Edible talkers with photos
In order not to confuse edible varieties with poisonous ones, they need to be able to distinguish them by their appearance. Distinctive features and description of edible varieties with photos are presented below.
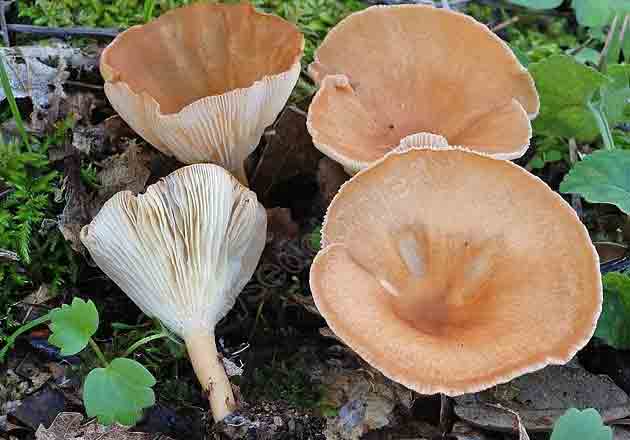
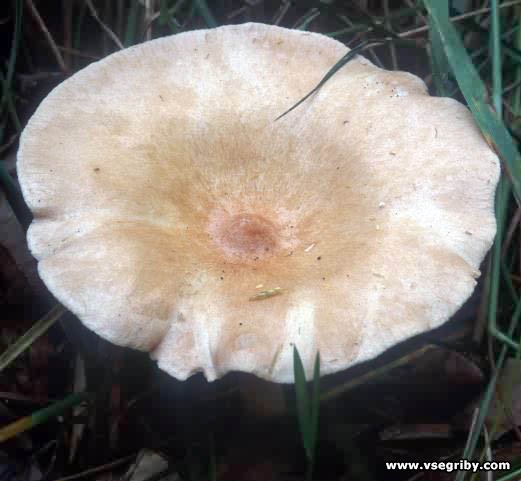
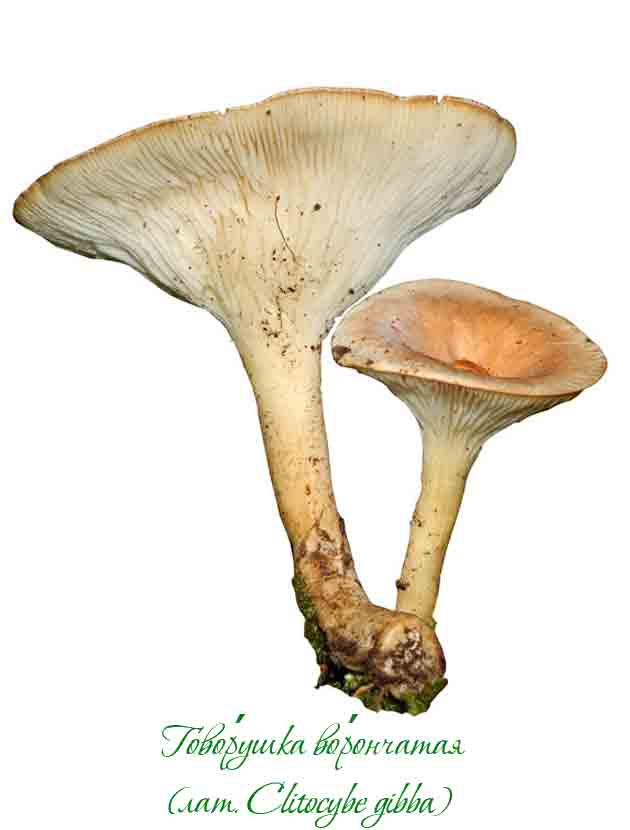
Bent talker
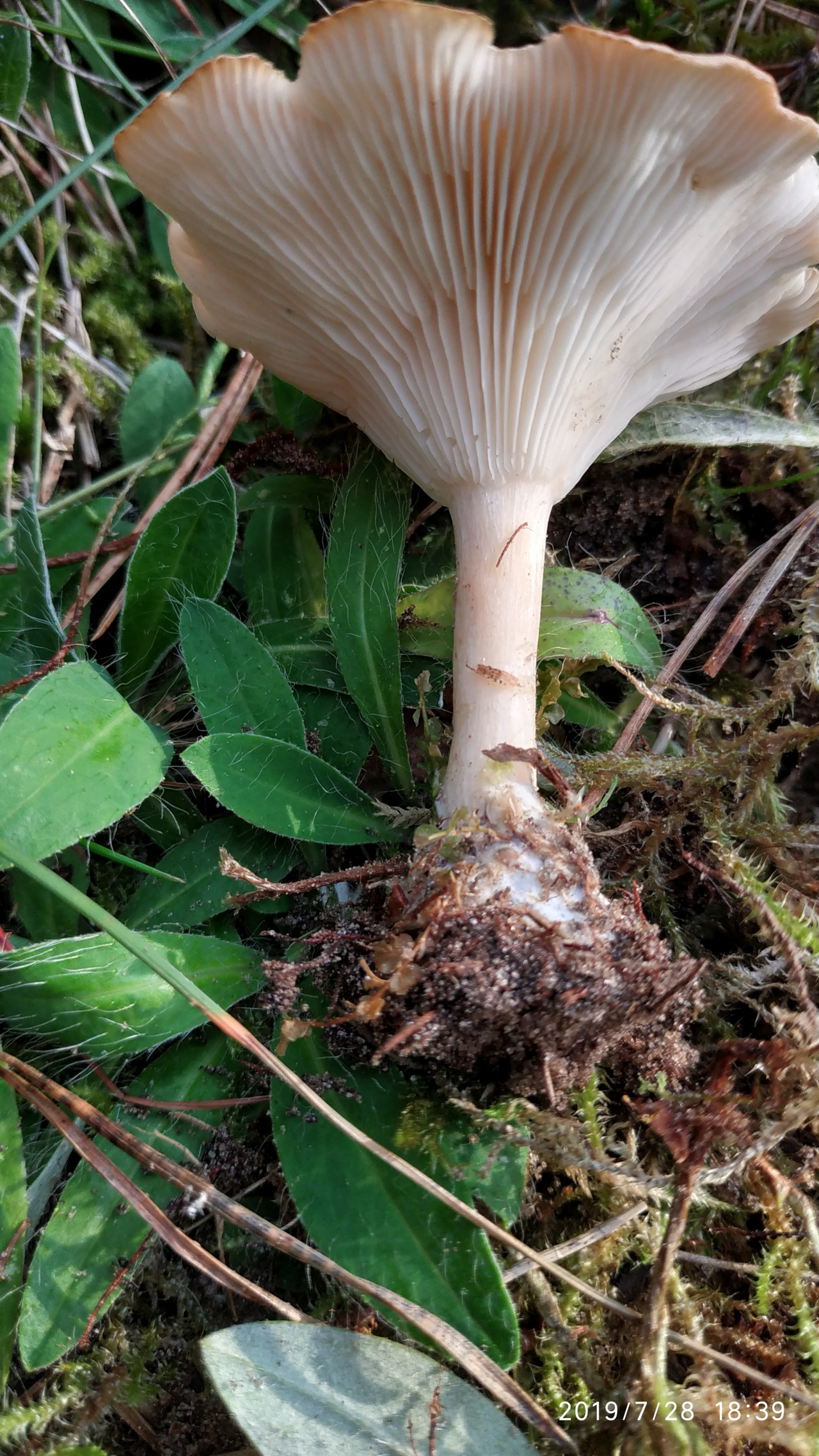
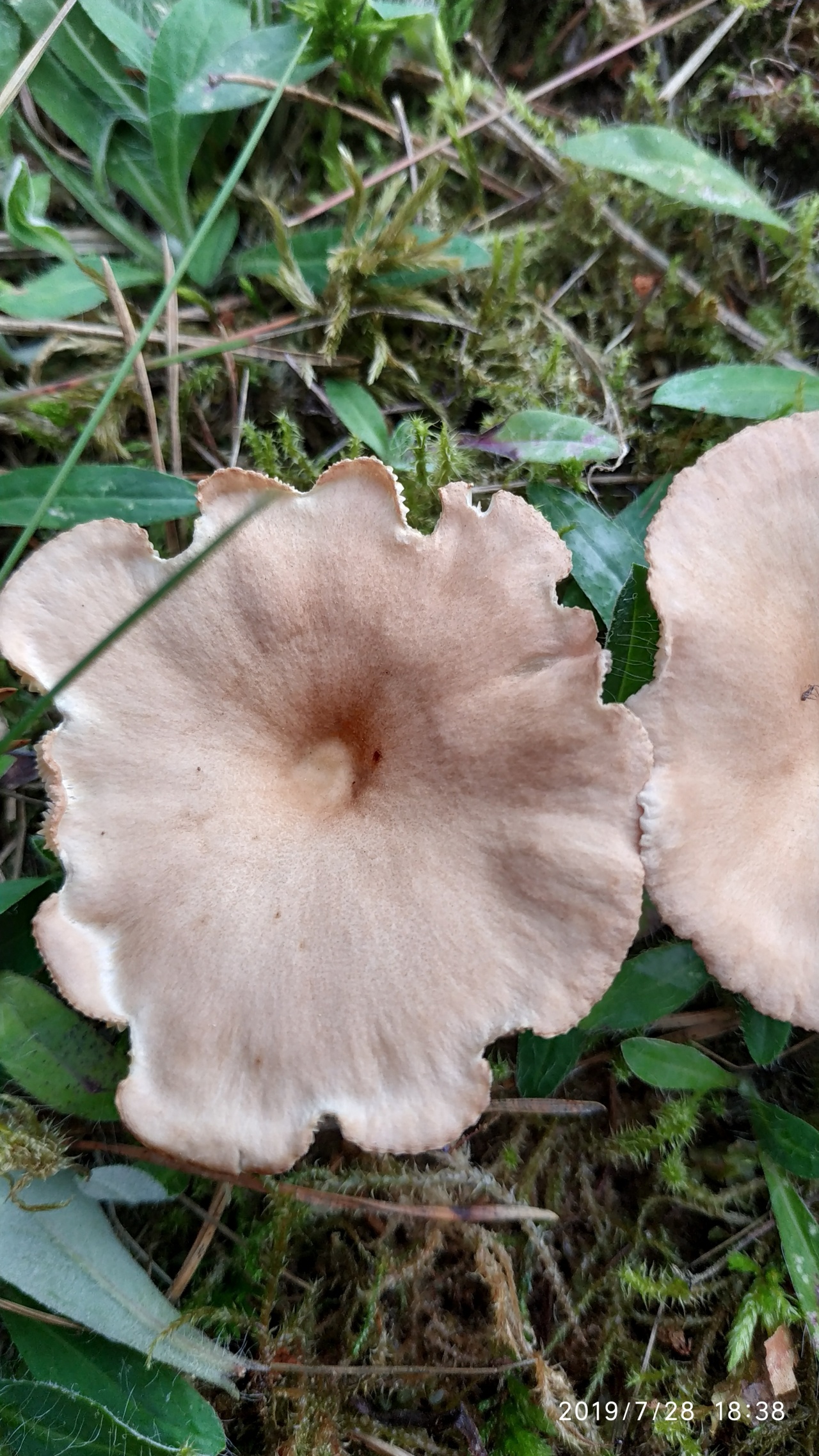
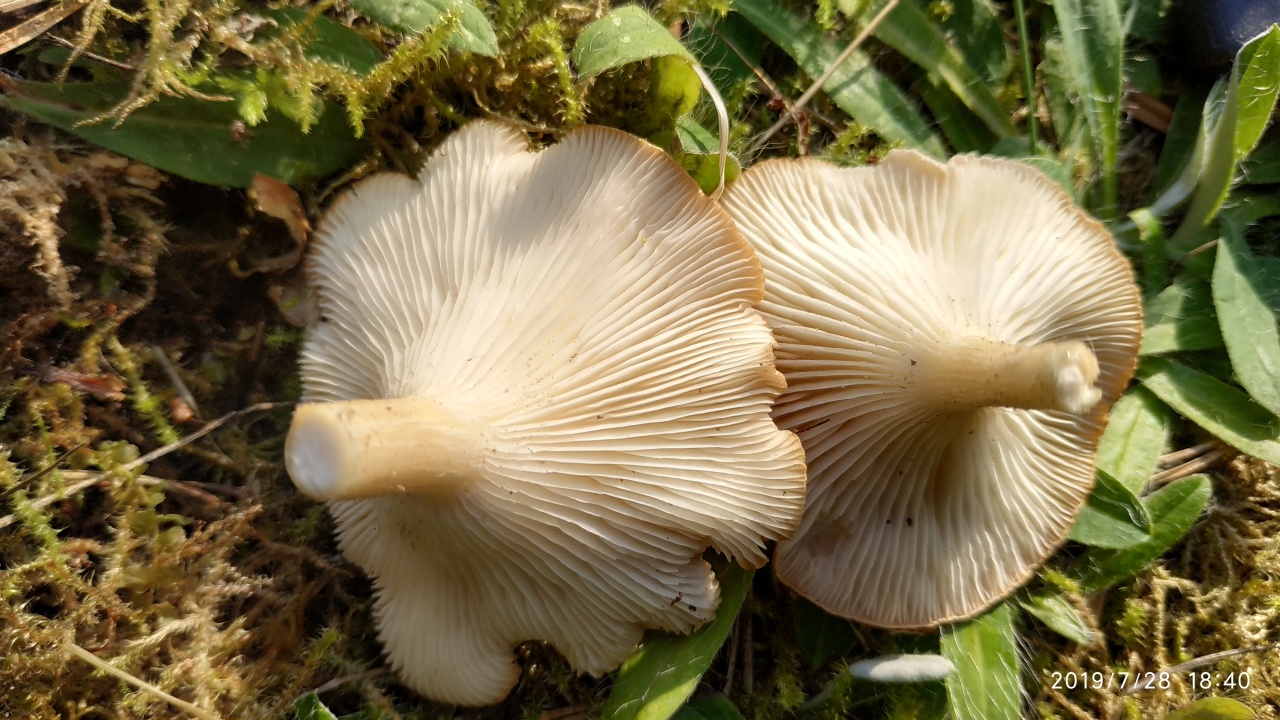
This mushroom grows both singly and in large groups-circles, which are localized mainly at the edges of the forest, near roads and in thickets of bushes. The mushroom has a large smooth cap, the diameter of which often exceeds 12 cm. It is dirty yellow in color. The plates are white, gradually acquiring a pinkish tint.
