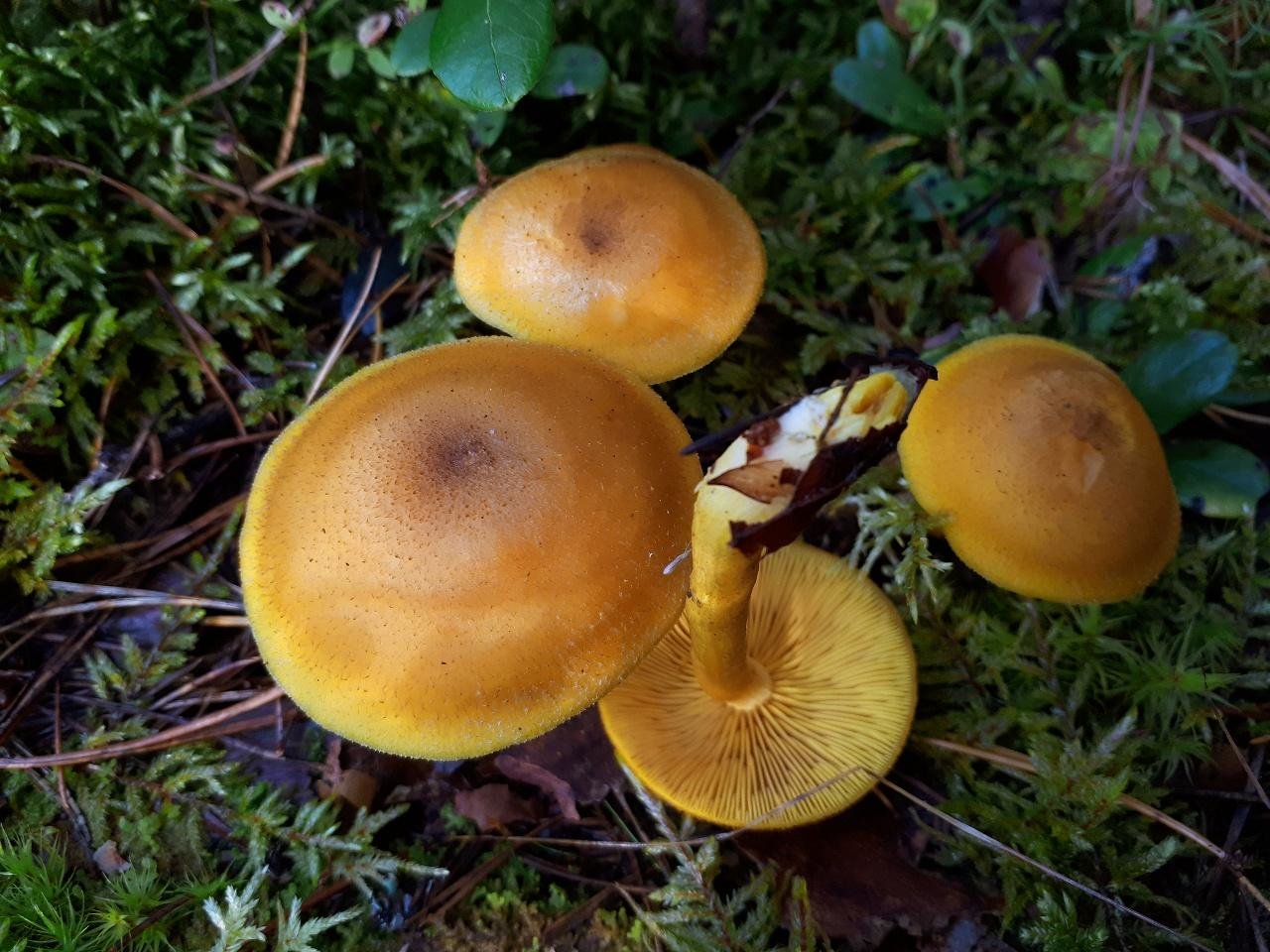
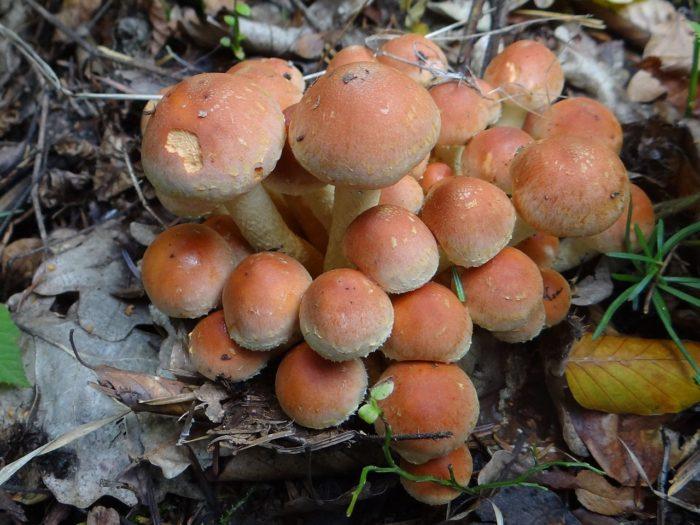
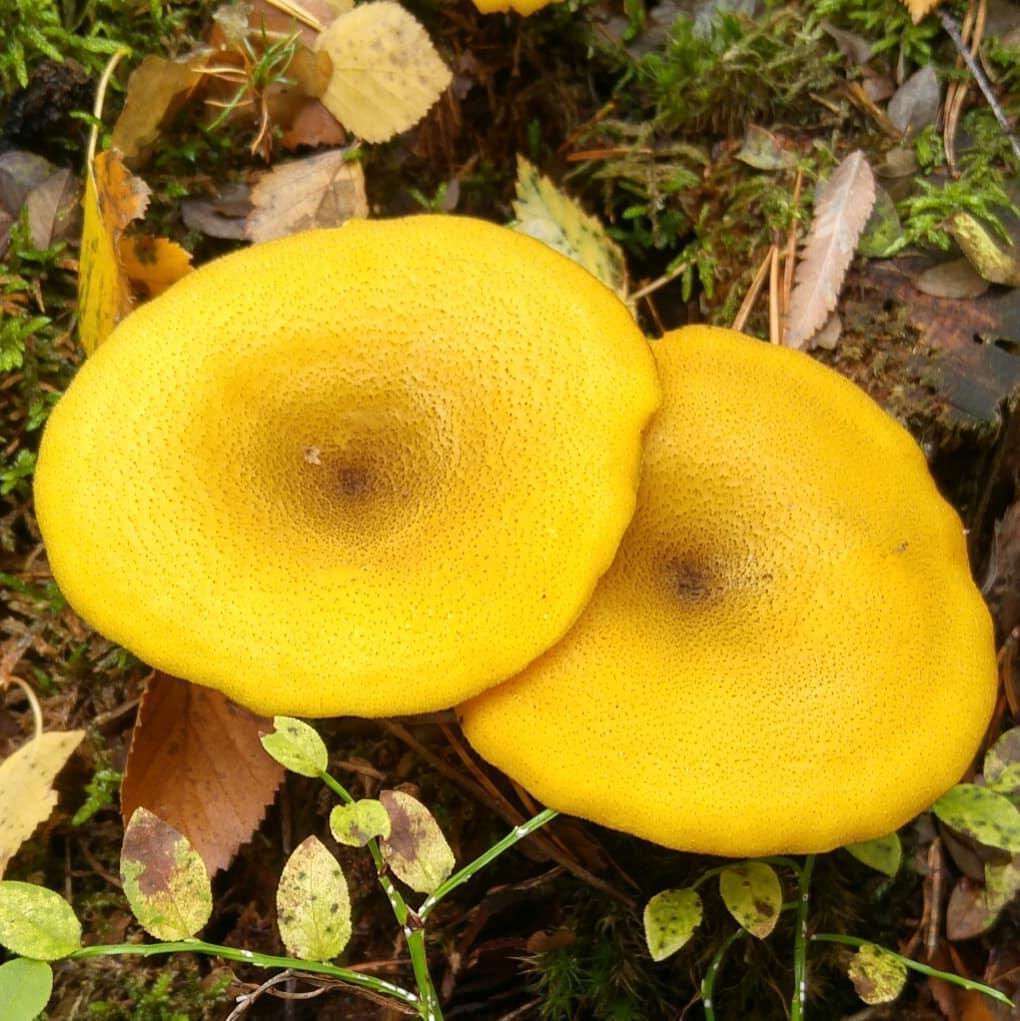
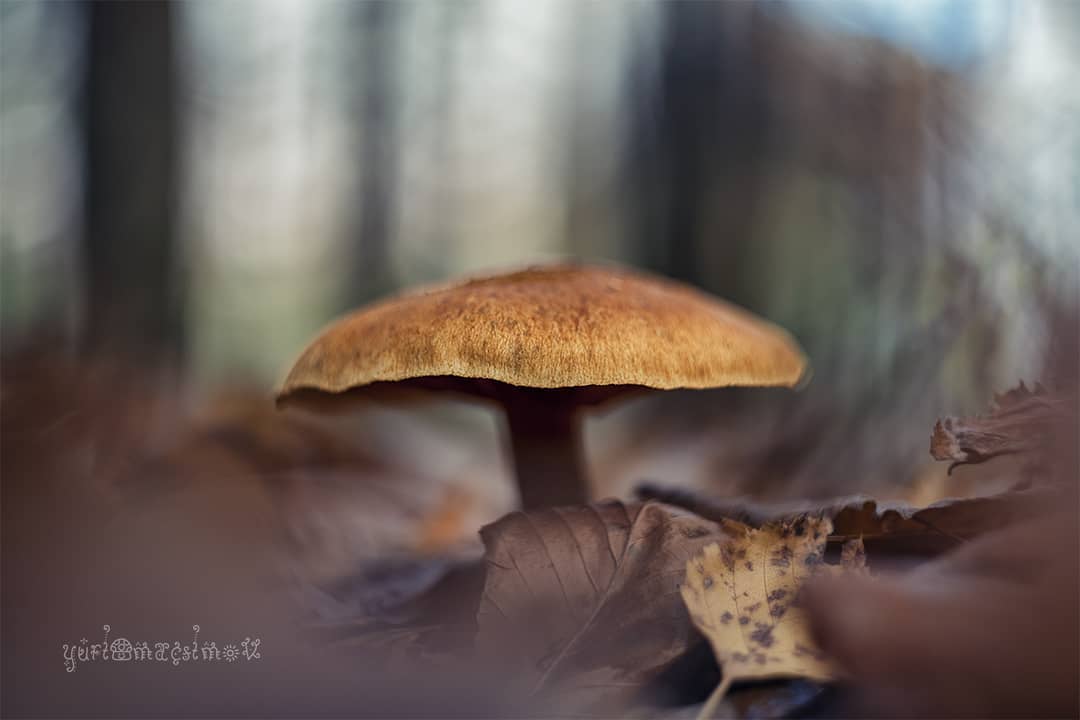
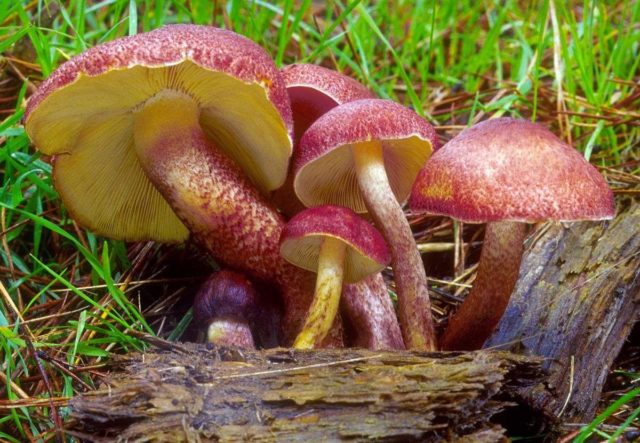
False or edible mushroom ryadovka yellow-red?
For most mushroom pickers, the ryadovka is yellow-red, the photo of which can be seen below, is a little-known mushroom. After all, the main commandment is to take only well-known mushrooms. And on the other hand, the reddening row looks edible. How to understand these issues and how to understand if the false row is yellow-red?
Note that in some scientific sources this mushroom is classified as a conditionally edible species, and in others it is classified as inedible. This unflattering judgment is usually associated with the bitter taste of the pulp, especially in adult specimens. However, after boiling, it is possible to get rid of the bitterness. Experienced mushroom pickers consider the yellow-red ryadovka an edible mushroom and successfully include it in their daily menu.
