Related species
Deer roach is a species of mushroom known to most lovers of quiet hunting, which is also called deer mushroom. The hats of this representative of the spit family are quite large; in some specimens, the diameter of the fruiting body can reach solid sizes - up to 200 mm. The color of the surface of the cap is brownish with different shades (variations - from light to dark). This type of mushroom has become widespread throughout the planet, most often the place of their growth is wood of trees of different species (both deciduous and coniferous). This mushroom belongs to the edible species, which can be used for the preparation of culinary dishes.
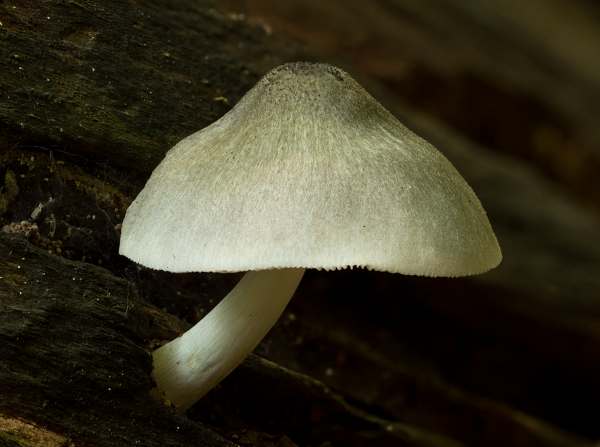
White creep is a fungus that is moderate in size (the diameter of the cap is no more than 50 mm). The cap, as the name of the species implies, is white; in mature mushrooms it acquires a grayish color. The surface of the cap is densely covered with brownish villi. Most often, this species can be found growing on the wood of trees in beech groves. This species, although edible, is nevertheless little known. The main place of growth is North Africa, the Western part of the European region and Siberia.
Umber plyutey is a medium-sized mushroom, the diameter of the cap does not exceed 100 mm, the color of this part of the mushroom is umber or dark brown. The surface of the cap is fleecy, completely speckled with small radial grooves. The place of distribution of this species is the Eurasian continent and North Africa. The species presented to our attention is included in the group of conditionally edible mushrooms. Pulp with a slight bitterness, which disappears after heat treatment (boiling mushrooms is meant).
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
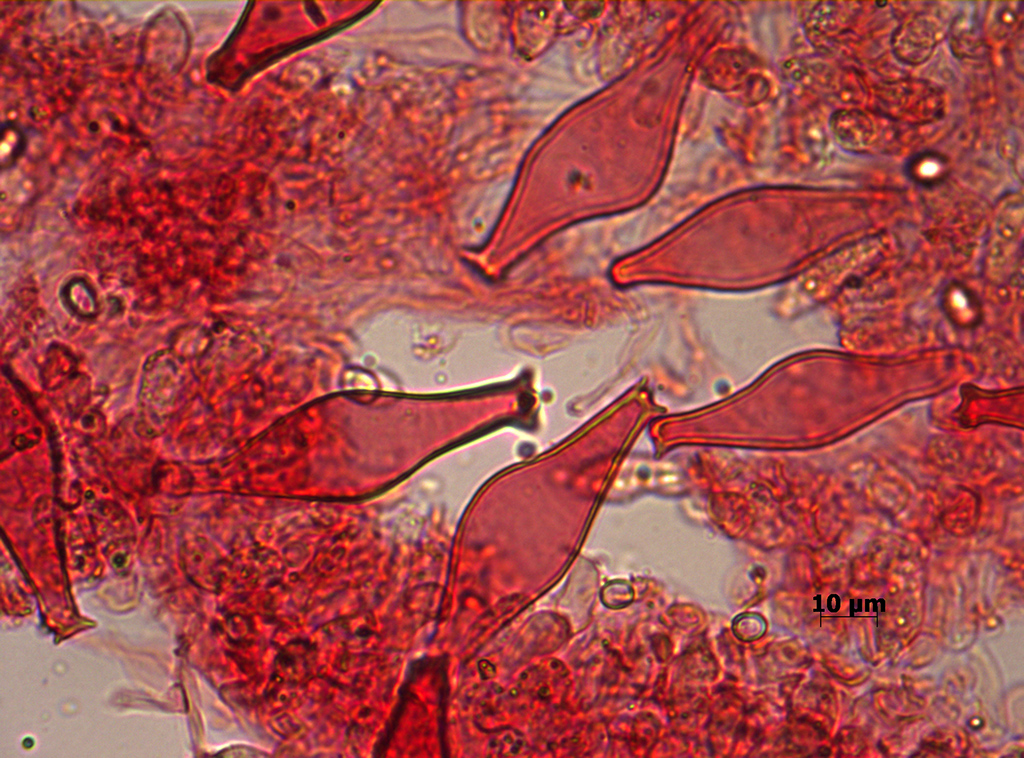
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
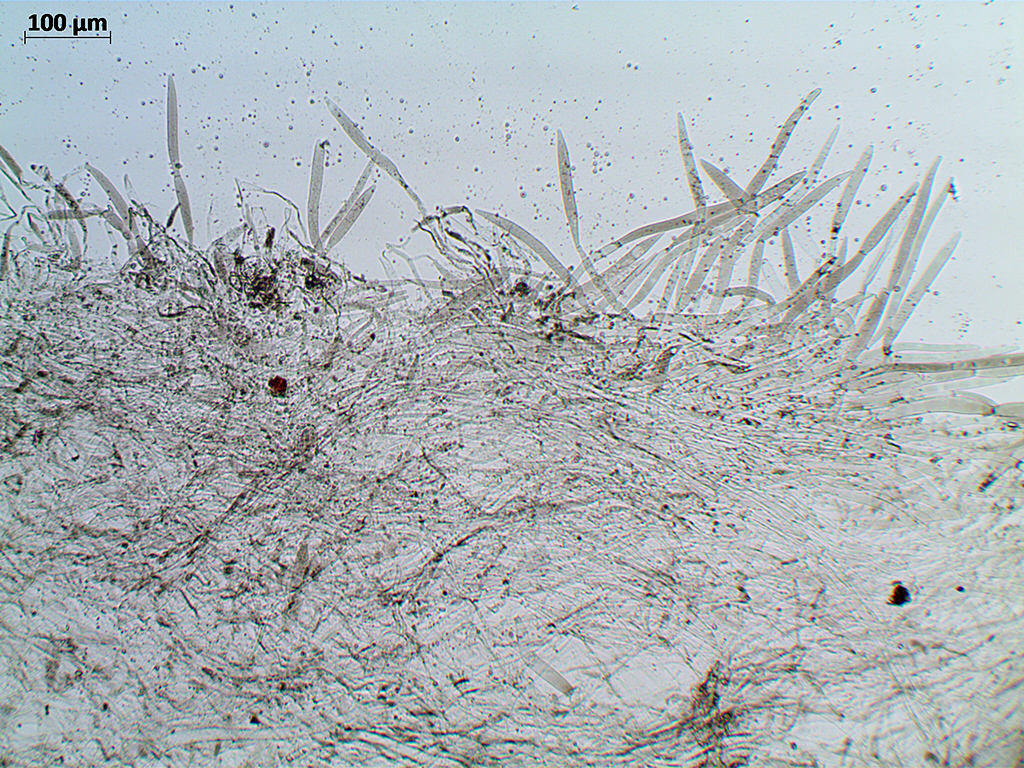
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Pileipellis (Pileipellis)
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Ixokutis
-
Cutis, consisting of hyphae immersed in mucus. The surface of the cap is oily, slippery or slimy.
Lat. Ixocutis.
See Cutis, Gifa.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
Similar types and differences from them
Even a novice mushroom picker can easily distinguish a willow spit from other spits. The main difference is the spots on the leg of a blue or green hue. However, this trait is highly dependent on the area where the fungus grows.
The hero of the article can be confused with small representatives of the species "reindeer whips" (in Latin - Pluteus cervinus), from which it will differ in the color of the pulp after the cut (in the deer, the cut does not change color). Also, a microscope will help to distinguish these two species from each other: the deer spit does not have the buckles on the mycelium, which the willow has.
Based on the foregoing, it is possible to eat willow sticks for food, but this must be done carefully and carefully.
Pay attention to where you collected it. Maybe not worth the risk and taste it
Growing a mushroom mushroom at home
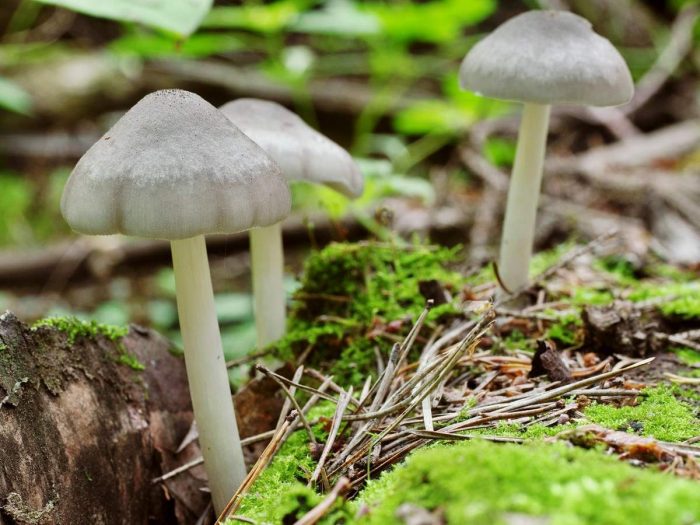

To grow the spit, a homogeneous or combined substrate of two or more constituents is prepared in any proportions (for example, just straw, or straw with sawdust and hay), it is placed in a container and poured with boiling water. The steamed substrate is allowed to cool down to 20-30 ° C. Then it is squeezed well and thoroughly mixed with mycelium (1 pack for 15 kg of moistened substrate). The resulting mixture is placed in a transparent plastic bag, lightly crushed and tied. To ensure air exchange, incisions are made about the entire area of the package (3-5 cm).
The mushroom block obtained in this way is left indoors or in a shady place in the garden. During the first month of germination, he does not need lighting. First, fluff appears, then the substrate becomes white or yellowish and turns into a dense block. After 1.5-2 weeks, the rudiments of fruiting bodies appear and the block is placed in the light, and film cuts are made in the places of the rudiments. Fruiting occurs in waves, every 2-3 weeks. The largest harvest comes from the first 2 waves.
Also, cakes are grown on deciduous non-rotten wood.
To do this, pick up bars and logs with a length of 30-40 cm and diameter 25 cm... They are soaked in water for a week. Next, holes are drilled or sawed into them, into which the mycelium is placed (1 package per 15 kg), and from above they are sealed with a watering can with tape or laid with straw. The mycelium grows from 3 to 6 months at a temperature of 7-27 ° C. At this time, the bars are placed in shady places in the garden or in ventilated areas. The crop is harvested 1-2 times in the spring and 1-2 times in the fall.
Characteristics of the mushroom plyutei
Hat
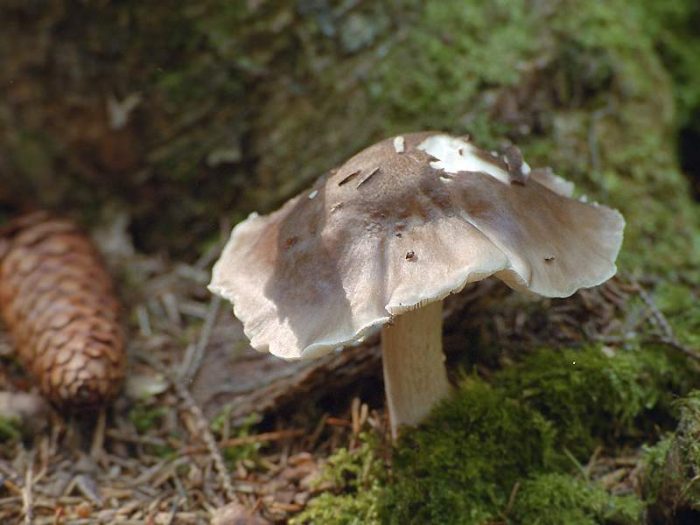

The cap of the mushroom is bell-shaped or prostrate, with a tubercle in the center, easily detached from the stem. The size of the cap varies from 1 cm in the smallest species to 20 cm in the large ones. The maximum cap diameter of 24 cm was recorded for the deer spit. The surface is smooth, fibrous, silky or scaly, dry, sometimes slimy or wrinkled, with mesh veins. The color of the cap is also different: from white to almost black, most often brownish-brown, or bright, yellow or orange.The edge is solid or ribbed.
