Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
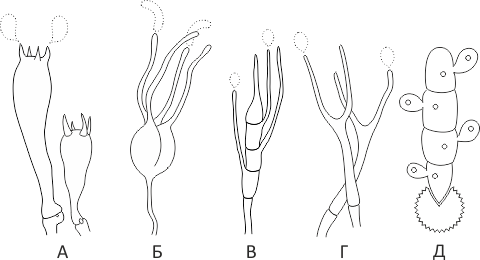
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
Mycena alkaline: description and photo
| Name: | Mycena alkaline |
| Latin name: | Mycena alcalina |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Synonyms: | Mycena is caustic |
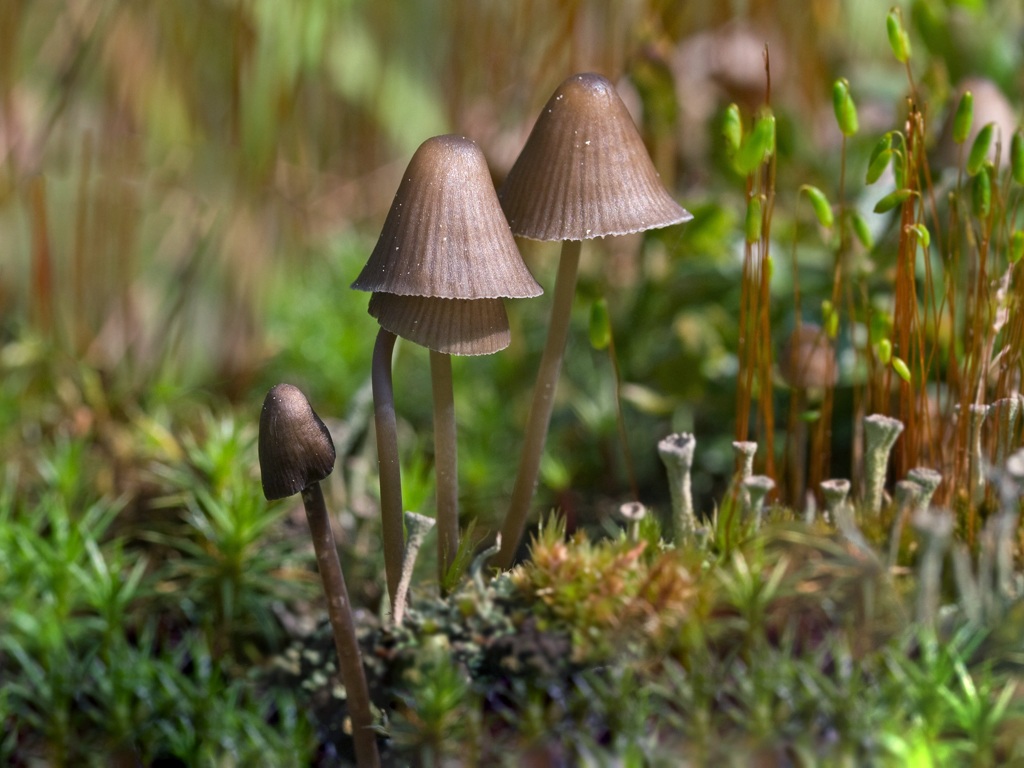
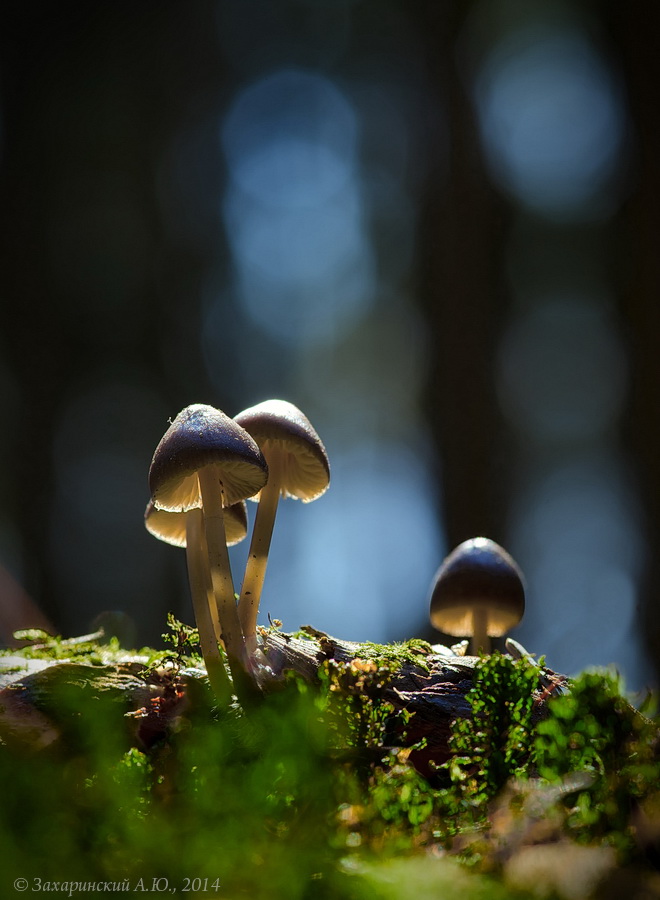
Mycenae alkaline, pungent, pineapple-loving or gray are the names of the same mushroom. In mycological reference books, it is also designated under the Latin name Mycena alcalina, belongs to the Mycene family.

