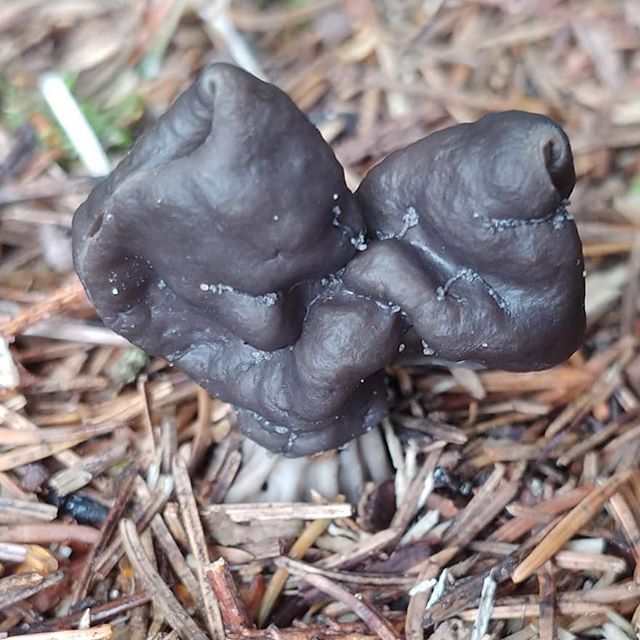
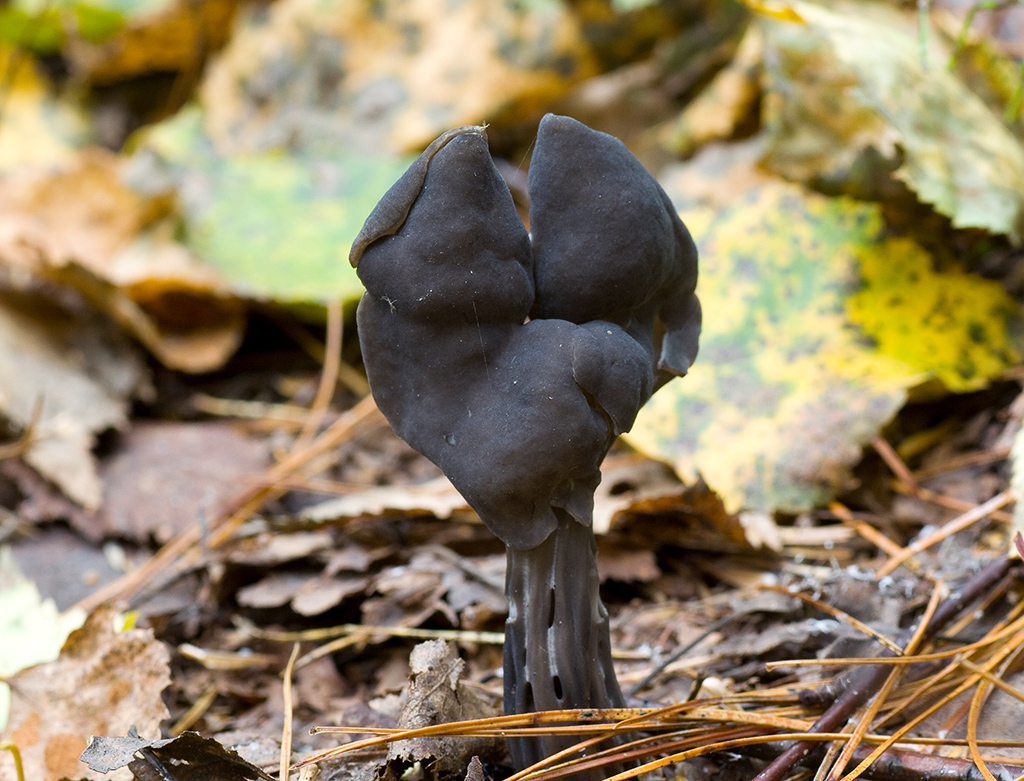
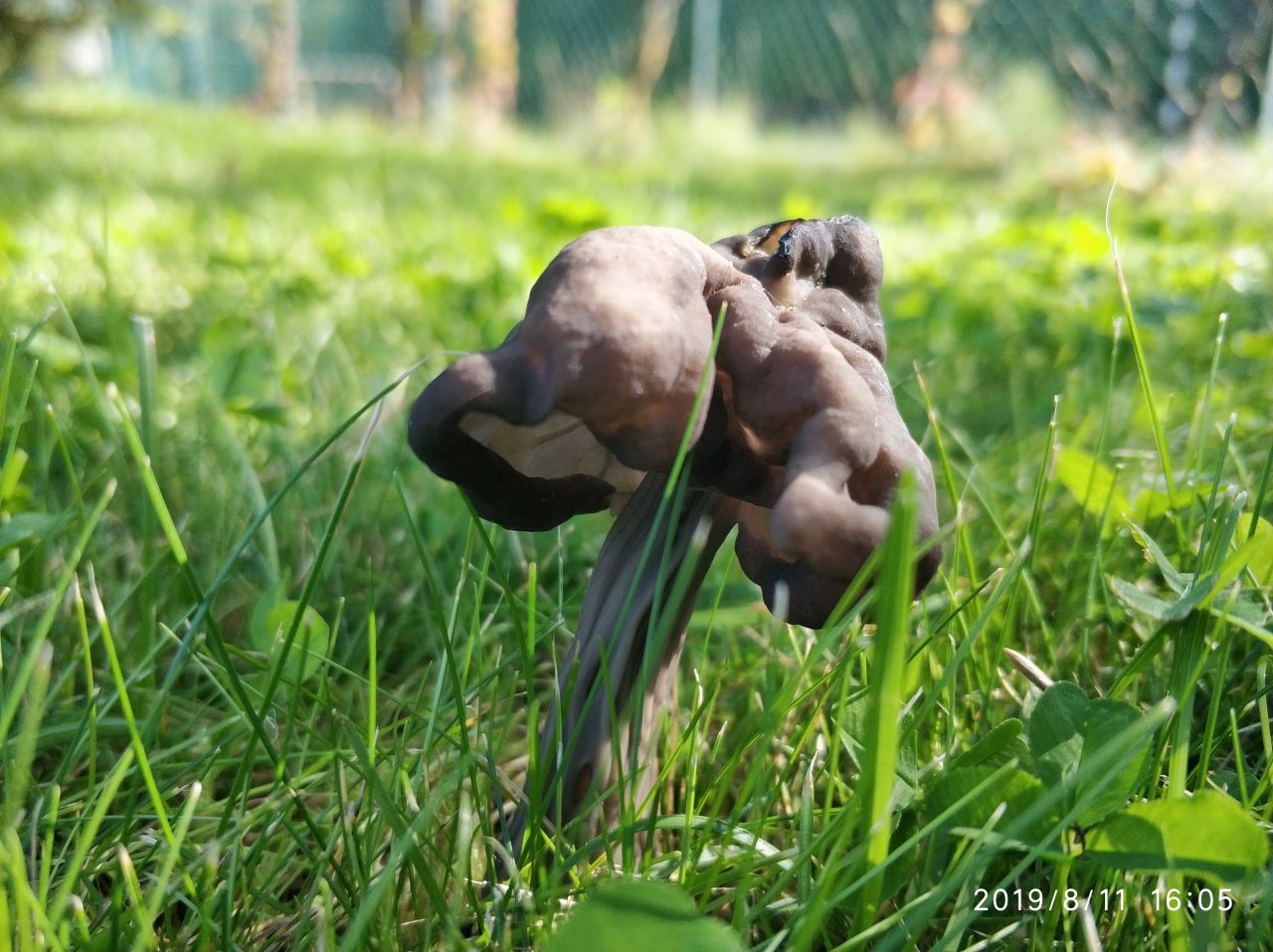
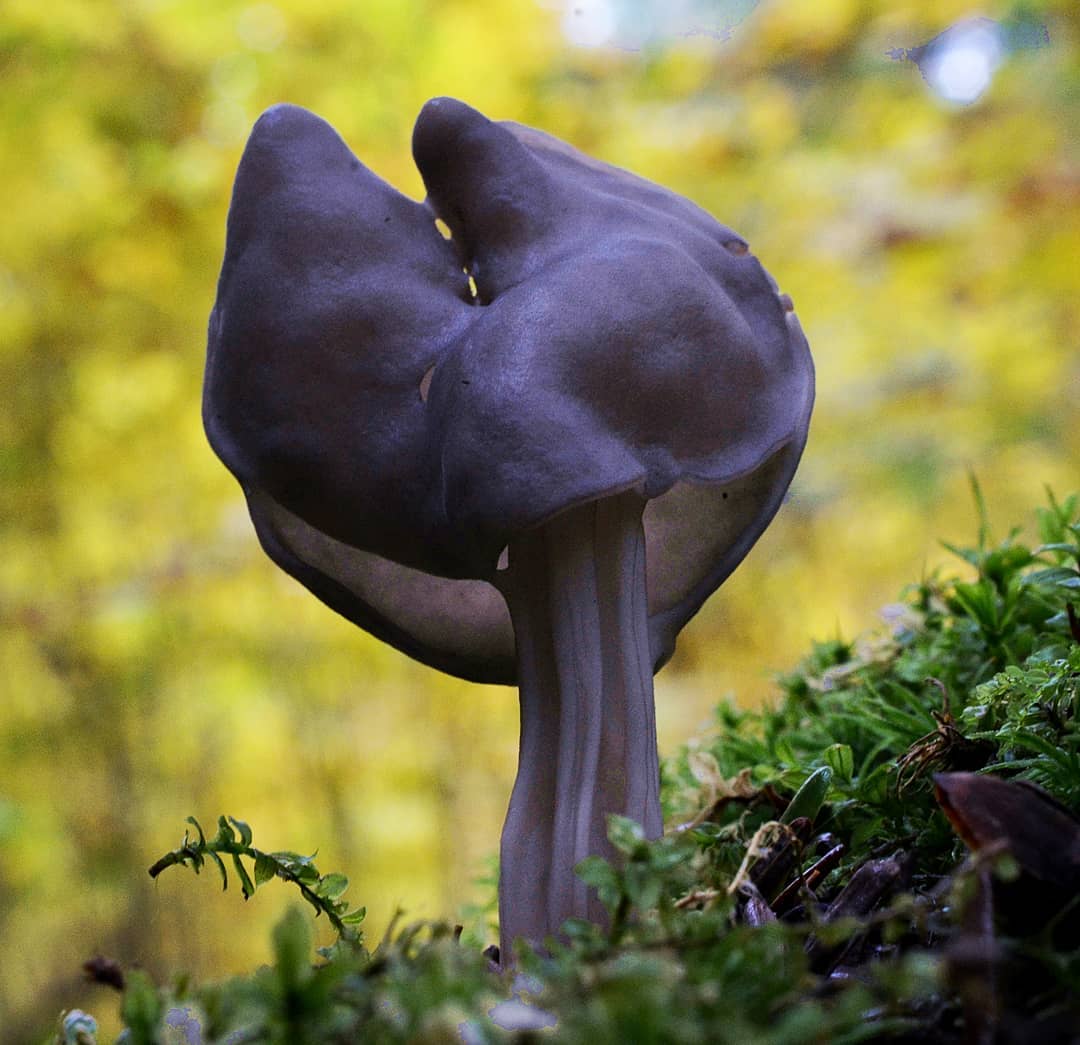
Lobules (Helvetia lacunosa)
Lobules pitted Helvetia lacunosa
Grade
The mushroom is edible. Young specimens are tasty, although somewhat tough.
Agrodelo
Curly loafer
Helvetia crispa (Scop.): Fr. Syn. Helvetia leucophaea Pers
Of the many types of blades that have become quite rare now, you can most often find curly blades.
Fruit bodies 5-12 cm tall, very fragile, hollow, with a white, whitish or pale ocher cap 2-5 cm wide, formed by thin curly lobes.
Stem white, slightly widened at the bottom, 3-8 cm high and 1-2.5 cm thick, with longitudinal ribs and elongated pits. Spores are colorless, smooth, elliptical, 15-18 x 10-12 microns in size. It is found infrequently or even rarely in July-September in deciduous and mixed forests - mainly on clay soil.
Edible, but should not be harvested due to its rare occurrence.
Curly lobster is similar to another species - the edible pitted lobe (Helvetia lacunosa), but in that the fruit body has a gray or gray-brownish color.
Habitat: The fungus is very widespread, the first mushrooms appear in July, but the main "layer" is in mid-September. It grows both in deciduous and mixed forests on calcareous and neutral soils, often on the edges of the grass and under shrubs on clay-sandy soils. Alone, the mushroom rarely comes across, mainly in small groups.