Pulp
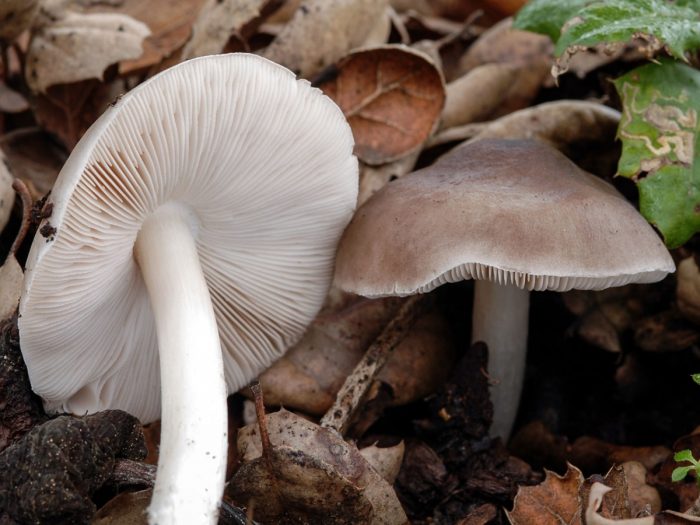

The pulp is light, fleshy, white, grayish or yellowish in color. On the cut, the color does not change, in some species a greenish or bluish tint appears, which is a sign of the presence of psilocybin in their pulp. Smell and taste are poorly expressed. In some species, the pulp is bitter.
Leg
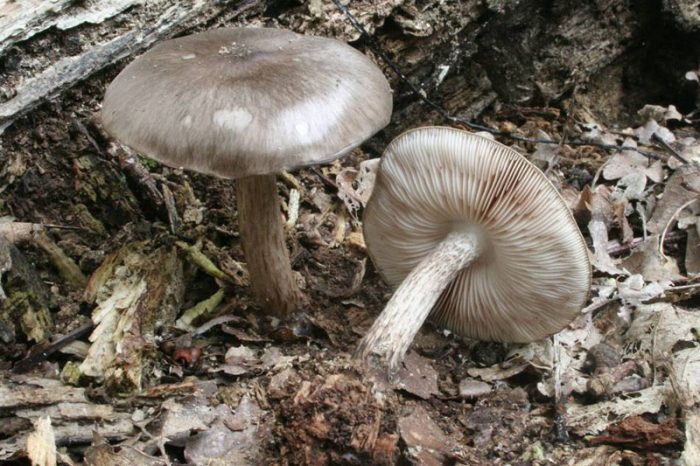

The leg is cylindrical, expands to the base or tuberously swells, fleshy, brittle, solid, sometimes hollow. The surface is naked, fibrous or covered with scales, the base is pubescent.
Types of mushroom plyutei
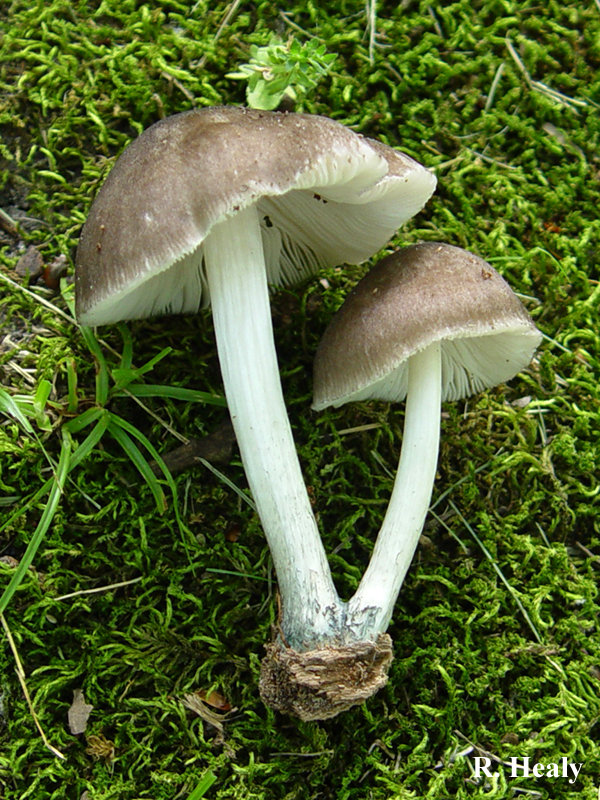
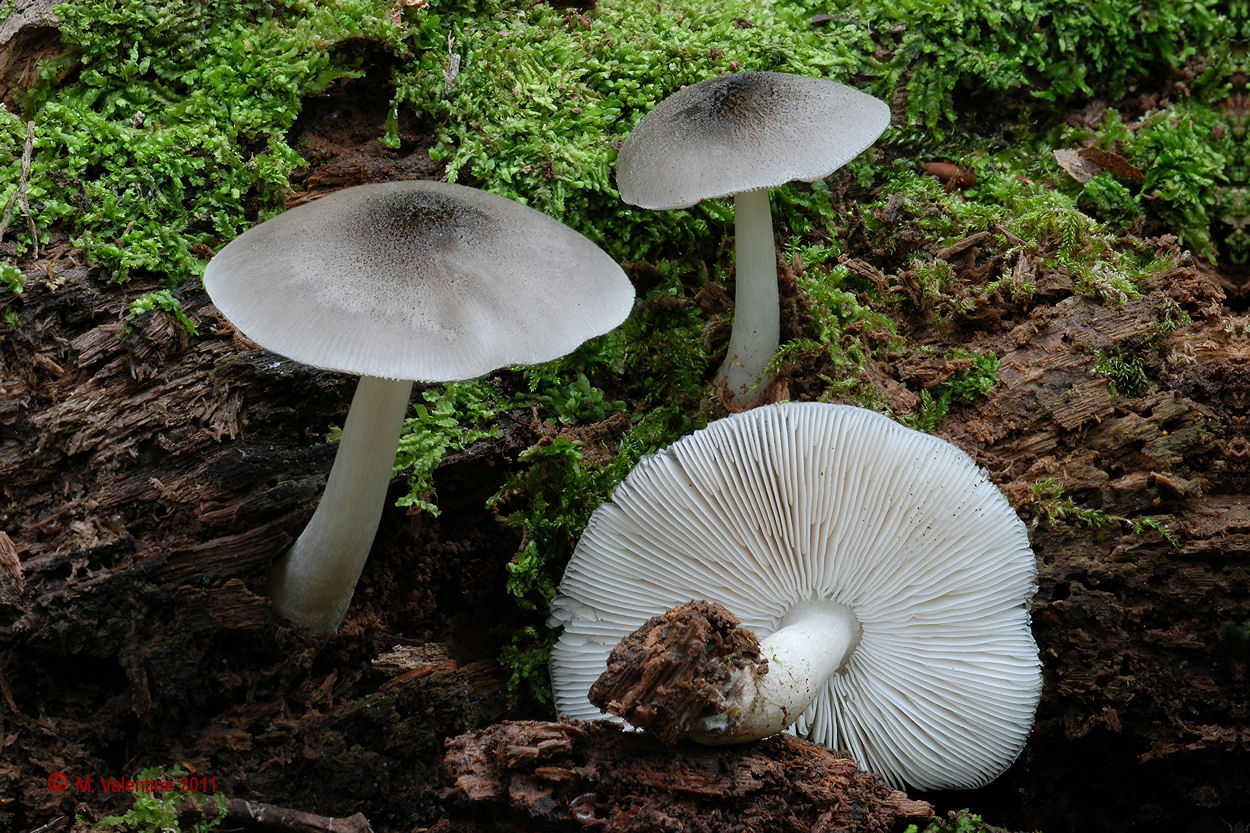
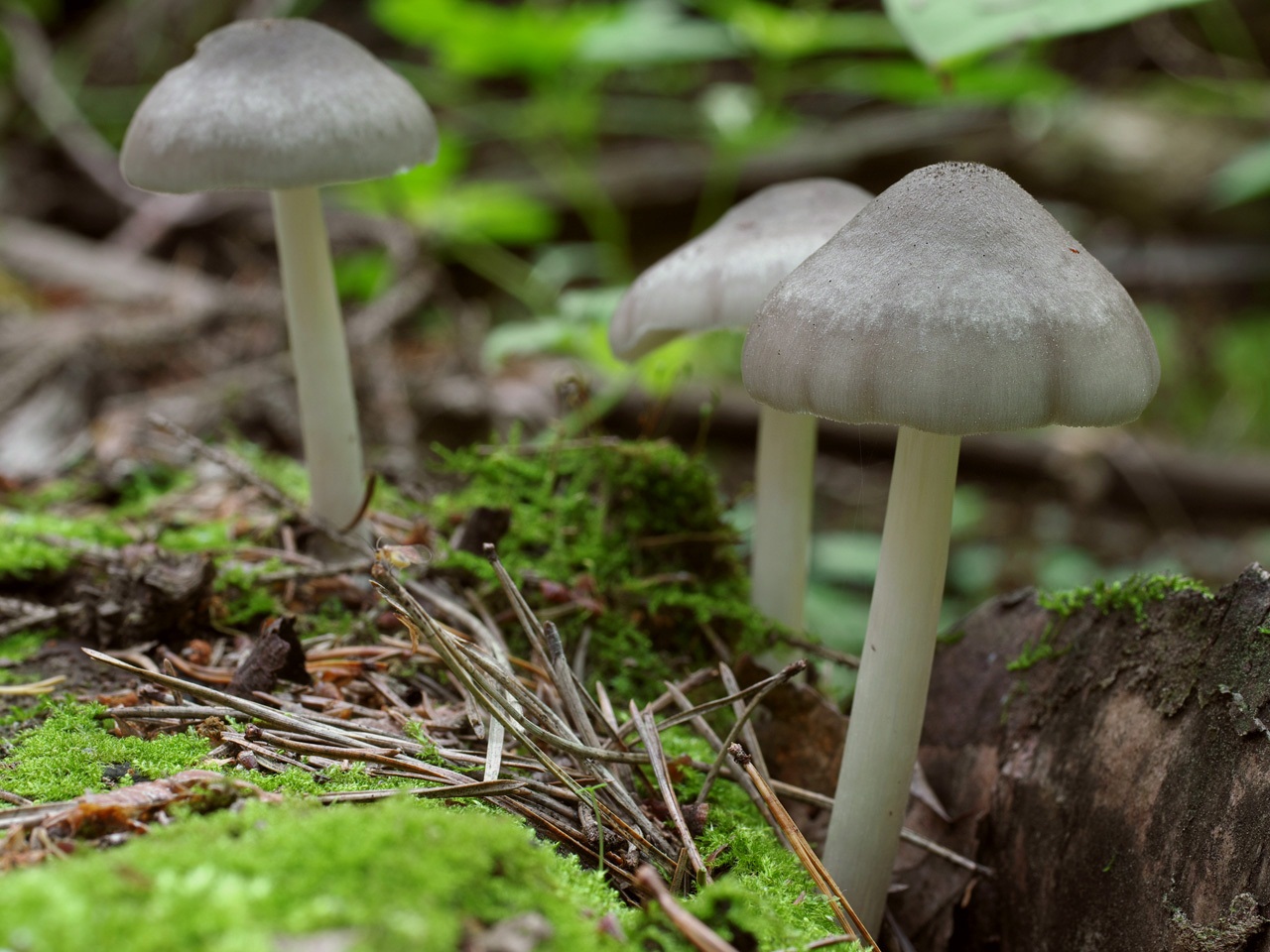
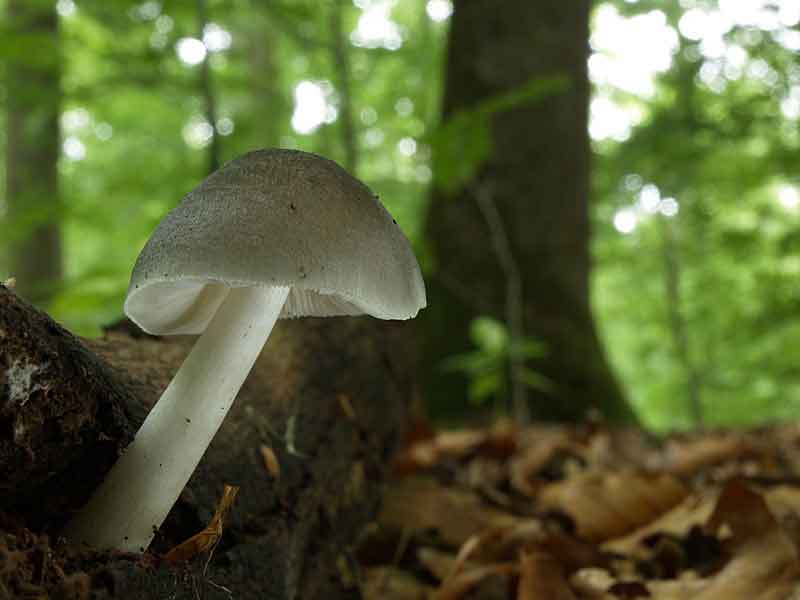
Deer roach (Pluteus cervinus)

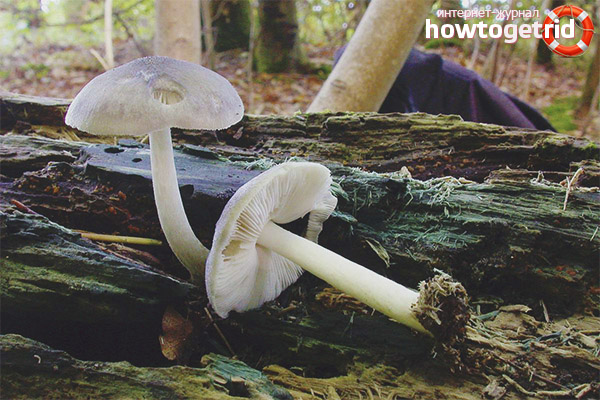
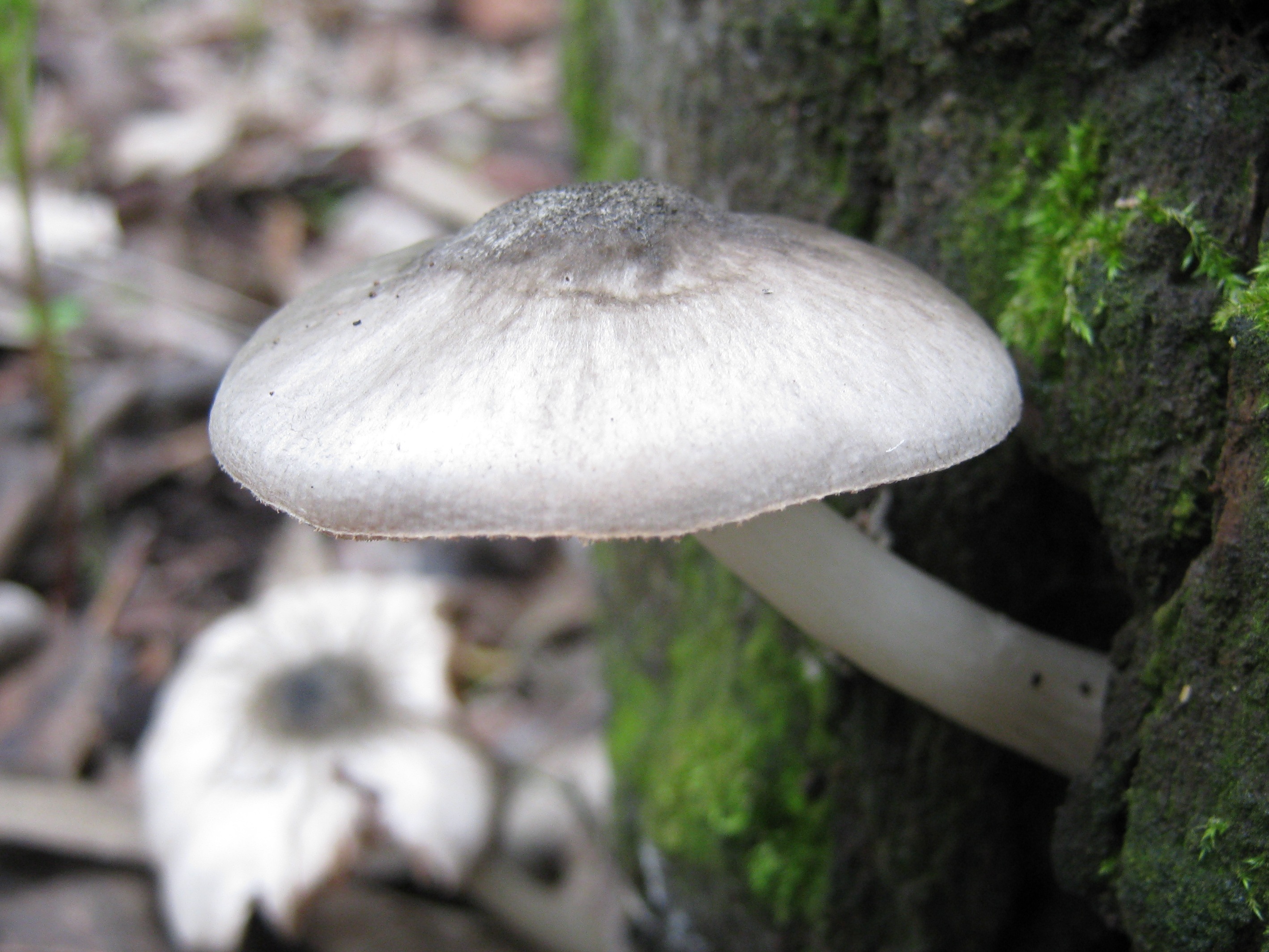
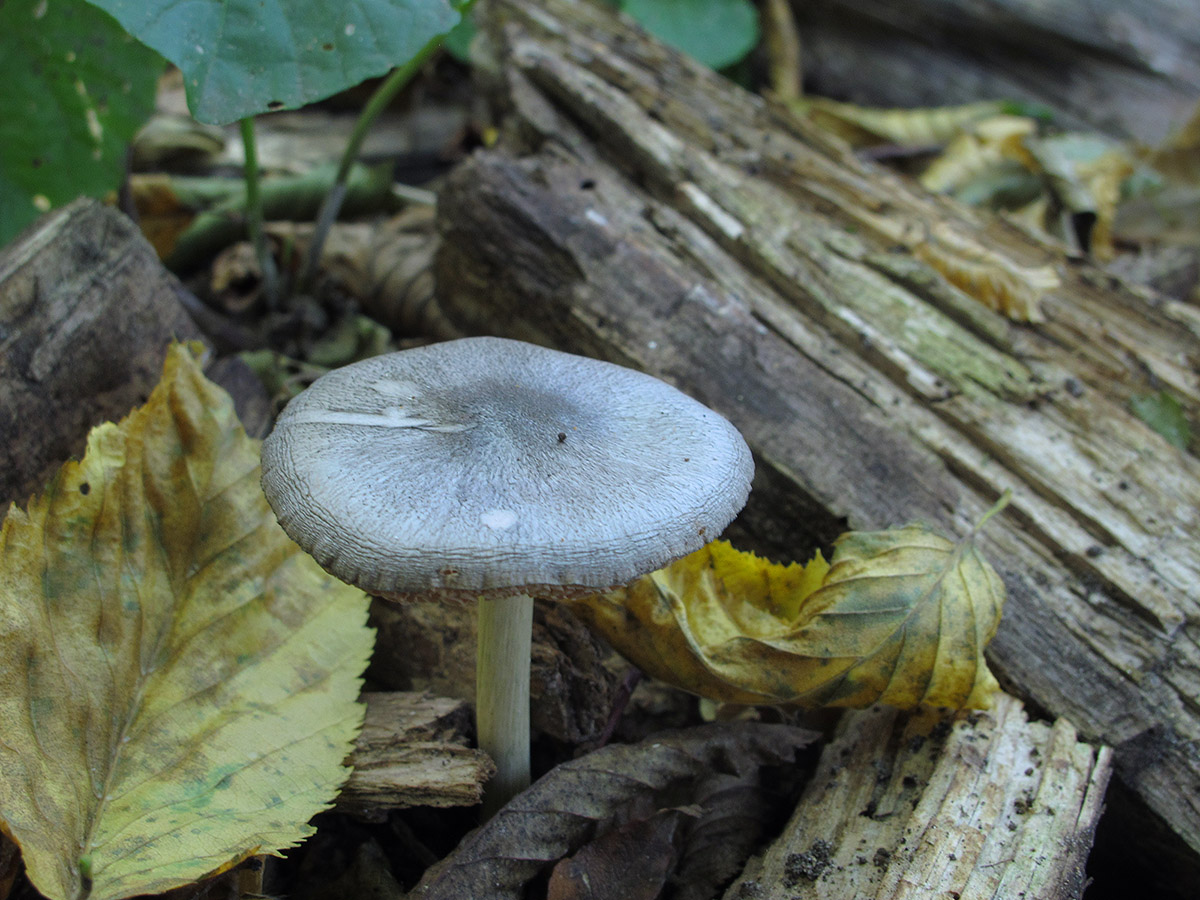