The leg is dense in consistency and high, about 15-20 cm. The color is the same as the cap. The pulp is dry. In young mushrooms, it is white, and over time it becomes brown and acquires an unpleasant odor, therefore only young fruiting bodies need to be collected. The peak yield occurs at the end of summer and lasts until October. For cooking, only young mushrooms are used, which are pickled or boiled.
Gray
The hat of this variety is inferior in size to the previous one and has an average diameter of 8-15 cm. It is thick and fleshy in consistency, and can be in different shades of gray in color. The plates are also characterized by a gray tint. The leg is wide, dense, low, matching the color of the cap.
The pulp exudes a soap-like aroma. Most often, the mushroom is found in mixed and coniferous forests in large groups. It can be found in the forest from late summer to November. Before salting or pickling a gray talker, it must be thermally treated - boil for 30-40 minutes in boiling water.
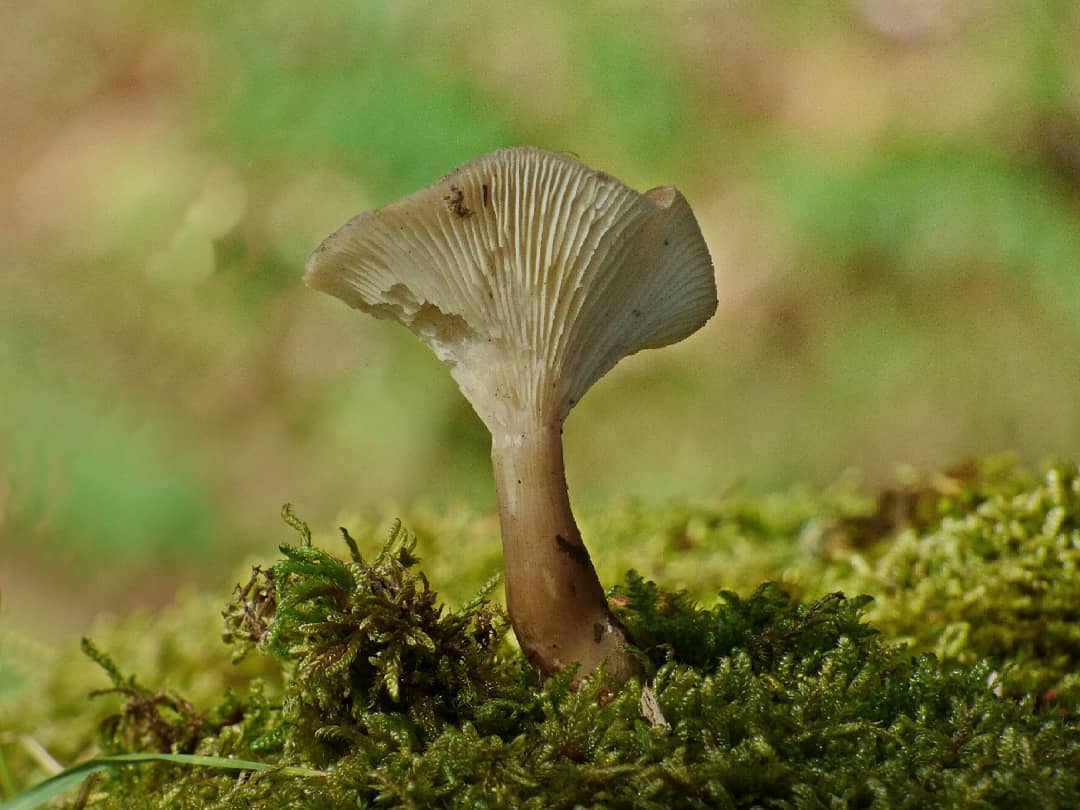
Goblet
A special feature of this variety is a goblet-shaped hat with a diameter of about 7-8 cm. It has edges wrapped inward, a glossy surface and is painted brown or ash gray. There are few plates, they are brown in color. The pulp is thin, watery in consistency.
The leg is high, about 10 cm, part of the ground is fluffy and widened. You can meet the goblet variety in coniferous, mixed, deciduous forests, where the forest litter is rich in organic matter. The peak of fertility occurs in August and lasts until September inclusive. They eat the mushroom boiled or salted.
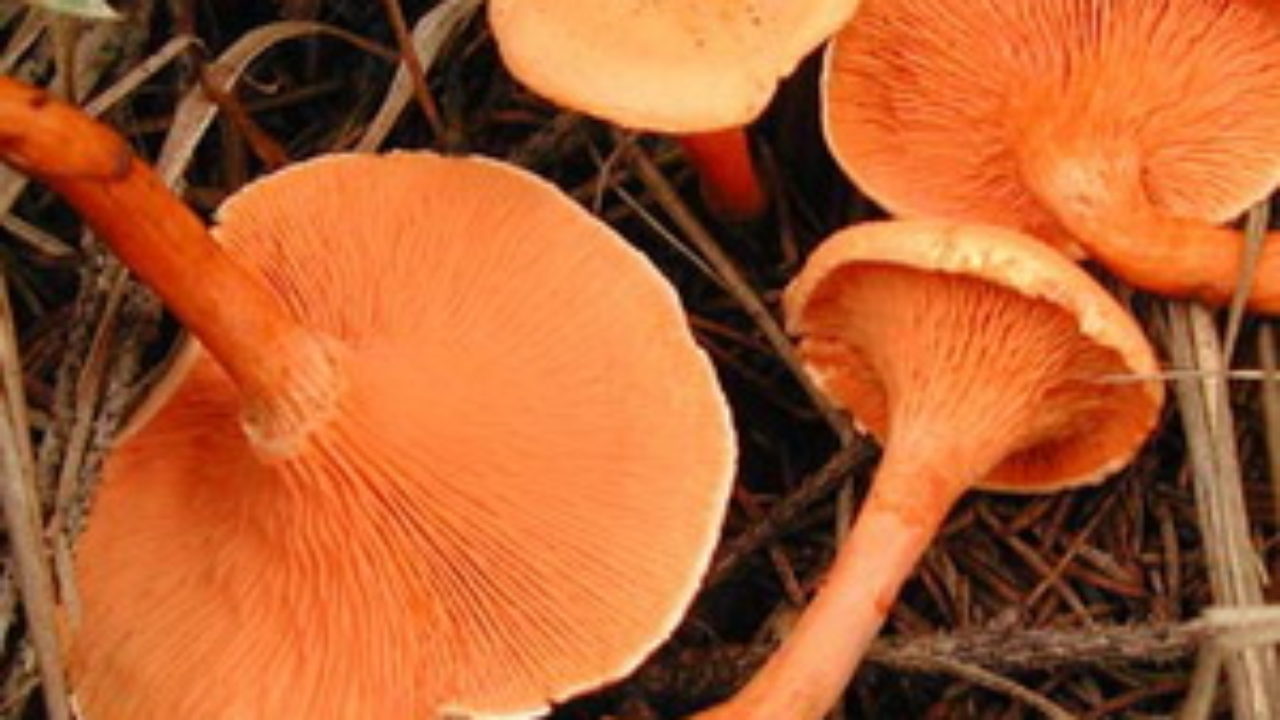
Orange
Orange talkers often grow in small groups or singly. Fruiting from late summer to October. They are found in the humid part of coniferous or mixed forests, the litter of which contains a large amount of moss and fallen rotten leaves.
The mushroom is small in size, yellow-orange in color, gradually becoming faded. The plates smoothly pass to the leg, when pressed, they change color to a darker one. The leg is low, on average 5 cm, rounded, becomes thinner closer to the ground. The pulp is yellowish, odorless. They eat only a hat that is fried or boiled.
