Similar types and differences from them
Even a novice mushroom picker can easily distinguish a willow spit from other spits. The main difference is the spots on the leg of a blue or green hue. However, this trait is highly dependent on the area where the fungus grows.
The hero of the article can be confused with small representatives of the species "reindeer whips" (in Latin - Pluteus cervinus), from which it will differ in the color of the pulp after the cut (in the deer, the cut does not change color). Also, a microscope will help to distinguish these two species from each other: the deer spit does not have the buckles on the mycelium, which the willow has.
Based on the foregoing, it is possible to eat willow sticks for food, but this must be done carefully and carefully.
Pay attention to where you collected it. Maybe not worth the risk and taste it
Description

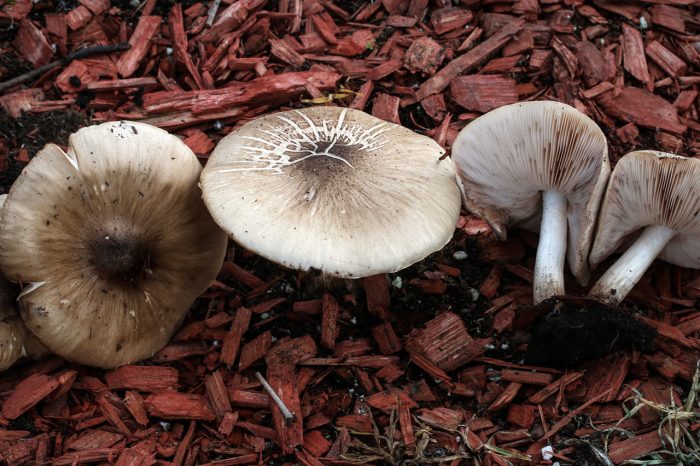
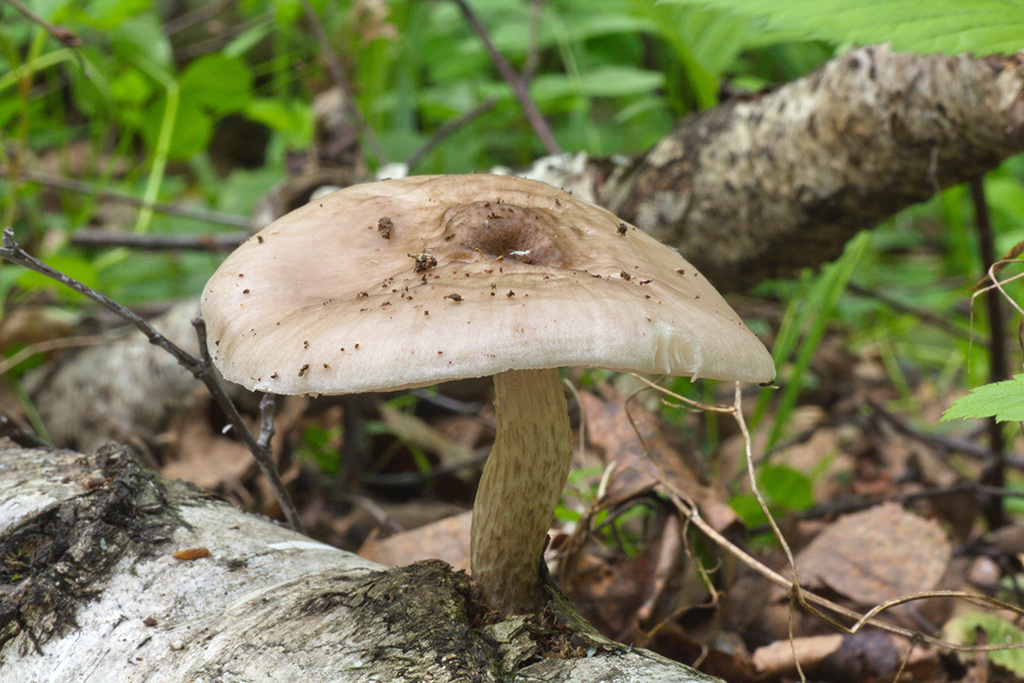
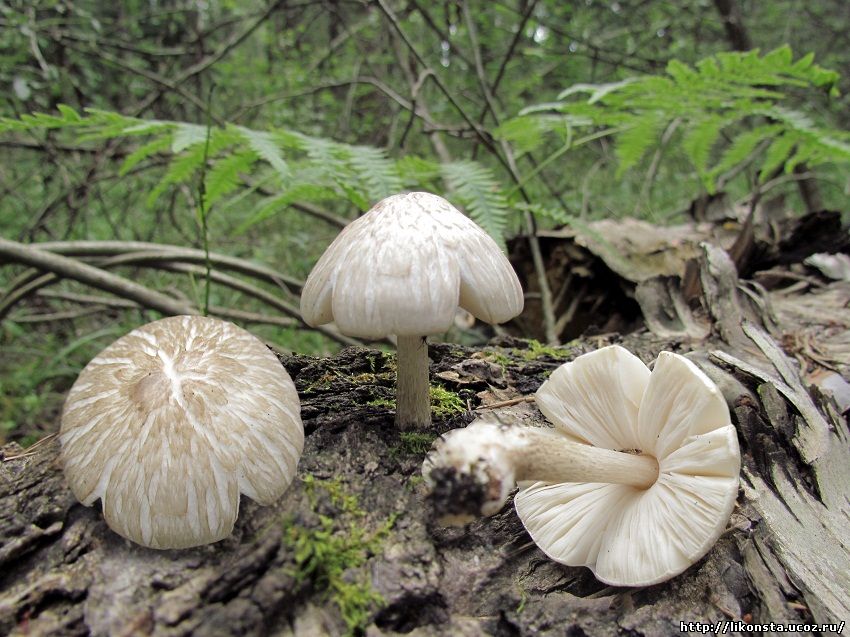
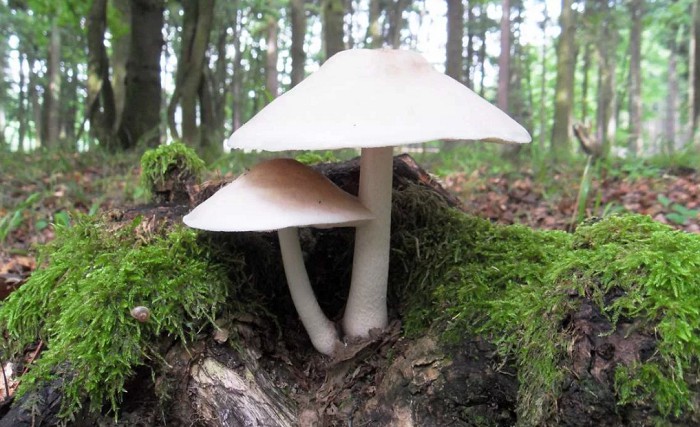
Pluteus noble (Pluteus petasatus), otherwise domestic plute, is a conditionally edible mushroom from the Plutey genus. Its appearance can be described as follows:
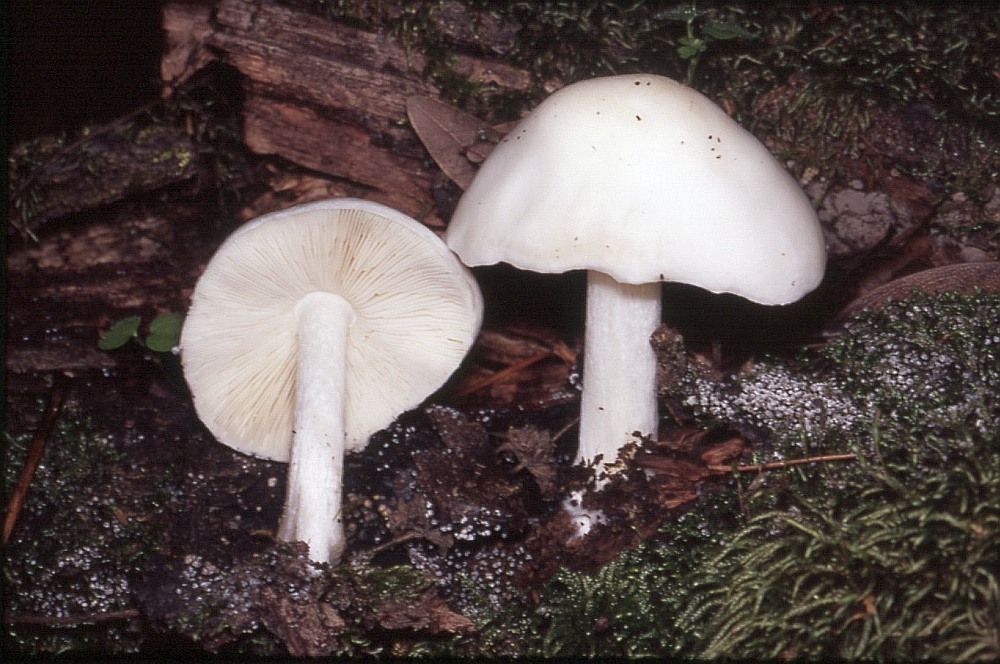
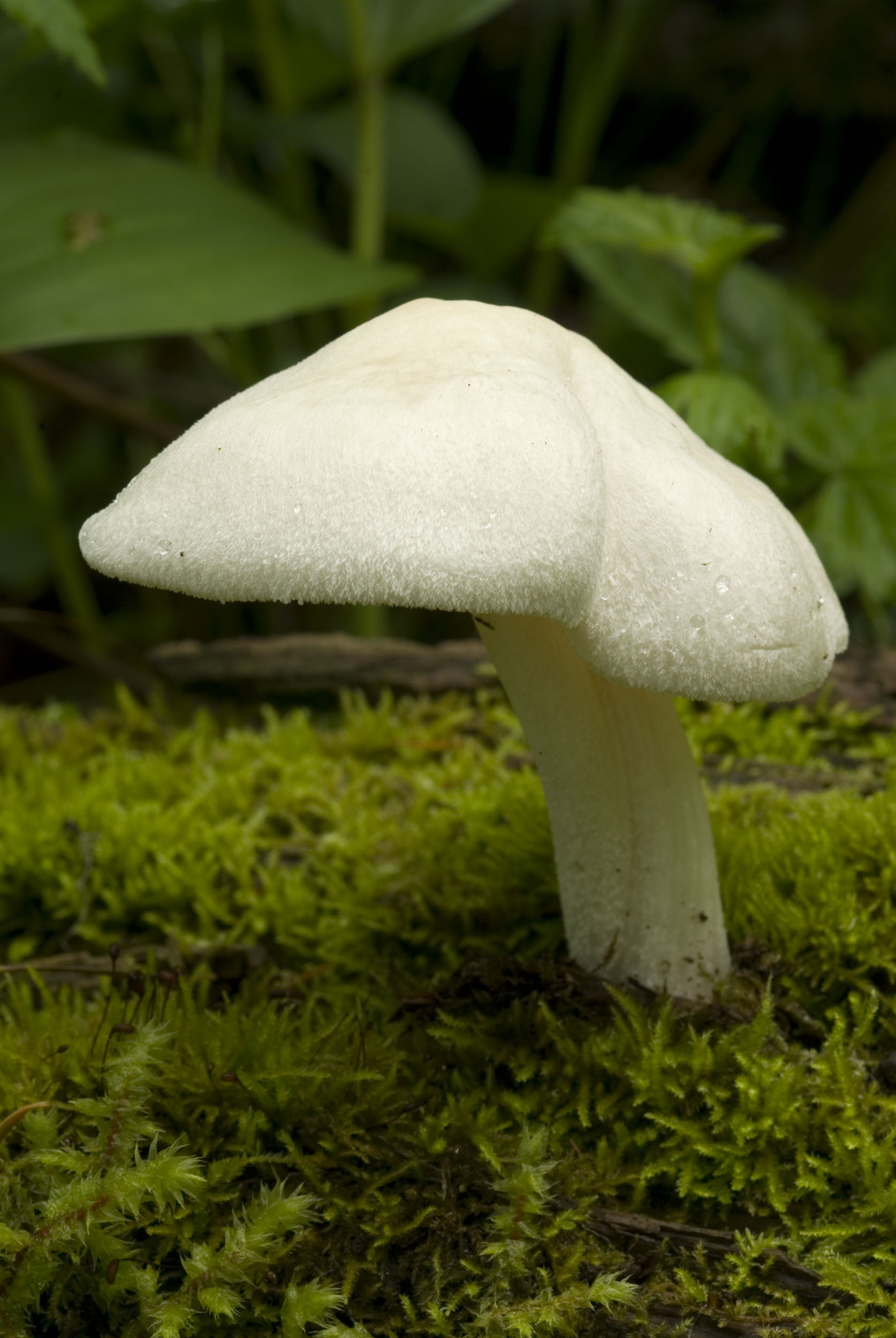
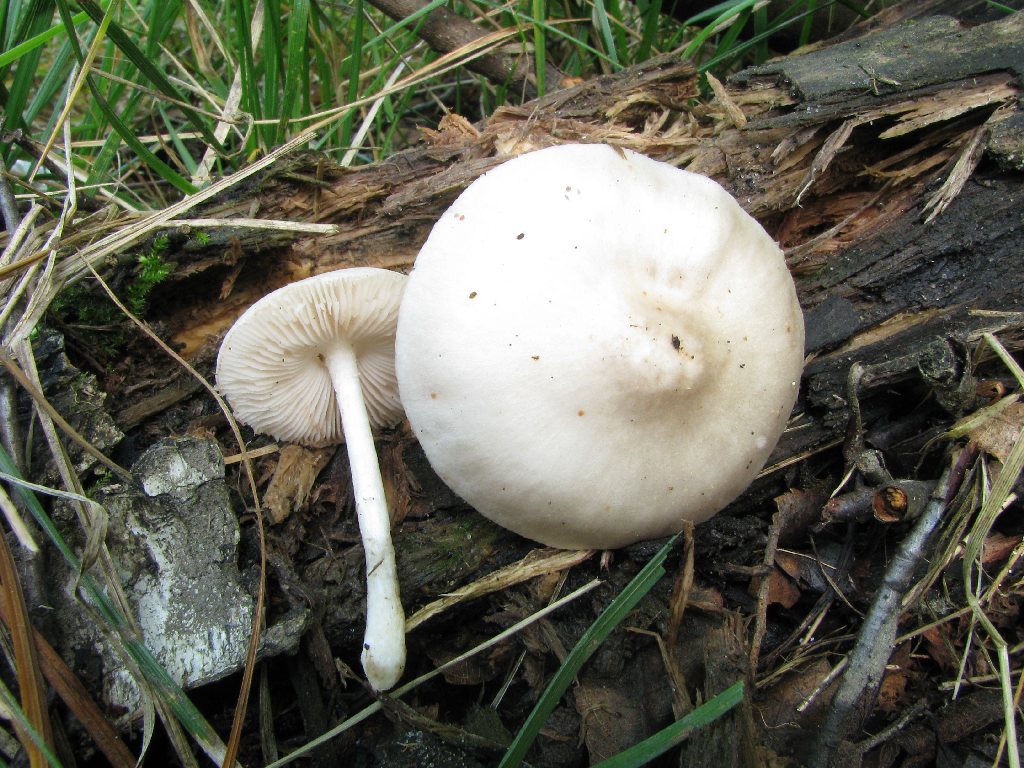
