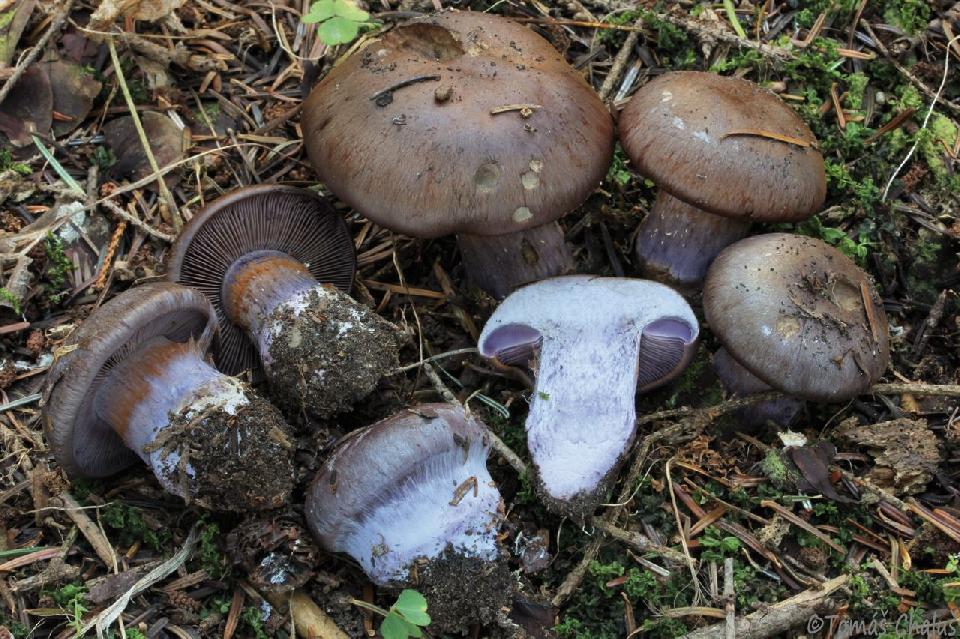
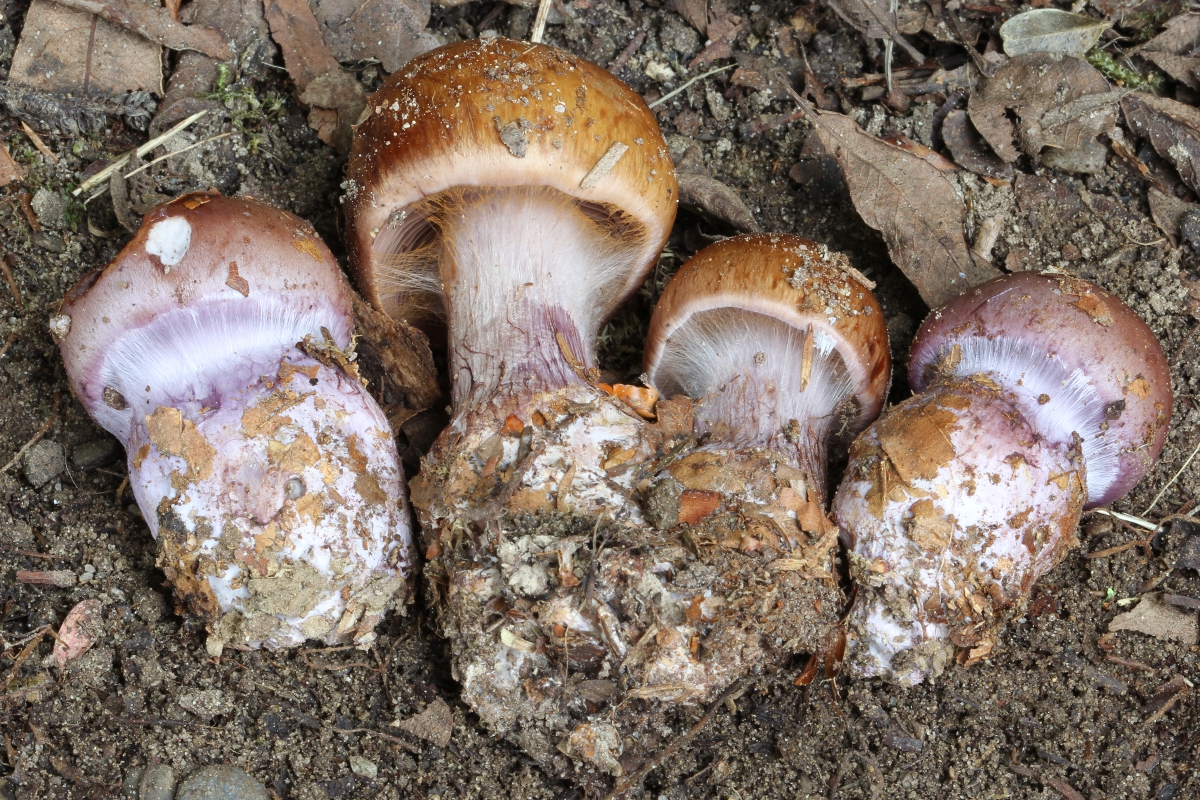
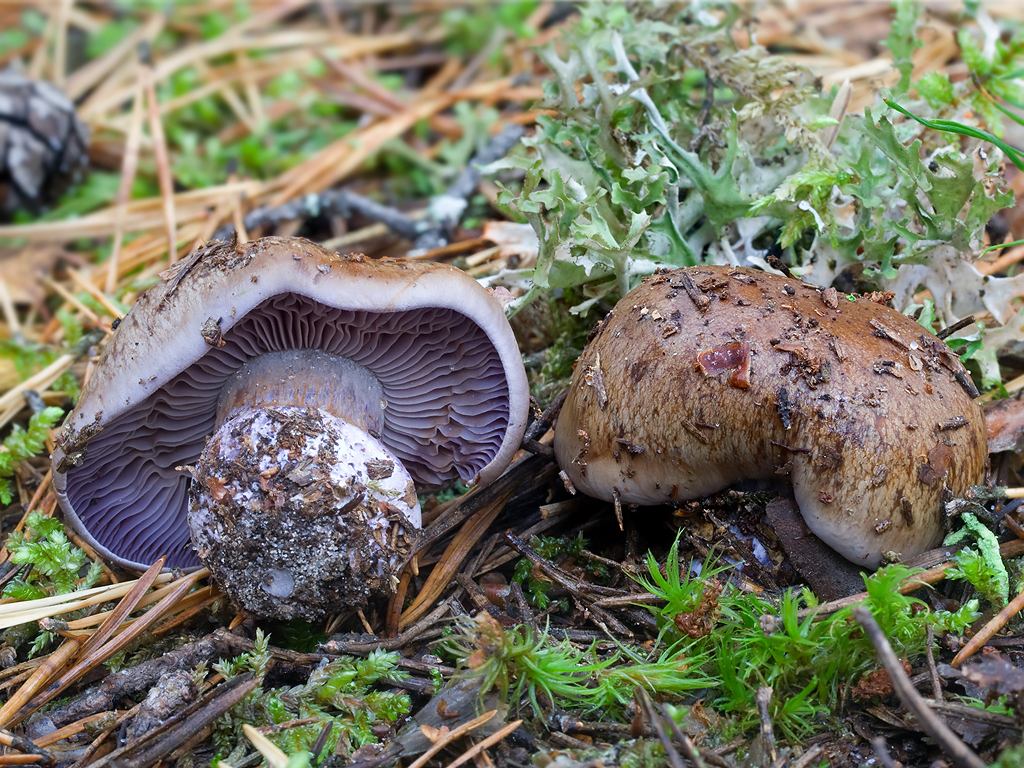
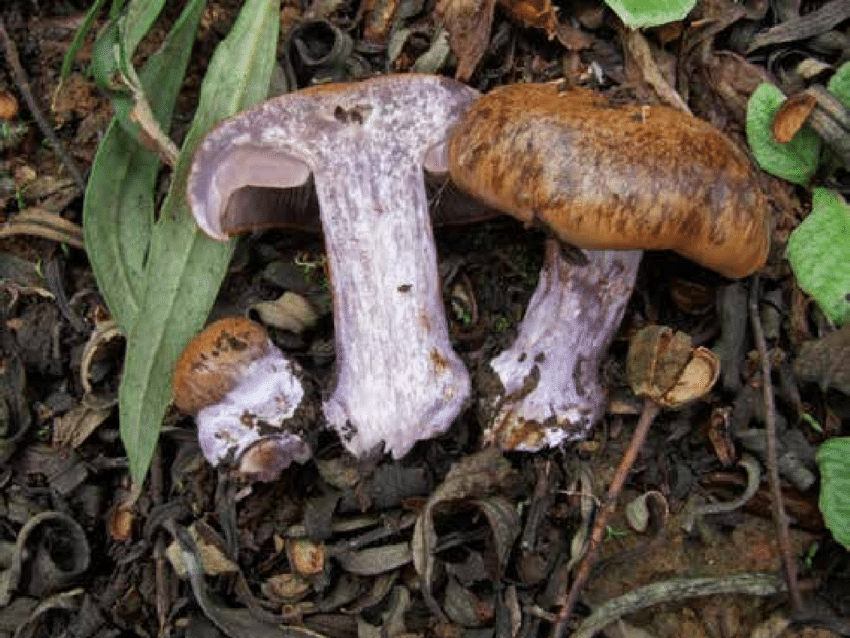
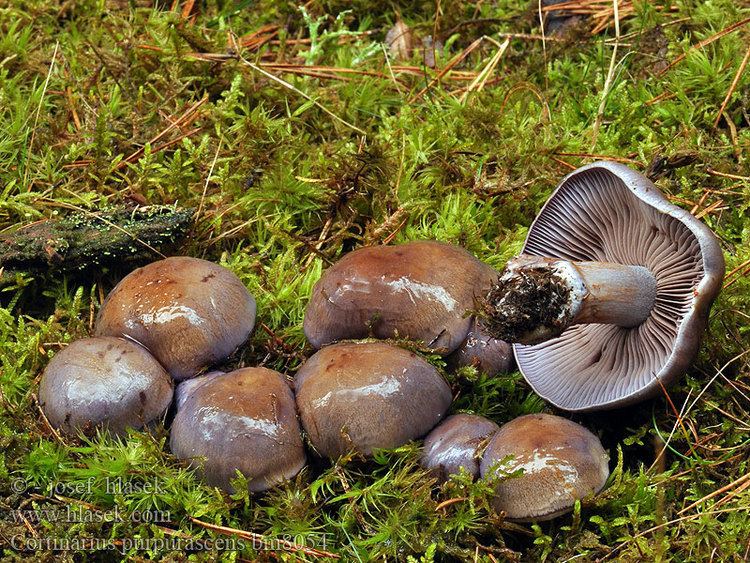
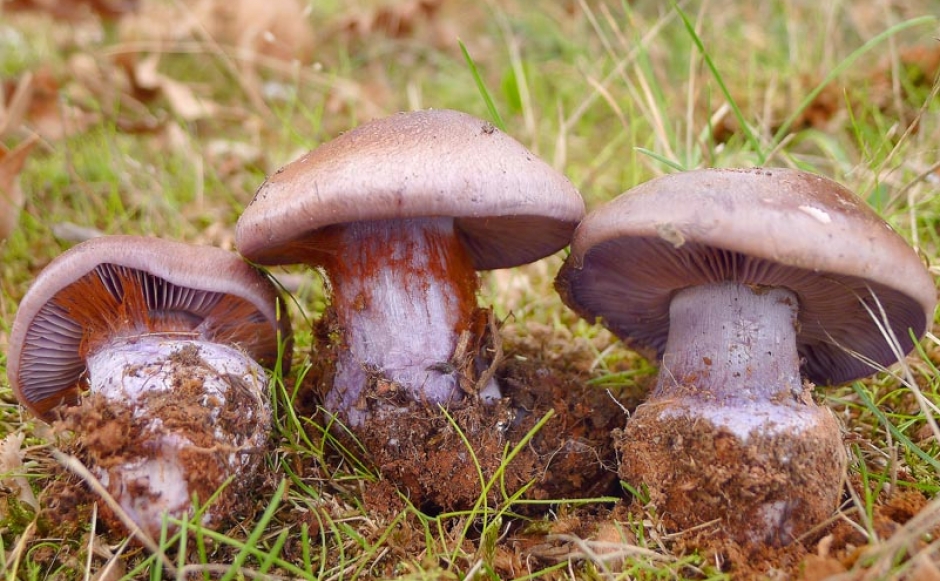
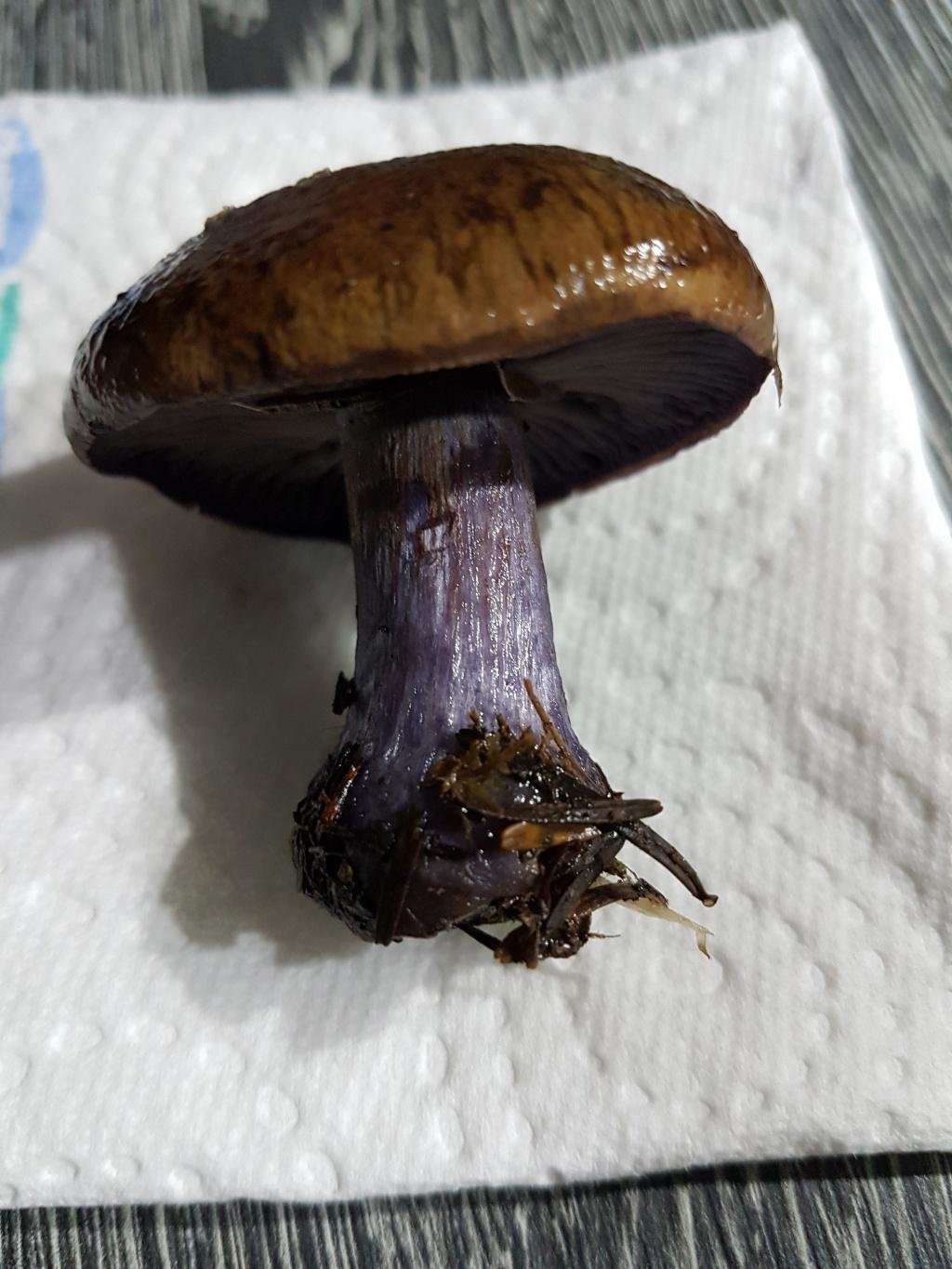