This article will allow you to get acquainted with a detailed description and photo of the yellow-red row mushroom.
Similar types and differences from them
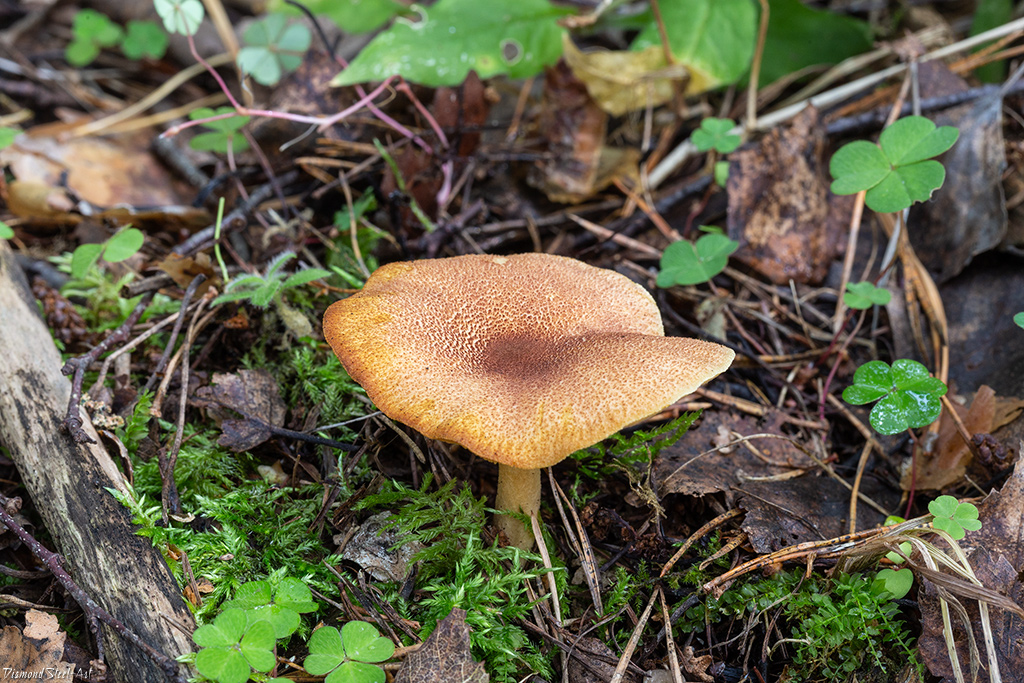
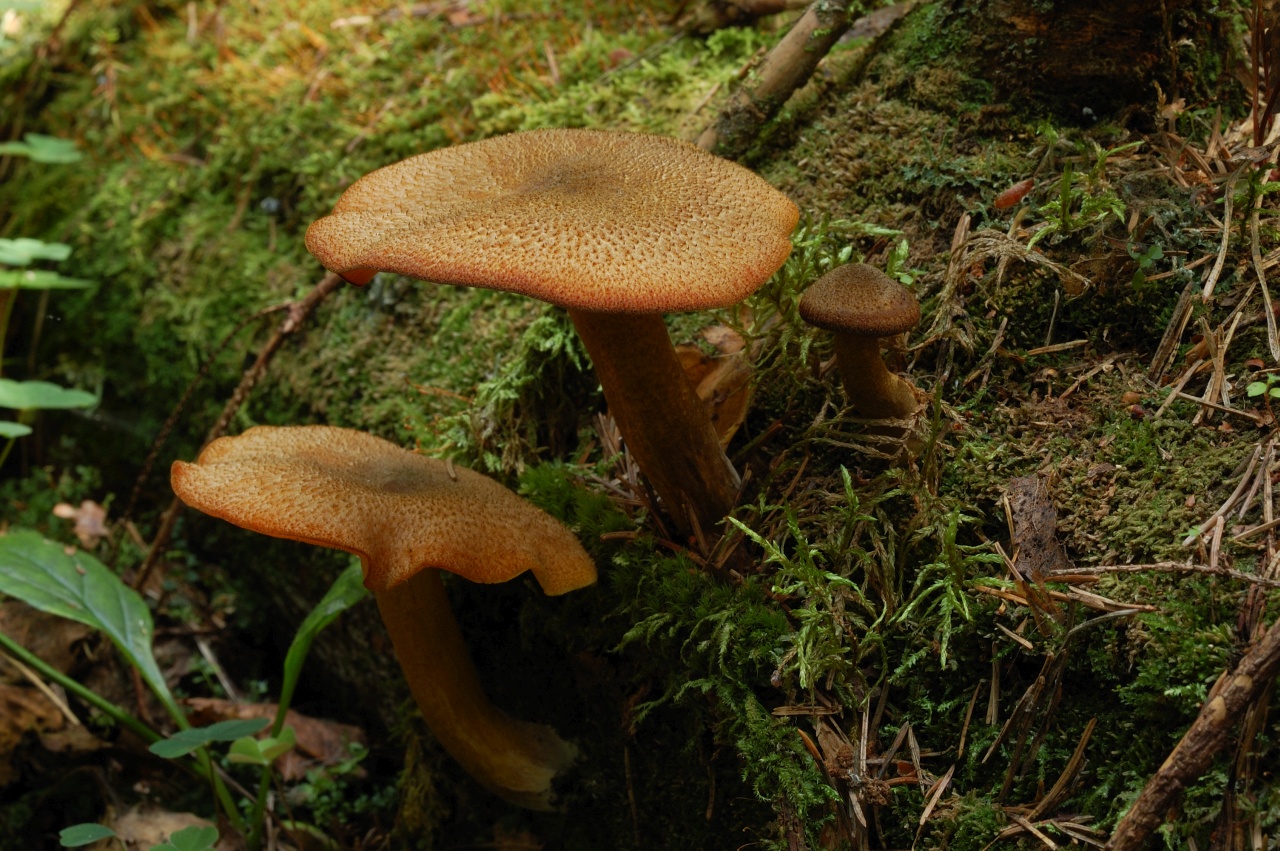
A bright, noticeable yellow-red row is easily recognizable, but, nevertheless, it has twins similar to it:
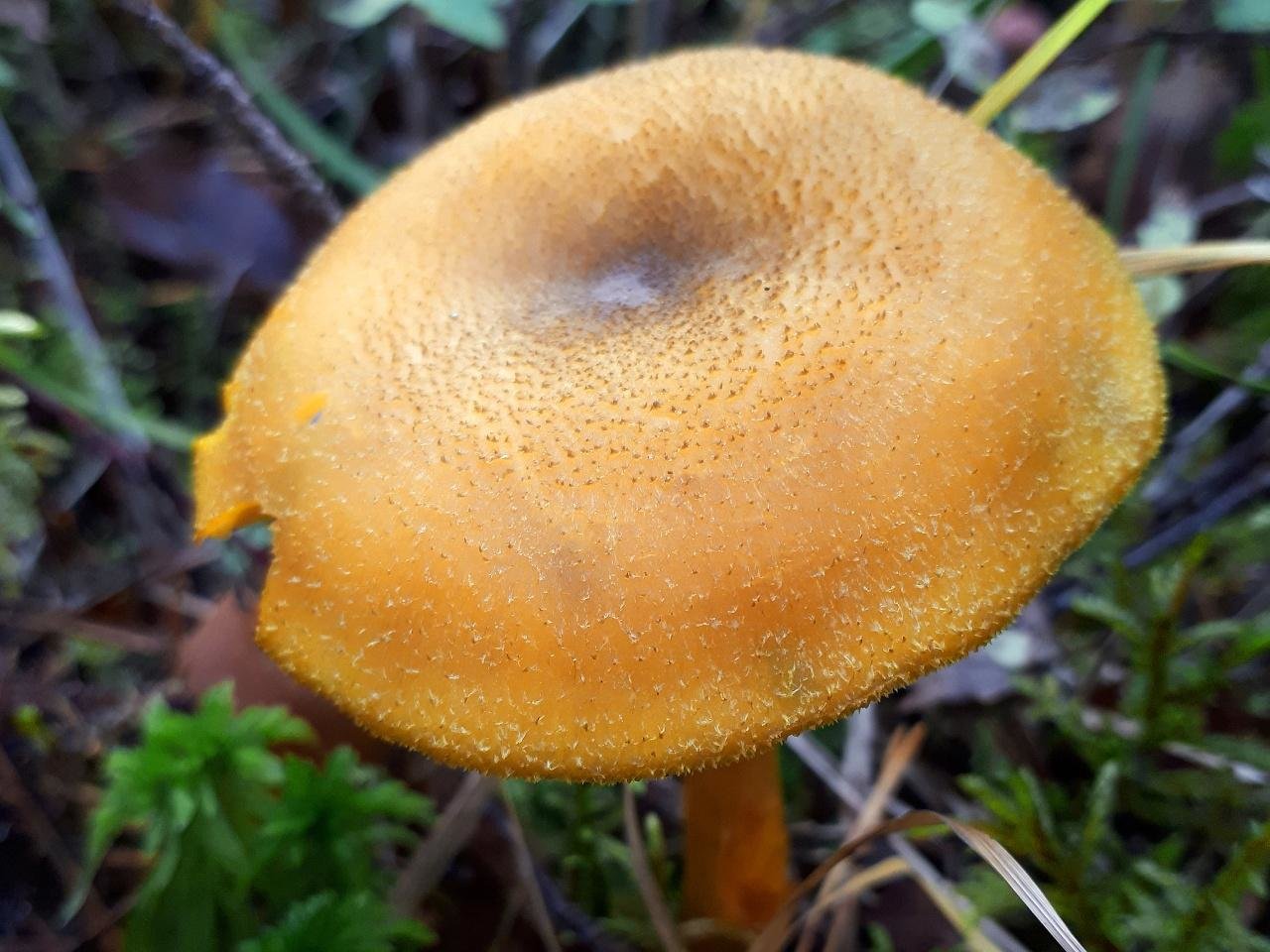
- the row is yellow or decorated (Tricholomopsis decora) - it is much less common, has a smaller size, there are no red scales on its cap. It is also conditionally edible, has a pleasant woody smell and a bitter taste. Requires preliminary boiling.
