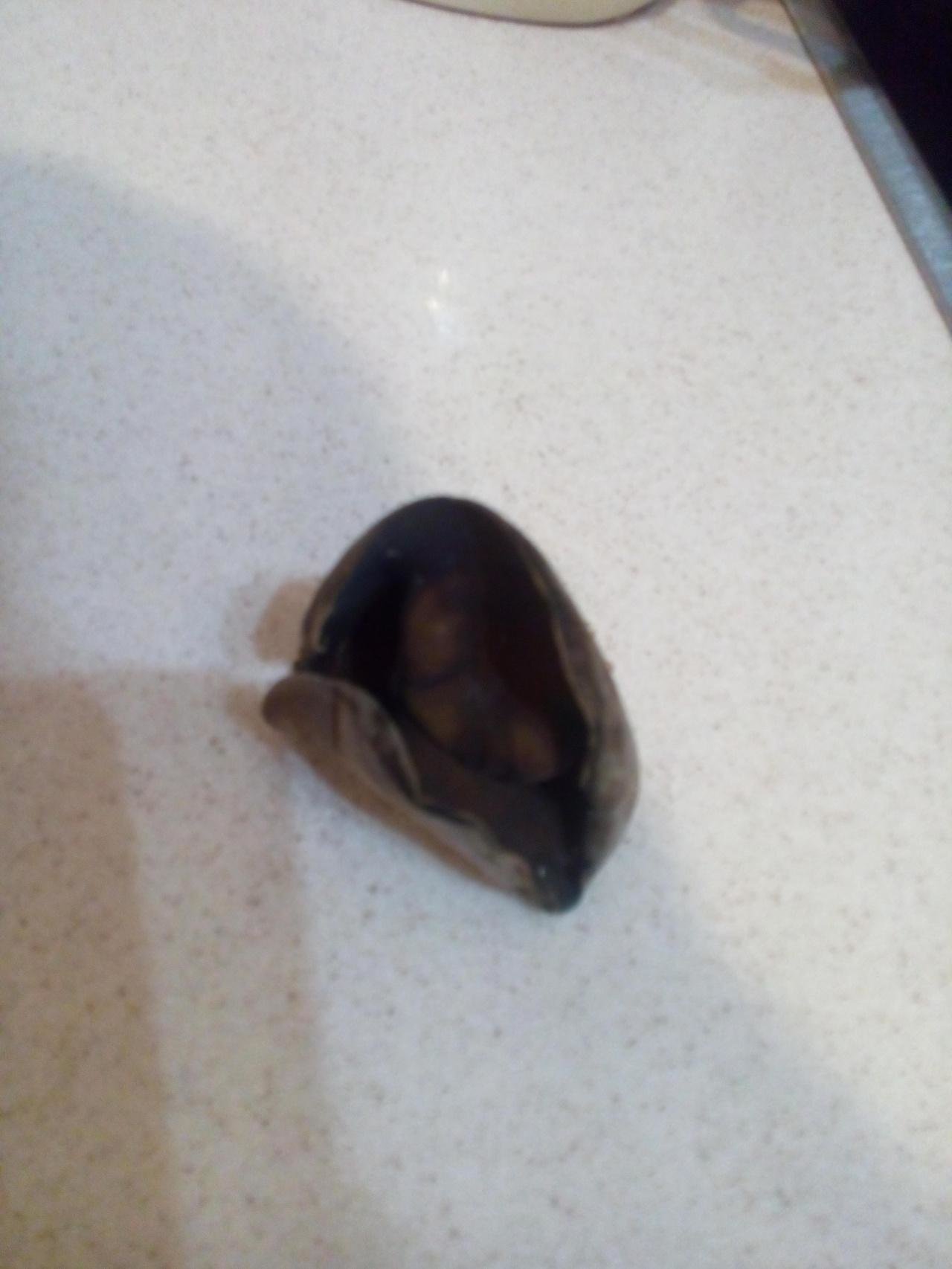
Description of the lobe pitting (furrowed), the place of distribution of the fungus
For a long time, there have been disputes around this mushroom regarding its edibility. Some say that pitted lobe can be eaten, but others forbid adding it to dishes. Let's find out what kind of mushroom it is, and decide if it can be eaten?
Description
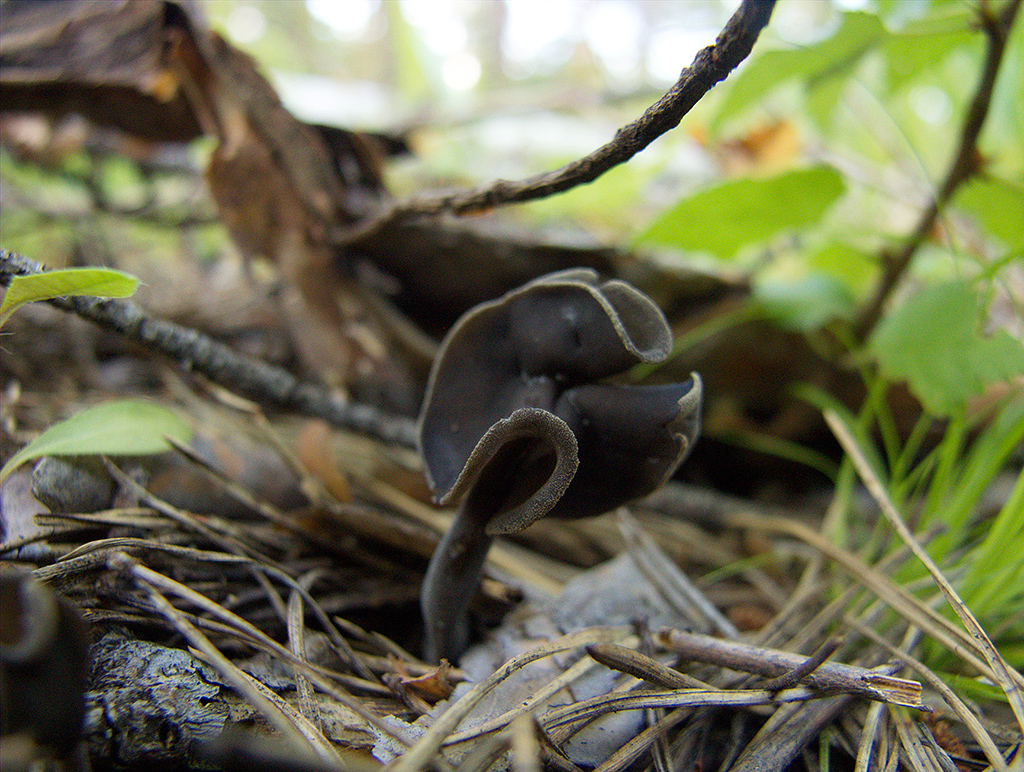
