What does it look like, where it grows, photo, is it possible to eat
Lead-gray flap: description and photo, edibility
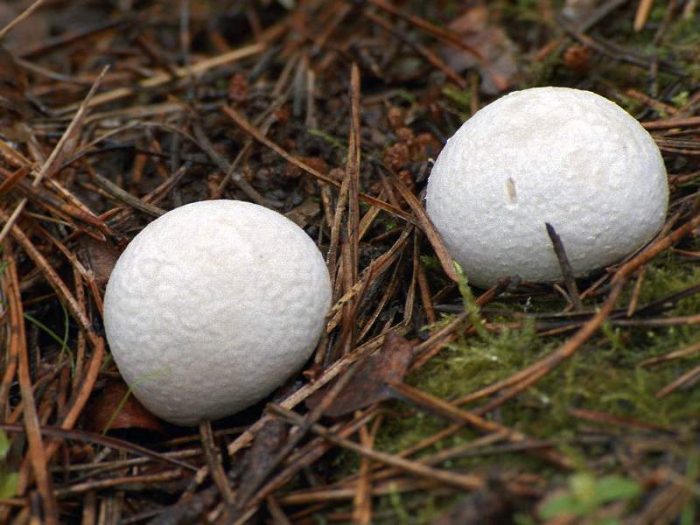
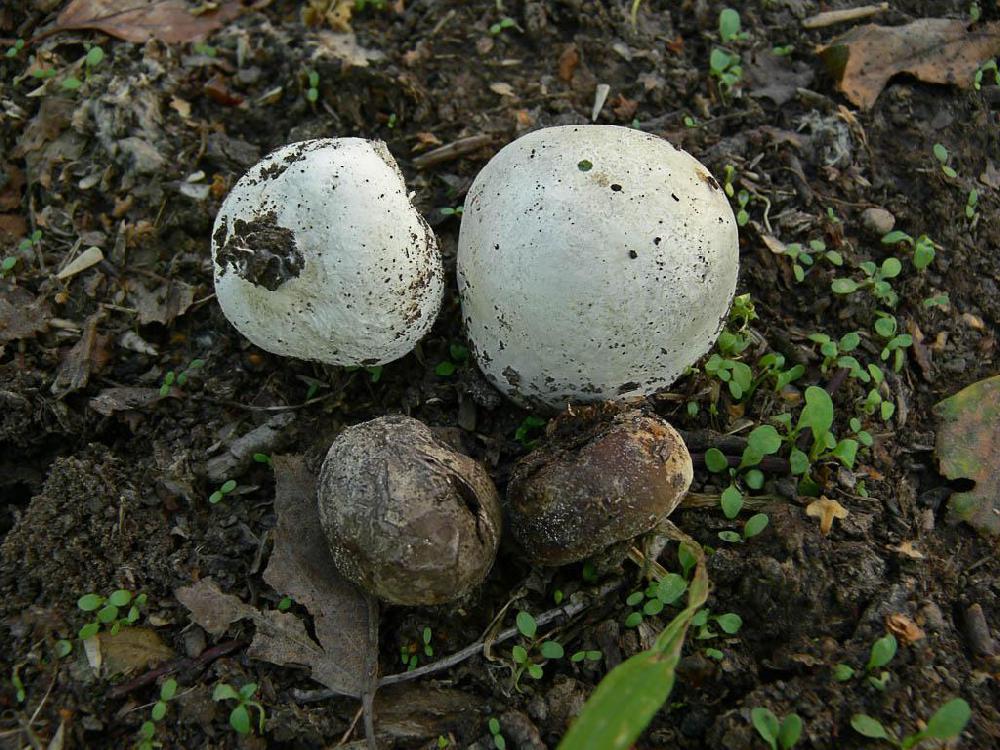
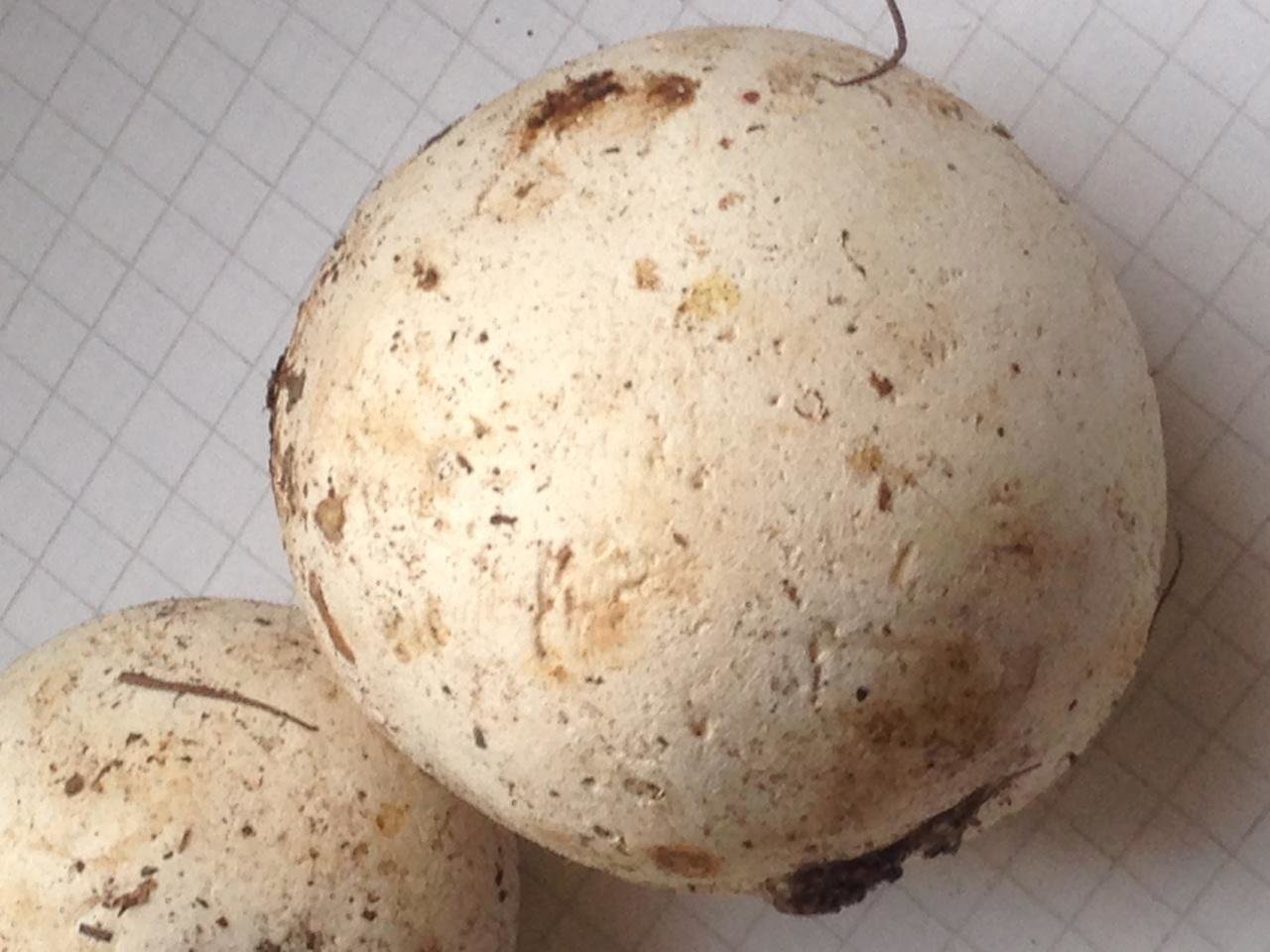
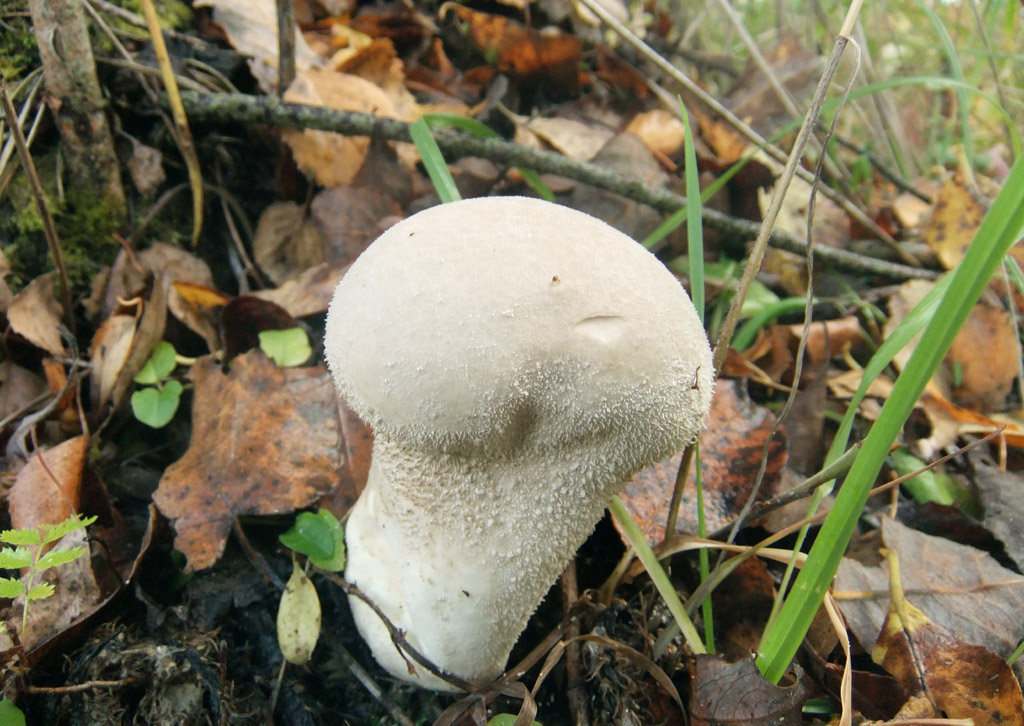
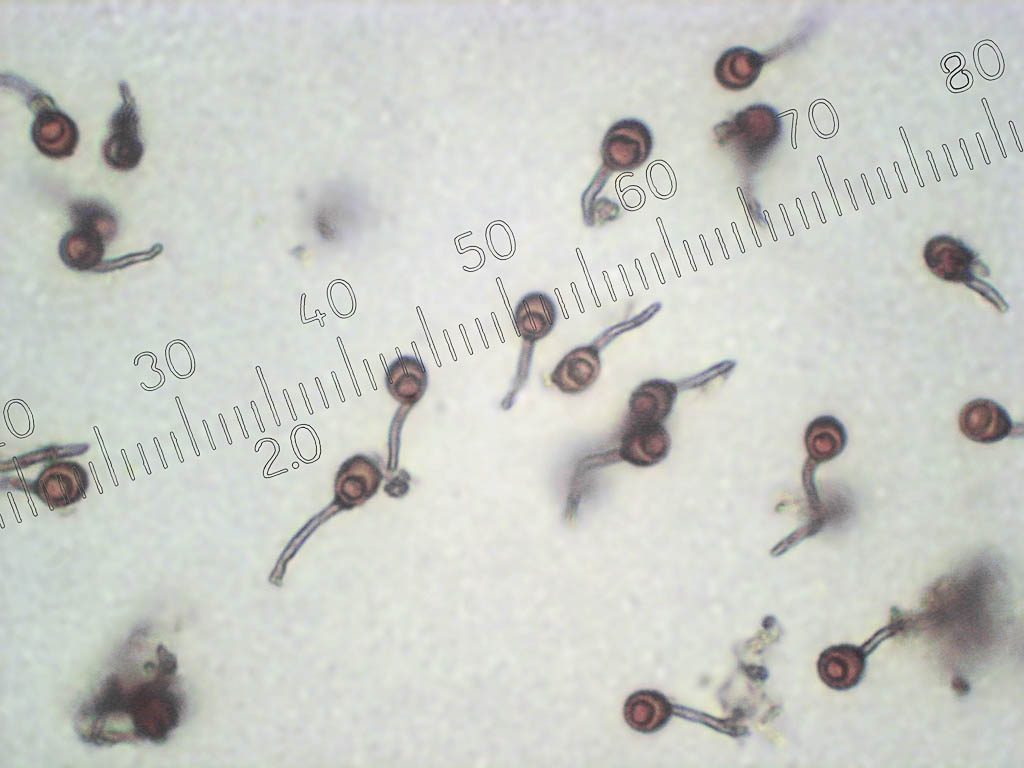
The lead-gray flap has the shape of a ball. White at a young age. When ripe, it becomes gray. The fruiting body is small. The mushroom was first identified by the mycologist Christian Heinrich Person. In fact, in his own work in 1795, he gave the mushroom the Latin name Bovista plumbea.