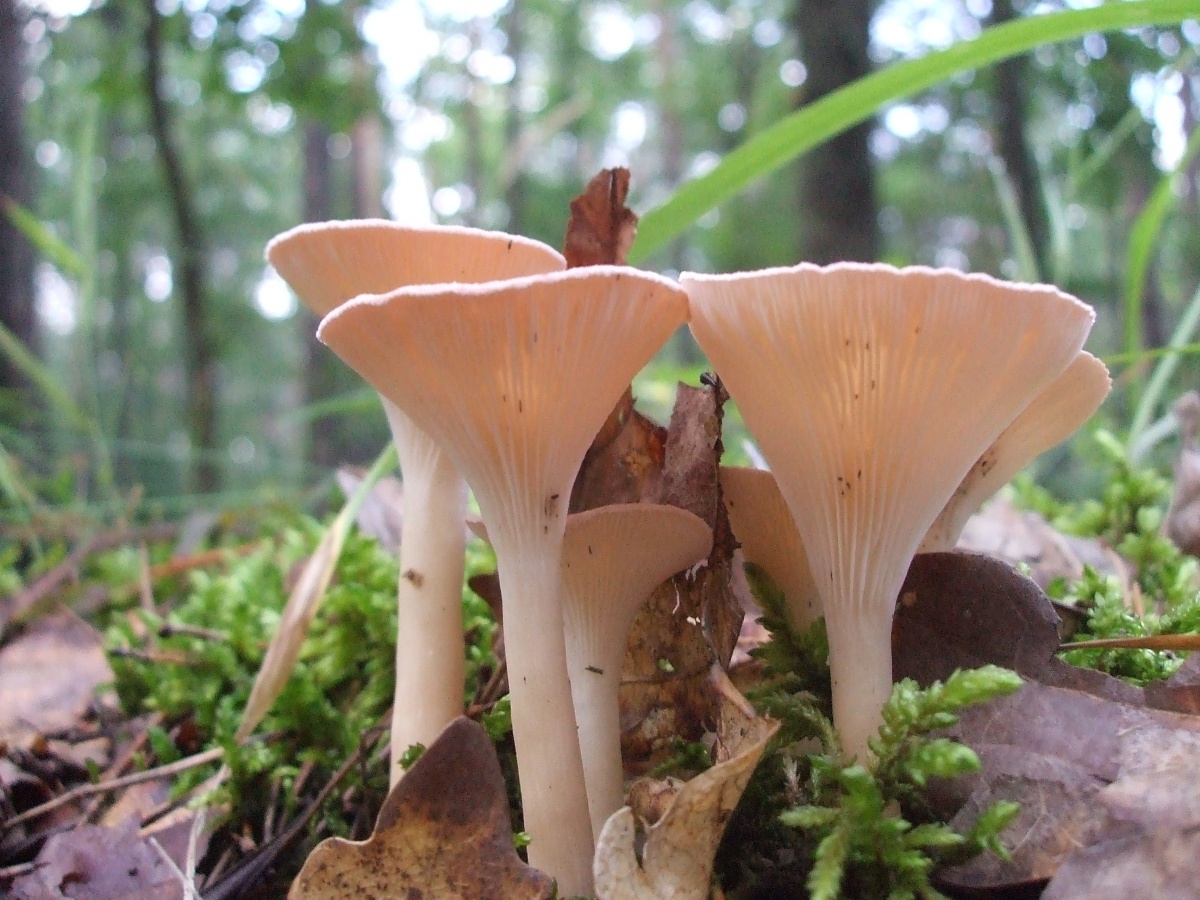
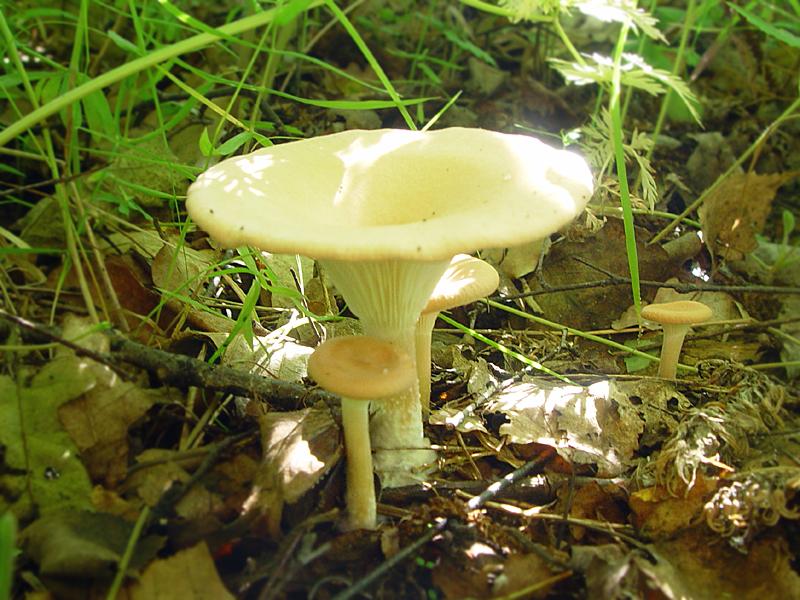
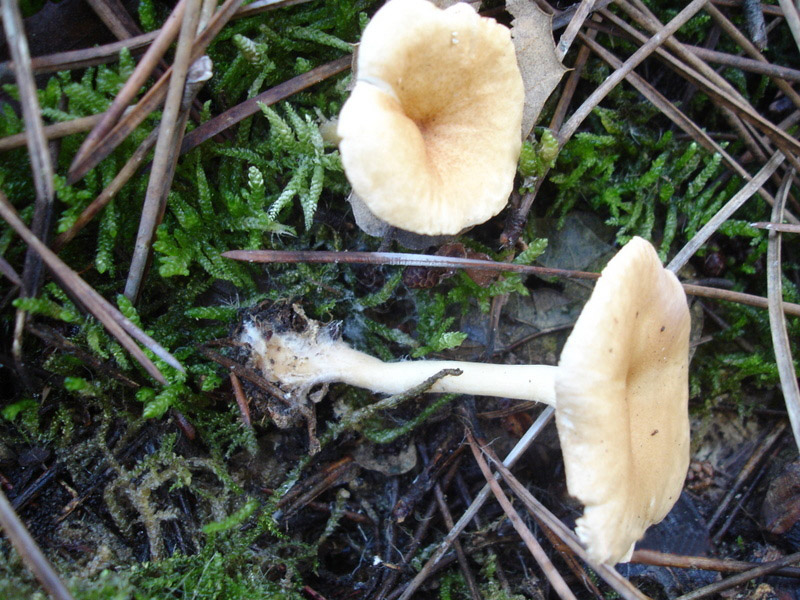
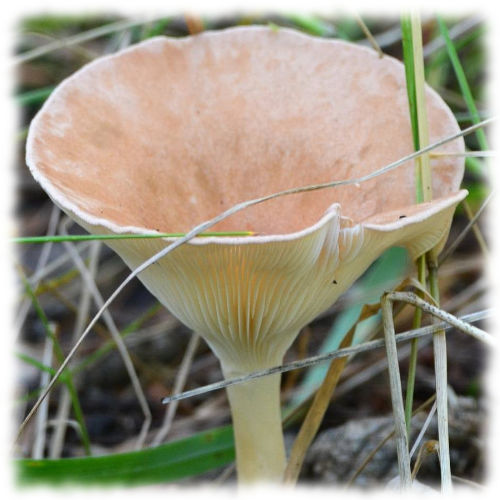
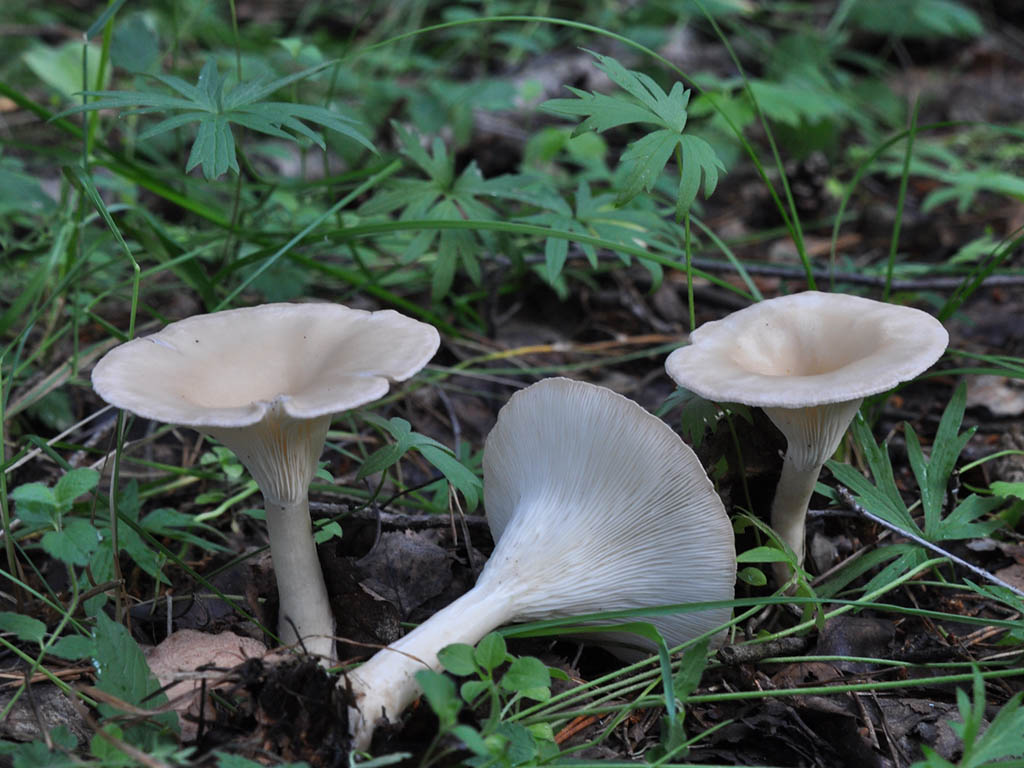
Funnel
The name of the variety speaks for itself, since the shape of the cap is very much like a funnel, it is about 8 cm in diameter. The surface is dry, the edges are wavy, and has a dirty yellow color. The plates smoothly pass onto the leg. The pulp has a mealy odor. The leg is high, 8 cm long, thin, solid.
Funnel talkers belong to the most common varieties of this species, and they can be found on fallen leaves near forest paths, in thickets of bushes in small groups or singly. Heat treated before cooking. This species can be dried and also consumed together with other mushrooms.
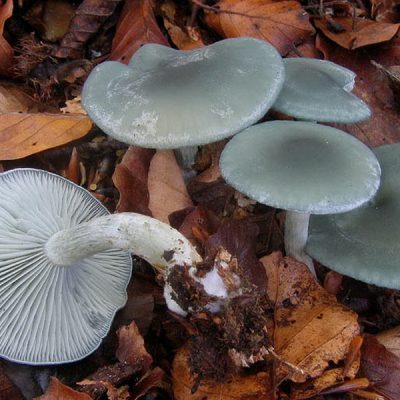
Anisova
Anise talkers belong to the less common varieties of this type. The main feature of this variety is the changeable shape of the cap. So, initially the mushroom has a cap curved inward, which straightens over time. The color is predominantly green, with a gray tint. The leg is low, rounded.
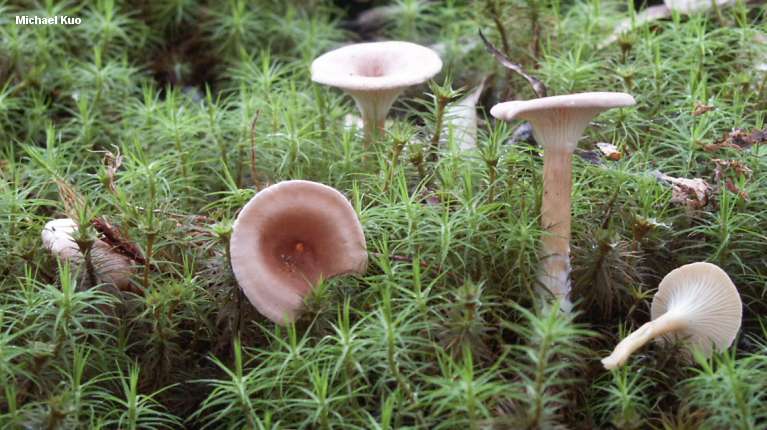
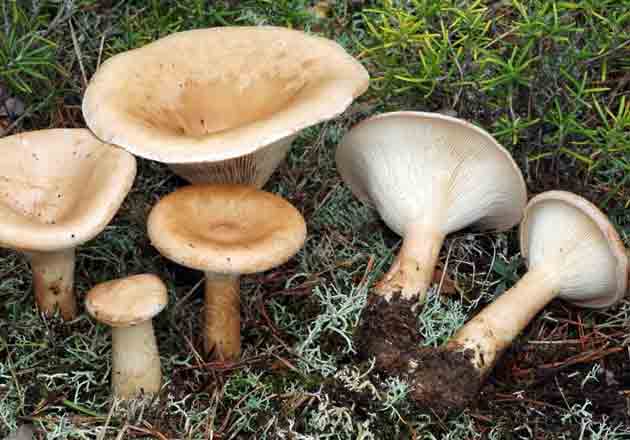
Giant
You can meet a giant talker in open areas, where it grows from August to October. The hat has a funnel-shaped shape and edges bent outward. The diameter is 12-15 cm, but some representatives can grow up to 30 cm. The surface is pleasant to the touch, silky, milky in color. The leg is dense and high.
Read also Useful properties of hazelnuts for the human body
Types of talker mushroom
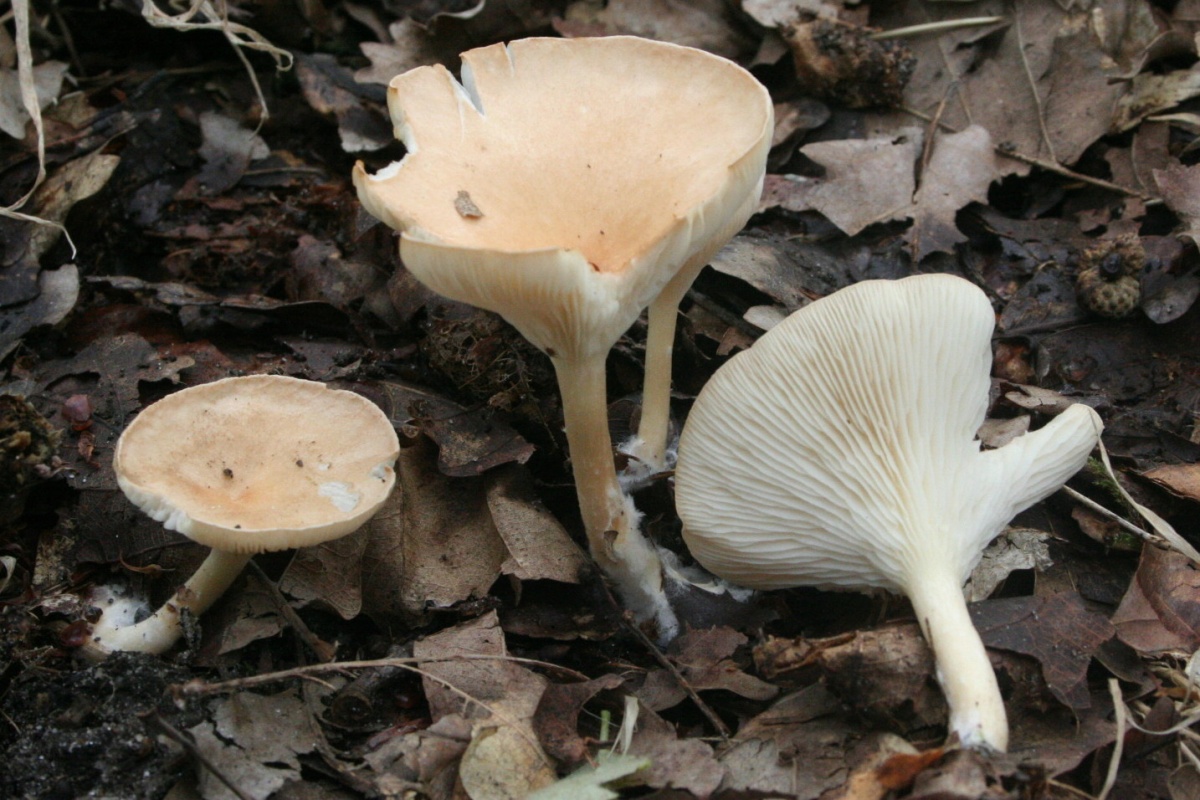
Bent Talker (Clitocybe geotropa)

Edible mushroom. The diameter of the cap is 4-12 cm, the structure is fleshy, the shape is broadly bell-shaped, in mature mushrooms it is flattened. The edge is thin, turned up. The skin of a young mushroom is smooth, shiny, later it becomes dry and dull. The color is reddish or yellowish-brown, sometimes fading to fawn or whitish. The pulp is white, dry, dense, does not change color on the cut, the taste is soft, the aroma is "almond". Leg length 5-10 cm, thickness 2-3 cm. The structure is dense, longitudinally fibrous, cylindrical in shape, light yellow in color. Spores are white.
