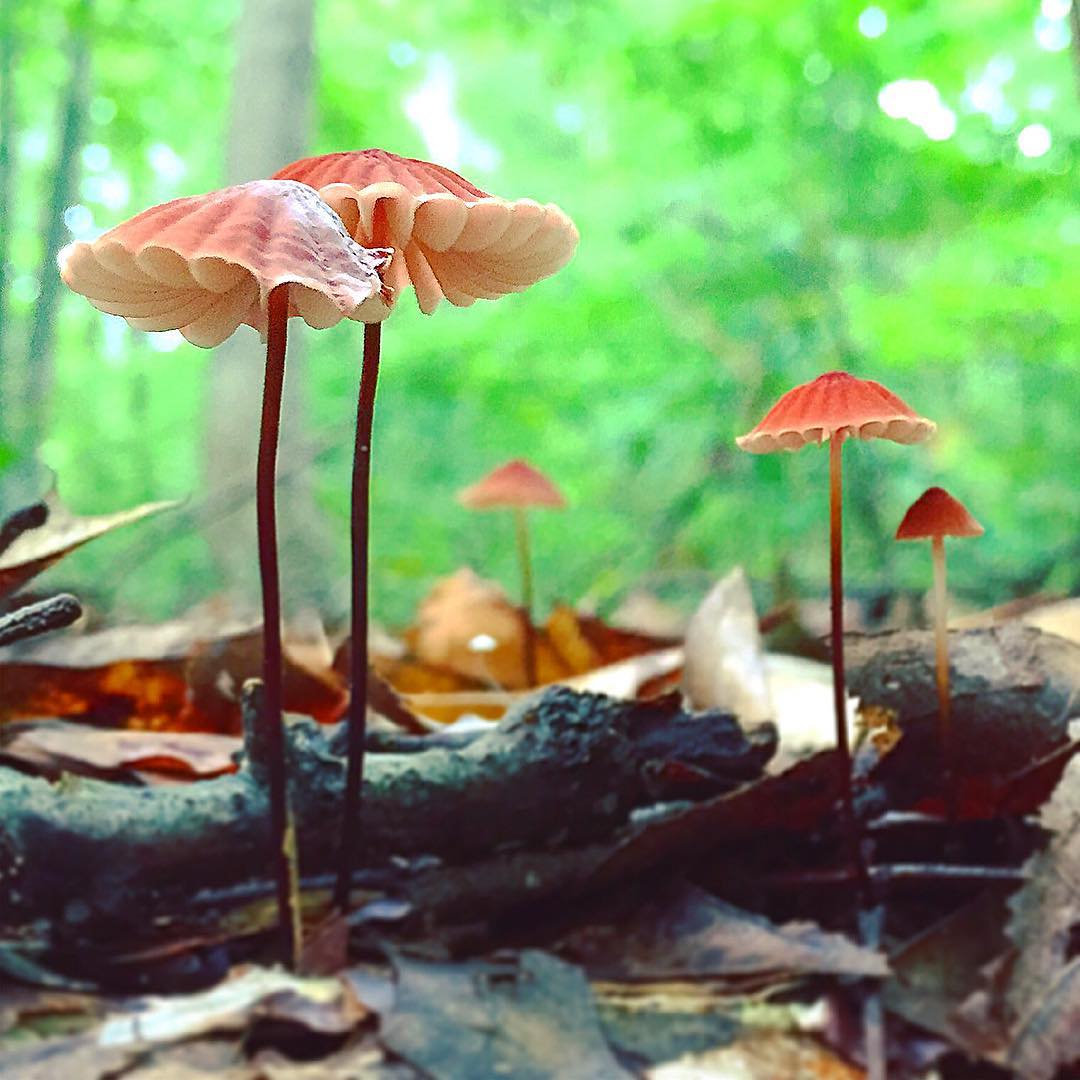
Negniichnik dry: photo and description
| Name: | Dry |
| Latin name: | Marasmius siccus |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Synonyms: | Agaricus siccus, Chamaeceras siccus |
| Systematics: |
|
Dry Negniychnikov is a member of the Negniychnikov family. The Latin name for this species is Marasmius siccus, which also has a number of synonyms: Chamaeceras siccus and Agaricus siccus.
What does a dry non-drip look like?
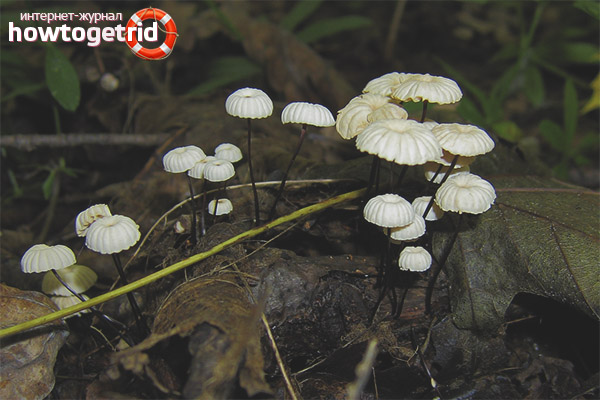
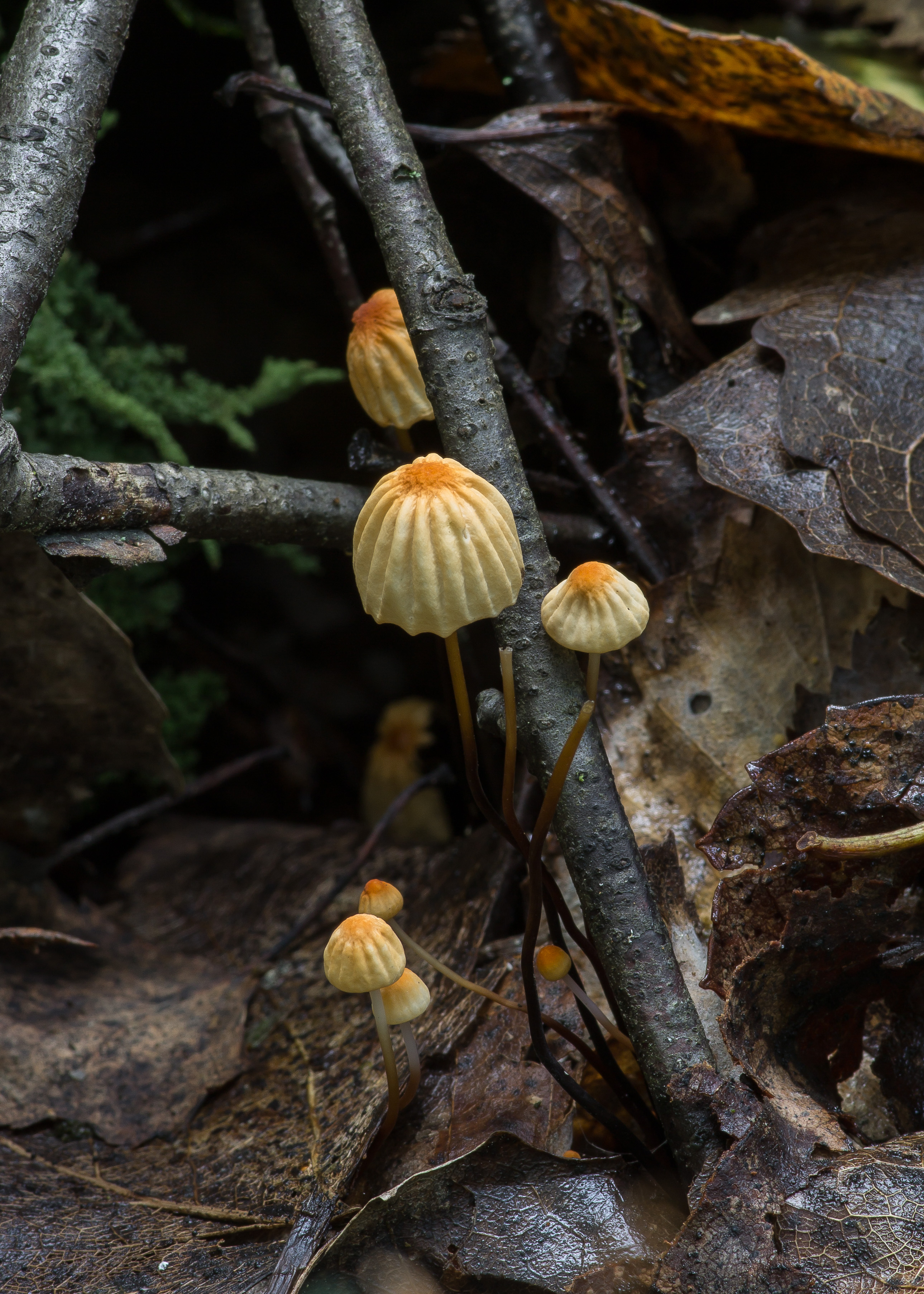