- the cap is quite dense, fleshy, with a diameter of 4 to 15 cm, white, grayish or pale brown, with a dry, shiny cuticle; in damp weather conditions the surface becomes sticky. Convex in young specimens eventually becomes flat-spread, retaining even turned edges and a small dark scaly tubercle in the center of young fruit bodies, which later turns into a depression;
- the pulp of a wadded texture, with a mushroom aroma and sweetish taste, white, does not change on the cut;
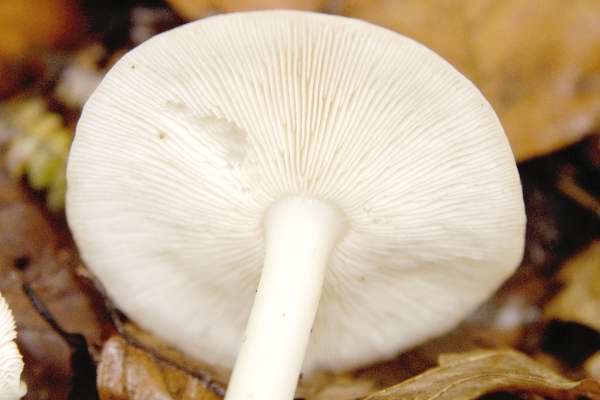
- the plates are often spaced, loose, light pink or pink in color;
- spores are smooth, spindle-shaped, their powder is pink;
- the leg is cylindrical in shape with a diameter of 5 to 15 mm, a height of 5 to 10 cm, dense, white, at the base with a slight swelling, covered with a fibrous light brown coating.
Sometimes the mushroom is confused with the edible deer spit (Pluteus cervinus) in which the cap is darker in color and has longitudinal fibers. Dark fibers are visible on the stem.
Composition, taste assessment and recipes
Reindeer roach mushroom is edible, but it is ranked only in the fourth nutritional value category.
In other words, it must be used with extreme caution and pretreated.
Taste and aroma qualities are rather modest. You can find both positive and negative reviews. The mushroom is disliked for the tastelessness and wateriness of the pulp. Also, many note the presence of a not very pleasant radish smell, which does not disappear even after prolonged processing.