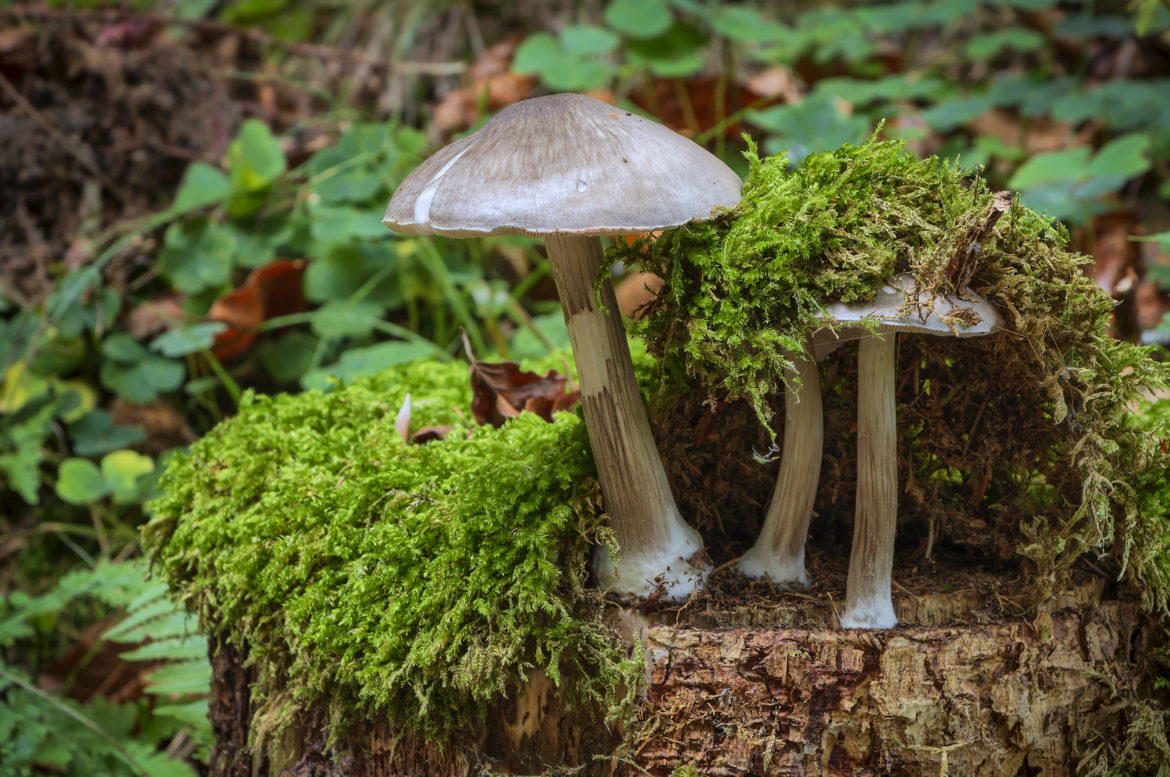
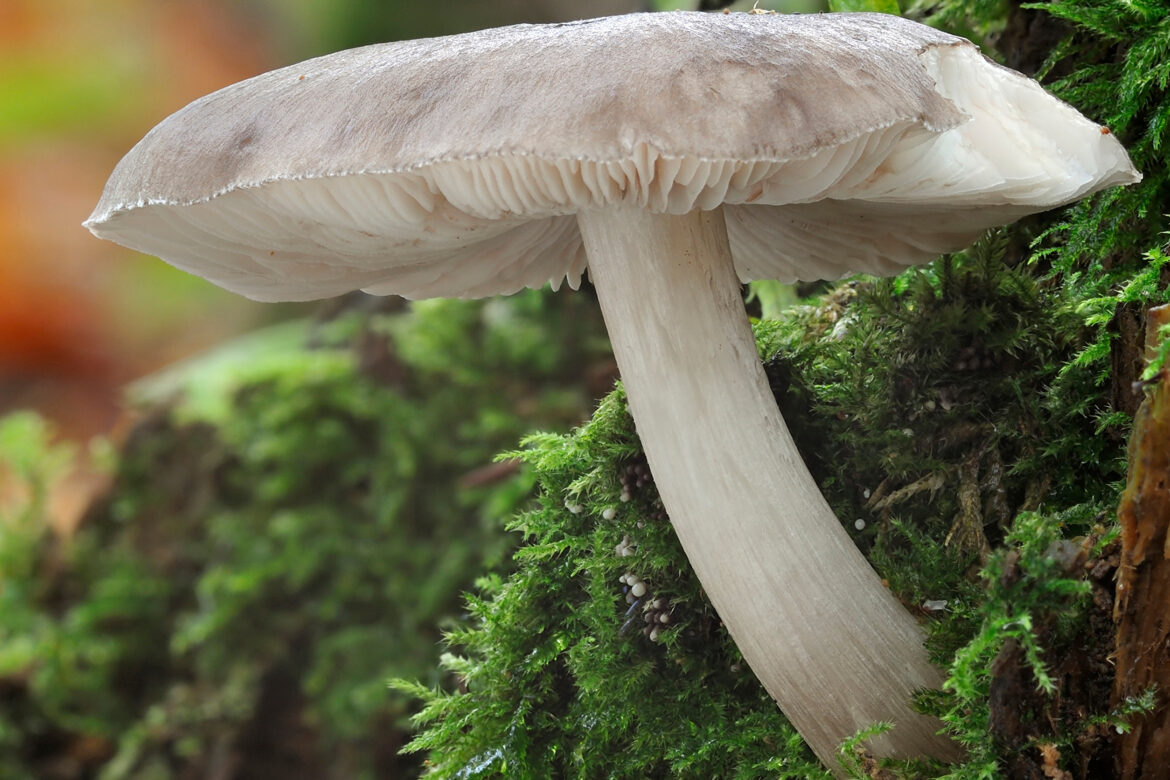
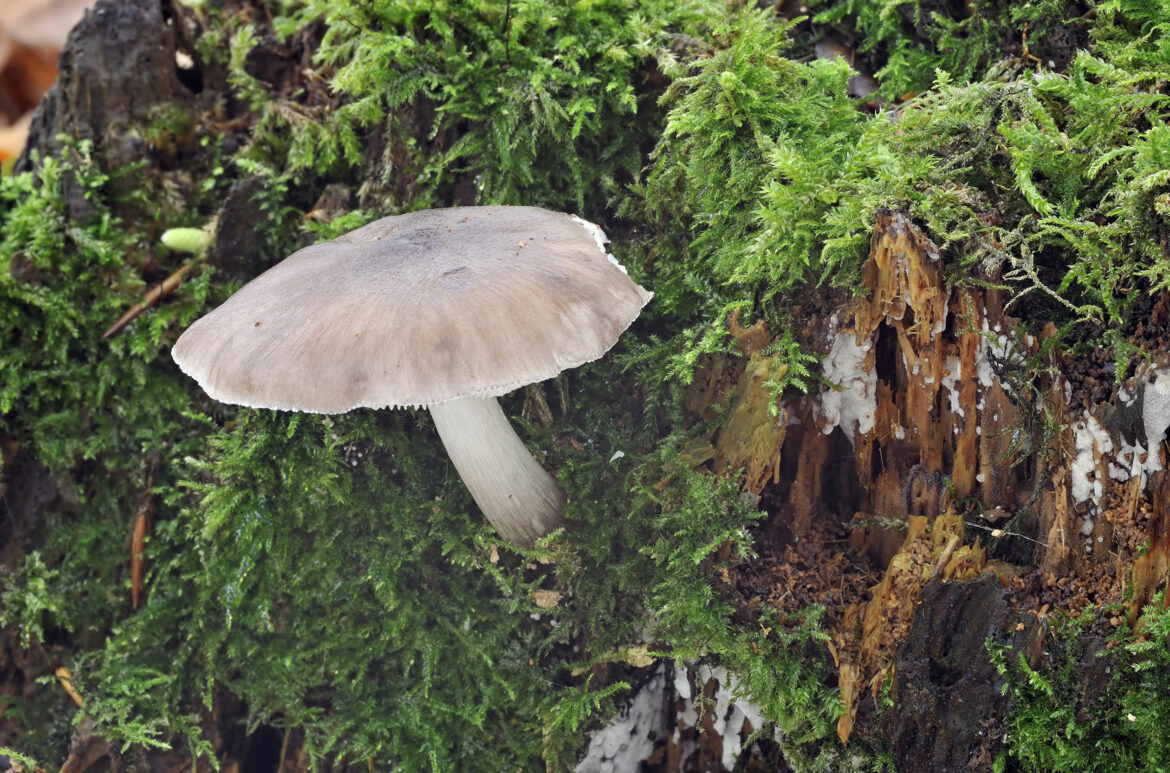
Also known as deer mushroom. Medium to large size, with a cap diameter of 4-10 cm, sometimes up to 20 cm.The surface is smooth, silky, fibrous, cracks in mature mushrooms, becomes dry or slightly mucous, gray or grayish brown, sometimes the color changes from fawn to dark brown and black. The length of the leg reaches 15 cm, the shape is cylindrical, curved, swollen at the base, the structure is dense, solid, the color is white or whitish-gray.
Deer roach is a cosmopolitan mushroom that is found all over the world, growing on the wood of deciduous and coniferous trees.
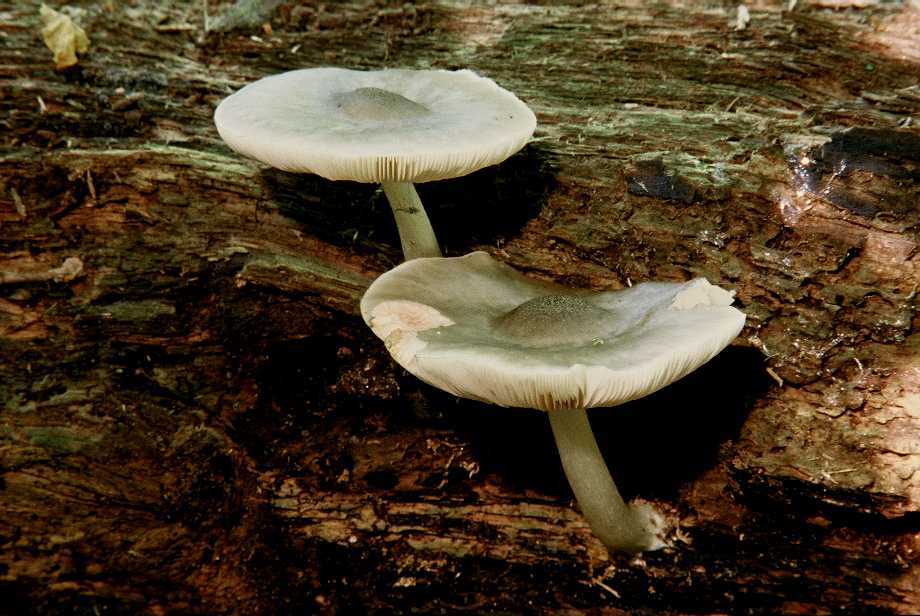
White corkscrew (Pluteus pellitus)

