Virulence
They absorb many toxins, heavy metal salts and copper isotopes. The first symptoms of poisoning appear at different times. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
Poisoning symptoms
Symptoms of poisoning appear 2-3 hours after eating the mutinus. First of all, weakness and indigestion are felt. Later, other symptoms appear:
- headache;
- lowering blood pressure;
- increased sweating;
- increased body temperature;
- cold extremities;
- inflammation of the stomach walls (pain in the stomach area).
If a large amount of a poisonous substance enters the body, the development of botulism is possible. Seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Such symptoms of poisoning do not appear every time. If a person has eaten a small portion of mushrooms, they may not be there at all. But toxins can accumulate in the body and cause a deterioration in well-being later. There is a risk of a rather large development of vein thrombosis in the body, anemia, as well as stroke, heart attack, and less often - pulmonary vein thrombosis.
Treatment for poisoning
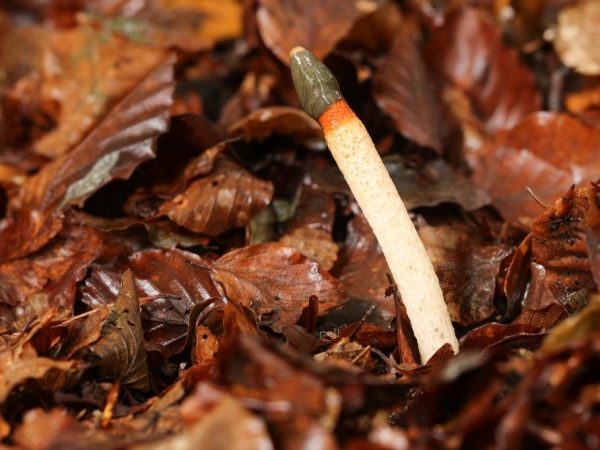

The fungus can cause severe poisoning
When the first signs of poisoning appear, they immediately call an ambulance. Before the arrival of the doctor, it is worth rinsing the stomach. First they drink a lot of water, and then they induce vomiting. This is necessary to remove pieces of the fungus from the stomach so that a probe can be inserted in a hospital. It is also useful to take a large portion of sorbents: 1 tablet of activated angle per 1 kg of body weight. To normalize the patient's condition, it is necessary:
- take a laxative if the victim does not have diarrhea;
- drink plenty of fluids to flush out toxins;
- regularly check the patient's temperature.
Attention! It is forbidden to give alcohol to the victim, because it accelerates the absorption of toxic substances into the blood
Also, do not eat anything, take painkillers or antipyretics. Do not benefit from vomiting and diarrhea remedies.
After hospitalization, the patient's stomach is washed again, but a saline laxative is injected through a special tube and intravenously. Also, the patient is detoxified, it can be hemodialysis or enema. The choice of method depends on how much dangerous substance the patient has eaten. In severe cases, a drip is placed and antibiotic treatment is started.
It is important to stick to your diet for faster recovery. It includes:
- refusal from spicy, salty, fatty and smoked foods;
- a ban on drinking and smoking;
- boiled and steamed food is introduced into the menu;
- all products are finely chopped and chopped.
Please note! Violation of the diet during the recovery period is unacceptable.
Mutinus Ravenel
This mushroom is NOT EATABLE!
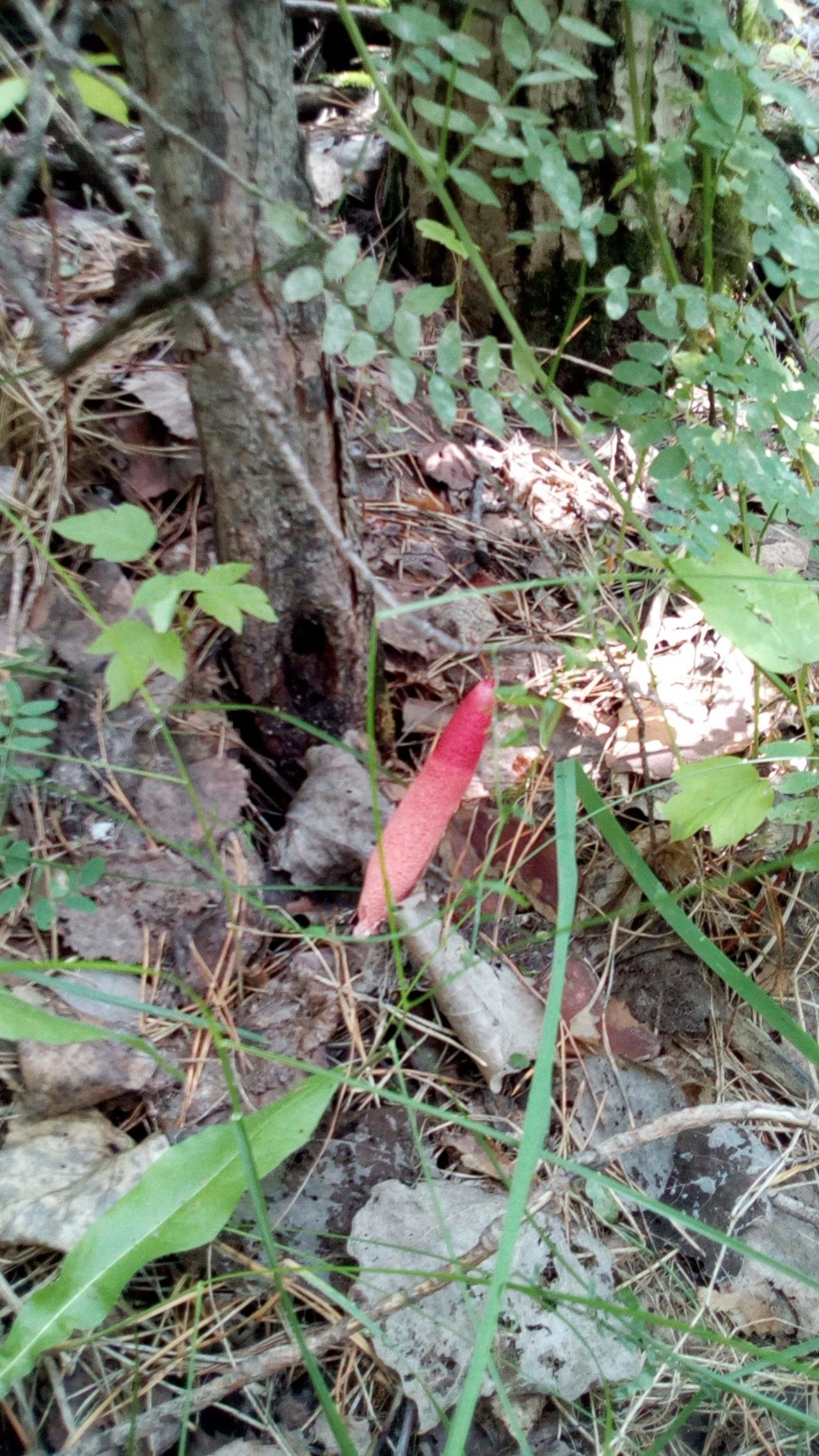
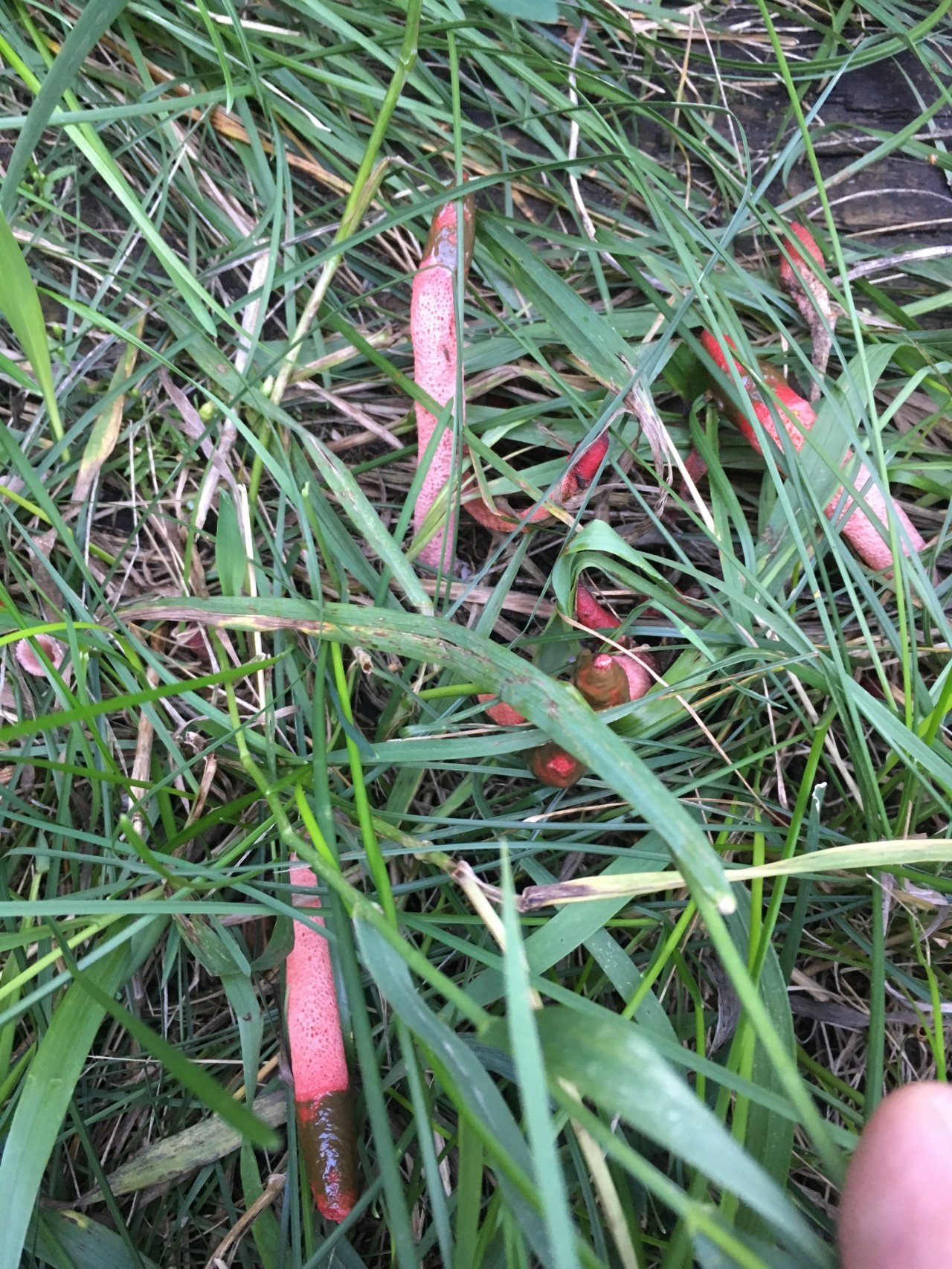
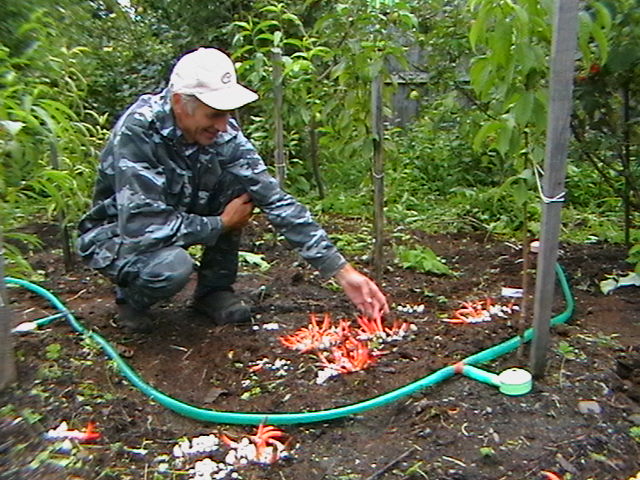
You can find this guest from America, once brought first to Europe, and then to our endless expanses, by the specific rotten smell with which this fun attracts flies. Suspecting that some mysterious creature suddenly died within the suburban area or somewhere nearby, the summer resident may find, instead of the mortal remains, a very entertaining mushroom colony.