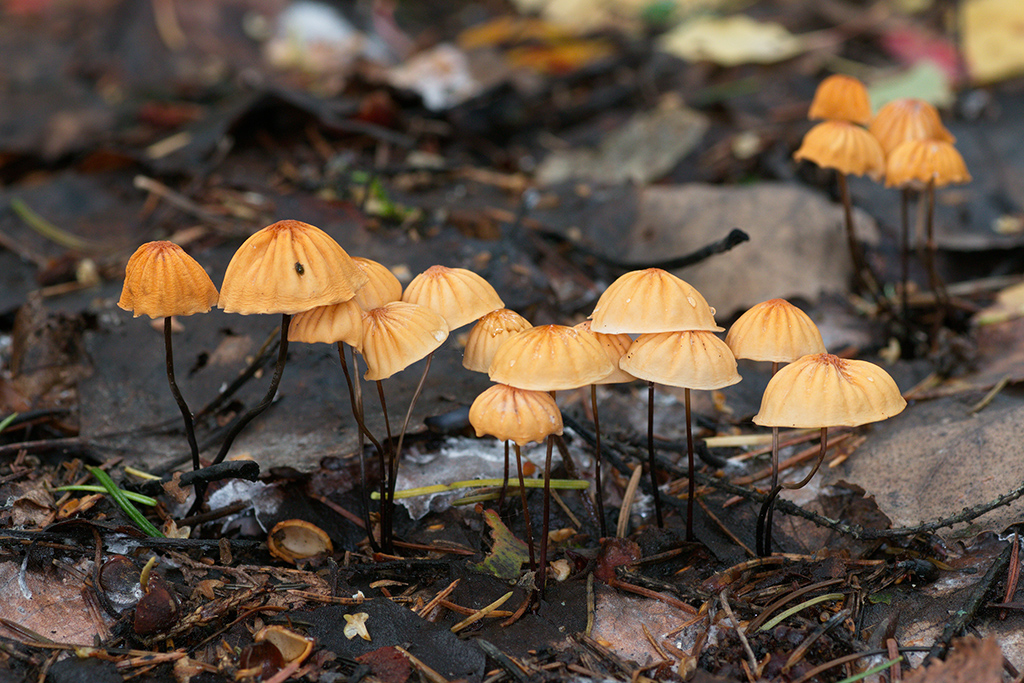
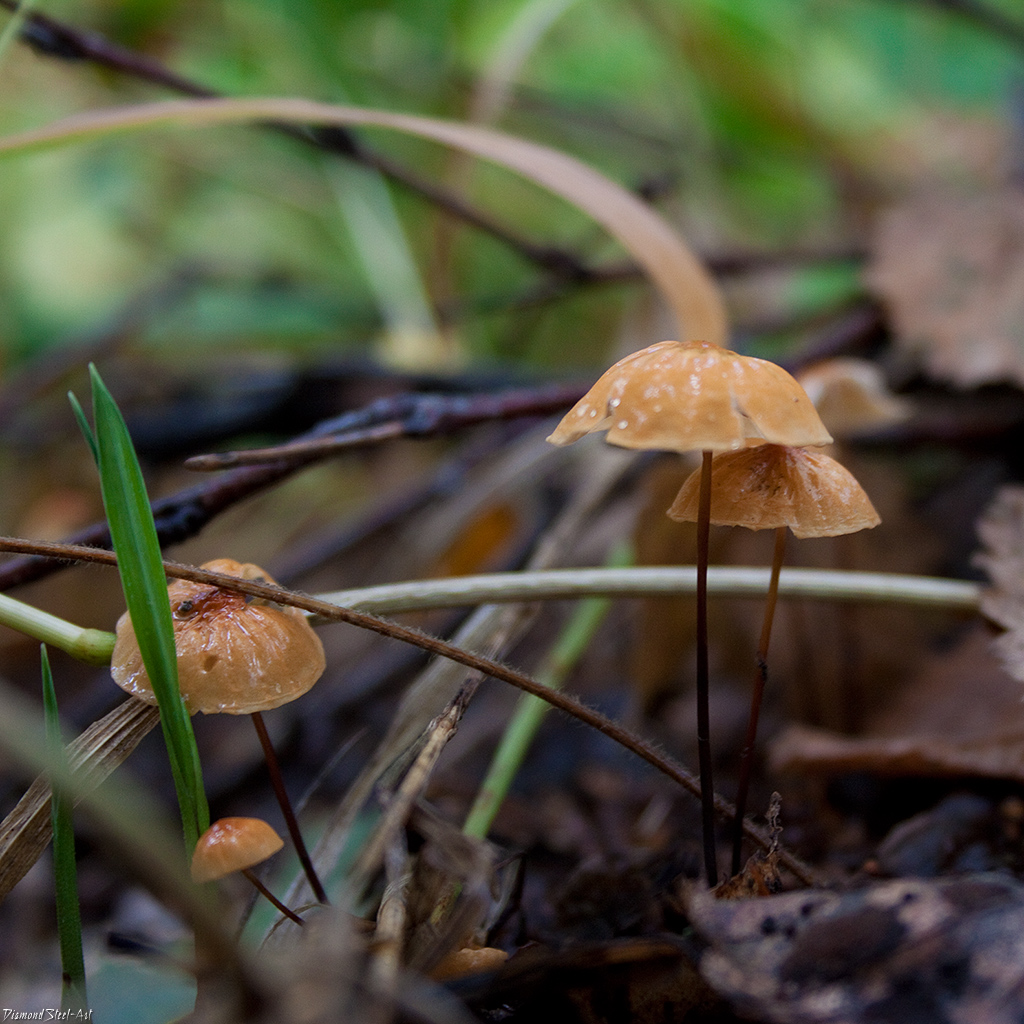
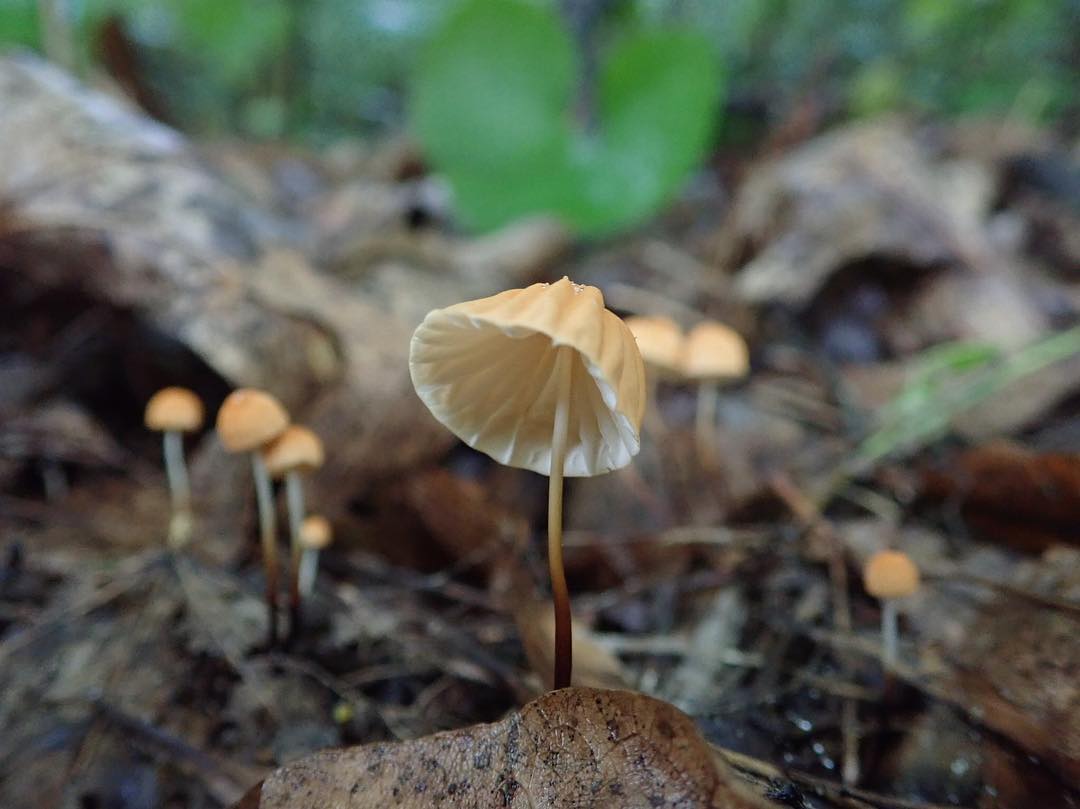
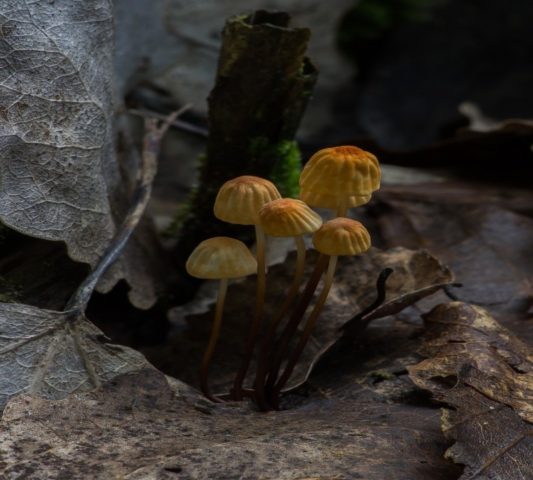
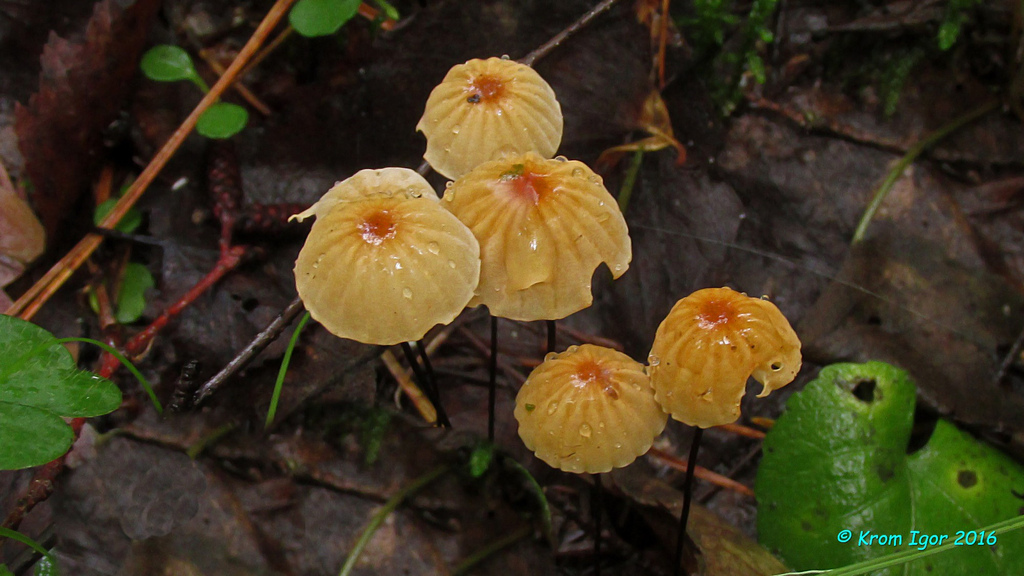
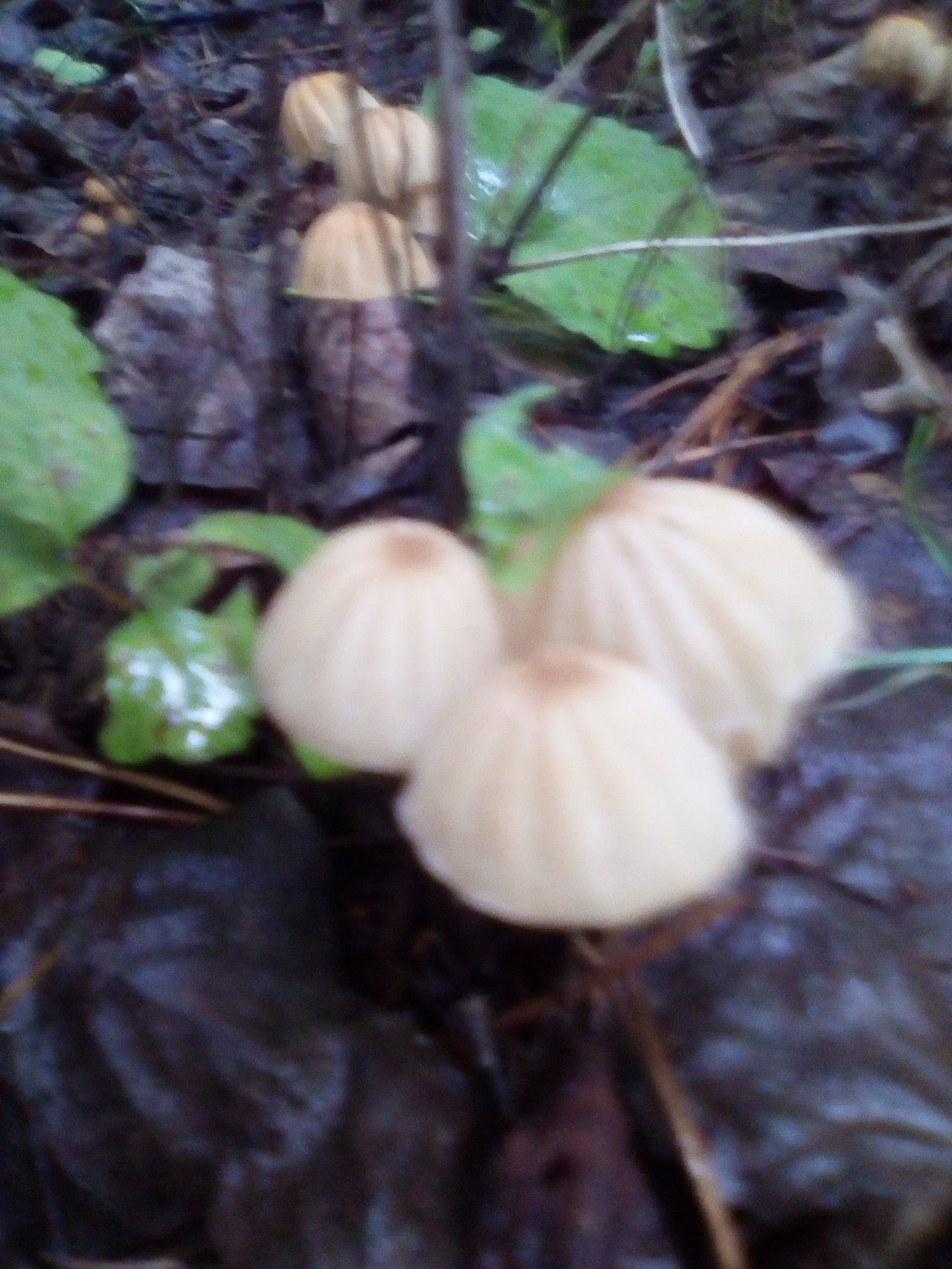
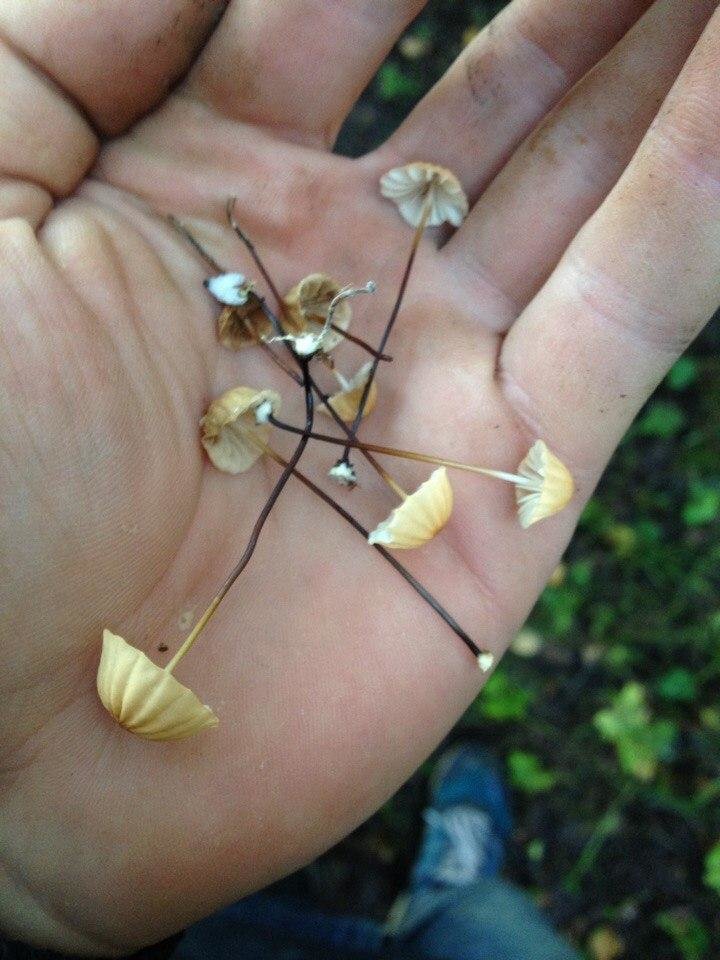
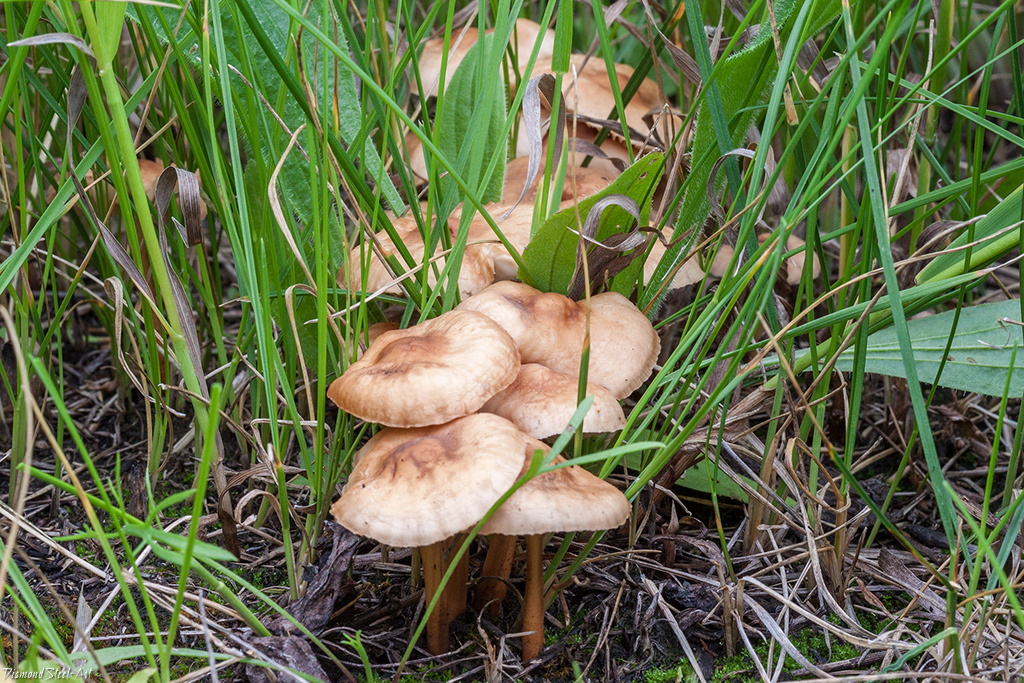
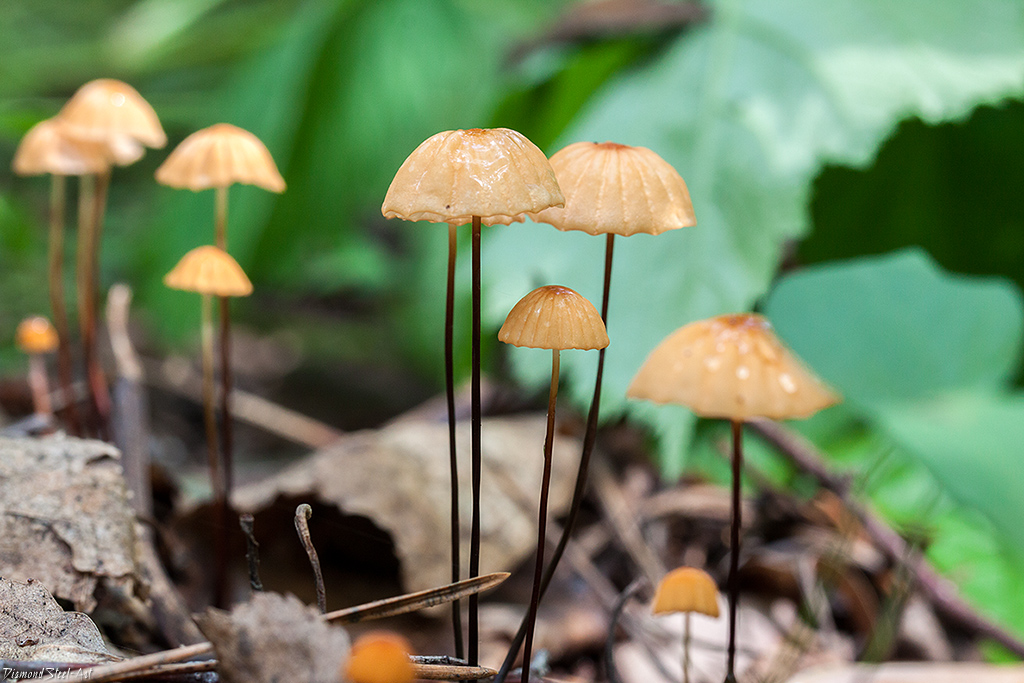
The mushroom is shaped like an umbrella
The fruit body of the specimen in question consists of a small cap and a long stem. The pulp is very thin, has a slight odor and a bitter taste.