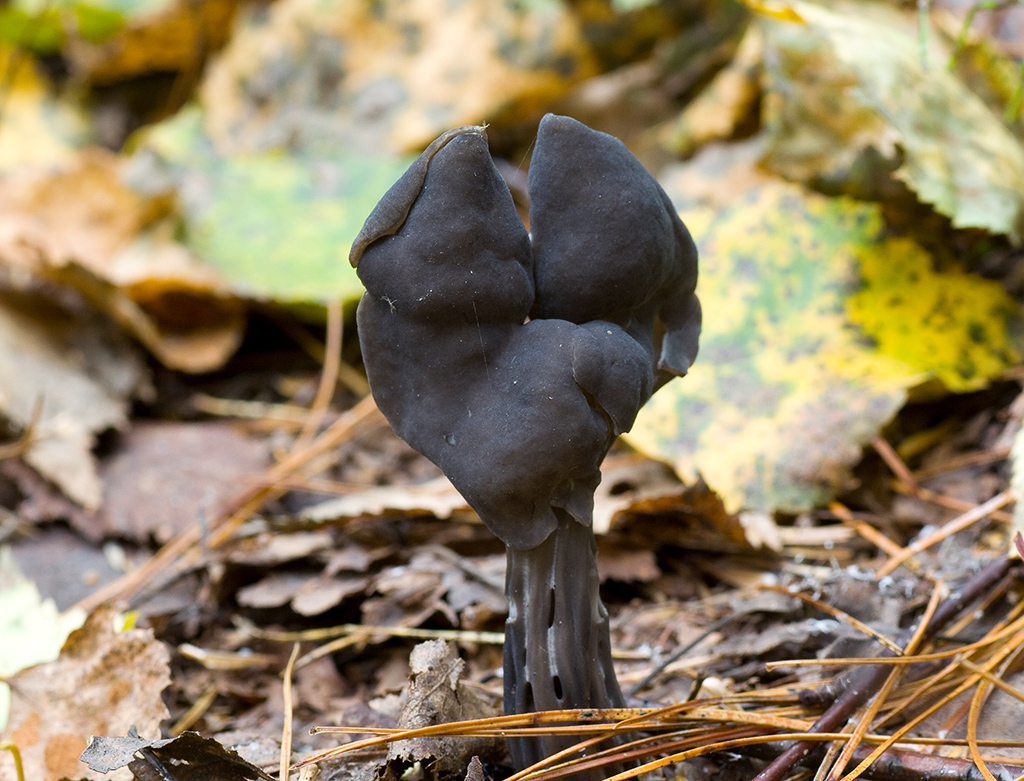
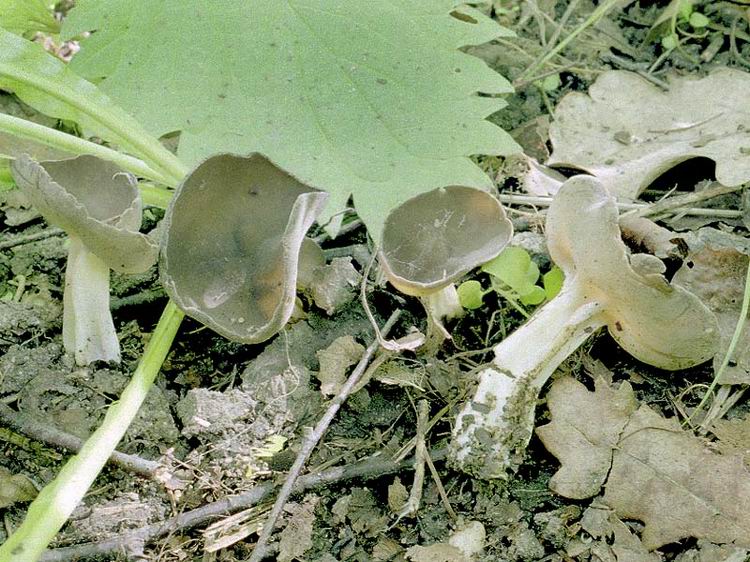
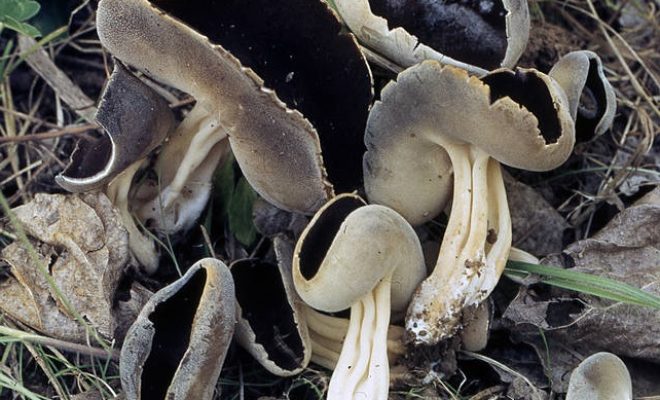
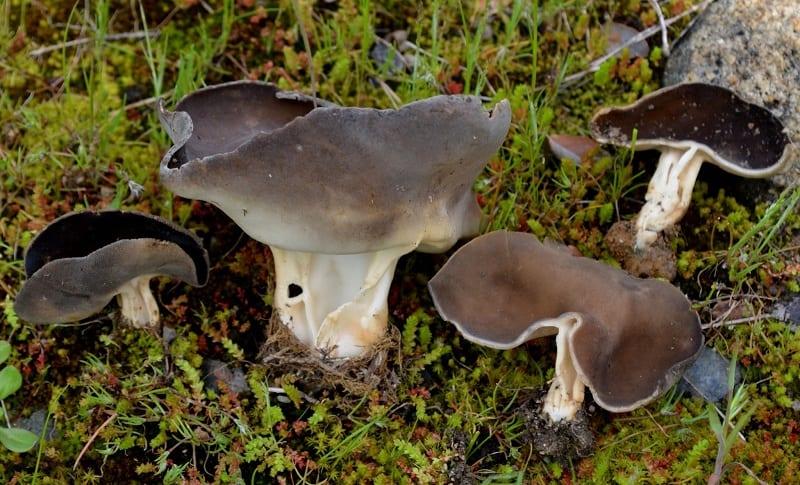
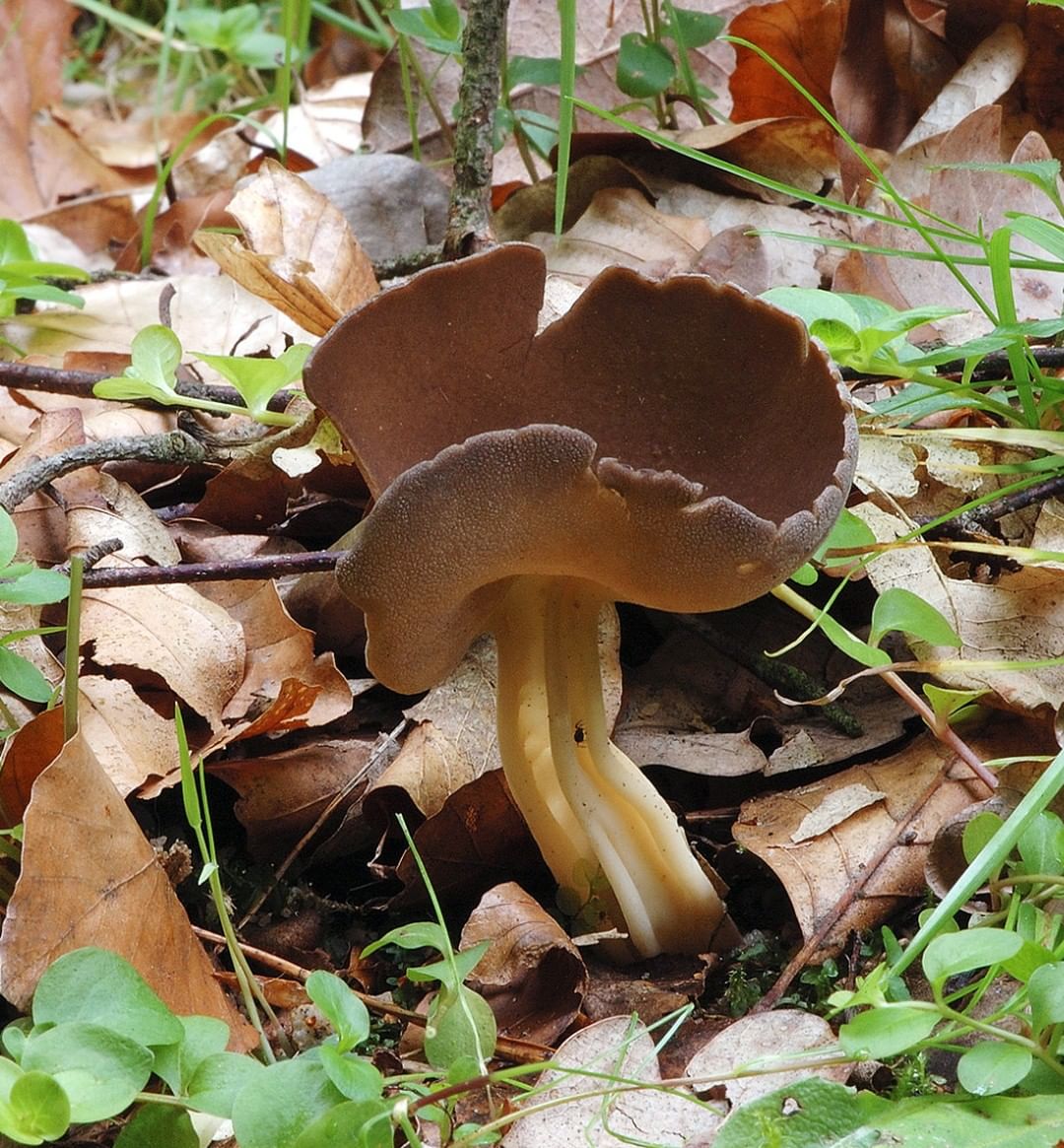
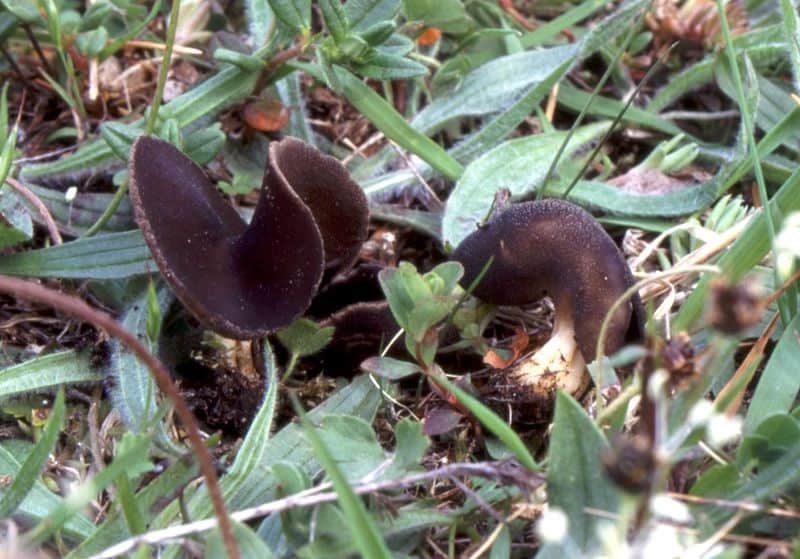
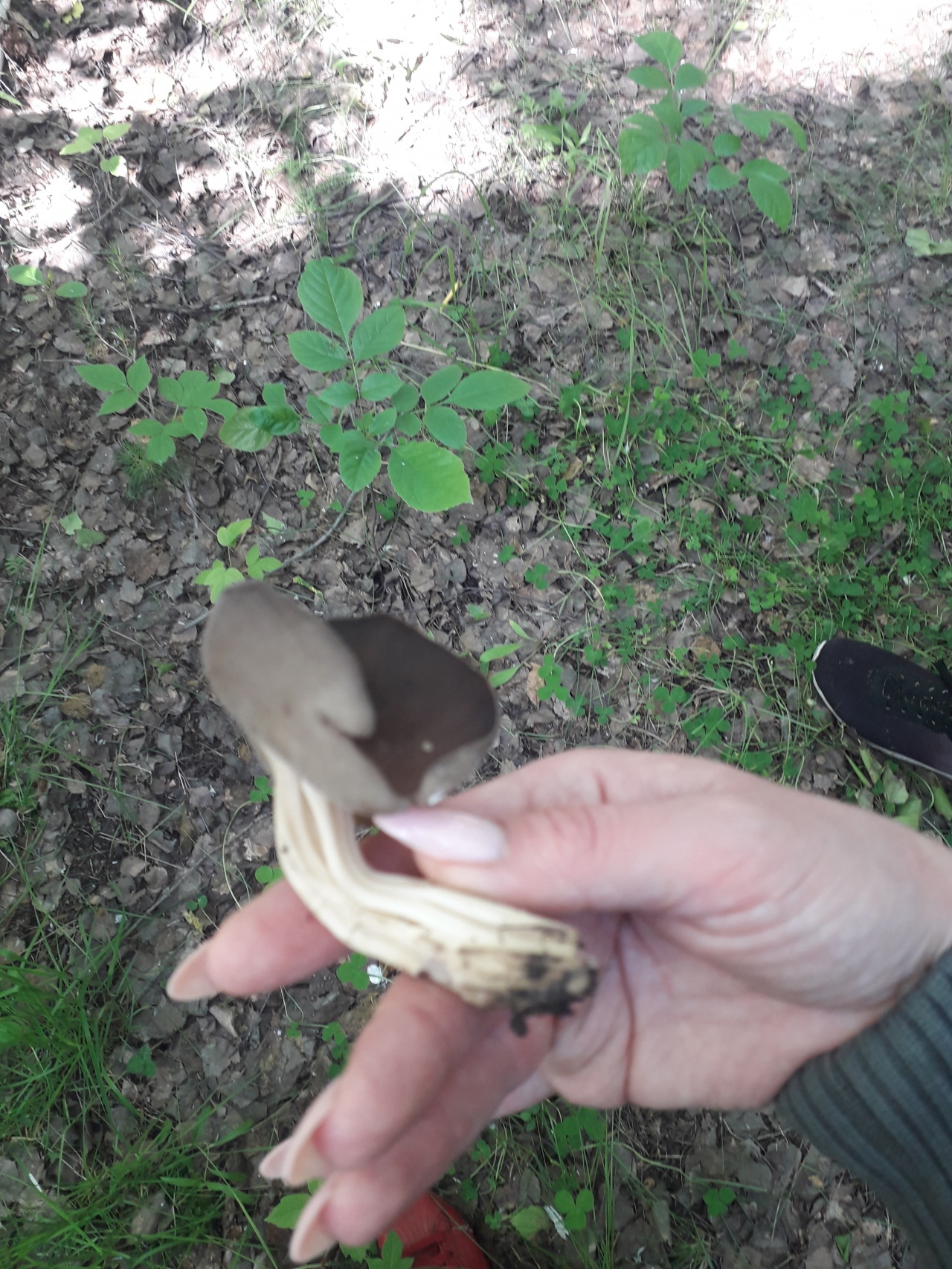
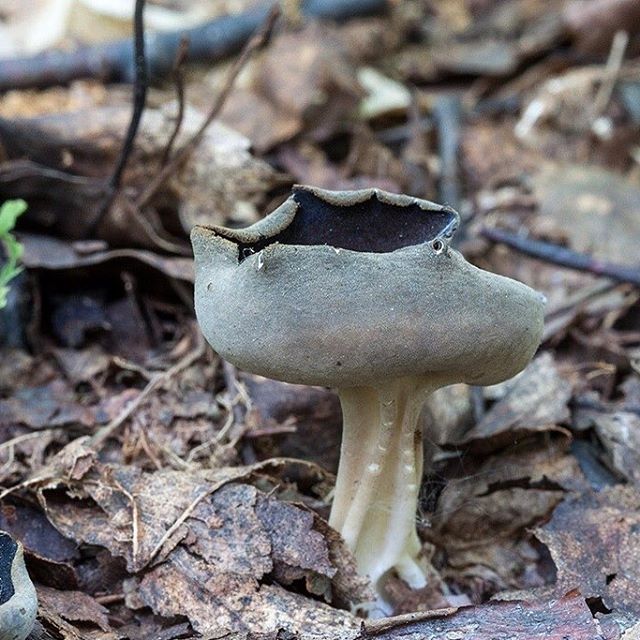
Lobules (Helvella lacunosa) belongs to the genus Lobules or Helvellas, the Helvellov family. The mushroom