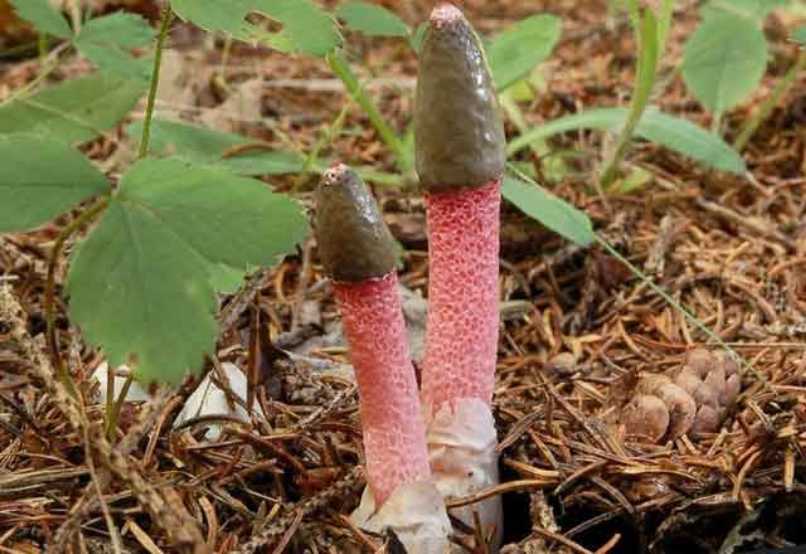
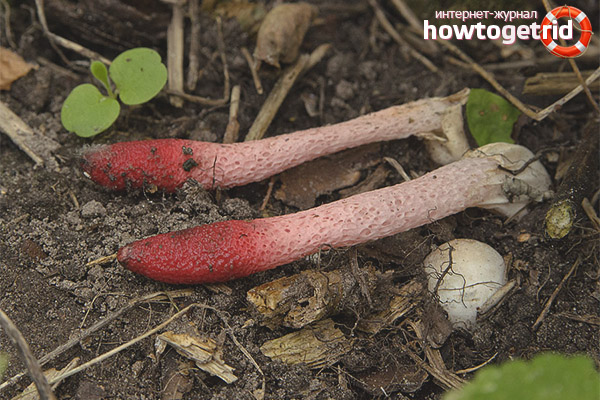
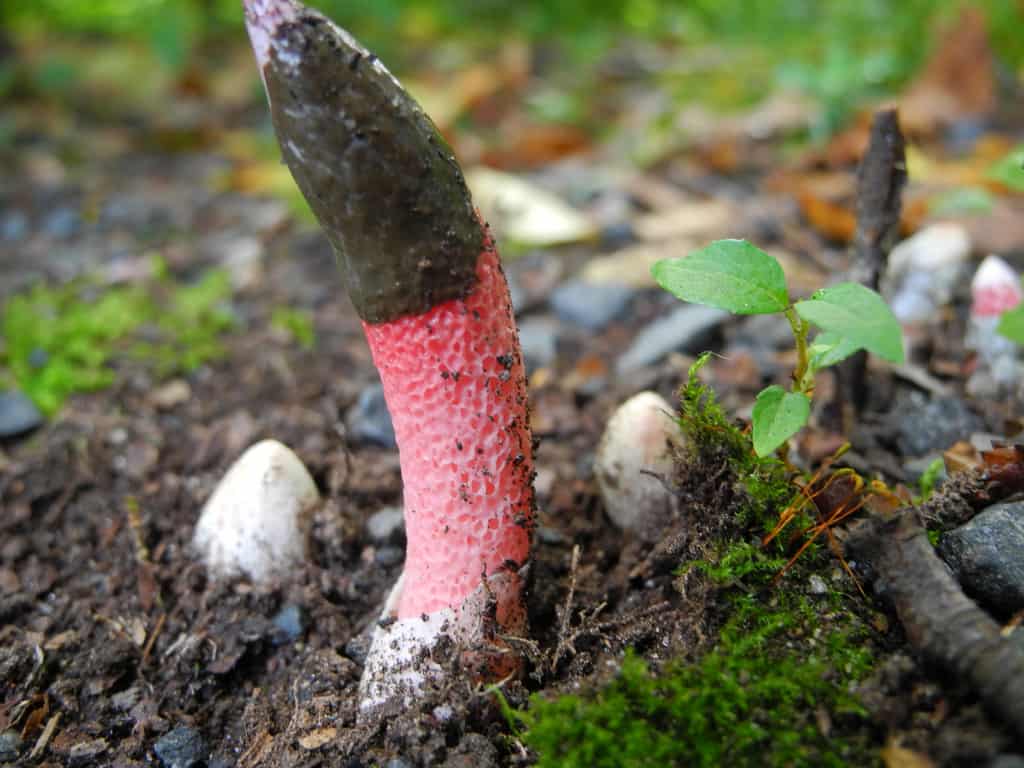
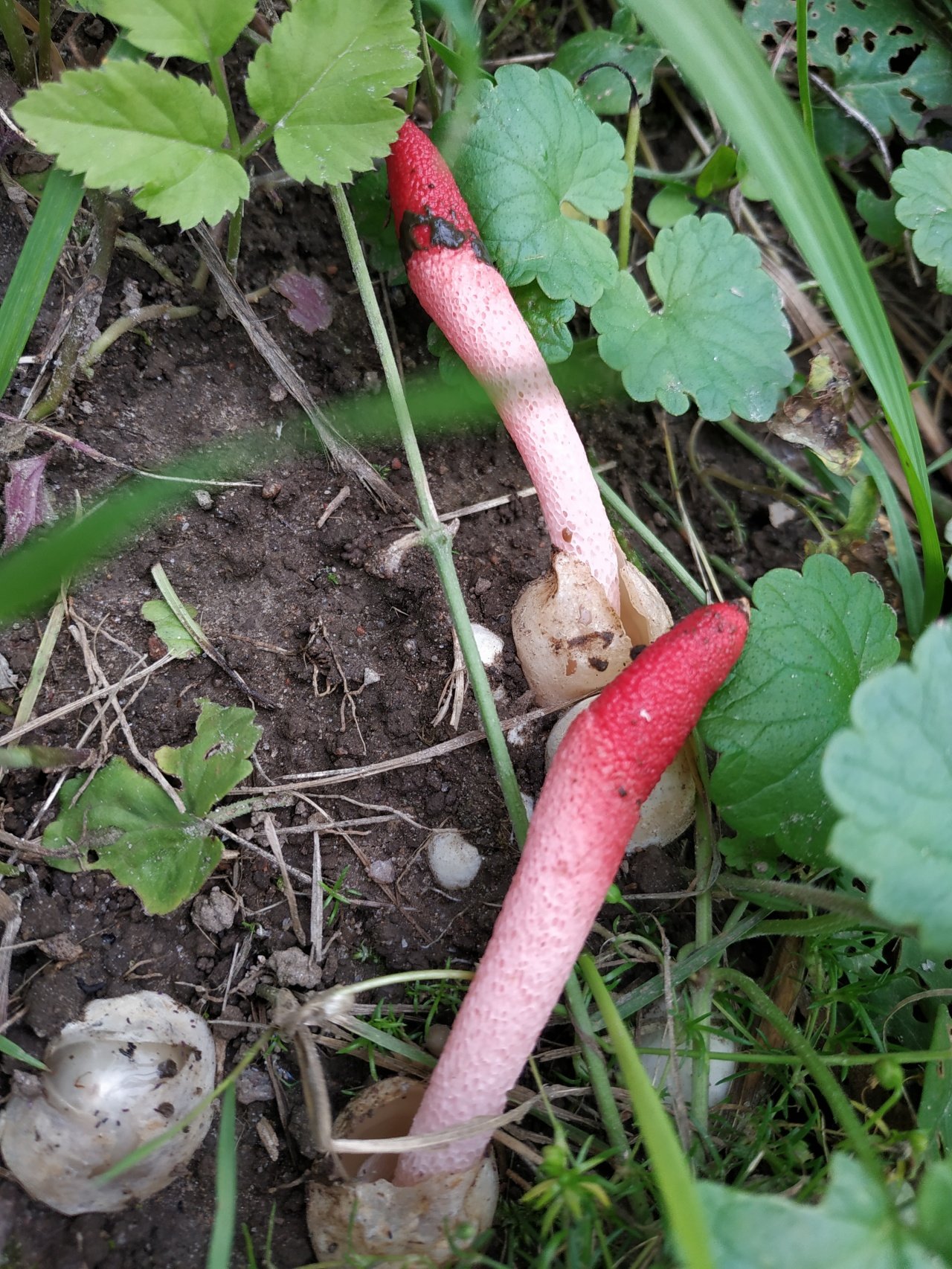
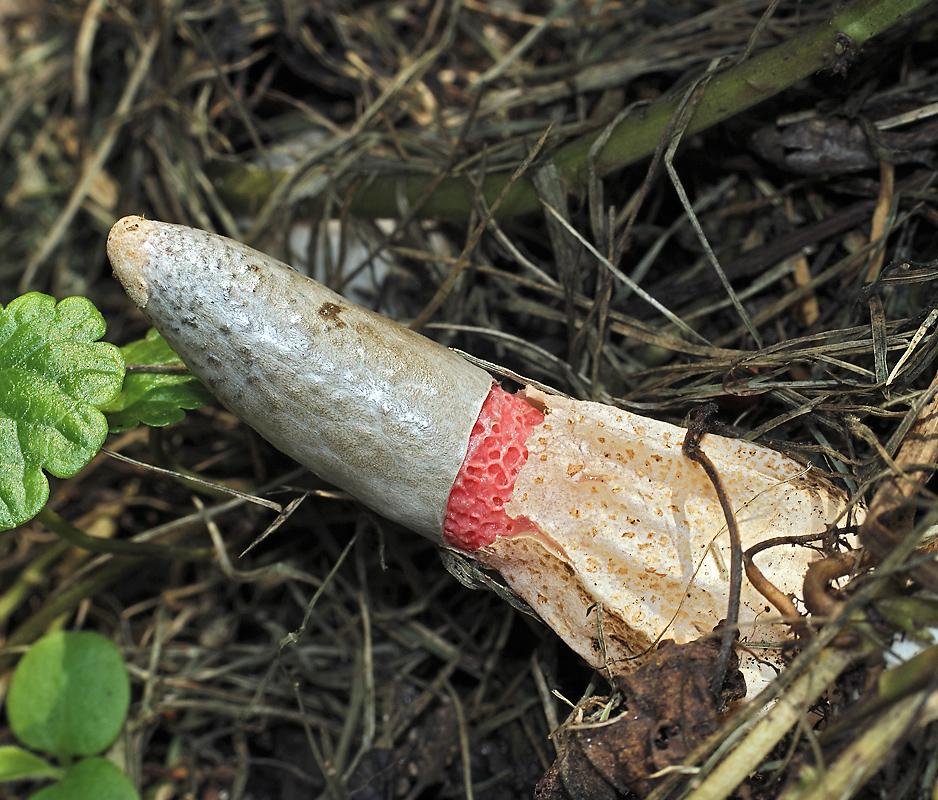
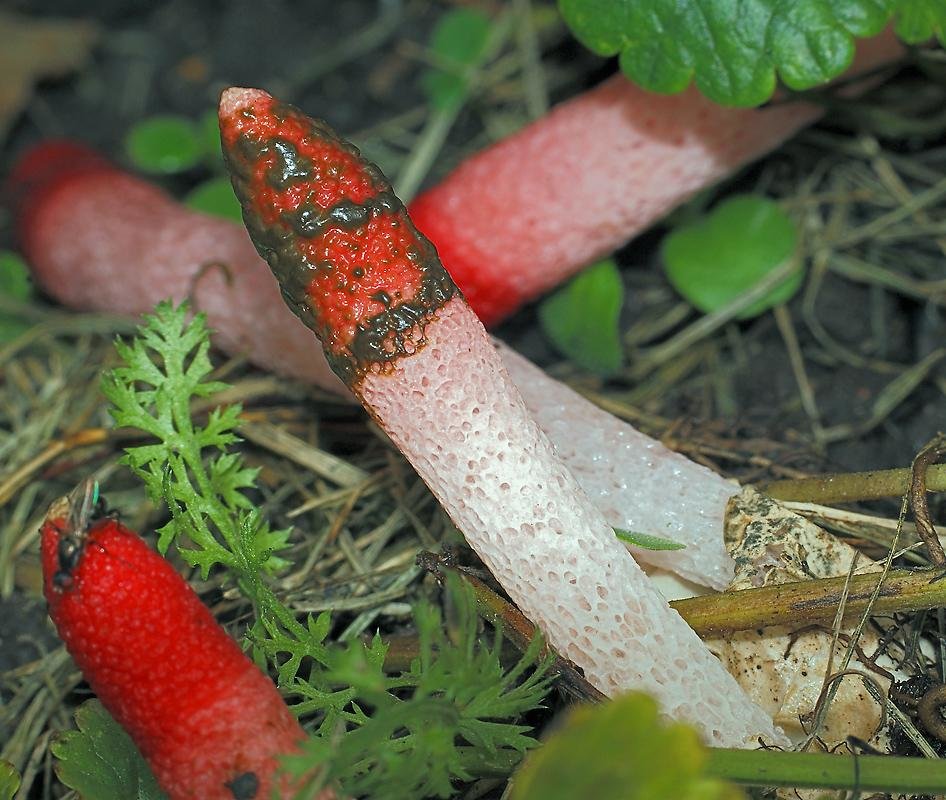
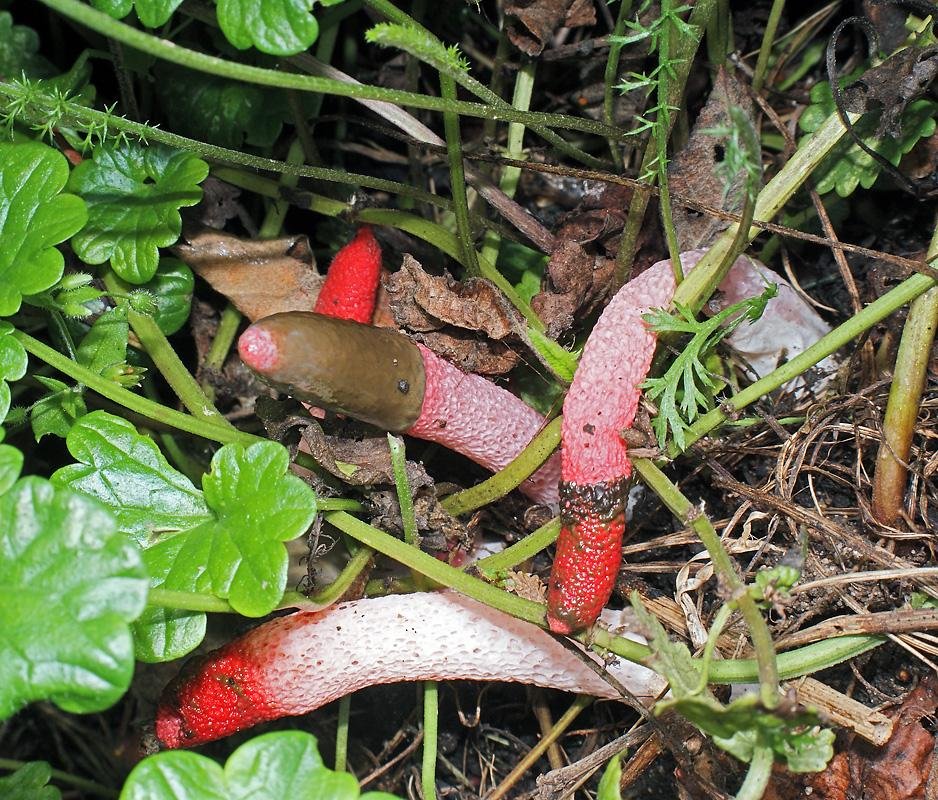
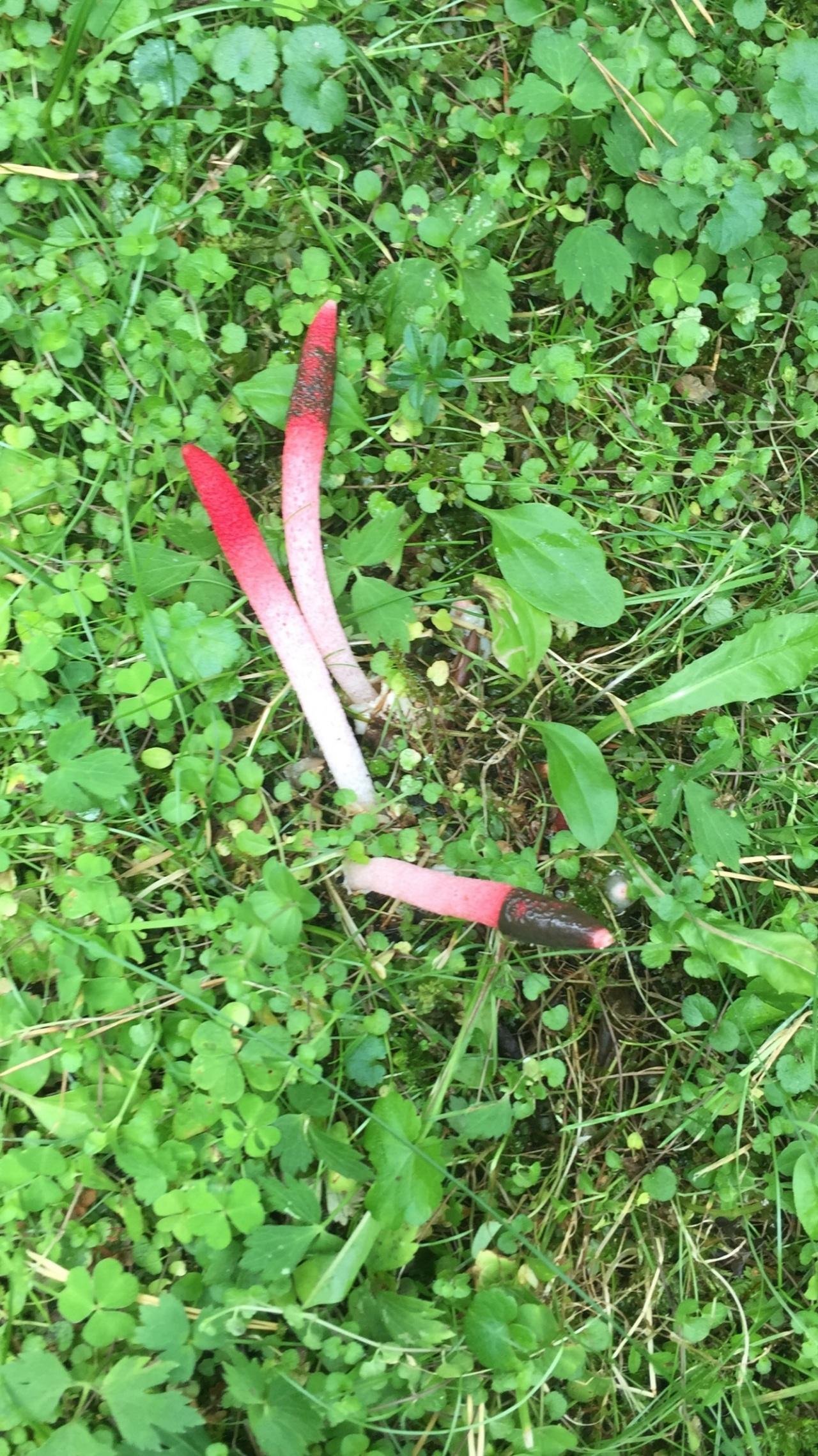
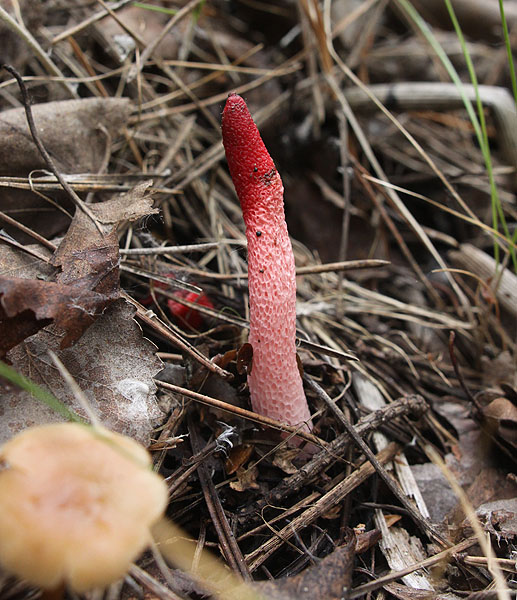
Pink-red tubular rods hatch from white eggs, on top of which a brownish-brown smelly mucus is wet. These are mushrooms called Ravenel's mutinus - Mutinus ravenelii. Domestic reference books awarded the same mushroom the name "smelly morel". The height of the tubular column is about 5-8 cm, in diameter it is 0.5-1 cm. According to my observations, on a clear day, the smell spreads to 3-4 meters, light gusts of breeze increase the spread of the smell by a few more meters. The scent is intense, overpowering the aromas of flowers and herbs.