In scientific works, there are also definitions:
- Bovista ovalispora;
- Calvatia bovista;
- Lycoperdon bovista;
- Lycoperdon plumbeum.
The most popular name for this variety in Russian is Porkhovka lead-gray. There are others: Devil's (Grandfather's) tobacco, Lead raincoat.

How lead-gray flaps look
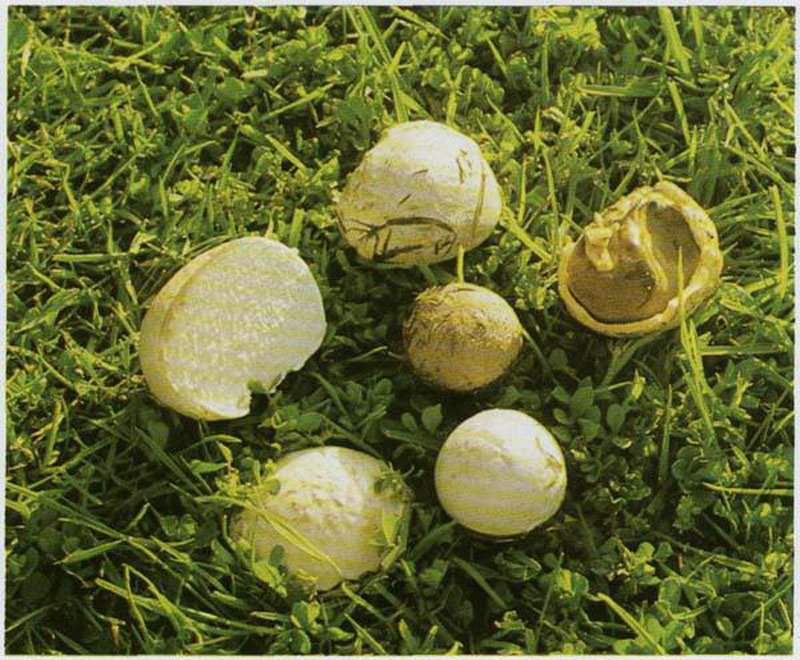
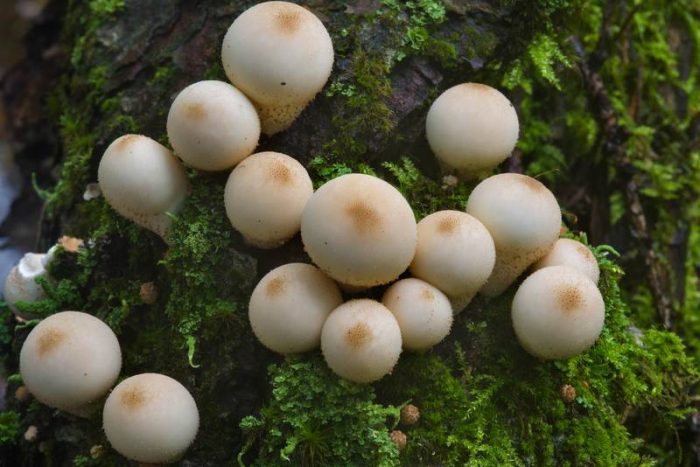
Fruit bodies are rounded. Smaller (1-3.5 cm diameter). The leg of the lead-gray flap is absent. The spherical body goes directly to the root system. It consists of a thin mycelium. They grow in groups.
Primarily white (both in the middle and on the outside). With some period of time, the lead-gray flare acquires a shade of yellow. At maturity, the color can change from greyish brown to olive-brown. The pulp is white, plastic. Then it turns gray or black-green, as it fills with ripe spores. There will be much more than a million of them. Stepping on an adult, darkened raincoat, a cloud of dust appears.
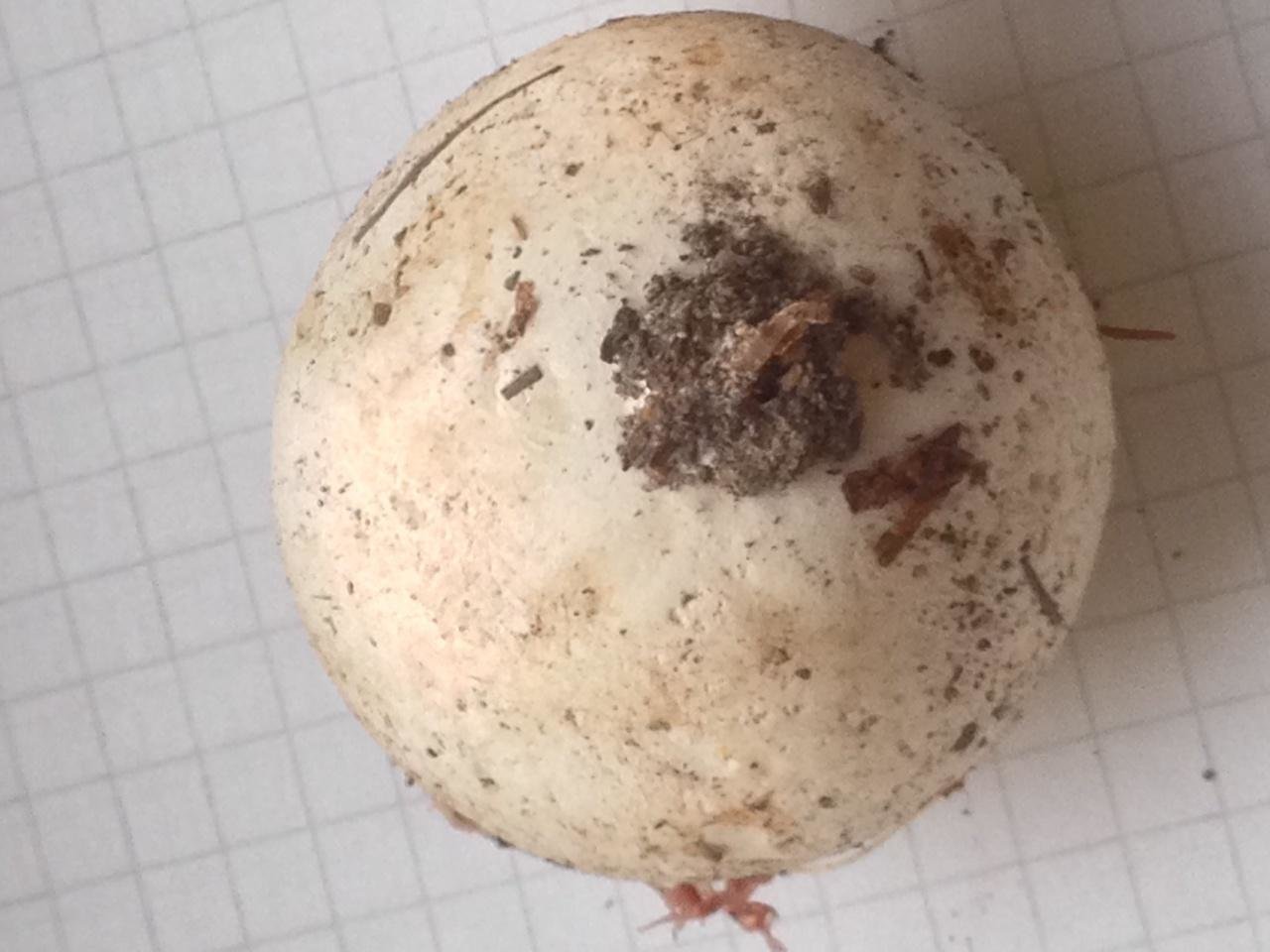
The spore print is brown. The seed powder exits through the apical pore appearing at the top of the fungus.