The species is found in deciduous and mixed forests, on forest edges, roadsides, glades, in bushes. It grows in rings. The season starts in July and lasts until the end of October.
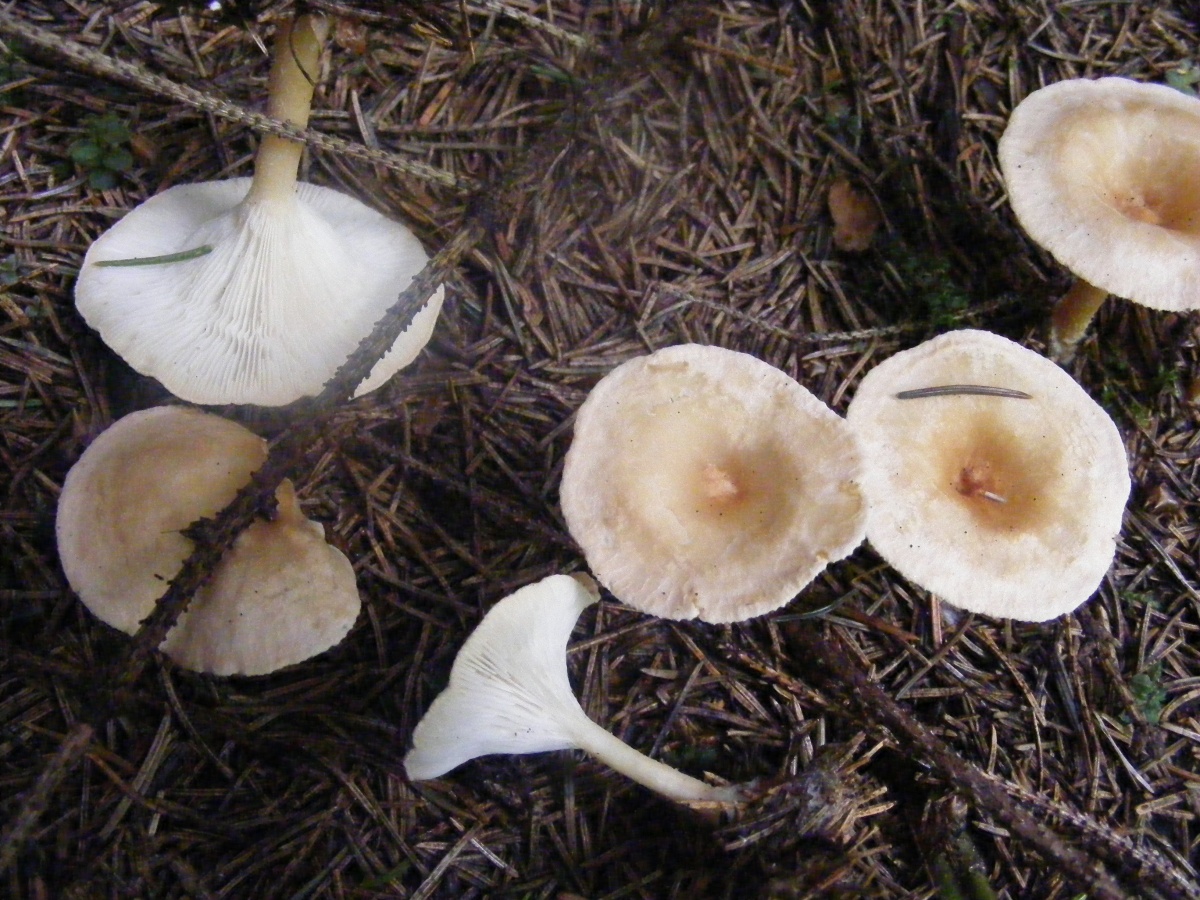
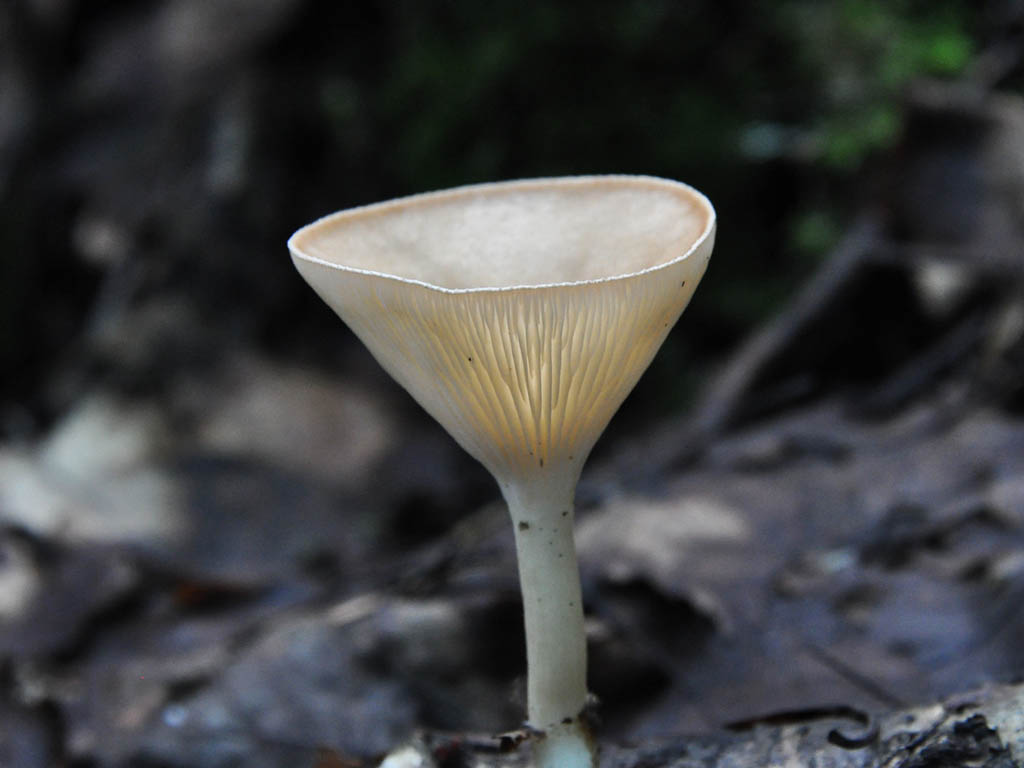
Funnel talker (Clitocybe gibba)
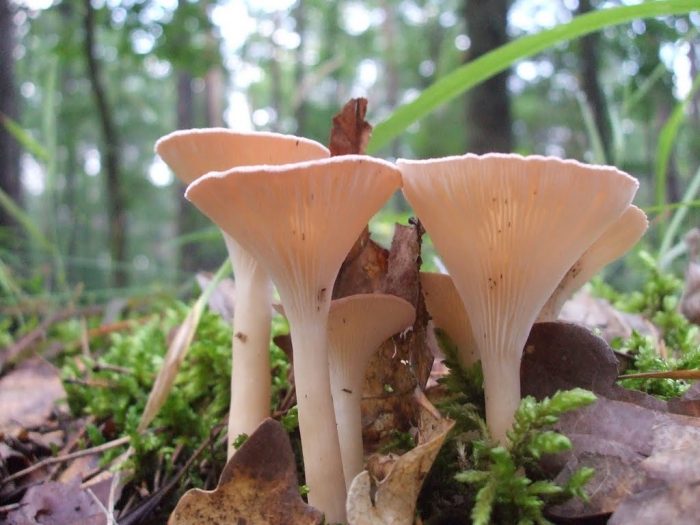

Edible mushroom. The diameter of the cap is 3-7.5 cm, the shape is flat, gradually depressed and becomes funnel-shaped, the color of the cap is pinkish-buffy, fading with age. The flesh is whitish, the taste is insipid, the smell is almond. The leg is 4-6.5 cm long, cylindrical, ocher or whitish in color, smooth.
The species grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, on the edges and roadsides.
Fragrant talker (Clitocybe odora)
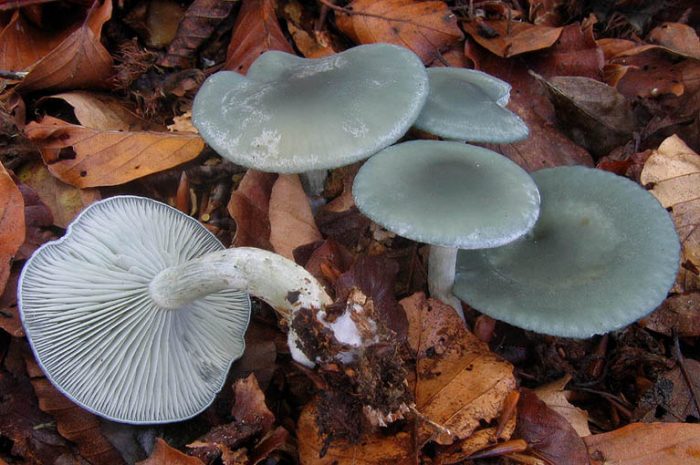

The cap is 3-8 cm in diameter, the shape is convex, gradually becomes flat and depressed, the edge is wavy, there is a tubercle in the center, naked, bluish-greenish. The pulp is white, with a strong aniseed aroma and taste. Leg length 3-6 cm, cylindrical shape, bluish-greenish color, not hollow. Spores are white.
Edible mushroom, used as a seasoning.
It is found mainly in deciduous forests.
Snow talker, or powdered (Clitocybe pruinsa)
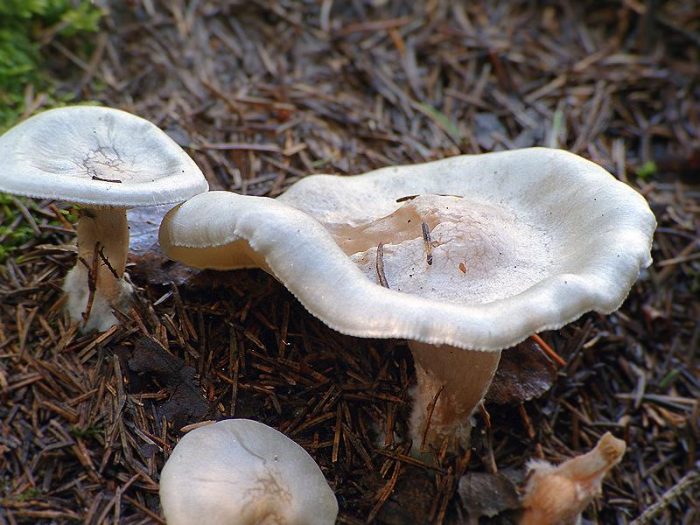

The diameter of the cap is 2-4 cm, at first it is flat-convex, in the old mushroom it is depressed, the structure is fibrous, covered with a whitish coating on top, the color of the cap is gray-brown, gradually fading. The pulp is whitish or creamy, the smell is earthy, the taste is pleasant. The leg is 3-4 cm long and 0.3-0.4 cm thick, cylindrical, reddish-cream colored, leathery.