The essence of the life of stinkers is both simple and peculiar. The brown mucus is devoured by flies, collecting for the smell in fair quantities.Together with the treat, they receive a portion of mushroom spores, which are carried around the neighborhood and germinate in any suitable places. Grass and leaf litter with sufficient moisture are suitable.
The mutinus is rarely found, which is probably due to the inattention of mankind to what stinks underfoot, and the difficulty of survival of the mutinus in our climate, which is not too favorable for it. However, the mutinus successfully settled practically throughout the entire territory of Russia, which is very successful for a small mushroom.

Mutinuses belong to the Veyolkovy family (Phallaceae), of which the most famous Veselka ordinary, which entered folklore due to its similarity with the anatomical feature of the male body. Mutinus Ravenel does not very much resemble the primary sexual characteristic, but it was his columnar shape that led me to the idea of where, in general, to look for information about what kind of dirty trick adorned my summer lawn.
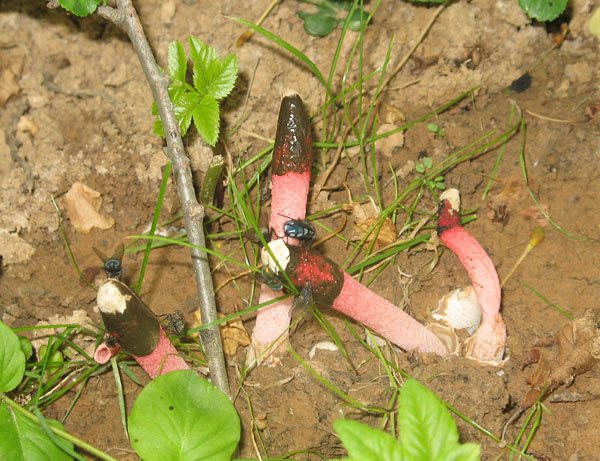

Wikipedia provides a bunch of Latin synonyms for mutinus - Corynites ravenelii, Ithyphallus ravenelii, Dictyophora ravenelii. Only the mention of Ravenel remains unchanged in them. The first attempt to find out who this Ravenel was, led me to another mushroom that bears the same name. The Ravenel's bullet gun (Pulveroboletus ravenelii) fascinated me with its name, and I even tried in vain to memorize it so that I could intelligently swear on occasion, comparing some opponent to a bullet gun.
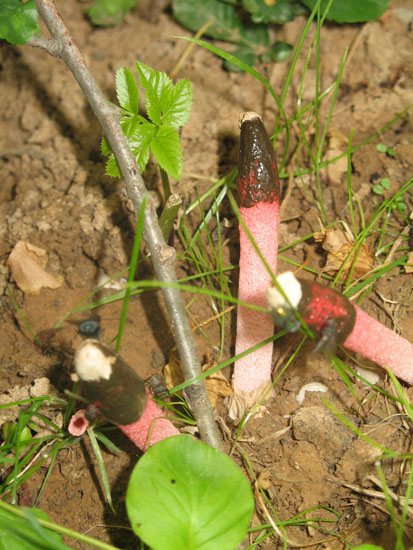

It turned out that the name of the American botanist and mycologist Henry William Ravenel (1814-1887) is well known in a narrow circle of mushroom lovers in the scientific sense. For twenty years of his life, Ravenel worked as a planter in South Carolina, and then devoted himself to scientific activities. Ravenel is one of the pioneers in compiling descriptions of American mushrooms and their classification in accordance with the ideas of the 19th century. In honor of him, not only the mutinus and the bullet gun are named, but also the whole genera of mushrooms - Ravenelia and Ravenelula. As they say, young people on the note - to perpetuate their name, it is not necessary to fly into space, sometimes it is enough to competently describe some stink.
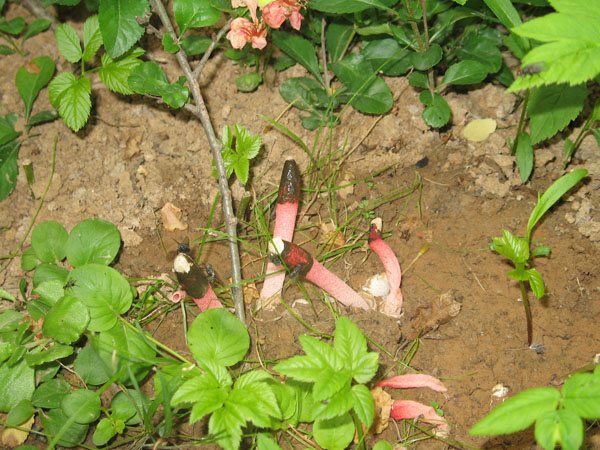

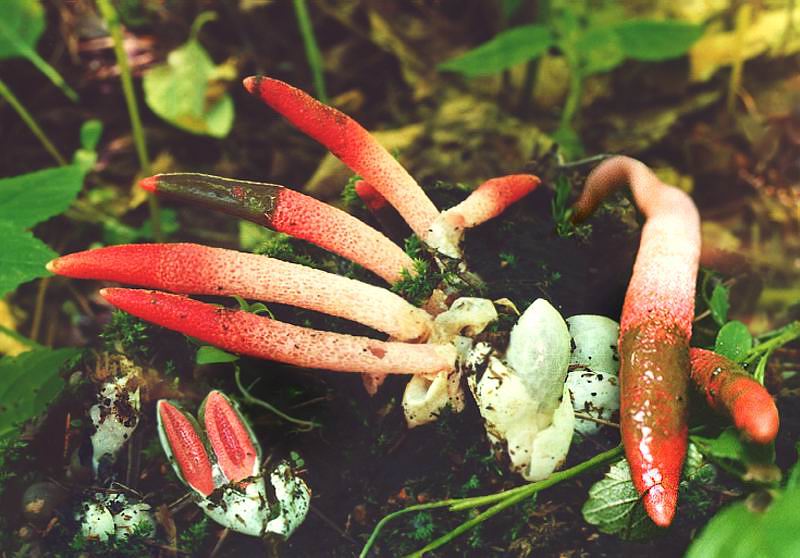
The mutinus Ravenel colony lived on my lawn for about 7 days. Every day in the morning, from one to three new mushrooms were discovered, by lunchtime flies flew to them from all the neighborhoods, in the afternoon the tubular bodies began to lean to the ground, and then fell. The last eggs of the mushroom plantation were flooded with torrential rains, and they did not grow. A couple of days later, a neighbor complained to me about a strange unpleasant smell, the source of which she could not find. Knowing what to look for, I saw a mysterious source through the fence, but did not enlighten my neighbor. Let the mutinuses continue their march through our dachas.
Text and photo - Lazy Summer Resident, 2015
Ravenel's mutinus mushroom - what is this species and why is it better not to pick it?

There are many types of mushrooms. Some are tasty, beautiful and noble, others are nondescript and bitter, or with a lot of milky juice, and still others emit eerie odors. And the mutinus of Ravenel, in addition to an unpleasant aroma, also has a very ambiguous appearance. At first glance, not everyone will take him for a mushroom.
Description of the mushroom
Mutinus Ravenelli (he is also called that) belongs to the genus Mutinus, the Veselkov family. The Swiss mycologist and botanist Eduard Fischer gave it the Latin name Mutinus ravenelii in 1888. It was then that the first specific description of this fungus appeared.
This type of mutinus has another name, which is more common among the people - smelly morel. The mushroom is listed in the Red Book of the RSFSR, Saratov and Novosibirsk regions, Altai Territory, in connection with which its protection and reproduction in botanical gardens and arboretums has been introduced. In general, the species is poorly studied.