Description: Fruit body: 5-9cm. Hat: 2-3 (5) cm in diameter, curved, two- or four-lobed with a free wavy-curly edge (adhered in places), light yellow or ocher. Spore powder is white.
It is irregular in shape, wavy, mainly has a lobular-patchwork structure. Often the edges of the "cap" hang down and grow to the stem.
The upper side (fruit layer) is whitish, cream or dirty ocher, later slightly brownish, smooth. The underside is more or less equally colored, slightly fluffy, 1-4cm thick and up to 10cm long.
Stem: usually thin, cylindrical, sometimes thickened downwards or somewhat swollen. Its whitish surface is longitudinally ribbed and slightly transversely sinewy, with deep longitudinal grooves, pitted. The inside of the leg is oblong-chambered.
Pulp: waxy in appearance, whitish at a young age, cream-colored by old age, very fragile, without any special smell or taste.
Conditionally edible mushroom of the fourth category: hard mushroom. It is advisable to boil it before using it.
Doubles: Similar to helvella lacunos. These mushrooms often grow in the same places. Lobules are more dark-colored, usually gray-brown or gray-black, and curly lobes have neither gray nor black tones.
Notes: The word crispus in the name of the mushroom means "curly".
In this article we will try to consider the most common types of downloads. We bring to your attention a description and a photo of podgruzdka. Podgruzdok is often found in conifers, deciduous and mixed ...
The funnel is horn-shaped. This mushroom does not have a cap, legs and plates as such, but is a funnel, sometimes with strongly curved edges, which can pass for a cap with a smooth or che ...
Elm lyophyllum, or elm oyster mushroom, is a rather rare edible lamellar mushroom in Russia. Elm lyophyllum grows in small groups, sometimes in bunches ...
Oyster mushroom is one of the most common mushrooms cultivated in artificial conditions. In natural conditions, it is found on almost all continents. Refers to wood ...
Deer roach (Latin Pluteus cervinus) is an edible mushroom from the genus Pluteaceae family.
More information on the topic:
Long-legged lobe: what it looks like, where it grows, photo
| Name: | Long-legged lobe |
| Latin name: | Helvella macropus |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Synonyms: | Helwella long-legged, Macropodia long-legged |
| Specifications: | |
| Systematics: |
|
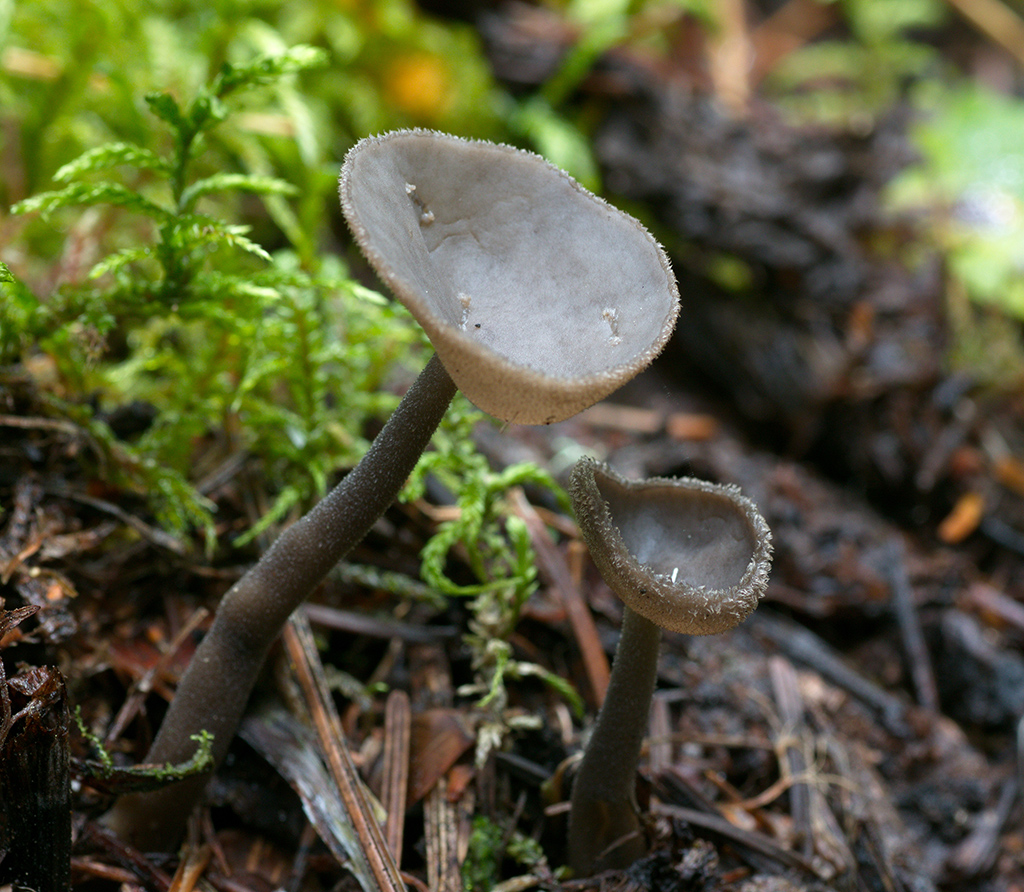
Long-legged lobe is an unusual mushroom of the Helwell genus. Having met his family in the forest, you might think that in the middle of the clearing, someone has placed a service. This is because the top of the mushroom resembles a glass in which morning dew collects. This species is also called macropodia and long-legged Helvella, and in the official reference books of mycologists it can be found as Helvella macropus.