Edible look.
Grooved talker, or grayish (Clitocybe vibecina)
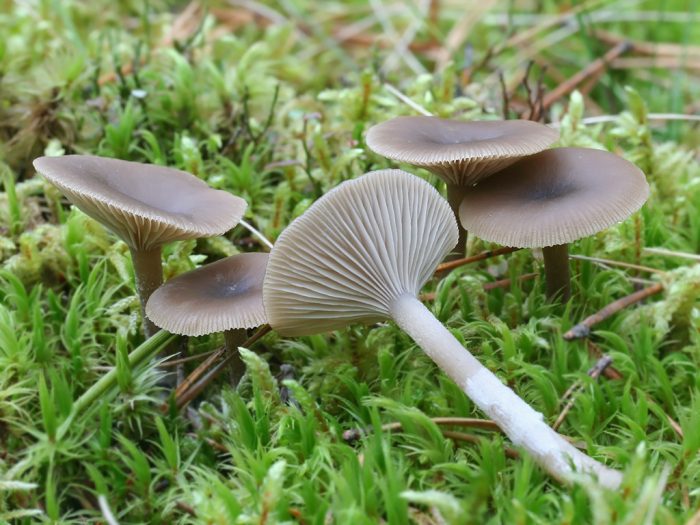

The cap is from 1 to 5 cm in diameter, in a young mushroom is flat-convex, then flat, depressed and funnel-shaped. The surface is bare, sticky in wet weather, grayish or brown in color. The pulp is grayish-brown in color, watery, smell and taste of rancid flour. Leg length 2-7 cm, thickness 0.2-0.7 cm, cylindrical shape, grayish-brown color, similar to a cap.
Grooved talker is an edible, but difficult to identify fungus, which is why it is indicated as conditionally edible.
Grows in groups, rings on decaying foliage and needles in forests, shrubs, meadows. It is widely found in Eurasia from September to late autumn.
Inverted and aniseed talkers
 Talker inverted in the photo
Talker inverted in the photo  Hat with a diameter of 4-8 cm
Hat with a diameter of 4-8 cm
Inverted talker (reverse lepist).
The hat is 4-8 cm in diameter, as the fungus grows, it becomes wide-funnel-shaped, brick- or red-yellow-brown, fades over time, shiny in damp weather. The plates are frequent, descending to the stem, light yellow, then brown-yellow, sandy-buffy. The flesh is thin, grayish-yellow or pale yellow, light brownish, with a faint sour odor. The stem is tapered, elongated at the base, often curved, rigid, solid, then hollow, reddish, usually lighter than the cap, or rusty-brown. The inverted talker can be found in pine forests and plantings on coniferous litter, in mixed forests on litter.Fruit bodies form large groups in August - October.
Cooking.
Insufficient edible mushroom. Suitable after boiling for salting. Some authors classify this mushroom as inedible.
 Anise talker in the photo
Anise talker in the photo  Fragrant talker in the photo
Fragrant talker in the photo
Aniseed talker is an edible lamellar mushroom.
Other names are fragrant talker and fragrant talker. A fairly rare mushroom that grows singly or in small groups from early August to late October, giving large yields annually. Most often it can be found in mixed and spruce forests.
When describing this talker, it is worth noting that its convex cap with the edges bent downward in the process of growth straightens and takes on a prostrate shape. In the center, it usually has a small depression, less often a tubercle. The cap is painted gray-green, lighter along the edge.
The spore-bearing layer contains adherent plates, whitish in young mushrooms, pale green in mature ones. The leg is rounded, wider at the base, grayish-yellow in color with a greenish tint. Its height is about 5 cm with a diameter of no more than 0.5 cm. The surface of the stem at the cap is smooth, slightly pubescent at the base. The flesh is thin, watery, pale green or off-white in color, with a strong smell of anise.
Aniseed talker belongs to the fourth category of mushrooms. It is eaten in boiled, salted or pickled form, and as a result of heat treatment, the characteristic smell of anise is significantly weakened and becomes not as pronounced as in fresh mushrooms.
Waxy and giant talkers
Waxy talker is a rare poisonous lamellar mushroom. Grows singly or in small groups from late July to late September, preferring open, sunlit areas of mixed or coniferous forest with sandy soil or low dense grass.
In young mushrooms, the cap is convex, but in the process of growth it becomes slightly depressed or open, with wavy edges. There is a small tubercle in the center of the cap. The surface of the cap is smooth, matte, light gray in color, but in damp weather it darkens, and barely noticeable concentric zones appear on it. The spore-bearing layer is formed by descending cream-colored plates. The leg is rounded, even, wider at the base, solid inside. Its height is about 5 cm with a diameter of 1 cm. The surface of the leg of this poisonous talker is painted in an off-white color, its upper part is smooth, and the lower part has a slight pubescence. The pulp is thick, with an unpleasant odor, elastic in the leg, fragile in the cap.
The tissues of the waxy govorushka contain a poison that is dangerous to the human body, which can cause serious food poisoning.
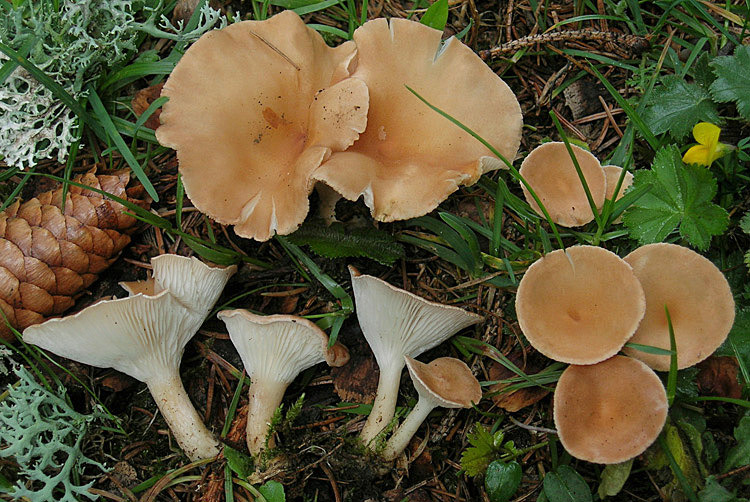
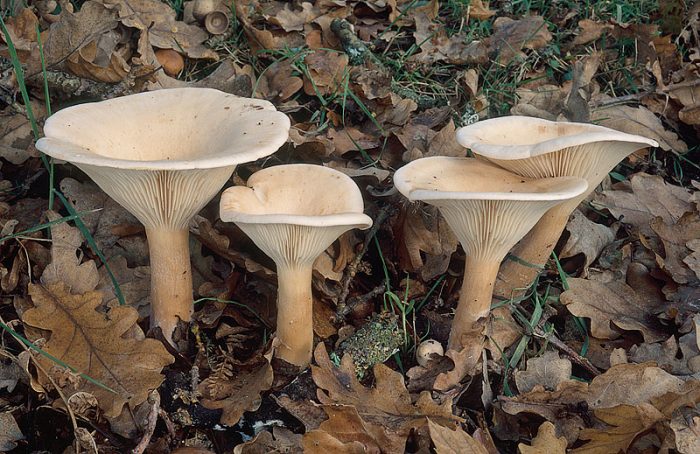
Giant talker is a rare conditionally edible lamellar mushroom. It grows in large groups, forming the so-called witch circles, from late August to late October. Produces bountiful harvests annually. Prefers to settle in open areas of the forest, as well as in pastures.
The convex cap of the mushroom eventually becomes funnel-shaped, with thin, upward-curved edges. As a rule, the diameter of the cap of a mature mushroom does not exceed 13–15 cm, but there are also giants with caps up to 30 centimeters or more in diameter. It was they who gave the name to this type of mushroom. The surface of the cap is matte, silky to the touch; depending on the habitat, it can be covered with small scales. Most often it is snow-white, less often the color of coffee with milk. On the underside of the cap there are descending plates with bridges. Their color changes from beige to yellow as they grow. The leg is white, dense, up to 8-10 cm high and about 3-4 cm in diameter. The flesh is also white, fleshy, firm, with a faint powdery odor, in old mushrooms with a bitter taste.
The giant talker belongs to the fourth category of mushrooms.It is eaten only after preliminary boiling, after which you can prepare the first and second courses from it, as well as prepare it for future use - salt or pickle. The mushroom pulp contains a natural antibiotic - clitocybin A and B, which has a detrimental effect on the tubercle bacillus.
Possible harm from the fungus
The harm from the use of a govorushka can be in those cases if you do not adhere to the main rules of the primary processing of raw materials, preparation technology and dosages.
- In addition, it is necessary to take into account contraindications, which include:
- children under 12 years of age;
- individual intolerance;
- genetic predisposition to allergies;
- any diseases in the stage of exacerbation;
- gastritis and ulcers in the acute phase.

Since funnels are capable of accumulating toxins and harmful chemicals, it is allowed to eat only those mushrooms that were collected in ecologically clean regions. Also, experts do not advise eating mushrooms at night or on an empty stomach. Before using the talker, it is imperative to soak it in cold water and boil it for at least 30 minutes.
The funnel-shaped talker is a rather difficult mushroom to collect, since it has many similar inedible and poisonous "relatives". Experts advise only experienced mushroom pickers who know exactly its specific features to collect the funnel. It should be remembered that the consequences of the use of poisonous specimens can be extremely difficult, even fatal.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
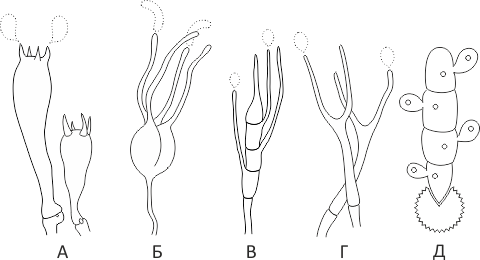
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
Poisoning by a poisonous talker
Poisoning by a talker is extremely dangerous not only for health, but also for human life. After eating a poisonous mushroom, after a few hours (sometimes less), the first alarming symptoms of intoxication begin to appear. Poisoning can be recognized by the presence of:
You may be interested in: What is the difference between edible talkers and false mushrooms How many days after the rain mushrooms grow Bitter mushroom: photo and detailed description
- severe weakness;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- sharp, spasmodic pain in the abdomen;
- profuse salivation;
- hyperhidrosis;
- diarrhea;
- intestinal cramps;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- circulatory disorders;
- constriction of the pupils of the eyes;
- deterioration of vision;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- convulsions.
Important!
The higher the dose of the mushroom consumed, the faster and more severe the symptoms of poisoning will appear. In case of untimely assistance or the absence of medical intervention, a lethal outcome occurs. Usually, for a person's death, it is enough to use only 1 g of talker. Under the influence of toxic substances, severe damage to the heart occurs, the development of bronchospasm and general dehydration of the body. It is these conditions that are the cause of the death of a person.
The whitish talker is an extremely dangerous, insidious mushroom. Its use can have dire consequences, especially for children. But adults are not immune from poisoning, therefore, when going on a quiet hunt, you need to know exactly which fruit bodies are edible. And if you see a suspicious mushroom - bypass it.
Sprouting
The funnel-shaped talker can be encountered by mushroom pickers near the paths, in the most different forests. Quite often, these mushrooms grow in large numbers in groups. Prefers to grow in litter, but rather shallow. Can be harvested from mid-July to late September. Prefers shrubs, mixed and deciduous forests, pastures. Mushroom pickers can meet the funnel-shaped talker in the North Caucasus, Western Siberia, and the European part of Russia. Belongs to the fourth category, edible mushroom species. For cooking, you only need mushroom caps, which can be dried, salted, boiled. Initially, you need to boil the mushroom, and pour the broth.
Common misconceptions
For example:
| Myth | Reality |
| a cut onion or silver spoon will darken if boiled mushrooms contain poisonous | Darkening is caused by certain enzymes, such as tyrosinade, which are found in both edible and poisonous mushrooms. But from a pale toadstool, silver cutlery does not change color. |
| Worms, snails, insects do not damage poisonous species of mushrooms | Many poisonous mushrooms, for example, the satanic mushroom, happily eat worms and slugs. And they bypass the chanterelle. |
| Poisonous mushrooms all give off an unpleasant odor and taste bitter. | Poisonous talkers smell pleasantly of fresh flour, a pleasant smell in a pale toadstool. |
| Only overripe, old mushrooms are poisonous | Poisonous mushrooms have a toxic effect at all stages of development |
| Poison accumulates only in the skin of mushrooms | In the pale toadstool, all parts of the fungus are poisonous, even the spores. This is true for all types of poisonous mushrooms. |
Botulism in mushrooms
If, when collecting talkers, focus on these signs, then poisoning will be very likely.