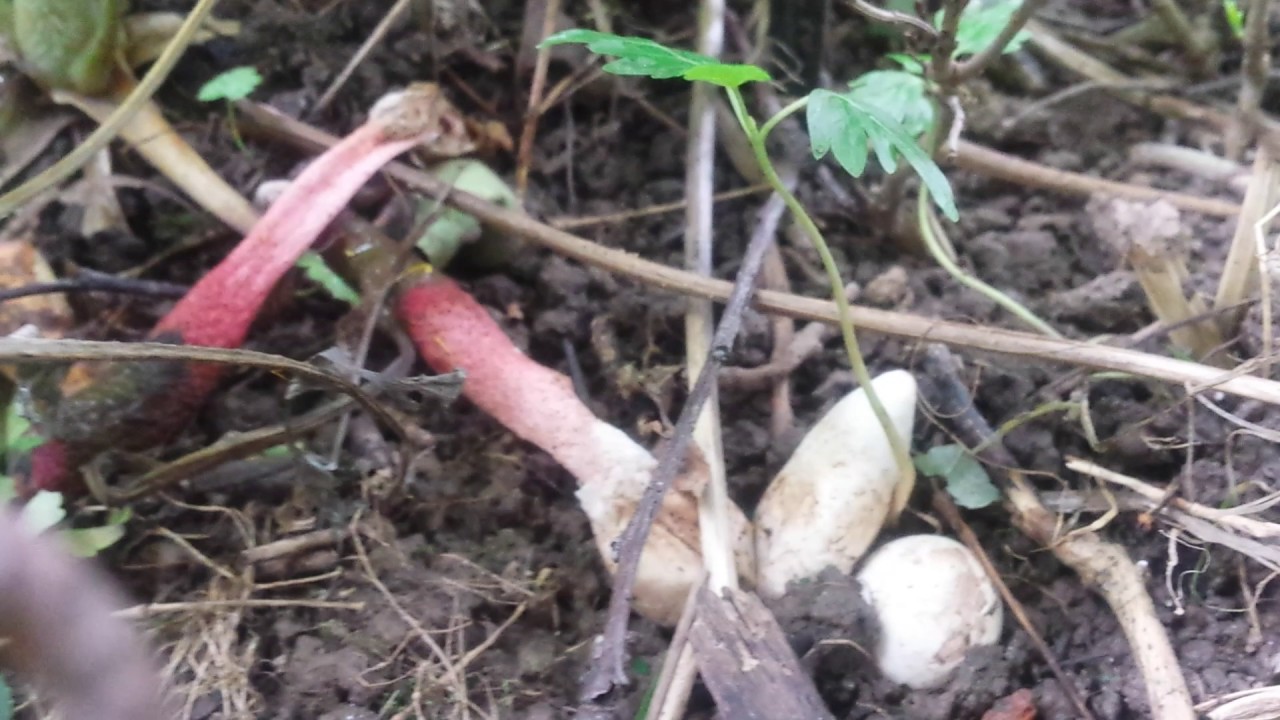
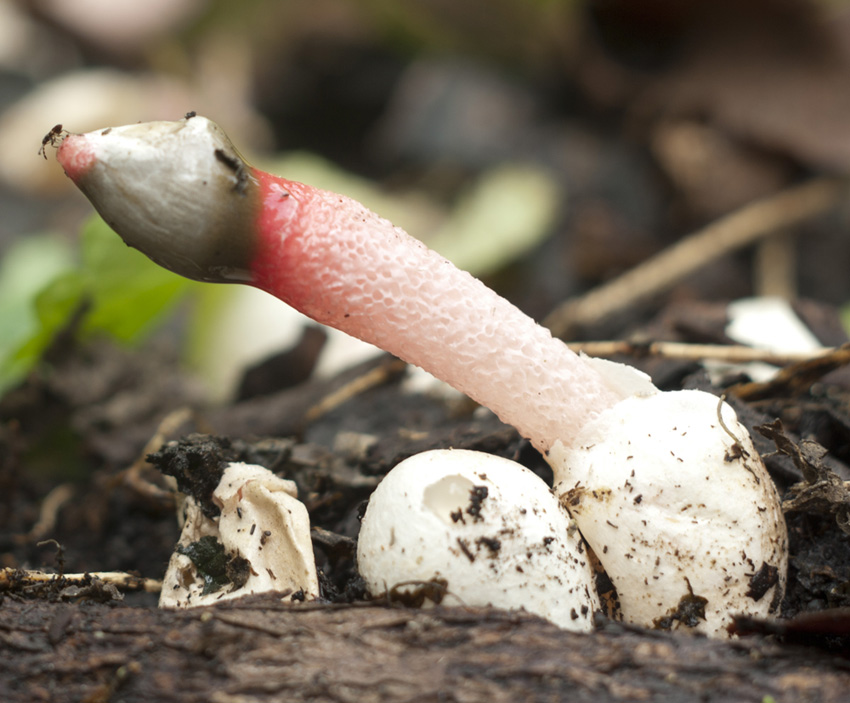
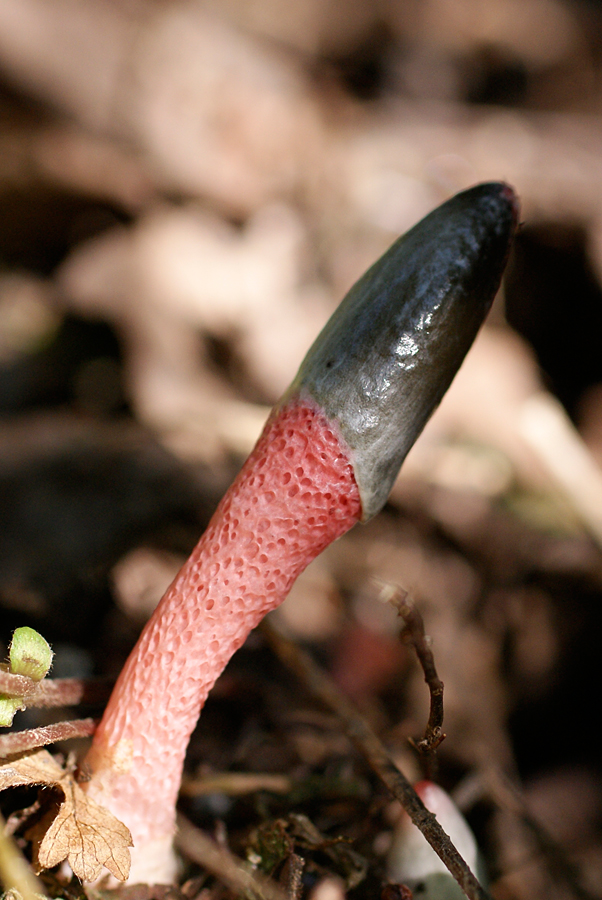
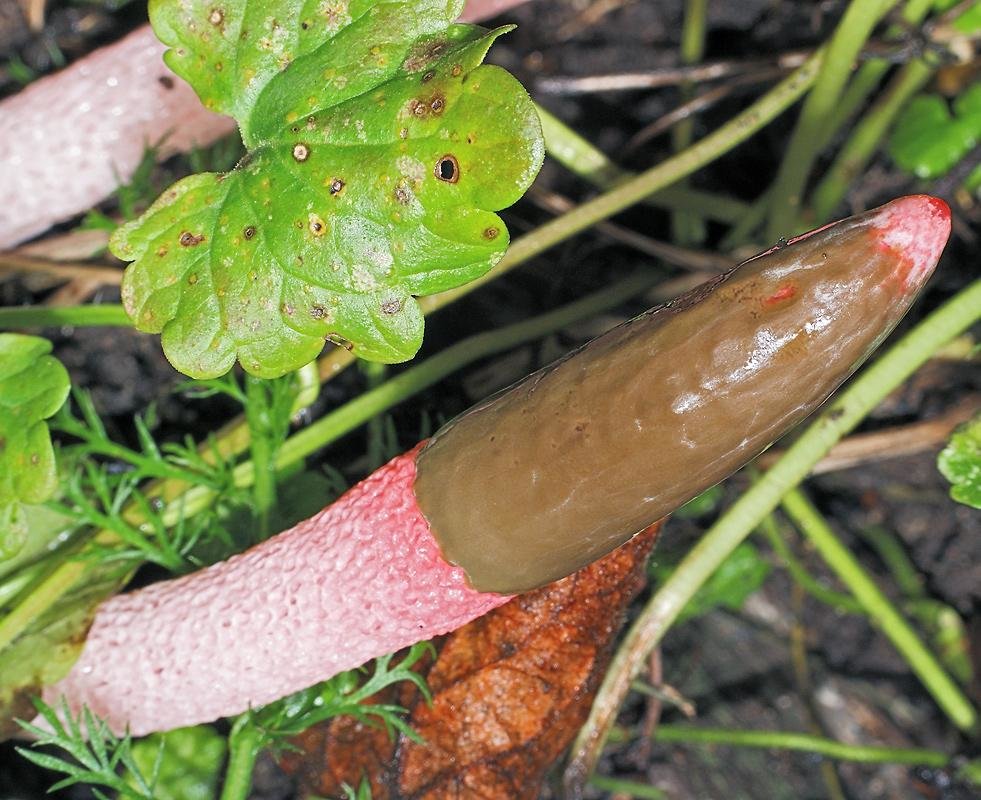
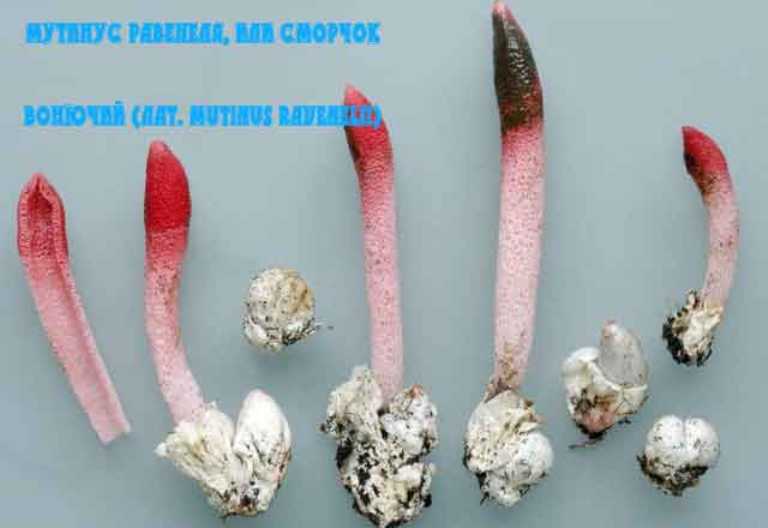
The cap of the mutinus is absent, respectively, and the hymenophore, i.e., its lower part.The body grows from a white ovoid formation, a fruit stem appears, which can stretch up to 8 cm with age.
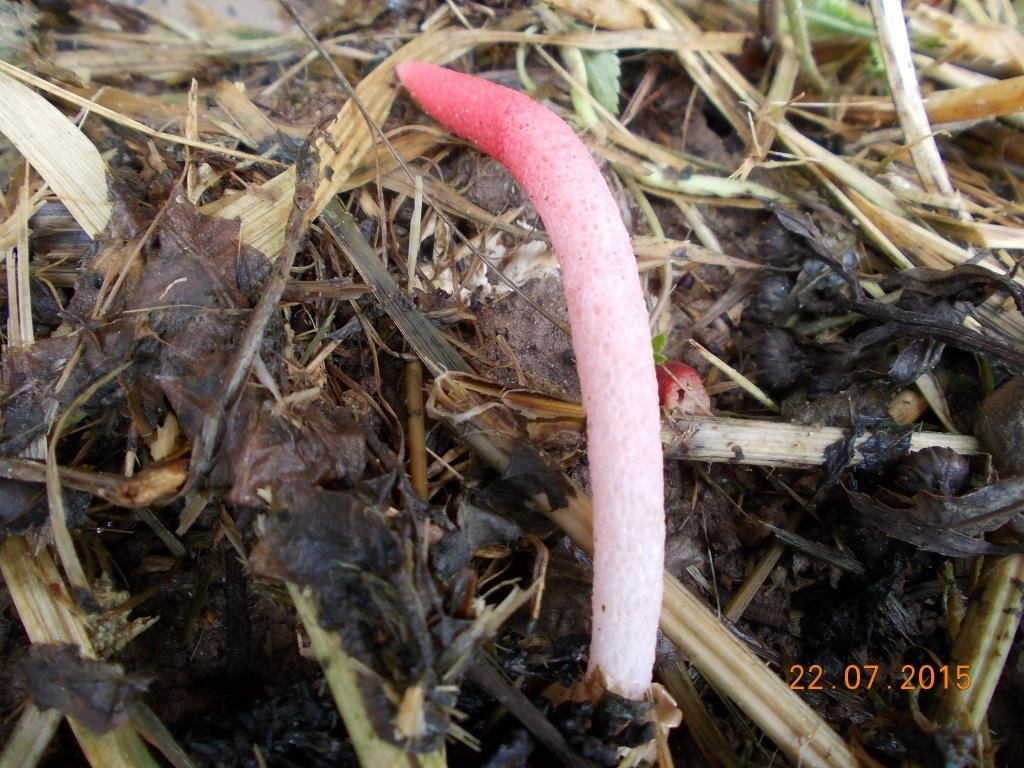
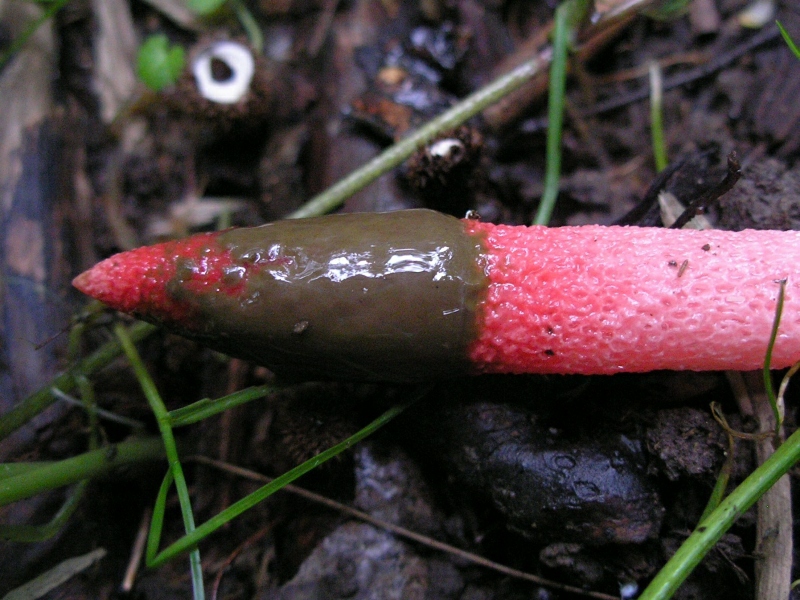
It is a leg tapering upwards, hollow inside. Its bottom is whitish, then turns red, as it grows, it becomes covered with controversial mucus, which is carried by flies attracted by the smell.
Difference from false doubles
Since morels stink very much, no one picks them for food, many do not even expect that this forest miracle can be called a mushroom. The use of smelly morel was most often practiced by traditional healers or in alternative medicine. They treated with it:
- all stages of cancer;
- ulcers that did not heal for a long time;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- kidneys and liver;
- various joint diseases;
- gout.
Morel smelly contains phytoncides that can kill the herpes virus, hepatitis and flu.
Important! Treatment with any types of mushrooms should be carried out only in consultation with specialists!
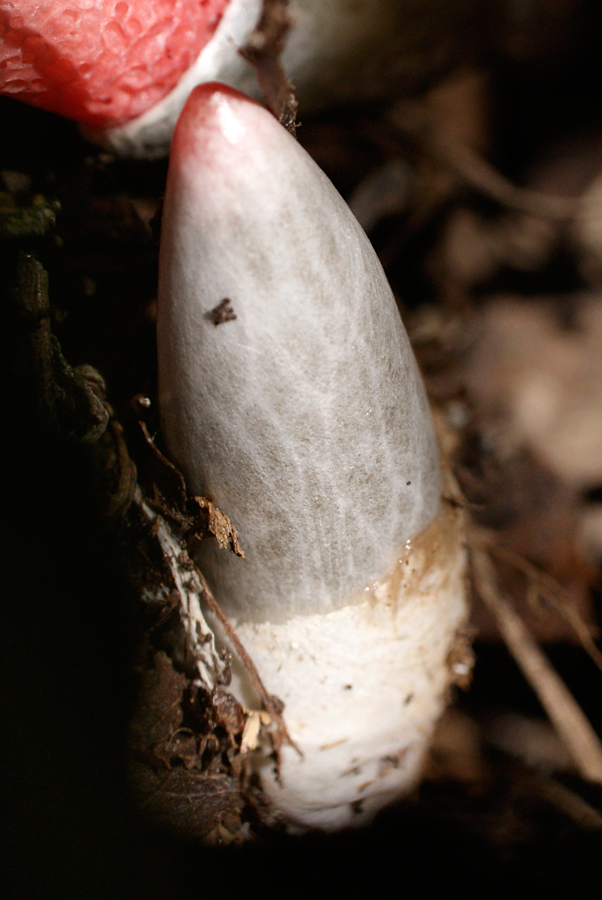
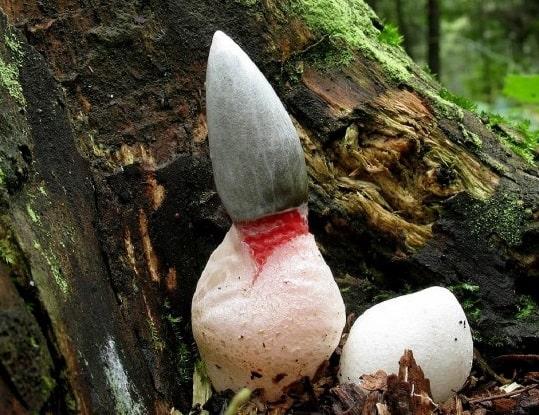
There is a danger of confusing the mutinus in the state of the egg with the pale toadstool, it is during this period that these two completely different mushrooms are very similar.
Find out how similar species may differ:
| Name | Fruit body at a young age | Cutaway | Virulence |
| Mutinus Ravenel | White, skinned | Under the skin of the egg is the red body of the fungus, in the upper part there is a small layer of spore-bearing mucus | Inedible, dangerous |
| Death cap | White, covered with foil | White, with a pronounced forming cap | Highly poisonous, deadly |
| Anturus Archera | White with gray, pink or brown tint | Under the layer of the egg surface, a red or orange body, in the center a greenish spore-bearing mass | Inedible |
Importantly, none of these mushrooms are edible, and carelessness can be fatal.
Evaluation of taste
There is practically no pulp from the Ravenel mutin, the leg is hollow inside. Considering that this mushroom can be considered a plant "scavenger", hardly anyone will have a desire to try it, and the number of flies nearby will scare off even the most daring discoverer from using it.
Interesting! It is believed that in the egg stage the mushroom is edible, but for this you need to be very well versed in the varieties, since a pale grebe can appear from such a whitish cocoon, and this is already a deadly poisonous species.
Interesting Facts
In the 20th century, biochemists made a sensational discovery - the healing properties of the Veselkovs can be equated with those of the Japanese medicinal shiitake mushroom.
The smell of Ravenel's mutin is exuded by spores (not the mushroom itself), which appear in the form of mucus on the tip of the leg. It is believed that it does not form mycorrhiza with trees, but in dry summers it is able to give them the moisture accumulated in the body in reserve.
This unusual mushroom arouses genuine interest, attracts attention with its unusual appearance and repels it with an eerie stinking smell. Also, do not use the Ravenel mutinus due to its small number, in addition, this representative of the mushroom kingdom is listed in the Red Data Books of Russian regions.
Also, you should not use the Ravenel mutinus due to its small number, in addition, this representative of the mushroom kingdom is listed in the Red Data Books of the regions of Russia.
Description of the Ravenel mutin
Mutins Ravenelli belongs to the genus Mutinus. He is a representative of the Veselkovye family. It was first described by the researcher, botanist and mycologist Eduard Fischer. It was at that time, in 1888, that the fruit received its Latin name, Mutinus ravenelli. But not everyone uses the official name of this specimen. The people called it easier - morel or smelly veselka.