- Brick-red false honey fungus (Hypholoma sublateritium) is a poisonous and very bitter mushroom. It differs in a ring on the leg and the remains of a fibrous blanket from the bottom of the cap. The plates are not yellow, but grayish, creamy, olive, noticeably darkening with age.
Yellow-red ryadovka is a little-known conditionally edible mushroom with a bitter pulp. Experienced amateur pickers confidently find it in pine forests and, after the necessary processing, successfully include it in mushroom assortments.
Dirty row (Lepista sordida)
- Other names for the mushroom:
- Weed row
- Titmouse
- Lepista dirty
- Lepist weed
Other names:
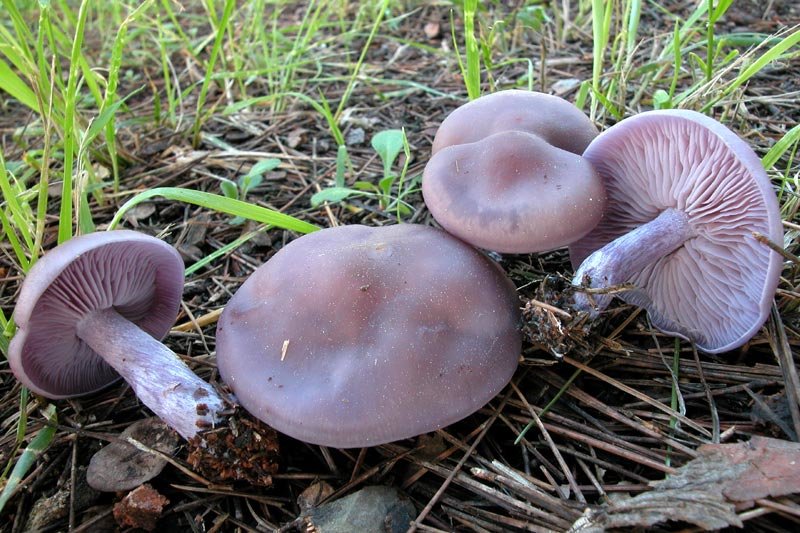

Dirty Ryadovka (Lepista sordida) is a poorly studied mushroom belonging to the Tricholomov family (Ryadovkov) and the Ryadovok genus.
