Definitioner
- Paraphysis (Paraphysis)
-
Multicellular or unicellular non-spore-bearing outgrowths in some algae, fungi and mosses, which protect the genitals or spore-bearing organs from drying out and mechanical damage.
- Paraphysis (Paraphysis)
-
Multicellular or unicellular non-spore-bearing outgrowths in some algae, fungi and mosses, which protect the genitals or spore-bearing organs from drying out and mechanical damage.
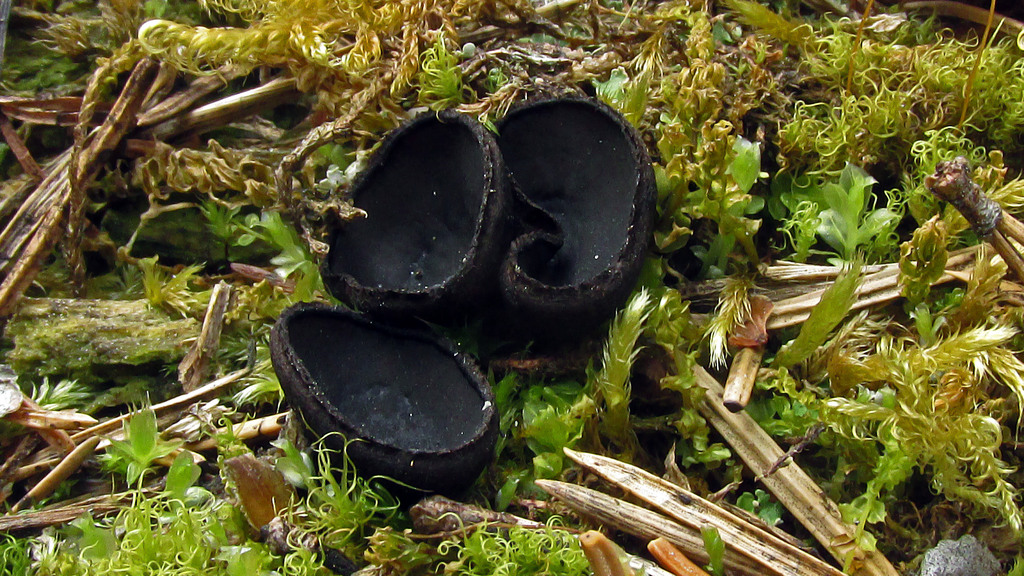
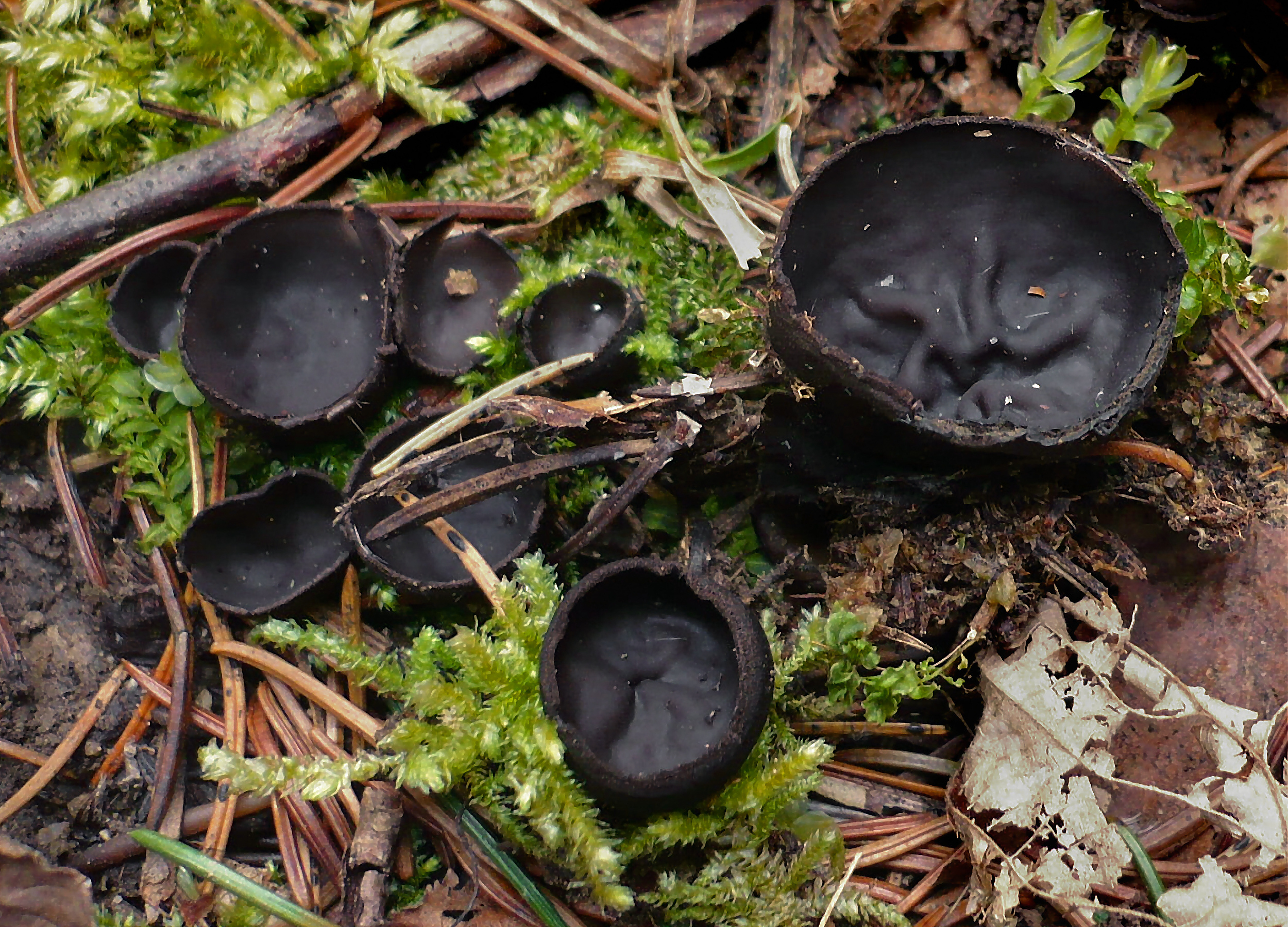
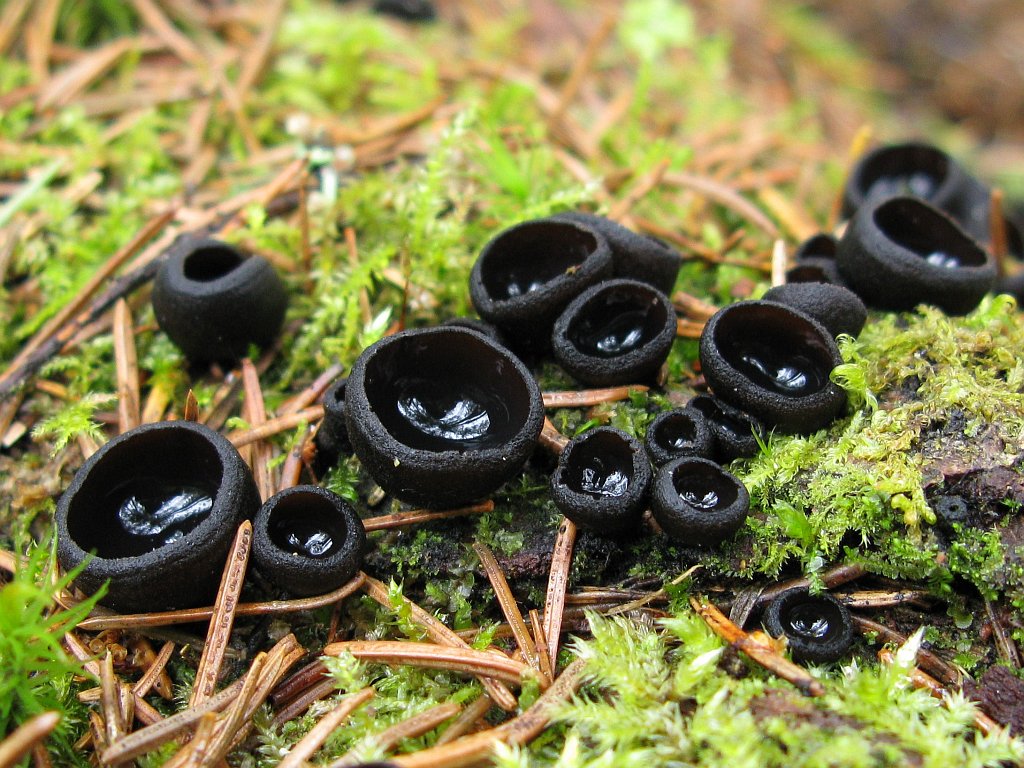