Nevertheless, some substances beneficial to the body have been found in the spit, such as:
- Vitamins. Some researchers report the presence of B, C, and D groups in fruits, and in large quantities. Pluteus cervinus can compete with beef liver in terms of its vitamin content.
- Lecithin. Natural fighter against cholesterol and a remedy for the overall health of the body.
- Enzymes. Substances related to dietary supplements. Although their value has not yet been scientifically proven.
It works well for the following dishes:
- Beef stroganoff. Dried mushrooms crushed into crumbs are used. Meat breaded in flour is fried with sour cream and onions, adding mushroom powder to this mixture.
- Soup. Stewed vegetables and chopped spits are used as a base. The mixture is fried and then added to the broth.
- Marinated mushrooms. To prepare the dish, the fruits are peeled and the top layer of the cap is removed from them. Next, they must be boiled in salted water with spices. After that, the product is placed in a sterile container, tamped and poured with vinegar and broth remaining after cooking.
Types of mushroom plyutei
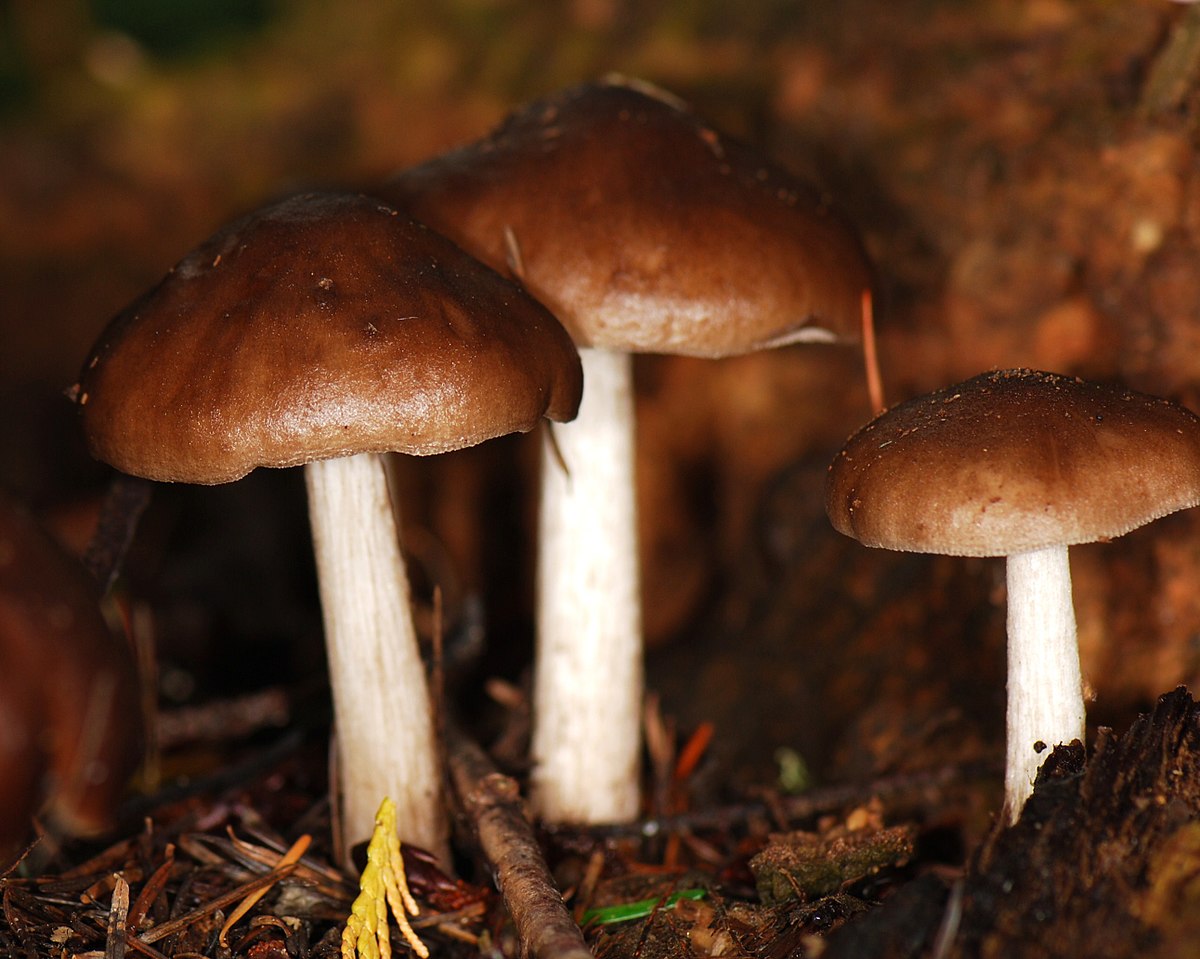
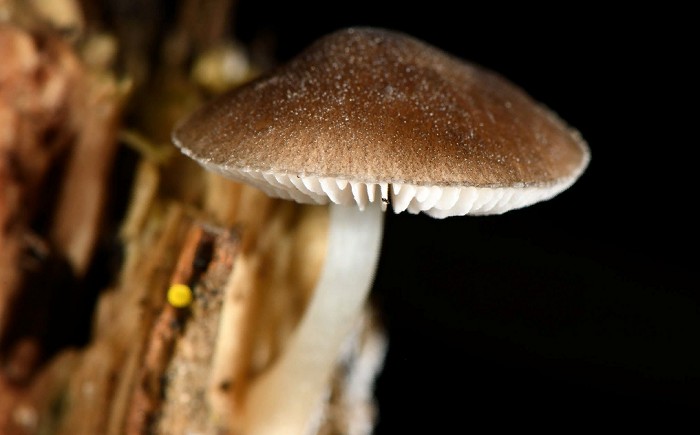
Deer roach (Pluteus cervinus)