has other names - furrowed lobe or furrowed helwella. He also has Latin synonyms - costapeda lacunosa and helvella sulcata.

This is a conditionally edible marsupial species of mushrooms, its spores are in special bags. Its fruiting body is called apothecia and looks like a cap with a stalk.
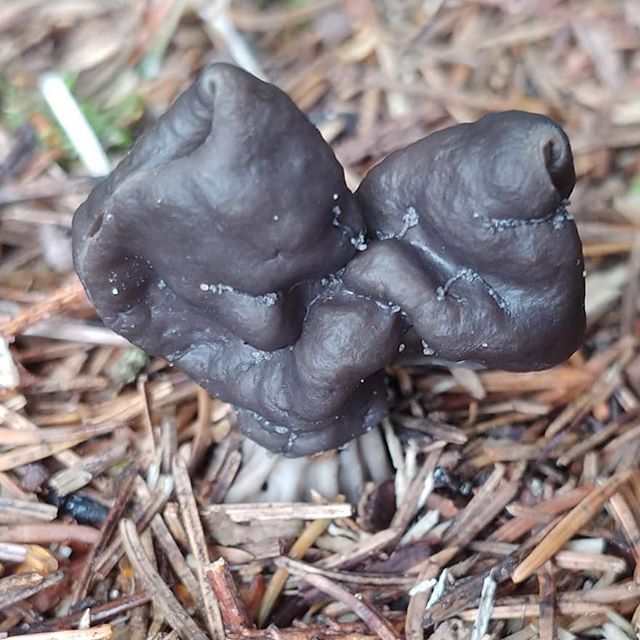
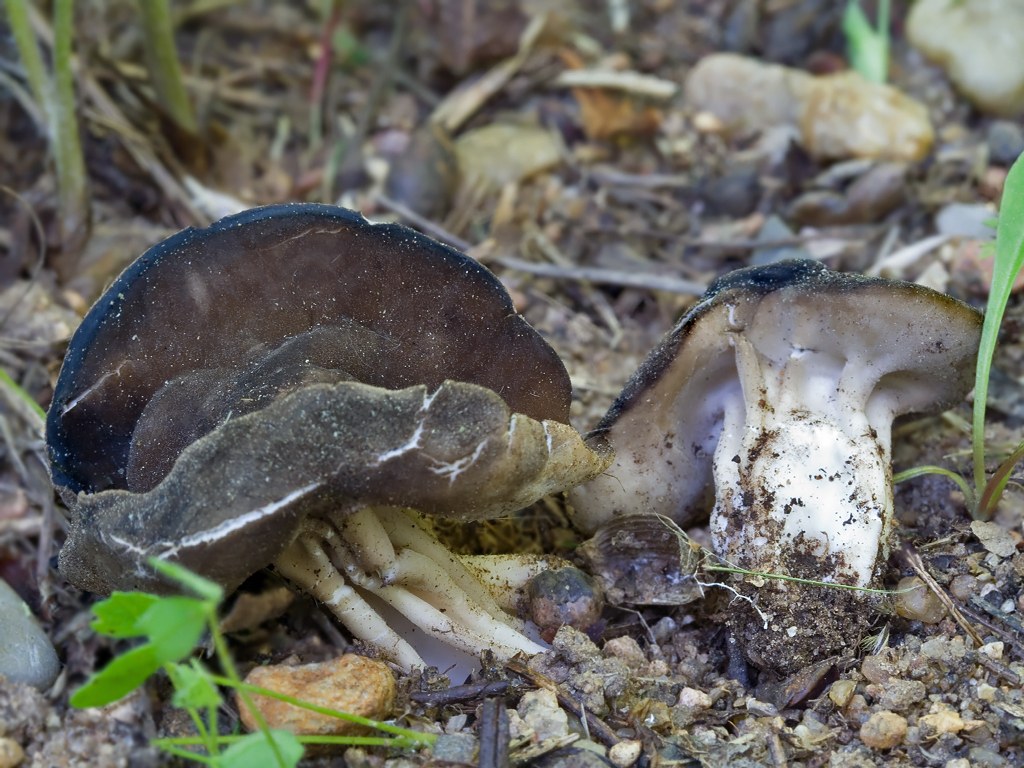
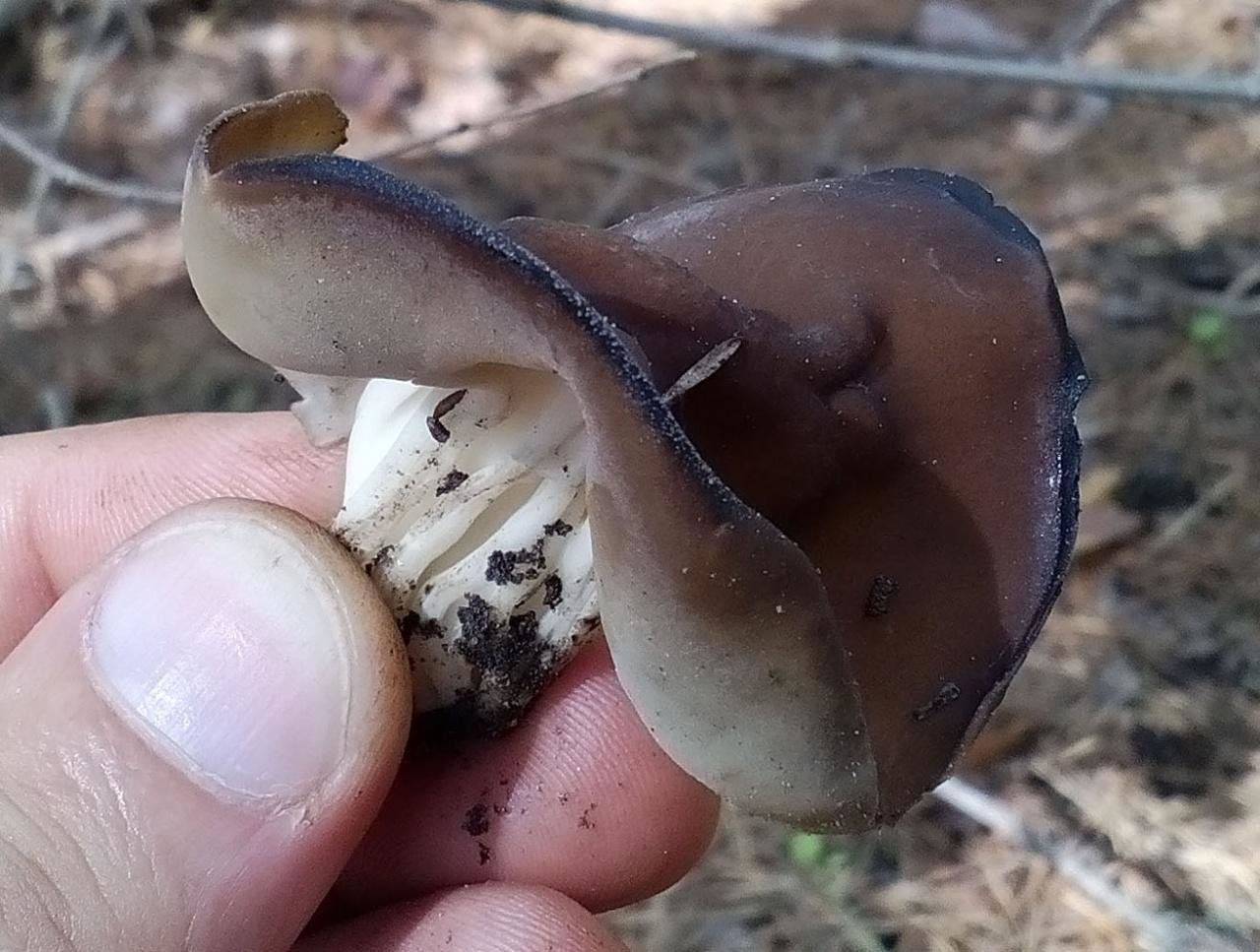