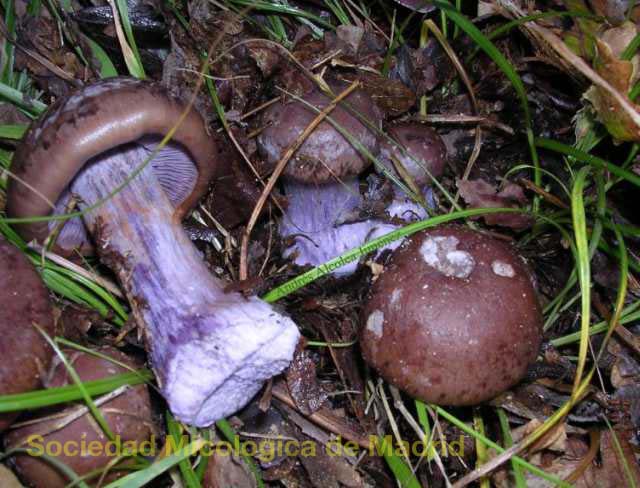
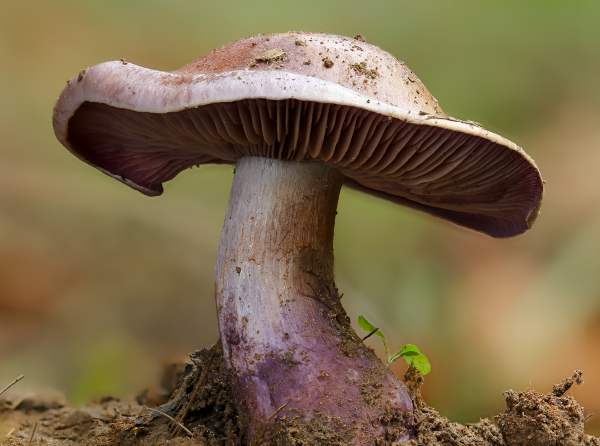
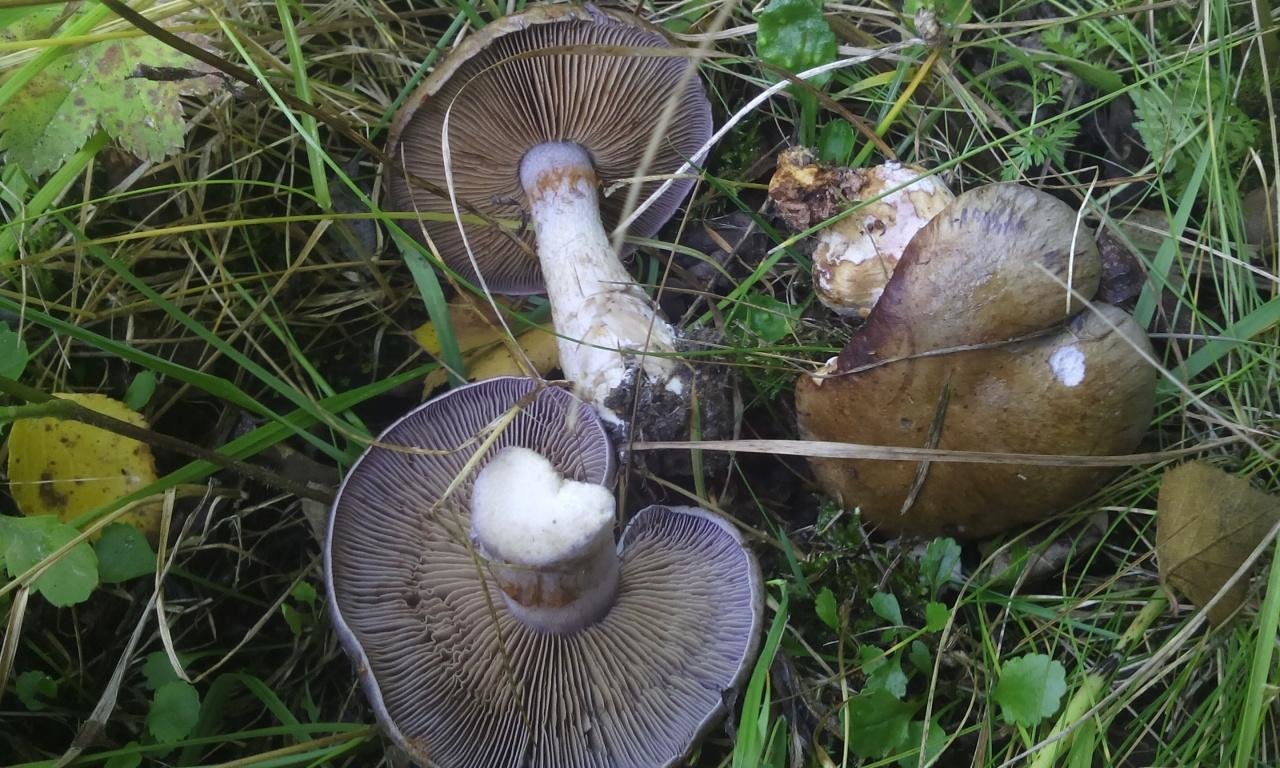
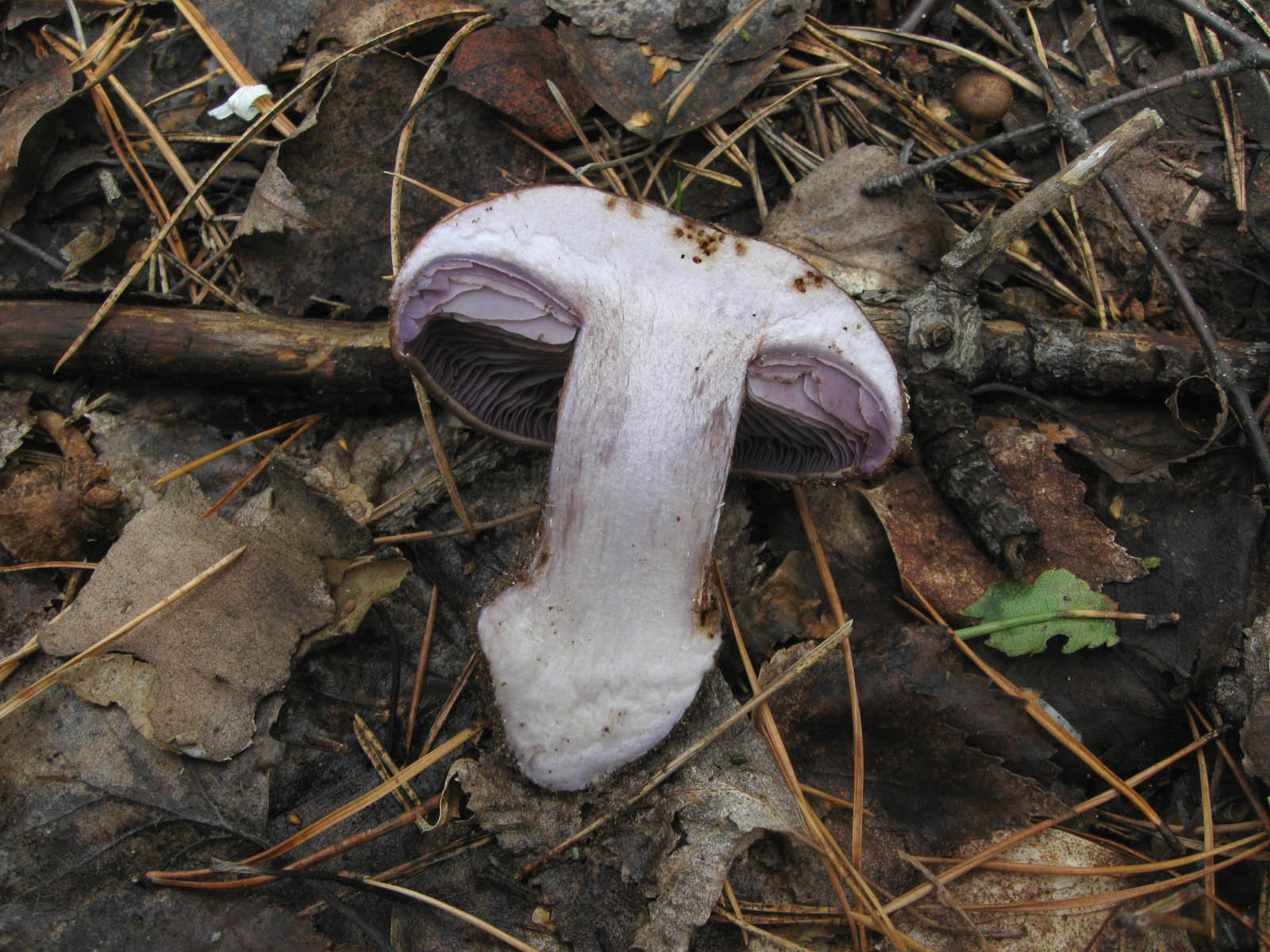
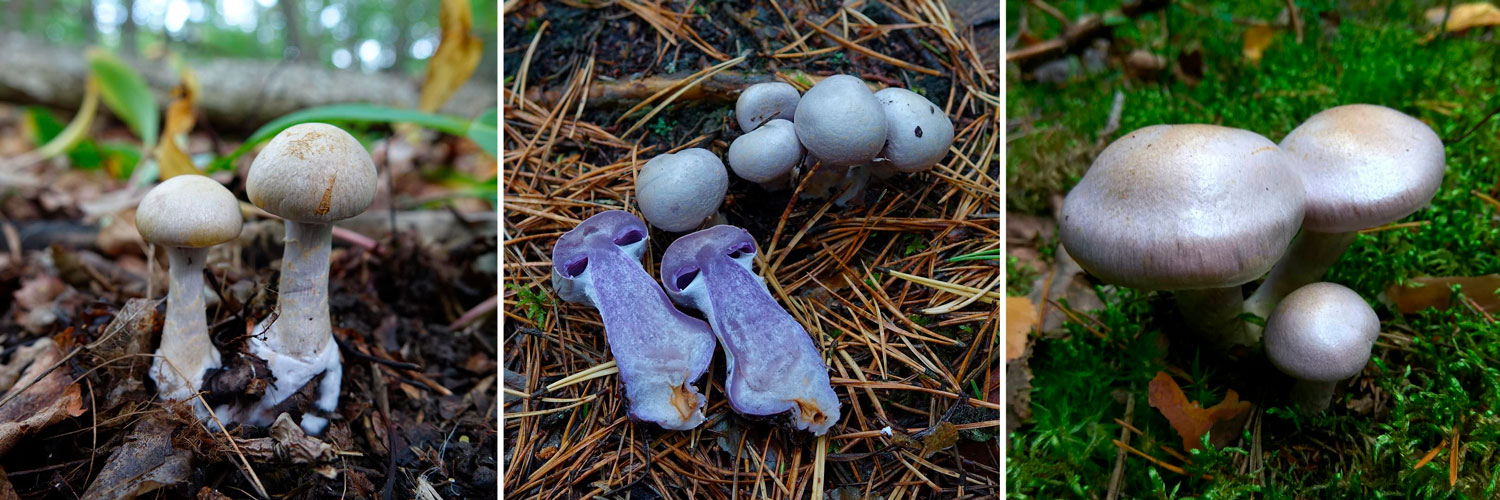
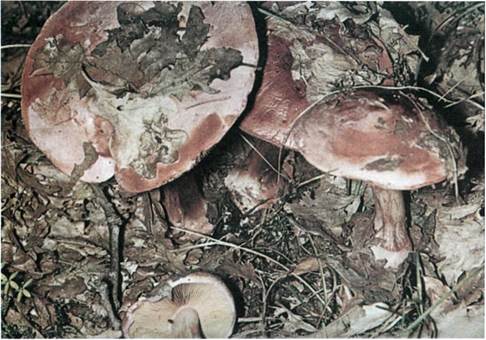
Crimson webcap (Cortinarius purpurascens)
Scarlet webcap (Cortinarius purpurascens) - a mushroom, which according to some sources belongs to the edible, belongs to the Spiderweb genus, the Cobweb family. The main synonym for its name is the French term Cortinarius purpurascens.