Also known as deer mushroom. Medium to large size, with a cap diameter of 4-10 cm, sometimes up to 20 cm.The surface is smooth, silky, fibrous, in mature mushrooms it cracks, becomes dry or slightly mucous, gray or grayish brown, sometimes the color changes from fawn to dark brown and black. The length of the leg reaches 15 cm, the shape is cylindrical, curved, swollen at the base, the structure is dense, solid, the color is white or whitish-gray.
Deer roach is a cosmopolitan mushroom that is found all over the world, growing on the wood of deciduous and coniferous trees.
Edible mushroom.
White corkscrew (Pluteus pellitus)

The cap is 3-5 cm in diameter, finely fleshy, with a tubercle in the center, the edge is torn, lobed. The surface is smooth, whitish in color, gradually acquires a grayish, grayish-brown or bluish color in the center, covered with pink or brown fibers. The length of the leg is up to 6 cm, its surface is shiny, fibrous.
Distributed in Eurasia from Western Europe to Western Siberia, and in northern Africa, a rare species. Grows on beech wood.
Little known edible mushroom.
Pluteus lion-yellow (Pluteus leoninus)
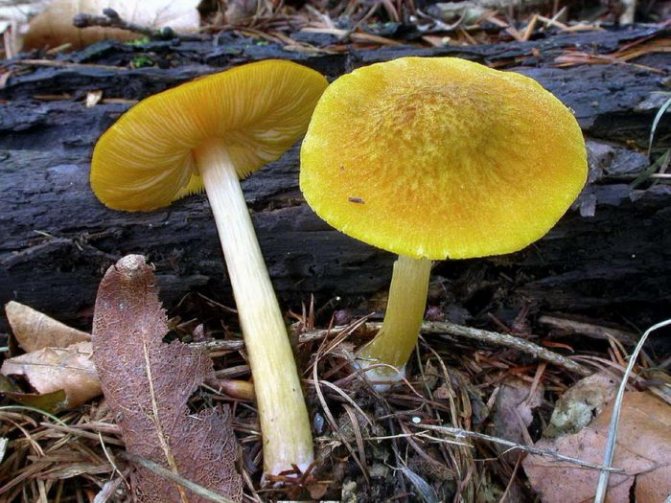