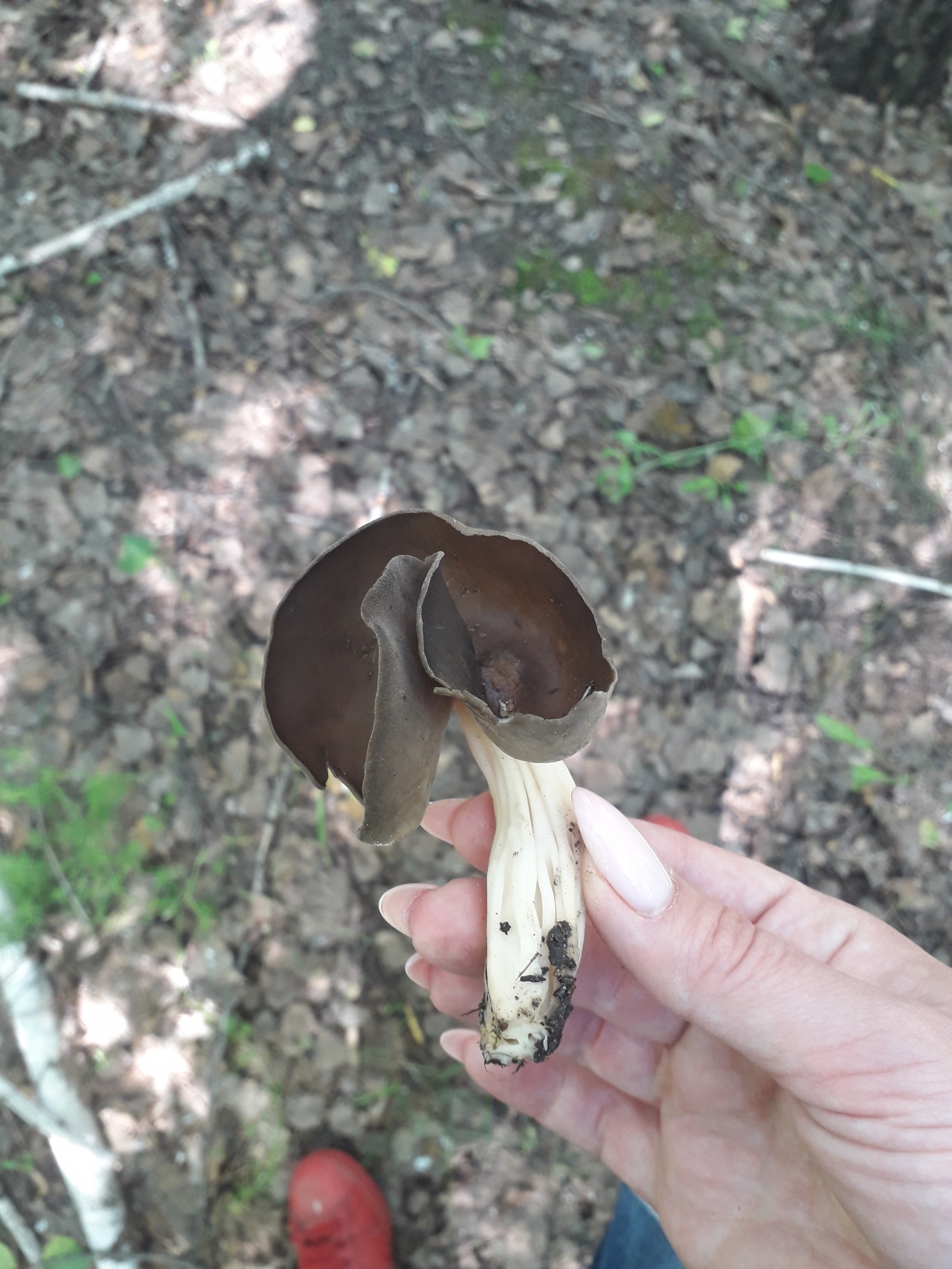
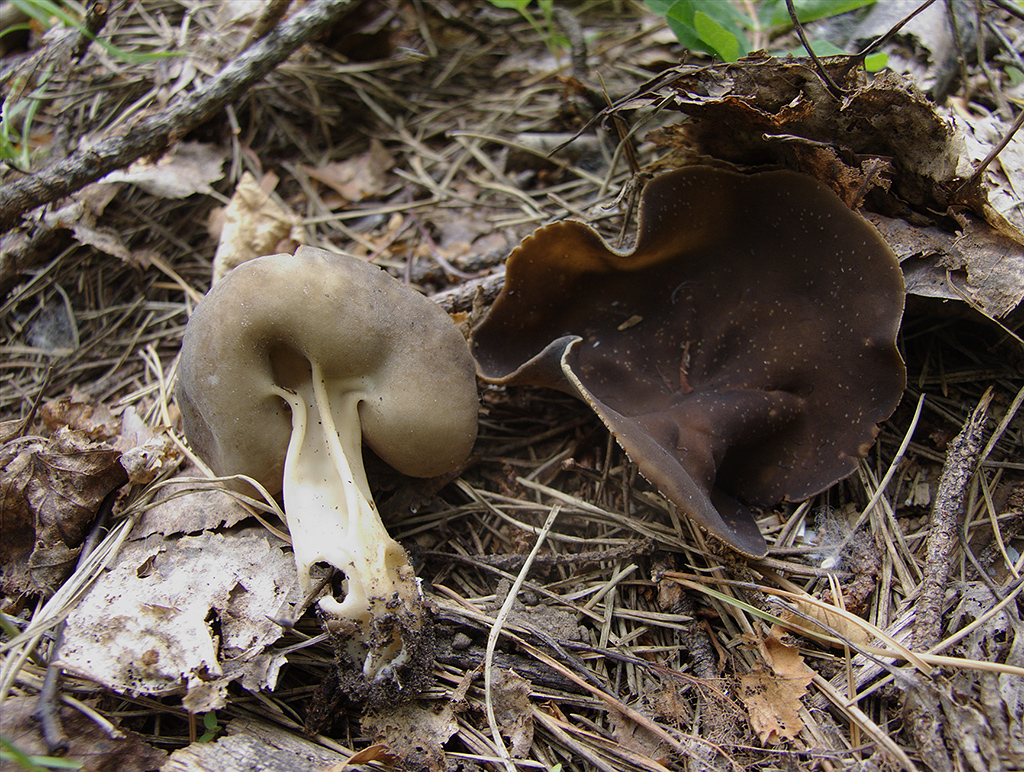
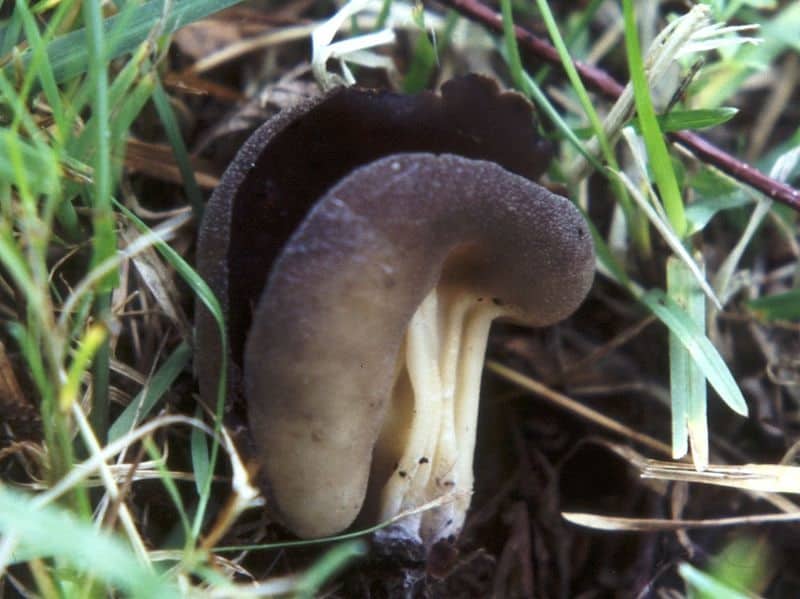
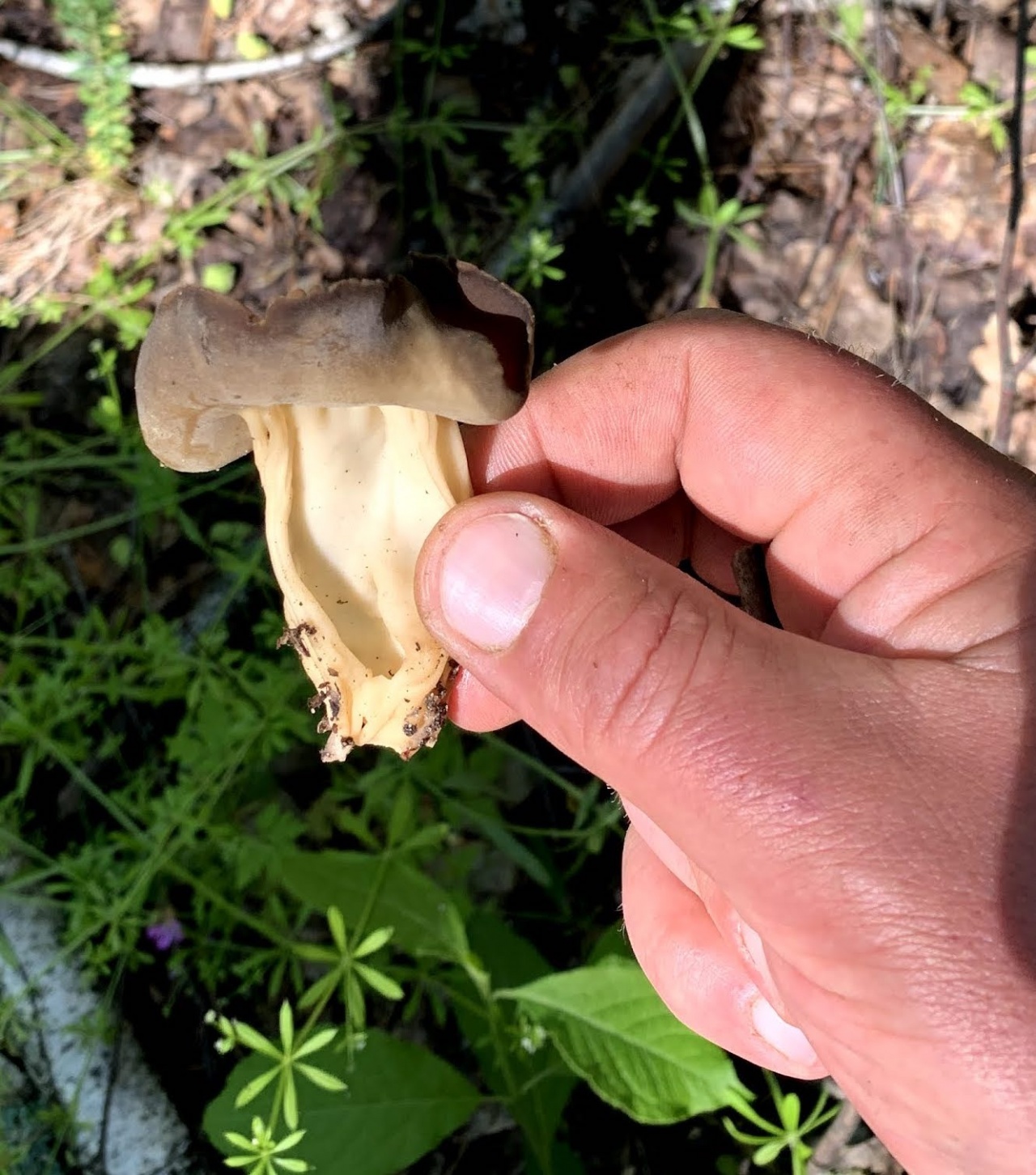
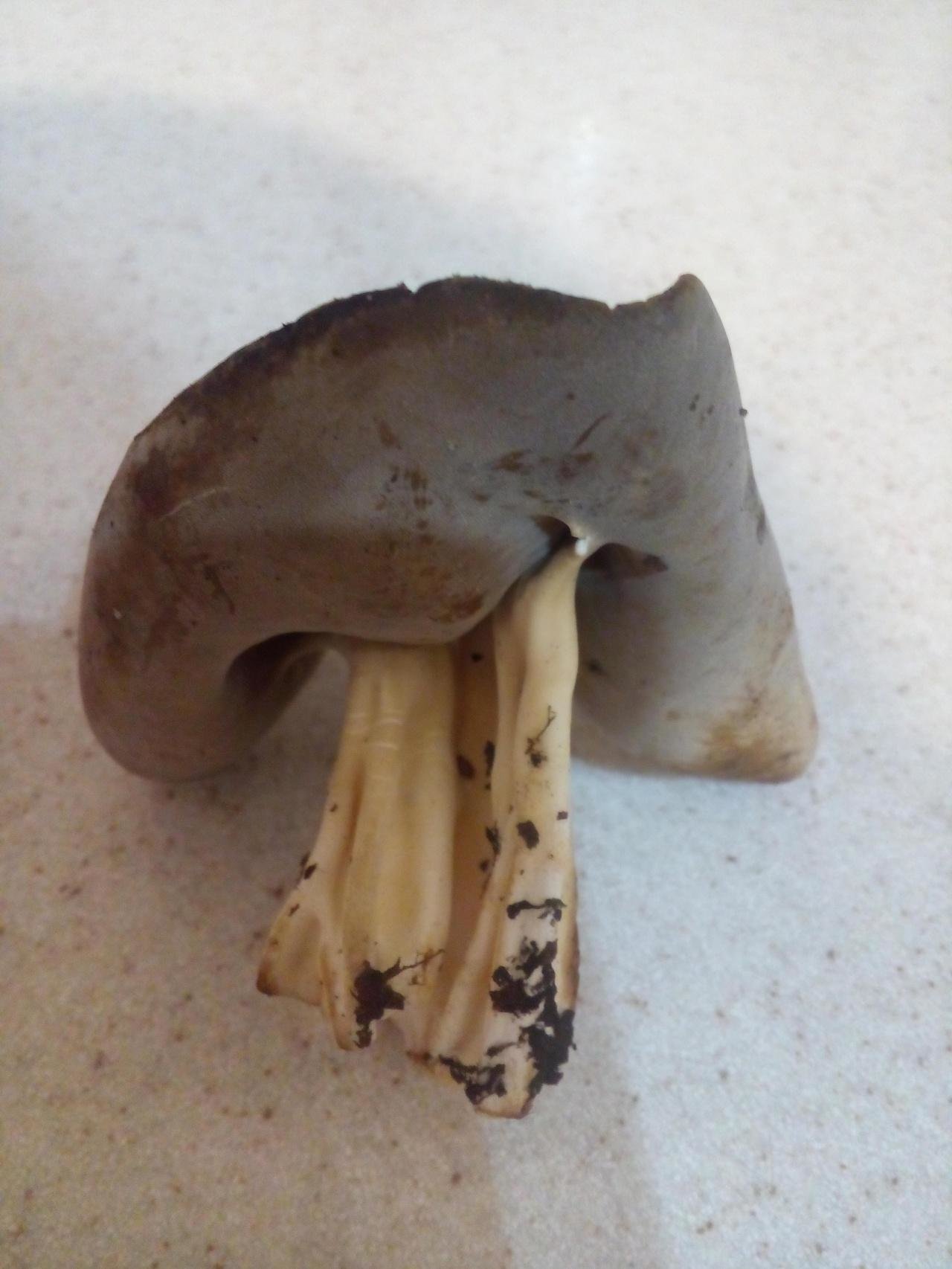
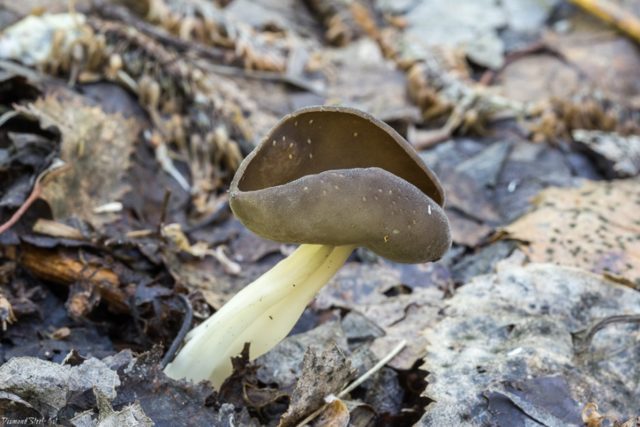
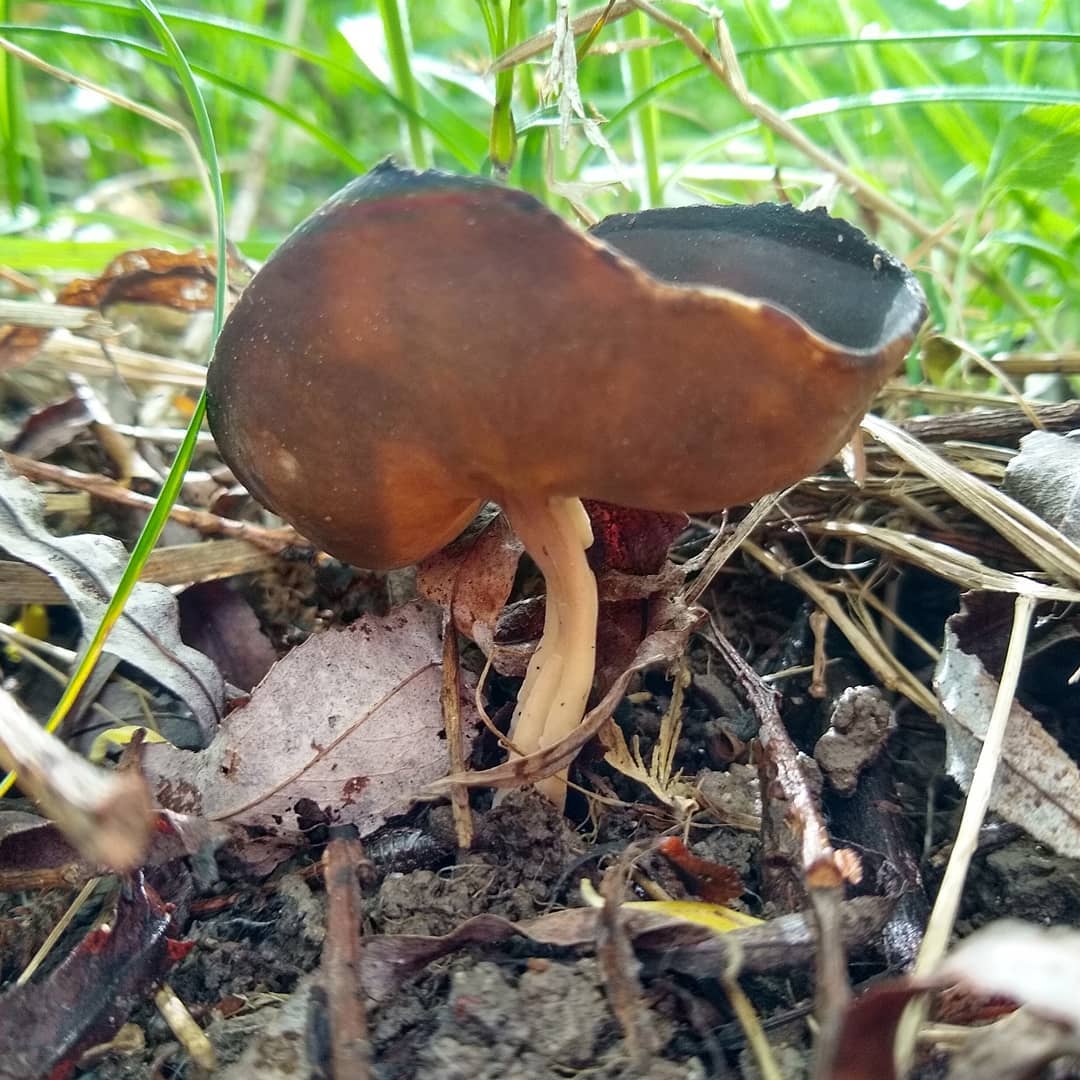
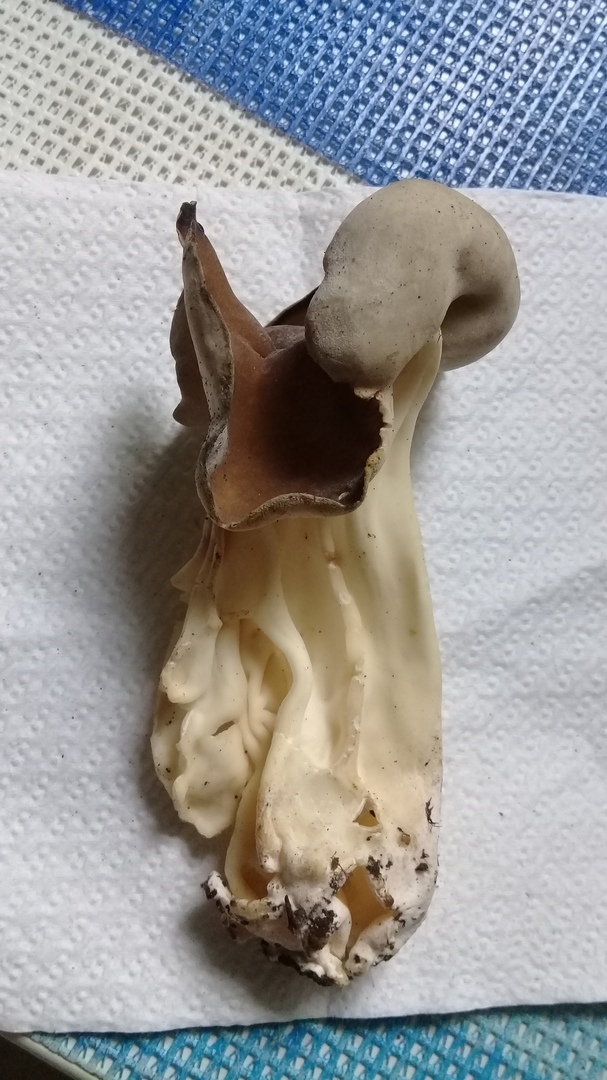
- the cap is quite changeable and may have a torn or twisted appearance, often takes the shape of a saddle, folded. Sometimes it is not even possible to understand what it looks like - the hat is so shapeless. It consists of 2-3 lobes, the edges of which hang down freely. The width usually varies from 2 to 5 cm. The surface color is gray in various shades, black. By the way, it is on top of the skin that the spore-forming layer is located. The skin is either smooth to the touch or has slight wrinkles on the outside. And under the hat it is lighter;
- the leg is from 2 to 8 cm in height and up to 1.5 cm in diameter, usually straight, hollow inside, consists of, as it were, accreted tubes, in the lower part it has a thickening. Outside, folded or deep furrowed. The surface is grayish, darkening as the fungus develops;
- the flesh is thin, fragile, watery, colored grayish-white or gray. It has no special taste or aroma;
- spores are white.