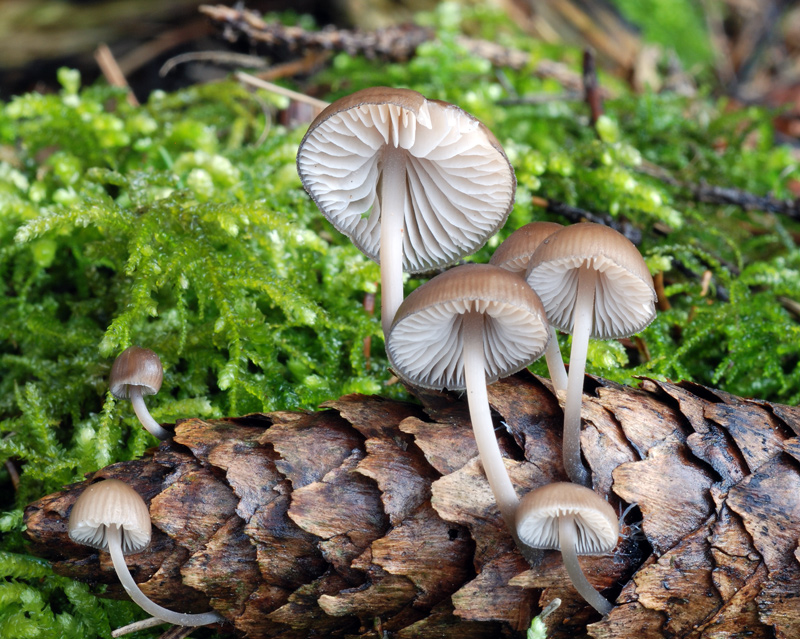
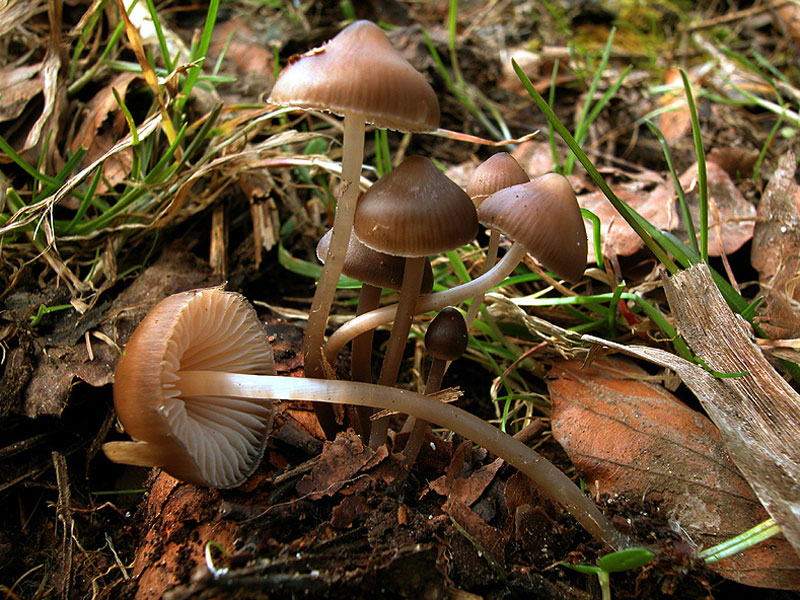
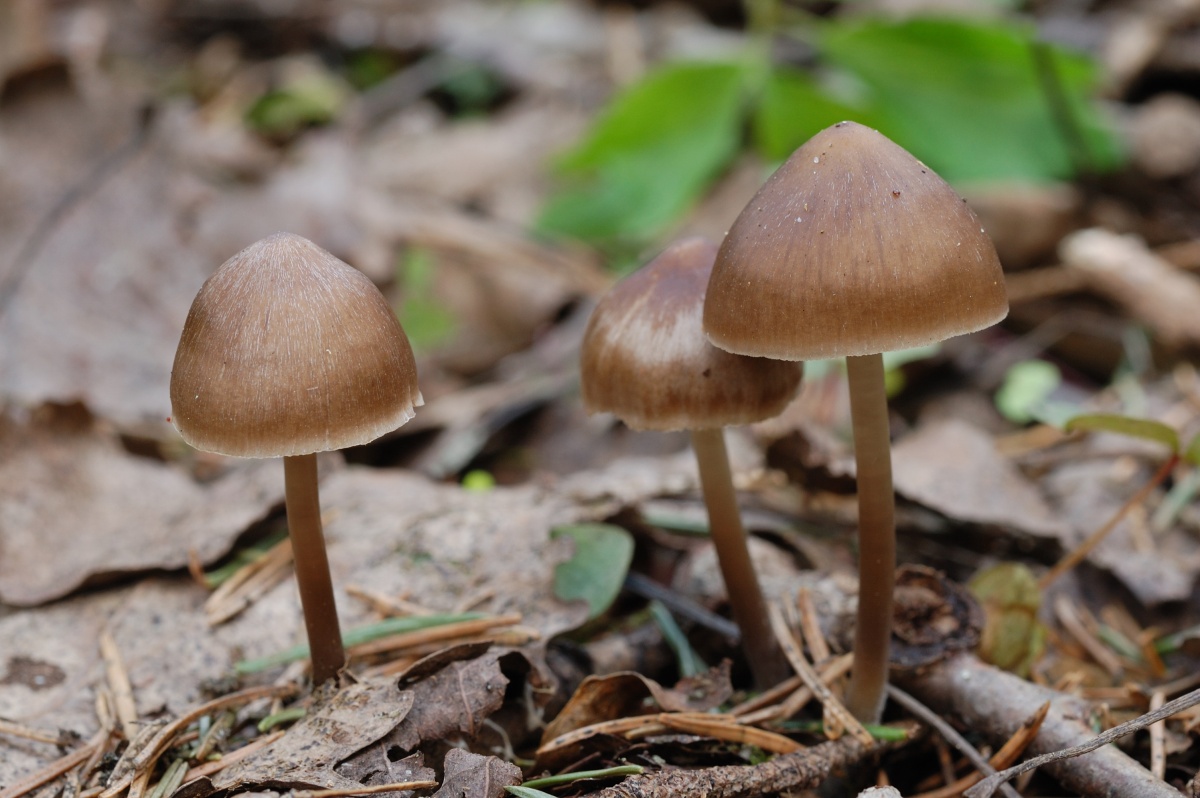
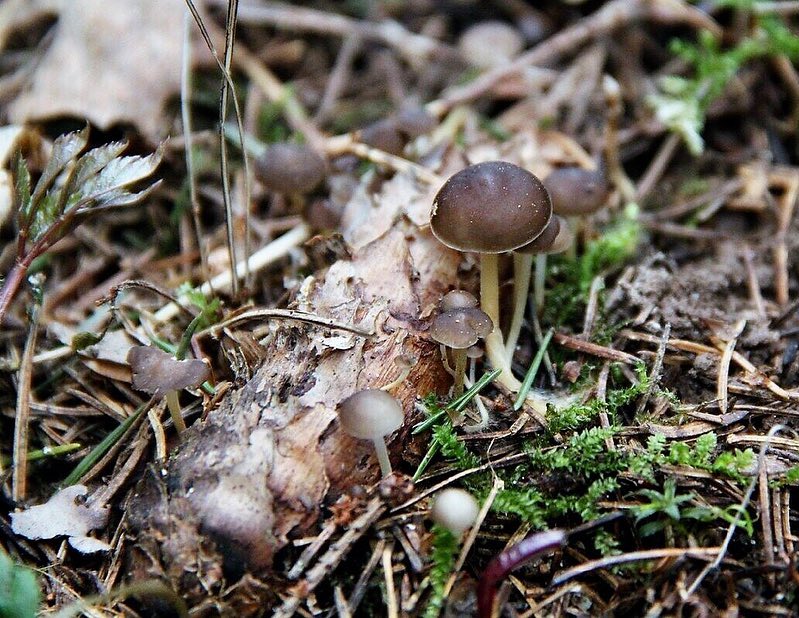
Fruits grow in compact groups covering large areas
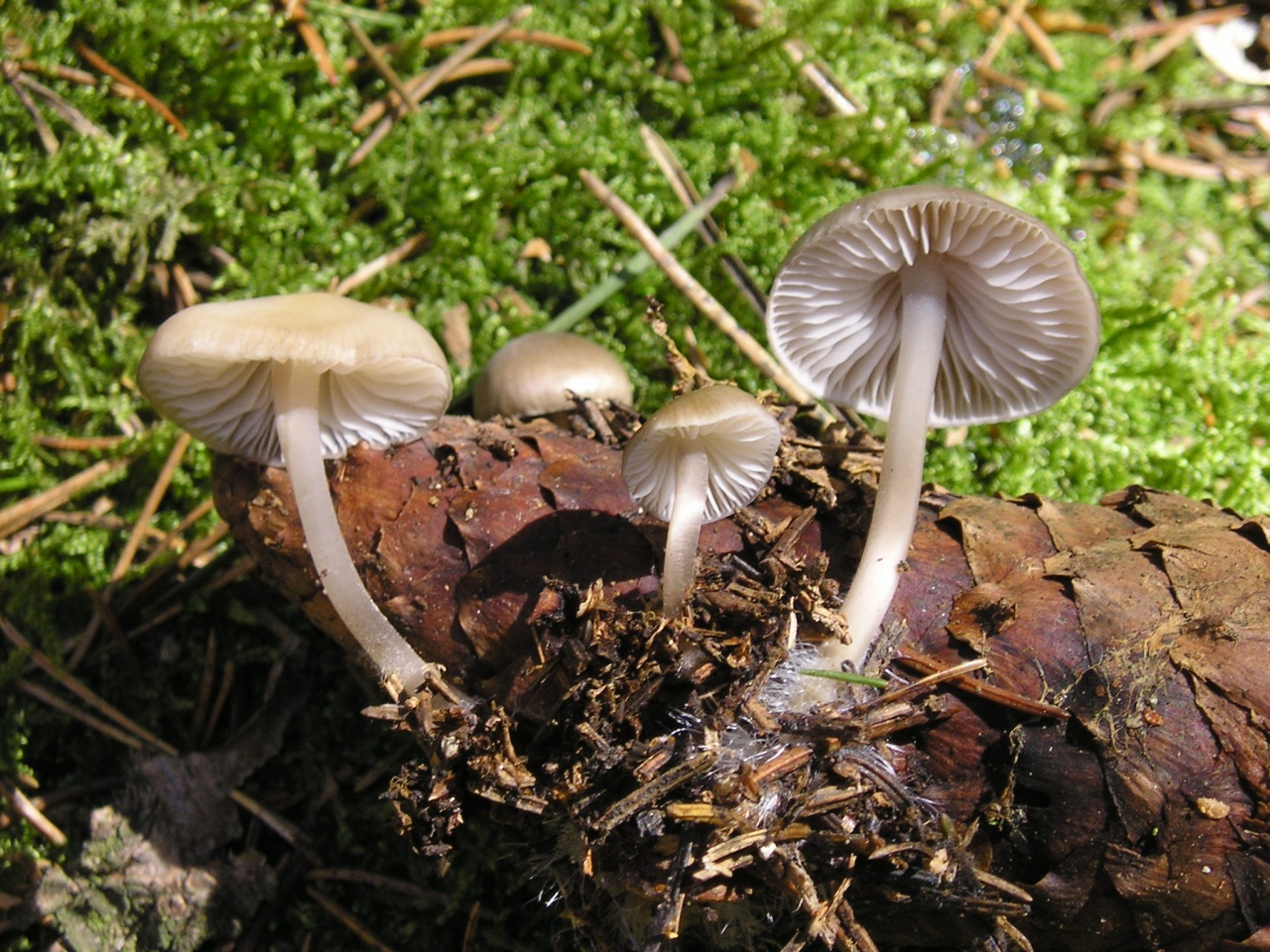
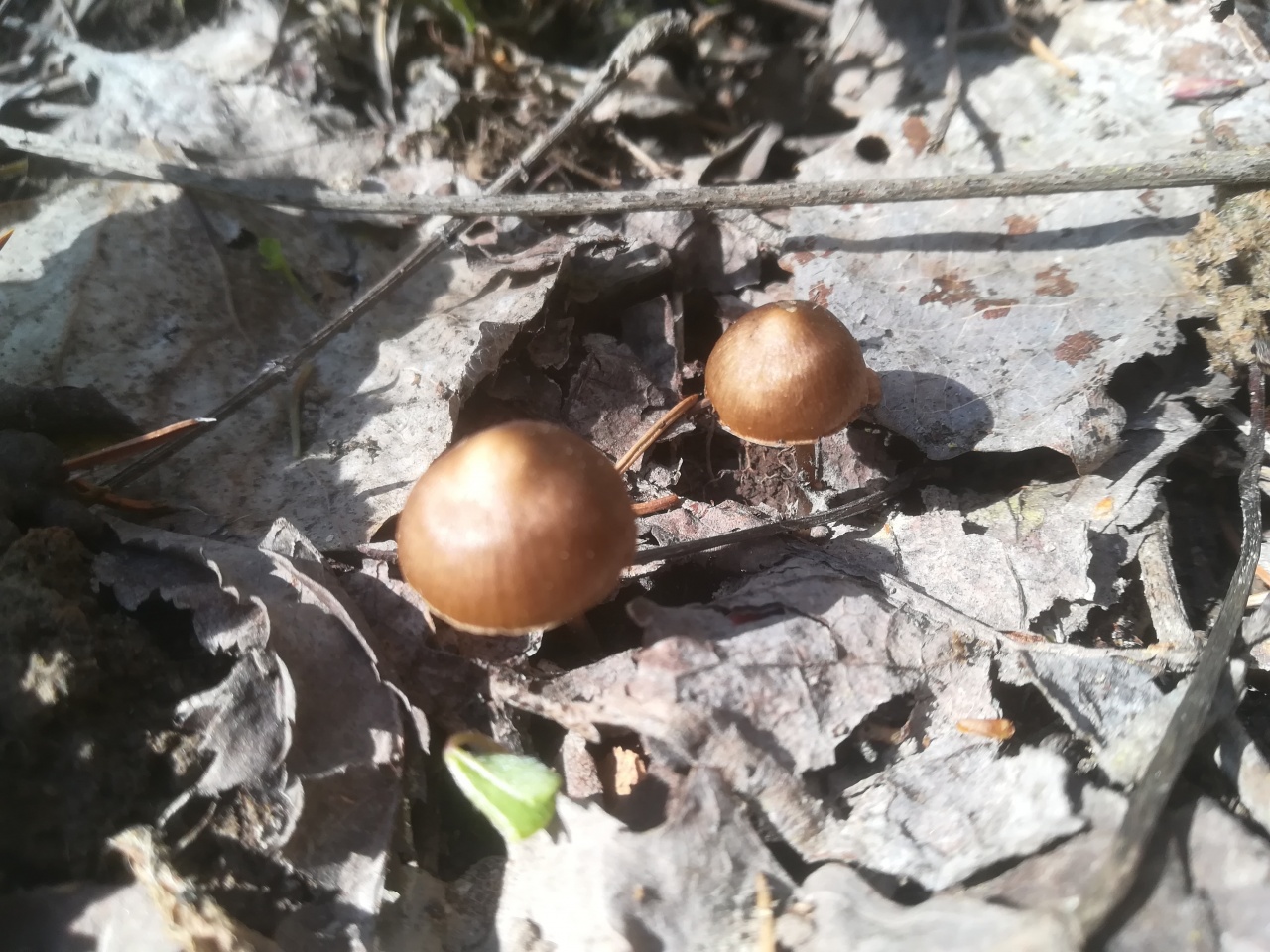
What do mycenes alkaline look like?
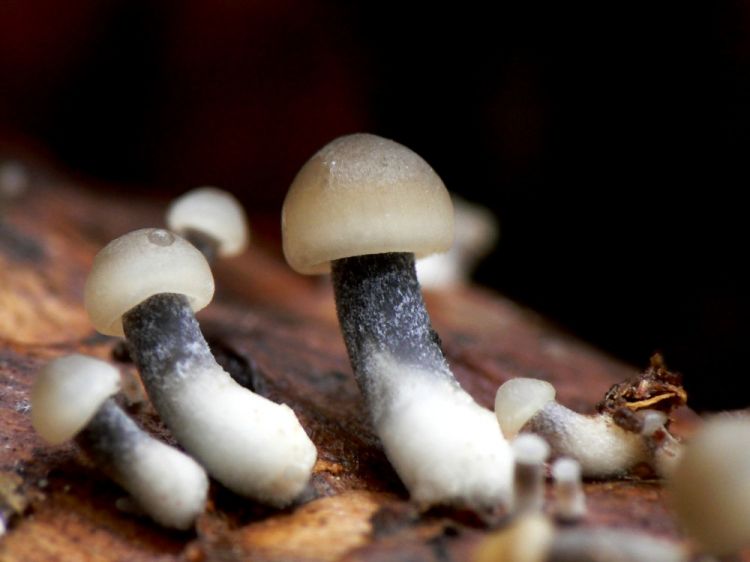
The species forms small fruiting bodies, consisting of a stem and a cap. The shape of the upper part changes during the growing season, the base of the lower half is hidden in the substrate.
The external characteristics of the alkaline mycene are as follows:
- At the beginning of growth, the cap is semicircular with a conical bulge in the center, over time it straightens and becomes completely extended with clear slightly wavy edges, the unevenness is created by protruding plates.
- The minimum diameter is 1 cm, the maximum is 3 cm.
- The surface is velvety smooth, without a mucous coating, with radial longitudinal stripes.
- The color of young specimens is brown with a cream shade, during the growing season it brightens and in adult mushrooms it becomes fawn.
- The center is always different in color, it can be lighter than the main tone or darker depending on the lighting and humidity.
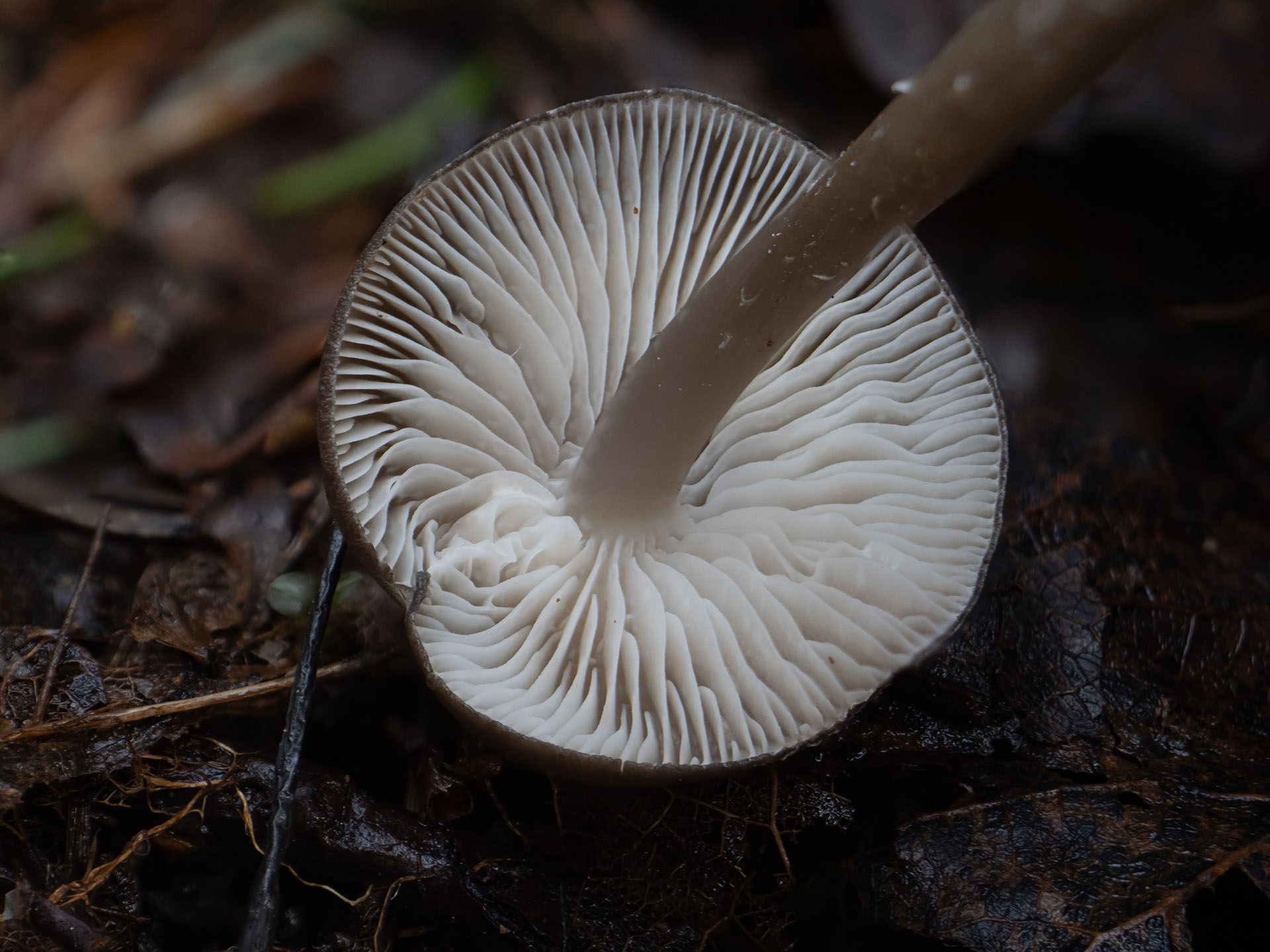
- The lower part is lamellar. The plates are thin, but wide, with a clear border near the stem, rarely located.Light with a gray tinge, do not change color until the aging of the fruiting body.