Features of the species Mutinus ravenelii
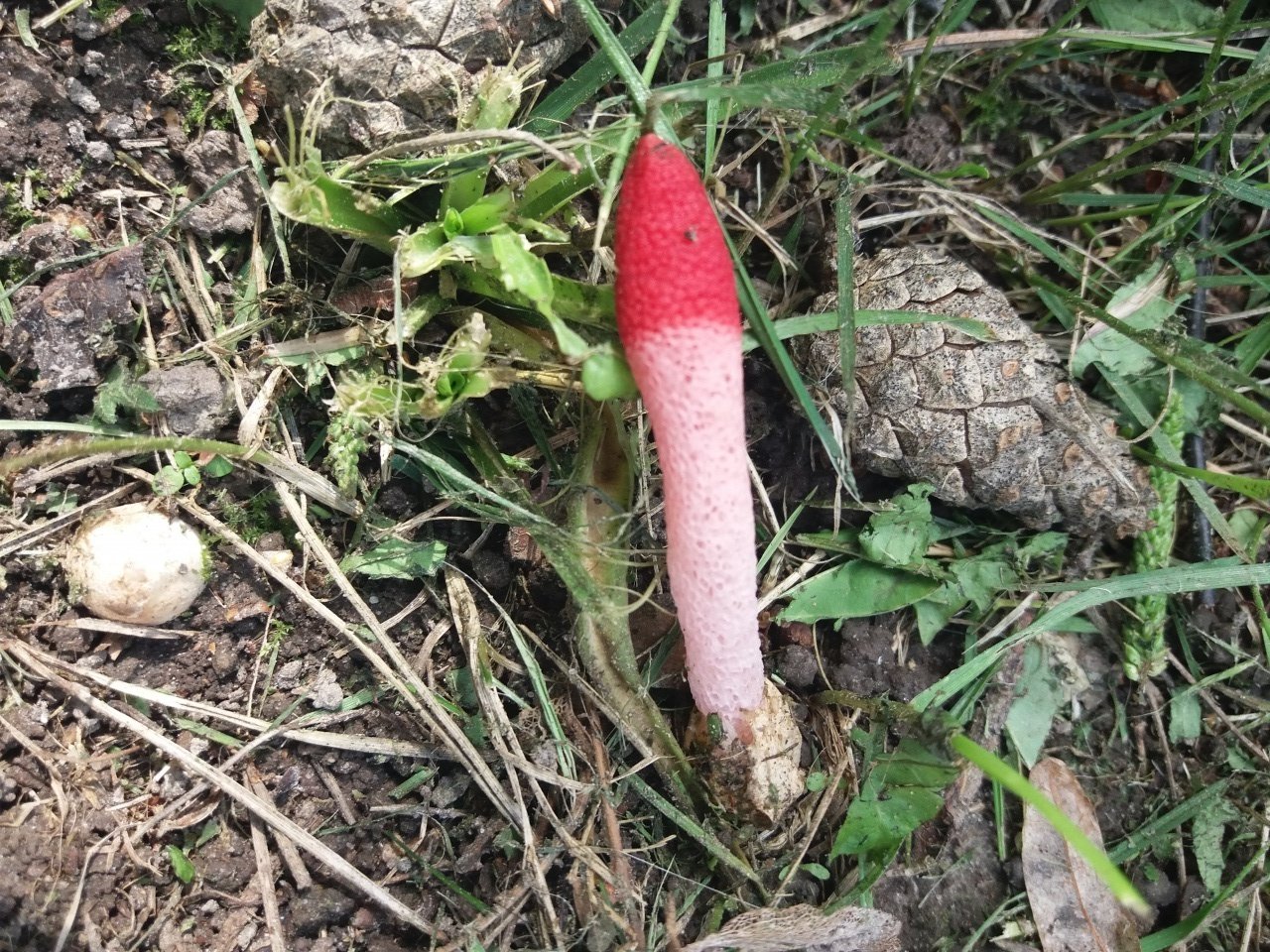
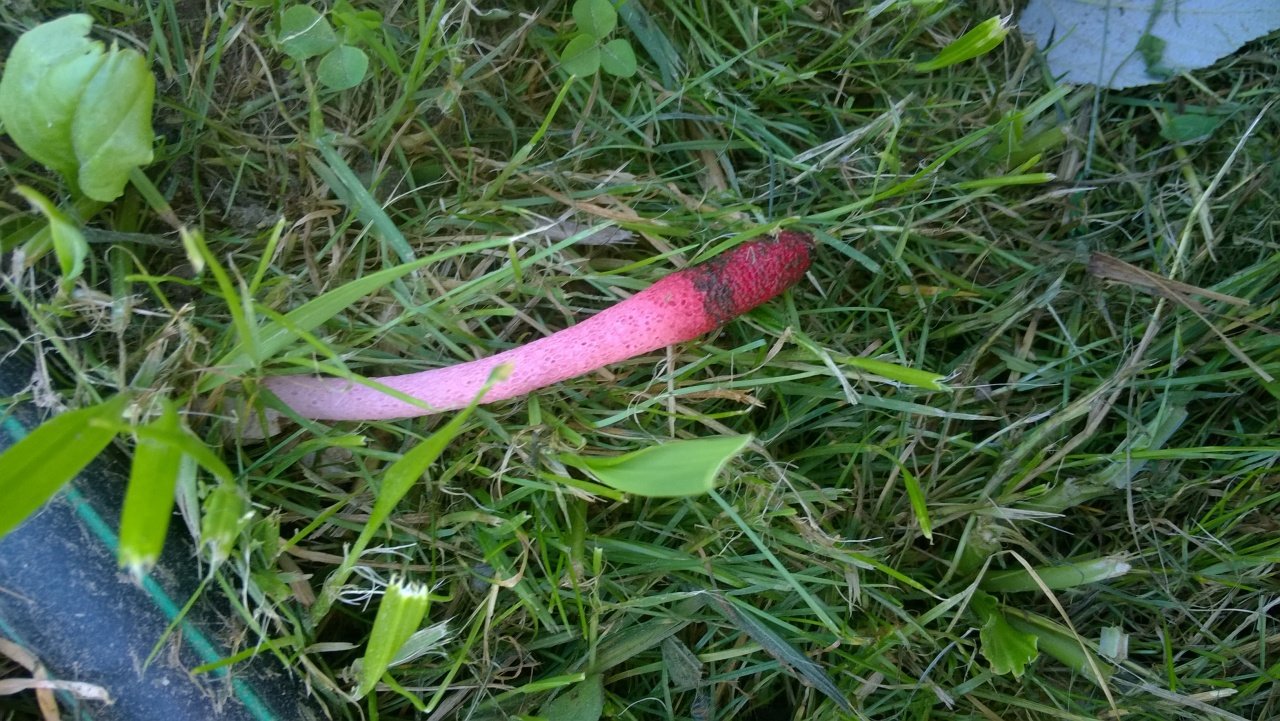
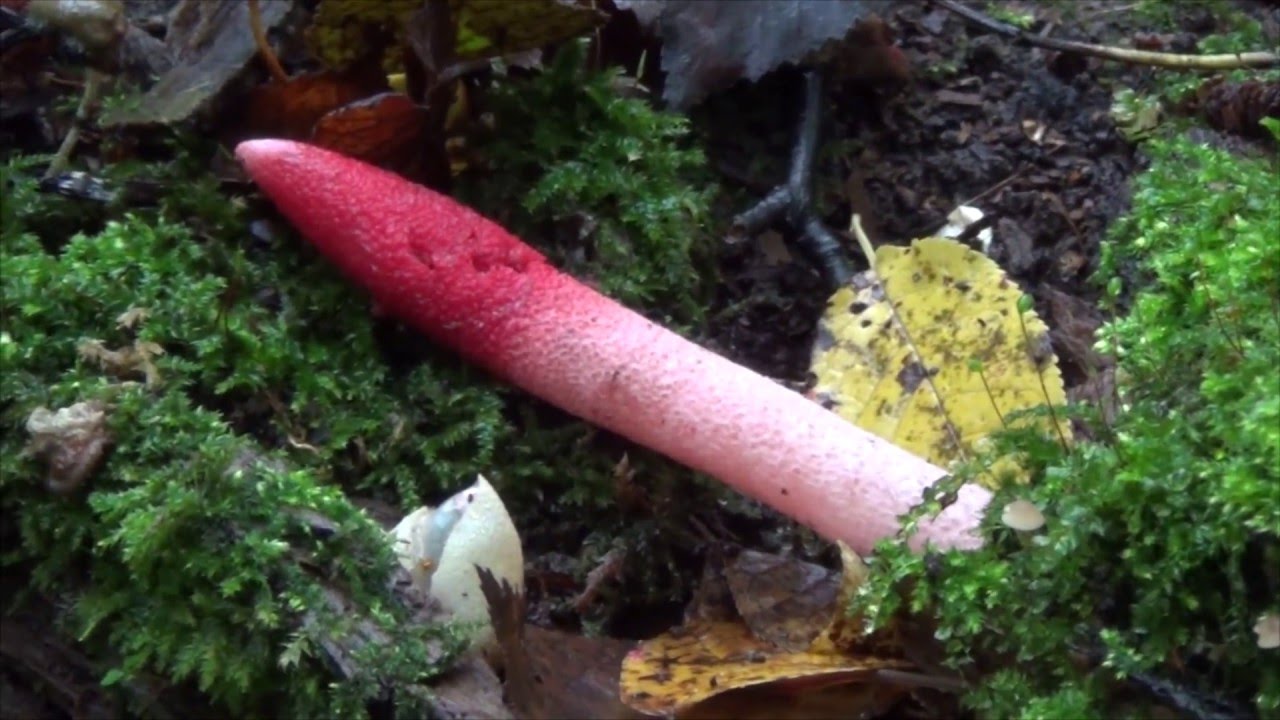
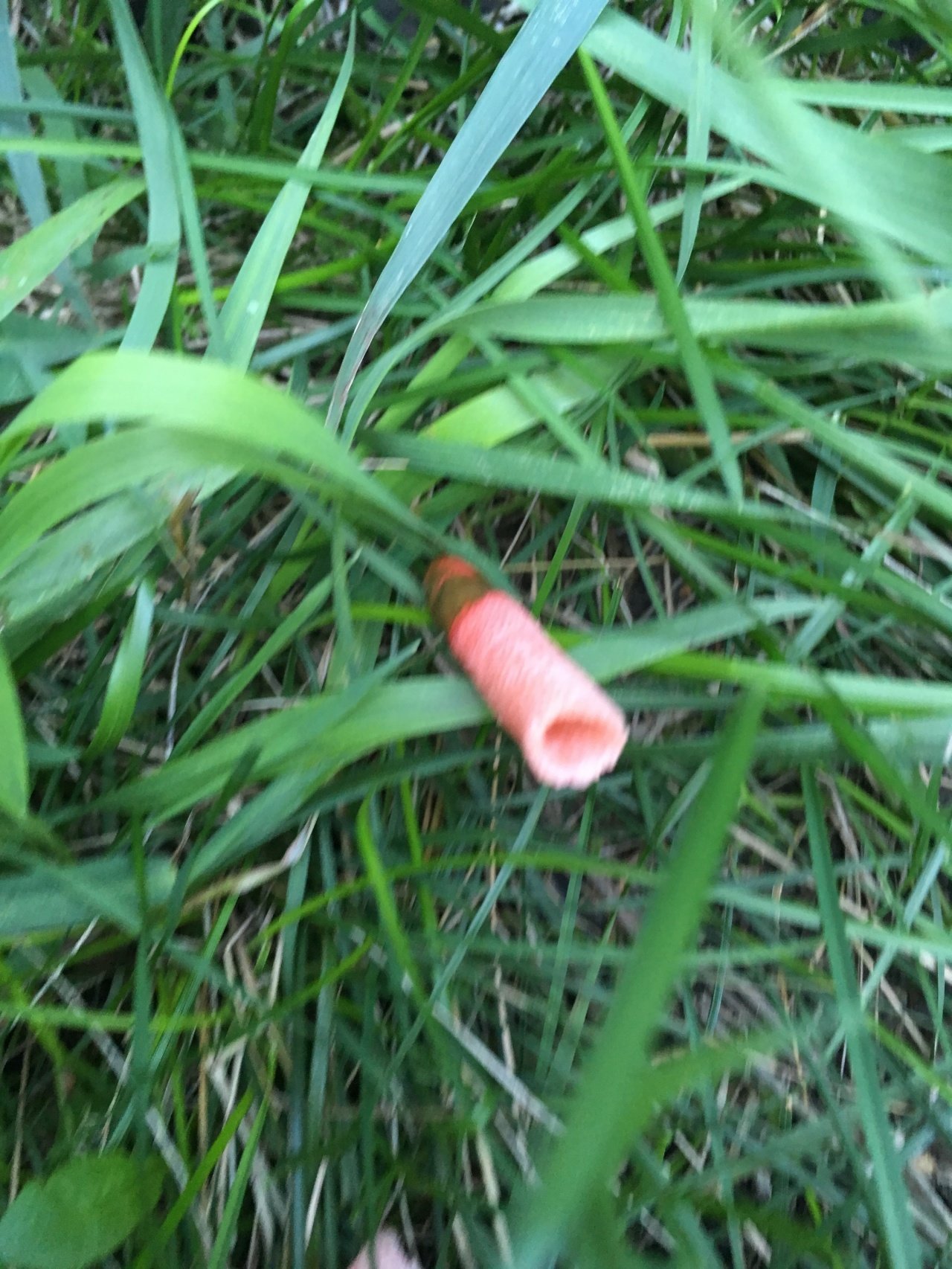
The main feature of the mutinus is the absence of a hat as such. Consequently, the fetus does not have a hymenophore either. At the first meeting, few people may think that in front of him is a representative of the mushroom kingdom.The fruit looks like a tube or fleshy branch of a pinkish-white or reddish hue.
The ravenelli mutinus can only be recognized by its unusual fruiting body. At first, it has an ovoid shape, after which it gradually stretches out. After the appearance of the mushroom "embryo", after a short period of time, a fruit stem is formed. It is small, narrow and petite. But during the entire life cycle of the fungus, it can grow up to 8 cm in height and 1 cm in thickness.
The mutinus recipe (leg) can be colored ocher or ginger with a reddish tint. The spores are ellipsoidal, their color is greenish with an olive tint. The mucous layer gives off an unpleasant smell of rotten meat. For this reason, the mutinus is called the smelly morel.
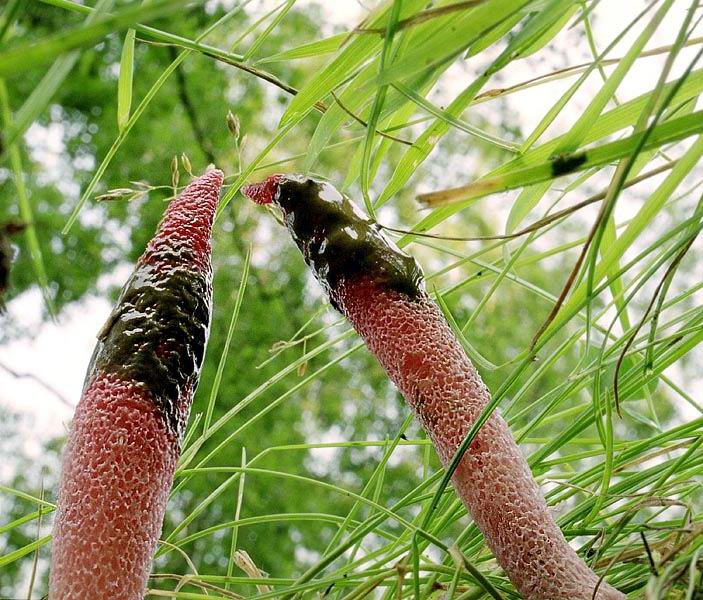
The fruit body of the mutinus tapers upward. In this part, it is colored bright pink. At the bottom, the recipe is noticeably expanded, and its shade becomes lighter all the way to completely white. Over time, it turns red, as the fungus ages, its surface is covered with a layer of spore-bearing mucus. It is carried by insects, in particular flies, which are attracted by the smell of mutinus.