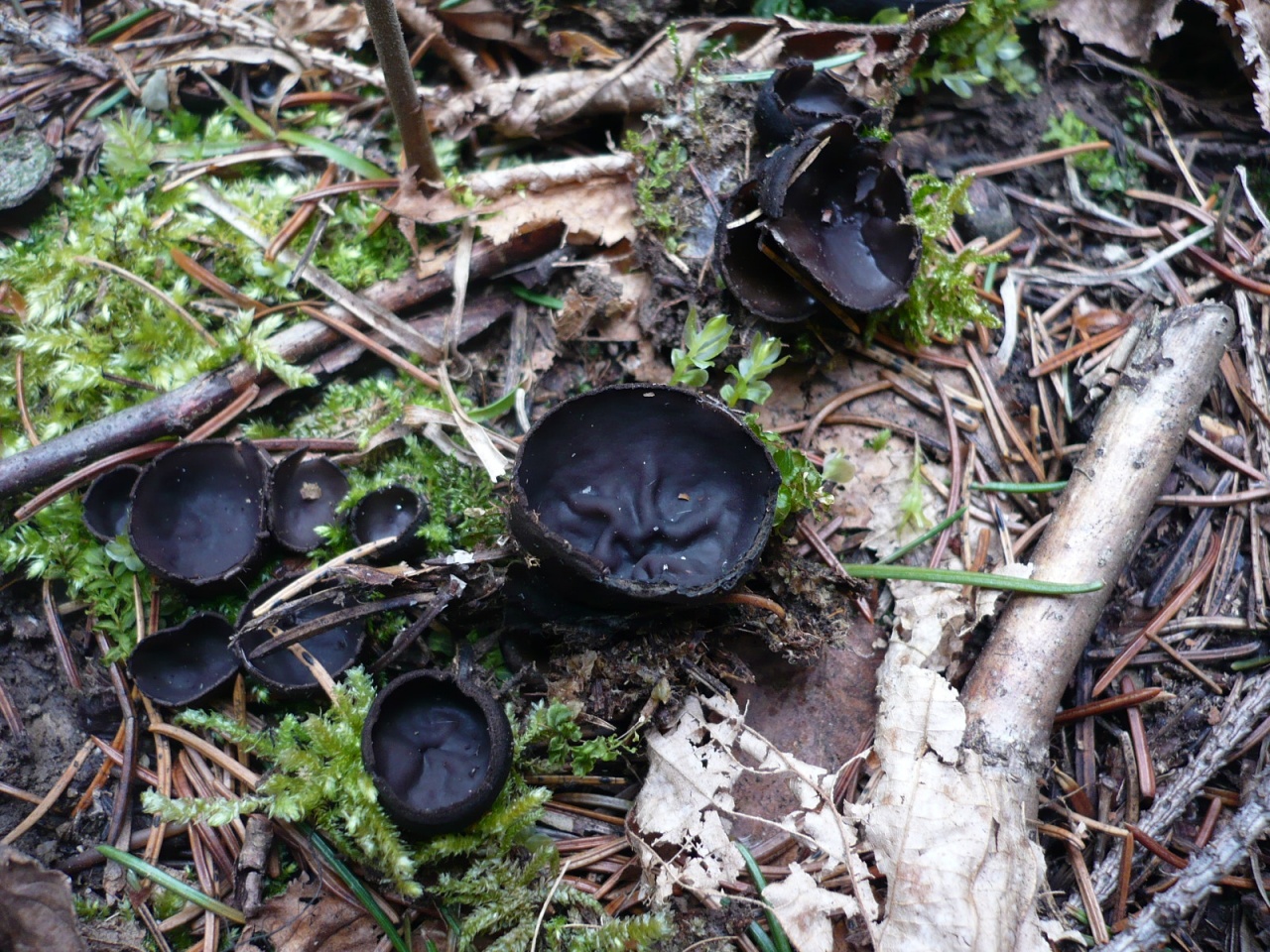
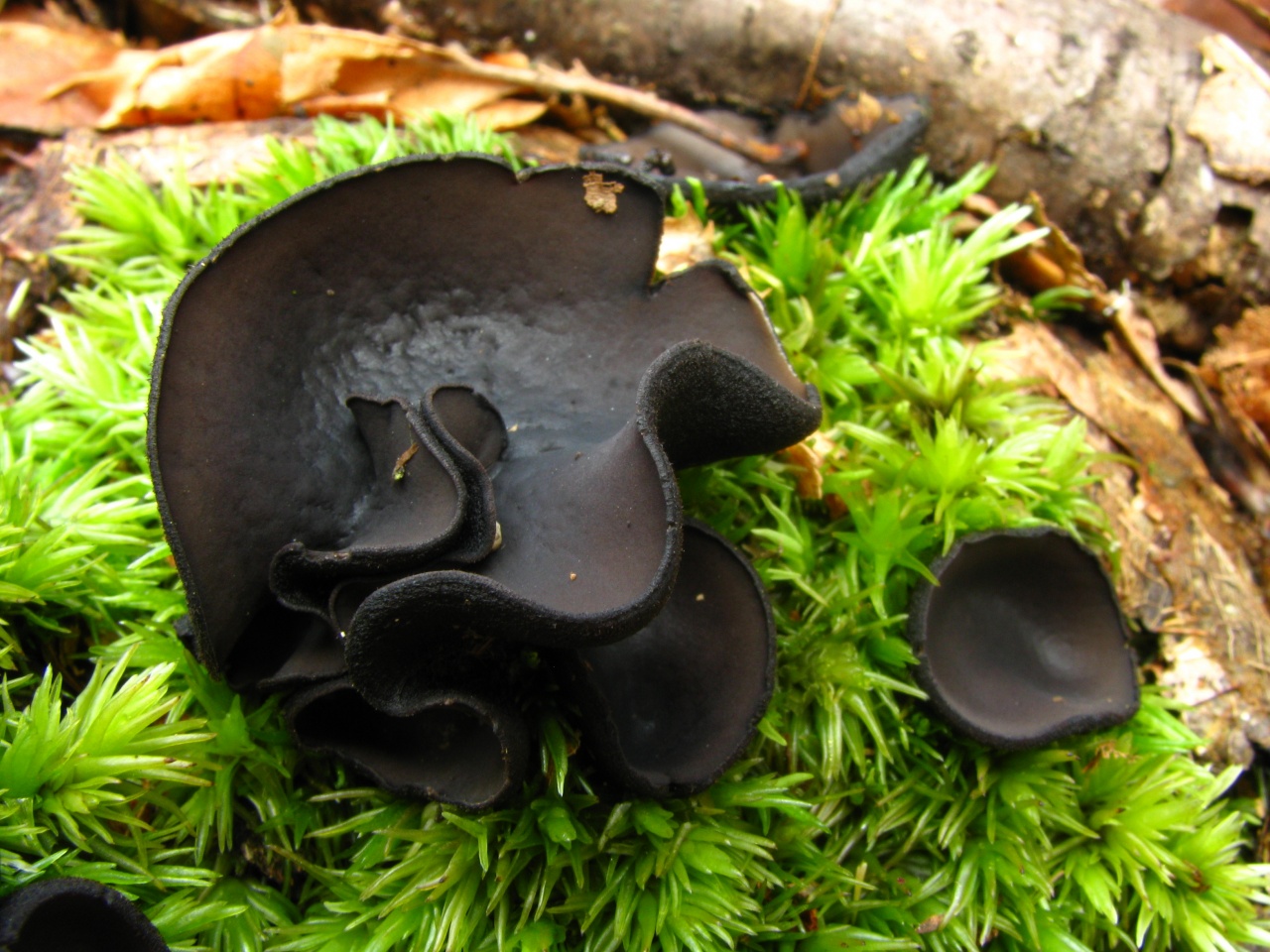
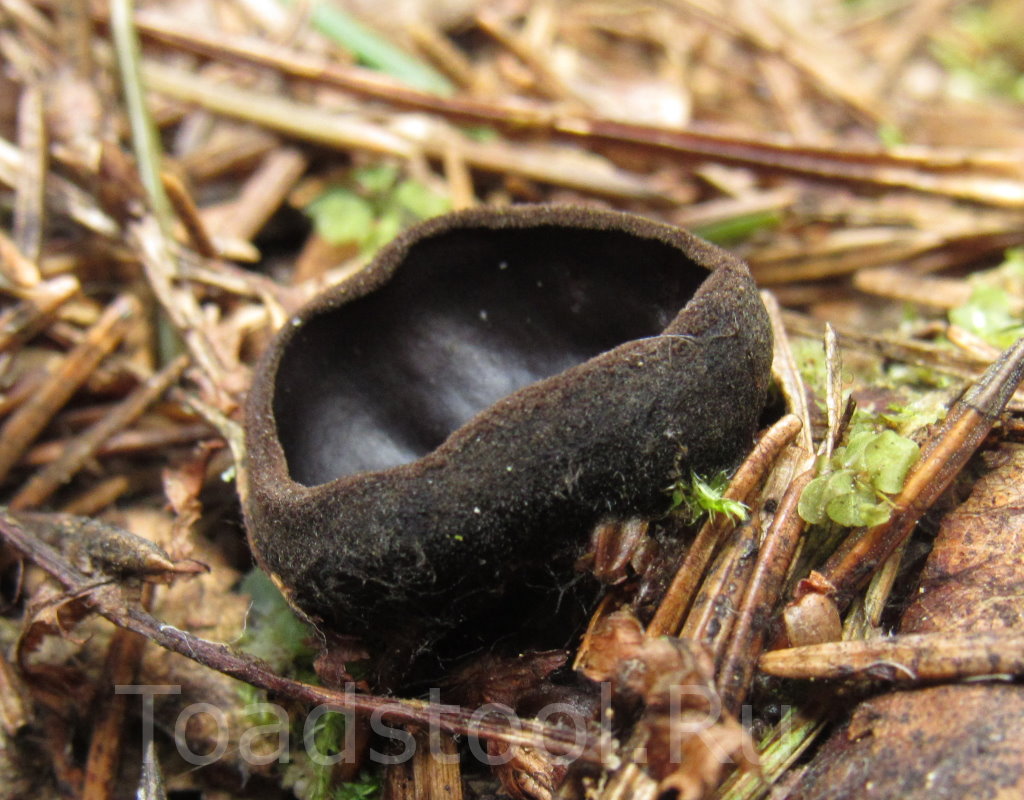
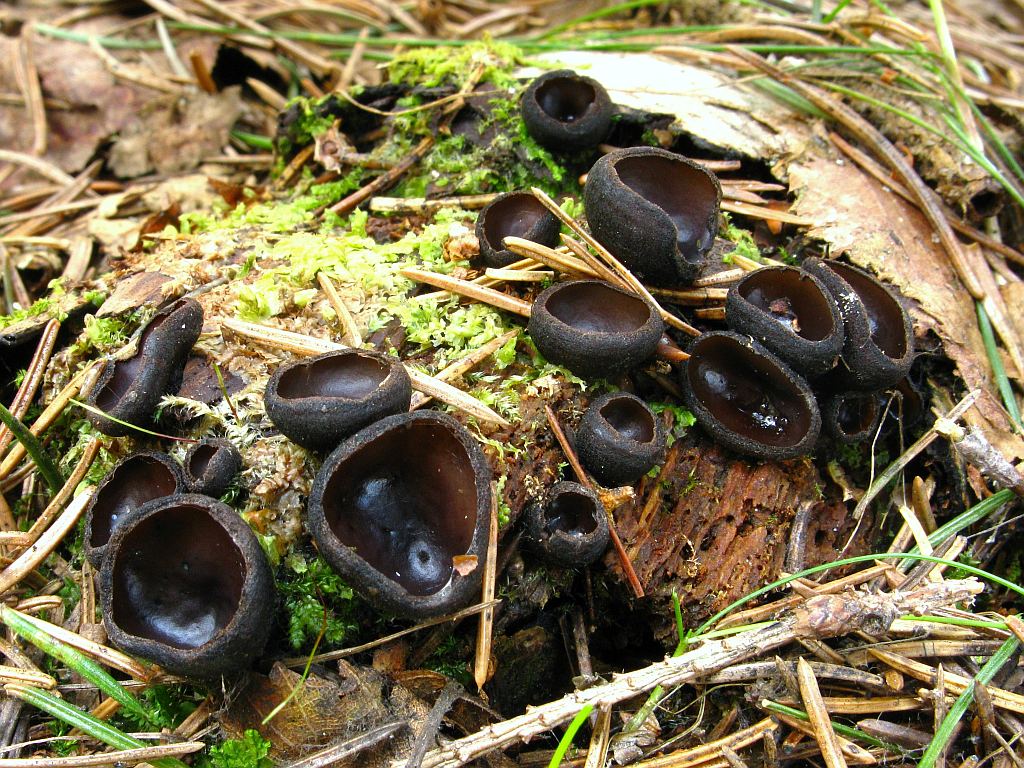
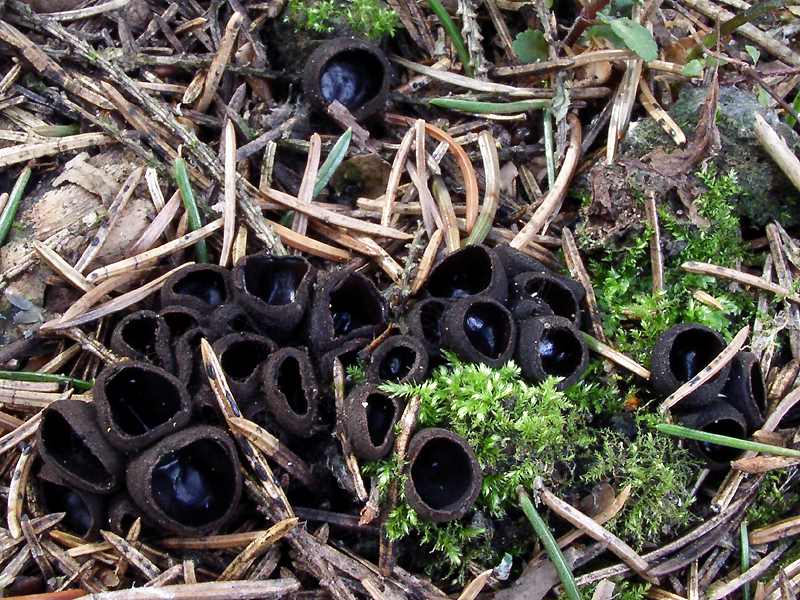
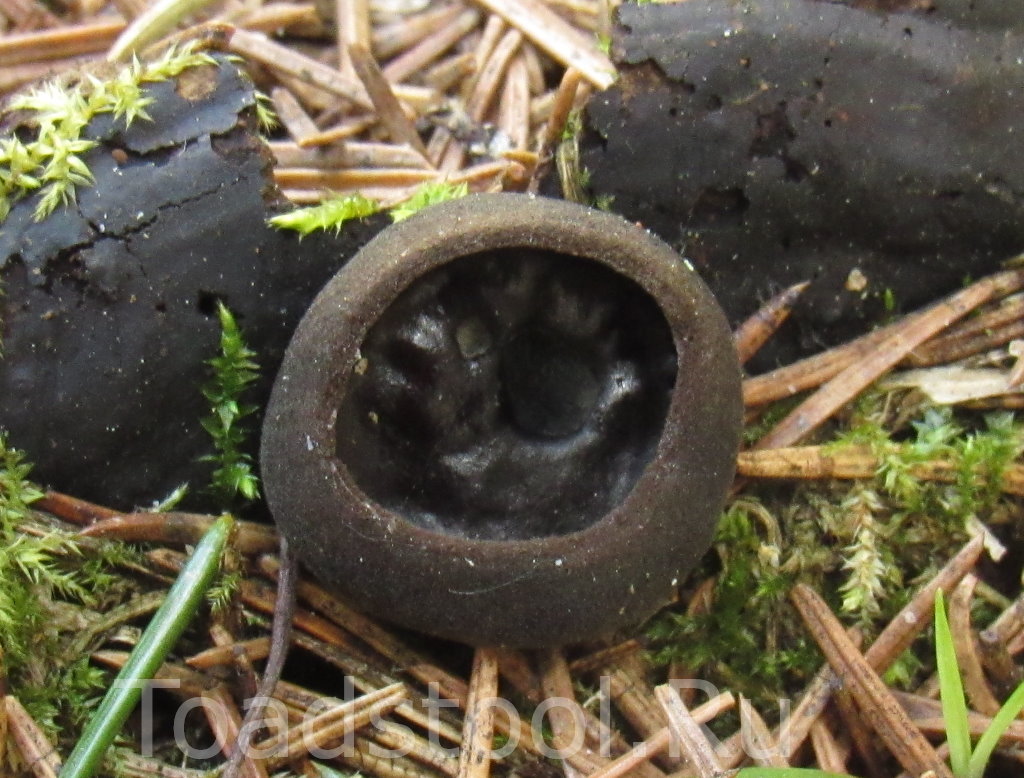
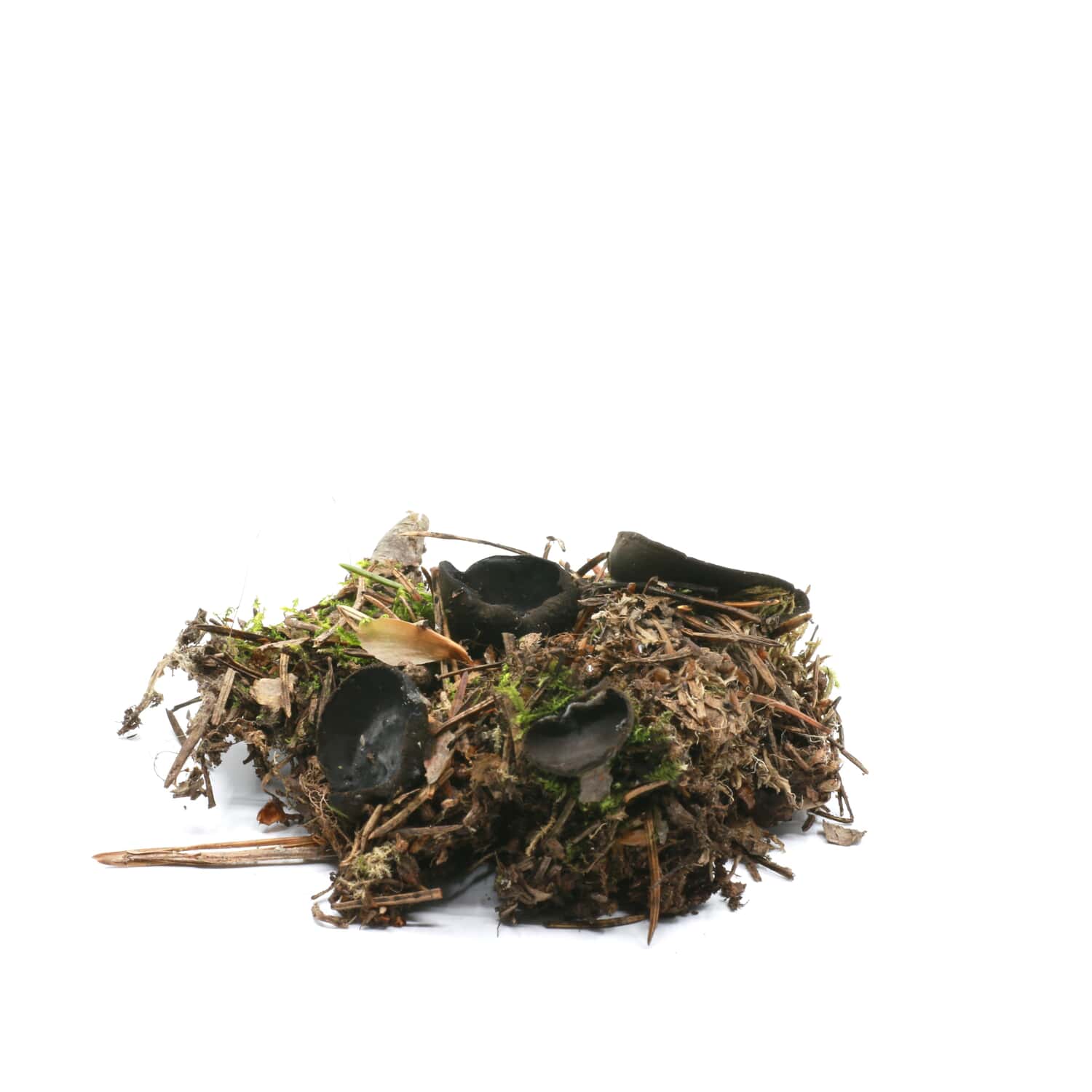