- The pulp is fragile, thin, breaks when touched, beige in color.
- Microscopic spores are transparent.
- The leg is high and thin, of the same width along the entire length, often most of it is hidden in the substrate. If it is completely on the surface, then thin white filaments of mycelium are clearly visible near the mycelium.
- The structure is fragile, hollow inside, fibrous.
The color is the same with the upper part or a tone darker, yellowish fragments are possible at the base.
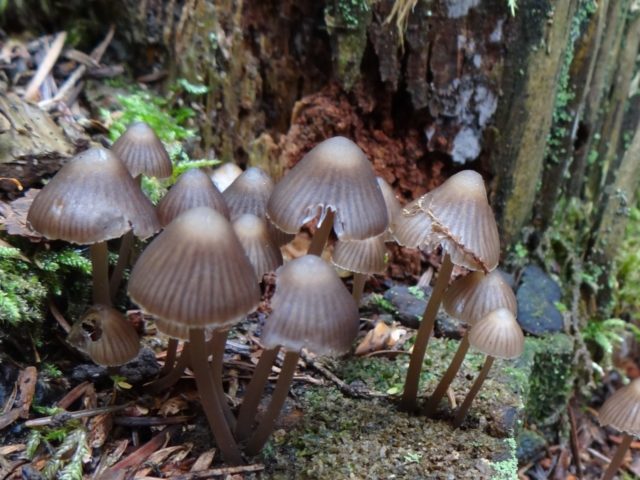

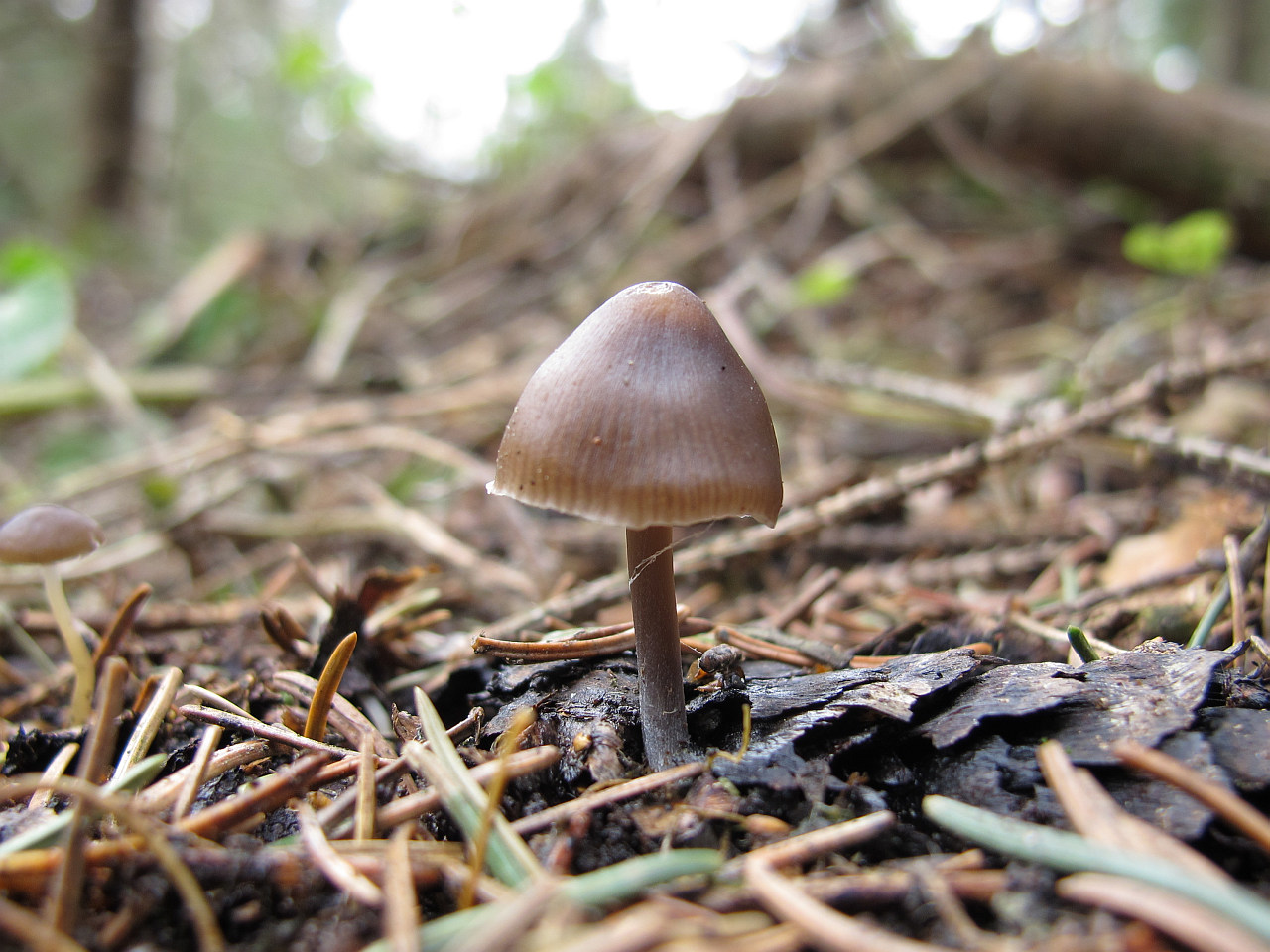
Mycenae of the correct proportional shape, cap type
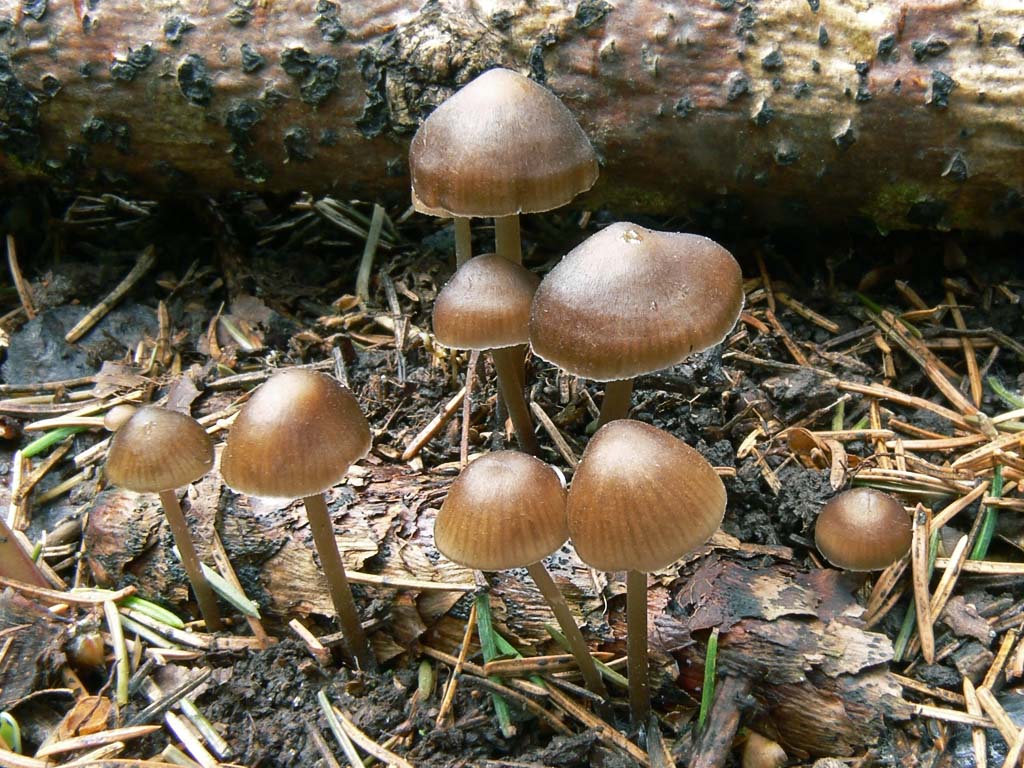
Where do mycenes alkaline grow?
It is difficult to call a common fungus, it forms numerous colonies, but it is rare. It is listed in the Red Book of the Moscow Region as a rare species. The small area is associated with the way mycene grows; it enters into symbiosis with conifers. The peculiarity is that it grows only on fallen fir cones.
If the mushrooms are covered with rotten perennial coniferous litter or are hidden under decaying dead wood, then the lower part of the fruiting body develops in the substrate. Only the caps protrude to the surface, the mushroom looks squat. The false impression is created that the mycelium is located on rotting wood. Grows in all regions and types of forests where spruce predominates. Fruiting is long, the beginning of the growing season is immediately after the snow melts and before the onset of frost.
Is it possible to eat mycene alkaline
The chemical composition of the alkaline mycene is poorly understood; the species with a small fruiting body and fragile thin pulp does not represent any nutritional value. The acrid chemical smell does not add popularity either.
Conclusion
Mycena alkaline is widespread in coniferous and mixed massifs, creates a symbiosis with spruce, or rather grows on fallen cones. Forms dense colonies from early spring to the onset of frost. A small mushroom with an unpleasant smell of alkali has no nutritional value, it is classified as an inedible species.