Places of distribution and period of fruiting
Pit-lobe prefers to settle on alkaline and moist soils, in fairly open spaces, on old fireplaces, conflagrations. It grows both in coniferous and mixed forest belts, but is very fond of deciduous, mainly birch forests. Perhaps, it is with birches that it forms mycorrhiza. It often grows next to the campfire moth (Phollota carbonaria) and cinder flakes (Pholiota highlandensis).

This lobe grows both in groups and in splendid isolation. Fruiting usually in the summer from June to August, sometimes occurs in the fall to October. The fungus is quite rare, but you can find it all over the Eurasian continent in the alpine or temperate climatic zone.
Similar species and how to distinguish from them
It is difficult to confuse the lobules with any other representative of the mushroom kingdom, but nevertheless there is a certain similarity with the conditionally edible curly Helvella (Helvella crispa), which has a lighter color of the fruit body.
Edible, primary processing and preparation
As for the edibility of this representative of the mushroom kingdom, the opinions of mycologists were divided. Some believe that the furrowed lobe is a conditionally edible species, others argue that it is inedible. The fact is that the representatives of the Helwell genus have one feature - they contain special toxins. It can be muscarine, gyrometrin, which can only be partially removed from the pulp during drying. However, no poisoning by lobe blades has been recorded to date.