Is it possible to have lead-gray flaps
Lead-gray flap is an edible mushroom. It can only exist at a young age, when the pulp is full of white.
Mushroom flavor qualities
The taste of the lead-gray flutter is rather weak. Some people do not feel it at all. The aroma is pleasant, but barely perceptible.
This variety is ranked as type 4 by and large due to its very small size. Similar mushrooms are advised to be available in the exceptional case when there are no alternatives. The 4th category also includes russula, oyster mushrooms, dung beetles.
Benefits and damage to the body
Lead-gray flap is not in demand among mushroom pickers, although it increases immunity very well, strengthens the cardiovascular system. On its basis, doctors make anti-cancer drugs.
It contains the following minerals:
Has the ability to absorb heavy metals and other toxic substances. Once in the body, the fungus absorbs harmful parts, and then removes them.
But the ability to absorb substances from the external environment can be harmful. The fungus absorbs toxic elements from the soil, accumulates them in the tissues, and when it gets into the human body, it releases them. Therefore, the lead-gray flap should not be collected along roadsides and in environmentally unfavorable areas.
False doubles
This mushroom can be confused with all other raincoats. For example, with Vascellum field. It differs from the lead-gray flutter by the presence of a small stem and a diaphragm that separates the spore-bearing part.
The potential confusion with neighboring species is fairly harmless. However, there is a mushroom that, when young, looks like a lead-gray flap. This is a pale toadstool. It is very dangerous - 20 g is enough to cause death.
At a young age, the mushroom also has an ovoid spherical shape, but is wrapped in a film. Pale toadstool stands out with a sweetish, fetid odor, the presence of a leg. Its fruit body is rounded, but not as merged as that of the flap. Spore print white.
Collection rules
Only young mushrooms should be picked. They should not have dark spots. Pigmented areas on the fruiting body indicate the beginning of the formation of spores and the loss of nutritional parameters, the quality of taste.
Consumption
The lead-gray flap has 27 kcal in 100 g. Rich in protein (17.2 g). It is fried, stewed, pickled, salted, added to soups and stews.
Conclusion
Lead-gray flap is considered an excellent food product, as it is saturated with trace elements. Very beneficial to health due to its absorbent properties. And regardless of belonging to the 4 category of edibility, it is tasty and nutritious
It is important not to confuse it with a pale toadstool.
Mushroom giant raincoat and its description
- Family: Raincoats (Lycoperdaceae).
- Synonyms: giant bighead.
A description is offered in which the giant slicker mushroom will appear in a completely new light.
Cultural, historical and other interesting information. Strangely, despite the fact that calvacin, the bioactive component of the giant raincoat, was discovered back in the 1960s, and its anticancer and antibacterial activity was confirmed, and the use of this mushroom in folk medicine against dozens of serious diseases has been known for many centuries. no serious laboratory biochemical studies of the active substances of Langermannia have yet been carried out. At least, such studies are unknown to me. Why? No answer.
This raincoat is characterized by the possibility (extremely rare among other mushrooms) - use for the treatment of pets.
In Nepal, in the Dolpa region, where communication between mountain villages is possible only with the help of pack animals, most of them suffer from open, poorly healing wounds resulting from constant friction of the harness with the load. When such a wound or rubbing occurs, local residents prepare a mixture of spores of a giant raincoat and water and treat the wound surface with it. Fruiting bodies are specially harvested for veterinary purposes and stored in homes. It takes about half of the mushroom to process one donkey.
The following is a description and photo of the mushroom raincoat, from which you can learn about how it looks.
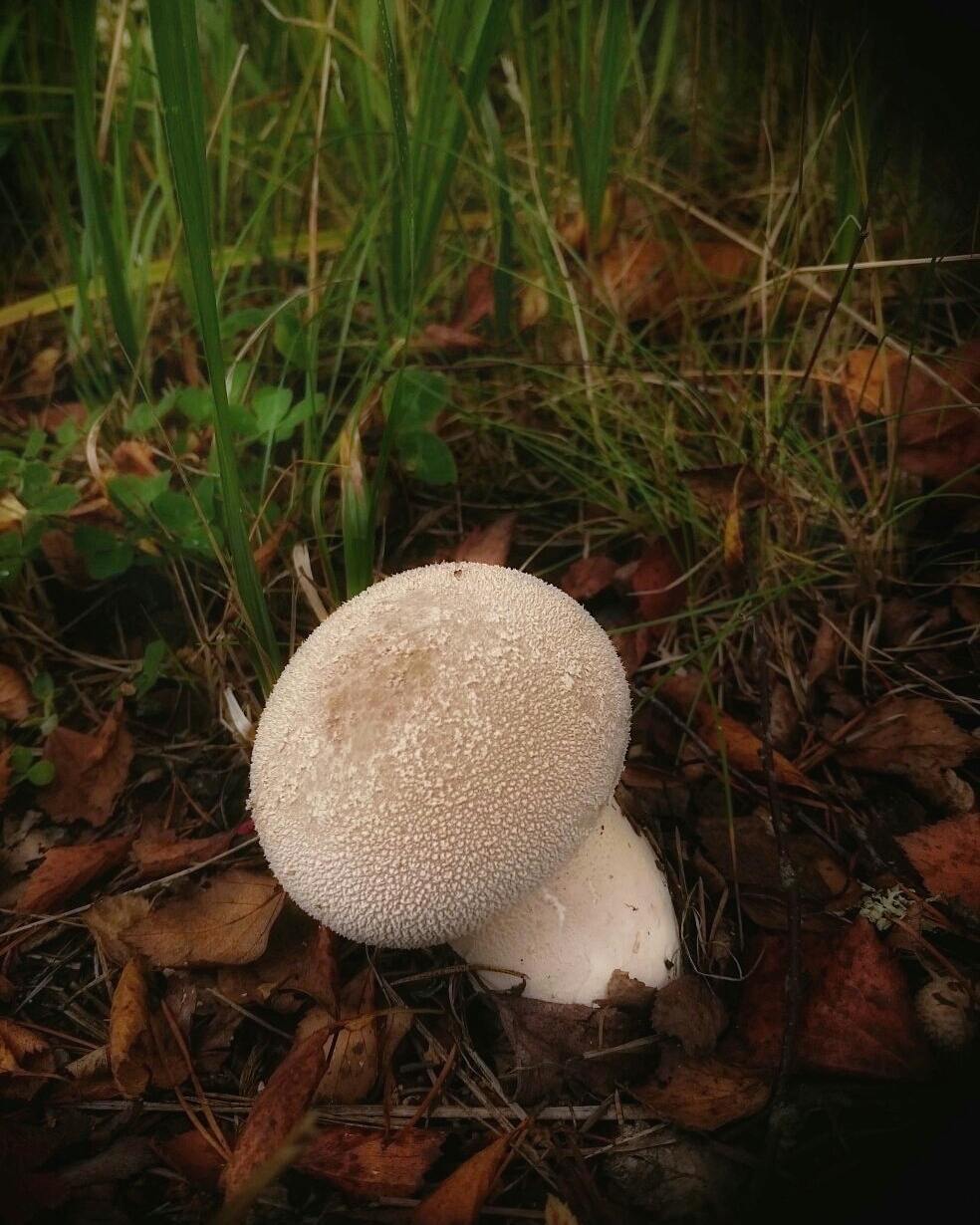
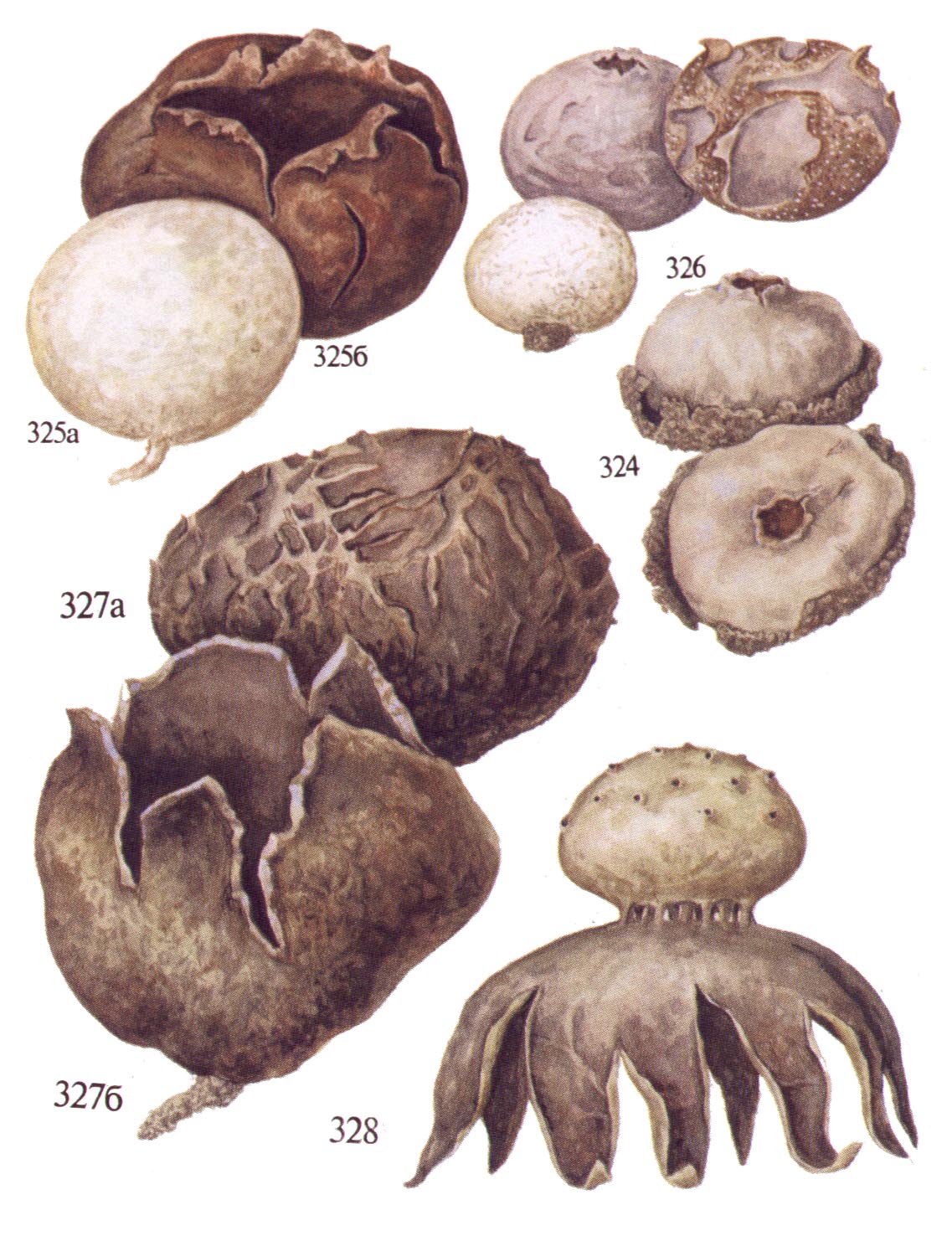
The fruit body is very large, spherical-flattened, 20-50 cm in diameter and weighing up to 10 kg. The outer shell is white, smooth, falling off with age. The inner shell is papery, yellowish-brown in mature mushrooms, breaking down in irregular fragments to release spores. The young flesh is white, firm, with a very pleasant taste and smell; as it ripens, it is yellowish-olive and finally brownish brown.