How long-legged lobes look like
The fruiting body of this species consists of a pseudo cap and an elongated stem. The diameter of the upper part reaches 2-6 cm. Its shape is irregular, round-disc-shaped with the edges turned upwards, which in appearance resembles a glass. However, there are specimens similar to a saddle, since their pseudo-hat is flattened on both sides. Inside, the surface is smooth and light in color, and on the outside it is fuzzy-pimpled, and its color is darker, ranging from brown to purple. Due to the structure of the upper part, water is often collected in it.
The flesh of the long-legged lobe is watery thin. It crumbles easily even with little physical impact. It has a gray tint at the fracture, which does not change upon contact with air. There is no pronounced mushroom smell.
The leg reaches a length of 3-6 cm, depending on the age of the mushroom. The bottom part is 0.5 cm thick. Its shade is light gray, like the inside of a pseudo hat. The surface can be smooth or slightly bumpy. At the bottom, the leg is slightly thickened. When cut, you can see the cavity inside.
The hymenophore is located on the outside of the upper part. The spores are white in color, their size is 18 - 25 × 10.3 - 12.2 µm. They are elliptical or spindle-shaped.
Often, the leg of this lobule narrows in the upper part.
The long-legged lobe has a pronounced characteristic feature that sets it apart from other bowl-shaped relatives - an elongated narrow stem. However, it can be distinguished from less common representatives of this genus only by microscopic signs in laboratory conditions.
Where long-legged lobes grow
Long-legged lobe belongs to the category of saprotrophs, therefore, certain favorable conditions are necessary for its growth. For nutrition, he needs a substrate based on organic compounds, which are formed as a result of the decomposition of plant remains. Therefore, most often the long-legged lobe grows on half-rotten stumps and tree trunks, which are in the last stage of decomposition. It can also grow directly on soil rich in organic matter, in grass and moss.
This species grows in families of 4-10 specimens, but in exceptional cases it can be found singly.
This species can be found in mixed and deciduous forests in the central part of Russia and European countries. The representative belongs to the category of rare mushrooms.
The fruiting period of long-legged lobe begins in mid-summer and lasts until early October. Its duration depends on weather conditions.
Is it possible to eat long-legged lobes
Long-legged lobe is considered inedible. You cannot eat it even after preliminary heat treatment. Although this fact remains questionable, since special studies in this direction have not been carried out.
But, judging by the appearance and prevalence of long-legged lobe, it is unlikely that a mushroom picker (even a beginner) will want to collect and harvest it.
Conclusion
The long-legged lobe is a bright representative of the Helwell genus. It is considered little known among lovers of quiet hunting, as it belongs to the category of inedible. But it enjoys increased interest among mycologists.
This mushroom can rarely be found in the forest, but if you managed to find it on occasion, you should not pluck it out of idle interest. It is better to admire him from the outside and allow the disputes to fully mature, which will allow him to leave behind offspring.
Edibility
In a number of authoritative sources, there is information that curly loafer or curly helvella is a conditionally edible mushroom that requires prolonged digestion or prolonged drying before use and belongs to 4 taste categories. It is advisable to soak the mushrooms in cold water before boiling, since the leg consists of cavernous depressions and folds, insects may be inside.