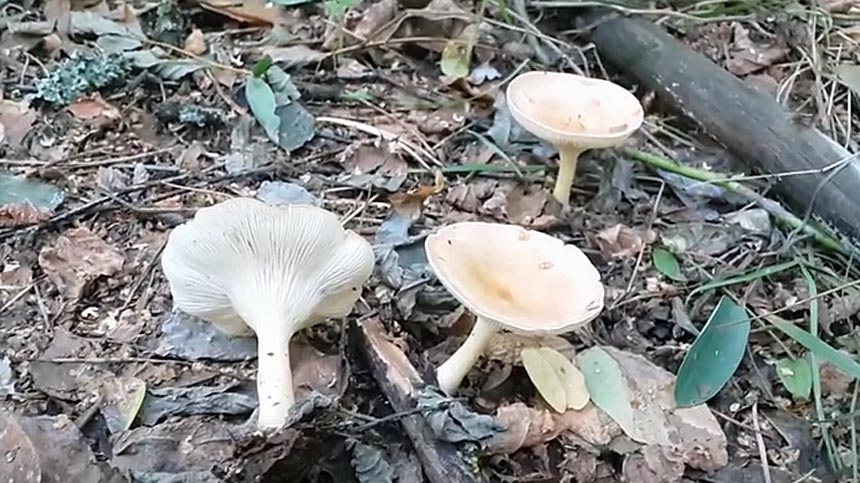
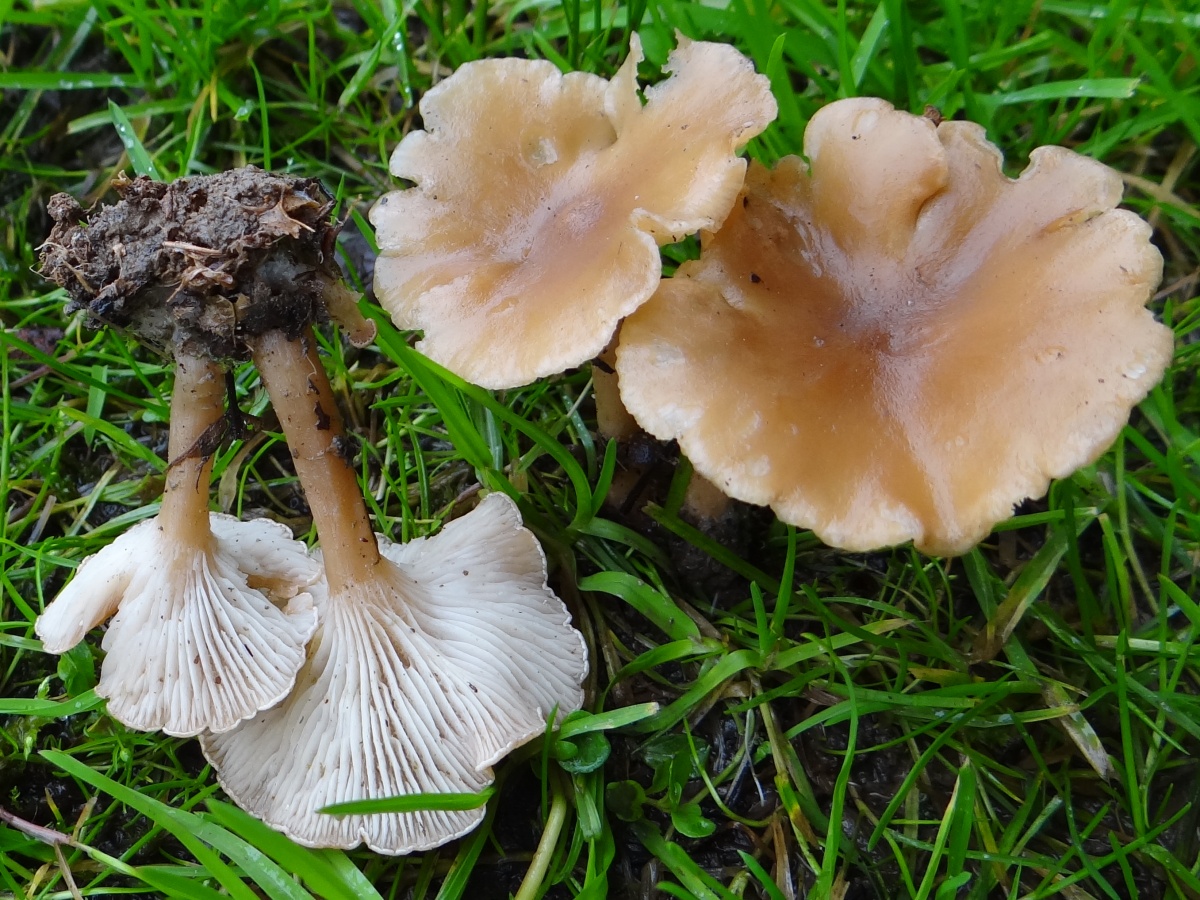
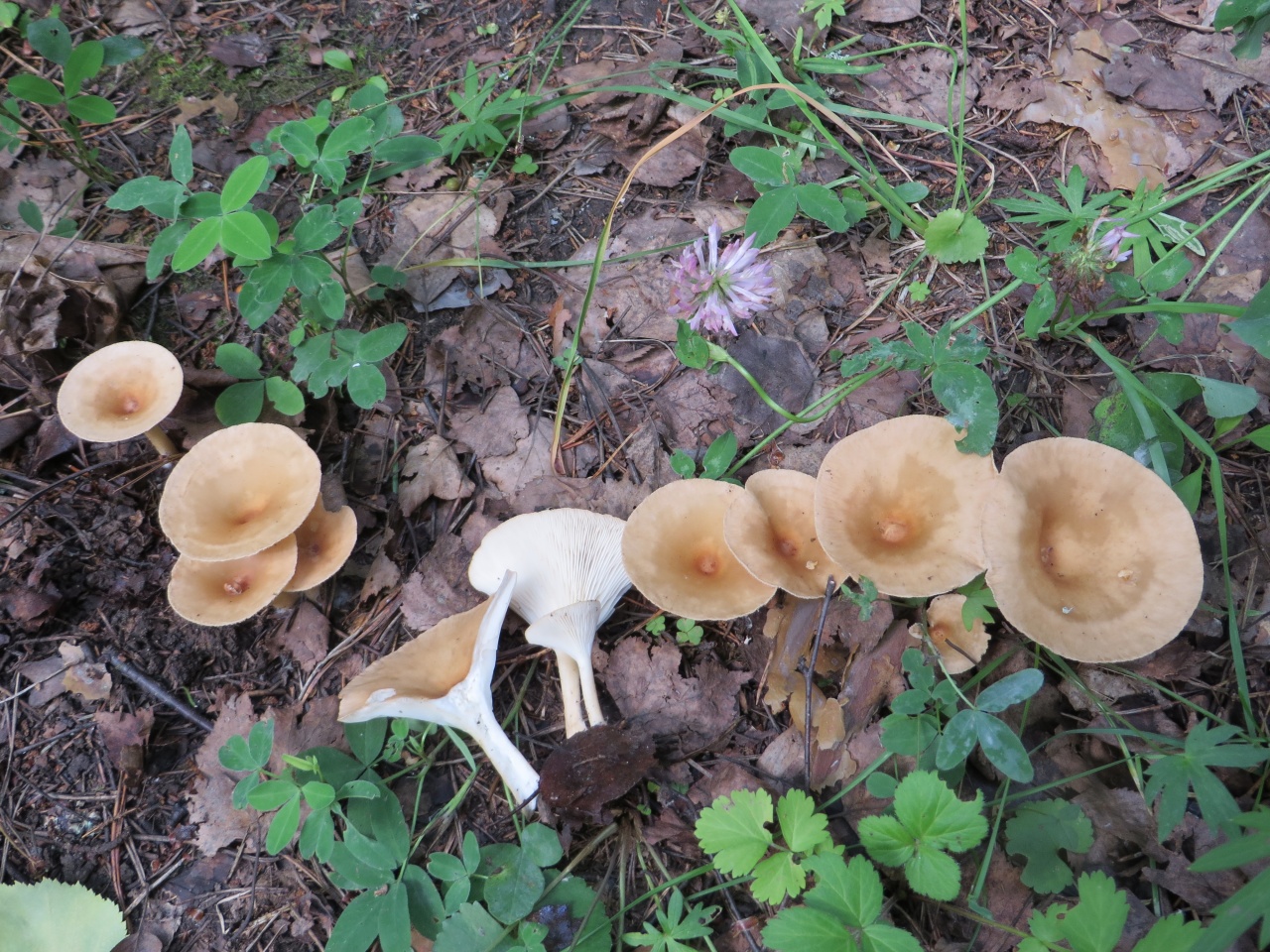
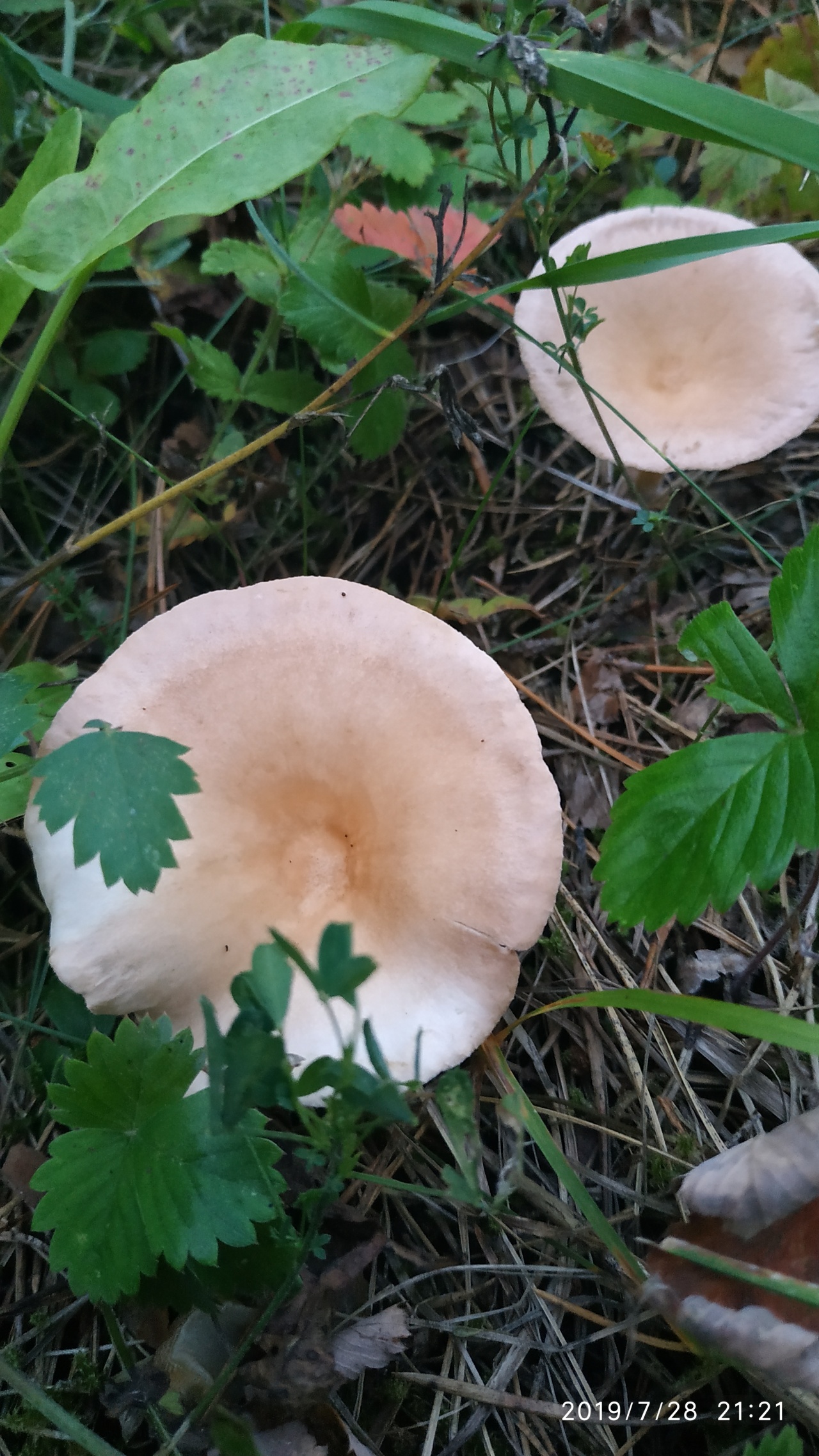
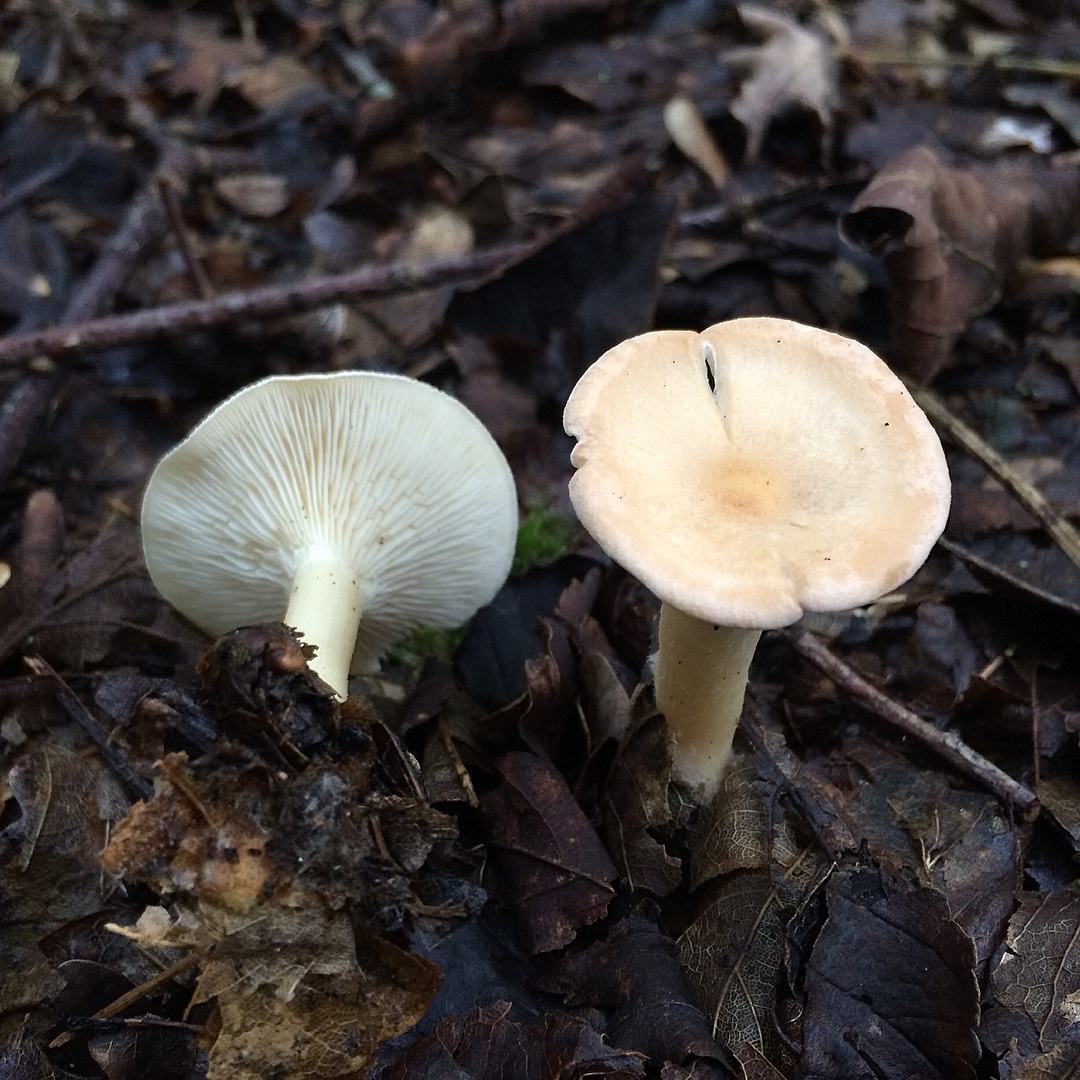
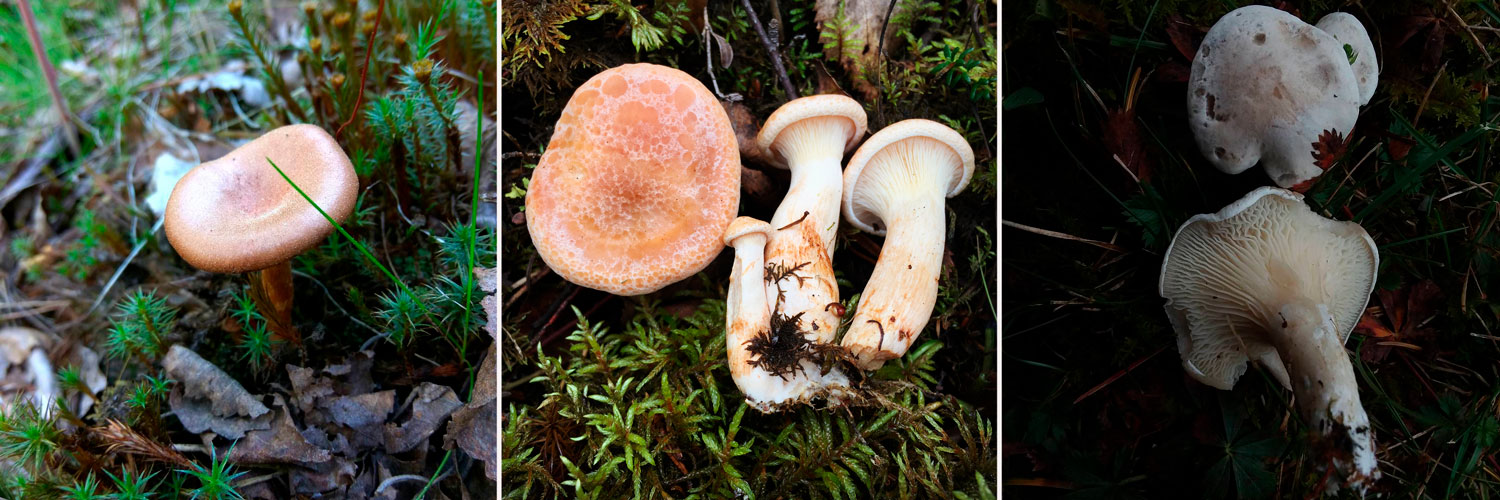
Goblet and orange talkers
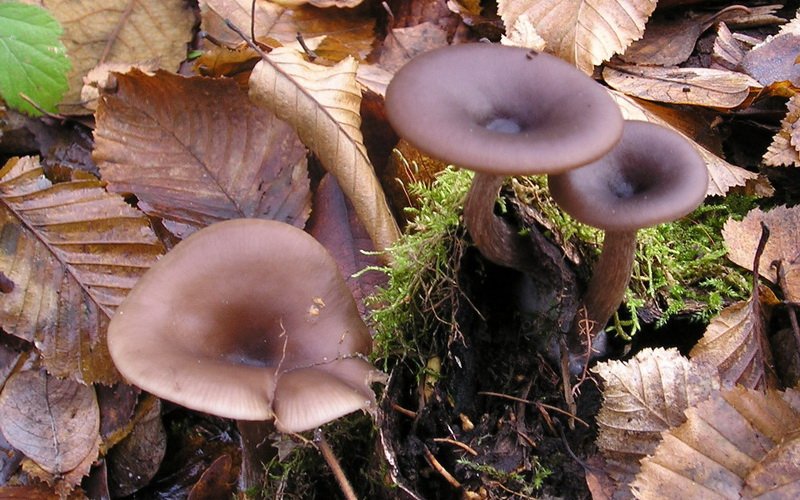

Goblet talker in the photo
Goblet talker. The hat is up to 8 cm in diameter, wide-funnel-shaped, goblet or cup-shaped, with the edge turned down, shiny, silky, when moistened, as it were, saturated with water. The whole mushroom is dark ash gray or brownish fawn. The plates are adherent or descending along the pedicle, rather rare, sometimes branched, light brown or brownish brown. The pulp is thin, grayish, watery. The spore nut is white. The