It is found throughout the temperate climatic zone of Russia on rich soils, prefers open spaces - fields, meadows, pastures, parks, sometimes grows along the edges of the forest, in forest glades in small groups, half rings, and individual specimens can be quite far apart from each other. Over the course of many years, a giant raincoat rarely grows in one place twice, but in the case of a successful season, it can give out two or even three waves of fruiting. It grows from late May to early November.
Similar species. In an adult state, such a large mushroom cannot be confused with other raincoats. Young, still medium-sized Langermannia resemble an immature leathery mycenastrum (Mycenastrum corium), which, when ripe, bursts from above in a star-like manner, which differs well from a giant slicker.
Blackening flap: what it looks like, edibility
| Name: | Blackening flap |
| Latin name: | Bovista nigrescens |
| Type of: | Conditionally edible |
| Specifications: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
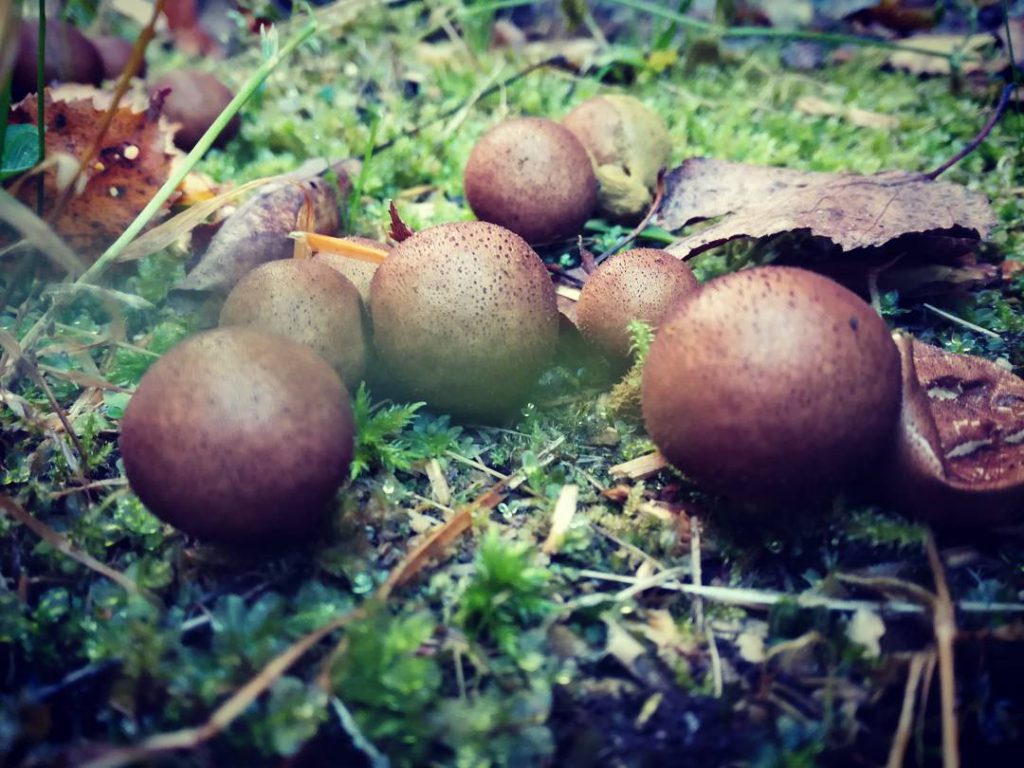
Porkhovka blackening is a conditionally edible species of the Champignon family. This specimen is referred to as rain mushrooms, in appearance it resembles a bird's egg. This mushroom is edible, but only young representatives of the species are used in cooking.Since this family contains poisonous and inedible specimens, in order not to harm your body, you must carefully read the external data, view photos and videos.
False doubles
This forest dweller has edible and inedible counterparts. These include:
- Lead-gray is an edible mushroom; only young representatives are used for food. It can be recognized by its small size, The fruiting body is spherical, up to 3 cm in diameter. The surface is covered with a whitish skin, which turns dark gray with age. The pulp is dense and fleshy, without a pronounced aroma and taste. It prefers to grow in small families on sandy soil, along roads, in illuminated glades, in woodlands. Begins fruiting from June to September.
- Common pseudo-raincoat is an inedible representative of the forest kingdom. It grows among deciduous and coniferous trees, begins to bear fruit from the end of autumn, it lasts until the first frost. The fruit body has a round shape, up to 6 cm in size. The skin is smooth, fine-flaked, painted in a dirty lemon or brown color. The pulp is firm, fleshy, white at a young age, gradually turns purple-black.
Interesting facts about flap
This mushroom is not a separate species, but an ordinary old raincoat. Often it is difficult to distinguish him from the false "brother", which has a hat with a marble pattern of white and yellow. Its pulp, unlike flitting, is white-yellow at the very beginning of ripening, and over time it acquires a gray-purple hue. You should be alerted by a pungent bitter smell and numerous scales on the surface.
This representative of the Champignon family is collected from June to September... He begins to grow actively immediately after heavy rains, as he loves moisture. Young mushrooms are most delicious, overripe give off bitter, and in order to get rid of this taste, they need to be boiled for a long time.
Porhovka is not particularly popular; boletus, butter mushrooms, milk mushrooms and other more common mushrooms are preferred to it. It is almost impossible to find it in the market or in the store. But if it is not used very often for culinary purposes, then it has already become indispensable in the fight against aphids and other garden pests.
Watch the video about the mushroom porkhovka:
How not to do
However, there are a number of contraindications. First, bypass the adult bighead. A mushroom that has managed to overripe is not suitable for food. He has accumulated in his pulp such a quantity of toxins that in terms of destructive power he can compete with all kinds of fly agarics and toadstools.
Young mushrooms are completely safe. However, even they cannot be included in the menu for children under eight years old. This limitation applies to absolutely all forest mushrooms, since the child simply does not have enough enzymes necessary to digest and assimilate mushrooms.
Otherwise, there are no taboos. Cook bighead mushrooms the way you like, eat it yourself and treat your guests.
Did you know that one of the species of this mushroom got into the Guinness Book of Records because of its enormous size? Such a bighead was found in England, and its growth reached 1.7 m in height. It is often confused with a raincoat, but these are completely different types. How it looks, as it is called by the people, and most importantly where the collection time grows, you will learn from this article.
The first question is: is the mushroom edible or not? Is it worth taking him home or is it better to walk by? Of course, Golovach or in Latin Calvatia from the mushroom family is edible, belongs to the fourth category in terms of taste.
The baggy bighead is considered the best for eating. Only young specimens can be eaten, since in adulthood the mushroom cap breaks to release the spore powder from the pulp or scientifically gleba.
Giant Golovach
The Latin name is Calvatia gigantea. Other names: Langermany.
Peculiarities:
A spherical hat, slightly flattened, can grow up to one meter in diameter and weigh up to 35 kg. At a young age, milky white, turns brown with aging and becomes unsuitable for food.The pulp resembles cottage cheese or marshmallow. It grows rapidly, so small specimens are practically not found. It is unique in its size and weight.
Where it grows:
In forests of any type, prefers acidic and nitrogen-containing soils, likes forest outskirts, meadows and pastures, found in parks. Grows singly or in a small group.
When it grows:
From August to September, after heavy rains, in the south of the country it grows to November.
Baggy golovach
The Latin name is Calvatia utriformis. Other names: round, saccular head.

Type of:
Edible, 4th category. The inside of the hat is suitable for eating. You need to collect only young specimens, while the pulp is white. Be sure to remove the skin before cooking. Suitable for frying, can be eaten raw.
Peculiarities:
The main difference: the surface of the cap has a warty structure, it grows in diameter up to 20 centimeters. Has a false stem. Young specimens are white, turn yellow over time and become brown in old age. The pulp with a pleasant smell, sterile and able to stop bleeding.
Where it grows:
In deciduous forests and mixed types, can be found on forest edges, meadows, glades and gardens. It grows mostly alone.
When it grows:
May to September.
Golovach oblong
The Latin name is Calvatia excipuliformis. Other names: elongated raincoat.