However, some domestic experts regard it as inedible, and abroad consider it poisonous, considering that mushrooms may contain carcinogenic substances. Apparently, the peculiarities of the chemical composition of the pulp of fruit bodies in specific places of growth are affected.
Ultimately, it is safer and safer to assume that curly helwell is inedible. What is the point of risking your health to try tasteless mushrooms that have lost all taste after long digestion? You decide.
Folded "horned" caps, furrowed high legs immediately distinguish curly lobes from other forest mushrooms. Unusual appearance in this case is a warning that this conditionally edible species requires careful heat treatment before consumption.
Related Videos
mushrooms in the forest - white-legged lobe MOV Rare mushrooms in the forest. Gray lobe. Mushrooms of the season 2017. Part 13 (my new items) X
Categories
- Avocado
- Oranges
- Watermelon
- Banana
- Barberry
- Porcini mushroom dishes
- Oyster mushroom dishes
- Mushroom dishes
- Milk dishes
- Umbrella Dishes
- Chanterelle dishes
- Honey mushroom dishes
- Camelina dishes
- Champignon dishes
- Hawthorn
- Cowberry
- Grape
- Growing
- Hallucinogenic
- Blueberry
- Grapefruit
- Mushroom places
- Mushroom soups
- Mushrooms for the winter
- Other
- Melon
- Hedgehog
- Frying
- Honeysuckle
- Blank
- Freezing mushrooms
- Salting
- Fig
- Irga
- Dogwood
- Strawberry
- Cranberry
- Gooseberry
- Kumquat
- Lemon
- Raspberries
- Mango
- Tangerines
- Passion fruit
- Pickling
- Local berries
- Cloudberry
- Inedible mushrooms
- Sea buckthorn
- Return
- Mushroom poisoning
- Pitahaya
- Pizza with mushrooms
- Salads
- Currant
- Currant
- Mushroom Picker Handbook
- Drying
- Edible mushrooms
- Conditionally edible
- Fruits
- Blueberry
- Rose hip
- Exotic berries
- Berries
- Poisonous
Recent Entries
- Pickled mushrooms champignons recipe
- How to plant blackberries
- Lasagne with mushrooms
- How to tie raspberries
- Pumpkin is a berry or vegetable
Description
Curly lobster (Helvella crispa) is a marsupial mushroom, about the edibility of which you can find different opinions. A number of mycologists classify it as conditionally edible. At the same time, in foreign sources, it is ranked as poisonous, and in a number of domestic sources - as inedible. Sometimes this mushroom is also called helwella curly or ribbed.

The species has the following differences:
- the saddle-shaped folded cap is deeply dissected into 2-4 lobes with hanging, uneven, wavy edges. The color is beige-waxy or light ocher, the underside is slightly darker, has a yellowish tint and a velvety texture. The smallest diameter of the cap is 2 cm, the maximum is 6 cm;
- white spores;
- the light, hollow, fusiform leg is often curved. Its maximum dimensions are 8 cm long, 3 cm thick. The surface is furrowed with longitudinal folds and depressions, ribbed projections grow into the cap;
- thin white-waxy pulp, watery, brittle, with a weak mushroom odor.