External description
Dirty row (Lepista sordida) is a mushroom that grows singly or in small groups. In colonies, the fruiting bodies of this species grow together with the base of the legs.
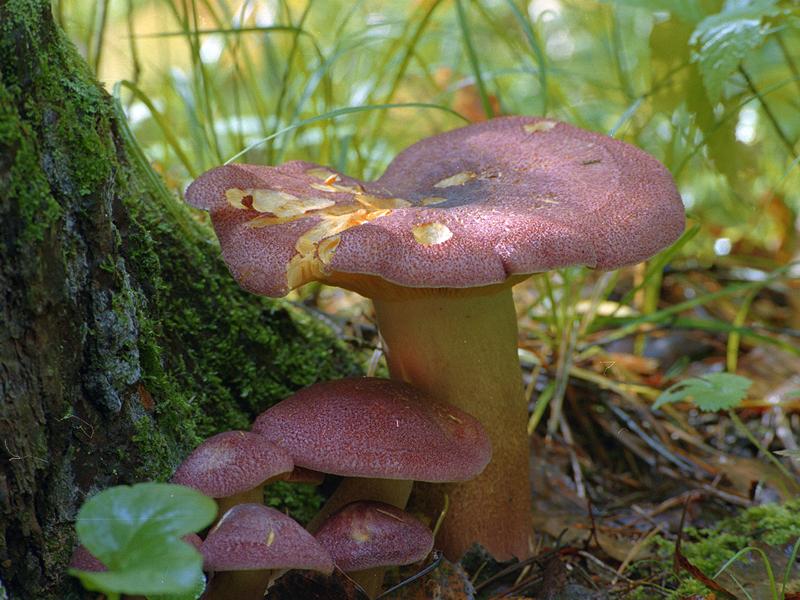
The cap of this mushroom can be 3-8 cm in diameter. Its shape in young mushrooms is more often spherical, and in mature fruiting bodies it becomes widespread, characterized by a lilac or brown-purple hue, and eventually loses the brightness of colors. It can also be brownish or red-brown in color, slightly ribbed, has barely noticeable stripes on the surface. In its central part, a tubercle is visible in mature mushrooms. At the edges, the head of a dirty row can be wavy. In immature mushrooms, the edges of the cap are often turned up, gradually straighten, becoming wavy, and even when ripe can even be bent upward. The mushroom pulp near the dirty ryadovka is very thin, oversaturated with moisture, has a pleasant aroma and taste, and is characterized by a gray-violet color.
The fungal hymenophore is lamellar, and its constituent elements (plates) grow together with the surface of the fruiting body with a tooth, have a dirty purple hue, and are often located. The spore powder in this type of mushroom is characterized by a pinkish color.
The leg of a dirty row reaches 4-6 cm in length, and can be from 0.7 to 1 cm in thickness. It is characterized by strong fiber and the same color as the cap, has a cylindrical shape, located in the center. Near the base, the leg may expand slightly. In young fruiting bodies of a row of dirty, the leg is dense, complete, and in ripe mushrooms, it becomes empty inside.
Season and habitat of the mushroom
Grows in gardens, orchards, parks, squares, on the edges of forests or not deep in light forests. Can be found in meadows. It grows in a group / bunch of several fruiting bodies, rarely occurs singly.
The most active fruiting of this type of rowing begins in July and continues until the end of September.

Edibility
Despite the low popularity among fans of mushroom gathering, the dirty ryadovka mushroom belongs to the edible category. It is advisable to boil it before eating, but the broth from it is not suitable for consumption and therefore it is better to pour it out. Also, dirty rows are delicious when pickled.
Similar types and differences from them
In appearance, the dirty rowing (Lepista sordida) looks like a purple rowing. Its main difference from the named mushroom is thinner, not fleshy pulp and fragility. In addition, in dirty rows, the caps fade, and the pulp of the purple row has a characteristic smell of fruit. The dimensions of the fruit bodies in dirty rows are smaller than in purple ones. The purple row forms "witch circles" and rows, and the Dirty one - in small heaps.
Edible and poisonous mushrooms: how to tell?
Edible and poisonous mushrooms: how to tell?
Before going into the forest, you need to understand how to distinguish between edible and poisonous rows. Most varieties are safe and can be fried or boiled for food.
But how can you tell the difference between edible and poisonous mushrooms? It is very difficult to do this, since outwardly mushrooms are very similar, so it is important to learn the characteristic features of each species.
- Poisonous mushrooms have flat, almost all species have perfectly even white caps. But there are representatives who have a tubercle. The main difference between poisonous rows is an unpleasant pungent odor that makes you even frown.
- Edible mushrooms look attractive. Their hats and legs are of different colors (pink, purple, purple, gray, and others). Bright plates of beautiful color are located under the head. The flesh of the edible mushroom will be the same shade as the plates under the cap.