Peculiarities:
Unlike its counterparts, it has a club-shaped cap, and not a spherical one. It grows up to 15 centimeters in length and up to 5 centimeters in diameter. With age, it turns from white to brown. In youth, they have growths on the surface, old ones are smooth. Over time, the cap breaks and falls off completely.
Where it grows:
In deciduous and coniferous forests, young plantings, throughout Russia. Loves bright places, meadows and edges. It grows both singly and in groups.
When it grows:
July to October.
Interesting facts about the mushroom
Young specimens of flutter outwardly resemble bird eggs that have fallen out of the nest. Mushroom pickers discover their mistake only when they try to lift such an "egg" and find a small leg in it.
It is not recommended to collect flaps after rain. Like all raincoats, this species absorbs moisture, so instead of a mushroom, you can get a soggy mass.
Porkhovka contains special enzymes, thanks to which the mushroom is used to treat cancer.
Porkhovka is rich in vitamins, macro- and microelements. The mushroom contains vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, D, E, C potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium and zinc. This mushroom is advised to be eaten with mental fatigue, severe fatigue, anemia, uremia. It is good for inclusion in the diet of vegetarians and those who do not eat meat, as it contains the proteins the body needs, as well as fats and carbohydrates, so that flap can be a complete substitute for meat and meat products.
Composition and calorie content of flashing

This mushroom cannot claim to be the most useful of all. It is significantly inferior in its chemical composition to boletus, mushrooms, chanterelles, mushrooms. It is appreciated for its high percentage in the composition of various micro and macro elements. There are not so many vitamins in it to seriously consider this product as their source.
The calorie content of flashing per 100 g is 27 kcal, of which:
- Proteins - 4.3 g;
- Carbohydrates - 1.5 g;
- Fat - 1 g;
- Water - 81.5 g;
- Ash - 1.2 g;
- Dietary fiber - 2.1 g.
Vitamins per 100 g:
- C, ascorbic acid - 6 mg;
- B1, thiamine - 0.09 mg;
- B4, choline - 13.2 mg;
- B6, pyridoxine - 0.07 mg;
- D, calciferol - 0.06 mg;
- PP, niacin - 1.245 mg.
Macronutrients per 100 g:
- Potassium, K - 215 mg;
- Magnesium, Mg - 11 mg;
- Sulfur, S - 23 mg;
- Phosphorus, Ph - 72 mg;
- Calcium, Ca - 95 mg.
Microelements per 100 g:
- Aluminum, Al - 25 μg;
- Iron, Fe - 0.038 mg;
- Iodine, I - 7 mcg;
- Rubidium, Rb - 21 μg;
- Zinc, Zn - 0.42 mg;
- Selenium, Se 2 - 55 mcg.
The composition of the flask also includes digestible carbohydrates, represented by glucose and dextrose. In 100 g, they are contained in a total aggregate of no more than 2.5 g.These substances are important for brain function and satisfying hunger. The mushroom includes a few amino acids, essential, non-essential and fatty. The latter make it extremely beneficial for the health of the heart, blood vessels and mental activity. After heat treatment, the amount of these substances remains practically the same, in contrast to vitamins, micro- and macroelements, of which about 20% is lost.
Due to the presence of protein and calcium in the composition, flashing is a valuable substitute for animal products - milk, meat, fish. This allows adherents of a plant-based nutrition system to successfully take care of teeth, joints, tissues and just general well-being.
Flashing recipes
Porkhovka turns out to be very tasty after cooking. If not kept in water, it will be too hard and bitter. Therefore, such processing is always recommended, even if after it the mushrooms are planned to be fried, baked or pickled. It is not necessary to soak them before cooking, but it is very desirable, because this makes them softer and much more tender. To do this, it is enough to soak them in water for about 30 minutes.
Among all the recipes, you should pay attention to the following:
- Chicken fillet soup ... This ingredient needs no more than 300 g, it should be boiled, chopped and fried. Then pour 250 g of mushrooms with water, leaving for an hour, peel the potatoes and chop them. Next, wash the carrots (1 pc.) And the onion (1 pc.), Rub them and fry until golden brown. Then cut the mushrooms into cubes, add them to the potatoes, combine with the frying, chicken fillet and cook. After 40 minutes, salt and pepper the soup, season it with dill, grated processed cheese (120 g) and sour cream (3 tablespoons).
- Lasagna ... You will need her sheets (5 pcs.), Which are sold in almost any store. First of all, they need to be boiled in salted water and cooled. At this time, prepare the filling - fry the pre-soaked mushrooms (150 g), minced pork (120 g), onions (1 pc.), Tomatoes (1 pc.), Pepper (1 pc.) In oil. Then salt and pepper this mixture, add a little sour cream to it. Then oil a baking dish, place the first sheet on it, cover it with the filling, and repeat until you use the last one. Then just put the dish in the oven, preheated well, and hold it in it for about 30 minutes.
- Stuffed pepper ... Use mushrooms fried in vegetable oil (400 g) and boiled pork (250 g) as the filling. To them you need to add chopped onions and carrots (1 pc.), Slightly toasted. Boil the vegetables to be stuffed in salted water until they soften. Before that, they must be washed well, remove the tails, open the recess, cut off the top, and hold them in boiling water for 3-5 minutes. Next, the pepper should be stuffed to the very edges, pour over with tomato, salt, pepper and simmer for 20-30 minutes under the lid.
- Mushrooms in sour cream ... They need about 800 g. Wash, peel and soak this ingredient for an hour. Next, cut it, salt, pepper, boil and fry in oil. Then add grated hard cheese (150 g), pitted olives (80 g) and sour cream (7 tablespoons). You can also use cream, in which case you will need half as much. After that, stir the mixture, reduce heat and simmer for about half an hour under a closed lid. The finished dish is perfect for serving as a side dish. It goes well with mashed potatoes, pasta, noodles, buckwheat and other cereals.
- Salad ... Boil chicken fillet (300 g) and potatoes (3 pcs.). Next, cut them as small as possible, combine with salted crackers (50 g), corn and pre-soaked and boiled mushrooms (no more than 200 g). Then add sea salt and lemon juice to taste, 3 tbsp. l. mayonnaise. Such flashing recipes are suitable for both weekdays and holidays.
- Casserole ... First of all, boil the soaked porkhovka (250 g) and peeled potatoes (6 pcs.), Which will then need to be removed.Next, pour vegetable oil into the pan, fry the grated garlic there (7 cloves). Combine it with the rest of the previously chopped ingredients. Then beat 3 eggs, mix them with cream (50 g), grated cheese (70 g), salt and ground pepper. After that, grease a baking dish with butter, first put the first layer of mushrooms on it, and then the second potato layer and cover it on top with a mass of cheese and eggs. The next step is to sprinkle all of this with dill and put in the oven for 20-30 minutes, so that the dish is golden brown.
Important! Porkhovka is very fried, so you should not keep it in the pan for a very long time.
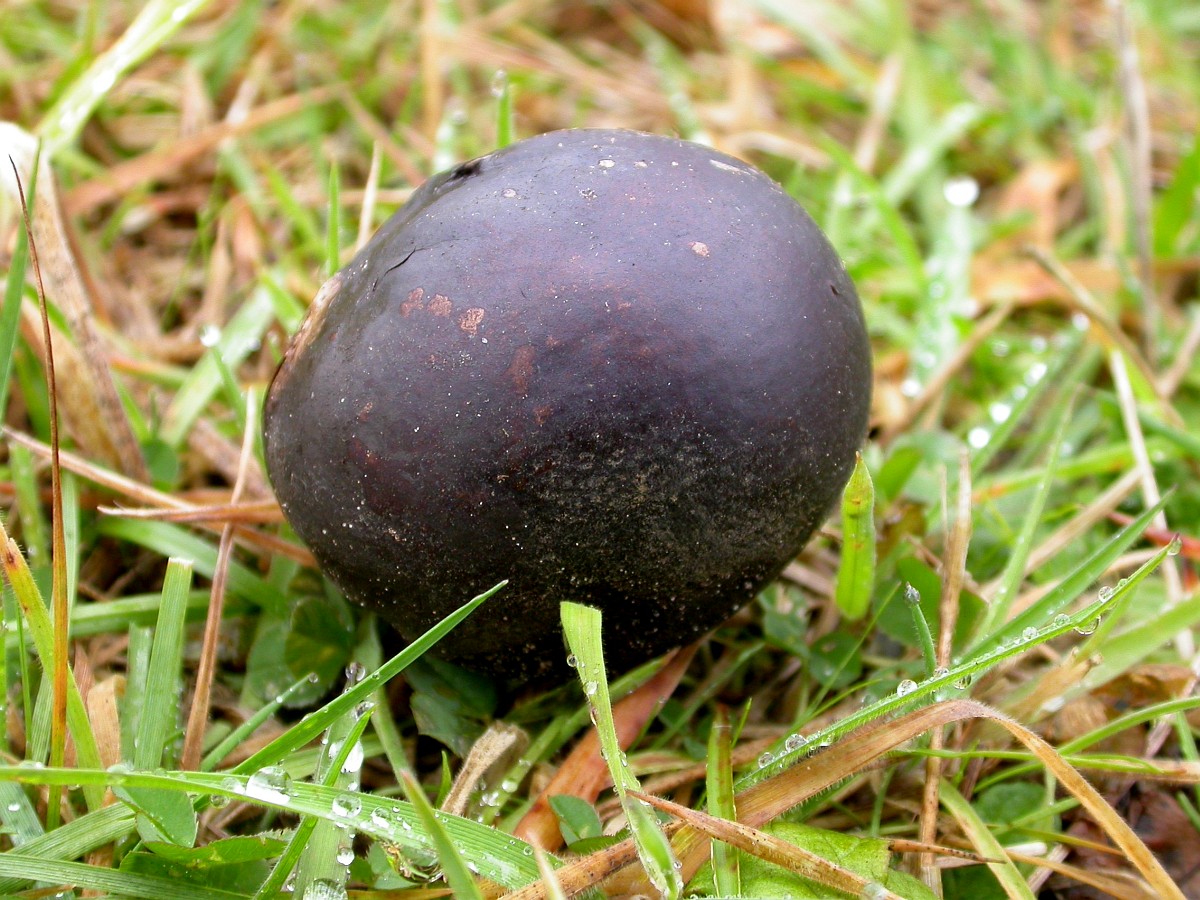
Porkhovka blackening: description and photo, where it grows, photo, is it possible to eat
Blackening flap, (Bovista nigrescens Pers., 1794)
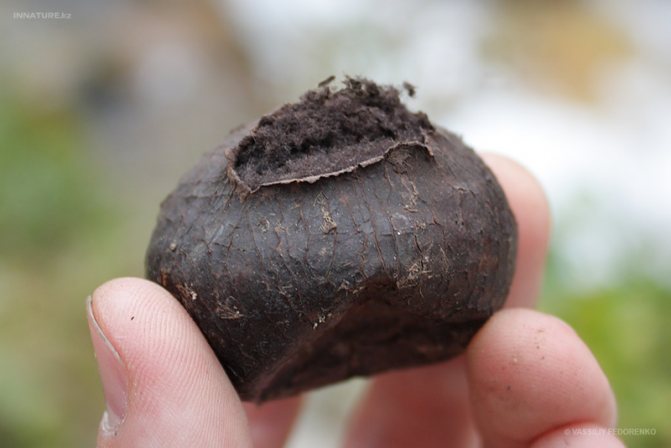

Insert-mushroom-tree Synonyms: Bovista nigricans Pers. : 24, 1809 Globaria nigrescens (Pers.) Quél. Lycoperdon globosum Bolton, 3: t. 118, 1789 Lycoperdon nigrescens (Pers.) Vittad. : 176, 1843 Sackea nigrescens (Pers.) Rostk., 5-18: 33, t. 15, 1839
Etymology: Bovista (Porkhovka) nigrescens (Latin nigrescens - blackish).