Description of the hat
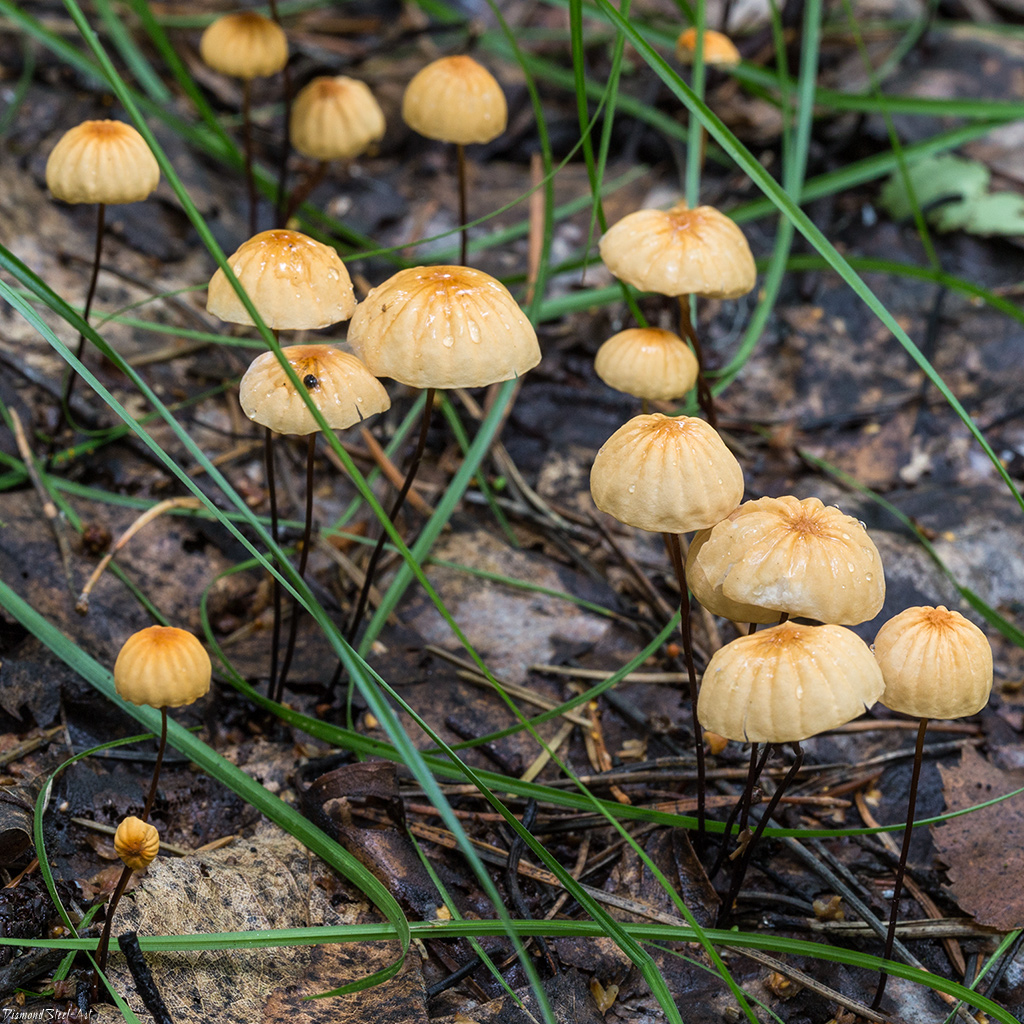
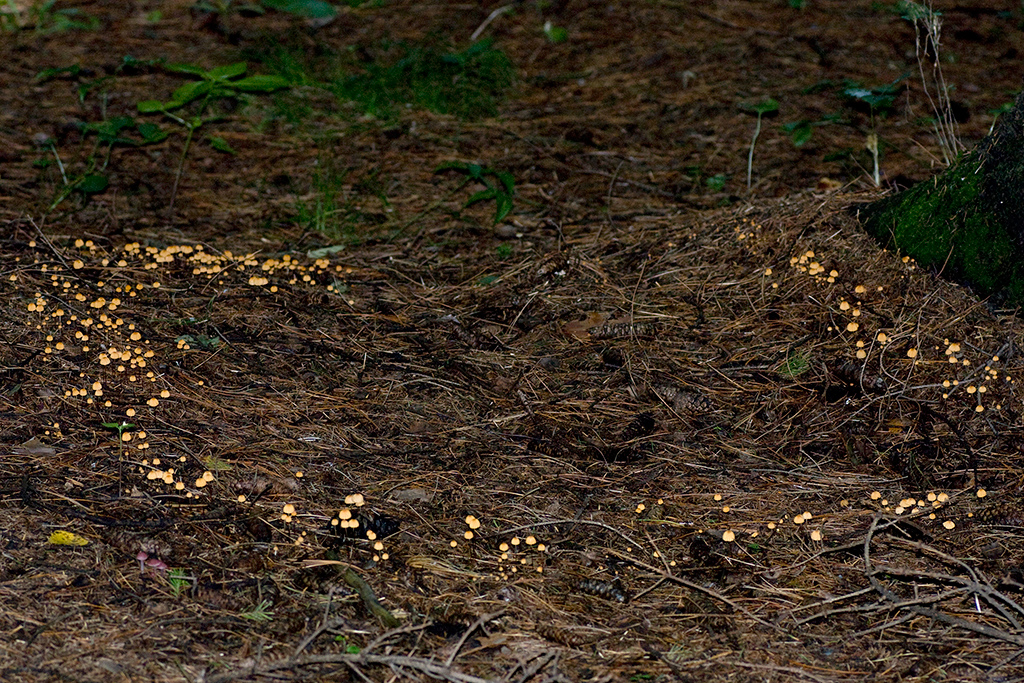
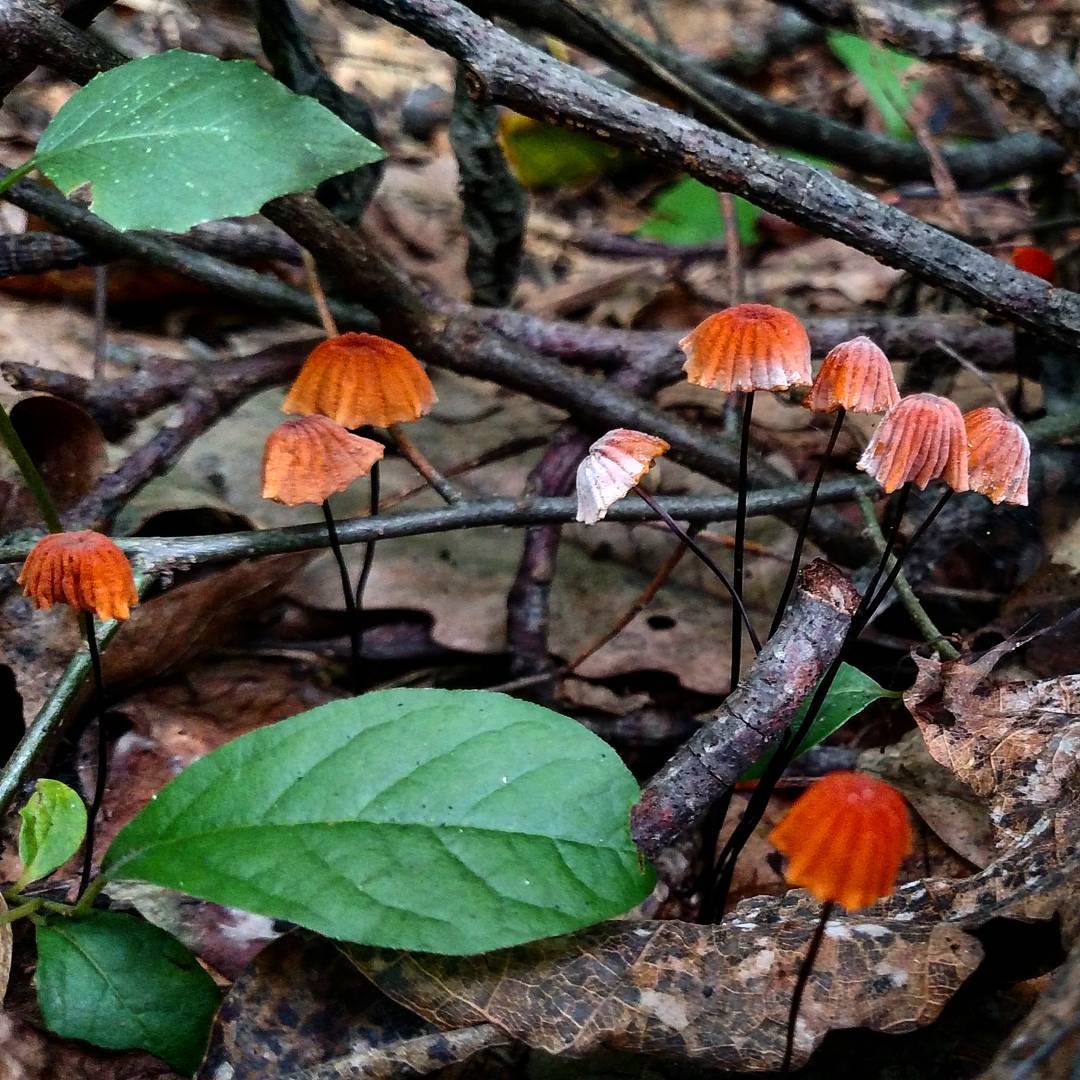
Always grows in large groups
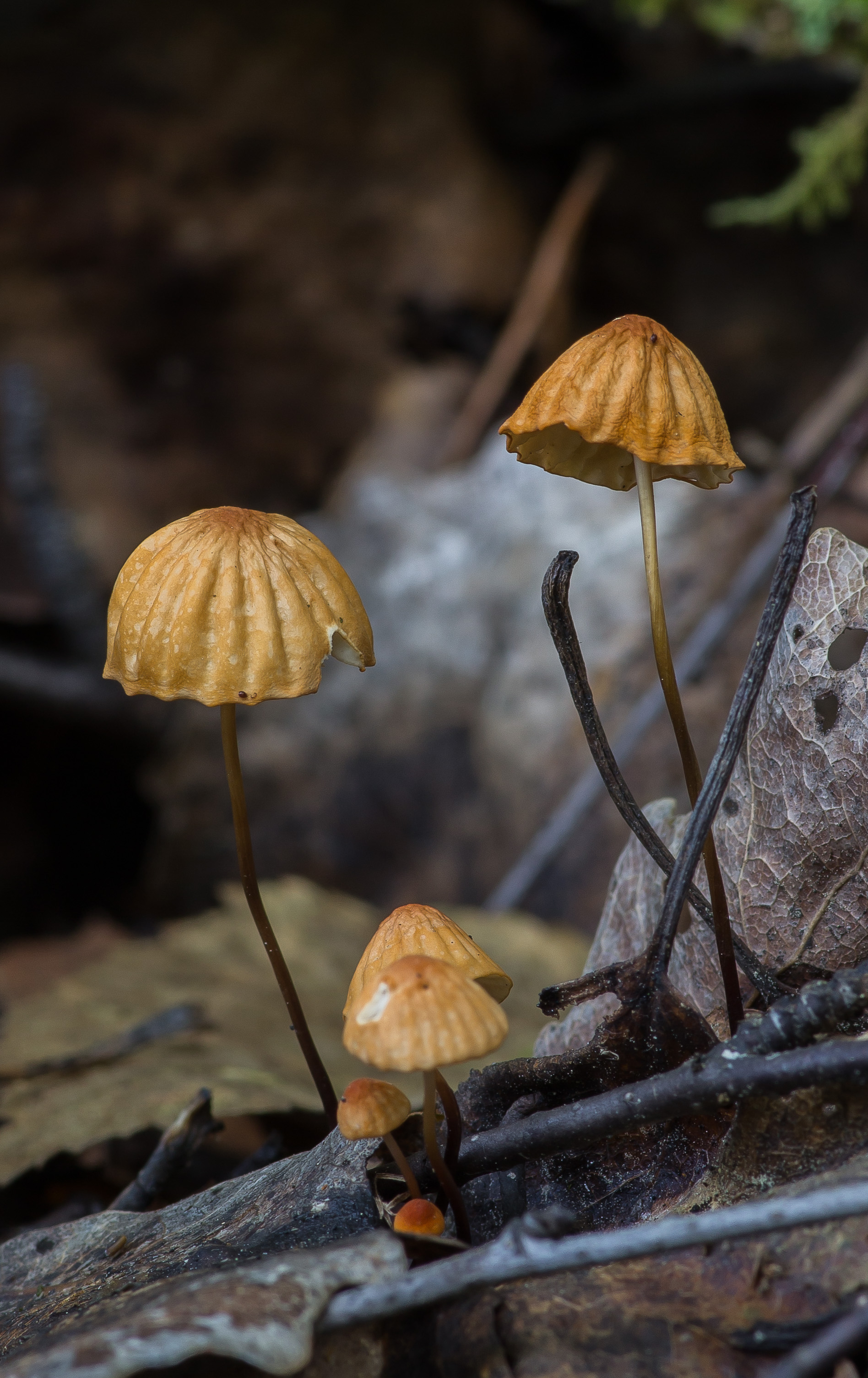
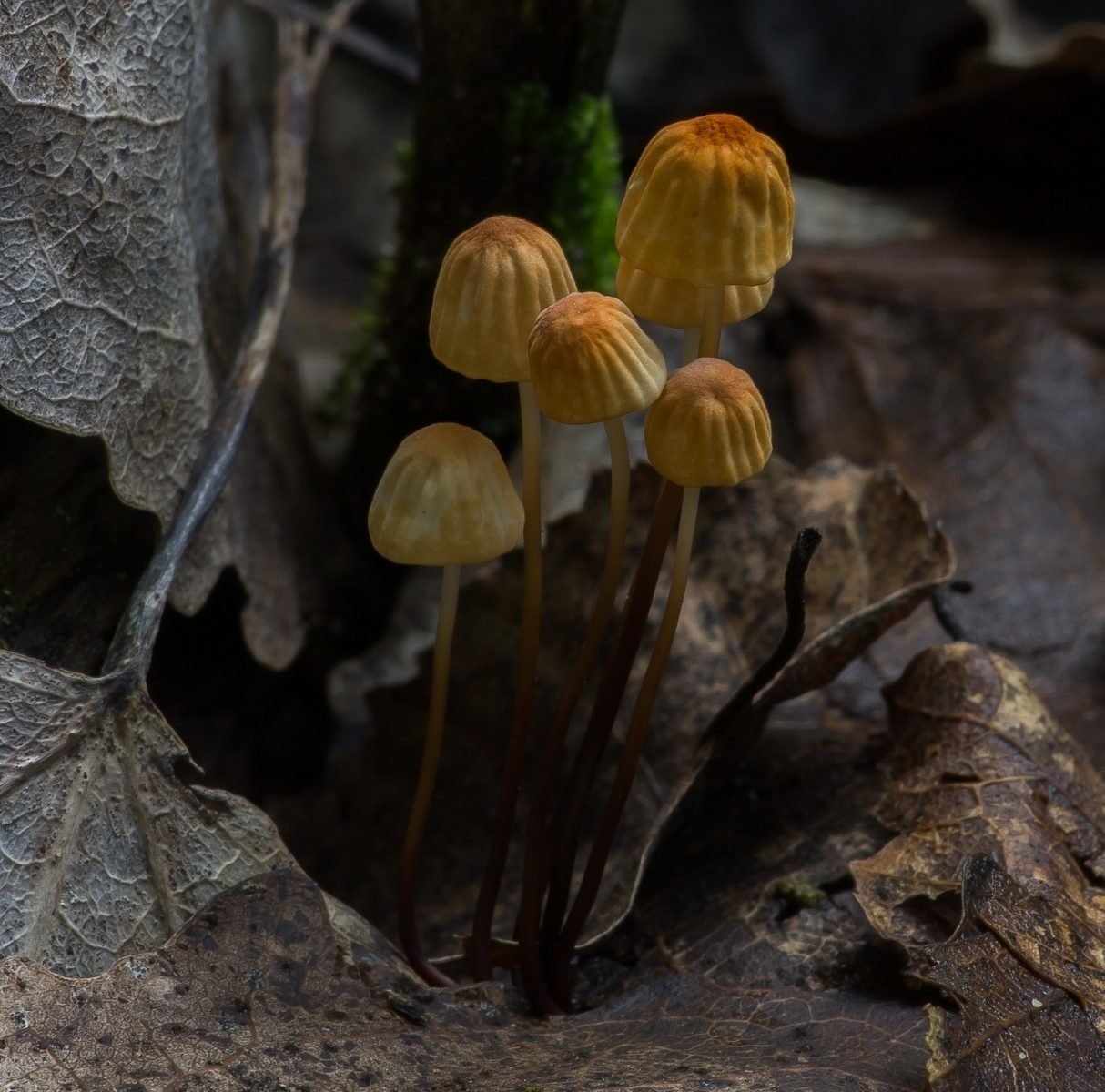
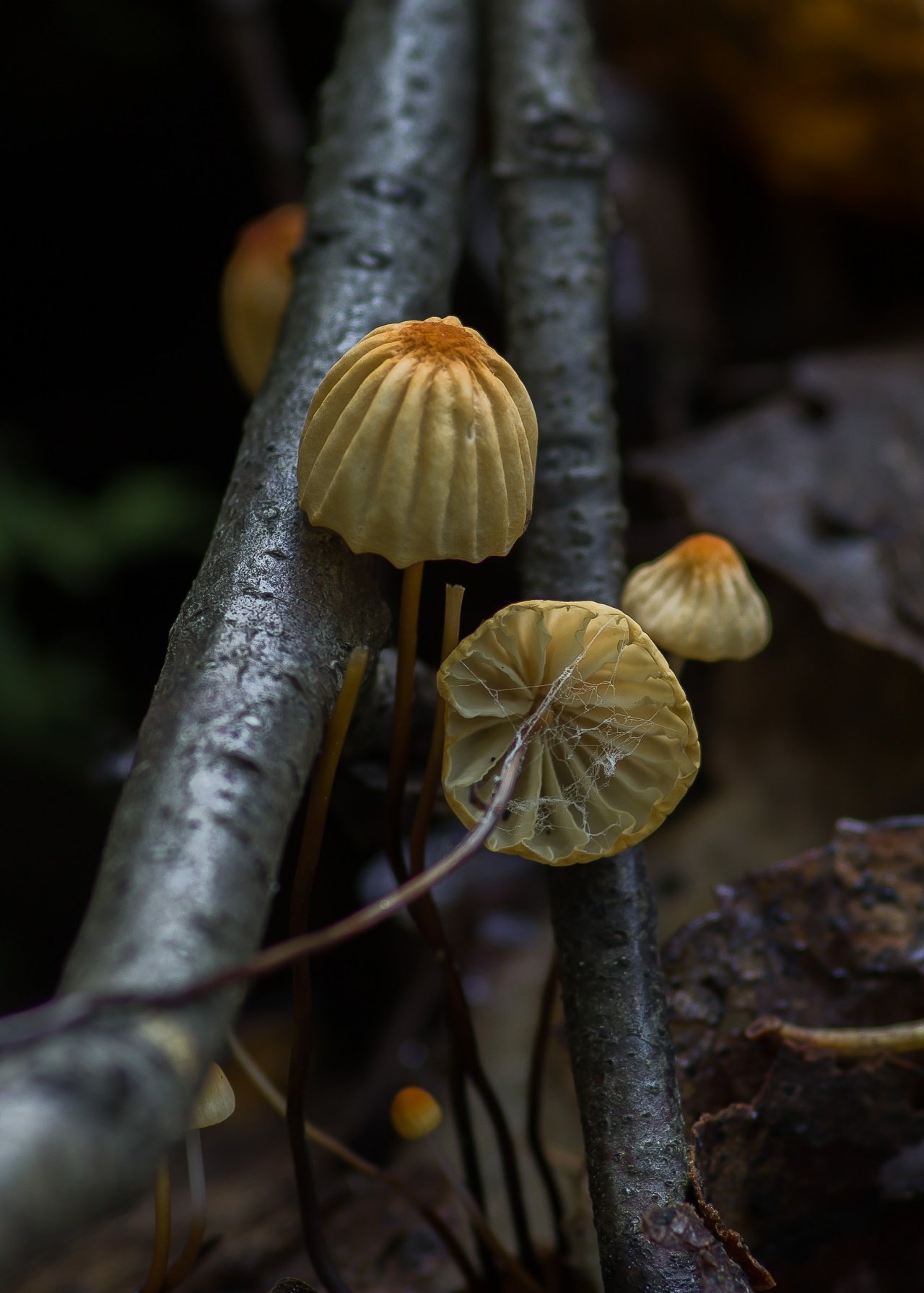
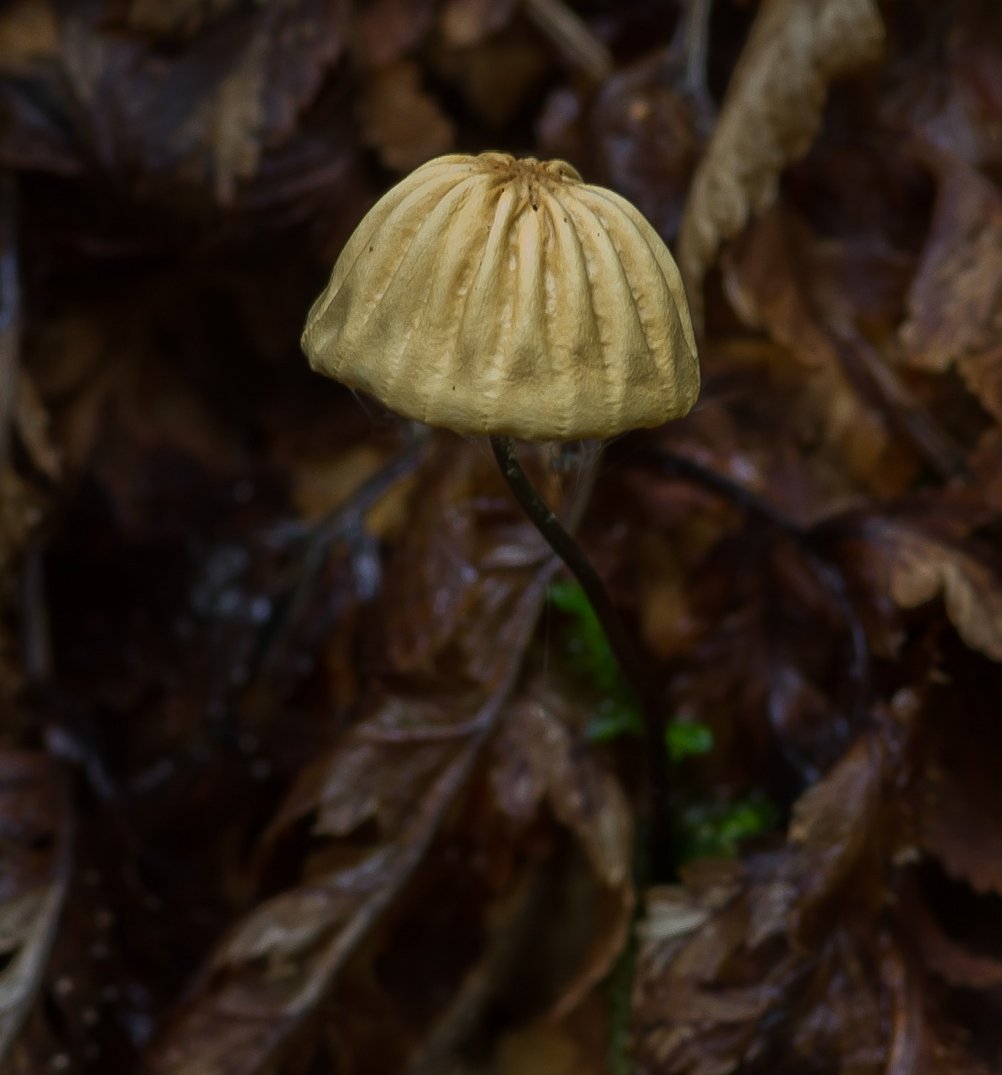
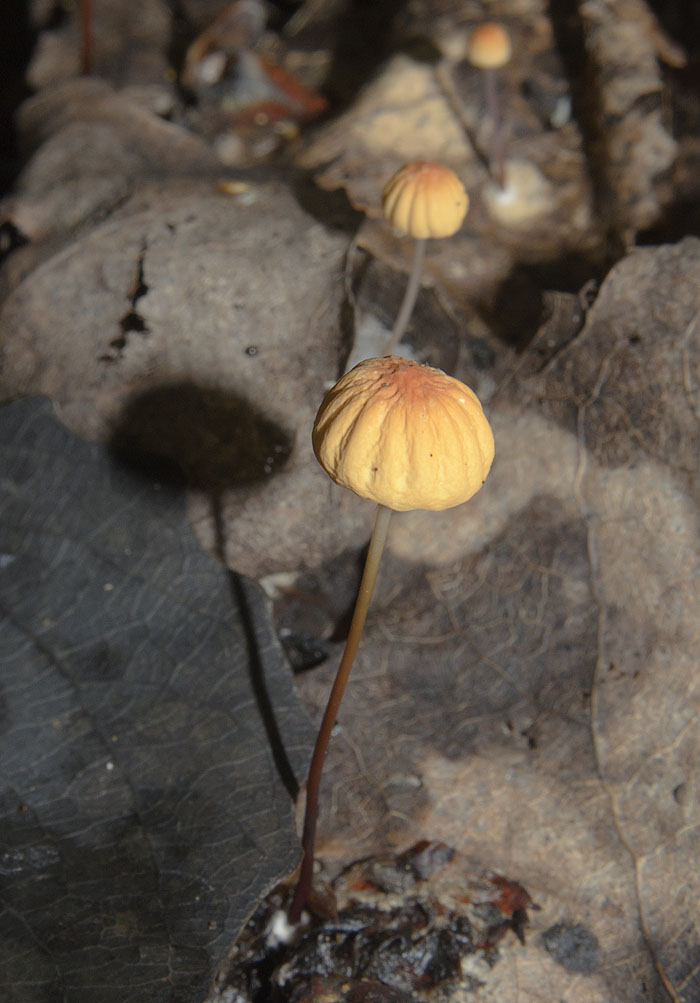
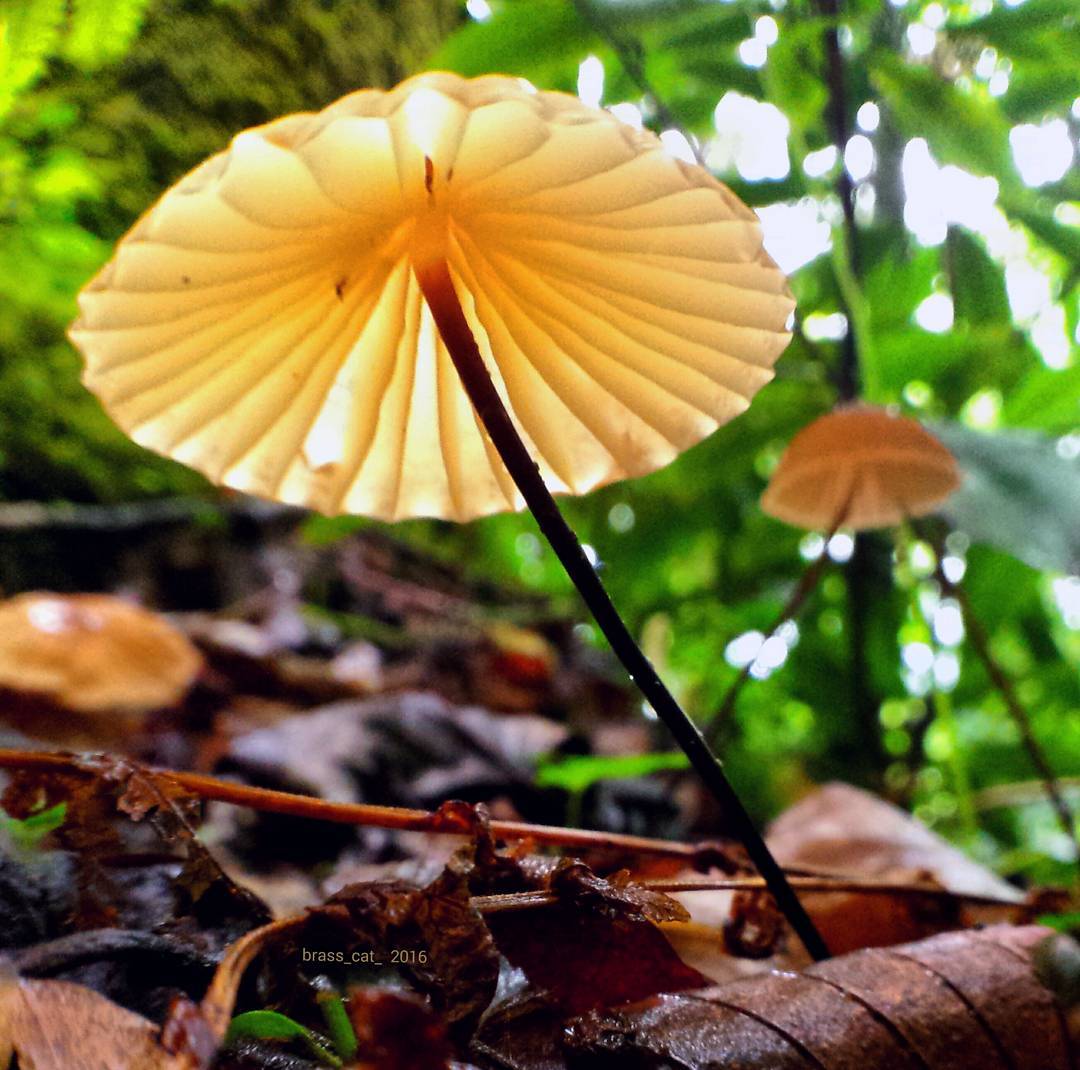
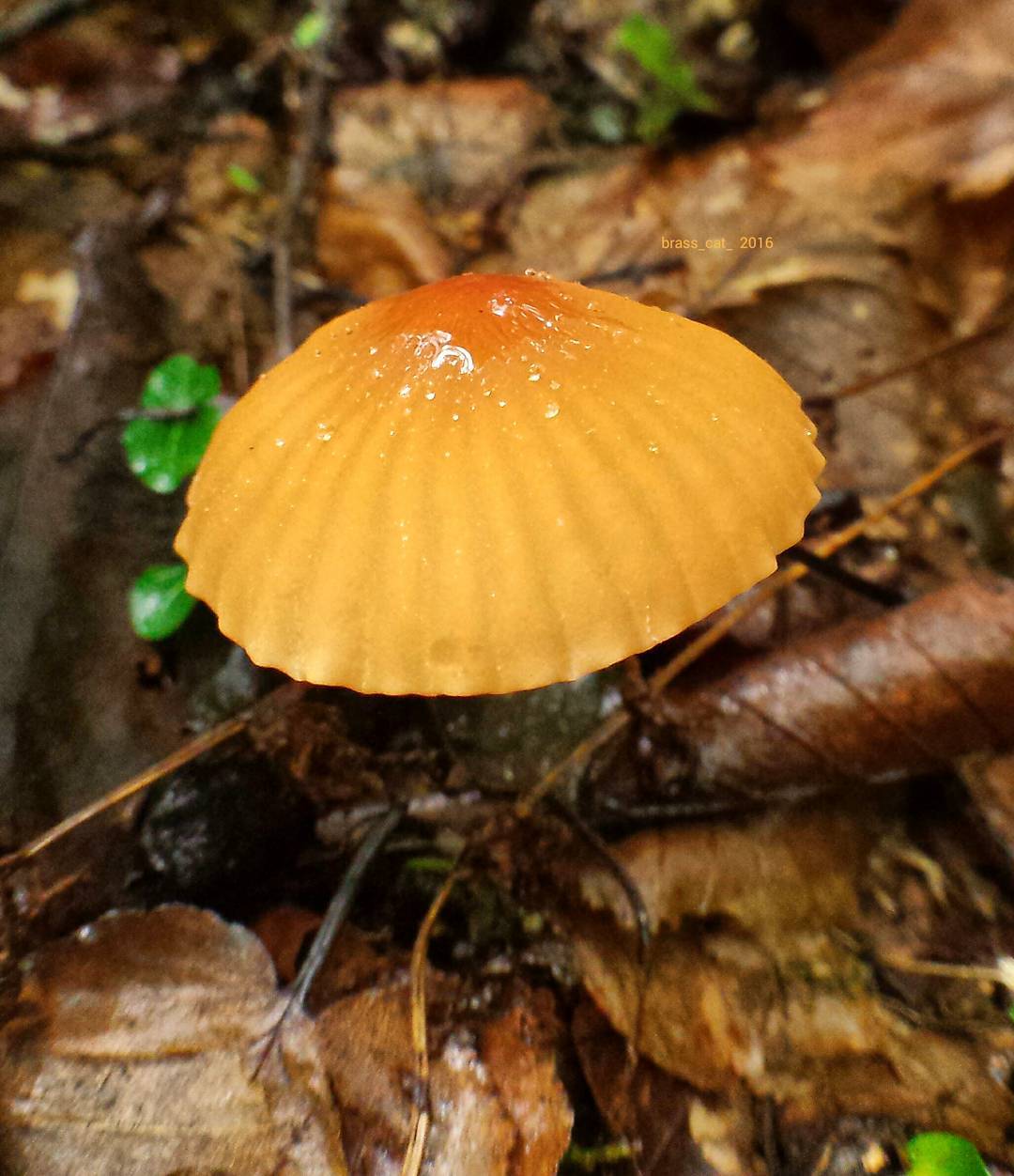
At the initial stage of ripening, the cap of the dry non-pot is bell-shaped or cushion-shaped; as it grows, it acquires an almost prostrate shape. In its central part, there may be a tubercle or a pronounced flat zone, less often - a small depression. The cap is small in size, it is only 0.5 to 3 cm. It is painted in bright red-brown or orange-brown shades, it fade in old mushrooms. In the central part of the cap, the saturated color lasts longer than along its edges. The surface is smooth, dry and matt with a pronounced radial groove.
On the inner side of the cap, there are rare, almost free, or adhered toothed plates. Painted in light cream or pale yellow tones. Spores are cylindrical or fusiform, smooth, sometimes slightly curved.
Leg description
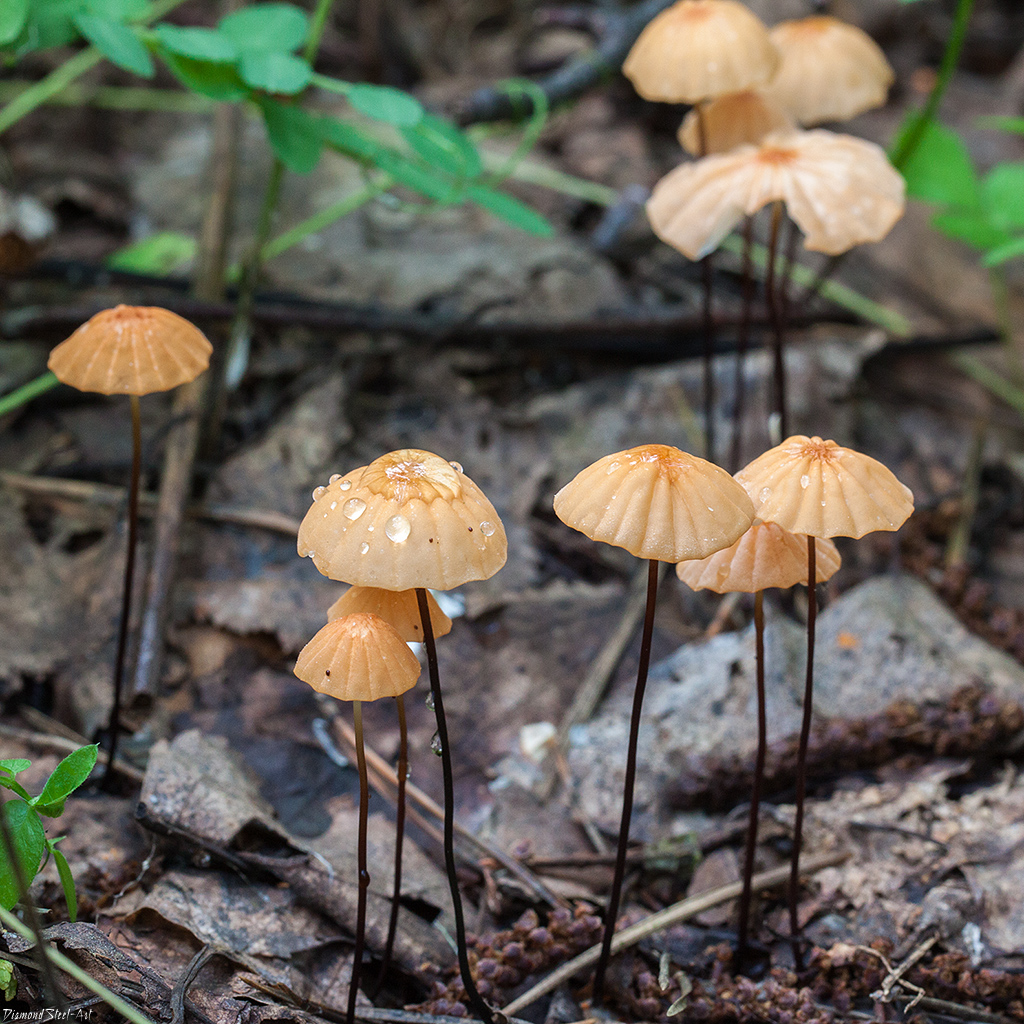
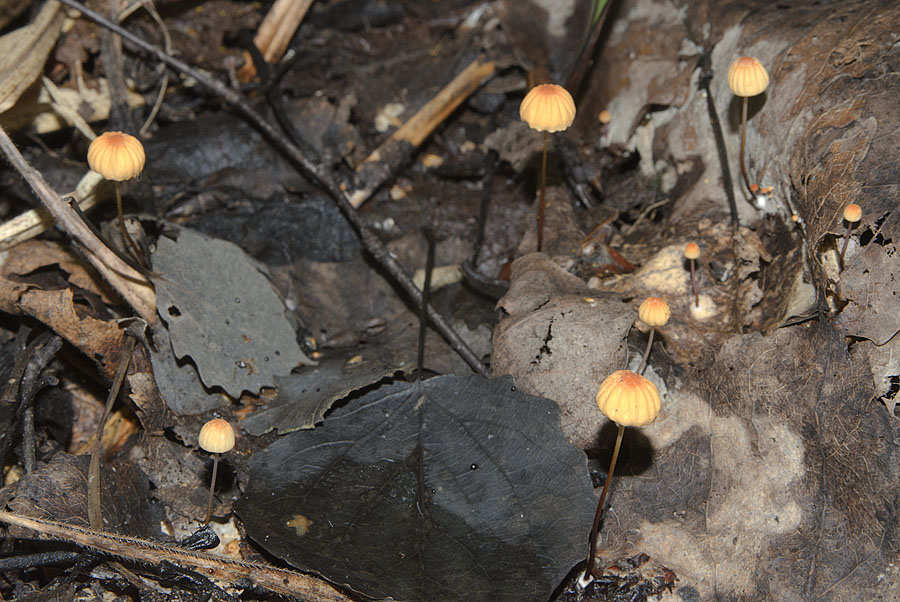
Grows throughout the summer and in the first half of autumn
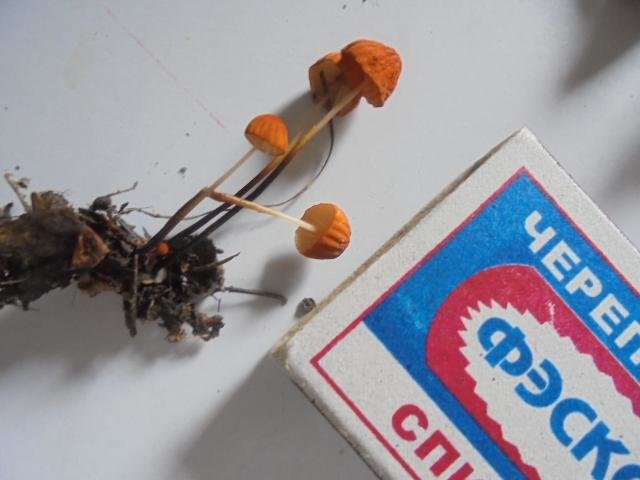
For such a small cap, the leg of a dry non-nylon is considered to be rather long, the height of which ranges from 2.5 to 7 cm. Its maximum thickness in diameter reaches about 1.5 mm. It is characterized as central, rigid, straight or slightly curved, even, without bulging. The surface is shiny, smooth to the touch. The upper part of the leg is colored white or light yellow, while the lower part is dominated by dark brown or black shades. At the base there is a white felt mycelium.