The cap is 3-5 cm in diameter, finely fleshy, with a tubercle in the center, the edge is torn, lobed. The surface is smooth, whitish in color, gradually acquires a grayish, grayish-brown or bluish color in the center, covered with pink or brown fibers. The length of the leg is up to 6 cm, its surface is shiny, fibrous.
Distributed in Eurasia from Western Europe to Western Siberia, and in northern Africa, a rare species. Grows on beech wood.
Little known edible mushroom.
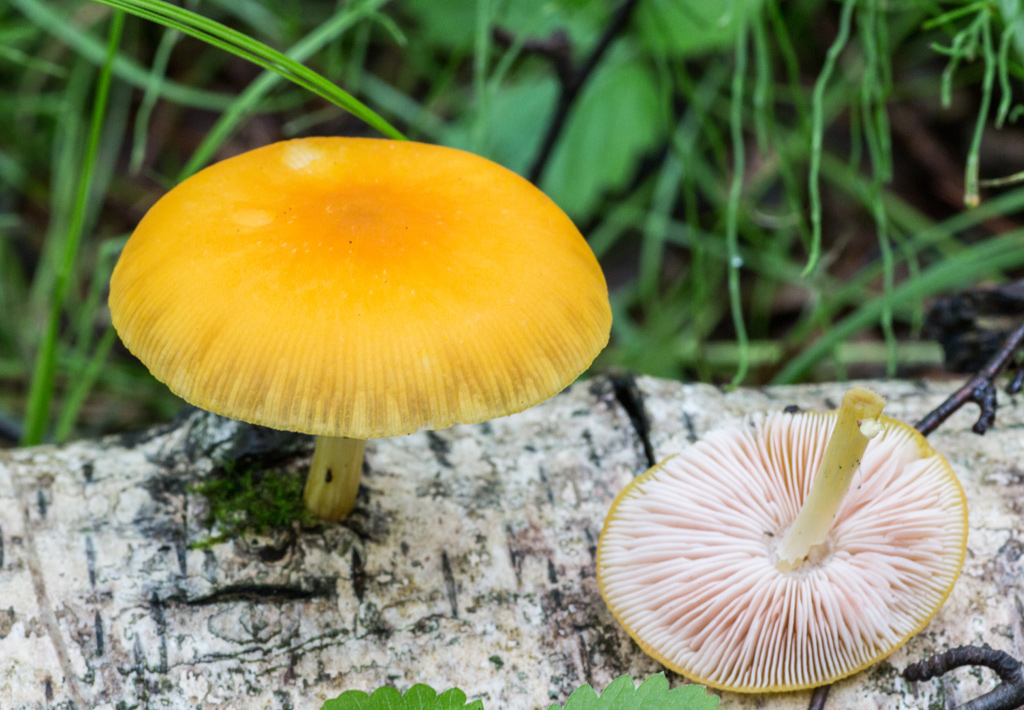
Pluteus lion-yellow (Pluteus leoninus)

The cap is up to 8 cm in diameter, the shape is bell-shaped or flat-convex, there is a tubercle in the center, the edge is serrated. The surface is bare along the edge, velvety in the center, finely scaly, bright yellow, dark in the center. The leg is up to 7 cm long, about 1 cm in diameter, smooth, white with a yellow base.
The species is widespread in Eurasia, in northern Africa, where it grows in oak and beech forests, and is rare.