External description
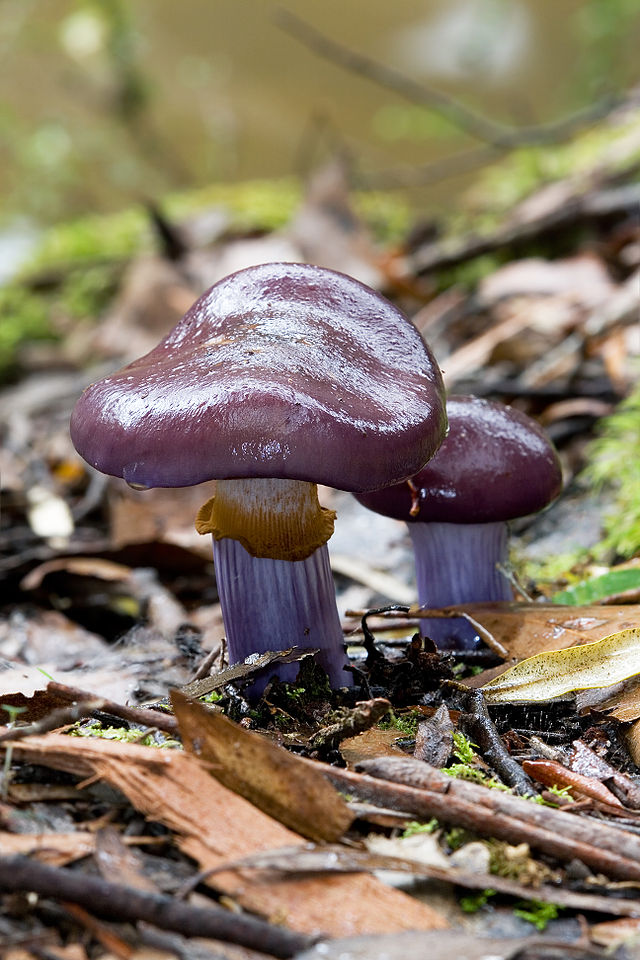
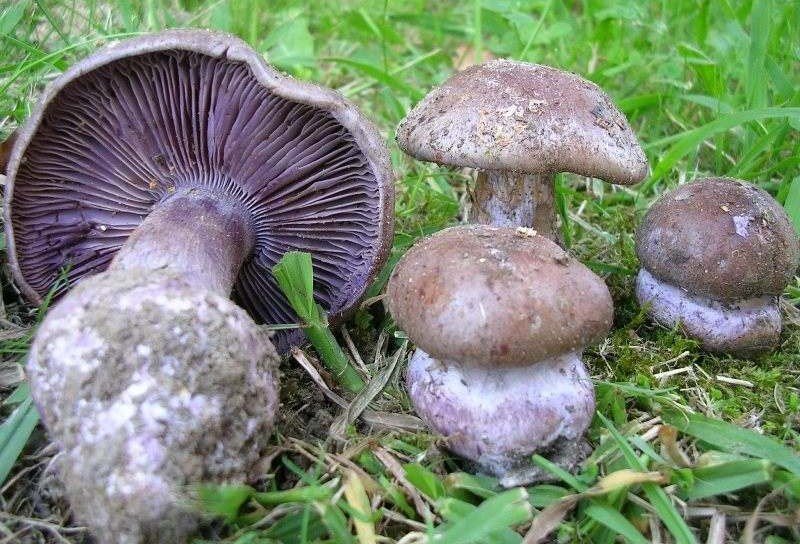
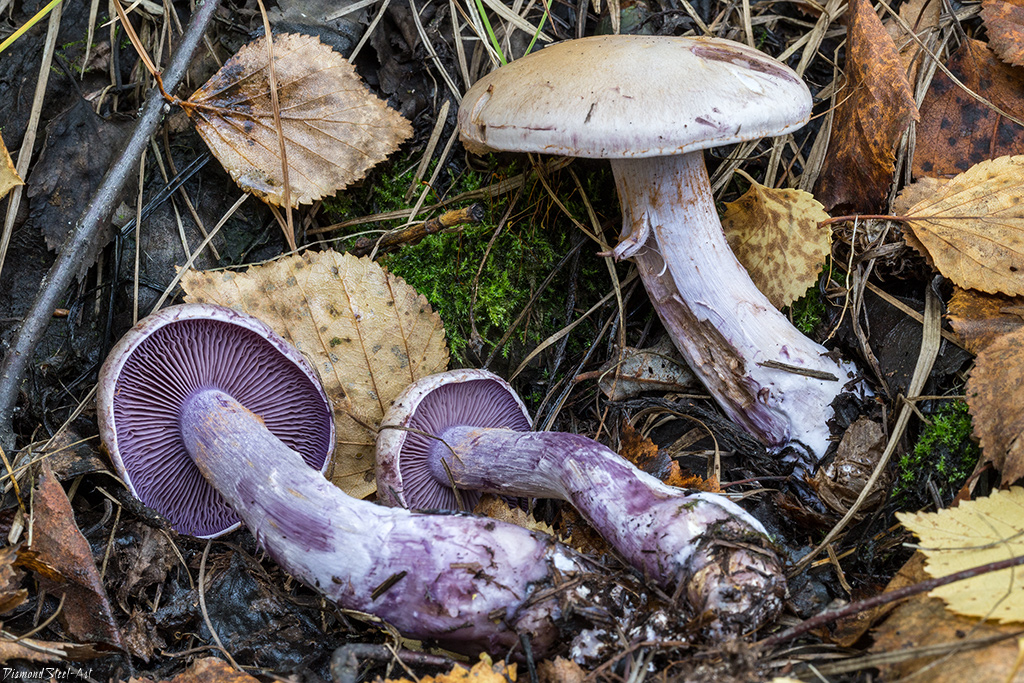
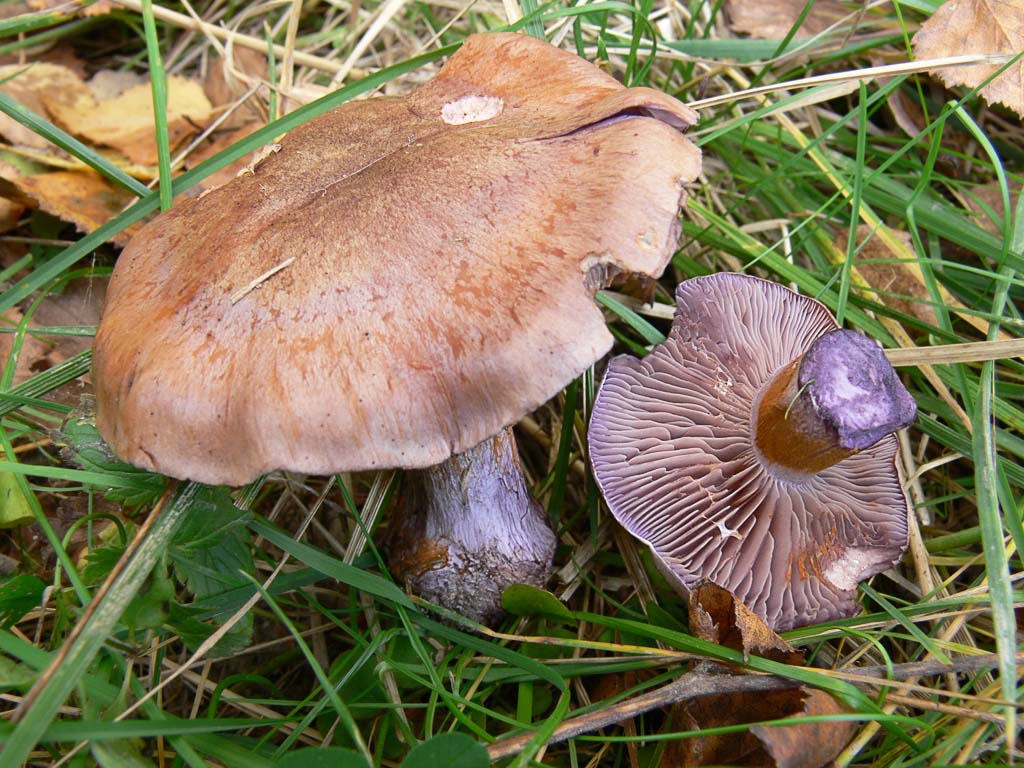
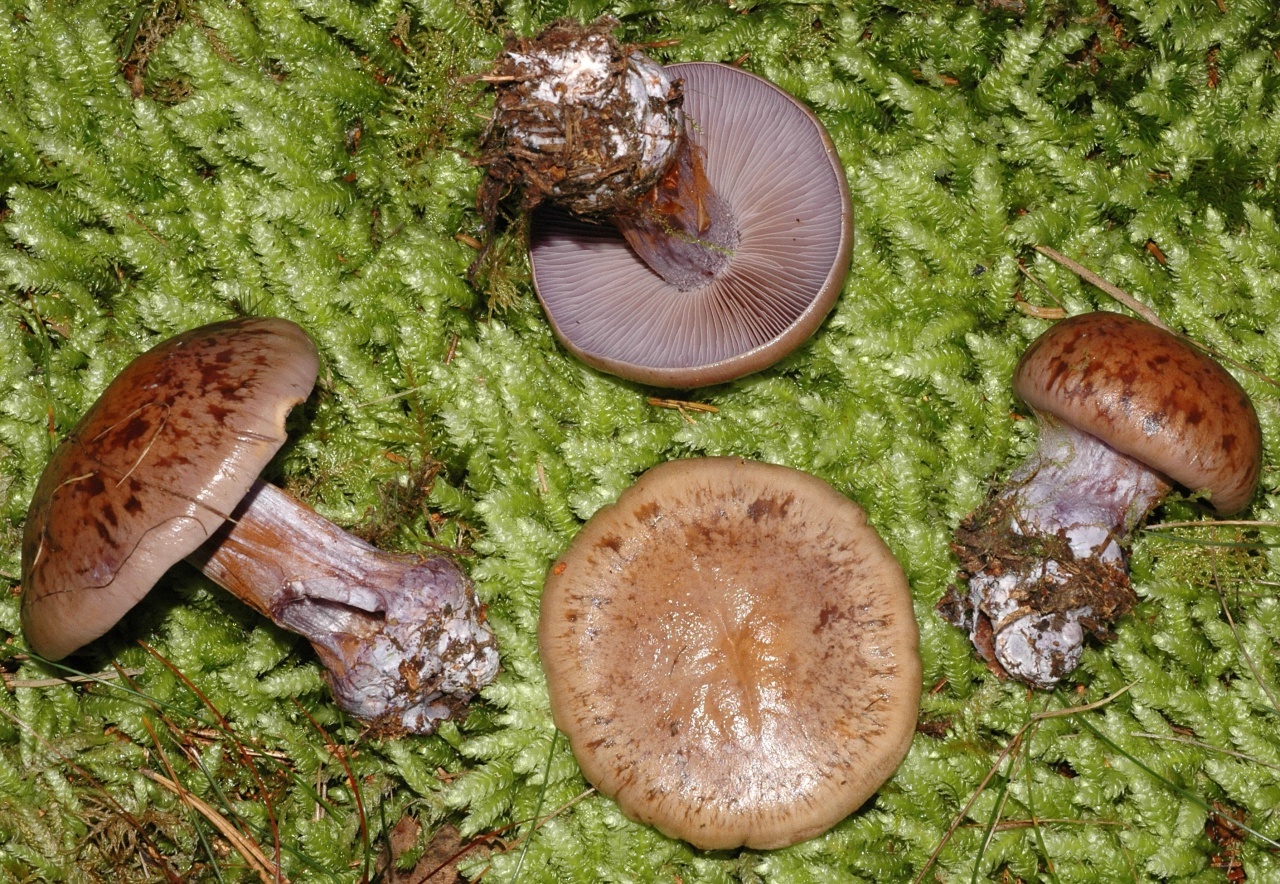
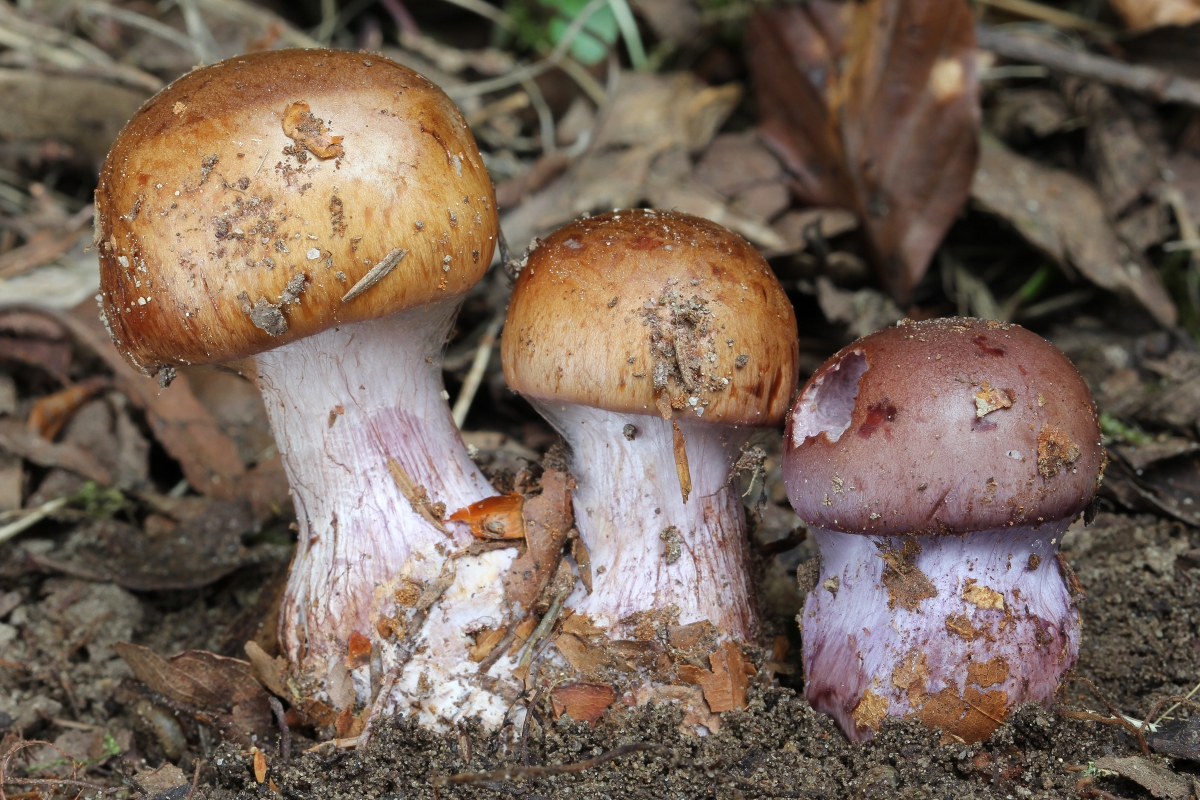
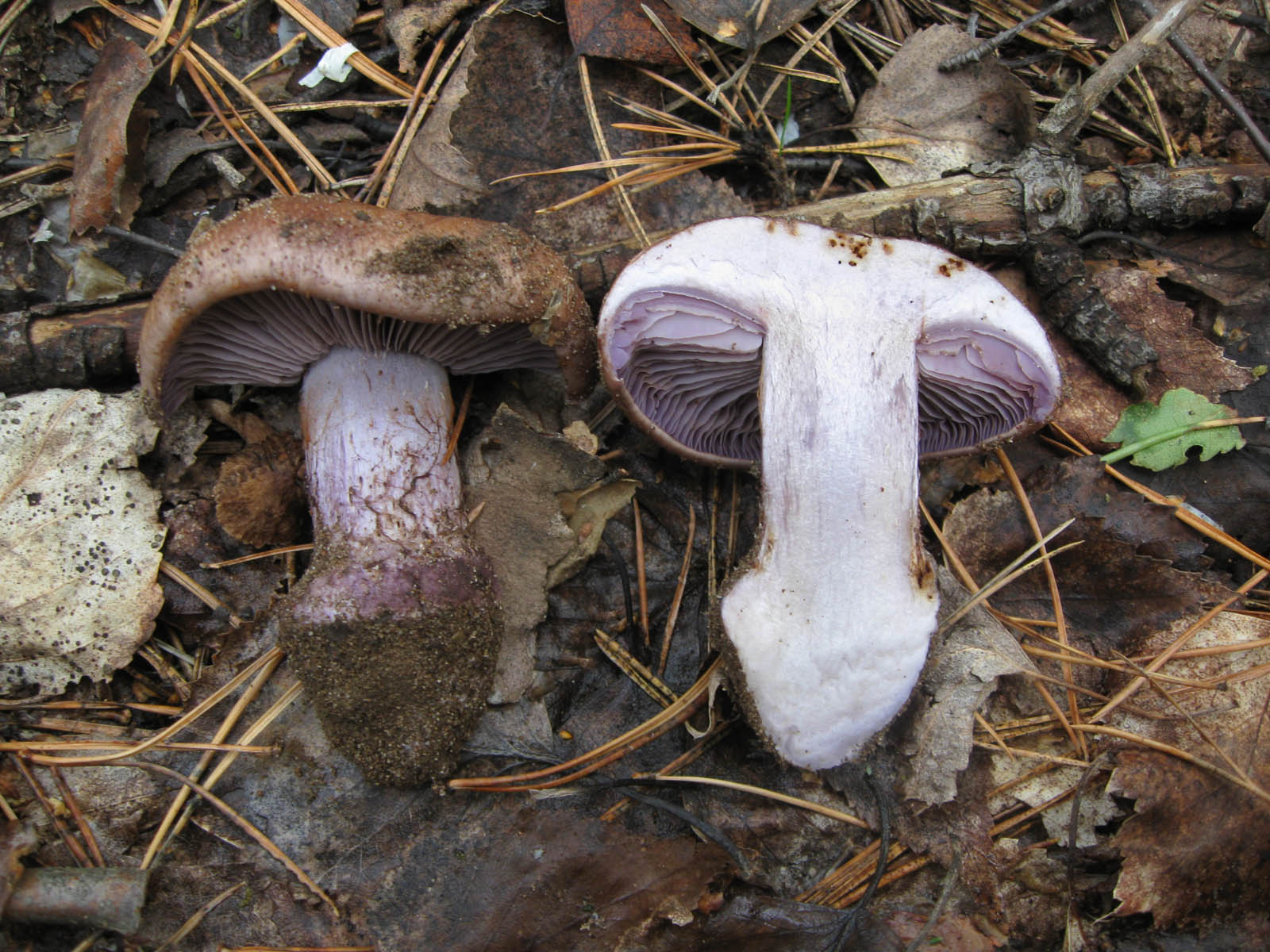