leg is up to 10 cm high, elastic, hollow, thickened at the bottom, fluffy at the base.It grows in coniferous, mixed, deciduous forests on forest floor, fallen needles, rotten wood, and is quite common. Fruiting in August - September.
Edible mushrooms are eaten boiled and salted. High quality mushroom.
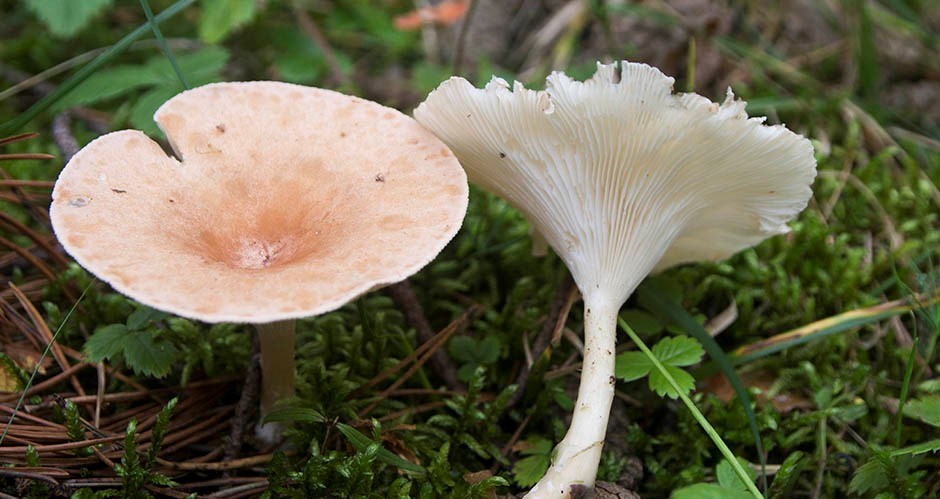
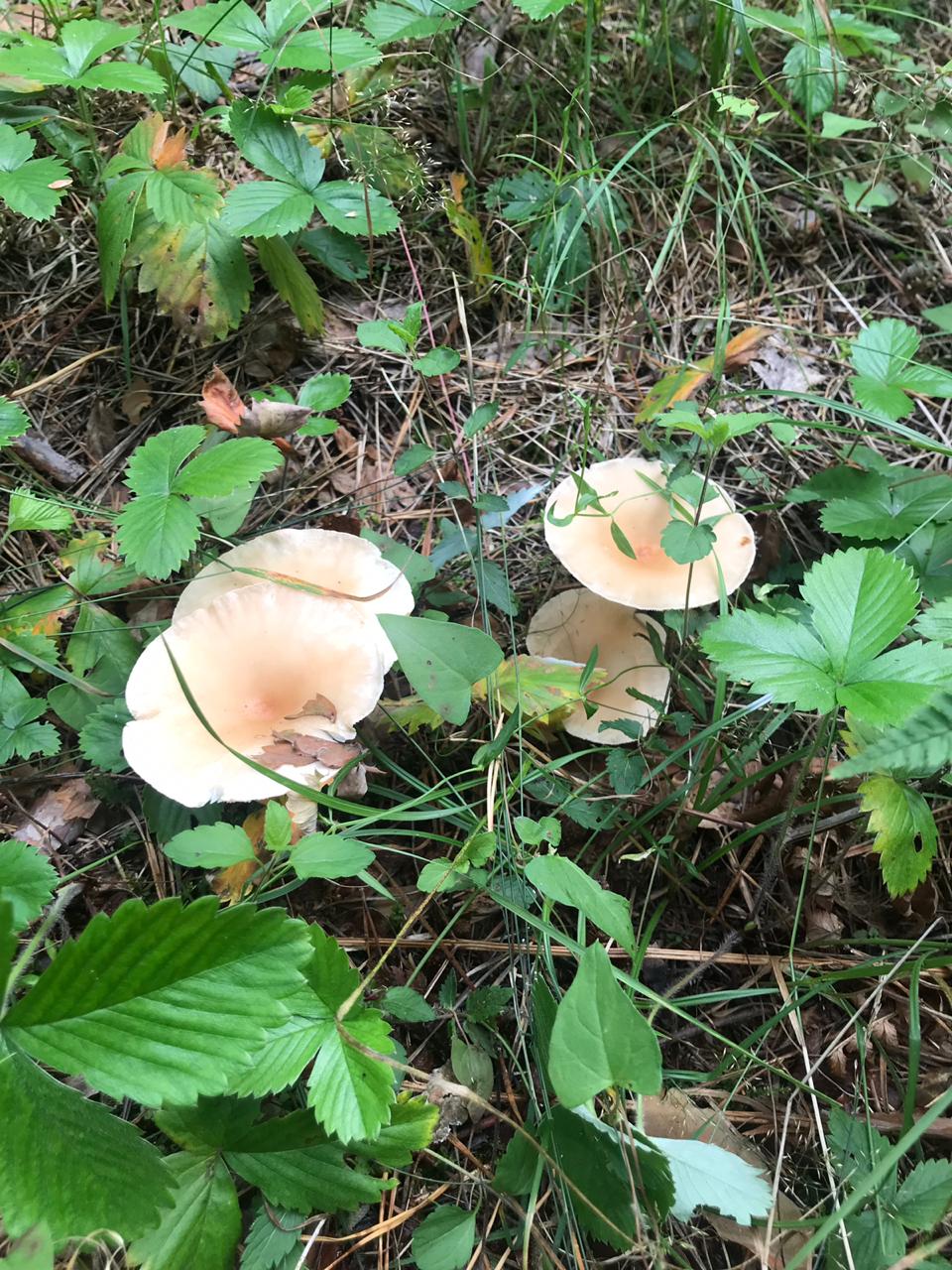
Orange talker is a rare edible lamellar mushroom. Other names are kokoshka or false chanterelle. Grows singly or in small groups, giving stable yields annually, from early August to late October. Favorite habitats are wet areas of mixed or coniferous forest, covered with a thick layer of moss or fallen leaves, as well as rotting trunks of pines lying on the ground.