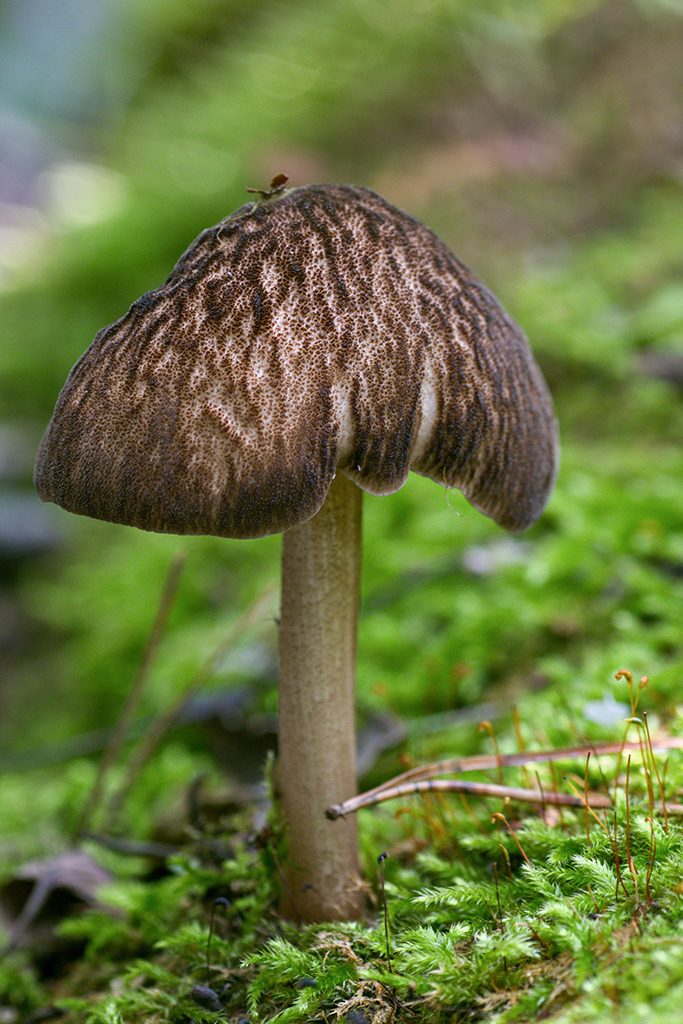
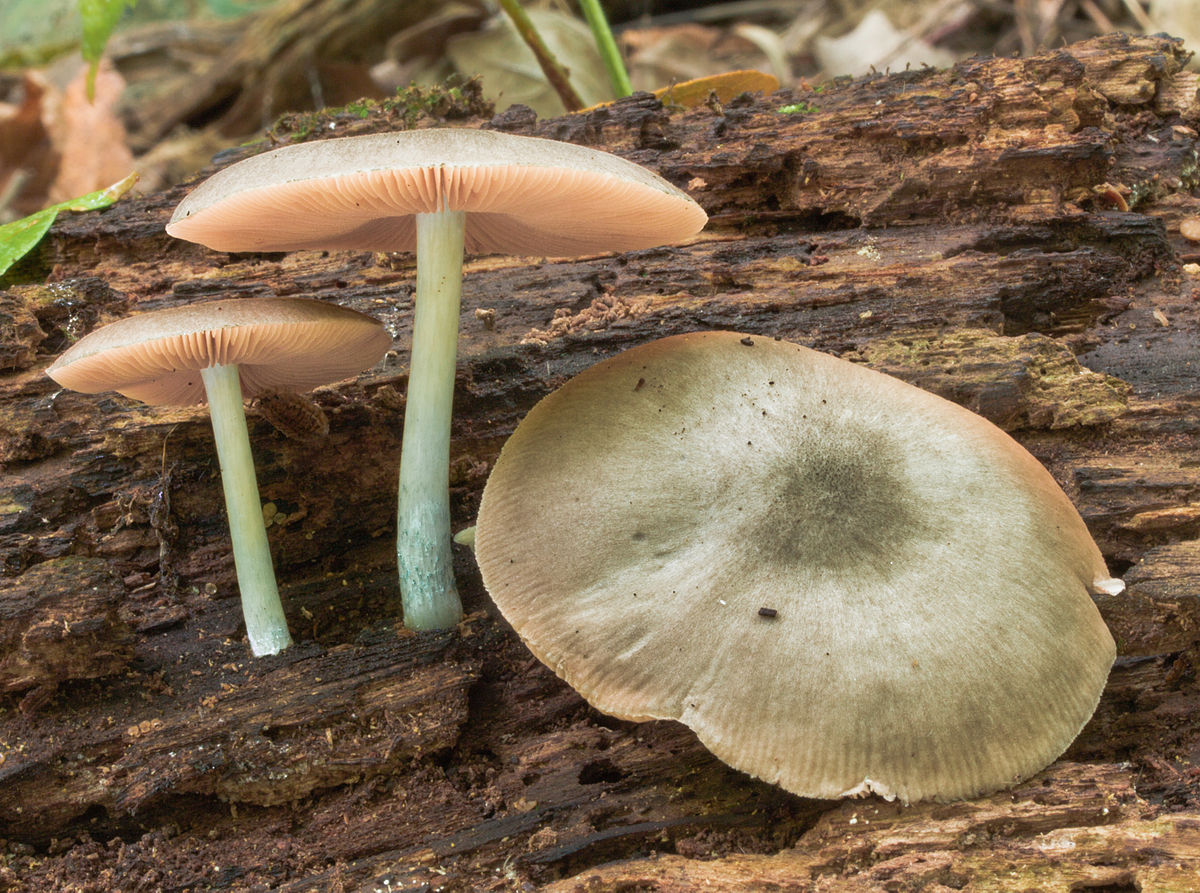
Umber roast (Pluteus umbrosus)
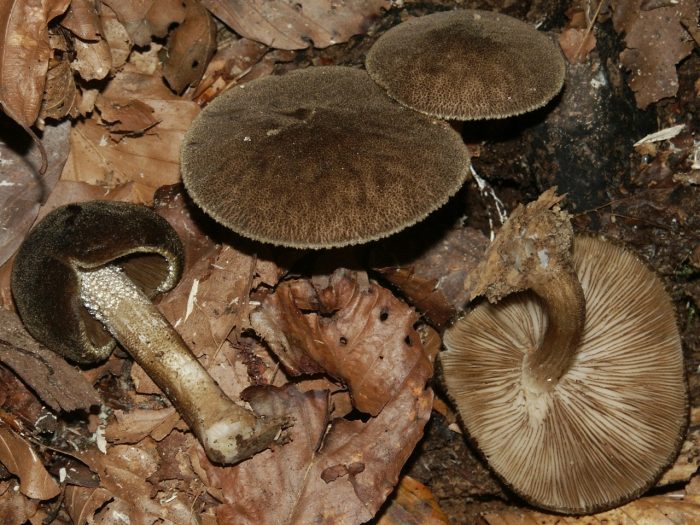

The mushroom is medium in size, with a cap diameter of up to 10 cm. The cap is tomentose, wrinkled, whitish or dark brown, the edge is serrated, fibrous. Leg up to 10 cm in length, whitish or brownish, longitudinally fibrous, scaly.
The species grows in Eurasia and North America, on the wood of deciduous trees, a rare species.
Conditionally edible mushroom, as its pulp is bitter, but during boiling the bitterness disappears.
Poisonous and inedible species of mushroom plyuch
Plutey noble (Pluteus petasatus)
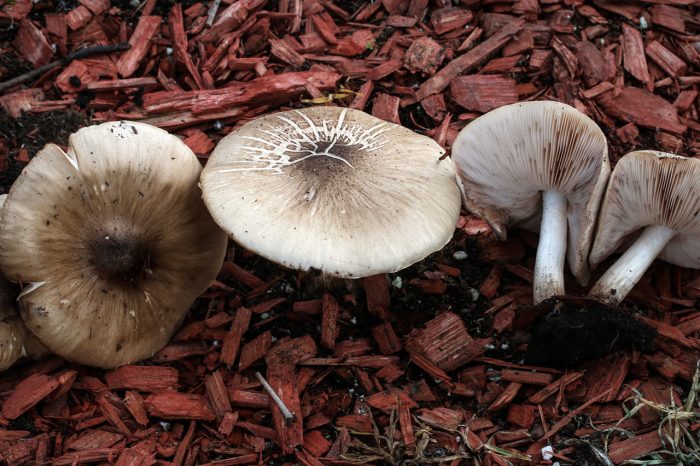

The cap reaches 15 cm in diameter. Its color is light, from whitish to ocher, the surface is silky, shiny, dry, rarely slimy, in the center it is covered with small brownish scales.
The species is found in Eurasia from Western Europe to the Far East, as well as in North America, but it is a rare species and is included in the Red Data Books of the Yaroslavl and Arkhangelsk regions of Russia. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests on beech, oak, poplar wood.
Scaly corkscrew (Pluteus ephebeus)
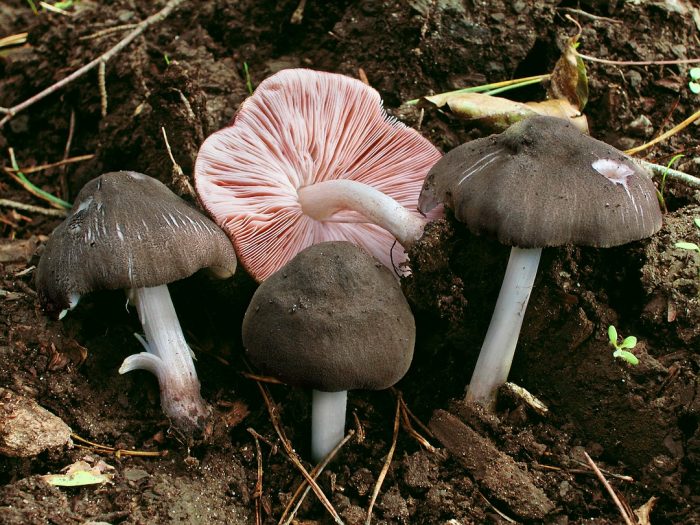