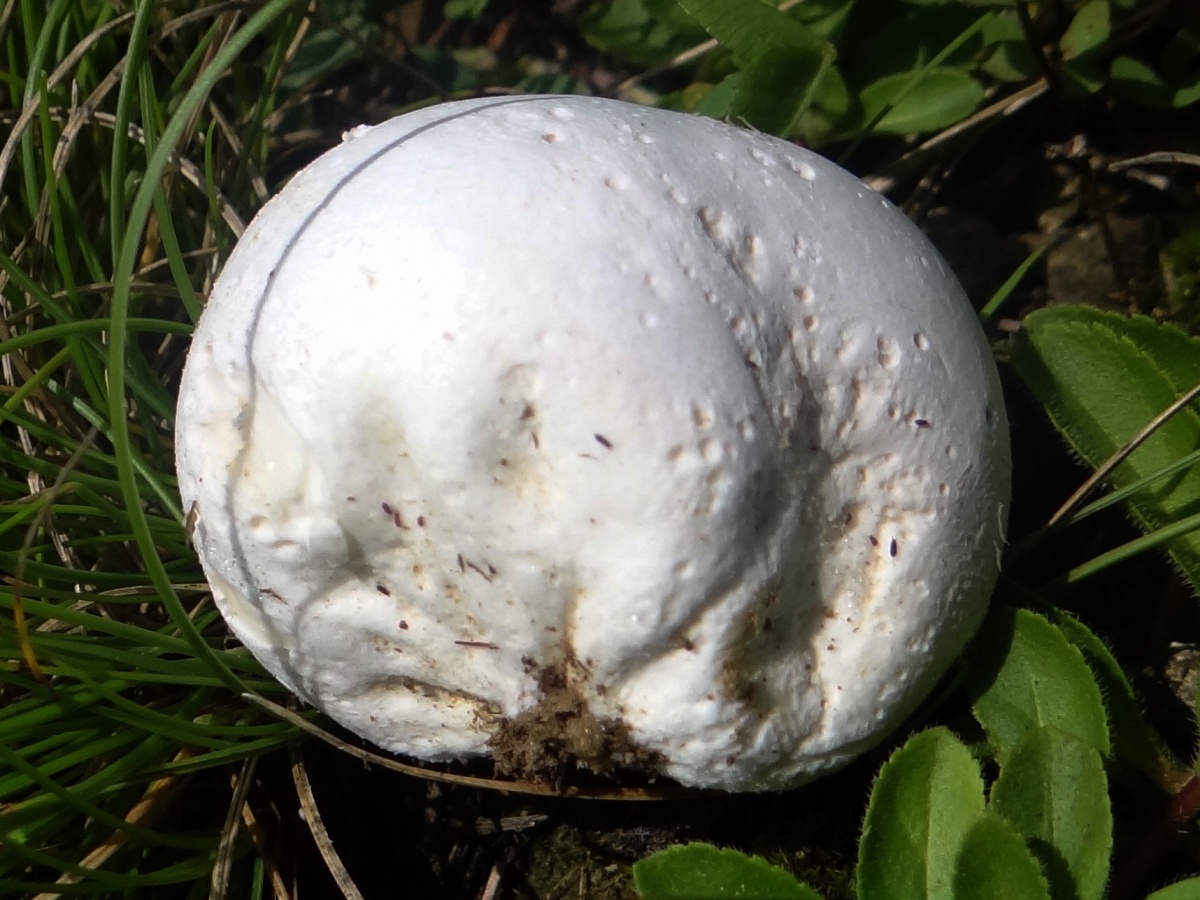
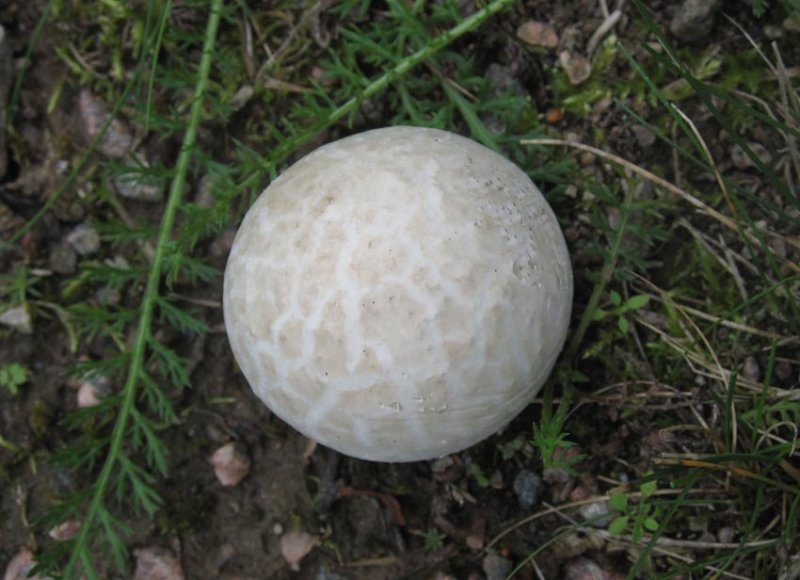
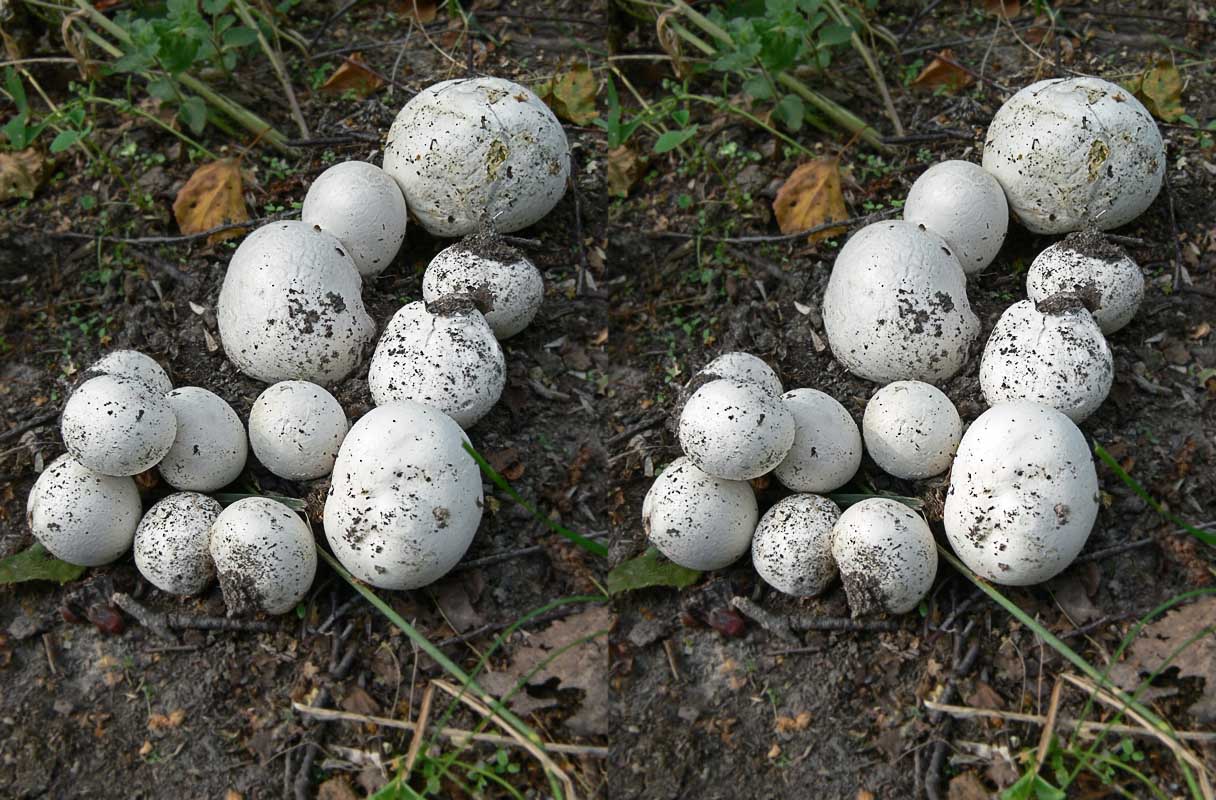
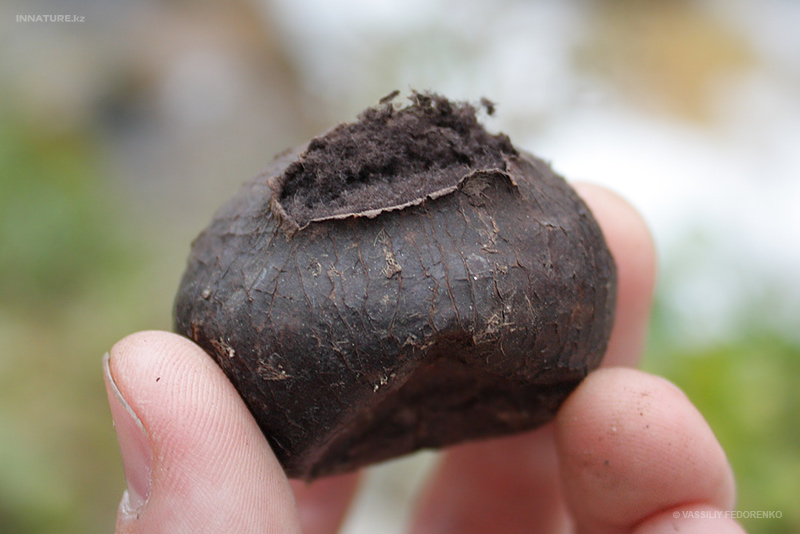
Fruit body Fruit bodies are spherical, flattened spherical, sometimes tuberous, 1.5-7 cm in diameter, covered with peridium, the sterile base is not developed.