Dangerous false doubles
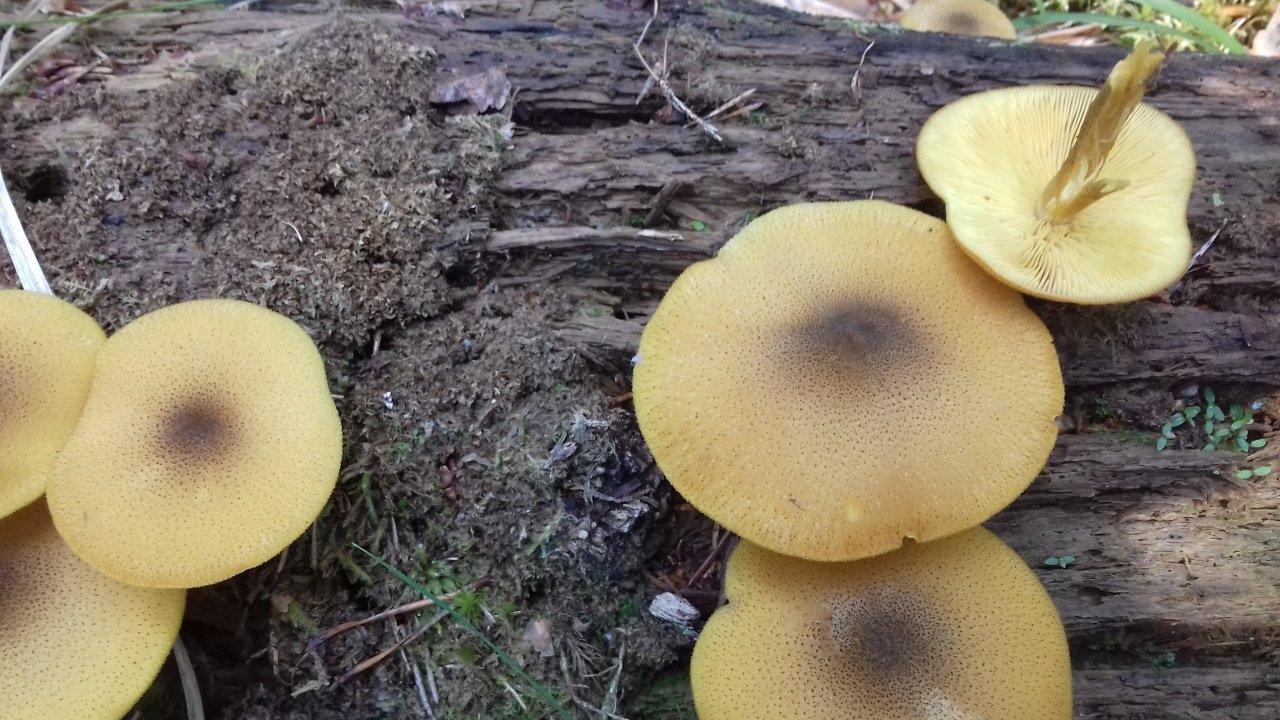
Red honey mushrooms can be easily confused with other types of mushrooms, edible and not only.
Pay attention to their differences in the table and in the photo:
| Peculiarities | Row olive yellow
|
False honey agaric yellow-red
|
| Hat | The shape varies from convex to rounded-bell-shaped with a flat crown. Its diameter reaches 8 centimeters. The color of the cap is dark yellow, olive yellow, gray-yellow. And the scales are brown-brown | The shape of the cap is bell-shaped, later round. |
| Pulp | Thin, with a bitter taste and woody smell. | Dense, white with a yellowish tinge, sometimes dirty yellow or brownish yellow. It tastes a little bitter, smells nice, not rich. |