The mushroom is medium in size, the diameter of the cap is about 9 cm, the leg is 10 cm long. The surface of the cap is fibrous, grayish-brown, covered with scales in the center, cracking. The stem is whitish, shiny, smooth, with grooves.
Rare view. Grows on the wood of deciduous trees, distributed in Eurasia and North Africa.
Dwarf clown (Pluteus nanus)
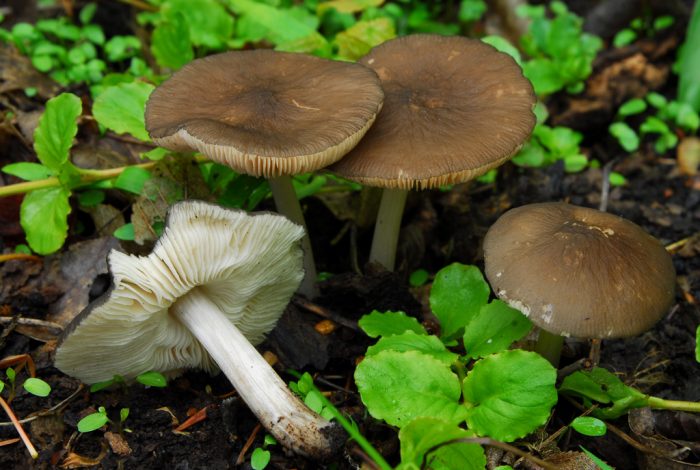

The hat does not exceed 5 cm in diameter, the surface is velvety, wrinkled, brownish or chestnut-brown in color with a green tint, covered with a coating. Leg up to 5 cm long, light, with a yellowish or brown tint, smooth, shiny, fibrous.
The species is common in deciduous forests of Eurasia and North America.
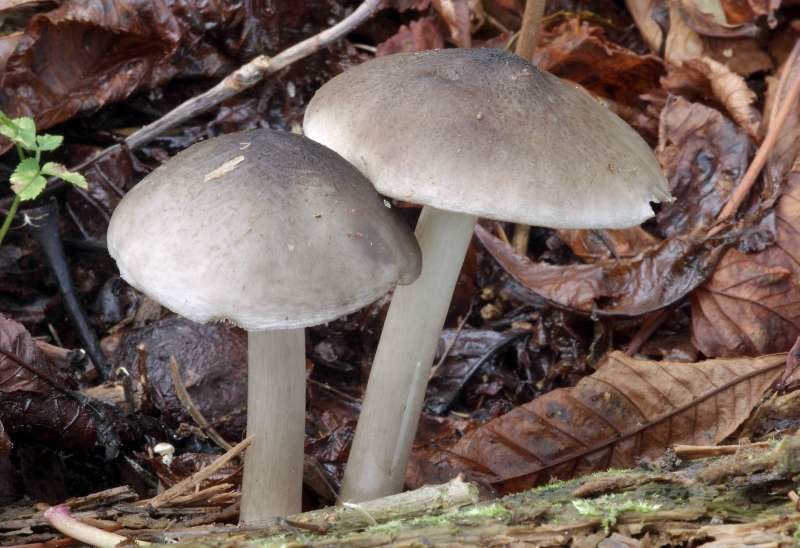
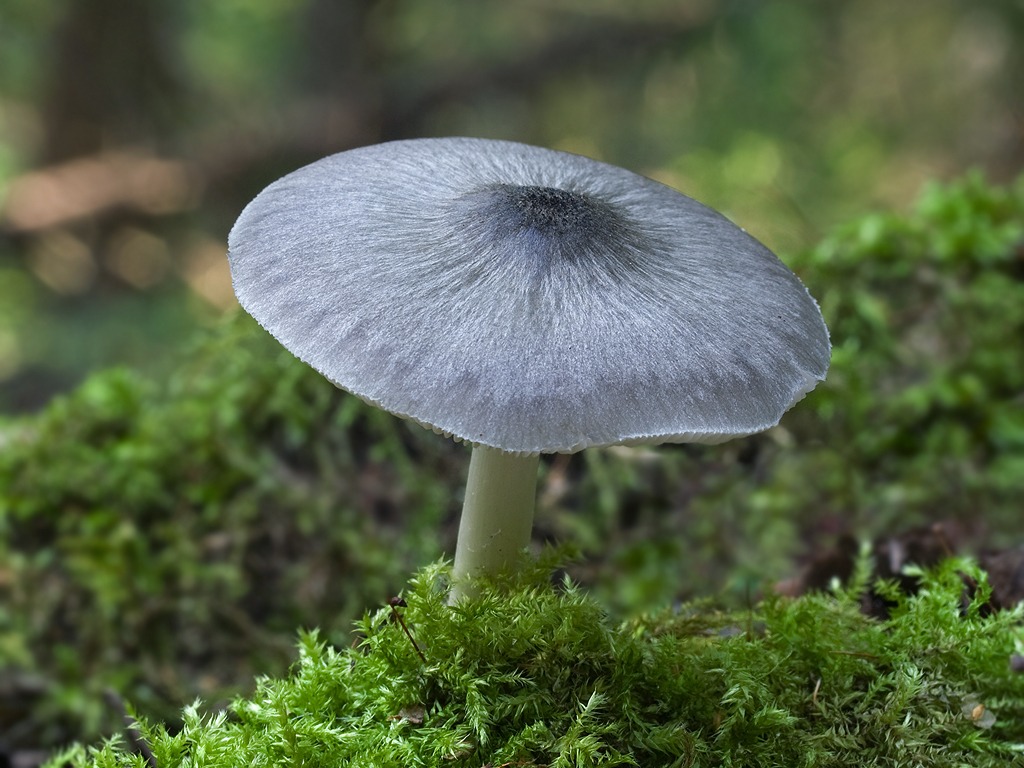
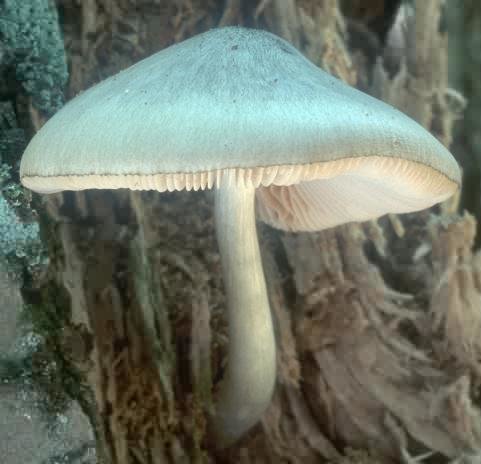
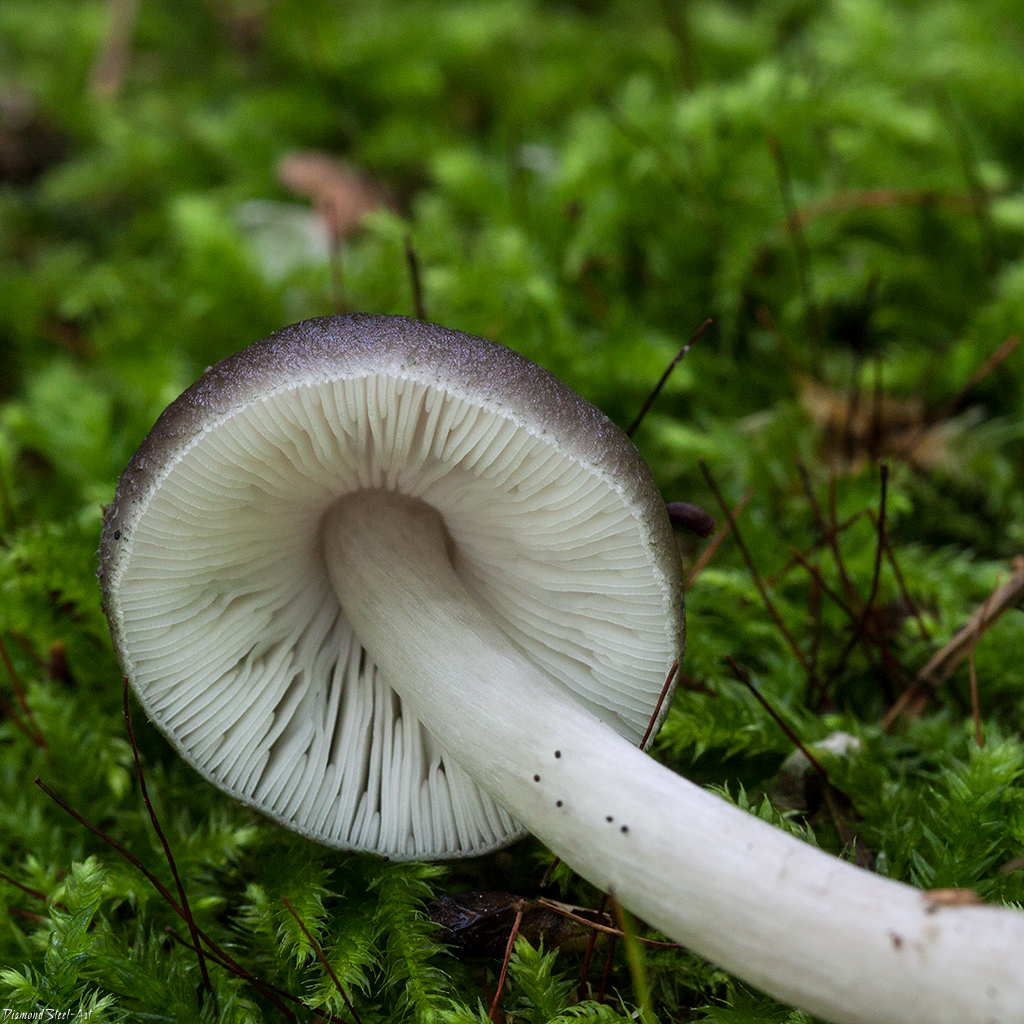
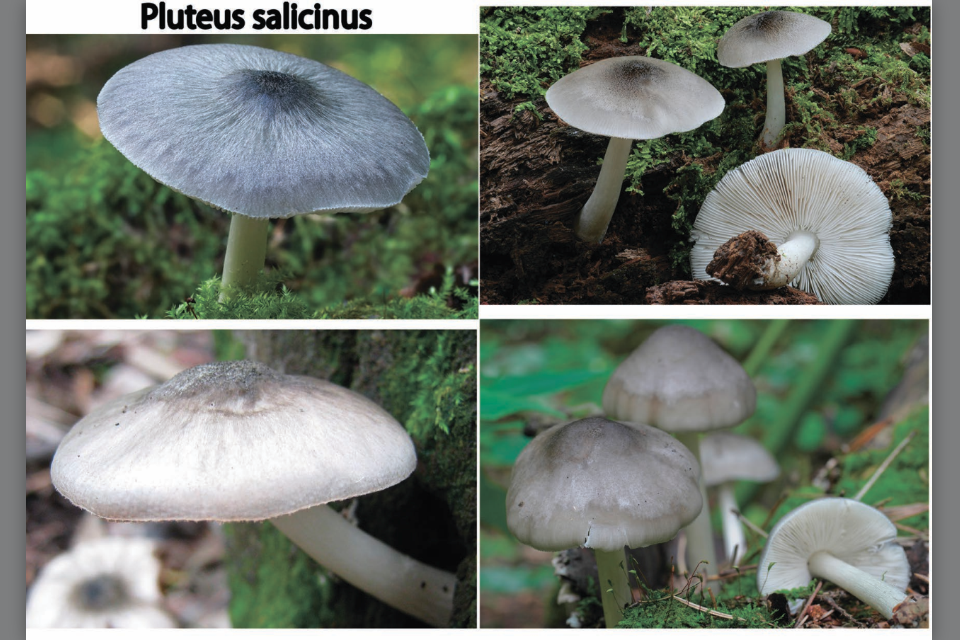
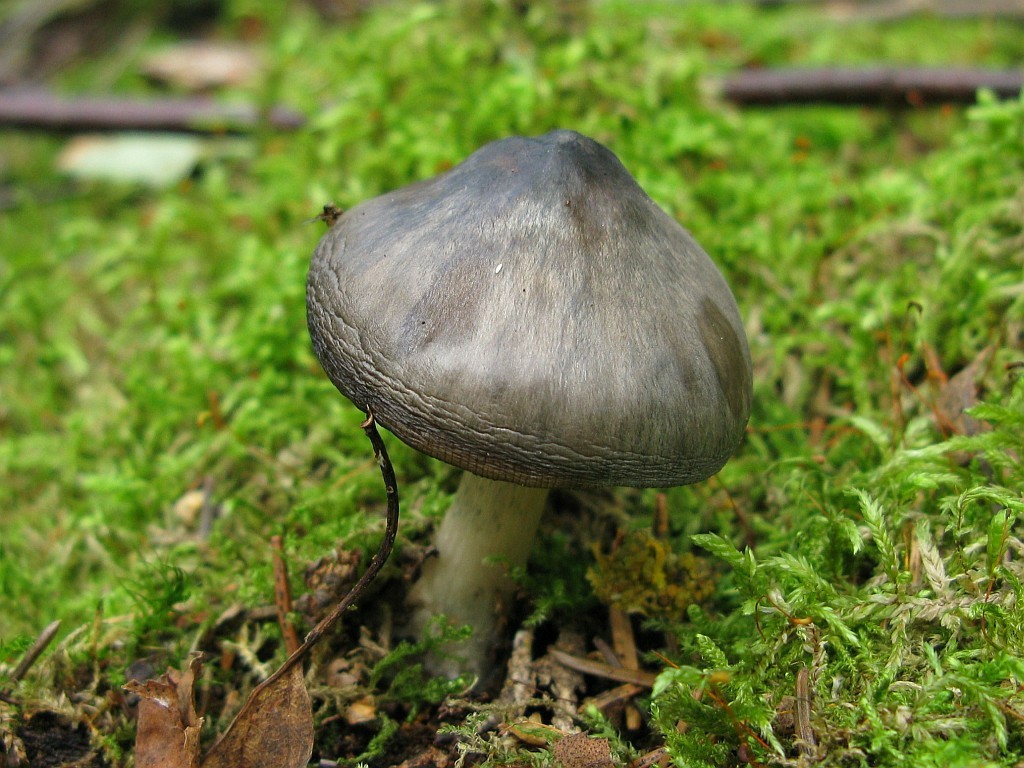
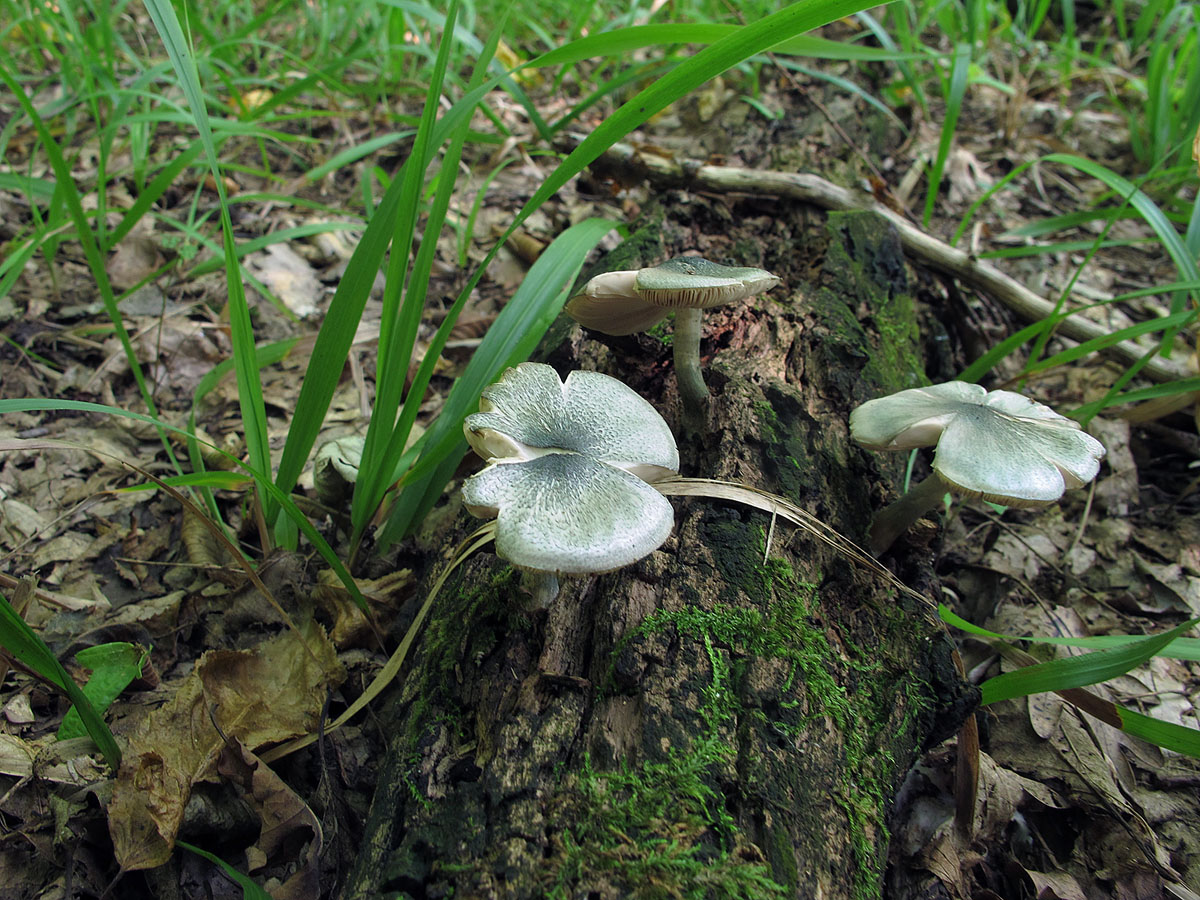
Willow roach (Pluteus salicinus)
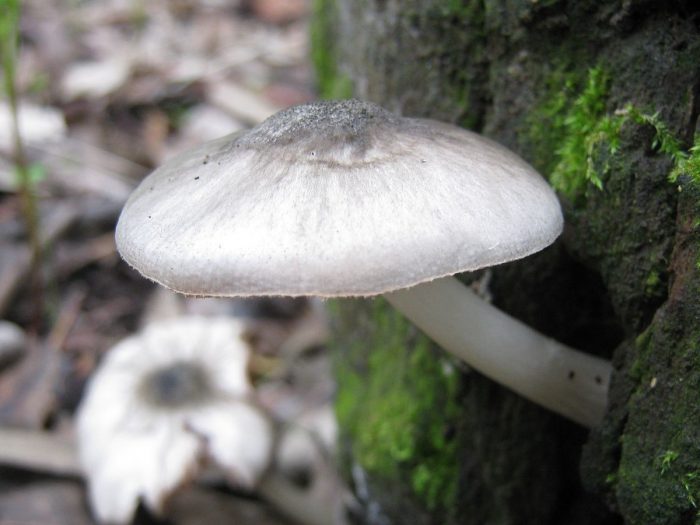

The diameter of the cap is up to 7 cm, the structure is thick-fleshed, the shape is from bell-shaped to flat-spread, with a tubercle. The edge is finely fleshy. The surface is shiny, wrinkled, covered with scales in the center, grayish or ash-gray with a bluish or pinkish-brown tint, darker in the center. Leg up to 12 cm long, shiny, bluish or grayish-olive.