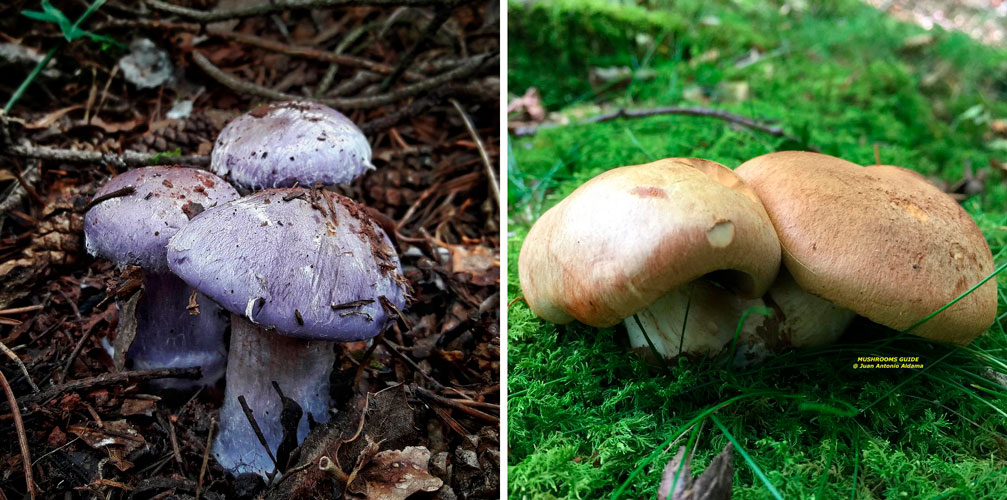
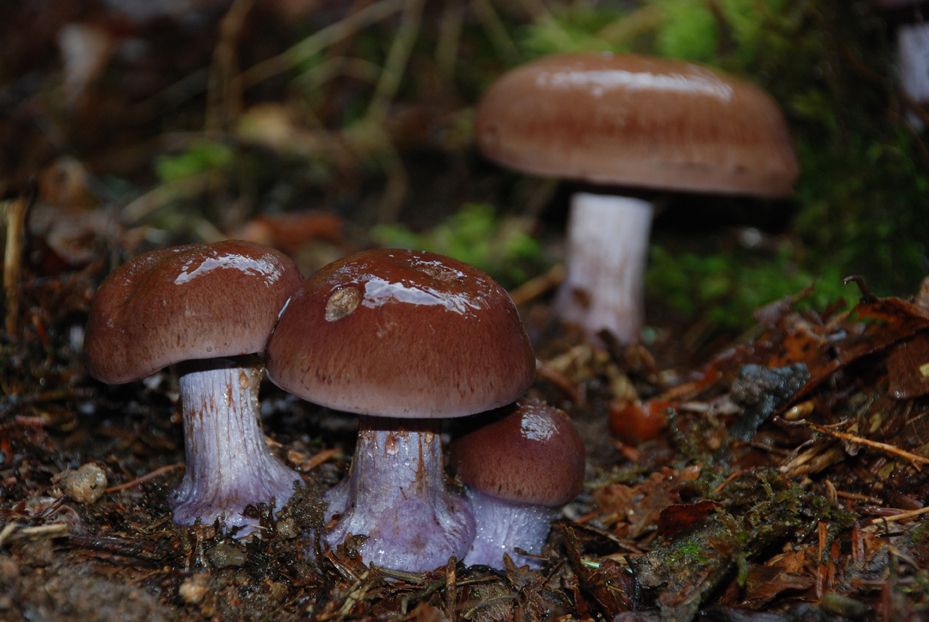
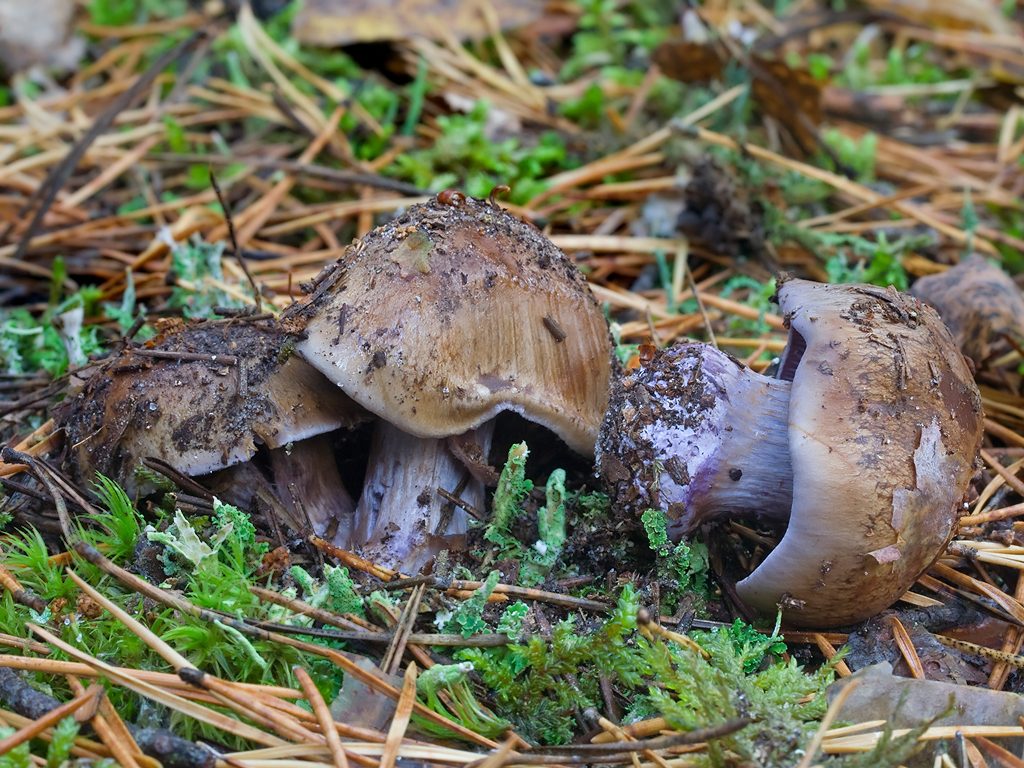
The fruit body of the crimson spider web consists of a leg 6 to 8 cm long and a cap, the diameter of which is up to 15 cm. Initially, the cap has a convex shape, but in ripening mushrooms it becomes prostrate, sticky to the touch and flat. The flesh of the cap is characterized by its fiber, and the color of the cap itself can vary from olive brown to reddish brown, with a slightly darker color in the central part. When the pulp dries, the cap ceases to shine.