Peridium: double layer.
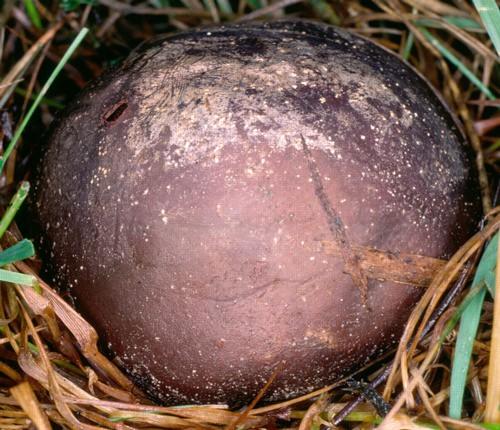
Exoperidium: at first white, slightly tomentose, then dotted with polygonal cracks and disappears. The inner layer of exoperidium persists for a long time, umber-brown, brown-chestnut to black or bronze-gnarled, cracks and persists for a long time.
Endoperidium: thin, paper-shaped, fragile, light gray-red-brown, to silvery, rarely yellow or gray-brownish, often purple or blackish in places, matte-shiny, opens at the apex of fruiting bodies at first small, rounded, then a significantly widening aperture, 1.5–4 cm wide, bordered by a lip-like raised, serrated edge.
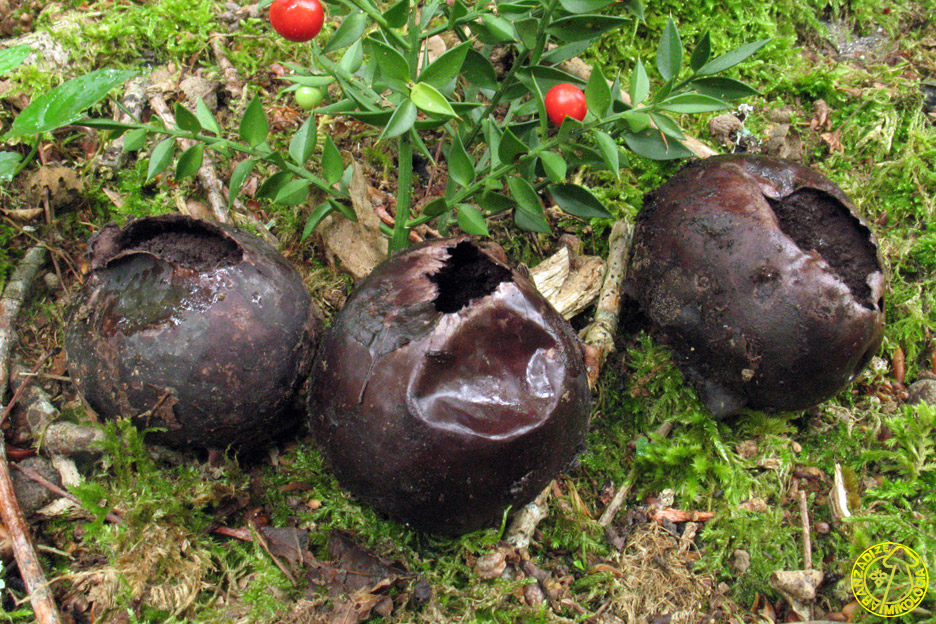
Gleb: first white, then black-brown, coffee.
Spores: spherical, 6-7 µm in diameter, warty, with one drop, black-brown, with a sterigma residue, 9.6 x 1 µm, straight or arcuate-curved, colorless. Warts are large, colorless. The capillium is highly branched, consists of a main trunk and branches with elongated sharp ends extending from not dichotomously branched branches. The main trunk is 24 µm thick, without partitions and pores, with walls 7.2 µm thick, black-brown or dark brown.
Habitat: grows on soil among grass, on meadows, rarely in deciduous forests, often in mountains.
Season: May to September.
Distribution in Kazakhstan: East Kazakhstan region, Almaty region.
Habitat: Siberia, Kuril Islands, Estonia, Ukraine, Armenia; Greenland, Iceland, England, Finland, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Austria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Italy, Switzerland, France, Israel.
Edible: like an ordinary raincoat, it is edible at a young age, while the flesh is white.
Useful properties of flapping

With such a diverse composition, the mushroom has a positive effect on all organs and systems of a person. It improves the functioning of the intestines, heart, kidneys, liver, pancreas. It can be safely consumed regularly by persons over 15 years old. With its help, even the strongest hunger is quickly satisfied, general well-being is stabilized and the body is reliably protected from external threats emanating from various bacteria and viruses. The mushroom has the following effects:
Increased hemoglobin. It is very important for humans, as it is necessary for the delivery of oxygen to cells. Without this, migraine, nausea, dizziness, drowsiness appear. This problem is especially common for pregnant women. In this case, the risk of miscarriage and fetal development disorders increases. The same product compensates for the iron deficiency, which is responsible for this blood count.
Promotes bone health. The mushroom caps contain more than 20% of the amount of calcium required for an adult per day. At the same time, it is quickly washed out of the body in the event of a lack of potassium, which is also present in the product. All this contributes to the effective prevention of abnormalities in the development of joints and rheumatological diseases - arthrosis, osteoporosis, bursitis, etc.
It is also very important here that plant calcium is absorbed quickly and almost completely.
Strengthening the immune system. It is very important for humans, as it repels external attacks of microbes, viruses and infections.
The presence of ascorbic acid flashing in the caps will help to strengthen it. This vitamin is also necessary for the full absorption of iron, without which anemia develops. As a result of such processes, a person quickly transfers various diseases and reliably protects against their recurrence.
Cleansing the body. Sooner or later, it will certainly become contaminated with toxins, heavy metal salts and other dangerous deposits. To bring them out, he needs fiber, which is contained in sufficient quantities in the flutter. Its main percentage is concentrated in the caps; there is not much of this substance in the legs. Regularly consuming these mushrooms, you can reduce to zero the likelihood of neoplasm growth and premature aging.
Normalization of the heart. To do this, he needs magnesium and potassium, which are in decent quantities in the mushroom. This allows it to be used for the prevention and treatment of rheumatism, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, stroke and other cardiac diseases.
It is especially important to pay attention to this after 40 years, when the risk of their development increases significantly.
Deceleration of aging. To achieve this, you need to constantly saturate your body with antioxidant substances.
These are the fatty acids in the flare, which replenish the oxygen reserves in the cells, protect them from premature destruction and start the regeneration process. Thus, it turns out to reduce the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis and enjoy youth longer.
Improving digestion. It has been proven that dietary fiber and fatty acids, which are found in sufficient quantities in these mushrooms, play a huge role in the prevention and treatment of constipation. They allow you to gently cleanse the intestines from toxins, reduce body weight, improve appetite, get rid of flatulence and bloating. Their use has a positive effect on the metabolism of matter.
Stabilize your mood. Zinc has a huge effect on this. With its significant deficit, the brain can be affected, as a result of which both ordinary depression and mental illness of varying degrees of complexity occur. Porkhovka is the source of such an important trace element.
Important! The benefits of flashing will be obvious only if you eat it in moderation and in a boiled form.
Tincture of raincoat mushroom for treatment
The raincoat mushroom is used in the treatment of various diseases in the form of pre-prepared preparations. The most commonly used tincture of the raincoat mushroom, which is based on alcohol of various concentrations.
For diseases of the lymphatic system (lymph nodes) and sarcoidosis - 1 teaspoon 2 times a day, the course - until cure.
Infusion: 1 dec. pour a spoonful of spore mushroom powder with a glass of hot water (70 ° C) and insist under a lid in a porcelain or glass dish for 40 minutes, take 1/2 cup 2 times a day before meals in small sips.
Tincture: prepared with vodka in a 1: 5 ratio. Infuse spores in a dark, warm place for 2 weeks. Take the tincture inside for 1-2 teaspoons 3-4 times a day before meals. The course is 3-4 weeks with a mandatory weekly break.
To prevent the formation of kidney and bladder stones, bread sprinkled with spore powder from a raincoat is taken inside.
In case of postpartum hemorrhage: 3 teaspoons of spore powder per 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, drain. Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day.
Collection and procurement rules for medicinal purposes. Fully ripe mushrooms are harvested to prepare spore powder or young fruit bodies with completely white flesh.
Beneficial features
Porkhovka is a very interesting and useful mushroom, which, perhaps, loses in taste, but nevertheless, the benefits of it for the body are invaluable.