Grows on wood of willow, alder, poplar, oak, beech. Found in Eurasia, North Africa and North America, a rare species.
In addition, there are genera of mushrooms with fruiting bodies similar to spits. One of them is entoloma, for which poisonous species are known. These mushrooms are distinguished by the fact that their plates are either narrowly adherent or creeping down, but they are never free, like that of a spit.
In the Rhodocybe fungi of the entolomaceae family, the plates are adherent and descending, the cap is with a depression in the center, and their spores are ornamented.
The clitopils have a depression on the cap, the plates are descending, the spores are striped.
Description of the mushroom mushroom.
Plutey is the general name for a whole genus of mushrooms, among which there are not only edible, but also hallucinogenic and poisonous. This genus is included in the Pluteev family, contains many varieties, the number of which is still not known exactly. Of the studied varieties, science knows only 50, but according to unofficial data, there are much more species - up to 300. Translated from Latin, the name of this genus means "shield".
The fungus is not a parasite, on the contrary, in nature it performs the most important function - it is responsible for clearing the forest. Plutey provokes the process of decomposition of dead wood, therefore it is rightfully considered a "forest orderly". Consider the external characteristics of edible varieties that are often found in forests.
- Willow rogue.
A common mushroom, found almost all over the world, except Australia. The most common mushroom in Eurasia, less common in Africa and North America. The willow roach is an edible variety that belongs to the third category.
The hat can grow up to 9 cm in diameter, is painted in unusual colors - it can be ashy, pinkish or gray-blue. The youngest mushrooms have a bell-shaped cap. In old mushrooms, the caps become flat, open, a network of wrinkles appears on their surface, and the edges become slightly darker.
Low, cylindrical stem in young mushrooms, starting at 3 cm in height. In mature mushrooms, the height of the leg is not more than 13 cm, and the diameter is up to 2.5-3 cm. The leg is tapering, fibrous, painted in a white or bluish tint. The plates are narrow and frequent, not adherent to the stem, from white to pinkish-cream shade.
- White rogue.
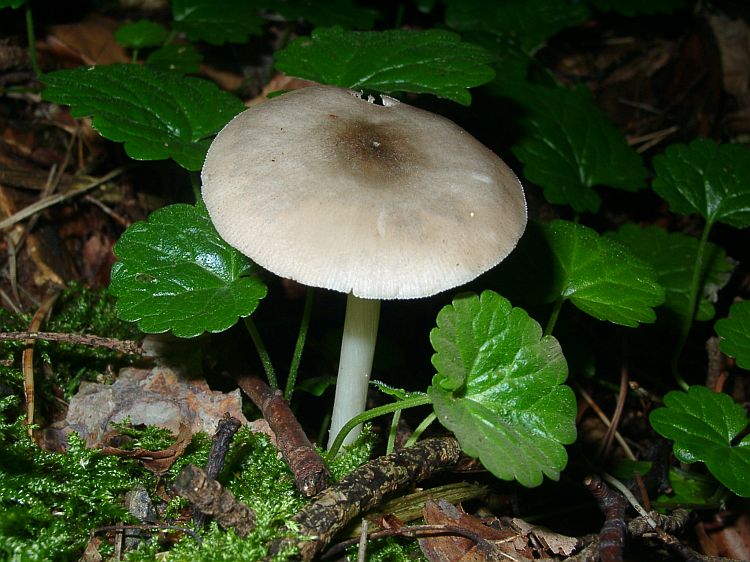
This variety is used for frying and drying and has good taste. White plyuti is widespread in oak forests and poplar plantations. The diameter of the mushroom cap is from 4 to 10 cm, from bell-shaped to open-ended, painted in a light yellow, white or lemon shade.
The plates are pale yellow or white, rare, can acquire a pinkish tint in mature mushrooms. The leg is up to 8-9 cm in height, closer to the cap it is narrower and wider at the base, dense and fibrous. The pulp is odorless and tasteless, pale yellow or white, does not change its color during oxidation.
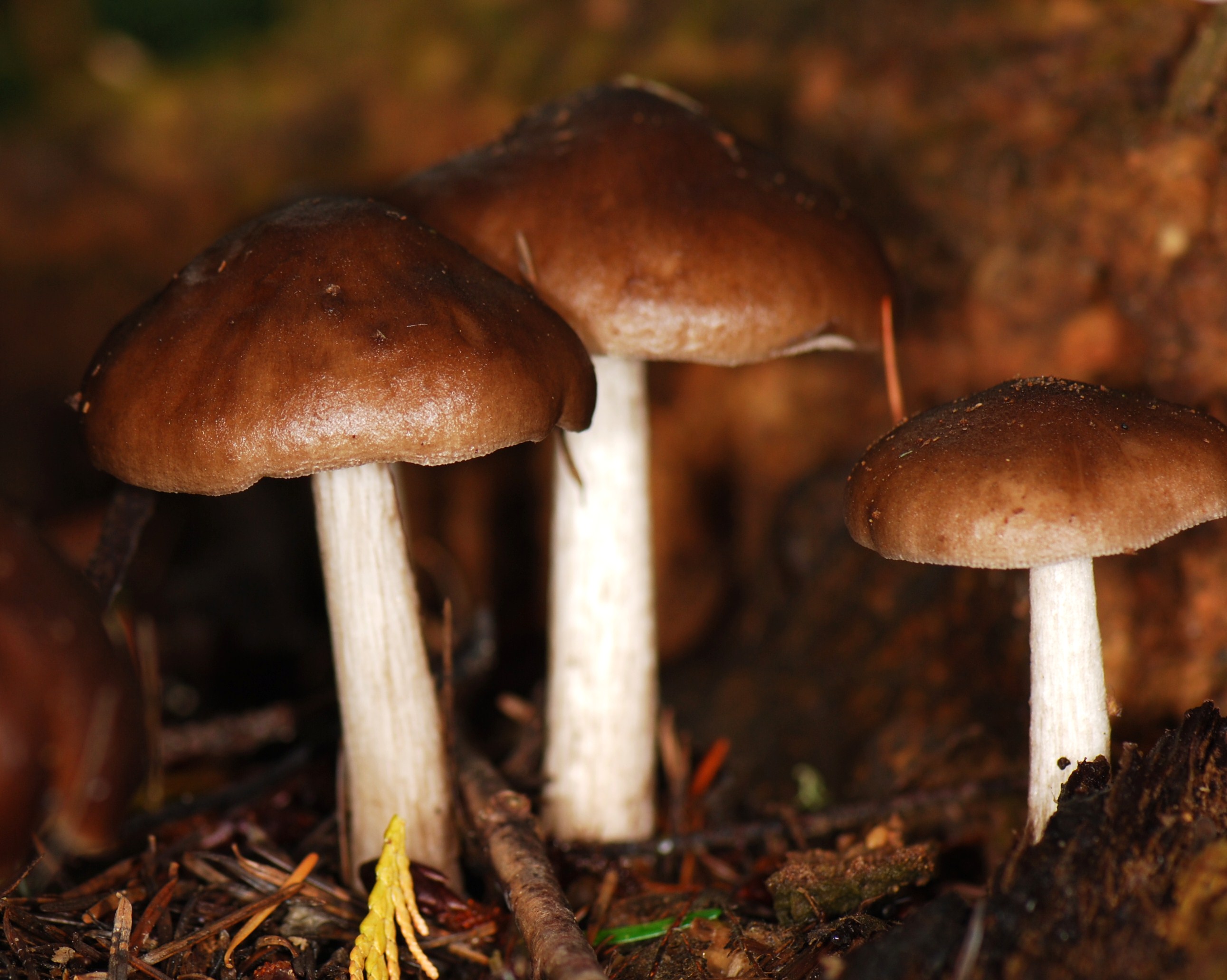
- Reindeer rookies.
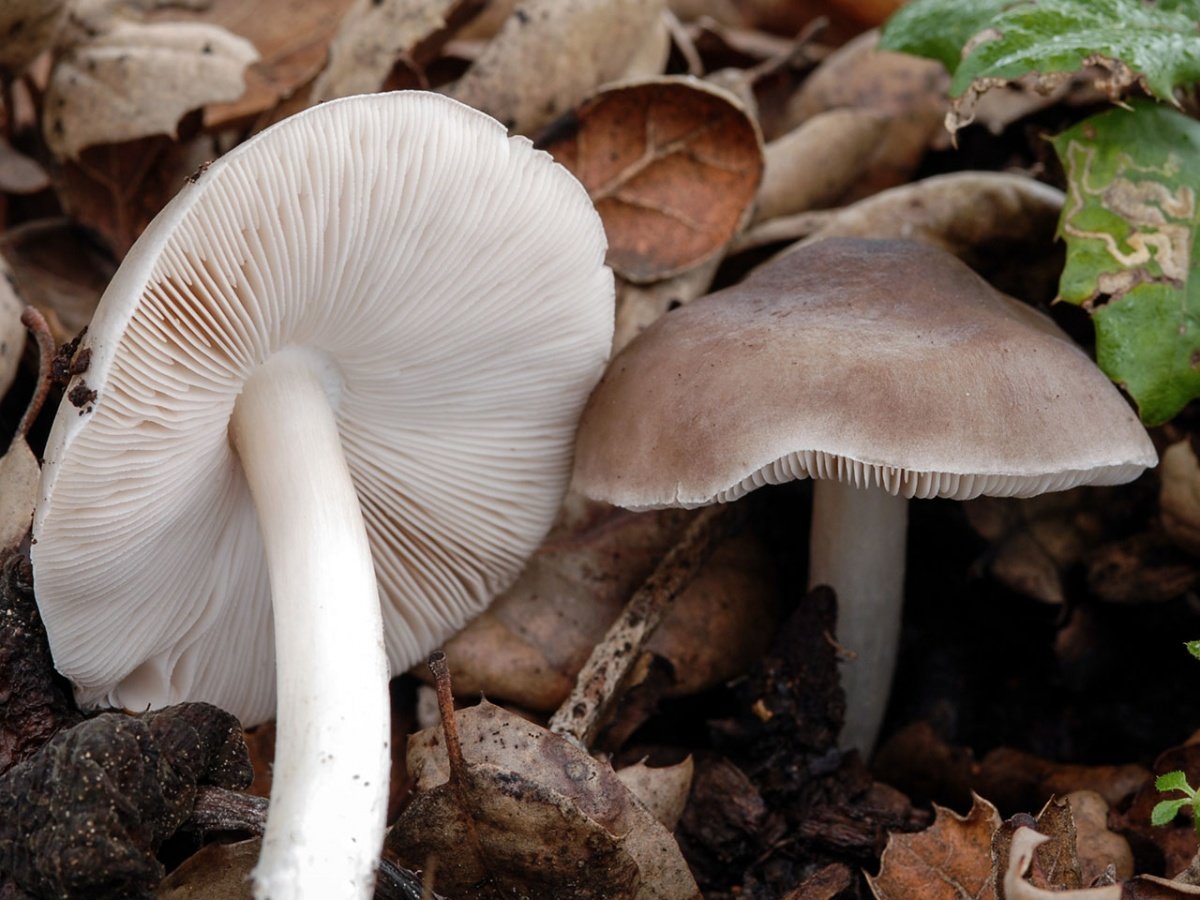
This species is the most numerous in the forests of Russia. Deer mushroom, or deer mushroom, is an edible mushroom that grows, like other species, among rotten wood. The cap of a deer mushroom is up to 9 cm in diameter, has the shape of a wide bell, and becomes flat-spread with age. The skin of the cap is colored gray-brown, it can be chocolate and even black.