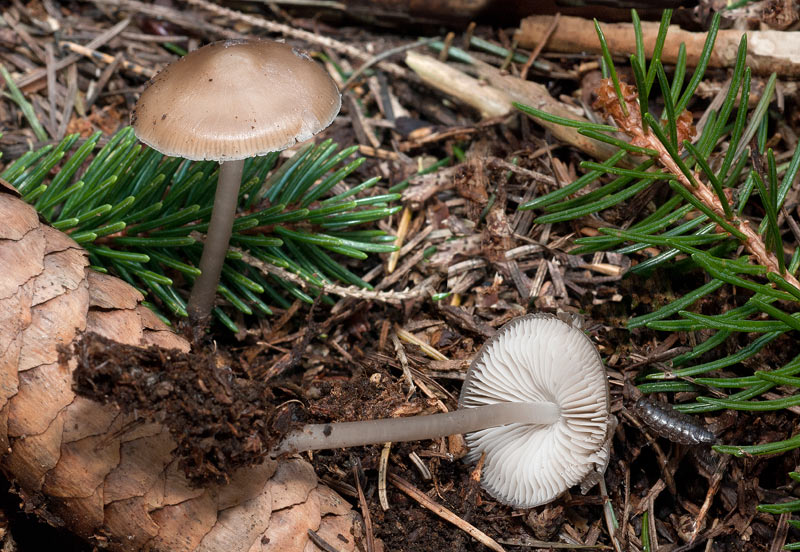
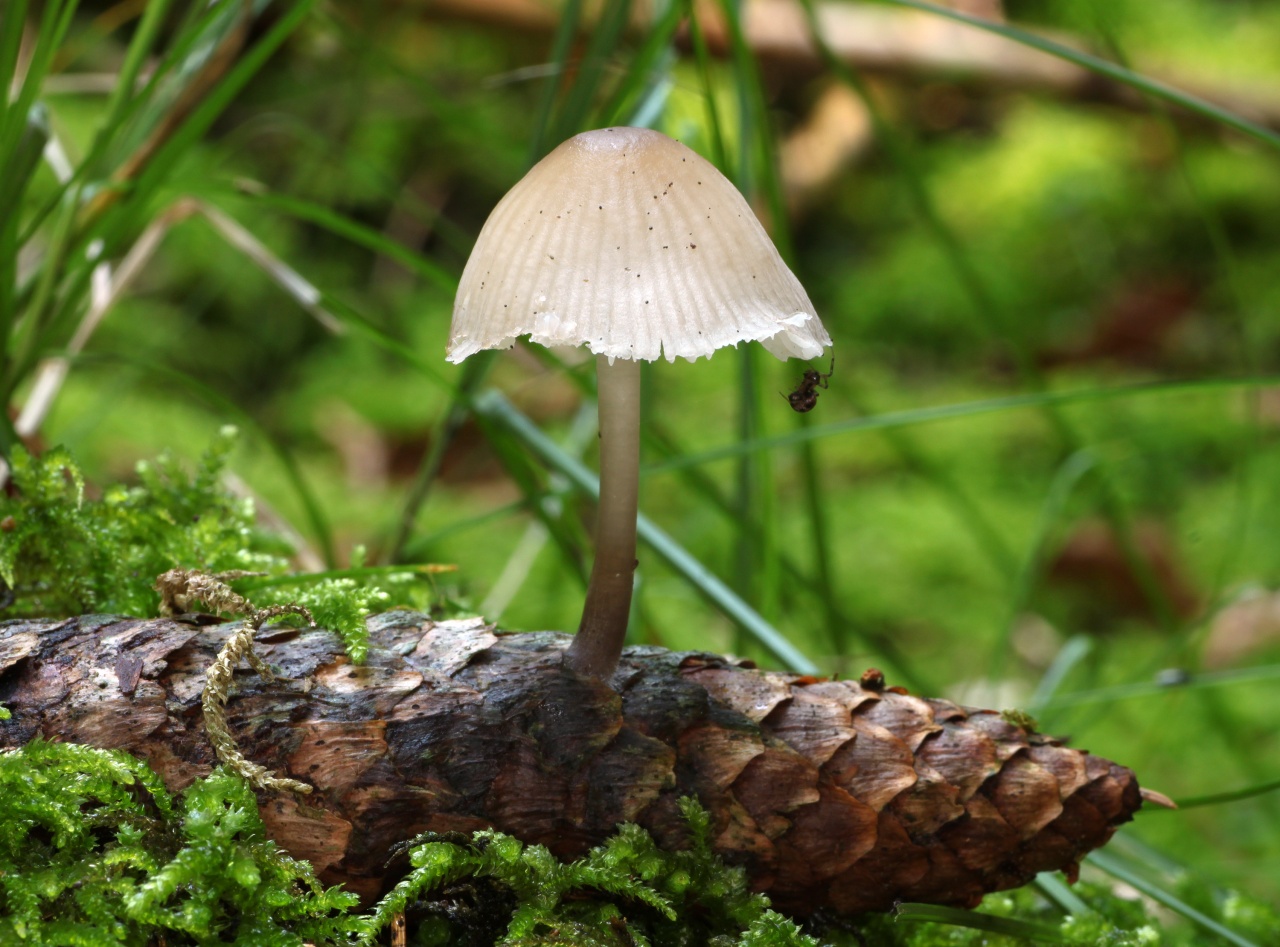
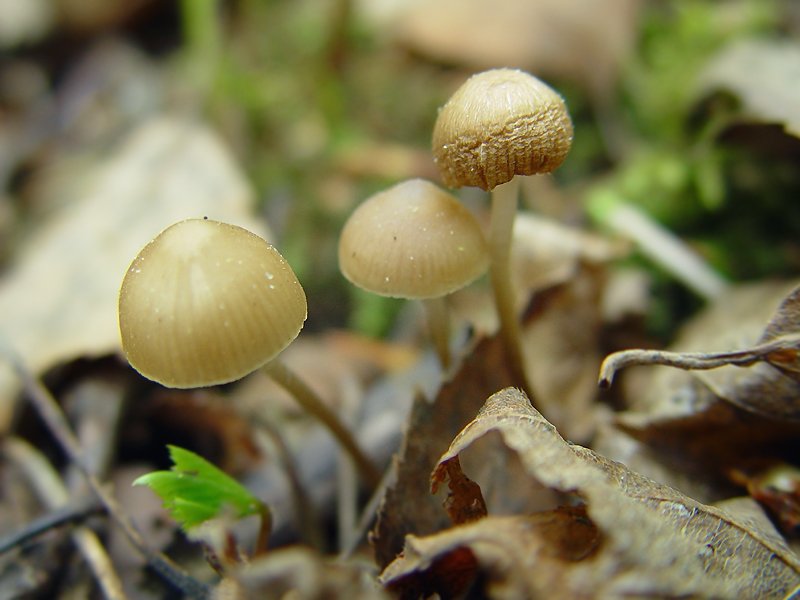
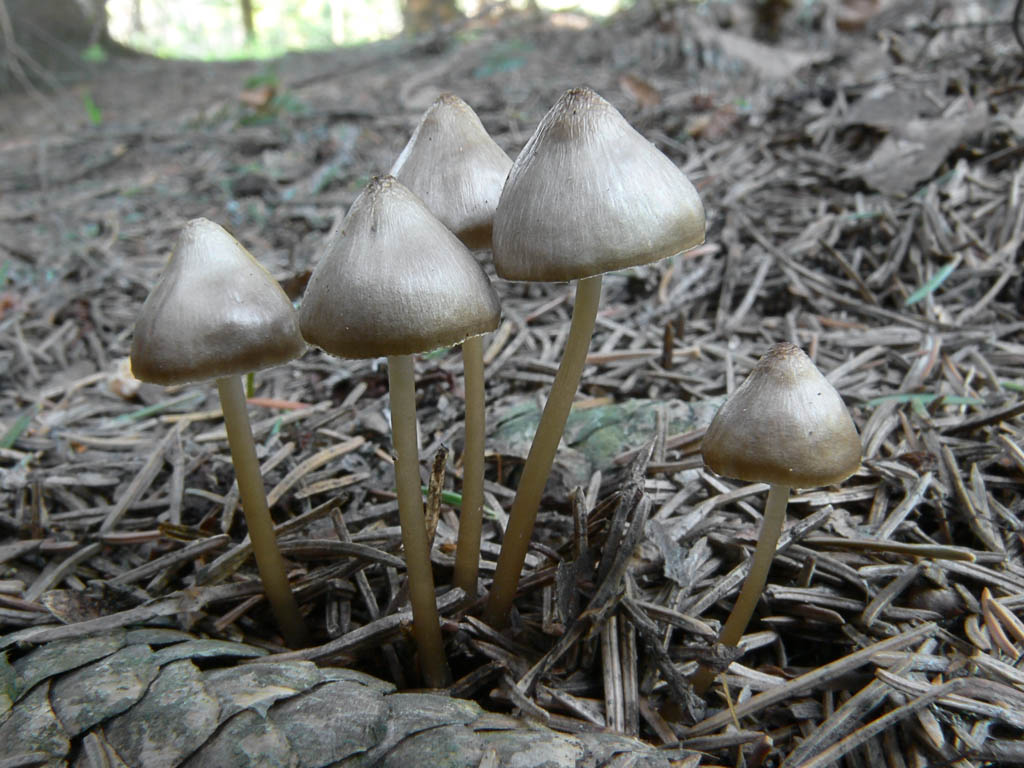
Description of mycena pineapple
In a young mushroom, the cap resembles a hemisphere; over time, it opens and becomes almost prostrate, while a noticeable tubercle remains in the center of the cap. It is a small fungus, its cap is only 3 centimeters in diameter. The color of the cap is creamy brown, but in the process of maturation it fades and becomes fawn.