Why is the mushroom listed in the Red Book
Mutinus Ravenel is listed in the Red Book of the Saratov and Novosibirsk regions, as well as the Altai Territory. This is due to the fact that this species is quite rare, and the number of specimens in Russia is very small.
Such fruits grow mainly in wildlife sanctuaries and reserves, and in normal natural conditions it is difficult to find them. Due to the high probability of extinction of this species, as such, it was decided to artificially grow in gardens and arboretums.
Mutinus Ravenel mushrooms and canine: photo and description, features of the development of the genus
In the photo Mutinus ravinelii
Ravenel's mutinus (Mutinus ravinelii) is confused with the canine mutinus (Mutinus caninus), which has a yellow-beige leg.
The kingdom of mushrooms occupies a separate place in biological science. There are more than 250 thousand of them. Mushrooms can live both on land and in water, with different readings of humidity and temperature.
Some species may outwardly be similar to each other, or they may be completely different, for example, the genus Mutinus, which has a very extraordinary appearance, bears little resemblance to a mushroom in the minds of most people.
They are considered quite rare.
He came to Western Europe in the middle of the last century from America. But on the territory of Russia you will not meet him so often. Loves fertile soil, grows actively at high humidity.
The main features of the development and structure:
- in the development process, there are two stages (ovoid and the appearance of a cylindrical leg);
- the body of the mutinus is spongy, porous;
- the stem ends with a tip that differs in color (usually brighter);
- it multiplies, like all mushrooms, by spores that are contained in the formed mucus with an unpleasant, putrid odor;
- the spread of spores occurs with the help of insects.
Mutinuses are not edible. But some mushroom pickers say that in the developmental stage of the "testicle", they can well be used in cooking and have the taste of an ordinary mushroom. But note that no research has been carried out on this score. Therefore, we still do not recommend eating it.
See what the mutinus mushroom looks like in the photo:
Dog mutinus: photo and description
Even an experienced mushroom picker cannot always boast that he saw him in the forests of our region. This species is more common in America, from where it was introduced to Europe. Canine mutinus, the description of which will follow below, is listed in the Red Book, a rather rare species of this species of fungi.
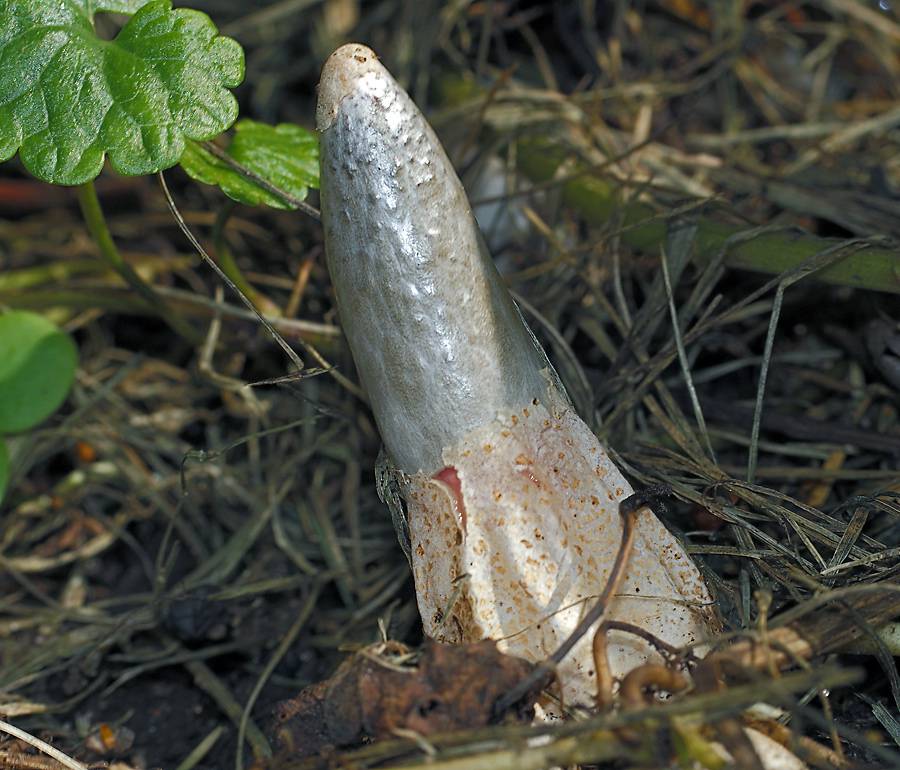
In the photo Mutinus dog
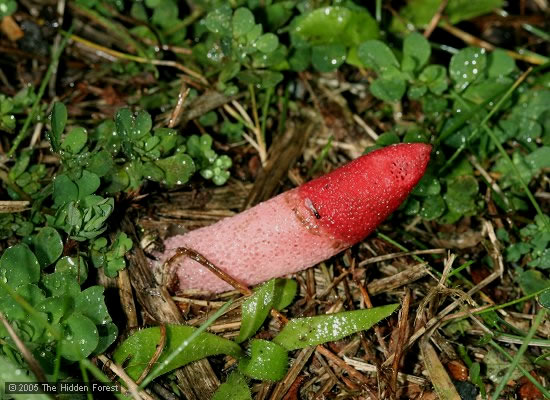
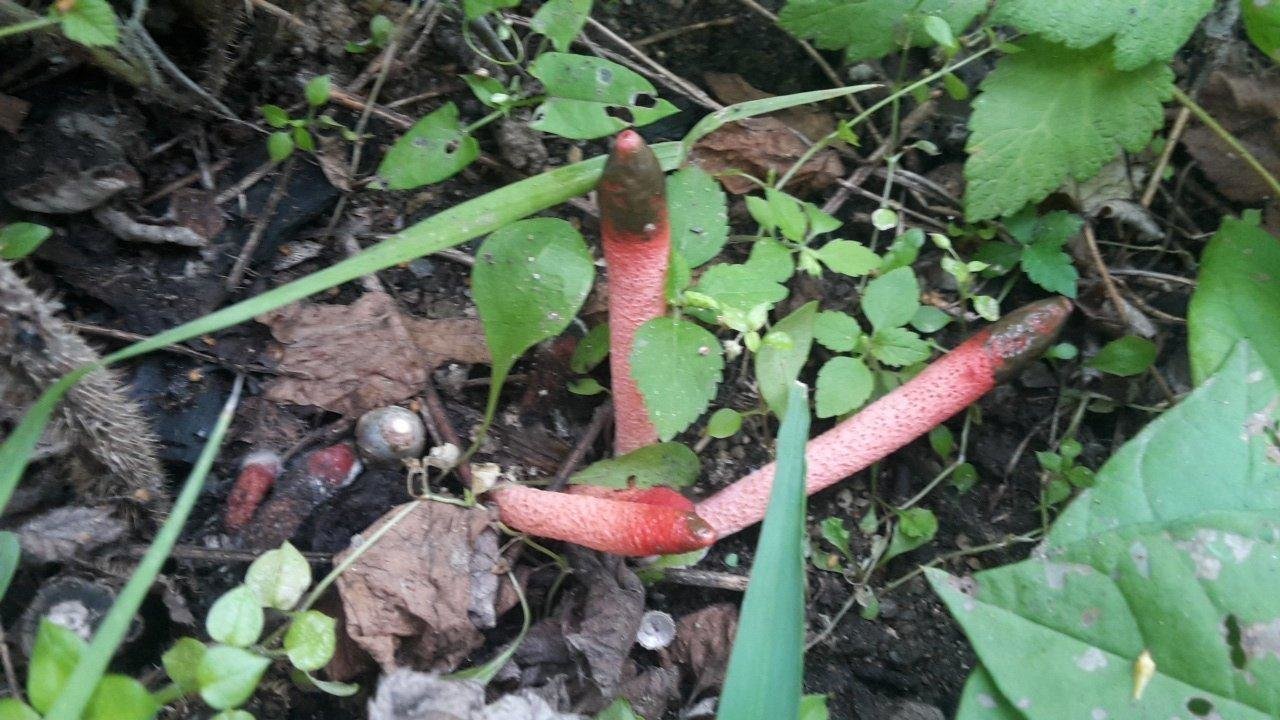
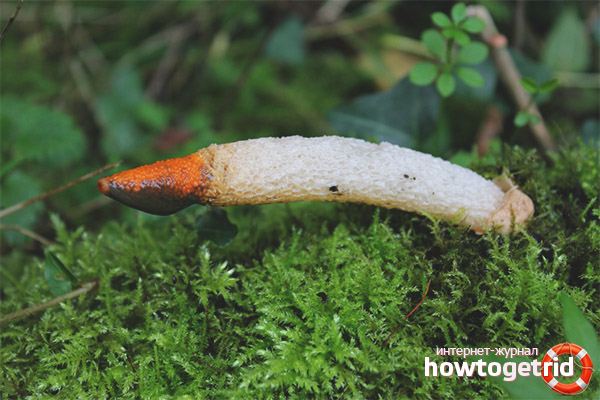
By its appearance, it resembles a part of the body of a dog, which is not clear how it sticks out of the ground. The color of the mutinus, starting from the ground, is pale pink, which gradually turns into a bright red tip. On the leg, under the cylindrical part, there is a mucous girdle.
Its size is no more than 2 cm. The shade of the discharge is greenish-brown. The spores of the fungus ripen here.Flies and other insects are constantly circling in this part. They are attracted by the specific smell that this mucus emits. In turn, it is the insects that carry the spores of the fungus.
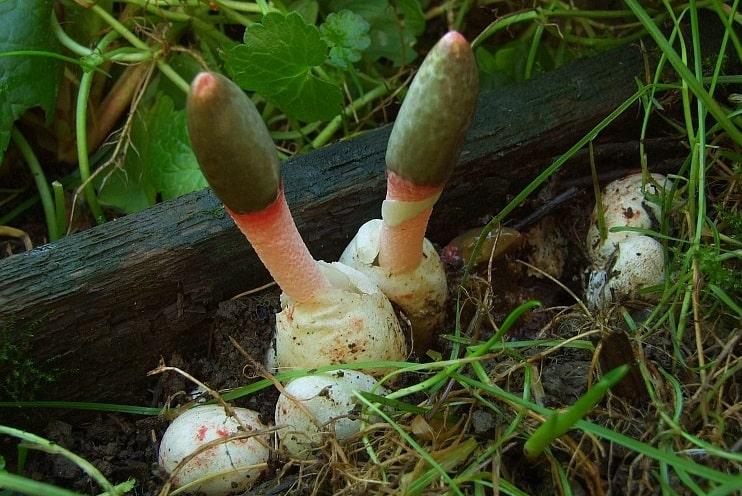
The development of the canine mutinus fungus begins with the appearance of the fruiting body. It looks like an egg up to 4 cm in diameter. Has a white color. Further, this egg bursts, forming blades, and the body of the fungus begins to grow from the core. Its height can reach 15 cm. The upper part later becomes pointed and acquires a specific red tint.
See what the dog mutinus looks like in the photo:
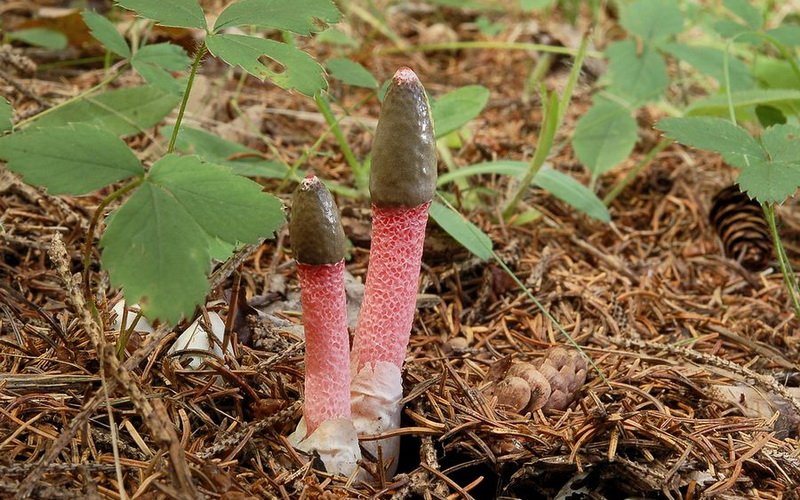
Mutinus Ravenel mushroom: photo and description
In the photo, the mushroom mutinus Ravenel
Outwardly, this variety of mutinus has a similarity to the dog. You can meet him in the forest from the end of July until September. Most often it can be found:
- on soils rich in humus;
- in places of decaying wood.
It grows especially quickly after heavy rains.
Outwardly, it looks very strange and not attractive. With all his appearance, he seems to show that he is inedible. In addition, it emits a rather nasty smell. It is for this peculiarity that the people received the name "smelly morel".