| Leg | The leg is dense, curved, with a thick base, scaly, yellow-brown in color. | Elongated, curved, fused from below with adjacent mushrooms. Its color is sulphurous yellow or with a brown tint. A characteristic difference is that there is a thin cobweb blanket covering the plates. The latter are gray, greyish-cream in color. |
| Growing places | Forests mixed with pine trees. They settle on rotten wood. Gather in small groups. Fruiting occurs in August-October. | Deciduous, less often coniferous forests. They grow in summer and autumn in large groups on stumps and fallen trees. Fruiting en masse in September. |
| Toxicity | Edible species | Inedible, poisonous mushroom |
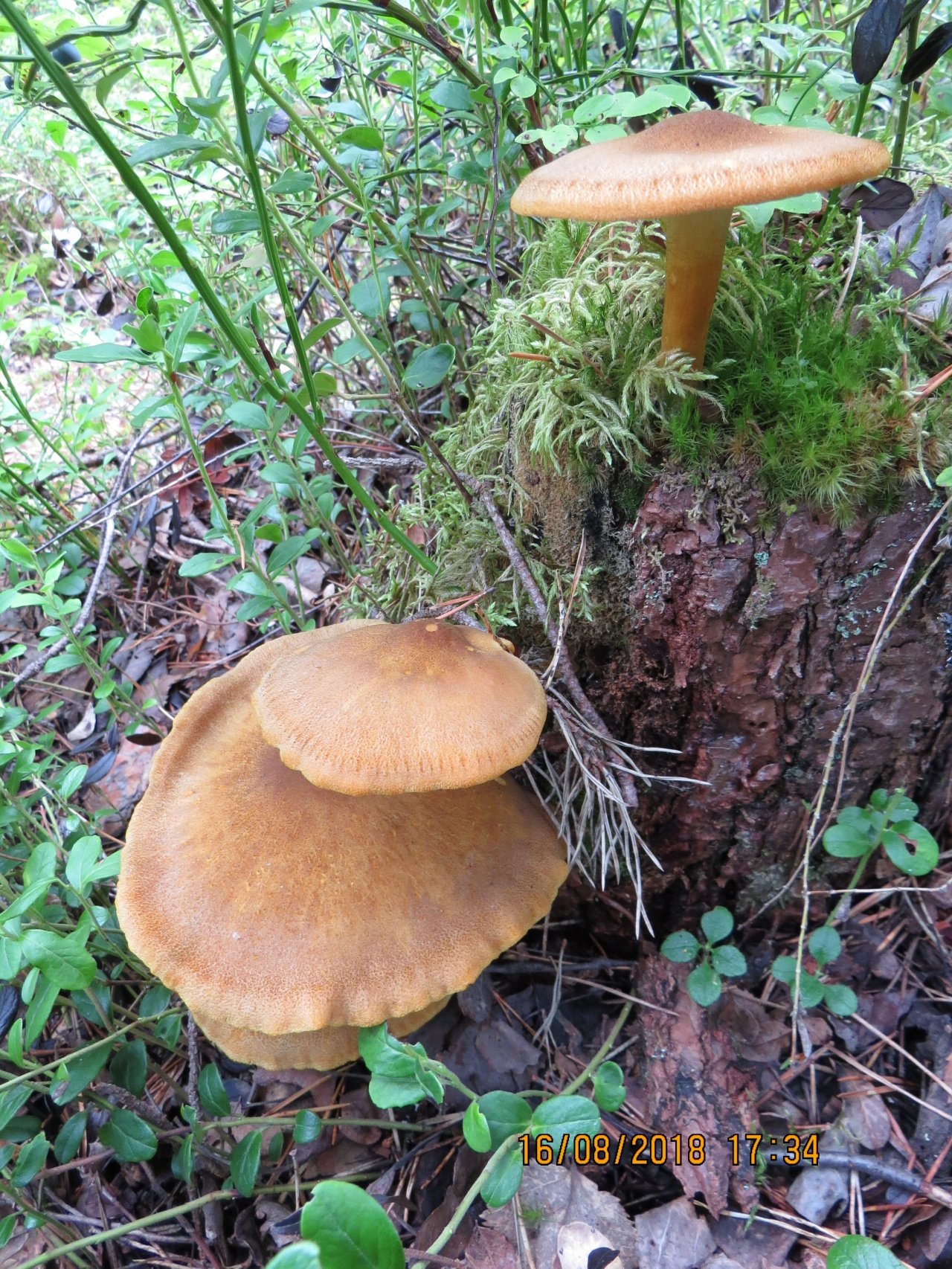
Characteristics of the mushroom ryadovka
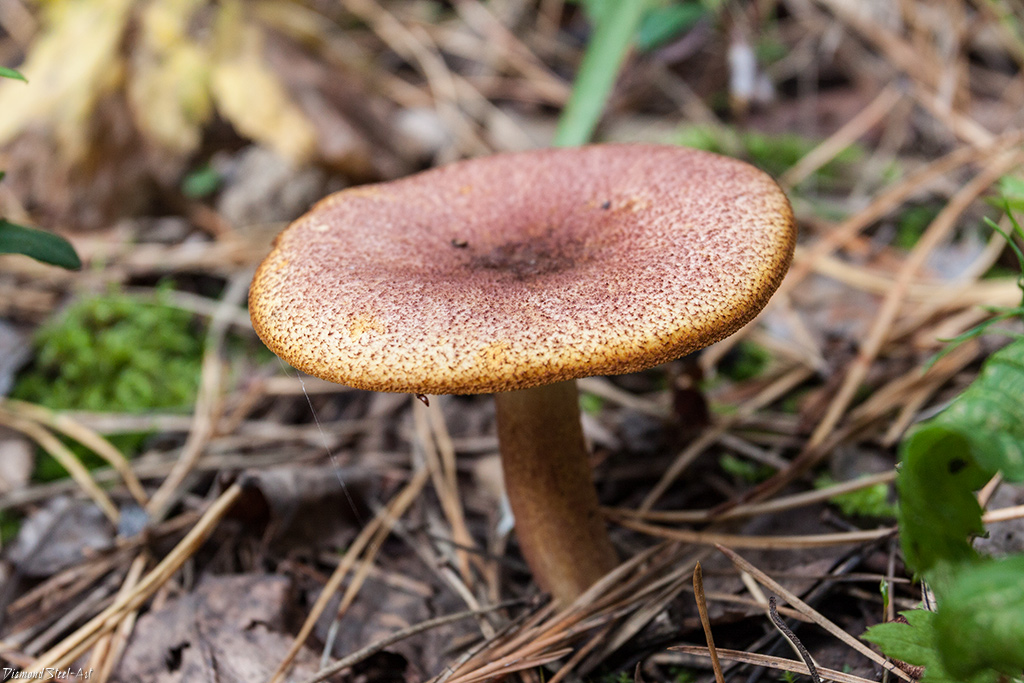
Hat