Where and how it grows
The optimal time for growing is the period from June to September. Most often, dry non-nipple dwells in deciduous forests on shallow deadwood or leaf litter, less often on needles. Widely distributed in Asia, America and Europe, including Russia, Belarus and Ukraine. This species does not tend to grow one at a time, usually occurs in large groups.
Is the mushroom edible or not
Dry non-fungus belongs to the category of inedible mushrooms. Due to the small size of the fruit bodies, it has no nutritional value and is not suitable for human consumption.
Doubles and their differences
According to its external features, dry non-nipple plant is similar to the following gifts of the forest:
- Blood-headed firebrand. It is an inedible and rare species that has the ability to glow at night. You can recognize the double by a small domed red hat and a rather long stem of dark shades.
- Wheeled nonnichi - this specimen is very similar in shape and size to the described species in the shape and size of the fruiting body. However, the distinguishing feature is the color of the mushroom. So, the hat of the twin in young specimens is painted white, and in mature specimens it is grayish-yellow. Not edible.
- Smelly stinker. It belongs to the group of inedible and poisonous mushrooms. A double can be distinguished by a yellowish-brown cap and a black, shorter stem, the maximum length of which is 3 cm. In addition, this species grows on old hardwood.
Conclusion
Dry firebug is a fairly common species of the Negniychnikov family, which can be found not only in Russia, but also abroad. However, such a specimen is not of interest to mushroom pickers, since it does not represent any nutritional value.