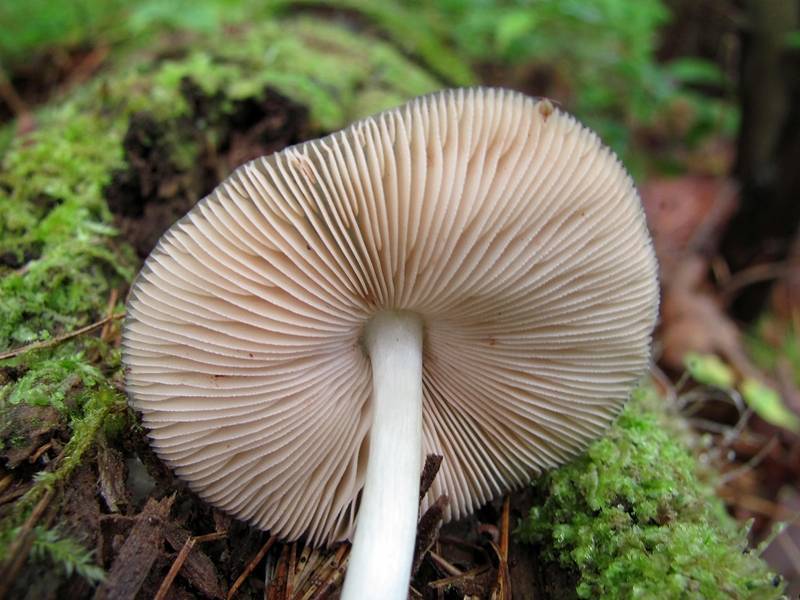
The plates of the deer mushroom are white, wide and frequent; with age, they can acquire a slightly pinkish or gray-pinkish tint. The pulp is characterized by the absence of taste and aroma, in the place of the cut is white or yellowish, practically does not change the shade. The leg of the mushroom is up to 2 cm in diameter and up to 15 cm in height, gray-white or white.
There are several other varieties that are conditionally edible, but picking and eating them is considered risky. Conditionally edible varieties are suitable for consumption only after thorough soaking and prolonged cooking, but even so, their use can provoke problems with the digestive tract.
The edibility of the spit

Among the edible species, the most famous is the reindeer roach, although it is rarely harvested, the umber roach, the dark-edged roach. The inedible ones include velvety-legged roaches, noble rooks. Some of the species are described as little-known edible mushrooms, for example, dwarf roach, vein roach. Species for which nutritional properties have not been studied are traditionally referred to as inedible.
Despite its fame, the edible plute is characterized by a pleasant, sweetish taste and smell, reminiscent of potatoes. The delicate and fleshy pulp of these mushrooms perfectly retains its properties when drying, frying and boiling. In traditional dishes of northern peoples, plute is used even raw.
Young mushrooms are eaten. A ripe stick acquires a peculiar sour taste, which is not dangerous to health, but spoils the nutritional quality of food.
Edibility and properties
In fact, such a mushroom as willow roach is considered edible, that is, it can be eaten, the only important condition for this is the mandatory preliminary boiling. This is due to the fact that with prolonged heat treatment, such an active substance as psilocybin is destroyed, and the use of this type of mushroom will not harm humans.

Eating spit raw tends to cause severe psilocybin syndrome, which is manifested by hallucinations. A person may begin to hear sounds, see very vivid and realistic visions, and panic attacks may occur. This effect occurs rather quickly - after several tens of minutes after taking these mushrooms for food raw, the duration of this state is several hours.
Edibility and hallucinogenicity of blue-footed spit
It is believed that after pre-boiling, blue-footed plutes are edible. When boiled in water at a temperature of 150 degrees, psilocybin turns into psilocin, and if boiling for a long time, then these toxic components are destroyed and the mushrooms become edible. And upon drying, about 50% of the activity of the psilocybin components remains.
These mushrooms contain psilocin, psilocybin and beocystin. They are considered moderately or weakly active. The concentration of psychoactive substances varies greatly depending on the place of growth. According to research, the bluefoot plutney contains 0-0.02% psilocin, 0.05-0.25% psilocybin and 0-0.008% beocystin.
Physical dependence after the use of blue-legged spit does not develop, but with their regular use, mental craving arises. The action of these mushrooms causes a hallucinogenic effect, a person hears sounds in the head, sees visions, loses the sense of time. It may seem to him that he is watching his body from the side. Eating psilocybin mushrooms can lead to feelings of euphoria and unbridled joy, but large doses can cause feelings of panic and dangerous behavior.
According to research conducted in the UK, psilocybin mushrooms are considered the least dangerous recreational drug. Some studies have noted the "striking non-toxicity" of psilocybin. But in any case, it is a drug, the use of which causes inappropriate behavior, possibly dangerous behavior and health problems.
Similar species
Another psychoactive willow mushroom is close to the blue-legged spitting.But the blue-footed rogue can be distinguished by its smaller size, the wrinkled center of the cap, the uniform color of the plates and the inexpressive taste and smell.
The fruit bodies of willow spitters also contain psilocybin. The diameter of the cap reaches 7 centimeters, the shape of the cap changes over time from bell-shaped to flat-spread. The cap is thick-fleshed, while the edges are thin. The surface is fibrous-wrinkled, shiny. The color is grayish or ash-gray with a bluish or pink-brown tinge. The leg height is 12 centimeters. The color of the leg is bluish with a gray-olive tint.
Willow spits grow on willow, beech, poplar, alder and oak wood. These mushrooms are common in Eurasia, North America and North Africa. They are rare. Listed in the Red Book of the Leningrad Region.
Description
Deer roach (Pluteus cervinus) belongs to the Pluteaceae family, the Plutey genus, and also has other names, including the deer mushroom, dark-haired roach. In Russia, it is often called a dark fibrous spit or brown spit. By the way, one of the variants of the origin of the name "deer" is a special color of this representative of the mushroom kingdom, which resembles the color of the wool of a noble animal.
Reindeer roach is an edible lamellar mushroom, but some sources claim that it should not be eaten. However, without explaining the reasons.
Interestingly, the deer mushroom has several variations in appearance.
- the cap is rather large, from 4 to 15 cm in diameter (but there are specimens up to 24 cm), it can have a different shape. It is simply convex (broadly bell-shaped), convex with a tubercle in the middle, and also prostrate. The skin is smooth to the touch, becomes slimy in the rain. Surface with longitudinal fibers, felt in the center. The color changes from gray-brown to dark chocolate; during a drought, the cap can fade. It is darker in the middle than at the edges;
- the leg is moderately thin, up to 15 cm long, up to 2 cm in diameter, has the shape of a cylinder. Dense, thickens at the base, easily breaks off the cap. Sometimes it is very curved (it depends on where the stick grows). The color is white, grayish, on a light background there are dark fibers, sometimes a mesh pattern is clearly visible;
- the flesh is white, does not change color at the break, thick, tough, but brittle. The fibers are clearly visible in the stem. Has a rancid odor. There is no taste as such;
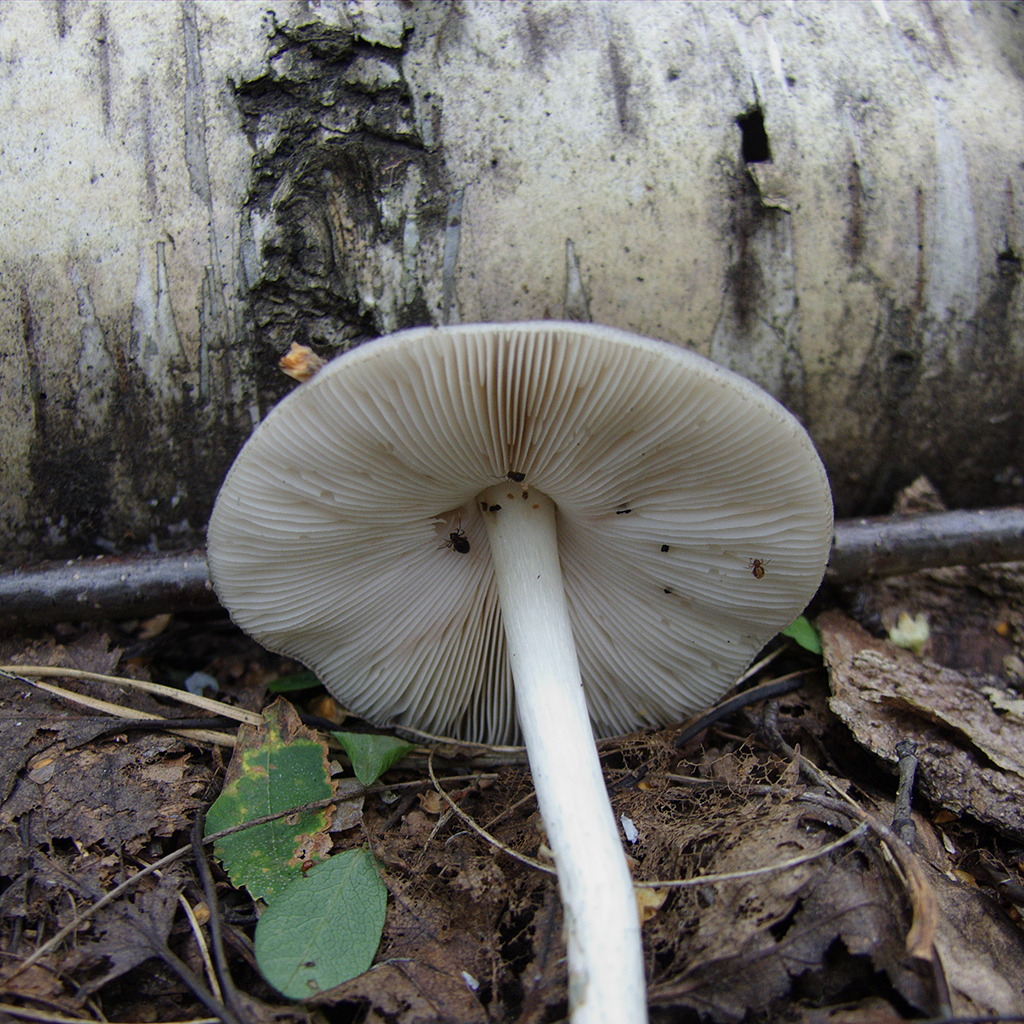
- the plates are loose, thick, wide, fairly frequent, white-pink in young spitters, pinkish-brown in old ones;
- spores are smooth, pink, ellipsoidal.
Description of scaly spit
The diameter of the cap of the scaly spit ranges from 4 to 9 centimeters. The hat is thick-fleshed. Its shape varies from semicircular to convex, but over time it becomes prostrate, with a tubercle expressed in the center. The surface of the cap is fibrous. Its color is grayish brown. The central part of the cap is covered with small, compressed scales. The caps often crack radially.
The pulp is whitish in color; on the cut, its color remains unchanged. The pulp has an astringent taste, and the smell is not pronounced. Spores are smooth, ellipsoidal or broadly ellipsoidal, sometimes ovoid. The plates are wide, free, often spaced. The color of the plates is pinkish-gray, but with age they become pink, and their edges are whitish.
The length of the leg is 4-10 centimeters, its diameter is small - 0.4-1 centimeters. The leg is attached in the center of the cap, its shape is cylindrical, it is dense in structure. There is a small tuber at the base of the leg. The surface of the leg is grayish or whitish, smooth, shiny. There are fibrous grooves in the lower part of the leg. There are no remnants of the bedspread on the leg.
Places of growth of squamous spit
These are saprotrophic mushrooms, they grow on dead wood residues and on the soil. They prefer deciduous trees. You can find scaly spit in mixed forests, as well as in parks and gardens.
Scaly spines bear fruit from August to October. These mushrooms are rare.In the European part of our country, they grow in the Samara and Rostov regions.
Other mushrooms of this genus
The lion's roach, or lion-yellow, or the heap is found in mixed and deciduous forests. They settle on rotting stumps and wood, often found on birches. Lion spits bear fruit from June to September, and peak growth is observed in July. They grow singly, are rare, fruits appear annually.
The diameter of the lion's spit hat is 2-6 centimeters. At first, its shape is bell-shaped, then it becomes convex, and then prostrate. The hat is thin, with a matte velvety surface. The color of the cap is brownish or honey-yellow. The edges of the cap are ribbed-striped. The length of the leg is 5-6 centimeters, with a thickness of 0.4-0.6 centimeters. Its shape is cylindrical, and a slight thickening is observed at the base.
The leg can be either flat or twisted. The color of the leg is yellowish, yellowish brown or brown, and the base is darker. The lion's flock is poorly understood. These are edible mushrooms, of poor quality, they are dried and salted.
The golden yellow roach has a hat with a diameter of 5-7 centimeters. Its shape is bell-shaped at a young age, and then it becomes prostrate. The hat is thin, velvety, bright yellow or dark yellow in color, while the middle is dark, brownish or ocher. The length of the leg is 5-7 centimeters, with a thickness of 0.5 centimeters. Its shape is cylindrical, it can be flat or curved, the base is tuberous. The color of the leg is yellow or yellow-brown, and the base is brown.
Spits grow golden yellow from June to September, the peak of fruiting is observed in July. These fungi settle on decaying deciduous wood, most often giving preference to birch, can also be found on conifers. They live alone. They bear fruit annually.