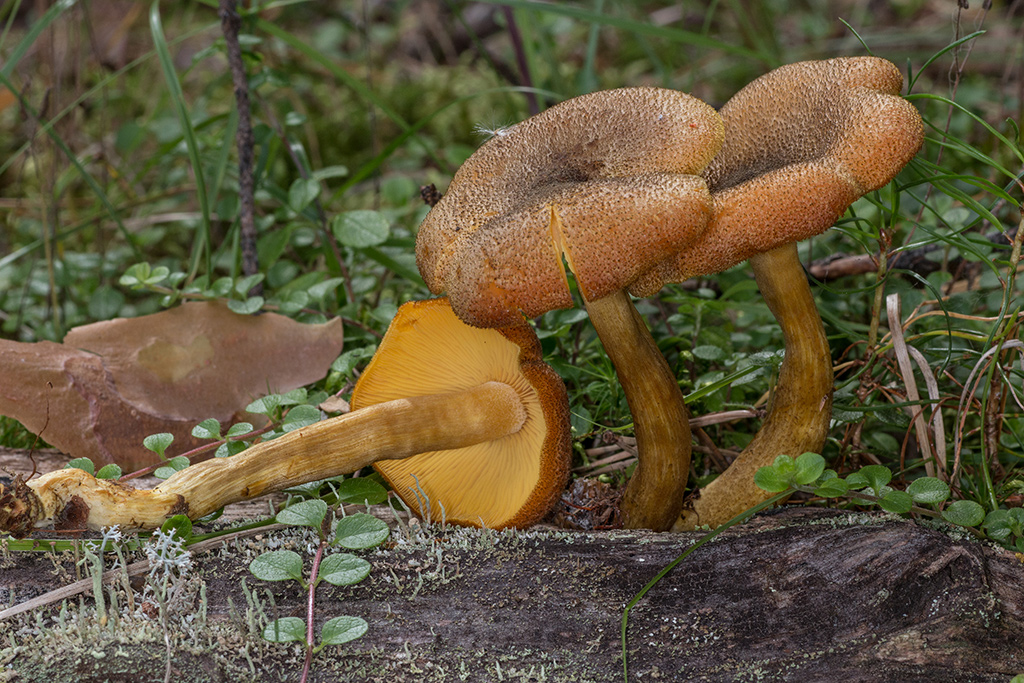
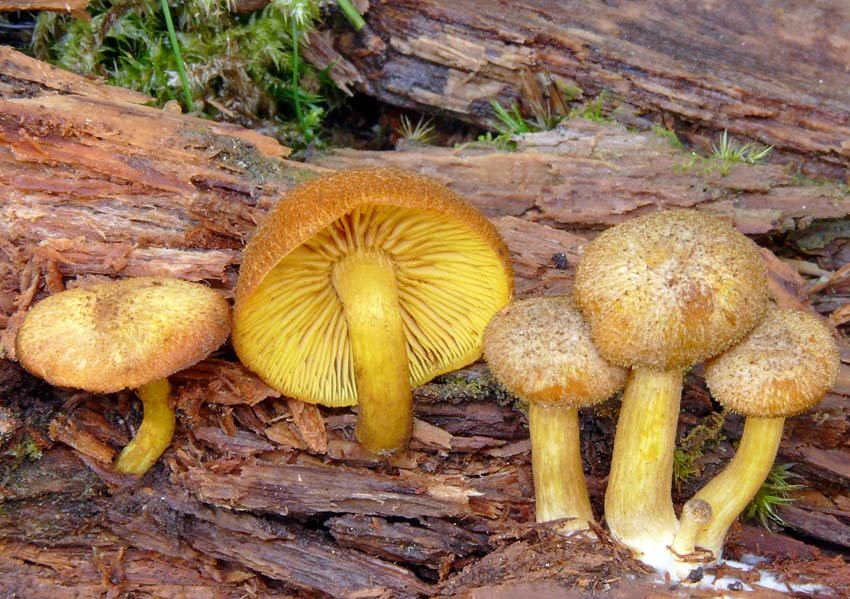
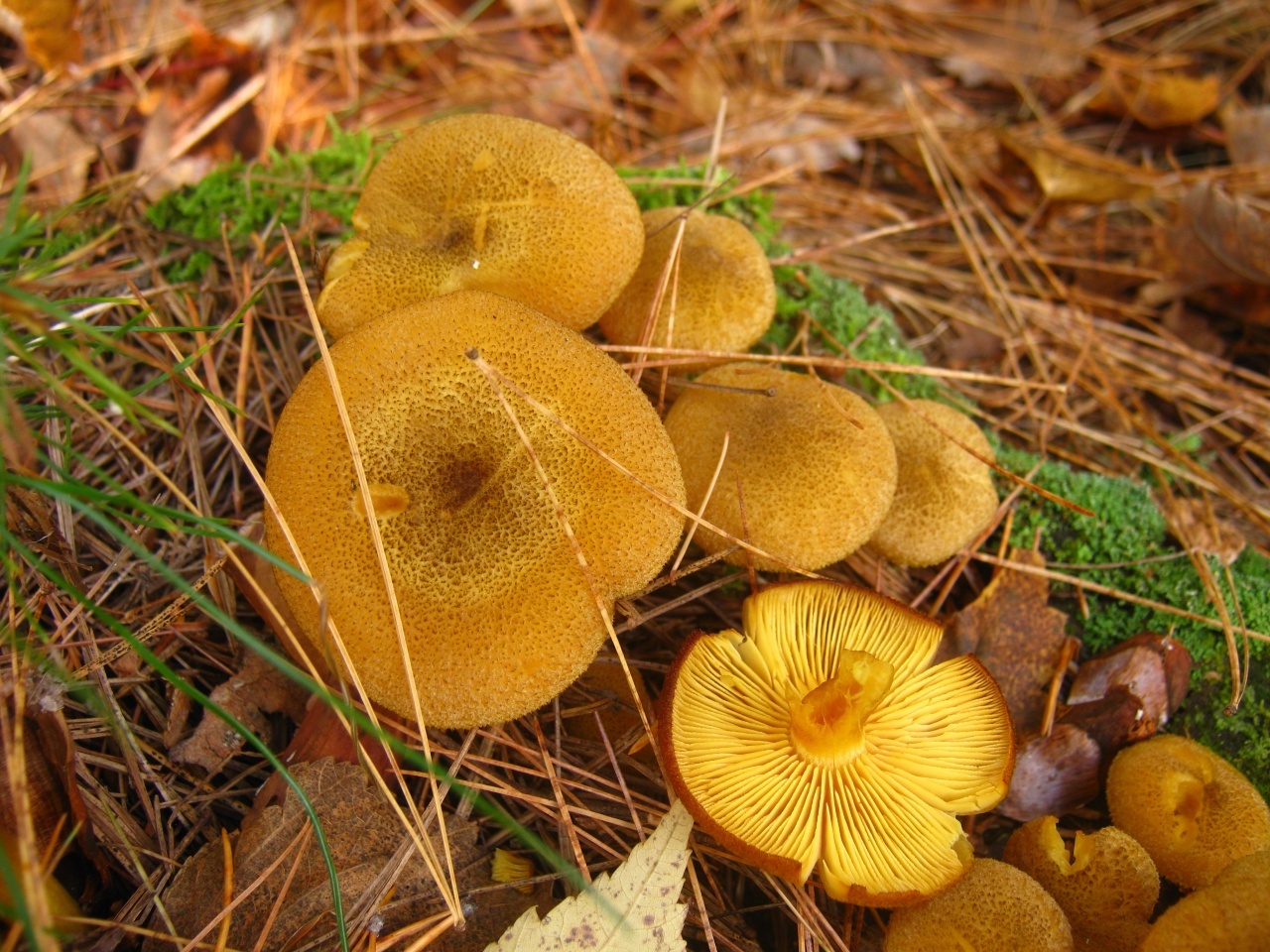
The hats in the rows are 6-15 cm in diameter, they are painted in different colors, occasionally they are white, in young mushrooms they are hemispherical or convex, later become flat-spread, the edge is wavy, wrapped inward or outward. The surface is fibrous or scaly.
Pulp
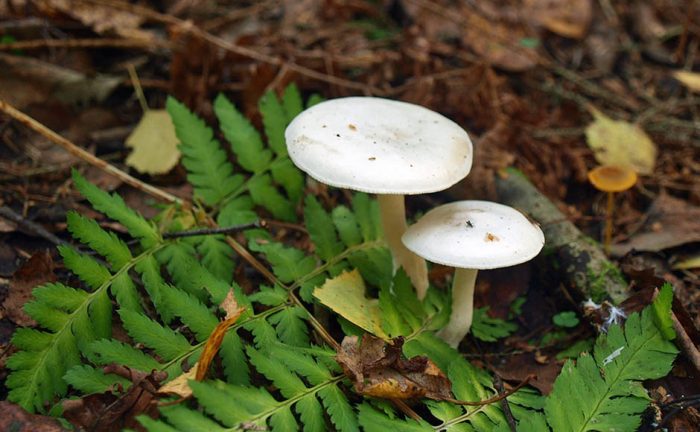

The pulp is white or yellowish in color, thick, with a flour smell and a weak mushroom taste. On the cut, the color does not change.
The leg is dense, central, about 10 cm high, up to 3 cm thick.The base of the stem is tuberous, thickened, felt. The color of the leg matches the cap.


























