Definitioner
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
Beneficial features
Meadow mushrooms, unlike autumn mushrooms, contain many vitamins B1 and C. 100 grams fully cover the daily need for them. There are many vitamins B2 and PP, there is folic acid, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, iron and manganese. The calorie content of 100 g is very low - only 22 kcal, proteins - 2.1 g, fats - 1.1 g, and carbohydrates - 0.6 g.
Meadows contain marasmic acid and scorodonin - strong antibiotics that effectively suppress Staphylococcus aureus. In folk medicine, this property has long been noticed. Meadows were used for bronchitis, pneumonia and tuberculosis.
They also contain a substance that inhibits the reproduction of cancer cells.
Grasslands are beneficial for thyroid disorders. In Chinese medicine, they are used for seizures, thrombophlebitis, arthritis and radiculitis.
What does a dry non-drip look like?
The mushroom is shaped like an umbrella
The fruit body of the specimen in question consists of a small cap and a long stem. The pulp is very thin, has a slight odor and a bitter taste.
Description of the hat
Always grows in large groups
At the initial stage of ripening, the cap of the dry non-pot is bell-shaped or cushion-shaped; as it grows, it acquires an almost prostrate shape. In its central part, there may be a tubercle or a pronounced flat zone, less often - a small depression. The cap is small in size, it is only 0.5 to 3 cm. It is painted in bright red-brown or orange-brown shades, it fade in old mushrooms. In the central part of the cap, the saturated color lasts longer than along its edges. The surface is smooth, dry and matt with a pronounced radial groove.