The cap is up to 8 cm in diameter, the shape is bell-shaped or flat-convex, there is a tubercle in the center, the edge is serrated. The surface is bare along the edge, velvety in the center, finely scaly, bright yellow, dark in the center. The leg is up to 7 cm long, about 1 cm in diameter, smooth, white with a yellow base.
The species is widespread in Eurasia, in northern Africa, where it grows in oak and beech forests, and is rare.
Edible mushroom.
Umber roast (Pluteus umbrosus)

The mushroom is medium in size, with a cap diameter of up to 10 cm. The cap is tomentose, wrinkled, whitish or dark brown, the edge is serrated, fibrous. Leg up to 10 cm in length, whitish or brownish, longitudinally fibrous, scaly.
The species grows in Eurasia and North America, on the wood of deciduous trees, a rare species.
Conditionally edible mushroom, as its pulp is bitter, but during boiling the bitterness disappears.
Poisonous and inedible species of mushroom plyuch
Plutey noble (Pluteus petasatus)
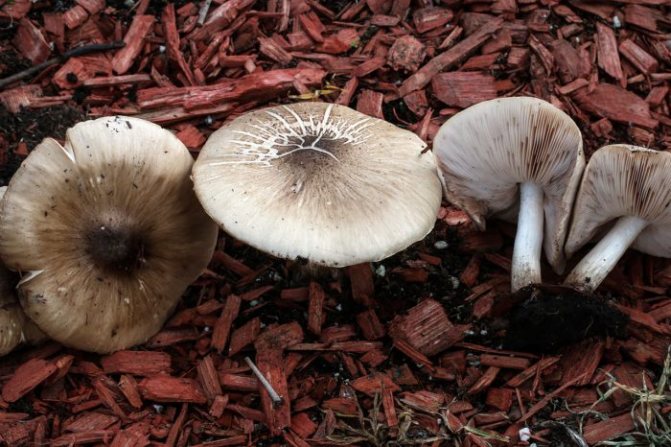

The cap reaches 15 cm in diameter. Its color is light, from whitish to ocher, the surface is silky, shiny, dry, rarely slimy, in the center it is covered with small brownish scales.
The species is found in Eurasia from Western Europe to the Far East, as well as in North America, but it is a rare species and is included in the Red Data Books of the Yaroslavl and Arkhangelsk regions of Russia. Grows in deciduous and mixed forests on beech, oak, poplar wood.
Inedible mushroom.
Scaly corkscrew (Pluteus ephebeus)
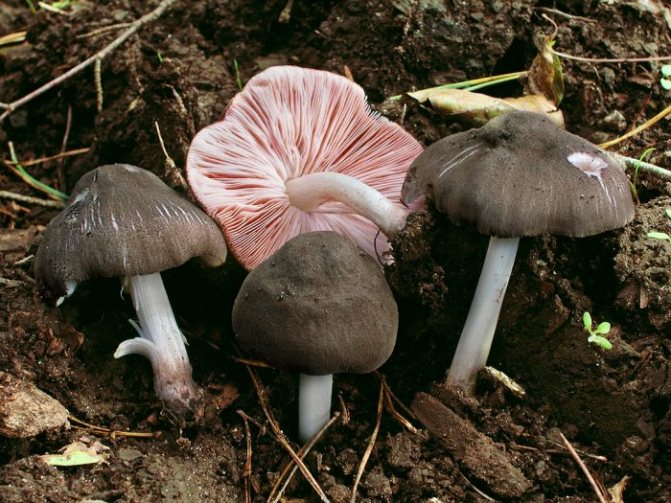

The mushroom is medium in size, the diameter of the cap is about 9 cm, the leg is 10 cm long. The surface of the cap is fibrous, grayish-brown, covered with scales in the center, cracking. The stem is whitish, shiny, smooth, with grooves.
Rare view. Grows on the wood of deciduous trees, distributed in Eurasia and North Africa.
Inedible mushroom.
Dwarf clown (Pluteus nanus)

Hat in diameter does not exceed 5 cm, the surface is velvety, wrinkled, brownish or chestnut-brown in color with a green tint, covered with a bloom. Leg up to 5 cm long, light, with a yellowish or brown tint, smooth, shiny, fibrous.
The species is common in deciduous forests of Eurasia and North America.
Inedible mushroom.
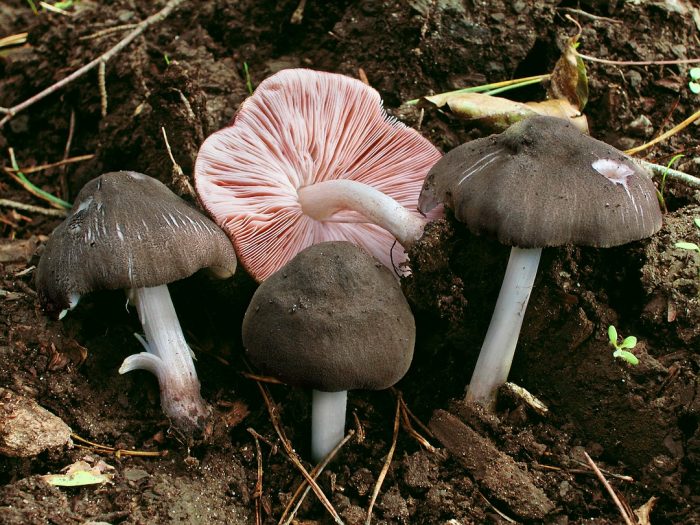
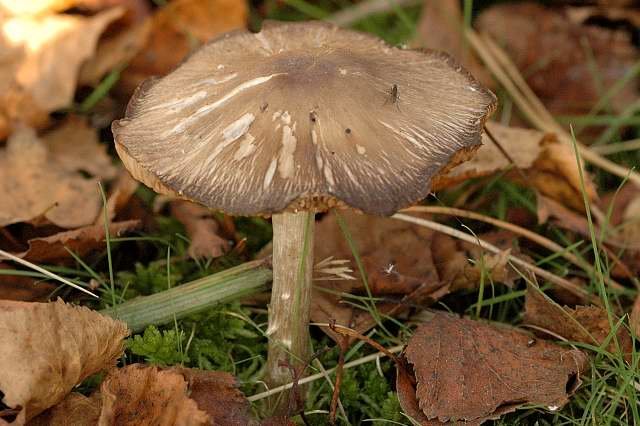
Willow roach (Pluteus salicinus)
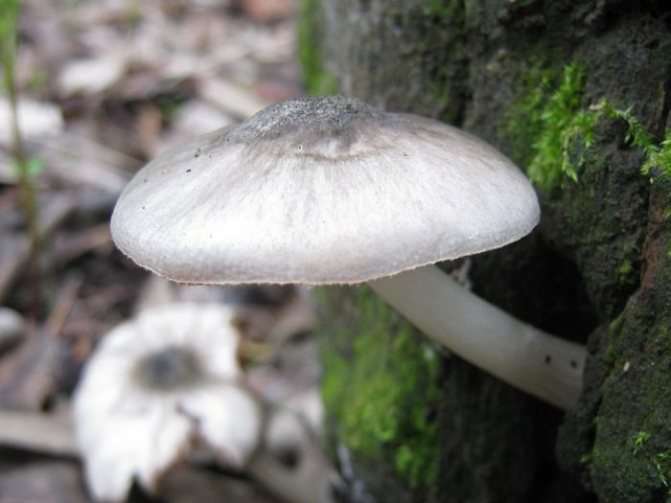