See what the Ravenel mutinus looks like in the photo:
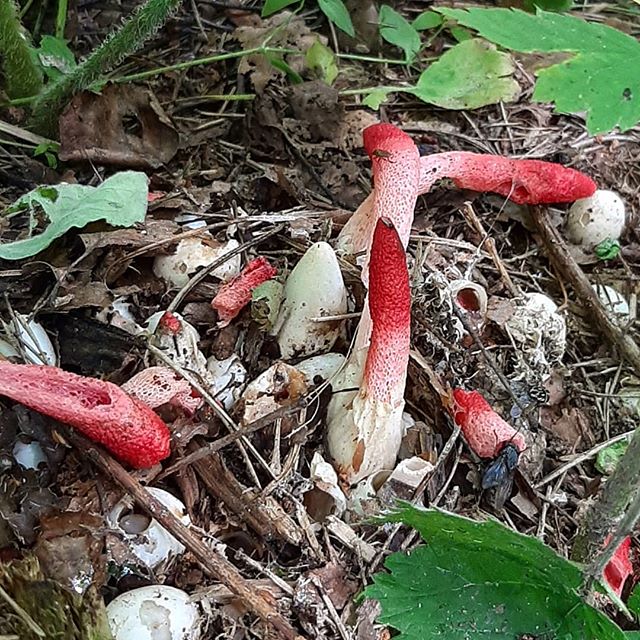
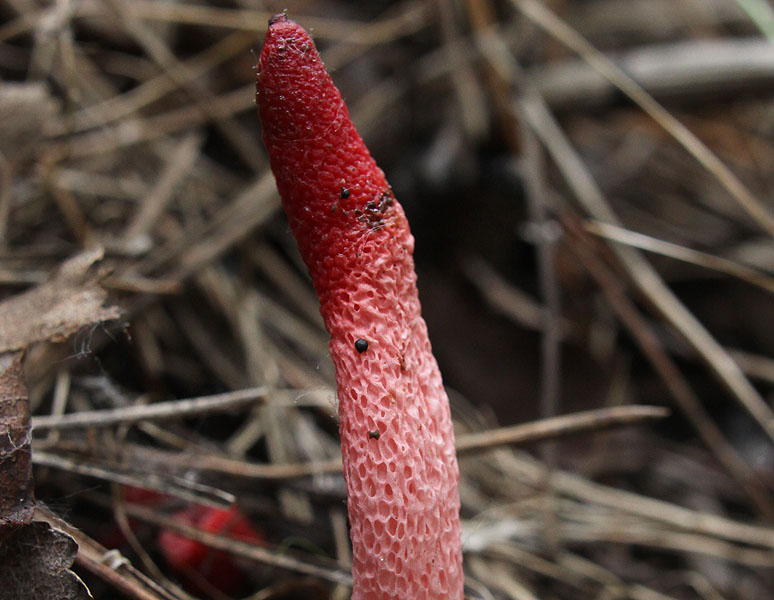
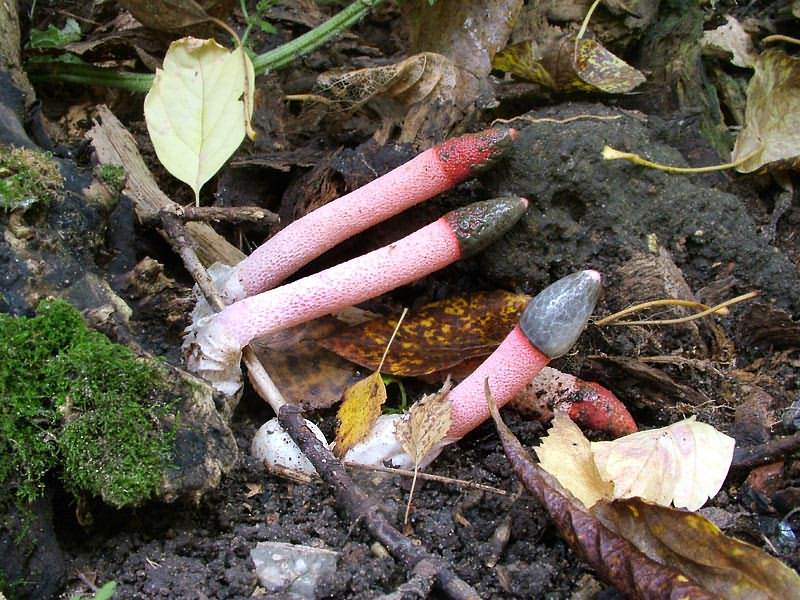
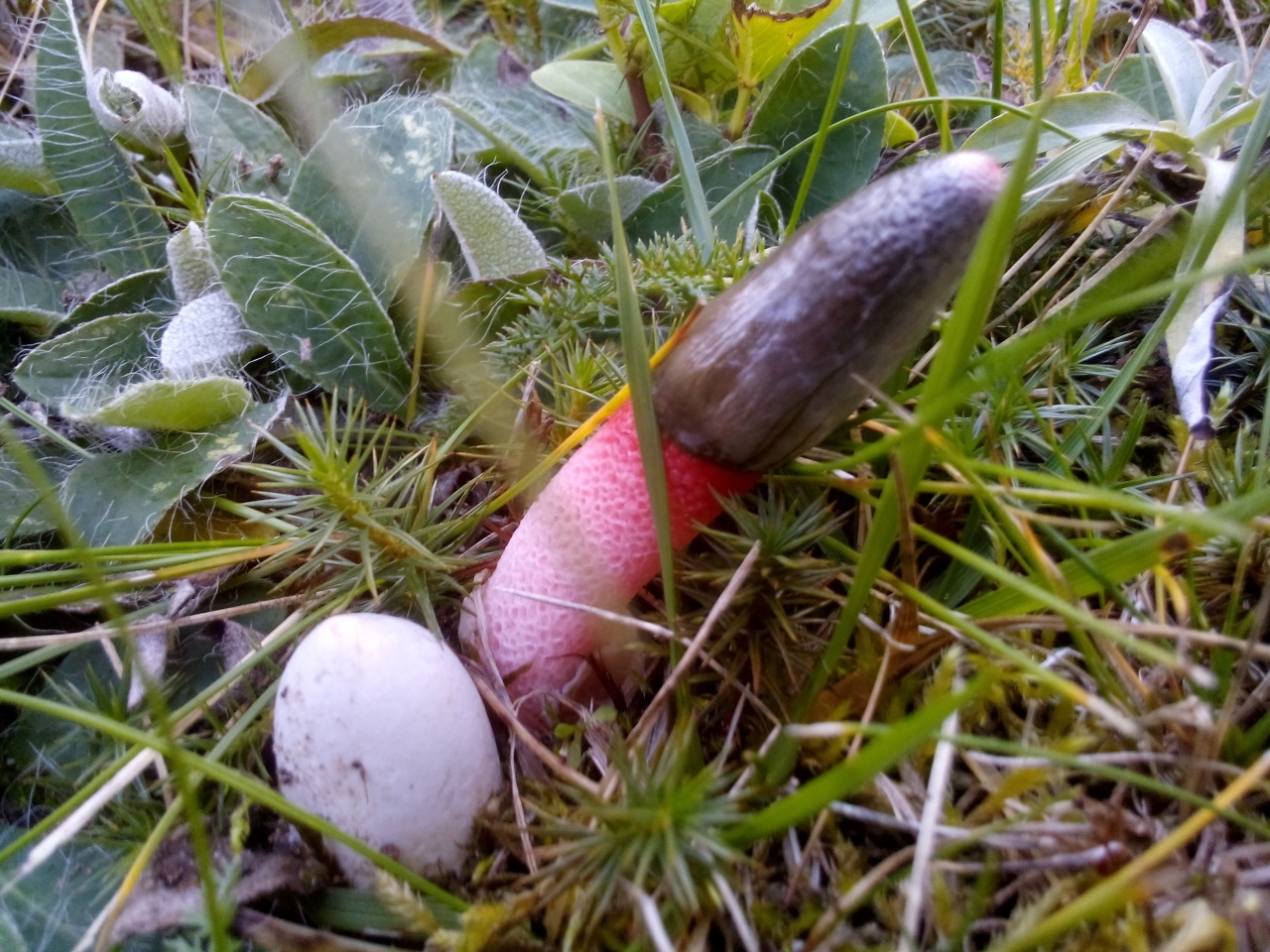
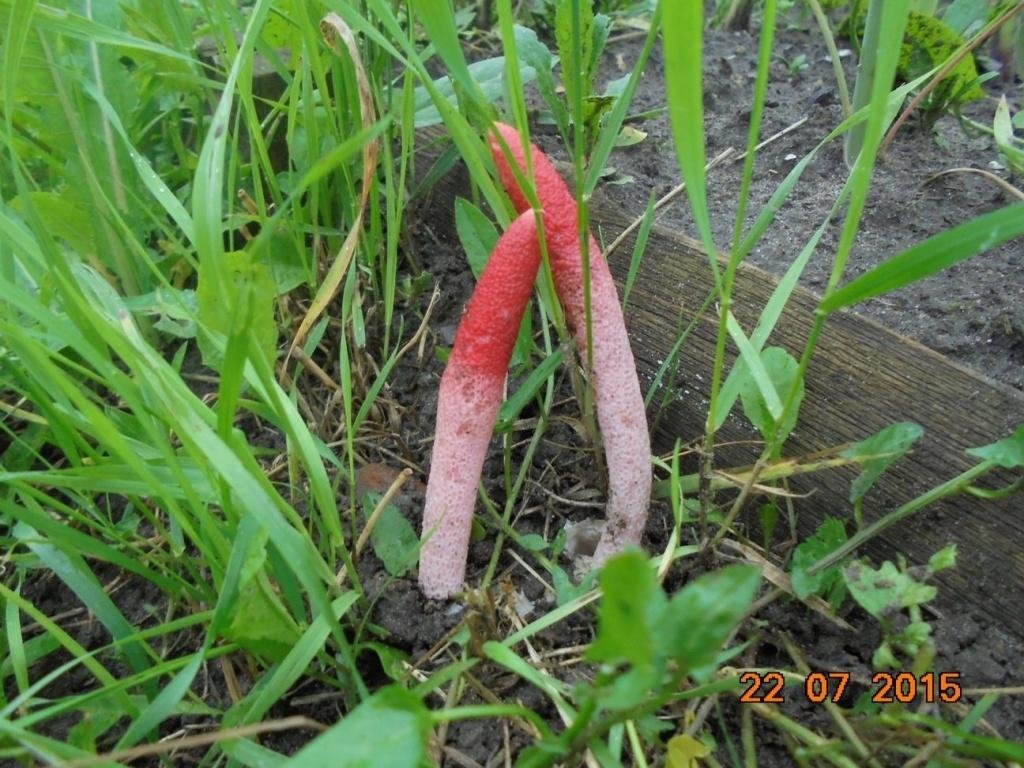
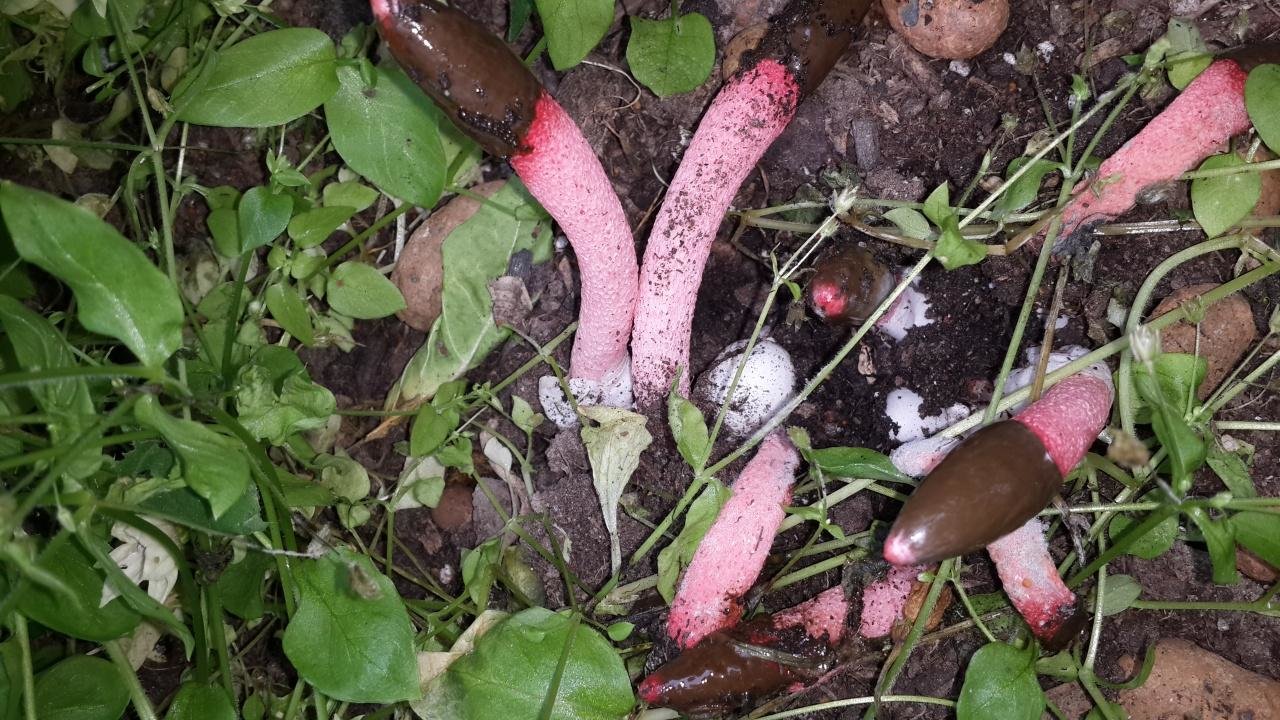
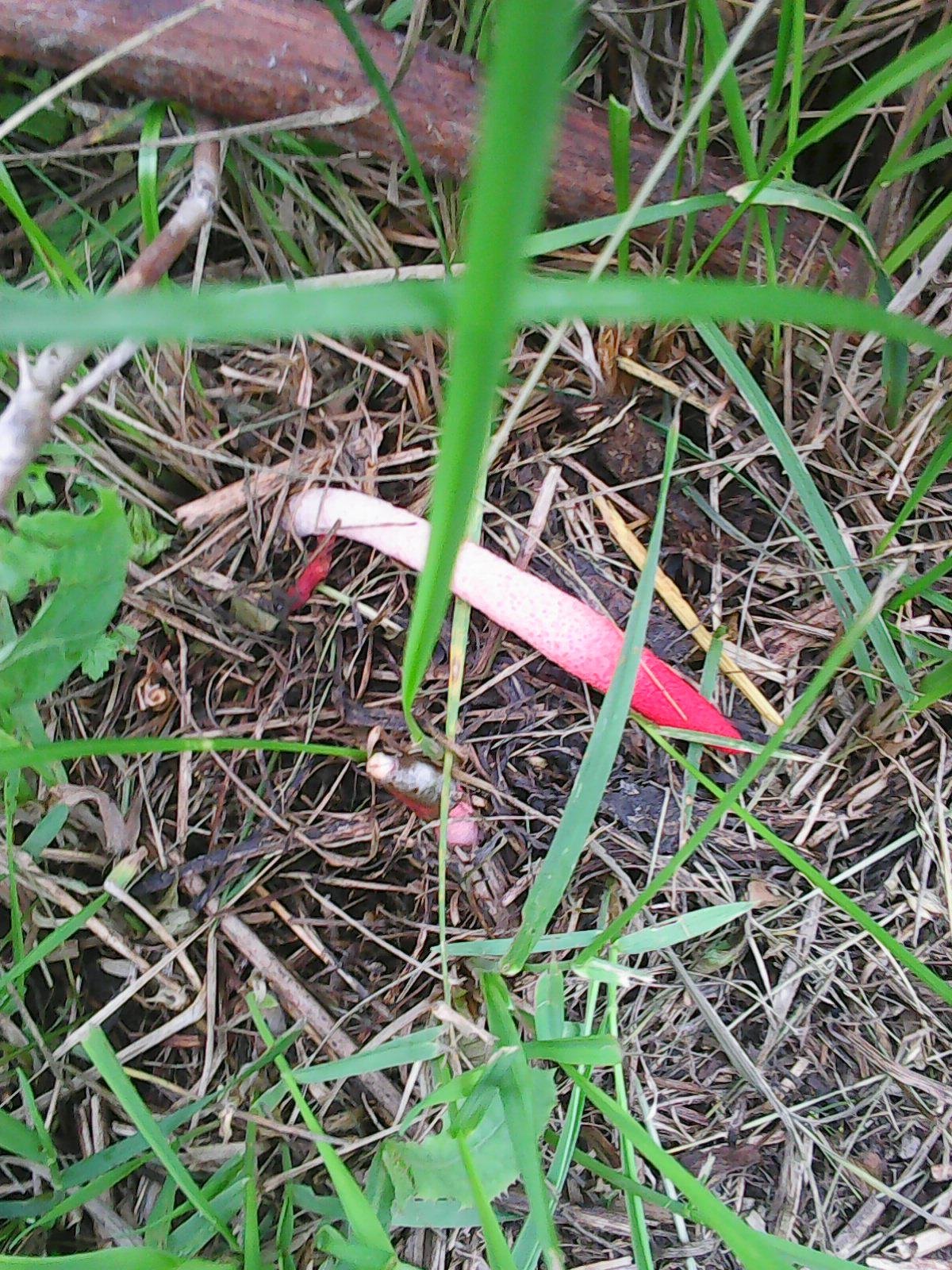
In the process of its growth, the fungus goes through two stages of development, like the canine mutinus. Initially, an egg-like formation appears above the ground. Its size is rarely more than 3 cm in diameter. A delicate film formation hides the rudiment of the leg of the body, it looks like a bright red process.