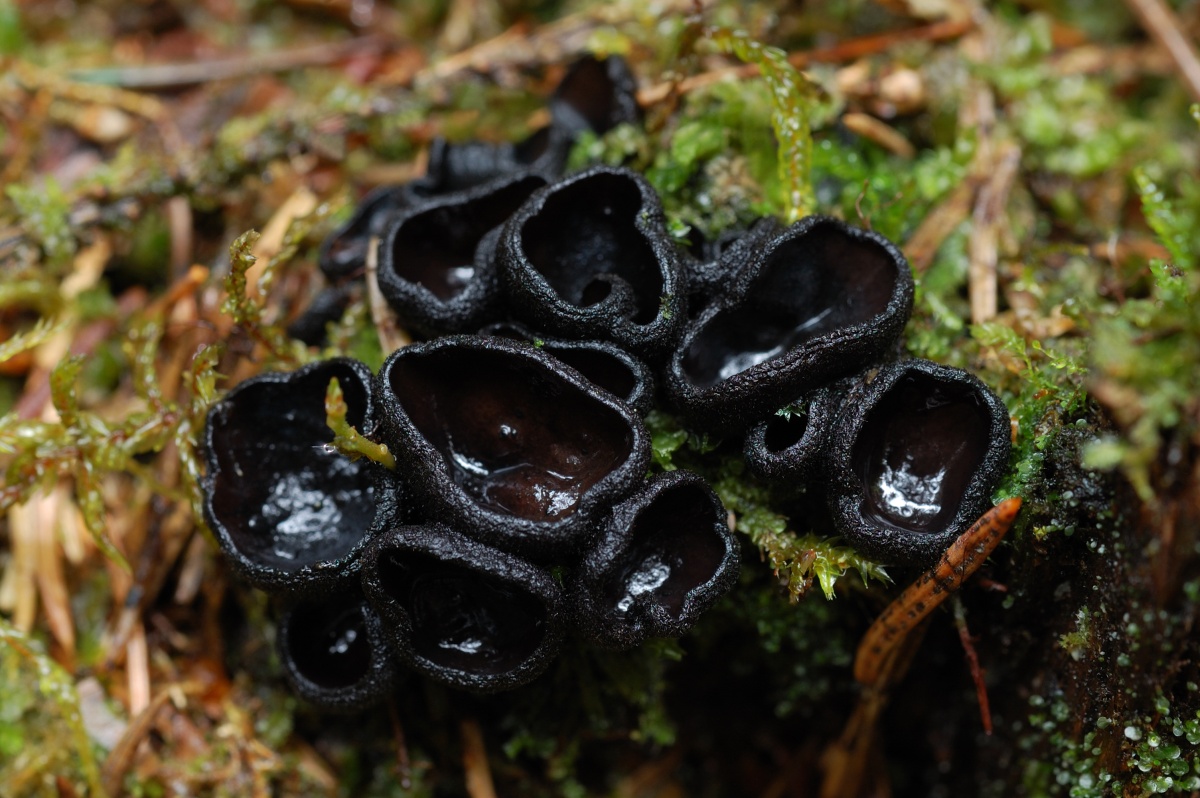
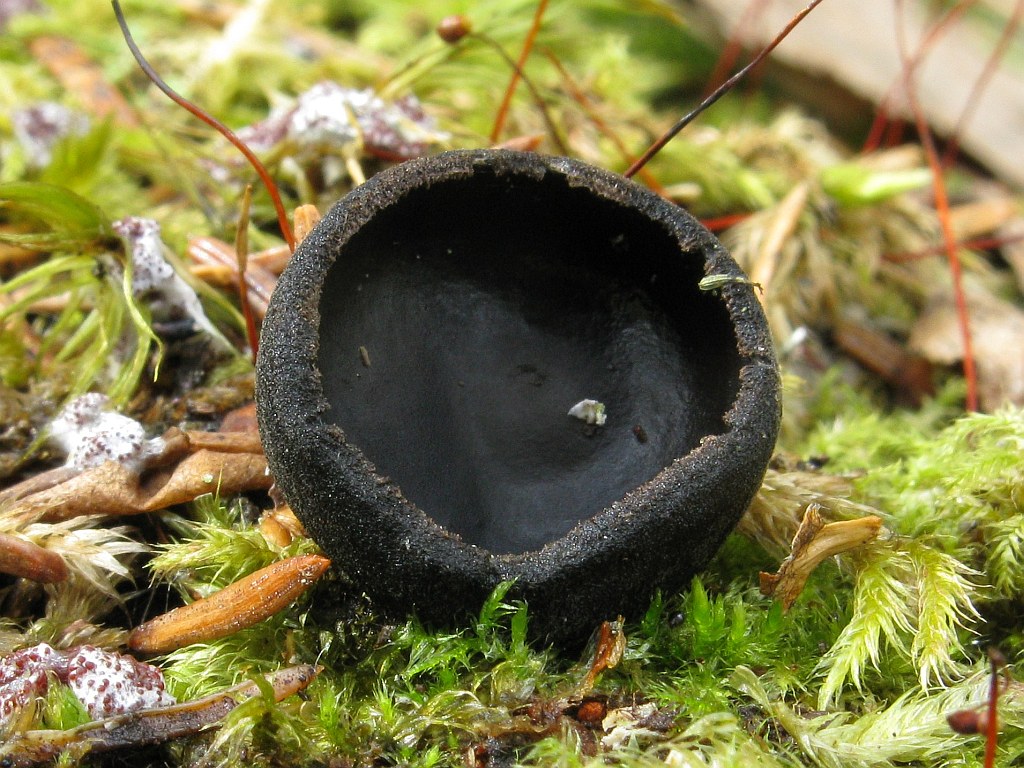
- Apothecia (Apothecia)
-
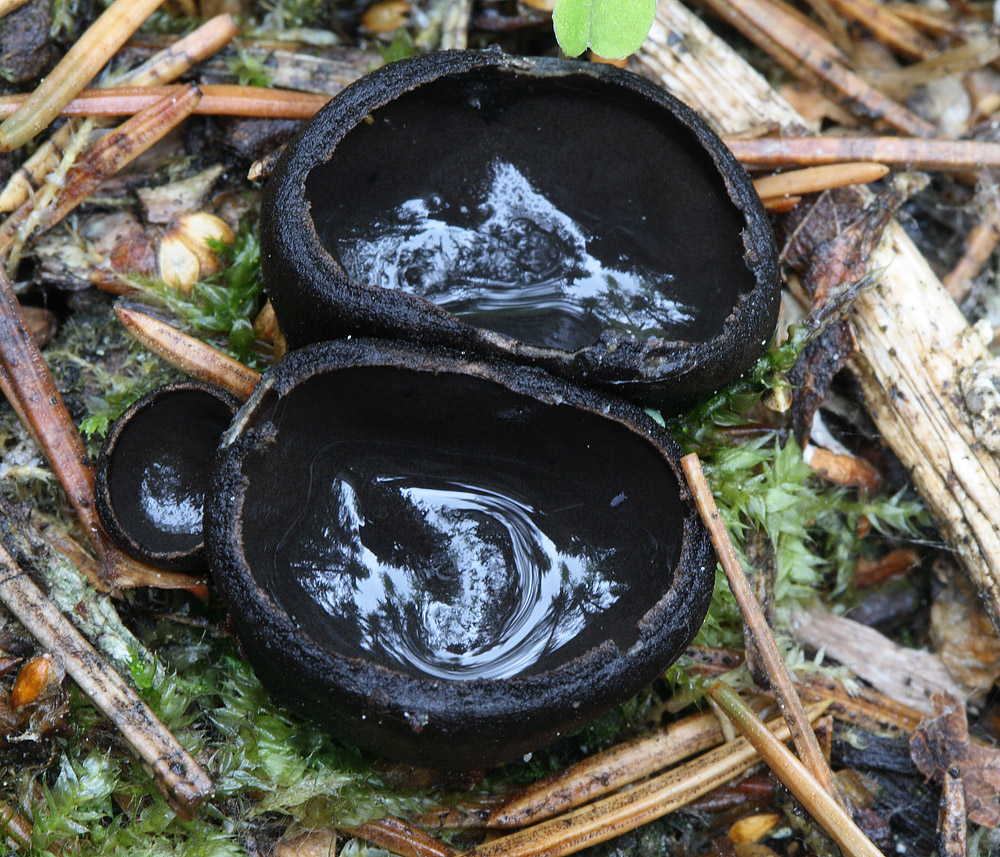
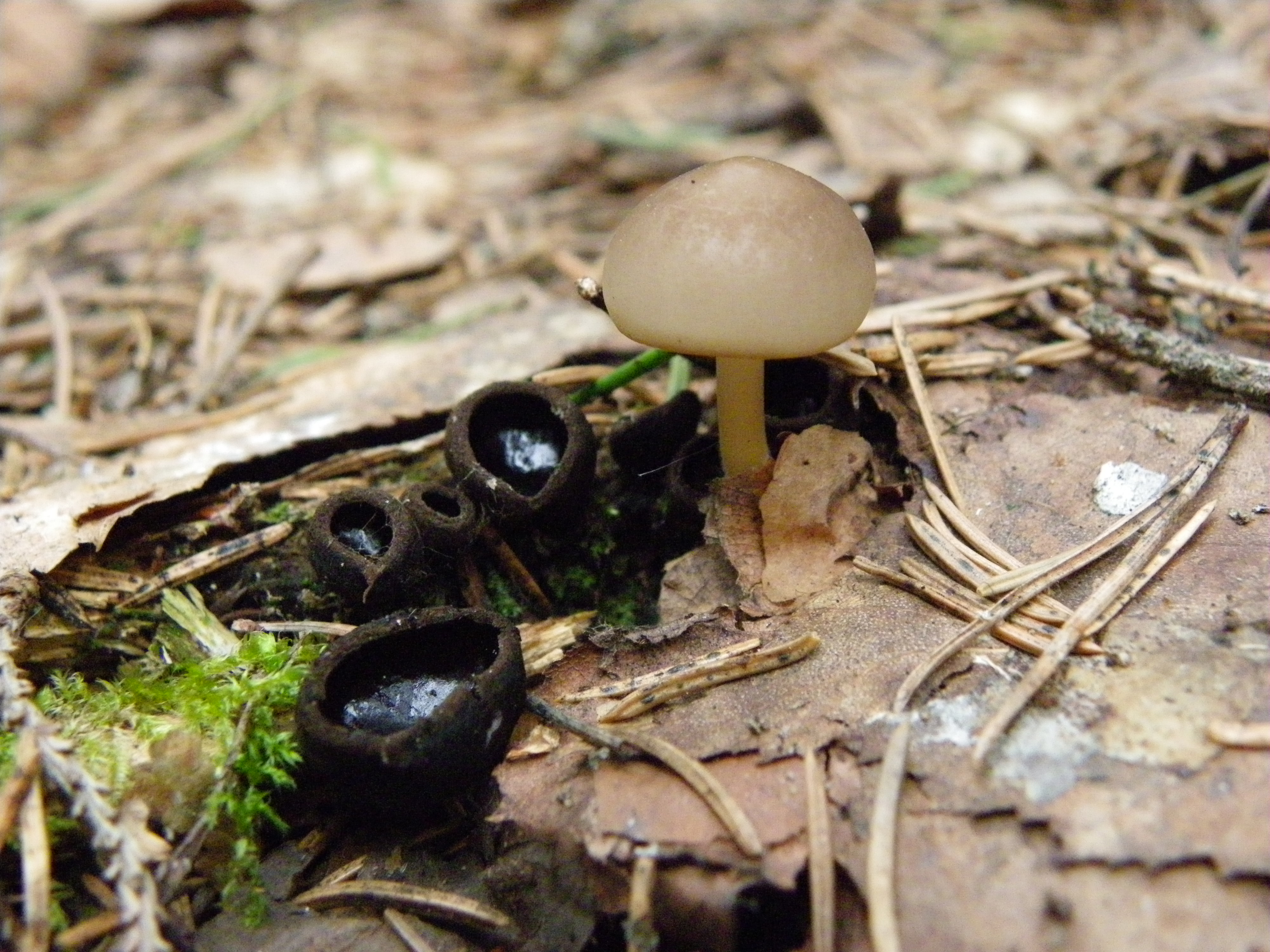
In the type, a completely open ascocarp, often saucer-shaped or goblet-shaped. On the surface of the apothecia there is an ordered hymenial layer, consisting of bags and sterile elements - the paraphysis, under it lies the subhymenal layer, in which the asci develop, and everything else is made up of sterile hyphae of the pulp - the excipule. Apothecia is characterized by the simultaneous maturation of many asci and the active release of spores. Secondary closed apothecia are found in fungi, whose fruiting bodies develop underground, for example, in truffles.
See Ascocarp, Hymenium, Discomycetes, Paraphysis.