On the inner side of the cap, there are rare, almost free, or adhered toothed plates. Painted in light cream or pale yellow tones. Spores are cylindrical or fusiform, smooth, sometimes slightly curved.
Leg description
Grows throughout the summer and in the first half of autumn
For such a small cap, the leg of a dry non-nylon is considered to be rather long, the height of which ranges from 2.5 to 7 cm. Its maximum thickness in diameter reaches about 1.5 mm. It is characterized as central, rigid, straight or slightly curved, even, without bulging. The surface is shiny, smooth to the touch. The upper part of the leg is colored white or light yellow, while the lower part is dominated by dark brown or black shades. At the base there is a white felt mycelium.
Let's go to rest together
If you are going to go to rest in these places for mushrooms or fishing or just sunbathe, then invite like-minded people to your company, it is more interesting to relax together.
All posted ads can be viewed in the Travel Book
Alekseevsky forest
A small group of friends | Going to a famous place looking for a company | There are places in the car | We are going to the woods for Alekseevka, today. To see what there is now from the mushrooms, we will stop by the Silver Spring. Join whoever wishes.
Other offers:
Monument to those killed in the Great Patriotic War
The building of the former zemstvo council
Mount Mayachnaya and the legend of the Maiden Mountains
Long-Range Aviation Museum
Ancient estates and manor parks of the Saratov region
Monument to the Soldier and the Wall of Memory
Museum of bast shoes and Chuvash courtyard
Monument to KS Petrov-Vodkin
The estate of the landowner P.S. Podyapolsky
Petrovsky Museum of Local Lore
Spring at the Holy Aleksievsky nunnery
Stolypin mineral waters
Sokursky suspension bridge-dam
Location Quarry Gorny
Peacock farm Petrovs
Monument to A.N. Tolstoy
Monument to the Victims of Political Repression
Volsky Museum of History
The estate of Count A.S. Yurievich
Monument to the "Dwarf" tractor
Tourist Saratov, 2018-2020. All rights reserved.
Spherical refractory: photo and description
| Name: | Spherical |
| Latin name: | Marasmius wynnei |
| Type of: | Edible |
| Synonyms: | Marasmius wynnei, Chamaeceras wynnei, Chamaeceras wynneae |
| Systematics: |
|
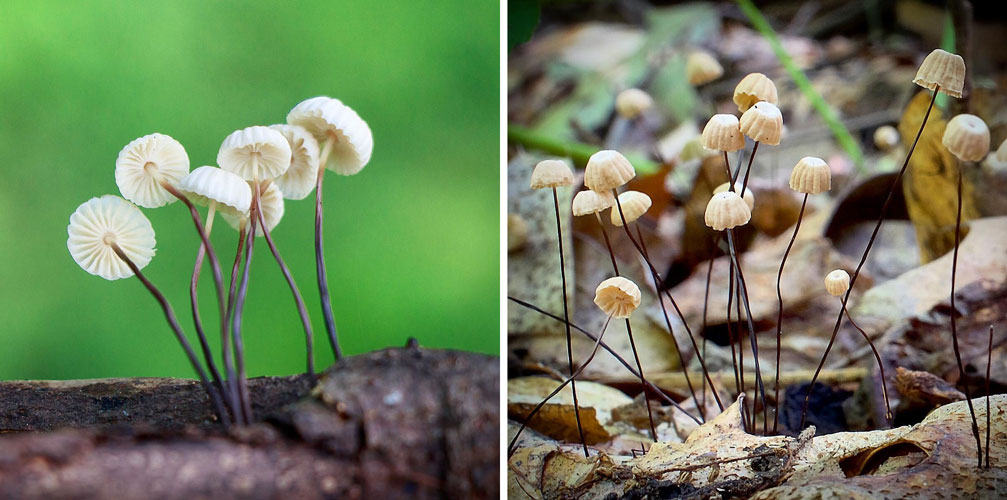
Spherical Negnium is an edible member of the Negnium family. The Latin name for this specimen is Marasmius wynnei.
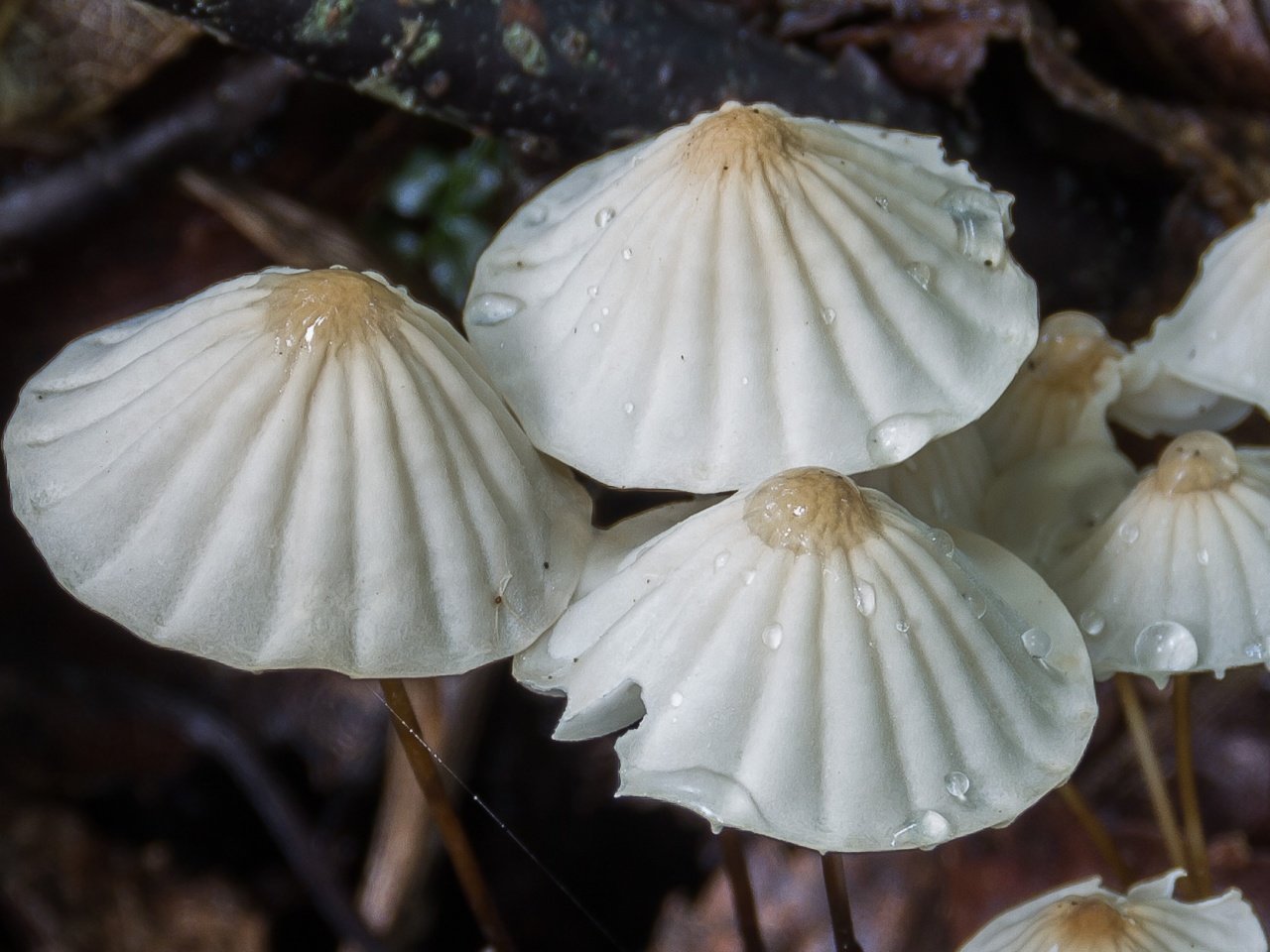
What does the spherical non-iron pot look like?
The fruiting body of the spherical nonnium is represented by a small white cap and a thin stem of a dark shade. The spores are ellipsoidal, smooth and colorless.
Description of the hat
In a young mushroom, the cap is convex, with age it becomes prostrate. It differs in a rather small size, which varies from 2 to 4 cm. The surface is smooth and white, with aging it can acquire a gray-purple hue. The edges are uneven, ribbed. On the inside, rare, white and pale gray plates are located high.
Leg description
The leg of the spherical non-nylon is rather short, its maximum length reaches about 4 cm, and the thickness is 2 - 2.5 mm. Slightly widened at the top. At the base, the color of the leg is brown, smoothly turning into light, matching the shade of the upper part.
Where and how it grows
The active development of this species falls on the period from July to October. The spherical iris prefers deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests. As a rule, it grows on deciduous litter, less often it grows on conifers.
Is the mushroom edible or not
Belongs to the category of edible mushrooms. It is believed that this specimen is suitable for use in food in any form, however, it is preferable to boil or salt it.
Doubles and their differences
The spherical iris has external similarities with the following varieties of forest gifts:
- Amanita muscaria that is poisonous. At a young age, it is difficult to confuse it, since at the stage of maturation, the cap is hidden by a veil, but with age it opens and acquires similar features with the species in question.One of the main differences from the globular nonnium is the rather large size of the fruiting body. So, the diameter of the cap of the fly agaric is more than twice and is about 10 cm. In addition, even an inexperienced mushroom picker will notice a cup-shaped volva near the base of the leg, which belongs to a poisonous mushroom.
- Common garlic - has a similarly shaped cap, however, a distinctive feature is the frequent arrangement of the plates, as well as a noticeable speck of a darker color located in the center of the cap. In addition, the double has a pronounced smell of garlic, for which it received the corresponding name. Edible.
Conclusion
It is possible to distinguish the globular nonnium from other mushrooms by its short brown stalk, rare plates and a white hat. You can meet him in almost any forest, as well as on lawns and in artisanal thickets. Having seen such a specimen, you should not pass by, since it belongs to the edible gifts of the forest.
Mr. Summer resident warns: a dangerous double
It is difficult to confuse a meadow with something, having seen it at least once. In some cases, such mistakes do not bode well, in others you can get to the hospital.
Most often, meadows are confused with wood-loving colibia, belonging to the same Negniychnikov family. They look similar, colibia is also called a spring or forest forest. The mistake is not dangerous: this mushroom is conditionally edible and edible after boiling. Its value is small: the hat is small, but there is no taste or smell.
It is easy to distinguish a meadow from a colibacillus. As can be seen from the picture, in the latter, the tubercle in the center of the cap is completely absent or weakly expressed. The plates in colibia are frequent, in old ones with reddish-rusty spots, and in honey agarics they are rare and even in color, regardless of age.
Another "twin" - a white talker (or otherwise whitish) can cause big trouble when used instead of meadows. Symptoms of poisoning appear after 30-40 minutes in the form of confusion, dizziness and sharp pain in the abdomen. Meadow mushrooms
Only completely inexperienced mushroom pickers can make a mistake, since talkers, often growing next to real mushrooms, have a white hat. In addition, the edge of the cap is even and tucked inward.
Among the talkers there are edible and conditionally edible ones, but there are also deadly poisonous ones. There are 250 species in total, which can only be distinguished by an experienced mushroom picker. In addition, even the most edible of them can lead to severe poisoning if consumed at the same time as alcohol. They contain substances that act like thiuram. Along with alcohol, weakness, sweating, palpitations, facial flushing occurs, in severe cases, can lead to fainting and even death.
Doubles and their differences
According to its external features, dry non-nipple plant is similar to the following gifts of the forest:
- Blood-headed firebrand. It is an inedible and rare species that has the ability to glow at night. You can recognize the double by a small domed red hat and a rather long stem of dark shades.
- Wheeled nonnichi - this specimen is very similar in shape and size to the described species in the shape and size of the fruiting body. However, the distinguishing feature is the color of the mushroom. So, the hat of the twin in young specimens is painted white, and in mature specimens it is grayish-yellow. Not edible.
- Smelly stinker. It belongs to the group of inedible and poisonous mushrooms. A double can be distinguished by a yellowish-brown cap and a black, shorter stem, the maximum length of which is 3 cm. In addition, this species grows on old hardwood.