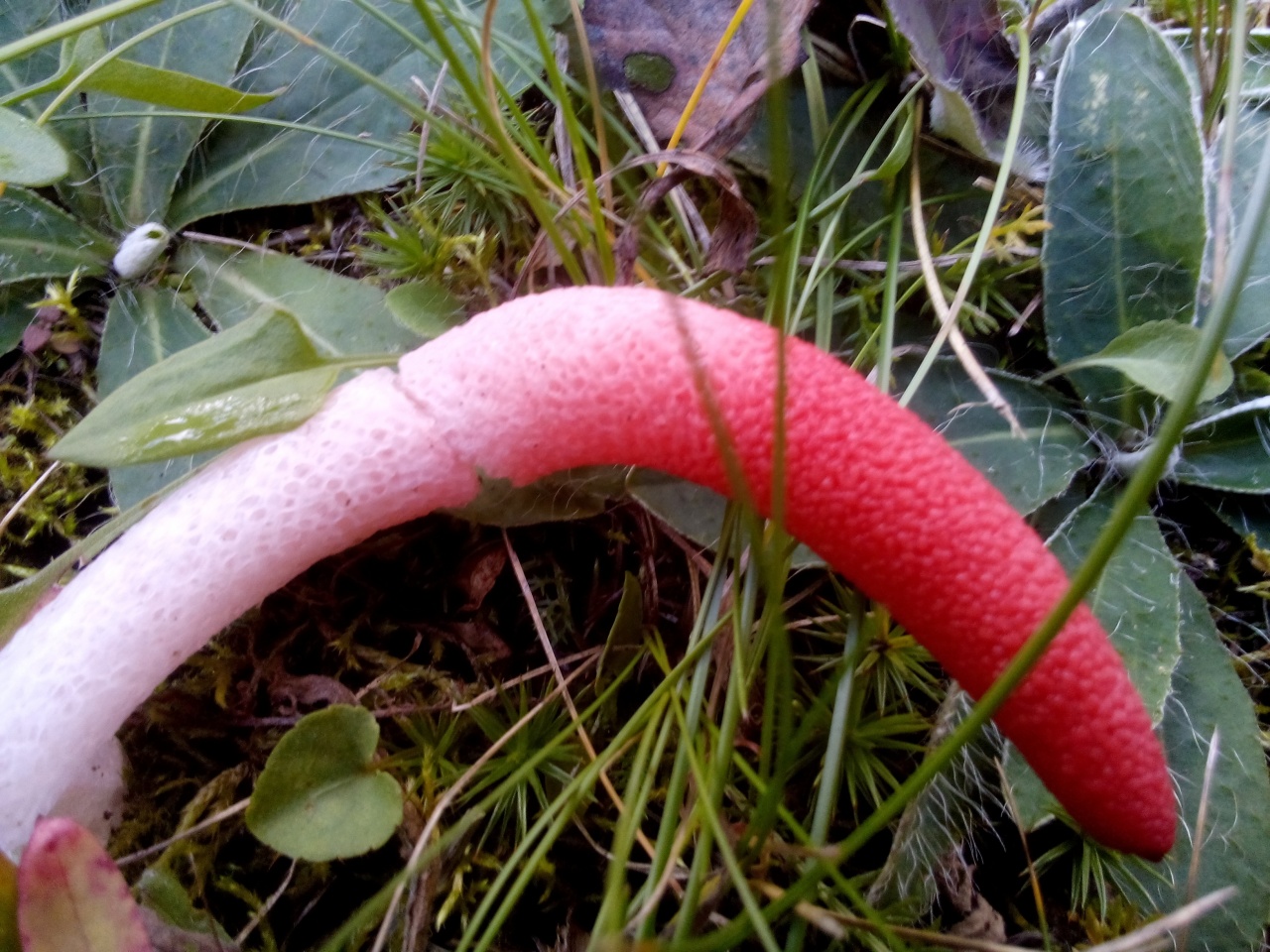
The egg has two lobes that break and allow the porous stem of the body to develop. Its length reaches 9 cm, and in diameter it is no more than 1 cm. Towards the end, the stem has a red pointed tip.
In an adult fungus, the upper part is covered with mucus with spores, which has a dark olive tint and gives off the smell of carrion. It is during this period that flies begin to circle near the mushroom, which are attracted by this stench.
Its pulp is tender and porous.
If you find a mutinus in the forest, then examine it carefully. Despite all its unpleasant appearance, the mushroom looks very extraordinary. Do not rip it off, as this species is quite rare in our area. Perhaps you will not see another such specimen for a long time.
Mutinus Ravenel mushroom: photo and description
In the photo, the mushroom mutinus Ravenel
Outwardly, this variety of mutinus has a similarity to the dog. You can meet him in the forest from the end of July until September. Most often it can be found:
- on soils rich in humus;
- in places of decaying wood.
It grows especially quickly after heavy rains.
Outwardly, it looks very strange and not attractive. With all his appearance, he seems to show that he is inedible. In addition, it emits a rather nasty smell. It is for this peculiarity that the people received the name "smelly morel".
See what the Ravenel mutinus looks like in the photo:
In the process of its growth, the fungus goes through two stages of development, like the canine mutinus. Initially, an egg-like formation appears above the ground. Its size is rarely more than 3 cm in diameter. A delicate film formation hides the rudiment of the leg of the body, it looks like a bright red process.
The egg has two lobes that break and allow the porous stem of the body to develop. Its length reaches 9 cm, and in diameter it is no more than 1 cm. Towards the end, the stem has a red pointed tip. In an adult fungus, the upper part is covered with mucus with spores, which has a dark olive tint and gives off the smell of carrion. It is during this period that flies begin to circle near the mushroom, which are attracted by this stench. Its pulp is tender and porous.
If you find a mutinus in the forest, then examine it carefully. Despite all its unpleasant appearance, the mushroom looks very extraordinary. Do not rip it off, as this species is quite rare in our area. Perhaps you will not see another such specimen for a long time.
Saprobiotic species of Basidiomycete fungi - this is how Canine Mutinus is characterized
Its unusual appearance will certainly attract the attention of a lover of quiet hunting, but you should refrain from collecting and eating this species, although the smell of mutinus will do everything by itself
What mushrooms can be confused with a mushroom and how to distinguish
The lattice has no false twins, so it is very difficult to confuse it with this or that fruit. But there are some individuals that outwardly are slightly similar to the specimen in question. There are 3 of them in total.
Javanese florist
This inedible fruit is included in the Red Book. The fruit body resembles a spindle or cigar in appearance. It consists of several parts - 3 or even 8.

Juveniles are whitish, while older specimens turn orange-red. The body is located on a leg, inside which there is a cavity. From the inside, it is covered with olive mucous gleb.
The flower stalk has a rather unpleasant and pungent odor. As with the trellis, this fruit smell attracts insects and other pests. They are the carriers of the dispute of this instance.
Archer's Flowerbird
Clathrus Archer is also a mushroom, although it is very difficult to guess about it by its external characteristics.
If you look at this specimen, you can say that it looks like an octopus. Confusing him with a lattice will definitely not work, although in the photo he looks a little like him:

This inedible fruit is native to Australia. This plant got its name in honor of the famous scientist-mycologist W. Archer. The fruiting body of the flower stalk is pear-shaped, its diameter is about 5-6 cm. The stem is completely absent. The mushroom has an unpleasant, pungent odor.

This specimen is a saprophyte. It grows mainly in deciduous and mixed types of forests. The fruiting period falls in July-October. Occasionally, Archer's flower stalk can be found on sandy soil.
Canine mutinus
Canine mutinus is one of the related species of the trellis. You can see it from the second half of summer to the end of October. It was at this time that its active fruiting was noted. Such a specimen grows in North America and European countries.
The main characteristics of the canine mutin are:
- oval-shaped fruiting body;
- fruit diameter up to 3.5 cm;
- the height of the "legs" is about 20 cm;
- cellular surface of the gleb.

The mutinus receptacle is colored in a dull red color, and its pulp, when broken, begins to exude an extremely unpleasant odor. Active fruiting of the mushroom begins in July and ends at the end of October. The fruit is very fond of the soil enriched with humus.
Mutinus Ravenelli
The fruiting body of the fungus goes through two stages of its formation and functioning. The shape of a young fruit resembles a pointed egg, the size of which does not exceed 2-3 cm. The flesh is covered with a thin yellowish membranous skin, which contains the rudiment of a “leg” of red-pink color. The egg breaks with two blades that reveal a porous, hollow "stem". Its length is 5-10 centimeters, and its diameter is about 1 cm.

When the Ravenella mutinus matures, its tip becomes covered with a thick, smooth, smeared spore-bearing mucus, colored in an olive-brown shade. The flesh of the fruit is porous, but very fragile and tender.
The mushroom bears fruit between June and September. It is located on soil well-saturated with humus. Prefers deciduous forests, gardens, shrubs, humid places. It can spawn near rotting wood residues.
All of the above fruits are only indirectly similar to the trellis. It is very difficult to confuse them with the "original", because in their appearance they are not very similar to it.
Veselka Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii)
Synonyms:
Aedycia ravenelii
Veselka Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) is a mushroom that belongs to the Veselkov family and the Phallus genus (Veselok).
External description
Initially, the shape of the Veselka Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) resembles a pinkish, lilac or purple egg.The “egg” develops rapidly, grows in breadth, and as a result, a fruiting body, shaped like a phallus, grows out of it. The yellowish-white stem of the mushroom is crowned with a cap the size of a thimble. Its width varies from 1.5 to 4 cm, and its height is from 3 to 4.5 cm. The total height of the fruiting body can reach 20 cm. The surface of the cap of Veselka Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) is fine-grained, and its edges are connected to the stem by a peri-cap ring. In some specimens, the cap is too wide and becomes tapered. the color of the cap in different specimens can vary from olive green to dark brown.
The mushroom leg is hollow, it can reach a height of 10-15 cm, and its diameter varies within 1.5-3 cm. It is white or whitish-yellow in color.
Veselka Ravenelli's spores (Phallus ravenelii) are characterized by thin walls and a sticky surface, are elliptical, smooth, colorless, 3-4.5 * 1-2 microns in size.
Season and habitat of the mushroom
Veselka Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) is widespread in eastern North America. Dominates other species west of the Mississippi, found in Costa Rica.
The described species belongs to sapbiotics, therefore it can grow in any habitat where decaying wood is present. The fungus grows well on rotten stumps, wood chips, sawdust. Veselka Ravenelli can often be seen in groups, but there are also specimens growing separately. the species is also common in city flower beds, lawns, meadows, park areas, forests and fields.
Edibility
Veselki Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) are considered edible only at a young age, when they look like an egg. Mature specimens exude an unpleasant odor, so seasoned mushroom pickers prefer not to collect them for food.
Similar types and differences from them
Merry Ravenelli (Phallus ravenelii) is often confused with Phallus impudicus and Phallus Hadriani. P. Impudicus differs from the described species in the net structure of the cap, the surface of which is covered with alternating grooves and ridges. As for the main difference of the P. Hadriani species, it consists in the presence of seeds on the cap. This species, in contrast to the Ravanelli merry, can be found very rarely.
Another similar mushroom belongs to the species Itajahya galericulata. It has a spherical cap, the surface of which is covered with several layers of spongy tissue, between which a loose inner tissue - gleba - is clamped.
The next species, similar to the one described, is called Phallus rugulosus. This mushroom is thin, it has a higher height, a light orange color of the fruiting body, a stem that tapers near the cap and a smooth surface of the cap itself. It grows in China, as well as in the southern and eastern parts of the United States.
granulosodenticulatus is a species of Brazilian mushroom that is rare and similar in appearance to the jolly Ravanelli. Its fruiting bodies are smaller and do not exceed 9 cm in height. The cap has a serrated edge, and the spores are large, measuring 3.8-5 * 2-3 microns.
Other information about the mushroom
Mushroom gleb gives off a characteristic unpleasant odor that attracts insects to the plant. they sit on sticky, spore-bearing areas of the fruiting body, eat, and then transfer fungal spores on their paws to other places.
Canine mutinus mushroom: description, photo and medicinal properties

Canine mutinus decomposes approximately as rapidly as it ripens: as soon as the flies eat up the entire spore-bearing layer from its surface, the fungus program is considered completed and the autolysis process starts, which completely decomposes the fruiting body after 3 days.
In the mutinus, substances were found that can activate the immune system, among the useful components it contains:
- tannin;
- alkaloids;
- glycosides and others.
The mushroom has received the characteristic of a natural antioxidant and antioxidant, it helps to improve well-being and get a boost of vitality for the whole day.
The chemical composition of the mutinus is not well understood, but in ancient times its juice was used to prolong and preserve youth, health and vitality.
Unusual mushrooms are rarely found on the way, and having found them in the forest, a lover of quiet hunting most often simply passes by, but knowing about their useful properties. Having learned how to properly prepare and use mutins, you can heal from many diseases, rejuvenate the body, tone the body and support the immune system.
False doubles
You should not be afraid of the canine mutinus doubles, because they are also inedible, like this mushroom. The main copy is the Ravenel mutinus, which is distinguished by a more colorful body and white shells of eggs of a young fruiting body. Both varieties are considered edible during the immature, unhatched mushroom stage, but after the appearance of the recipe, they become inedible.
In addition, both species are rare, are listed in the Red Data Books of different regions of Russia, and therefore it is not recommended to eat, trample or pluck them.
Pay attention to the photo
Despite the fact that the mushroom is listed in the Red Book, some gourmets, having found it in the forest, will certainly try to cook and taste it. In this case, you should be especially careful, because it can be confused with a very dangerous and poisonous pale toadstool.
| Name | Appearance | Sectional view | Virulence |
| Canine mutinus | White egg with a firm surface | Below the surface, the structure of the egg is visible, there is a gray jelly, then a small part of the spores of a dark gray-green color and a fruit body, consisting of half of white and pink | Inedible |
| Common fun | The surface of the egg has a beige tint, yellowish | Under the protective layer of jelly there is a spore-bearing khaki-colored mucus, in the middle is a white body | Inedible |
| Death cap | White egg covered with film | the eggs are completely white, the hatching is visible | Deadly, highly poisonous |
| Anturus Archera | The egg is gray, with a greenish tint | Layering is visible, a jelly-like shell is visible under the peridium, then a red body and spore-bearing olive mucus in the center | Inedible |
The use of mushroom eggs for food is very dangerous and not justified, such fruit bodies do not differ in special taste.
Canine mutinus is edible or not?
Still, the strong smell of the mushroom will not allow picking it, and even more so to cook and eat it. Canine mutinus is not poisonous, but inedible, besides, it has a pungent aroma and a strange repulsive appearance.
Contraindications to use are considered to be under 12 years of age, pregnancy and lactation, as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys. There were no medical fixations of poisoning with mutinus, no poisons were found in it, but it is not officially treated with it.