These wonderful mushrooms can absorb salts of heavy metals with radionuclides accumulated in the body and remove them naturally, cleansing the body and preventing the development of cancer. In addition, mushrooms have a good tonic effect, improve the functioning of the immune system, and help in the fight against chronic fatigue, stress, and insomnia. They contain a huge amount of vitamins, amino acids and useful minerals, without which the human body simply cannot function normally.
Harm and contraindications to the use of flashing

Mushrooms collected near roads, cities, and chemical plants can pose a danger. In this case, even if they are not poisonous, they can easily be poisoned. Intoxication makes itself felt after 8-13 hours after eating. Its first symptoms are nausea, weakness, abdominal pain, migraine, lack of appetite, hallucinations. If you have such problems, you should immediately call an ambulance and drink activated charcoal before she arrives, which will help flush the stomach. Do not give this product in the following situations:
- Small children ... We are talking about the age of 12 years, since their stomachs are not yet fully strong for digesting such heavy food as mushrooms, and even more so, they cannot be fried or pickled.
- Duodenal ulcer and stomach ... With such diseases, it is not recommended to eat this product in any form. The reason here is that it contains a lot of dietary fiber and ash, which negatively affect the health of the walls of these organs. As a result, they can aggravate the situation, up to the opening of internal bleeding.
- Severe heart disease ... This refers to what requires urgent hospitalization - myocardial infarction, heart failure, or edema of this organ. In such cases, you can not drink a lot of water, which complicates the situation, and so bad things are.
Important! In rare cases, there are false "brothers" in the flap, unsuitable for human consumption, therefore it is recommended to collect it only for experienced mushroom pickers.
Porkhovka
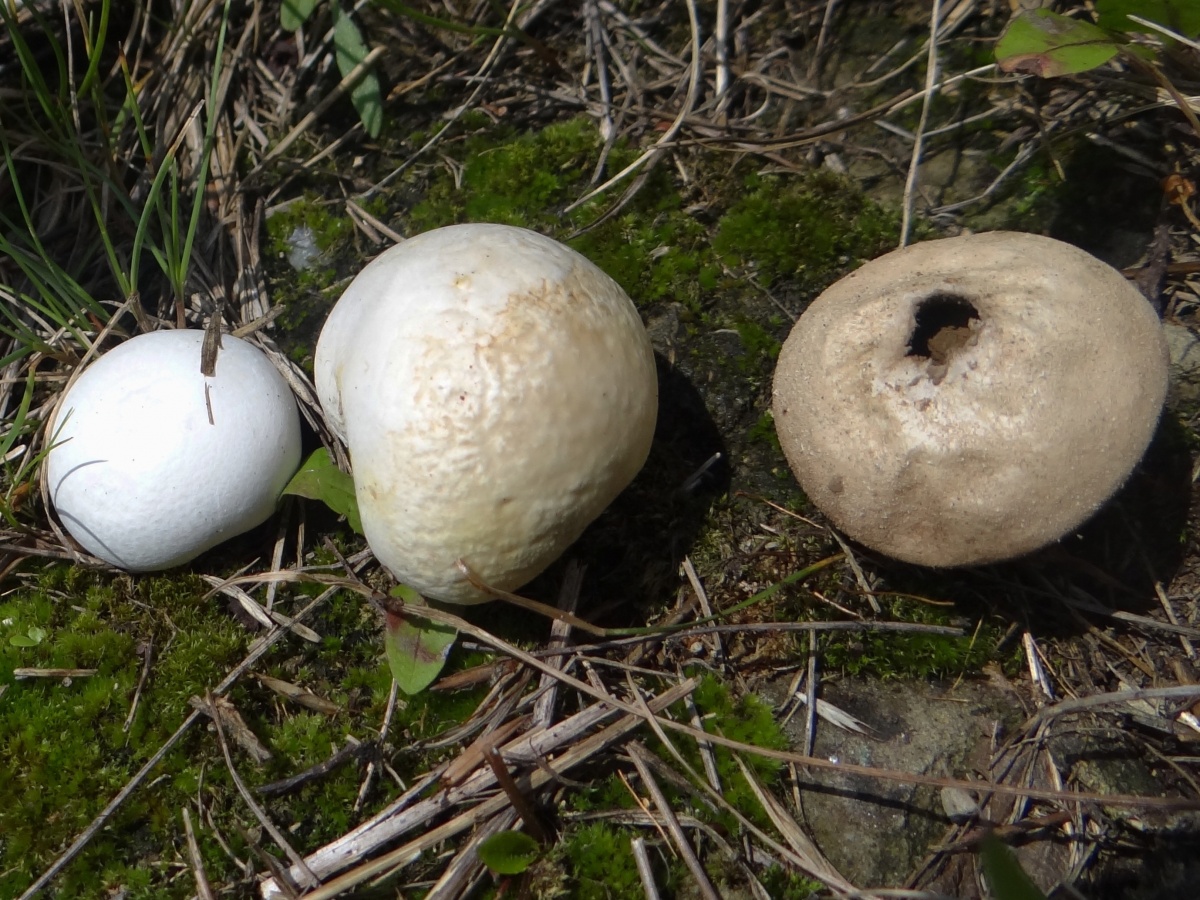
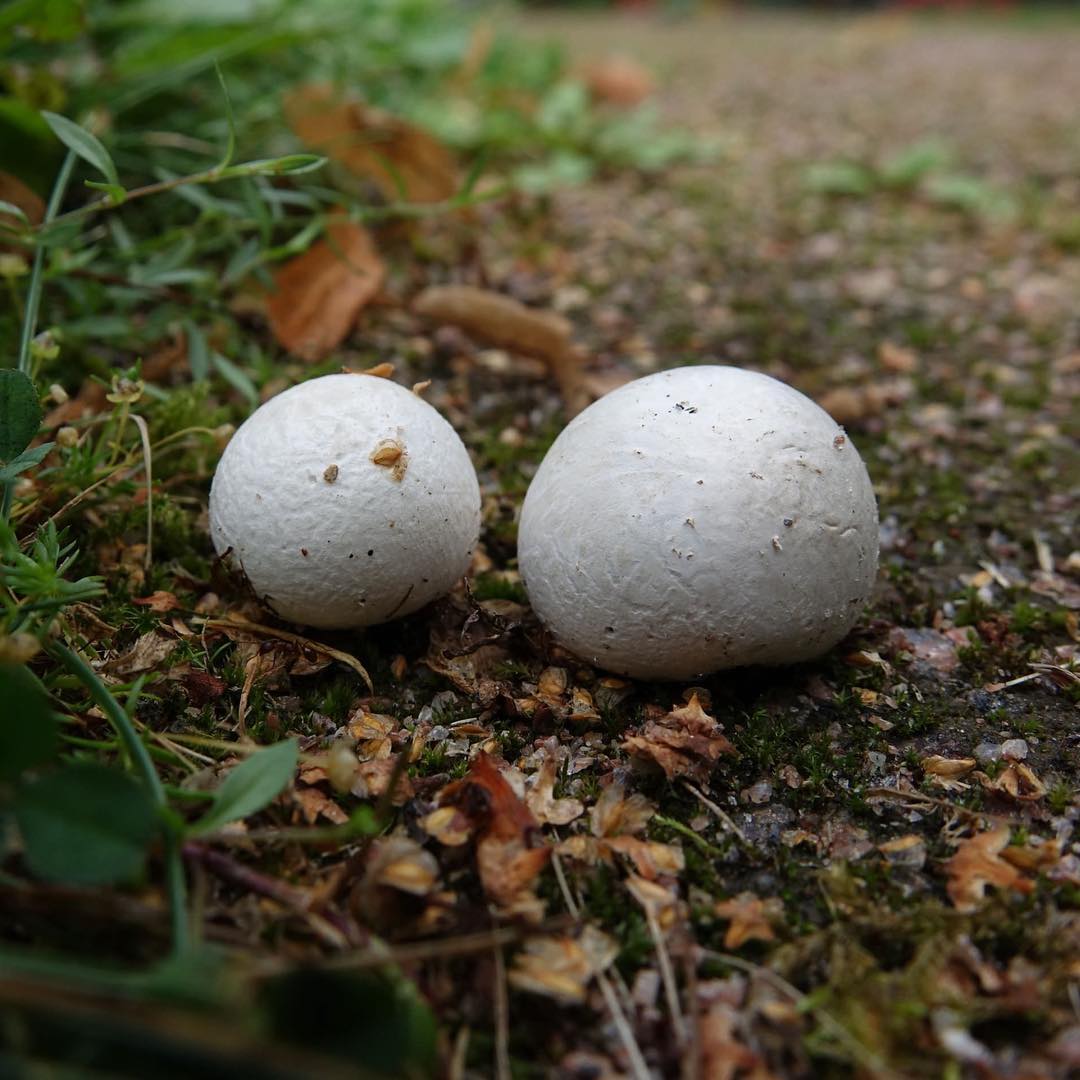
Porkhovka refers to the type of rain mushrooms, hence the fruiting body and the way of reproduction. Very often, young mushrooms can be confused with bird eggs that have fallen out of the nest. Inexperienced mushroom pickers are surprised when they try to pick them up and find a "leg" under them. This mushroom is edible, although it does not have any special taste. It can be eaten only as long as the pulp is white, when it begins to turn black, the mushroom bursts and throws out spores. The body has a spherical or ovoid shape, reaching from three to six centimeters in diameter.
The flares, which have entered the final period of development, begin to turn yellow, after which they very quickly turn black. They have no legs, white pulp with a rather pleasant smell and a barely noticeable taste. The spore powder is brown in color.
This mushroom only loves fertile soils. You can meet this mushroom in deciduous and coniferous forests. Quite often in meadows and pastures.
Basically, this mushroom "hides". At some stages of maturation, this mushroom can be confused with an ordinary raincoat, its difference is a coarser skin. You can collect flapper throughout the summer. The mushroom is edible.
Most often it is dried or boiled.