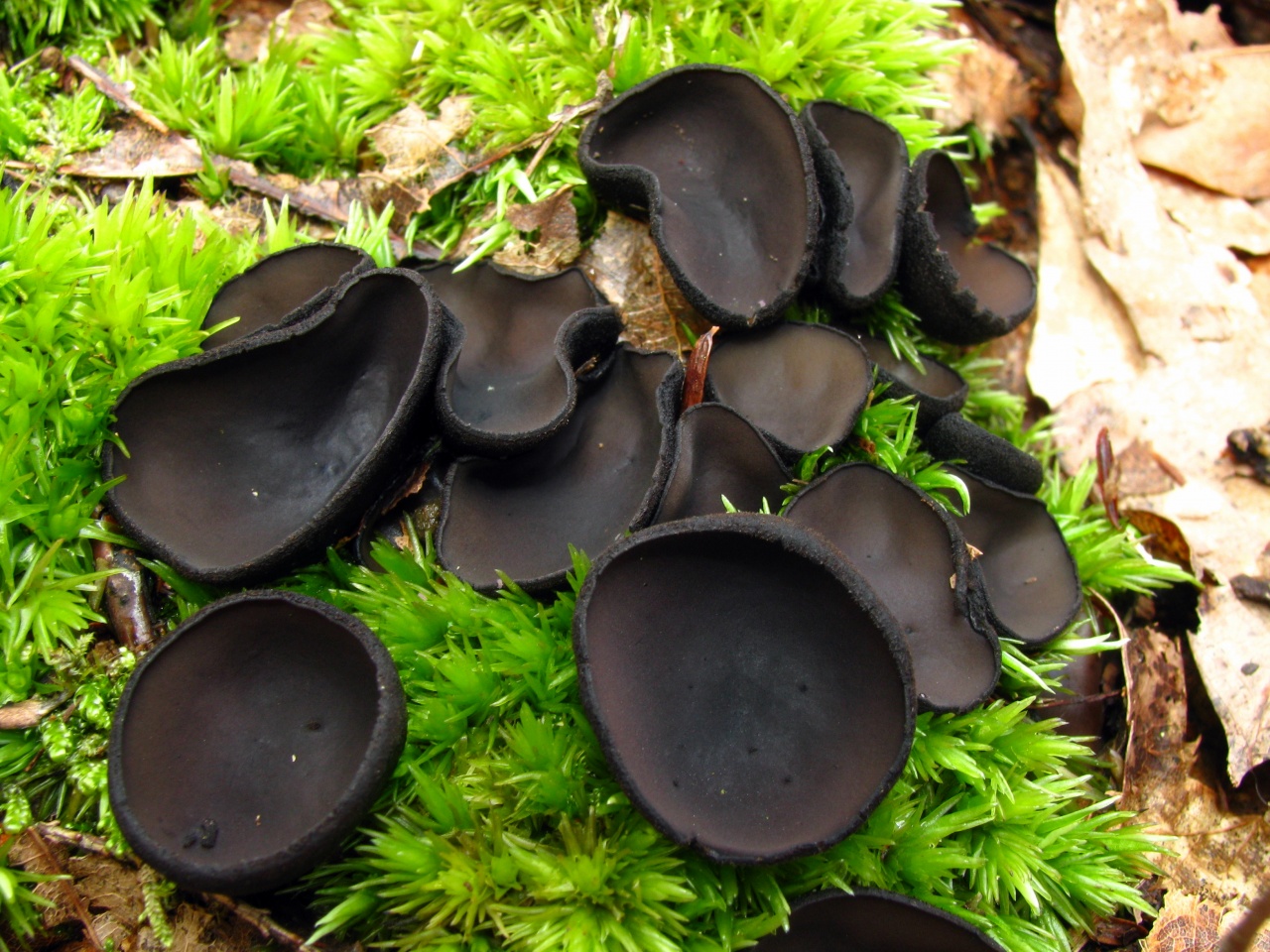
- Apothecia (Apothecia)
-
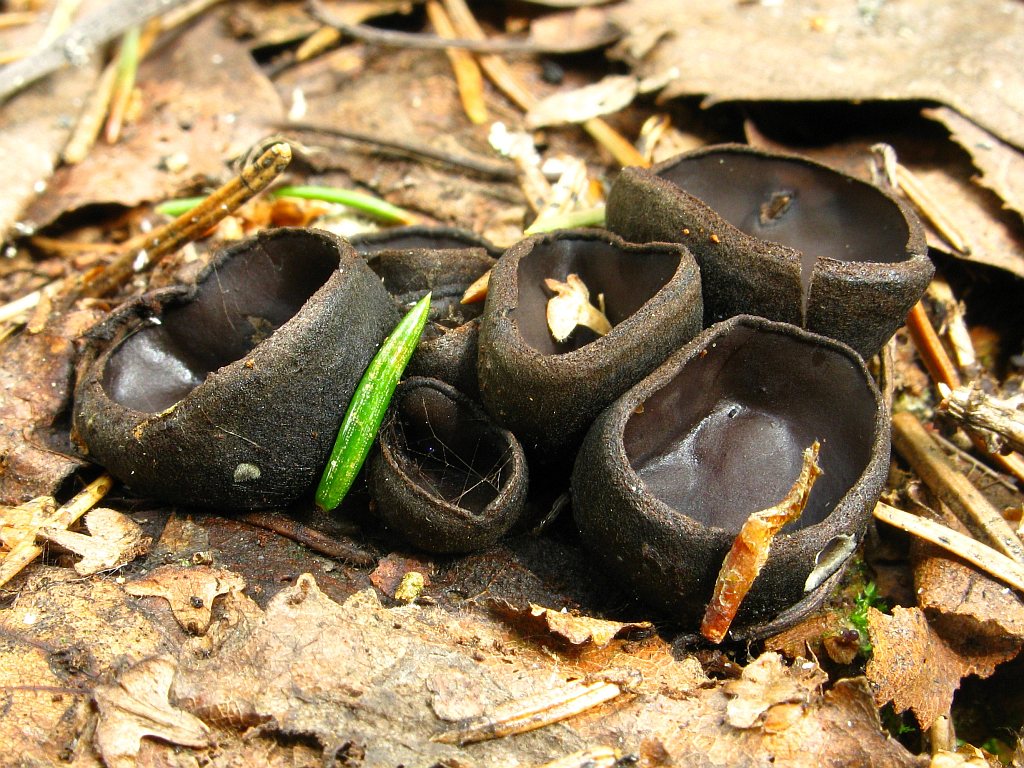
In the type, a completely open ascocarp, often saucer-shaped or goblet-shaped. On the surface of the apothecia there is an ordered hymenial layer, consisting of bags and sterile elements - the paraphysis, under it lies the subhymenal layer, in which the asci develop, and everything else is made up of sterile hyphae of the pulp - the excipule. Apothecia is characterized by the simultaneous maturation of many asci and the active release of spores. Secondary closed apothecia are found in fungi, whose fruiting bodies develop underground, for example, in truffles.
See Ascocarp, Hymenium, Discomycetes, Paraphysis.