Description
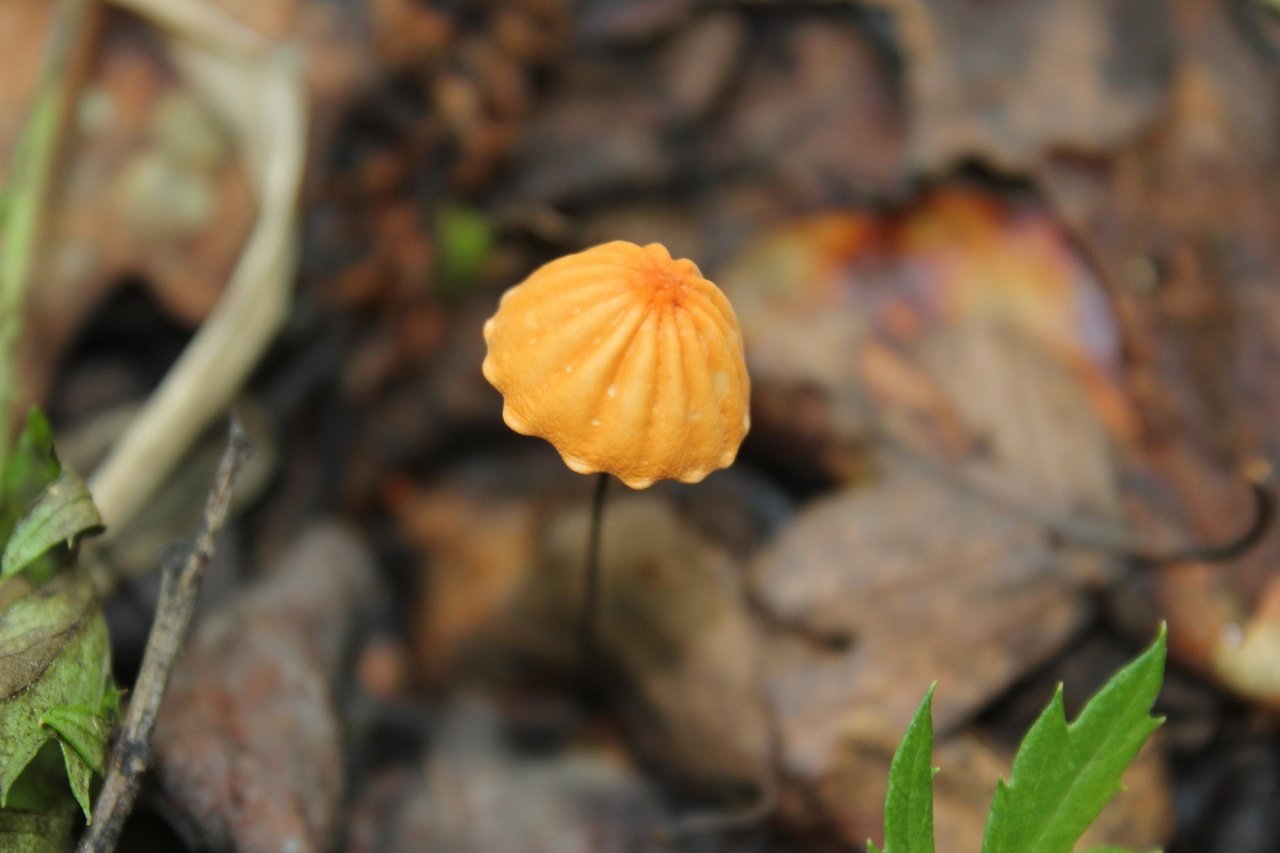
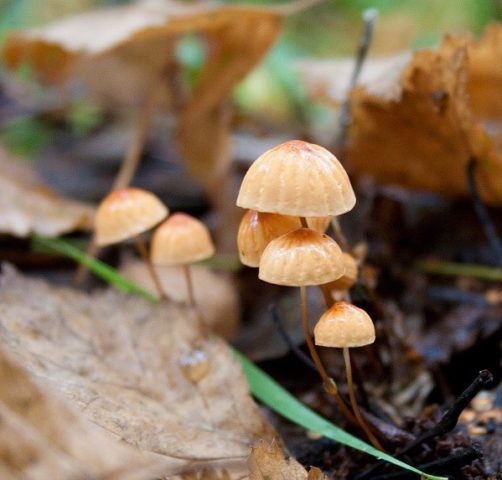
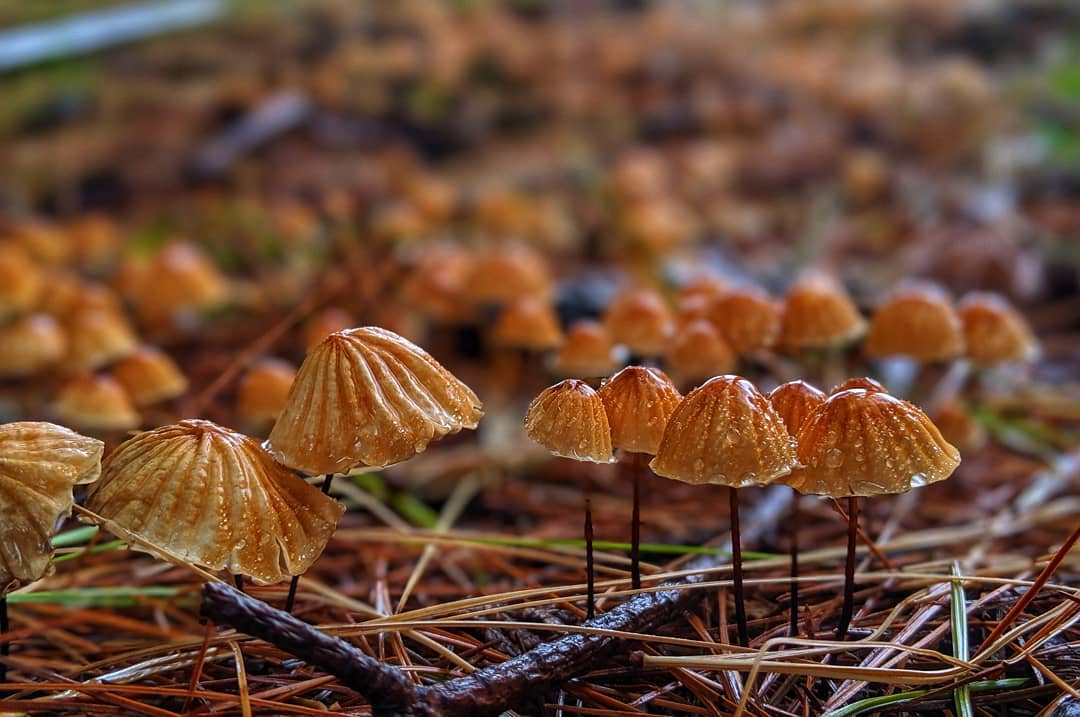
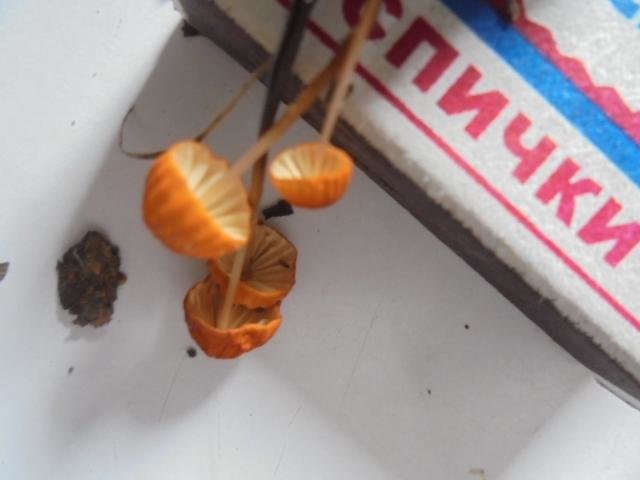
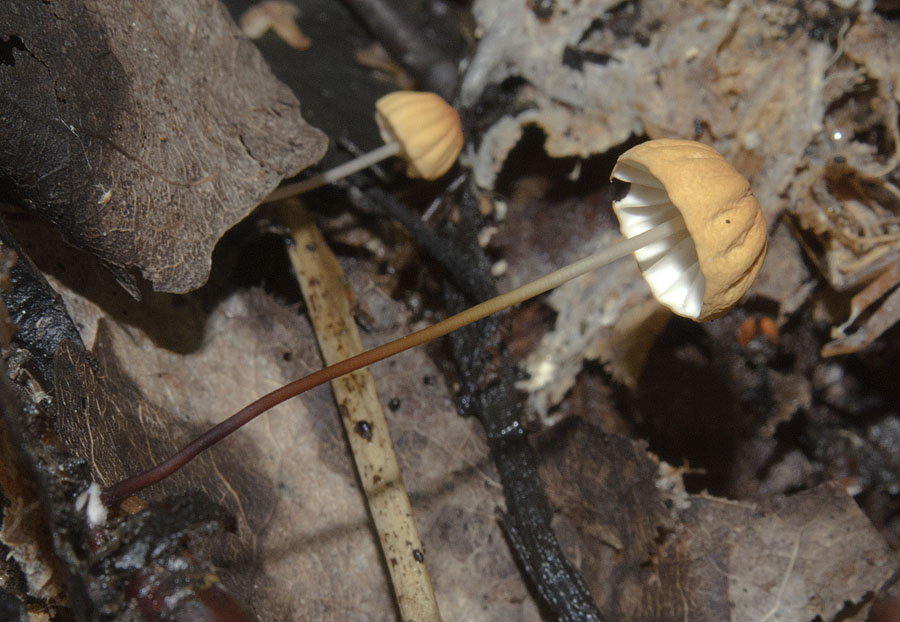
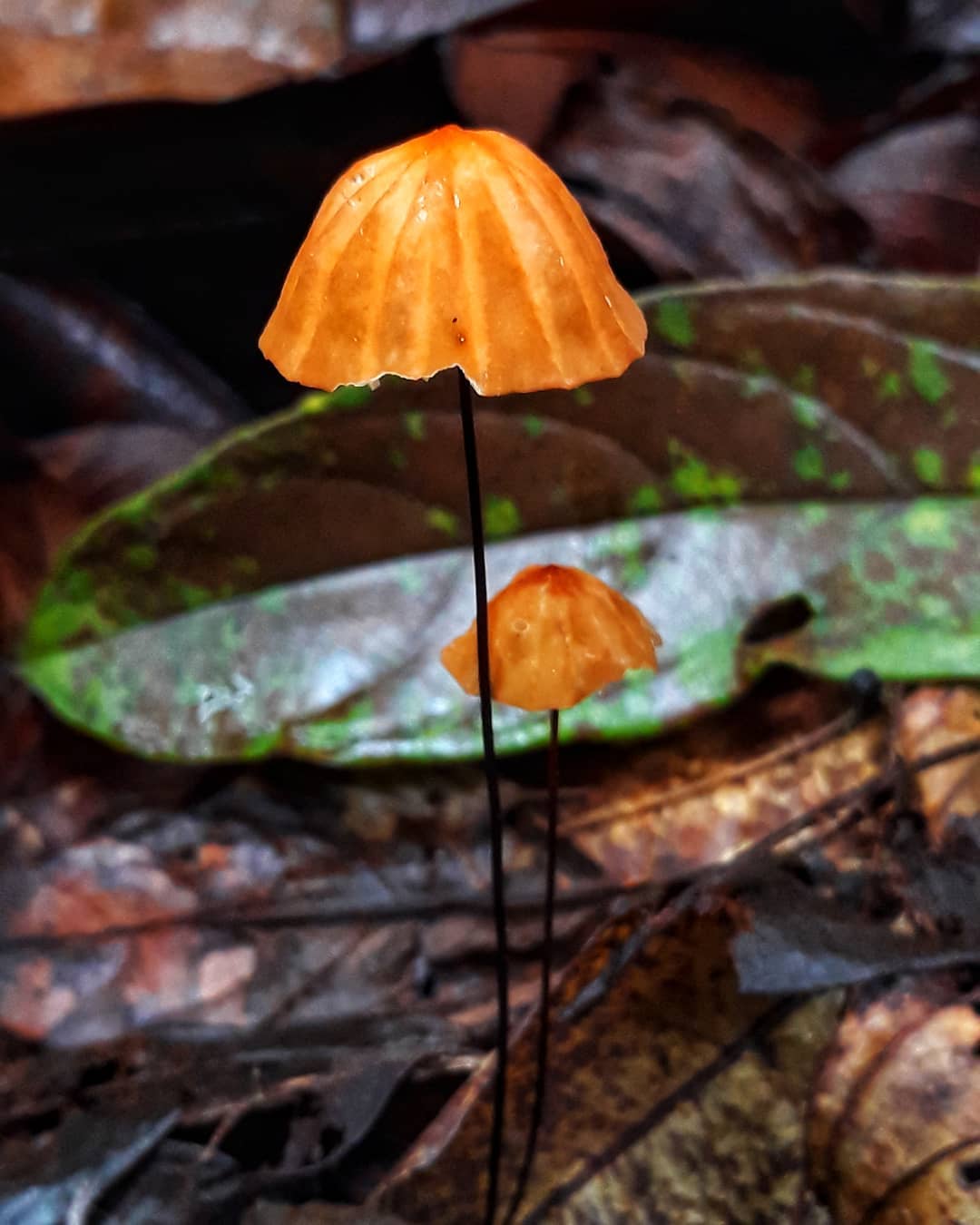
Dry Nebnichnik is a small, inedible mushroom with a matte folded surface with a long and thin, wire-like stem.
Hat
Reaches 3 cm in diameter. Its shape at first resembles a pillow or a bell, then it unfolds to open. The central part is practically flat, there can be a depression or, conversely, a tuberous outgrowth. The color is brownish, sometimes with a reddish tinge, with age it undergoes fading, starting at the edges. The surface is dry, even, radially grooved.
Leg
It has dimensions of about 7 * 0.1 cm, it looks like a wire, rigid, even. Its color, depending on the localization (lighter above, darker below), varies from white to almost black. The bottom is covered with white filaments.
Branchless nematode (branch marasmiellus): photo and description
| Name: | Sprigel nematodes |
| Latin name: | Marasmius ramealis |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Synonyms: | Marasmiellus branch |
| Specifications: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
Branching iris or branch marasmiellus, the Latin name is Marasmius ramealis. The mushroom belongs to the family of Negniychnikovye.
The lamellar non-iron pot consists of a central leg and a cap
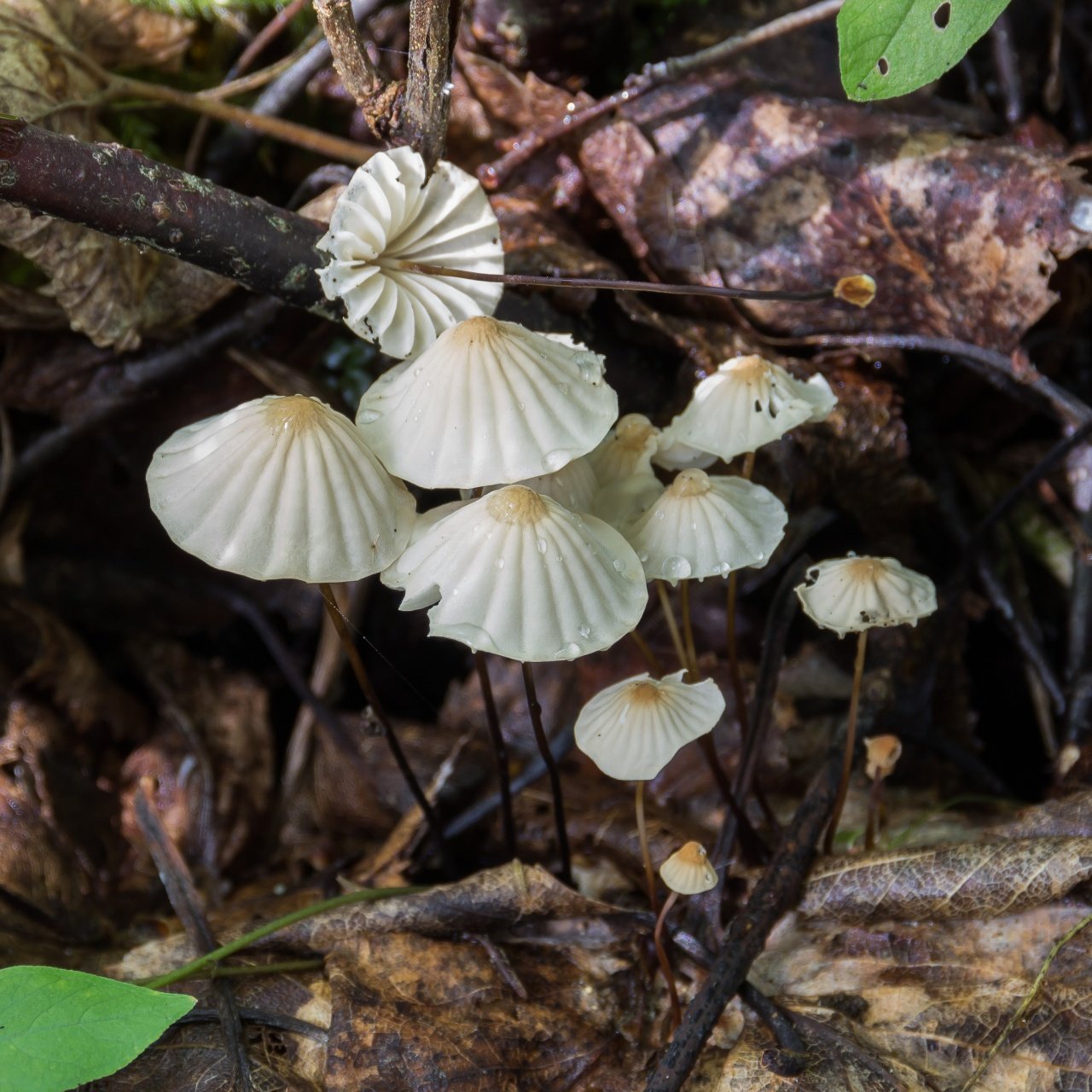
What does the branchless pottery look like?