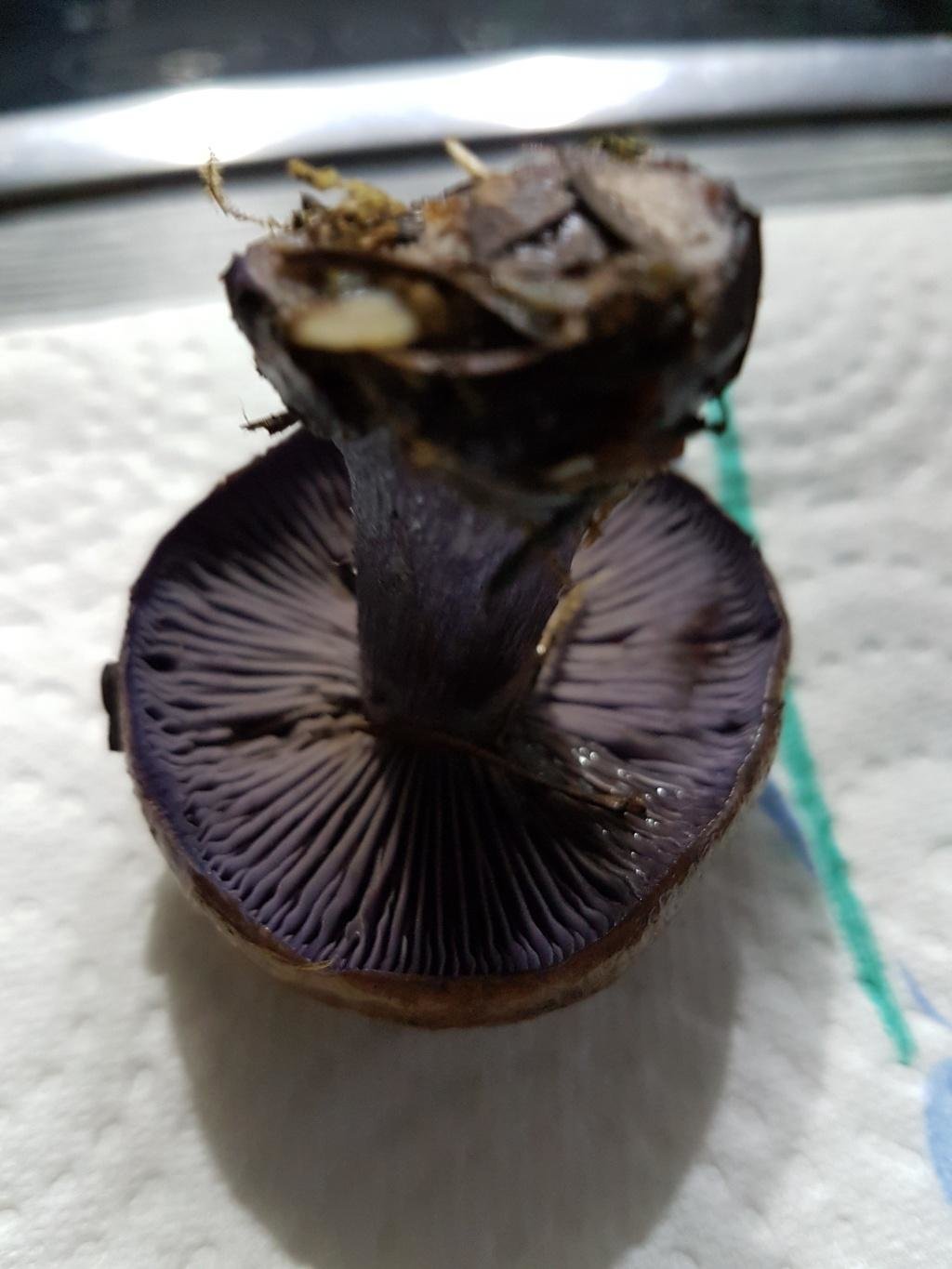
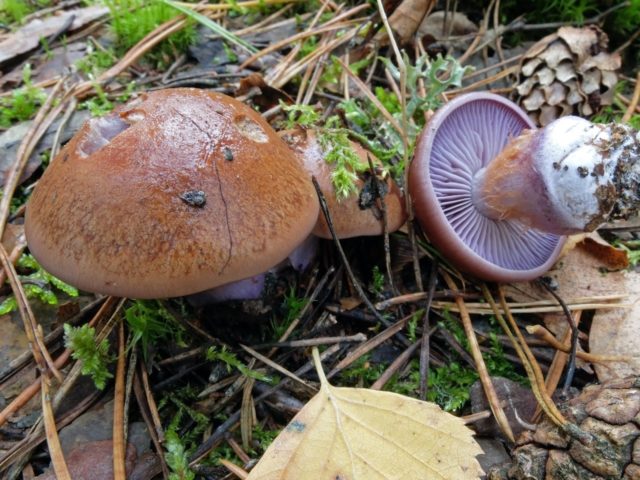
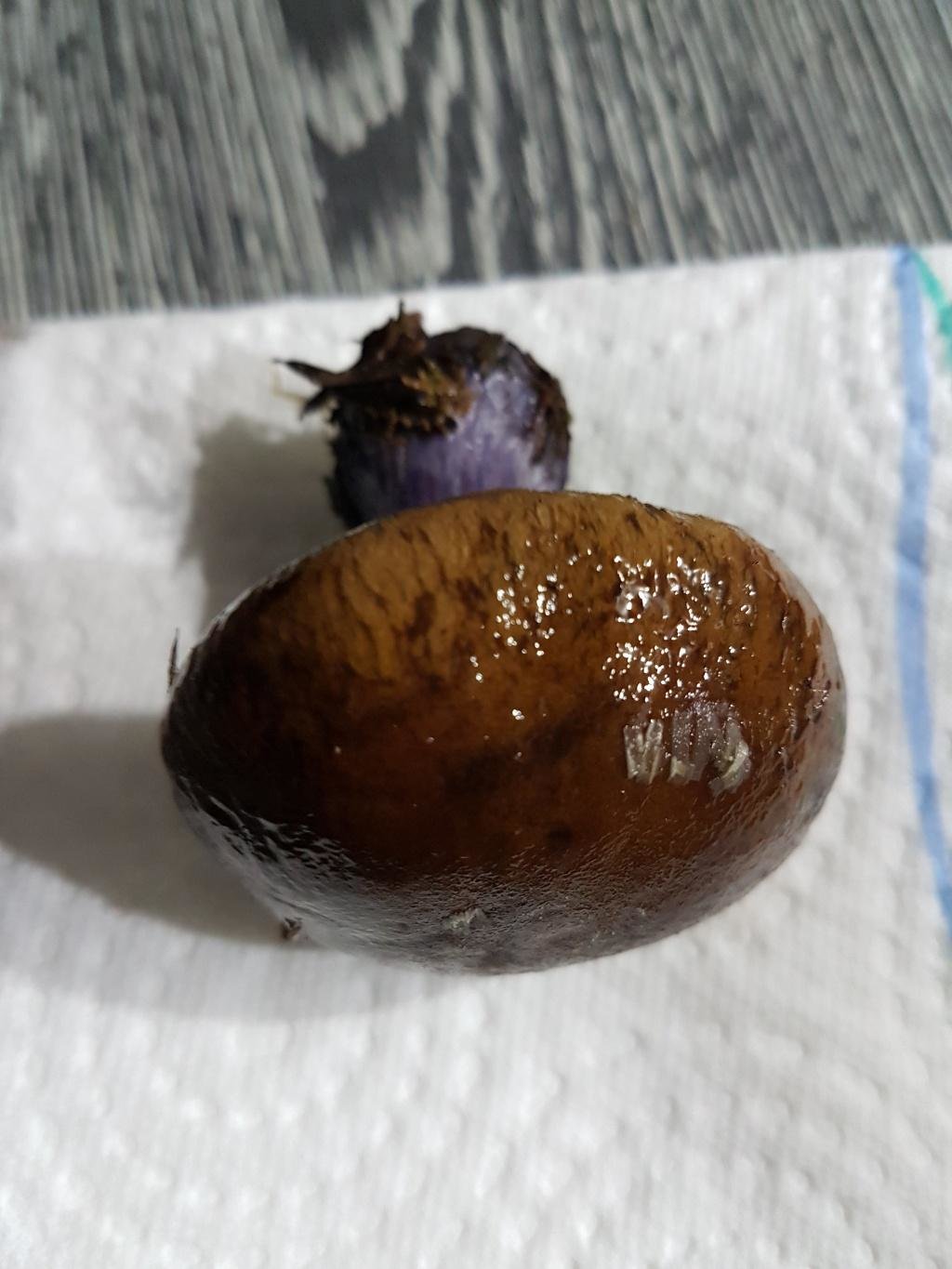
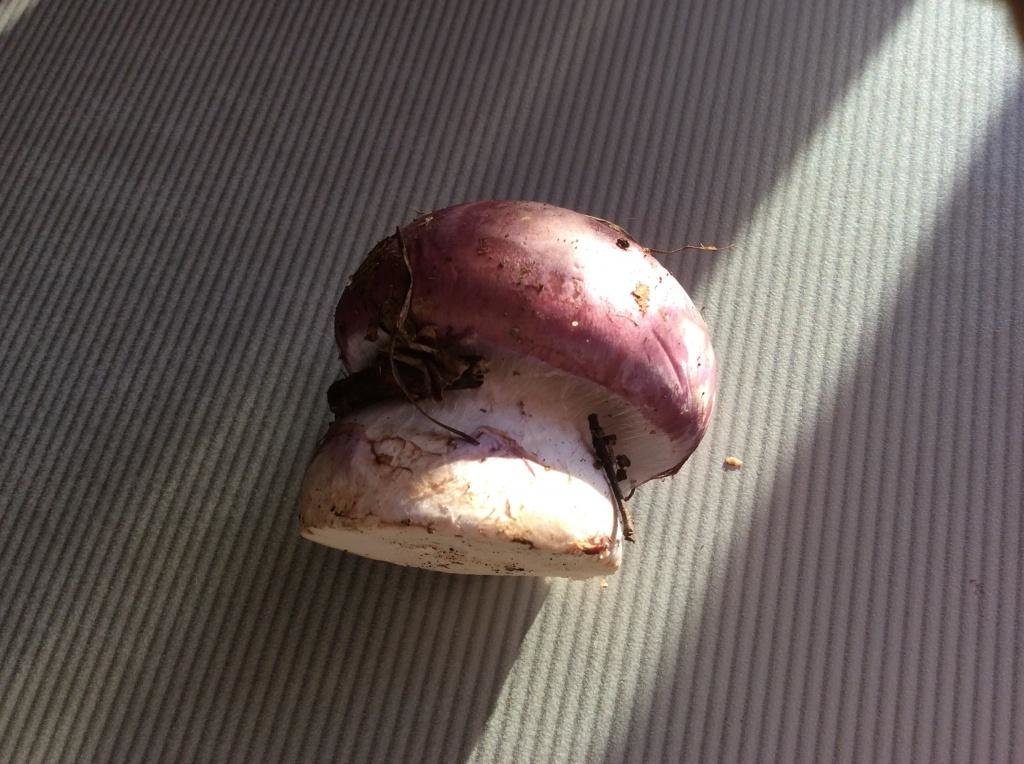
The mushroom pulp is characterized by a bluish tint, but upon mechanical action and cutting it acquires a purple color. The pulp of this mushroom, as such, has no taste, but the aroma is pleasant.