The diameter of the cap is up to 7 cm, the structure is thick-fleshed, the shape is from bell-shaped to flat-spread, with a tubercle. The edge is finely fleshy. The surface is shiny, wrinkled, covered with scales in the center, grayish or ash-gray with a bluish or pinkish-brown tint, darker in the center. Leg up to 12 cm long, shiny, bluish or grayish-olive.
Grows on wood of willow, alder, poplar, oak, beech. Found in Eurasia, North Africa and North America, a rare species.
Hallucinogenic mushroom.
In addition, there are genera of mushrooms with fruiting bodies similar to spits. One of them is entoloma, for which poisonous species are known.These mushrooms are distinguished by the fact that their plates are either narrowly adherent or creeping down, but they are never free, like that of a spit.
In the Rhodocybe fungi of the entolomaceae family, the plates are adherent and descending, the cap is with a depression in the center, and their spores are ornamented.
The clitopils have a depression on the cap, the plates are descending, the spores are striped.
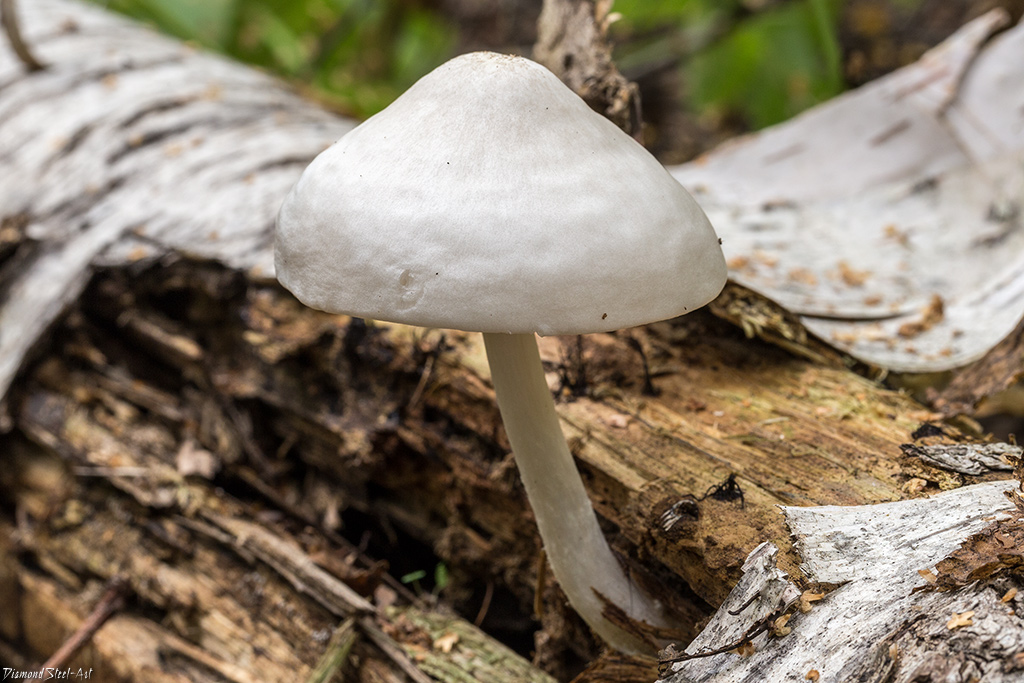
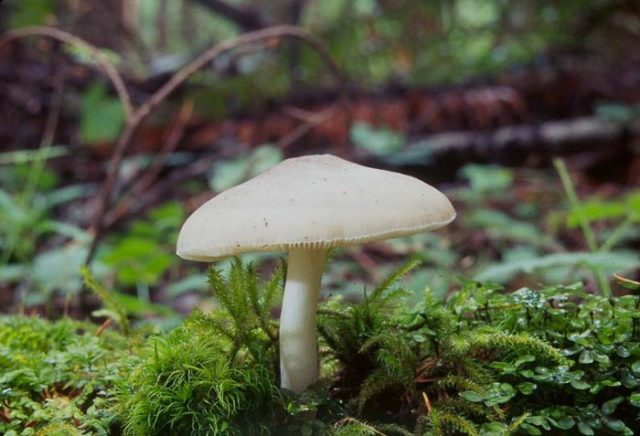
Description of the white spit.
The caps of young fruiting bodies have the form of bells or a convex-outstretched shape. Their diameters are 4-8 centimeters. In the central part, a pronounced dry tubercle is most often noticeable. The surface of the cap at a young age is off-white, and in the process of maturity it becomes beige or brown. The flesh in the cap is extremely thin, in fact, it is present only in the center, in the region of the tubercle. The pulp does not have a special taste, but there is a characteristic rare smell.

On the underside of the cap there are quite wide, free plates. Young fruit bodies have white plates, and when the mushrooms ripen, spores appear, which stain the plates pinkish. The color of the spore powder is pink.
The stem is almost even, cylindrical in shape, at its base there is a distinct tuberous thickening. Its height reaches 10 centimeters, and the girth does not exceed 1 centimeter. Sometimes, depending on the place where the fungus grows, the leg can be curved. The surface of the leg is grayish, there are gray scales against the main background, but they are less dense than that of deer spit. It is solid inside. The pulp in the leg is brittle, fibrous, white in color.