Small fragile fruiting bodies with a uniform color and a darker fragment in the central part of the cap. The color is creamy with a pinkish tinge, does not change during the entire growing season.
In wet weather, the surface is slightly slimy
Description of the hat
The shape changes during the growing season, in young specimens it is rounded, convex, of the correct shape. Then a depression appears in the center, the cap becomes prostrate with concave wavy or even edges.
- diameter in mature specimens is within 1.5 cm;
- the surface is silky, glossy, with slight radial ribbing along the edge;
- spore-bearing layer of white with a pink tint;
- the plates are loose, thin, sparsely located, and do not change color when the spores mature.
The pulp is white, monochromatic, thin and fragile, the structure is springy.
Young mushrooms are all the same and proportional in shape
Leg description
The stem is cylindrical, thin, central. If the mushroom cluster is compact, it can be curved in the central part. In single specimens, it grows upright. The structure is fine-fibered brittle, the middle is hollow. The surface is colored the same as the upper part of the fruiting body, perhaps a tone darker near the mycelium.
The surface of the leg is covered with flocculent segments
Where and how it grows
The sprigel nematus is widespread in Russia throughout the European part, the Primorsky Territory, Siberia and the Caucasus. Saprophytes grow on decaying wood, mainly on branches, less often on stumps in a damp, shaded place. Long-term fruiting - from June to the onset of winter. Forms dense colonies occupying vast areas, single specimens are almost never found.
Is the mushroom edible or not
Due to its small size and fine structure of the fruiting body, it does not represent nutritional value.
There are no toxins in the chemical composition, but non-nematous sprig is a poorly studied species, therefore, use is undesirable.
Doubles and their differences
Outwardly, the oak garlic looks like a branch marasmiellus. The fruiting body is small in size, but the color is darker with a pale yellow tint and a brown fragment in the center of the cap. It grows on litter or wood debris, mainly under oak trees. The species is conditionally edible.
A mushroom with a pungent garlic smell, it is used as a seasoning
Conclusion
Twig nematozoa is a small mushroom that grows on fallen branches or decaying stumps. Due to the structure of the fruiting body and the insignificant size of the nutritional value, it does not represent a branchless inedible species. Fruiting in compact groups from the beginning of summer until the onset of frost.
Cooking methods and recipes
You can cook many different dishes from meadow mushrooms. After initial processing, boil them quickly.For 2 liters of water, add 1 tbsp. l. salt. After 20 minutes, add the onion, salt and spices, and cook for another 40 minutes, then drain in a colander. The mushrooms are now ready for further cooking. They can be fried, caviar, salted, pickled or frozen for the winter.
To prepare for pickling, boil in the same way as for freezing, the difference is that spices are added to fresh boiling water, and they should cook a little longer - 60-80 minutes. Frozen and dried mushrooms are boiled in salted water for 25 minutes.
Grassland soup tastes better than other mushrooms, including porcini, and the recipe is simple. Boil as usual, then add potatoes, carrots, onions, spices to the broth and cook until tender. Sprinkle the soup with fresh herbs.
Drying
Mushrooms are dried in a not too hot oven or electrical cabinet in the same way as any others. Dry mushrooms are very fragile and crumble into powder. If you knead them with your fingers during drying, they will dry out and do not crumble.
Meadow mushrooms are extremely useful and tasty, although they were assigned to the 4th group in terms of nutritional properties.
Negniichnik dry: photo and description
| Name: | Dry |
| Latin name: | Marasmius siccus |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Synonyms: | Agaricus siccus, Chamaeceras siccus |
| Systematics: |
|
Dry Negniychnikov is a member of the Negniychnikov family. The Latin name for this species is Marasmius siccus, which also has a number of synonyms: Chamaeceras siccus and Agaricus siccus.
Dry (Marasmius siccus)

Current title
| Index Fungorum | Marasmius siccus (Schwein.) Fr. | |
| MycoBank | Marasmius siccus (Schweinitz) Fries |
Systematic position
Etymology of the species epithet
Synonyms
- Agaricus siccus Schwein., Schriften der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft zu Leipzig 1:84 (1822)
- Chamaeceras siccus (Schwein.) Kuntze, Revisio generum plantarum 3: 457 (1898)
Habit
Fruit body: Cap and stem (agaricoid)
Hymenophore: Lamellar (including folded or with rudimentary plates)
Hat
The cap is 0.8 - 1.5 cm, radially ribbed-furrowed, bell-shaped, convex, almost spread, matte, orange-brown to red-brown.
The plates are almost free, rare, light, cream.
Leg
Leg 4 - 6 × 0.1 cm, shiny, rigid, like a string, black-brown, white-pubescent at the top, at the base with a rosette of long dirty walnut filaments of mycelium.
Microscopy
Spores 15 - 23.5 × (2.5) 3.0 - 4.5 (5.0) µm, narrow-clavate, clavate, fusiform, sometimes slightly curved.
Basidia 20 - 40 × 5.0 - 9.0 μm, clavate, 4-spore.
Ecology and distribution
Grows in groups on dried leaves, needles, small twigs.
Fruiting
The divisions correspond to the decades of the month.
Nutritional properties
Related materials
- Vasilyeva L.N. - L .: "Science", 1973. - 331 p. - P. 137
- Antonin V., Noordeloos N. E. A monograph of Marasmius, Collybia and related genera in Europe. Part 1: Marasmius, Setulipes and Marasmiellus. - Eching: IHW-VERLAG, (Libri botanici, Vol. 8), 1993 .-- 229 p. - P. 81.
Link to this page for prints
Ageev D.V., Bulonkova T.M. Dry Negnium (Marasmius siccus) - Mushrooms of Siberia URL: https://mycology.su/marasmius-siccus.html (date accessed: 26.01.2020).
Share link
Discussions

| 3066 | |
| Dmitry Ageev | |
| 2013-09-07T02: 26: 49 | |
| Last modified date: | 2018-11-15T10: 44: 31 (Dmitry Ageev) |
OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOO OOOì
Age restrictions
Federal Law of the Russian Federation of December 29, 2010 No. 436-FZ "On the Protection of Children from Information Harmful to Their Health and Development."
Control
2010–2019 All rights reserved.
Definitioner
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
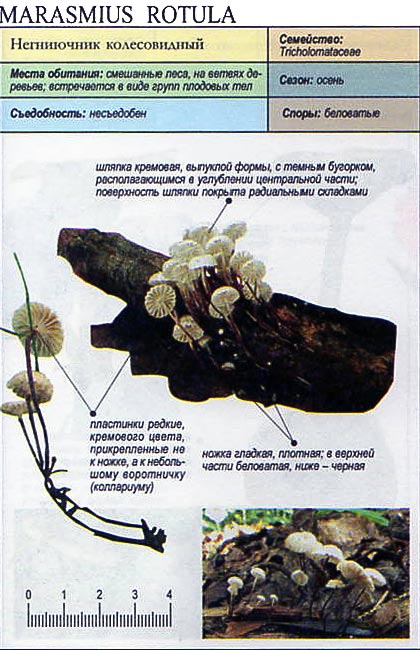
Wheeled Nebnichnik - description, poisonousness of the mushroom
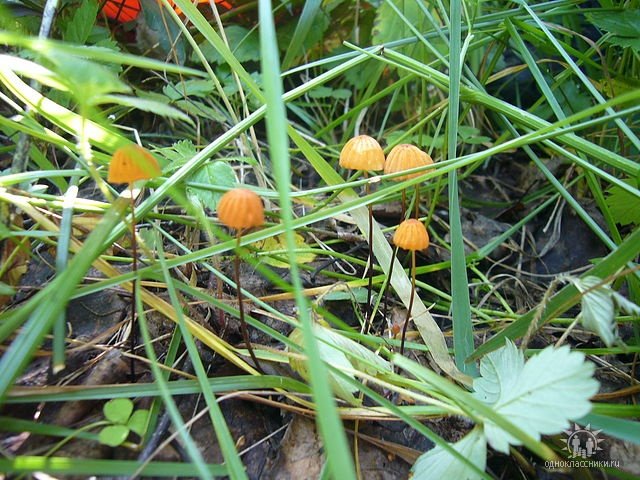
Wheeled non-fungus is an inedible species of mushrooms belonging to the non-fungus family. The Latin name for this species is Marasmius rotula.
Description
The cap of representatives of this type of mushroom is rather modest in size and reaches only 10 -15 mm in diameter. At the beginning of development, the shape of this part of the fungus is spherical, with growth it straightens and becomes more extended. In the central part of the cap, you can see a characteristic, albeit narrow, but rather deep depression. The surface of the cap itself has a fibrous structure, which makes it possible to clearly see all its details (tubercles, depressions). At the first glance at the mushroom, it may seem that the cap of the non-pot has absolutely no pulp, nevertheless, the latter is very thin and almost visually inseparable from the lamellar body. At the beginning of growth, the cap of the specimens is very light; with the growth of the fungus, it acquires a gray-yellow color. The aroma of the pulp, although weak, is quite sharp.
White plates are located with small gaps, most often grow to the characteristic collar bordering the mushroom leg. The spore powder has the same color as the lamellar body.
The Negnichnik has a rather thin leg, the length of which reaches 80 mm. This part of the mushroom is dark in color, almost black at the base.
Similarities with other species
Often this type of inedible mushroom is confused with Bullar's non-fungus, which has almost the same appearance (white color of the fruiting body, and a characteristic wheel-like shape). Nevertheless, the main difference between the wheel-like non-nipple is the presence of a pronounced collar located in the upper part of the leg, to which the plates descending from the lamellar body are attached.
Edibility
According to the available information, the wheel-shaped nonnium does not belong to the poisonous species of mushrooms, however, it is also not used in cooking, which is due to its very modest size.
Features of the view
The main feature of this type of mushroom is that during dry periods the non-fungi dry out almost completely, however, this does not mean their complete death. With the onset of the rainy season, the representatives of this species are completely restored to their previous form, and they begin to bear fruit and grow again.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that this type of mushroom, in fact, has no practical value. The only thing that scientists stand out is an enzyme like MroAPO contained in this mushroom, which is a kind of biosensor used for the analysis of aromatic substances.
Other non-burners
The Marasmius family of mushrooms includes about 500 different species, and only a small part of them are edible.The rest of the species, as a rule, are not collected, often the reason for this is the unattractive appearance of the mushrooms and their modest size.
Such a species as the most delicate non-pot is a modest-sized fungus that does not have any nutritional value. At the beginning of development, specimens of this species have a hemispherical cap, which straightens out with the growth of the fungus. In adult mushrooms, in the center of the cap there is a small tubercle of a characteristic dark brick color. The body of the cap is rather thin, the edge is wavy with rare radial folds. At the beginning of development, the cap is white; it darkens with the growth of mushrooms. The leg, like the cap, is of a deep brown color. The peak of fruiting of this type of non-nippers is from mid-summer to mid-autumn. Most often, these mushrooms are found in mixed forests.
Meadow honey fungus (Marasmius oreades)
Edible mushrooms
Meadow honeydew (lat.Marasmius oreades) - saprophytic, edible mushroom. Russian names: meadow nonnium, meadow marasmius, meadow, clove mushroom. Its flesh on the cut has a spicy clove aroma, and it was nicknamed the non-pot for its unique property of self-regeneration and the absence of decay processes. Meadow honeydew, like other species of the genus Marasmius, is able to withstand strong drying due to the high concentration of trehalose. After adding water to the dried mushrooms, they come to life again and can produce spores. Another interesting feature of the mushroom is its ability to emit a glow in the dark, as if it is saturated with phosphorus. Meadow mushrooms prefer to appear and bear fruit during the period from early May to late October before the first frost. Therefore, if the spring was warm and rainy, then the first crop can be harvested already at the beginning of June, in the summer, meeting mainly in open grassy areas - in meadows, pastures, pastures, in kitchen gardens, orchards, along the edges of fields, on the sides of roads, on edges or in forest glades, in ravines and ditches. Bears abundantly, often forming rows, arcs and "witch circles".
Meadow mushrooms are considered one of the most useful mushrooms, they are actively used in cooking and have excellent taste. The trehalose content imparts a sweetish flavor to the honeydew pulp. A versatile edible mushroom, also suitable for drying and soups. Suitable for all types of processing. Meadow honeydew contains marasmic acid, which is active against Staphylococcus aureus and other pathogenic bacteria.
Fruit bodies are very small, weighing about 1 gram. Hat 2-5 (8) cm in diameter, smooth; in young mushrooms it is hemispherical, later convex; in mature mushrooms it is flat-spread, with a blunt tubercle in the center. Old, dried specimens may become cupped. The edges of the cap are translucent, slightly ribbed, often uneven. The cap is hygrophane - sticky in wet weather, yellowish-brown or reddish-ocher under normal conditions, sometimes with a weakly noticeable zoning; when dry, the cap often takes on a lighter, off-white color. The center of the cap is always darker than its edges.
The flesh is thin, whitish or pale yellow, does not change color when cut, with a slight sweetish aftertaste and a strong peculiar smell, reminiscent of the smell of cloves or bitter almonds
Blades 3-6 mm wide, sparse, adherent in young fungi, later free, with clearly visible intermediate blades; ocher in damp weather, creamy whitish in dry weather. Spores - 7-8.5 x 4-5.5 microns, ovoid or ellipsoidal, smooth, colorless. Spore powder is white or creamy.
The stem is high and thin, 2-6 (10) cm long and 0.2-0.5 cm thick, sometimes slightly sinuous, cylindrical, slightly thickened at the base, solid, dense, in old mushrooms, stiff and fibrous, pale ocher, the same color with the cap or slightly lighter, fine velvety or mealy.
Meadow honeydew can be confused with the conditionally edible wood-loving collybia (Collybia dryophila (Bull.) P. Kumm.), Which occurs from May to December in deciduous and coniferous forests and is distinguished by more frequent whitish or ocher-cream plates, tubular-hollow stem and unpleasant odor.
It is more dangerous to confuse meadow honey with a poisonous whitewashed talker (Clitocybe dealbata (Sowerby) Gillet), which grows in approximately the same conditions, forming "witch circles", but differs in a whitish cap without a central tubercle, frequent creeping plates and a flour smell of pulp.
Meadow honey fungus can be cultivated in a summer cottage. For sowing mycelium, you should choose areas with a sufficient level of shade: near deciduous trees or bushes, in the beds. It is not necessary to loosen the soil and remove weeds. The mycelium is sown from September to the first days of December or from the end of February to May. One package of mycelium is enough for about 2.5-3 sq. m.
How to grow meadow mushrooms: Lay a layer of humus or compost on the garden bed at least 5-10 cm. Moisten. Sow mycelium. Additional insulation is not required. This mushroom tolerates a drop in temperature normally. The first crop will appear in 2-3 months. From 1 sq. m per month receive up to 6 kg of meadow mushrooms, and the planting itself bears fruit for 4-6 years.