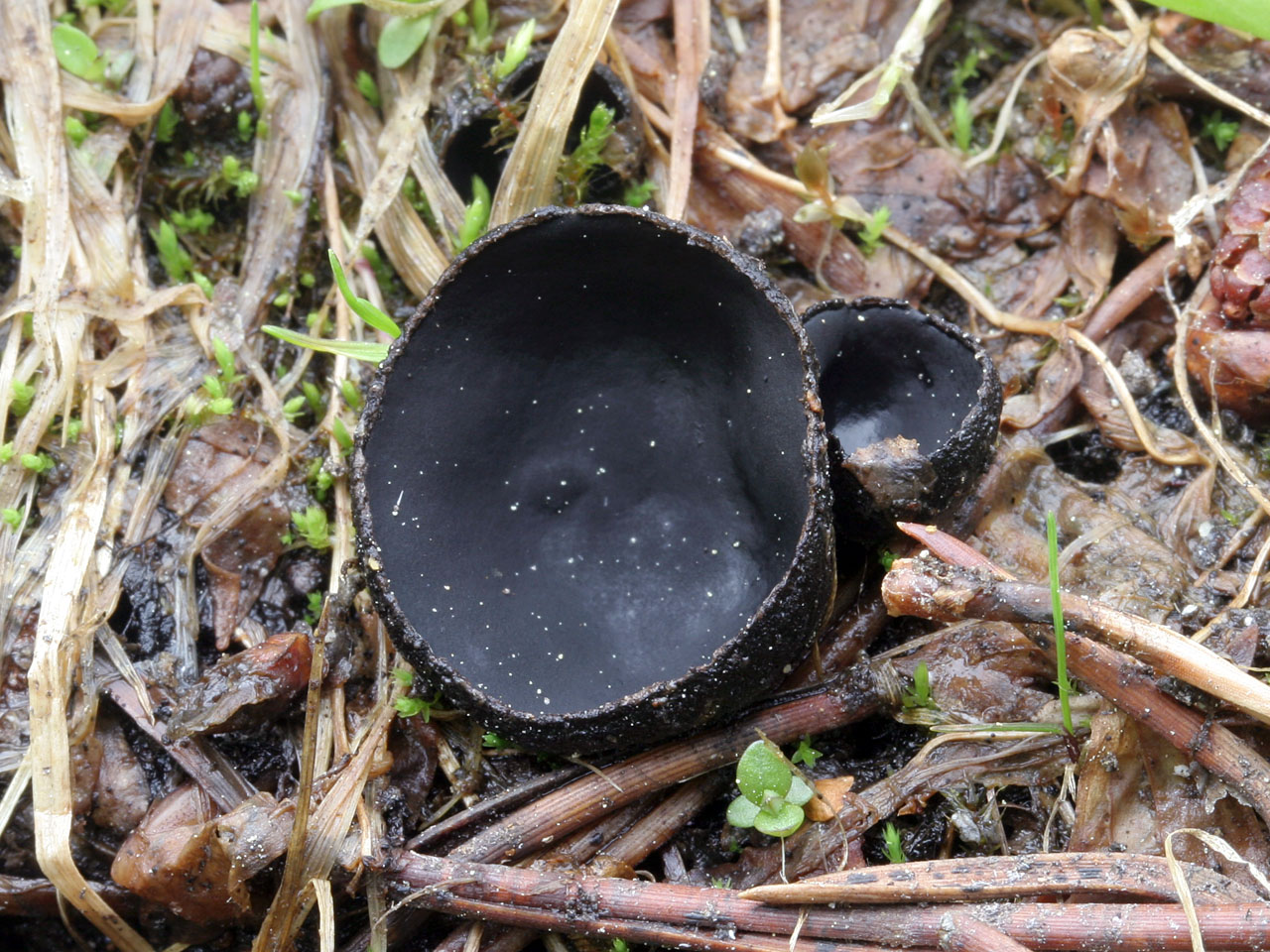
- Apothecia (Apothecia)
-
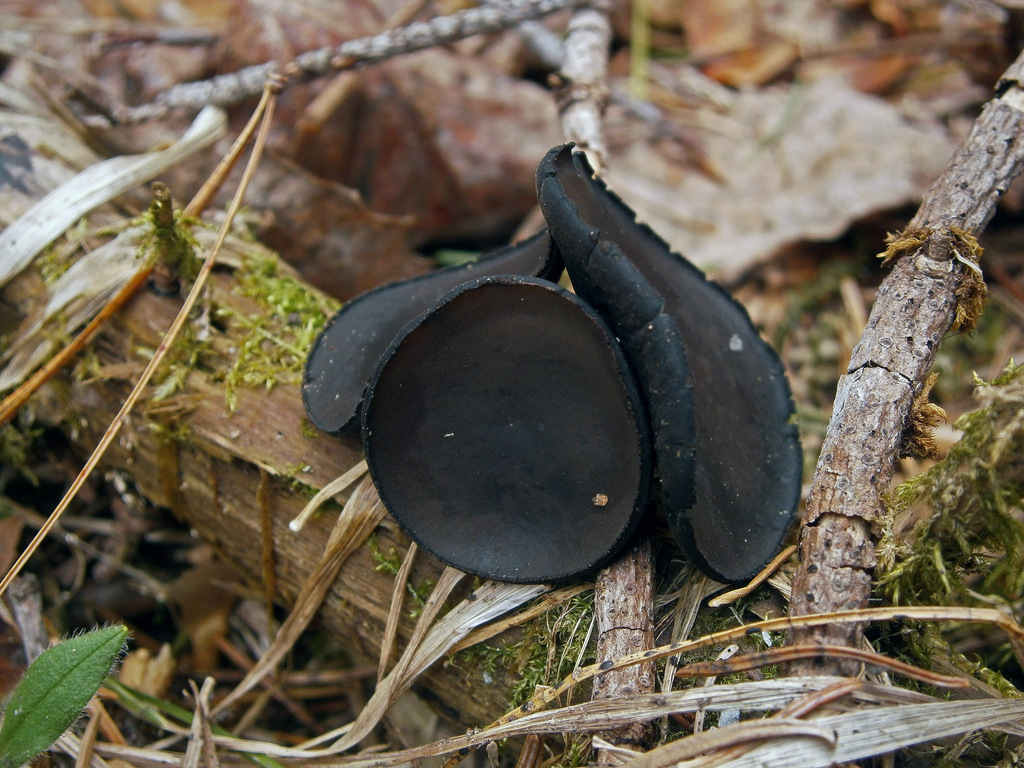
In the type, a completely open ascocarp, often saucer-shaped or goblet-shaped. On the surface of the apothecia there is an ordered hymenial layer, consisting of bags and sterile elements - the paraphysis, under it lies the subhymenal layer, in which the asci develop, and everything else is made up of sterile hyphae of the pulp - the excipule. Apothecia is characterized by the simultaneous maturation of many asci and the active release of spores. Secondary closed apothecia are found in fungi, whose fruiting bodies develop underground, for example, in truffles.
See Ascocarp, Hymenium, Discomycetes, Paraphysis.
- Bags (Ask)
-
A specialized cell of marsupial fungi (ascomycetes), inside which ascospores develop as a result of the sexual process.
The structure of the bursae is an important diagnostic feature used in the ascomycete system. There are prototunicate and eutunicate asci. The first ones have a thin shell, not divided into layers, which spreads out during the maturation of ascospores, and they are released passively. The latter have a denser, layered membrane, equipped with a specialized apical apparatus for opening, and ascospores are actively discarded.
Among eutunicate asci there are uniticate ones, the layers of the shell which grow together and open simultaneously, and bitunicate ones, whose shell consists of two sequentially opening layers. A further subdivision of uniticate bags is based on the structure of the apical apparatus.
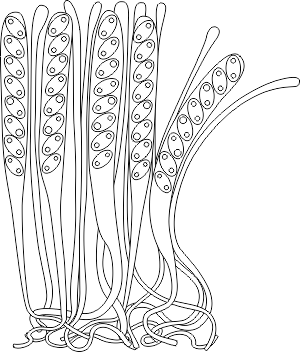
See Apical apparatus.
- Anastomosing (Anastomosis)
-
1) Fusion of cells of branched hyphae or germ tubes of germinating spores;
2) Connecting the plates of the fruiting bodies of the mushrooms with jumpers.


