As you can see in the photo, this talker mushroom has a convex cap with curved edges over time takes the shape of a funnel:
Its average diameter is 4–5 cm. In the process of growth, the yellow-orange color of the cap fades, retaining its saturation only in the center. The plates are descending, brighter in color than the cap, darken when pressed. The stem is rounded, thinner at the base, the same color as the plates on the spore-bearing layer. Its height is 4–5 cm with a diameter of no more than 0.5 cm. The flesh is thin, tasteless and odorless, yellow in the cap, soft, reminiscent of cotton wool, reddish in the stem, tough, elastic.
Only caps of young mushrooms are eaten, which can be boiled and fried.
Characteristic features of talkers
Talkers belong to the type of cap mushrooms and the family of ordinary ones. They also have some differences between themselves that need to be studied in order to distinguish edible varieties from inedible ones. There are also poisonous varieties in the genus, so only experienced mushroom pickers are recommended to collect this species.
Appearance and photos
All representatives have medium or small fruiting bodies. The average diameter of the cap is 3-7 cm. The cap is mainly of light shades, sometimes grayish, there is a small depression in the center - it has a funnel-shaped shape.
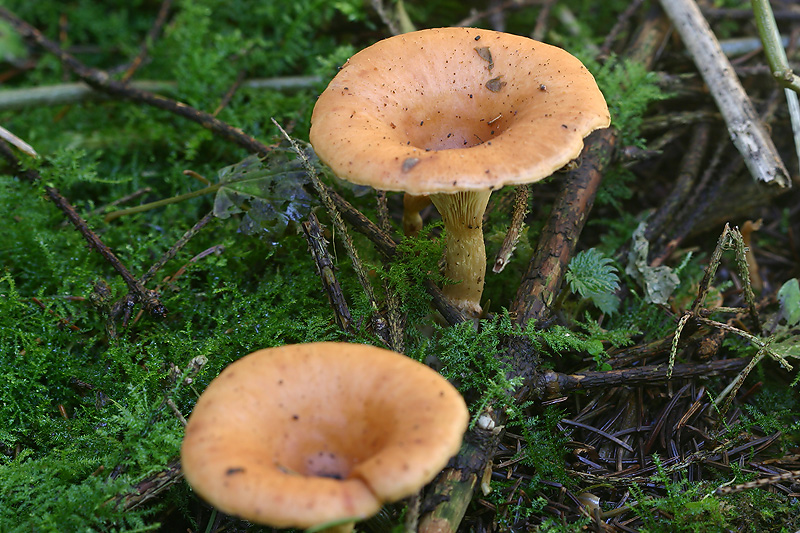
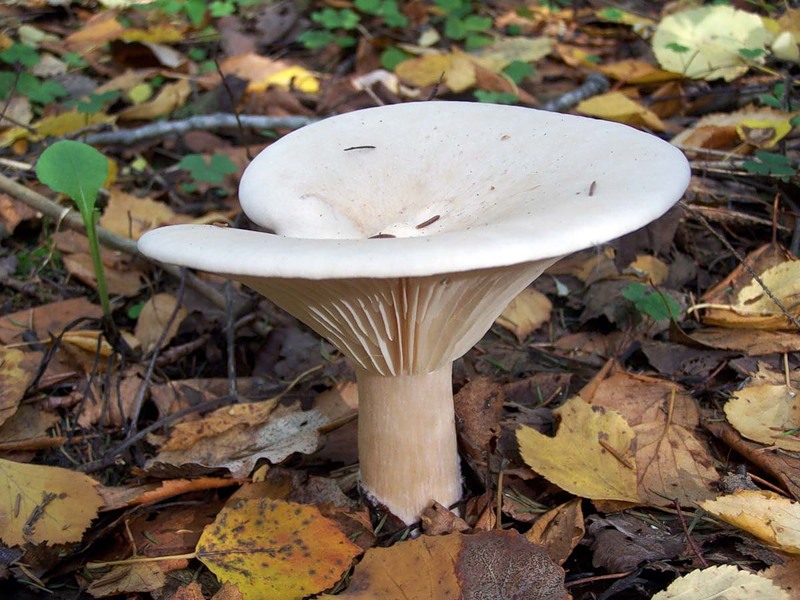






The hat is smooth and dry to the touch. The stem of the mushrooms is thin and high. On the back of the cap there are thin, white plates that go to the top of the stem. The spore powder of the fungus is light, sometimes creamy.
Place of distribution
You can meet talkers most often in deciduous forests. It is there that they form mycorrhiza with trees. Organisms grow in groups, which are often called the witch's circle. This phenomenon is accompanied by the growth of a large number of mushrooms in a circle, with an empty space in the center.
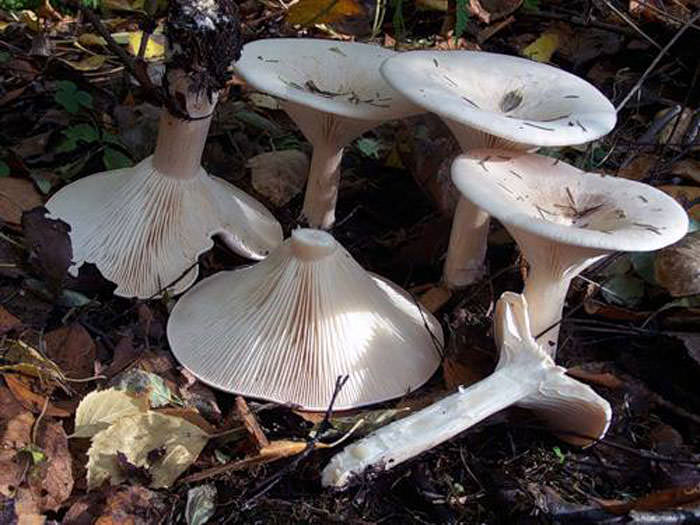






In addition to forests, this species can also be found in grassy areas, for example, in meadows or in parks. On the territory of Russia, mushrooms are common in temperate climates, and can also be found in the forests of Siberia and in the Primorsky Territory.
Collection rules
Experienced mushroom pickers recommend collecting talkers from mid-August to October. Their peak yields are in mid-September. Many varieties of talkers grow in groups, making harvesting much easier.
The place of collection of talkers depends on the characteristics of the variety, however, most of them grow in forests near trees, where a large number of fallen leaves or moss prevail.
How to cook a funnel-shaped talker
There are general rules for preliminary preparation for the use of conditionally edible mushrooms:
- Use the youngest specimens of mushrooms - the older they are, the more toxins they contain.
- Fruit bodies must be cleaned of dirt and damaged fragments. In this type of mushroom, only caps are usually used - the legs are considered too hard.
- Soak the peeled fruit bodies for an hour in water.
- Boil the soaked mushrooms over medium heat for 30 minutes with a little salt. Be sure to drain the broth - all the toxins have gone into it.
After boiling, the mushrooms are suitable for any kind of culinary use or preparation for future use.
Funnel Talkers can also be dried, but you need to dry it as thoroughly as possible, until it is completely dry and the toxins are destroyed.It is best to dry it in the sun, but you can also dry it in the oven, with the door slightly open at a temperature of 75 - 100 grams.
Funnel Talker contains:
- Vitamins B1, B2, B6 are necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system, supporting the body in moments of strong physical or psychological stress.
- Vitamin E - essential for metabolic processes, maintenance of beauty and youthfulness of the skin.
- Vitamin C - essential for supporting immunity, resisting bacteria and viruses.
- Manganese is essential for the processes of hematopoiesis, the regulation of blood sugar levels, and the normal functioning of the gonads.
- Copper is essential for the production of collagen, the main component of connective tissue in the body, and for maintaining neurological functions.
- Zinc - stimulates cell growth and division, essential for normal bone and muscle growth, hair and skin health.
Due to its low calorie content. these mushrooms are quite suitable as a dietary food, but it is imperative to follow the rules of preliminary preparation and a moderate dosage when using them.
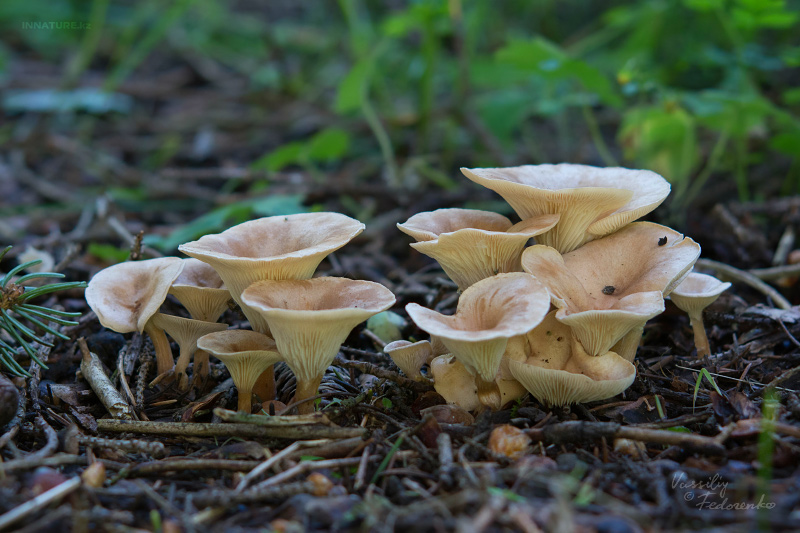

Providing emergency first aid
If signs of mushroom poisoning appear, it is necessary to call an ambulance and, before her arrival, provide the patient with all possible assistance to cleanse the intestines from toxins:
- give the patient 500-1000 ml of warm water with a small amount of salt;
- irritating the root of the tongue, induce vomiting;
- continue washing until clean wash water appears;
- give the patient a laxative by cleansing the intestines;
- to ensure the binding and elimination of toxins, and to reduce their absorption with the help of enterosorbents;
- with a decrease in the heart rate, they give stimulating drinks - strong sweet tea, coffee. You can put mustard plasters;
- if breathing is difficult, provide fresh air.
Excess glucose in the body
If the symptoms indicate a severe degree of poisoning, then the patient is hospitalized for assistance and monitoring of the condition in a hospital setting.
Useful properties of the mushroom
- The useful properties of the funnel talker have been known since ancient times. Hoods, decoctions and powder from a funnel allow:
- to establish the work of the digestive tract;
- normalize the functioning of the nervous system;
- cleanse the body of toxins, harmful substances and reduce the negative effects of free radicals;
- reduce the level of "bad" cholesterol;
- prevent the formation of blood clots;
- improve the condition of the body with urolithiasis;
- fight respiratory ailments;
- reduce the risk of tumors, including malignant ones.

Since mushrooms are low in calories, they are excellent for diet nutrition, and due to their high protein content, they can become an integral part of a vegetarian diet.






















