The pulp is brittle and thin. The pulp has a characteristic alkaline smell. The plates are not often located, they grow to the stem. The color of the plates is bluish, this is a characteristic feature that is characteristic of all mushrooms of this genus. Spore powder is white.
The leg is hollow inside. The color of the leg is yellowish at the base, and the rest of its surface coincides with the color of the cap. At the base of the leg, there are visible growths of mycelium, which look like a cobweb. Most of the leg is hidden in the ground or coniferous litter.

Places of distribution of mycena pineapple
These mushrooms are found settling on spruce cones. Fruiting of mycenae with pineapple begins in May. These mushrooms are common, they are ubiquitous, giving preference to coniferous litter. Pine-loving mycenae are not always detectable, as they sometimes hide in the ground. In this case, the mushroom has a squat appearance.
On the territory of the Moscow region, mycena shishkolyubivaya belongs to a rare species, it is listed in the Red Book of this region.

Evaluation of mycene by pineapple lover
There is no information about the edibility of these mushrooms. But mycena has an alkaline odor, so it has no culinary value. In addition, the size of the pineapple mycena is very small.
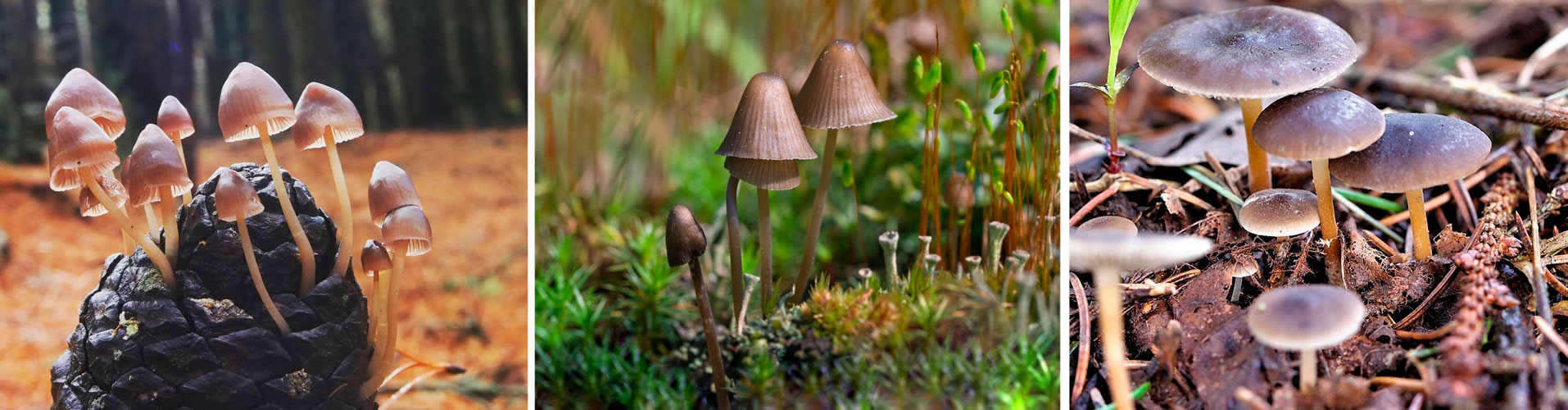
The similarity of the pineapple mycena with other mushrooms
The pineapple mycena bears a resemblance to many small species of mushrooms, which are also generally inedible. But you can distinguish pineapple-loving mitcena by its strong characteristic smell. In addition, it has a thin stem and a characteristic plate shade.

Other mycenes
Mycena Rene is an inedible mushroom. This mycene has an attractive appearance. Her hat is pinkish and the leg is yellow. The hat is small - no more than 2.5 centimeters in diameter.Its shape is spherical at first, and then gradually becomes bell-shaped. The leg is fragile, cylindrical in shape, with a slight edge along the entire surface. The pulp gives off a chlorine smell.
René mycenae grow in colonies, but they do not occur singly. The habitats of these fungi are deciduous and mixed forests. They prefer to settle on decaying wood, most often they can be seen on decaying beech trunks. They bear fruit from May to October.

Hairy mycena is an inedible mushroom. The height of these mushrooms is 1-3 centimeters. The width of the cap does not exceed 4 millimeters. The surface of the fungus is covered with fine hairs. These hairs have a protective function, they scare away animals and insects that can damage the fruit body.
Mycene hairy was found in Australia. These mushrooms are still poorly understood, so there is no information about the period of their fruiting. There is also no information about edibility, places of growth and similarity with other mushrooms.












