The girth of the mushroom stalk varies within 1-1.2 cm, the stalk is very dense in structure, at the base it acquires a tuberous swollen shape. The main color of the stem of the mushroom is purple.
The hymenophore is located on the inner surface of the cap, and consists of plates adhered to the pedicle with a tooth, initially having a purple color, but gradually becoming rusty-brown or brownish. The plates contain a spore powder of rusty-brown color, consisting of almond-shaped spores covered with warts.
Season and habitat
Active fruiting of the crimson spider web occurs in the autumn period. The fungus of this species can be found in mixed, deciduous or coniferous forests, mainly at the end of August and throughout September.
Edibility
Information about whether the crimson cobweb is edible is controversial. Some sources say that this type of mushroom is allowed to be eaten, while others indicate that the fruiting bodies of this mushroom are not suitable for eating, since they have low taste. Conventionally, the crimson spider web can be called edible, mainly it is eaten salted or pickled. The nutritional properties of the species have been little studied.
Similar types and differences from them
The scarlet spider web is similar in appearance to some other types of spider web. The main distinguishing features of the species is the fact that the flesh of the described mushroom, under mechanical action (pressure), changes its color to bright purple.
Spider web brilliant: photo and description
| Name: | The webcap is brilliant |
| Latin name: | Cortinarius evernius |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Specifications: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
The brilliant webcap (Cortinarius evernius) belongs to the Cobweb family and is extremely rare in Russia. During wet weather, its cap becomes shiny and becomes covered with transparent mucus, acquiring a glossy sheen, which is why it got its name.
What a brilliant spider web looks like
In accordance with its generic name, the mushroom has the remains of a velum with a spider-like structure. The flesh is tasteless, reddish in color with a slight unpleasant odor.
The spore body of the spider web is of a brilliant brown hue, consists of rare plates adhered to the leg. The spore powder has a rusty brown color. The spores themselves are medium-sized, smooth-walled, oval in shape.
In a young mushroom, the shape is at first sharp-bellied, dark brown in color with a lilac tint
Description of the hat
The cap of the mushroom is round in shape, its diameter is about 3-4 cm. With age, it opens, the fields increase, a small tubercle remains in the center. The color ranges from dark brown with a lilac tint to rusty orange.
The plates on the inner side, adhered with a tooth, are wide, have a medium frequency. The color is grayish-brown, later they acquire a chestnut color with a purple tint. The cobweb blanket remains white throughout the growth.
The flesh of the cap is also thin, but dense, has a brown color with a lilac tint
Leg description
The stem of the mushroom is in the shape of a cylinder, tapering towards the base. It is 5-10 cm long and about 0.5-1 cm in diameter. The color varies from gray to purple-coffee. White rings are noticeable along the entire length, which disappear with increased humidity.
Inside the leg is hollow, smooth and fibrous-silky
Where and how it grows
The most common cobweb is brilliant in the north of the European part of Russia and in the middle zone, it is also found in the Caucasus. The season starts at the end of summer - from the second half of August. Grows in mixed and coniferous forests.
Most often found in mossy places with high humidity: ravines, lowlands or near swamps. Glittering cobwebs grow in small groups of 2-4 mushrooms at the foot of pines and firs. Also found singly under bushes and among fallen leaves
Is the mushroom edible or not
The brilliant webcap belongs to inedible mushrooms. It does not contain any toxic substances and is not hazardous to health, but the unpleasant smell and taste of the pulp make it unsuitable for human consumption.
Doubles and their differences
The brilliant webcap can be easily confused with several more representatives of this species.
Slime cobweb (Cortinarius mucifluus) - is a conditionally edible species. The diameter of the cap is from 10 to 12 cm. The shape is bell-shaped at first, then straightens and becomes flat with uneven jagged edges. The leg is fusiform, 15-20 cm long, with a white color. The pulp is creamy, tasteless and odorless.
It differs from the brilliant cobweb in the absence of an unpleasant odor and mucus on the cap, even in dry weather
The most beautiful or reddish webcap (Cortinarius rubellus) is a poisonous mushroom that belongs to inedible. The length of the leg is 5-12 cm and from 0.5 to 1.5 cm in thickness, it expands downward. It has a brown-orange fibrous surface with light rings along its entire length. The diameter of the cap varies from 4 to 8 cm. The initial shape is conical. Further, it levels out, leaving a small convex mound at the top. The surface is smooth and dry with irregular edges of a brownish-red or brownish-purple color. The pulp is yellow-orange in color, odorless and tasteless.
It differs from the spiderweb of a brilliant rusty-reddish color and a lighter shade of the cap
Conclusion
The brilliant webcap is strictly not recommended to be cut and eaten. Having found it in the forest, you should be extremely careful: other edible spiderwebs can be confused with it. Most often it can be found in forests with a predominance of pines and birches.
Gallery: types of cobwebs (45 photos)

























Cortin.triumрhans - has a hemispherical or cushion-shaped, half-open upper part of an orange-yellow coloration with the remnants of a bedspread and a sticky or dry surface covering a thick, soft, whitish-yellowish pulp with a pleasant aroma. The plates are weakly adherent, narrow and frequent, light smoky-cream or bluish-brown in color with a rusty-reddish-brown spore powder. The lower part of the fruiting body is strongly thickened, cylindrical in shape.

Cortin.albоviolaceus - has a rounded bell-shaped, convex or convex-outstretched cap with an elevation in the central part and a silky fibrous, shiny, smooth, sticky surface of lilac-violet-silver or white-lilac coloration.Plates are medium-frequent, narrow, grayish-blue, gray-ocher or brownish-brown, with the presence of rusty-reddish-brown spore powder. The area of the leg is clavate, with weak mucous membrane. The soft part is thick and watery in places
, gray-blue, brownish, with an unpleasant odor.

Cortin.armillatus - has a hemispherical, gradually opening, cushion-shaped cap with a wide and obtuse tubercle in the central part, covered with dry and fleecy, orange or reddish-brown coloration with remnants of a red-orange-brown blanket. The soft part is thick and dense, brownish in color, with a pronounced musty odor in the absence of mushroom taste. Plates of an adherent type, wide and relatively sparsely located, grayish-cream, slightly brownish or rusty-brown in color, with brown-rusty-red spore powder. The lower part of the fruiting body is lighter
, with an extension at the base, with bracelet-like remains of the bedspread.
The webcap is special
Cortin.rubellus - has a conical or prostrate-conical cap, with a sharp tubercle in the center and a fine-scaly, reddish-orange, reddish-orange or bright brownish surface, covering the tasteless and radish-smelling flesh of a reddish-orange-orangish tinge. Thick and wide plates are rare, growing to the stem,
orange-ocher or rusty-brownish color, with rusty-reddish-brown, spherical spores with roughness. The lower part of the fruiting body is cylindrical, of sufficient density.
Webcap purple (video)
Cortin.pholideus - has a bell-shaped, slightly convex, with a blunt elevation in the center and numerous scales of a dark brown coloration of the cap, covered with a pale brown, brownish-brown skin. It is distinguished by rare, grayish-brownish plates with a lilac-violet tint and the presence of a brown spore powder. The lower part of the fruiting body is cylindrical or weakly clavate, with an extension at the base, solid or hollow, with a smooth, grayish-brownish scaly surface. Loose type, gray-violet-brownish the pulp has a faint musty odor.
Kira Stoletova
One of the most common types of mushrooms in the temperate zone is the spiderweb mushroom. It belongs to the group of conditionally edible mushrooms. The genus Spiderweb from the family of the same name Spiderweb is dangerous because there are poisonous species.