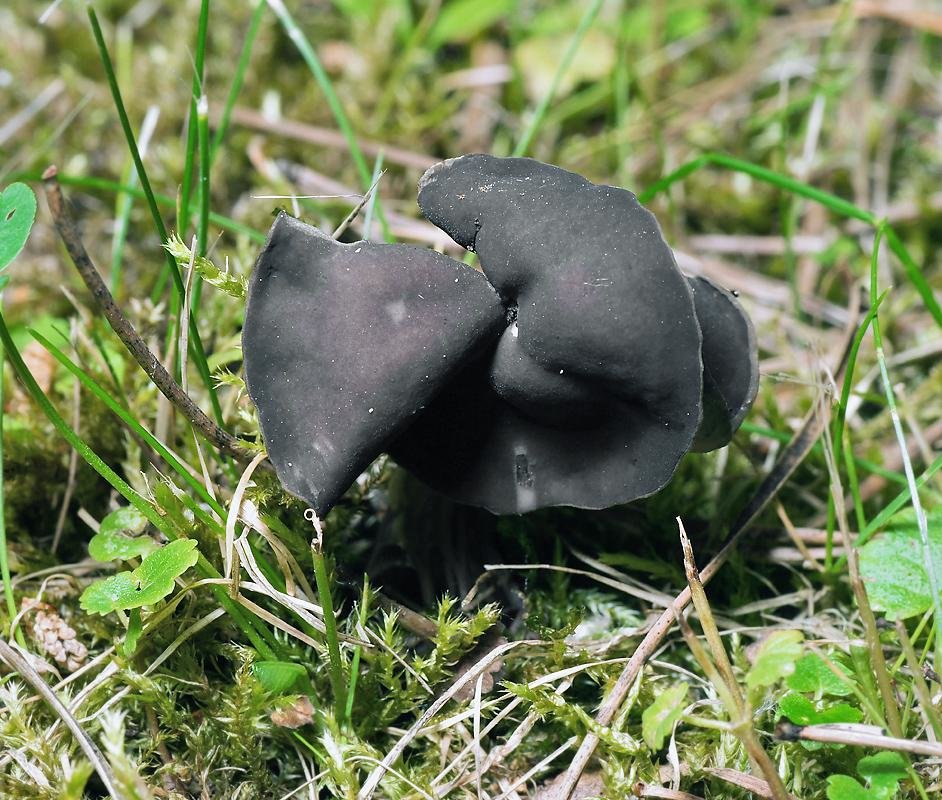
Black loafer: photo and description
| Name: | Black lobe |
| Latin name: | Helvella atra |
| Type of: | Inedible |
| Specifications: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
Black lobster (Helvella atra) is a mushroom with an original appearance, belonging to the Helwell family, from the Lobster genus. Other scientific name: Black leptopodia.
Black lobe is extremely rare in our forests.
What does a black paddle look like
Only the fruiting bodies that have appeared have the appearance of a kind of saddle on a pedicle or a fractured disc. The hat has a rounded centerline fold, whose outer corners are noticeably raised above the horizontal. The halves of the cap are strongly lowered down almost in a straight line or slightly rounded inward, the edge is often accreted to the stem. As it develops, the surface bends in bizarre waves, changes to shapeless lumpy. The edges can be noticeably turned outward, exposing the inner surface, or, conversely, hug the leg with a kind of cape.
The surface is matt, dry, slightly velvety. Gray to dark gray with brown or bluish tinge and shapeless blue and black spots. The color may darken to brownish black. Inner surface, hymenium, smooth or slightly wrinkled, with pronounced bristles, brownish or gray in color. The pulp is brittle, loose, tasteless. Its color is transparent gray, like wax. The diameter can be from 0.8 to 3.2 cm. The spore powder is white.
The leg is cylindrical, expanding towards the root. Dry, pubescent in the upper part, with longitudinal stripes. The color is uneven, noticeably lighter at the base. Color from beige, gray-cream to dirty bluish and ocher-black. The length is from 2.5 to 5.5 cm, the diameter is 0.4-1.2 cm.
Legs are often crooked, with shapeless dents
Where do black blades grow
Distributed in Japan and China, where it was first found and described. Then it was discovered on the American continent and in other regions of Eurasia. It is extremely rare in Russia, and it is a great success to see it.
Prefers deciduous forests, birch forests. Sometimes its colonies are found in pine forests, spruce forests. It grows in large and small groups, with loosely located individual mushrooms. Loves dry places, sandy soils, grassy meadows in gardens and parks. The mycelium bears fruit from June to October.
The black lobe feels great on rocky areas.
Is it possible to eat black blades
Black lobster is classified as an inedible mushroom due to its low nutritional value. There is no scientific data on its toxicity. It can be confused with other members of the Helwell species.
Lobules are pitched. Inedible. It has a larger size, fleshy thick leg.
The legs of these fruiting bodies have a characteristic cellular shape.
Lobule petsytsevidny. Inedible. It differs in a noticeably upward-curled edge of the cap.
The flesh of the cap is so thin that it shines through
White-legged lobe. Inedible, toxic. It has a pure white or yellowish stem, a light hymenium coloration and a blue-black cap.
Conclusion
Black lobster is an interesting rare mushroom from the Helwell family, a fairly close relative of pets. Inedible, according to some reports, toxic. It has an extremely low nutritional value, so you shouldn't risk your health. In Russia, several colonies of this fungus have been found in the region of Novosibirsk. Its habitat is China, Europe, North and South America. Grows in deciduous, sometimes coniferous forests from early June to mid-October.