Places of growth of white spit.
White spines bear fruit throughout the summer until the end of September. This type of fungus settles on the remains of deciduous trees. They often grow in beech forests, and are found in linden forests.
Evaluation of the edibility of white spit.
White cod is eaten, like all other representatives of this genus. It is an edible mushroom. The fruit bodies of white spitters are completely tasteless, so they are excellent raw materials for culinary experiments. This species has no particular nutritional value.

The similarity of white spit with other species.
It can be noted that the Plyutei genus is quite numerous and mysterious. It should be studied only in dry years, when there are no other fungi besides the spit. It is possible to distinguish white cakes from other varieties by their small size and light color.
Reindeer plyutey and white plyutey are combined in some sources, or rather white is considered a kind of deer. But the size of the deer spit is larger. The reindeer whip has a convex hat at first, and then a flat hat. Its surface is smooth, brownish or gray-brown in color. The leg is also smooth, the same color as the cap. The pulp has a smell reminiscent of a radish, its color is white.

Reindeer spits bear fruit from May to October. These are edible mushrooms. They grow on soil, dead wood and stumps.
The willow spit also has an external resemblance to the white spit. His hat is thick-fleshed, its shape is bell-shaped at first, and later becomes flat-spread. Its surface is fibrous-wrinkled, shiny, ash-gray, with a brownish-pink tint. The leg is cylindrical, it can be swollen at the base. The color of the leg is blue-white. The pulp has a pleasant aniseed smell and sour taste. The color of the pulp is gray-white, and it turns green when cut.

Willow roach can settle on the remains of willow, poplar, alder, beech, oak. They grow in forests and parks. Fruiting from June to October.
Where and how it grows
The noble rogue grows everywhere, but it is extremely rare. It is found in the European part of Russia, in the Krasnodar Territory, in Tatarstan, in Siberia and in the Urals. It grows in the territories of the United States and Canada, Japan and the British Isles. Loves deciduous and mixed forests, plain and mountainous, old parks. It settles on the remains of broad-leaved trees: beech, oak, poplar, birch, aspen, in humid places hidden in the shade. It can often be found on stumps and rotting trunks, in dead wood.Occasionally it grows directly on the soil or on damaged bark, in the hollows of living trees.
Fruiting of mycelium occurs twice a season: in June-July and September-October. In high-mountainous regions, it manages to grow fruit bodies once, in July-August. Grows singly or in small, closely planted groups of 2-10 specimens.
Comment! Plutey noble tolerates dry and hot periods without reducing yields.

Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
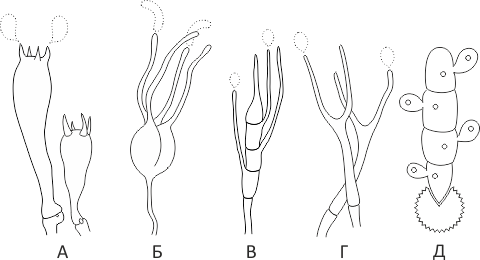
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Pileipellis (Pileipellis)
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Trichoderma (Trichoderma)
-
The type of cap skin, usually consists of straight, septate elements located more or less perpendicular to the surface and laid both at the same and at different levels; the ends of the hyphae can be morphologically modified and represent dermatocystids. The surface of the cap is velvety to almost felt.
Lat. Trichoderm.
Trichoderma, in turn, is subdivided into intertwined trichoderma and irregular trichoderma.
Intertwined trichoderm (Intricate trichoderm) - trichoderm, consisting of intertwined hyphae, located not parallel to each other and forming a tomentose pubescence.
Irregular trichoderm - Trichoderma, consisting of irregularly branching hyphae.
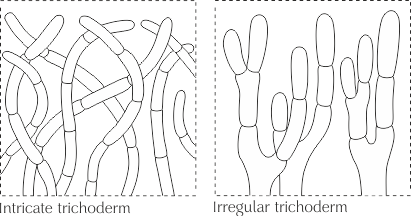
See Dermatotsistida, Hypha, Septa.
- Cutis
-
The type of cap skin, consists of creeping non-gelatinized hyphae located parallel to the surface. The surface of the cap looks smooth.
Lat. Cutis.
See Gifa.
Distribution and fruiting period
Reindeer wicker is a saprophyte, and therefore it grows on dead and decaying wood of both deciduous and various conifers, including, for example, birch, oak, pine. He respects not only tree trunks, but also old rotten and rotten stumps, branches, wood chips, sawdust, bark, dead wood. It comes across in deciduous forests, sometimes does not disdain conifers, it is found in gardens and parks, in clearings. In some cases, sticks can also be found on the ground, provided that there is a rotting stump nearby.
Growing regions - almost all of Europe, as well as in Russia. The fruiting period is from late spring to early autumn. It grows well even in drought conditions.
Taxonomy
Synonyms
- Agaricus petasatus Fr. 1838 basionym
- Pluteus cervinus var. ; petasatus (Fr.) Fr. 1874
- Pluteus cervinus var. ; patricius (Schaeff.) Quél.
- Agaricus patricius Schulzer 1874
- Pluteus patricius (Schulzer) Boud. 1904 - Domestic cigar
- Pluteus straminiphilus Wichanský 1968
Domestic ropes
(P. patricius ) according to MycoBank and Species Fungorum is synonymous, but some authors describe it as a separate species. EF Malysheva notes this species as critical, the distinctive features of which are probably not enough to consider it and the noble rogue as different species.] Homonyms and misused names
- Pluteus petasatus sensu Ricken (1913) - mistakenly used as the name for willow spit (Pluteus salicinus )]
- Pluteus curtisii sensu Sing. - mistakenly used for P. petasatus ; Pluteus curtisii Berk. (1887) is synonymous with deer's spit (Pluteus cervinus )]]
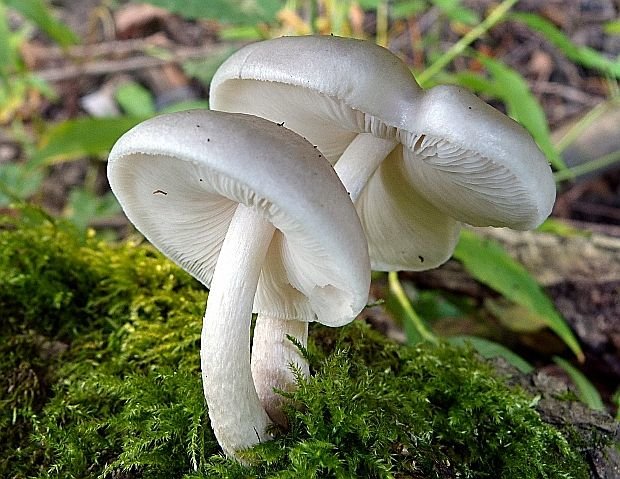
Description of the dwarf spit
The cap diameter of this small mushroom is 2-5 centimeters. The hat of the dwarf spit is thin fleshy. Its shape is semicircular or conical, but with age it opens up to a prostrate with a clearly visible tubercle in the center.
The surface of the cap is fine-fibred, velvety, with radial wrinkles in the center. The color of the cap is from chestnut brown to brown with an olive tint, darker in the center. The cap is covered with a soot-powdery bloom. The edges of the cap are so thin that they show through.
The flesh is whitish in color; at a break, its color does not change. The pulp has a pleasant taste and a weak mushroom smell. Spores are broadly ellipsoid or almost spherical, smooth. The plates are often located, wide, free. The color of the plates is whitish-pink, pink or brownish-pink, and the edges remain white.
The length of the leg does not exceed 3-5 centimeters, with a thickness of 0.2-0.4 centimeters. Its shape is cylindrical. The leg is located in the center. Its lower part expands noticeably. The surface of the leg is grayish, slightly yellowish or whitish, with age it becomes brownish. The stem is longitudinally fibrous, shiny. There are no remnants of the bedspread on the leg.
Places of growth of dwarf spit
Dwarf spits are saprotrophic fungi, they settle on the remains of wood and stumps, giving preference to deciduous tree species. They can be found in mixed forests as well as in parks.
Dwarf spits bear fruit from July to October. They are widespread in Europe and Asia, and are also known in North America. Dwarf spits are often found; for many regions, these mushrooms are a common species.
Other mushrooms of this genus
The umber roaster is distinguished by a very fleshy and thick cap. Its diameter can be up to 10 centimeters. At first, the shape of the cap is semicircular, but over time it becomes prostrate. There is a small tubercle in its central part. The color of the cap varies from whitish to dark brown. The hat is covered with a mesh or felt pattern. The edges of the cap are hazel-gray with a scalloped fringe of hairs. In the center of the cap is a cylindrical leg, which becomes thicker at the bottom. The leg is quite dense, solid inside. The color of the leg is brown or off-white.
Umber spits are found from July to September.The peak of fruiting occurs at the end of August, when these mushrooms are found in large quantities.
They grow in broadleaf and mixed forests. They prefer rotting stumps and wood. They grow singly or in small groups. This mushroom is conditionally edible. Among fellow rogues, the umber is the largest and most respectable.
Deer mushroom or deer mushroom is an edible representative of the genus. The hats are initially convex in shape, and then become flat with a tubercle in the central part. The diameter of the cap is 5-15 centimeters. The color of the cap is light brown or dark brown. The leg of the deer's spit is long, fleshy, thin, its structure is flaky-fibrous.
These mushrooms appear in early May and bear fruit until autumn. They grow in dead wood, on stumps and in the soil. Deer mushroom is not only edible, but also delicious.
Practical value
The genus contains edible species; mushroom pickers are best known for deer roaches (Pluteus cervinus(Pluteus umbrosus), dark-edge rogue (Pluteus atromarginatus). Inedible species include such species as velvety-footed sticks (Pluteus plautus), noble rogue (Pluteus plautus). Some common species in the special literature are characterized as "little-known edible mushrooms", but some authors classify them as inedible - dwarf cod (Pluteus nanus), venous crimson (Pluteus phlebophorus). In many species, nutritional or toxic properties have not been studied and are considered inedible.
For several species, the possibility of medicinal use is being studied. In experiments on mice, it was found that the extract of polysaccharides from deer spit suppresses the growth of malignant tumors, anti-cancer and immunostimulating effects were found in dwarf spit, lion-yellow (Pluteus leoninus), orange-wrinkled (Pluteus aurantiorugosus).
A small number of poisonous (hallucinogenic) representatives are known to contain psilocybin. In Central Africa, a mushroom little known to science with a pungent odor and bitter taste is used by the Banza and Eala peoples, the local names of the mushroom, respectively, abanda and Losulu... It has been described as a species of stag spine called Pluteus cervinus var. ealaensis Beeli 1928, detailed information about it in the literature was absent for a long time. In 2010, a modern description was published and the species was named Pluteus losulu... In the 1980s and 1990s, psilocybin was found in willow spit (Pluteus salicinus), blue (Pluteus cyanopus), P. nigroviridis and P. glaucus.
Sprouting

- The fundamental habitat of these representatives of the breed group is considered to be North America, as well as Eurasia. The specimens prefer moderate climatic conditions that extend to the mountains of the Far East.
- In the vastness of our country, this mushroom settles in the Volga region, Krasnodar and the region, Siberia in the east, Primorye, St. Petersburg and the surrounding area, as well as near Rostov.
- Considering the nature of growth, it should be said that this species chooses for itself the bark of trees, hemp, any remnants of deciduous trees. Therefore, spit is found on poplar, oak, beech remains, preferably in the shade, and not under the sun. Instances love humidity, but moderate.
- Of course, you can find them near living trees. They settle on high mountains among the forest, on flat terrain. They can grow not only in splendid isolation, but also in medium colonies.
- As for fruiting, it starts at the end of the spring season and lasts until about mid-autumn. In general, mushrooms appear in several approaches. The first batch is in June and the second in September.
- When planning to engage in gathering, you should carefully wield a stick so as not to damage the specimens. They break and weathered, so further cooking should be done as soon as possible. Also, do not confuse this spit with your fellows.
float gray - description where it grows, the poisonousness of the mushroom
Edibility
In addition to the low calorie content, a large amount of protein in its composition, the noble pile is distinguished by a high content of lecithin, which can reduce harmful cholesterol in the body. This is the main benefit of eating these mushrooms. Nutritional qualities - an unusual, slightly sweet taste, pronounced mushroom aroma - allow them to be used for preparing a variety of hot dishes: soups, roasts, casseroles.
Plyutei noble is not often seen in the forests, of which it is considered a typical inhabitant. The more interesting it will be for mushroom pickers to meet him, in order to be able to appreciate the qualities of this rare mushroom.






















