Most sources say that the dimple lobe belongs to category IV mushrooms, but it is advised to use it only after prolonged drying or intensive boiling. After boiling, they can be fried.
Fortunately, you rarely come across a dimple lobe on the way of mushroom pickers, and it does not look very appetizing, so you most likely will not have a desire to rip it off. And rightly so - why risk your health? As they say, it would be because of what - the mushroom is far from a delicacy.
Helvella Kele
Description
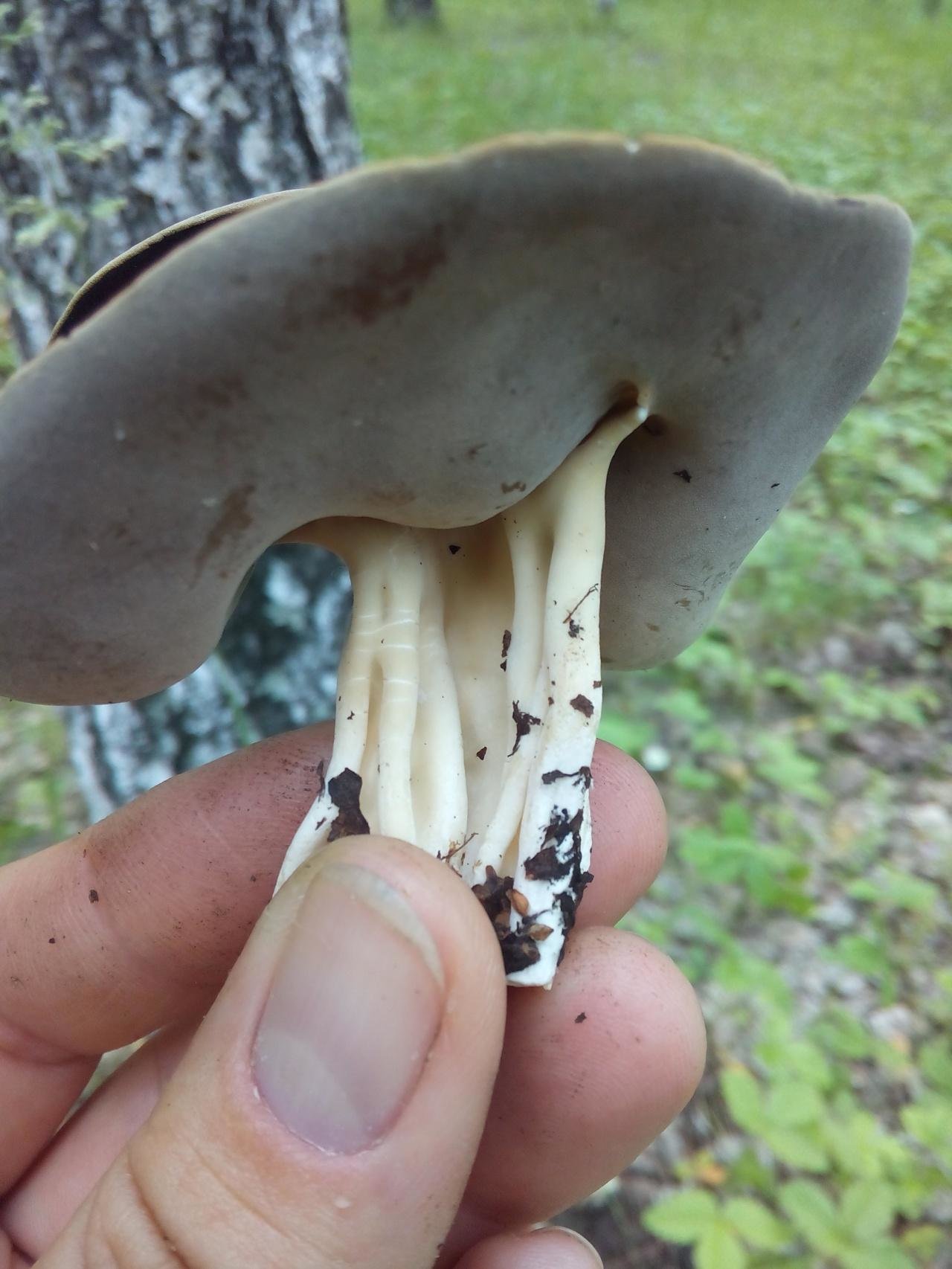
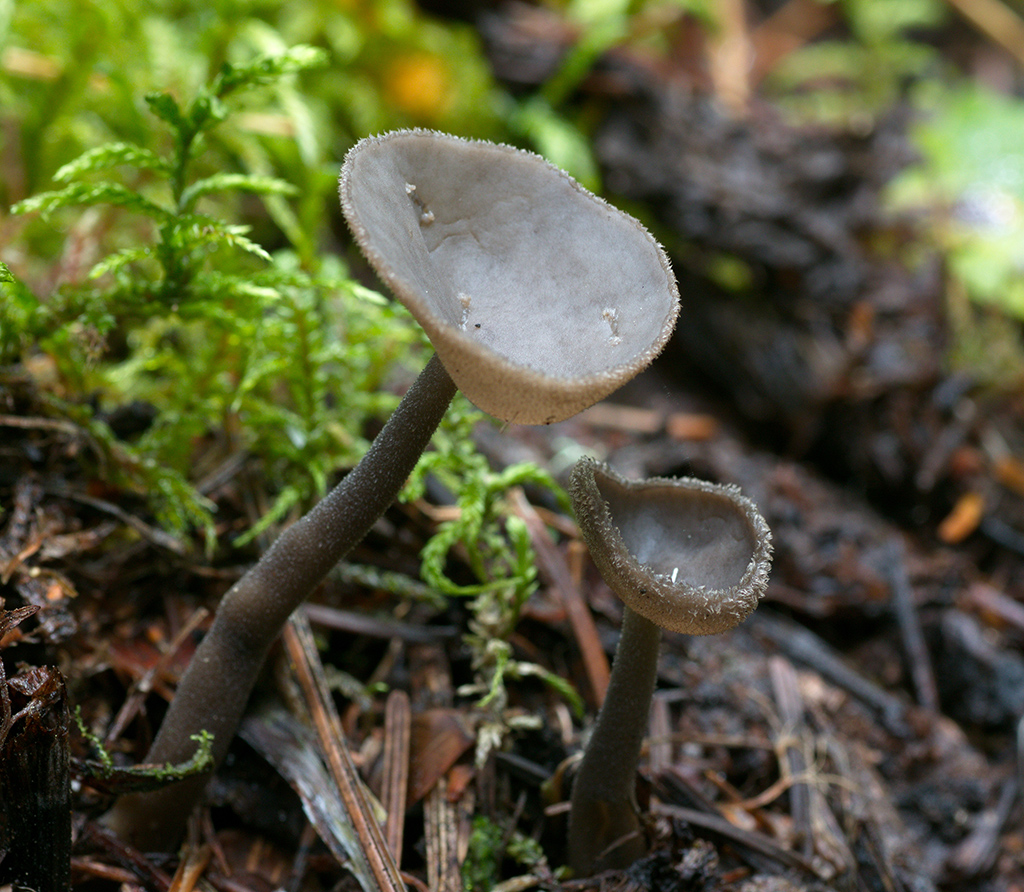
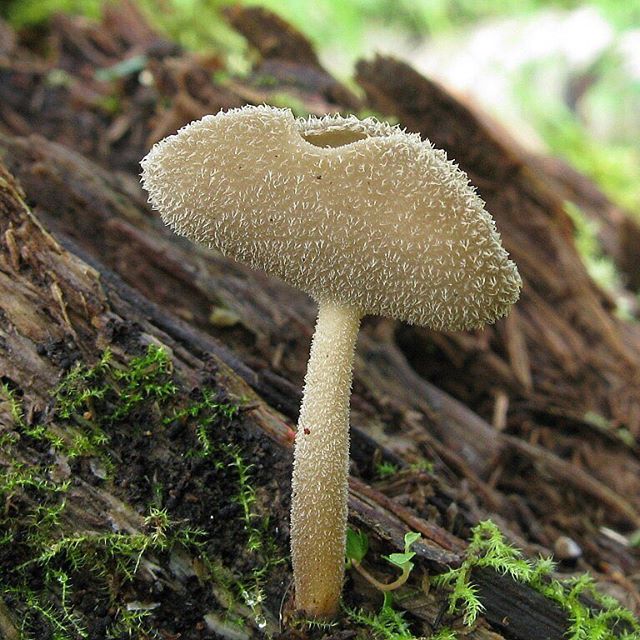
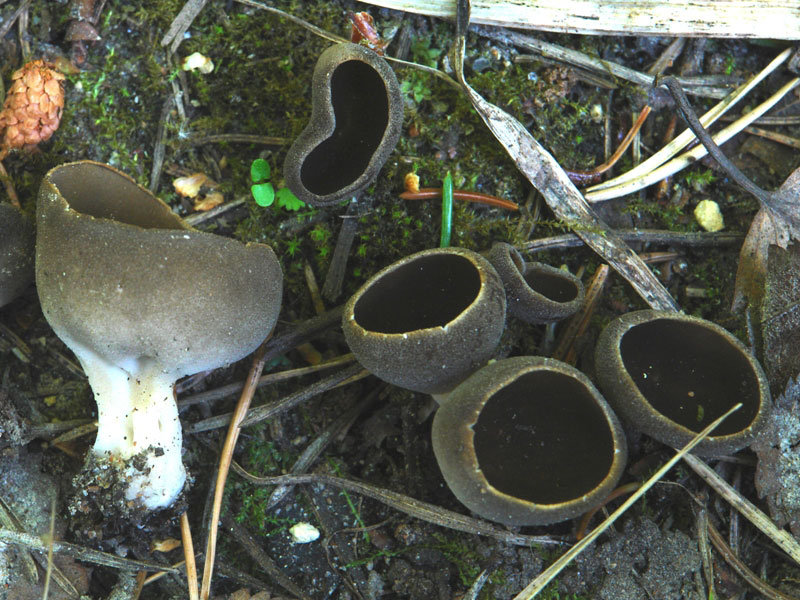
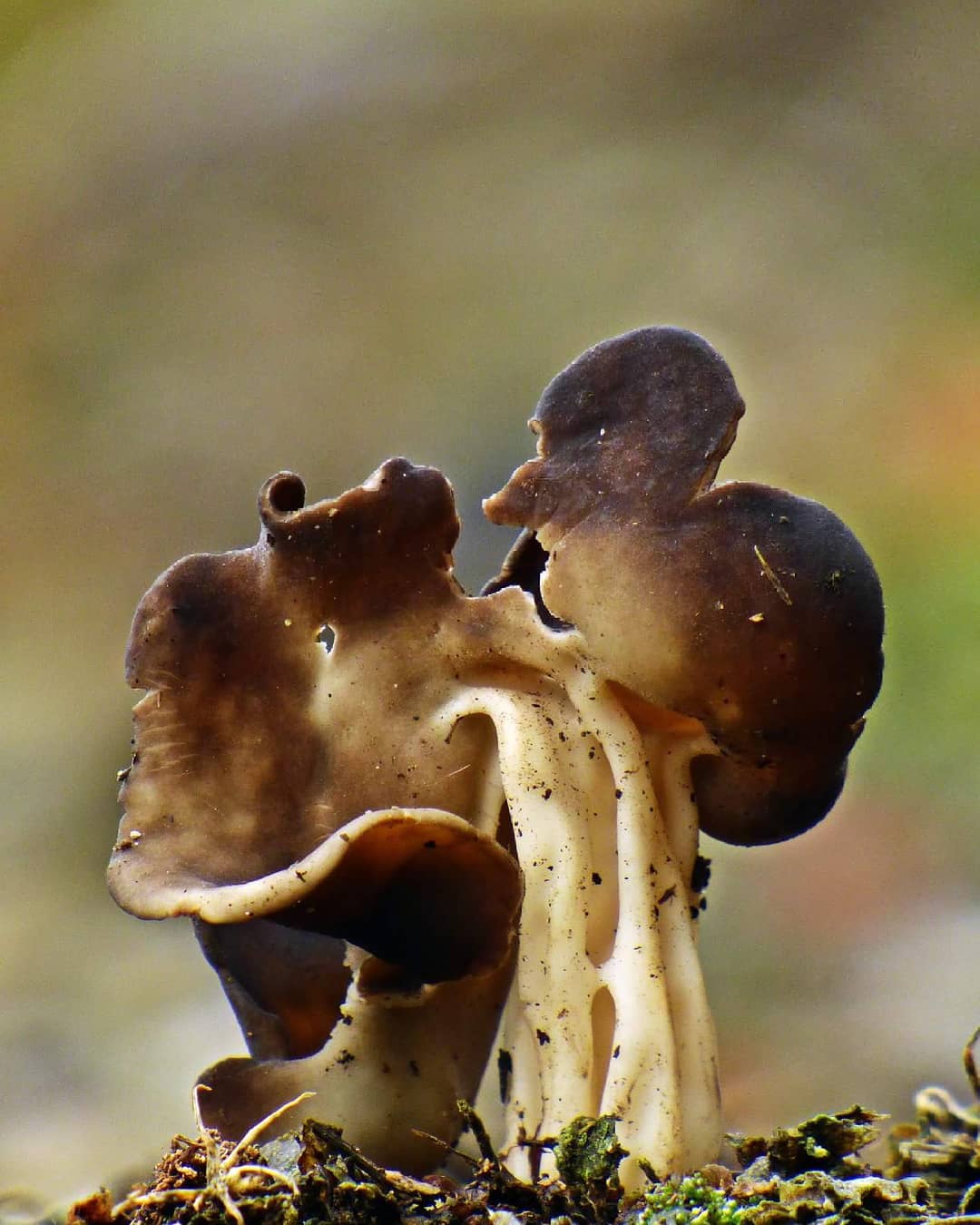
Hat: 1.5-6 cm.In young mushrooms, it is flattened from the sides, the edges can slightly curl inward. In mature specimens, it can acquire a saucer shape. The edge may be slightly wavy or “ragged”. The inner, spore-bearing surface is from grayish-brown to brown, brown and even almost black, smooth. The outer surface is much lighter than the inner one, pale grayish-brown to whitish when dry, on it you can see some kind of indistinct "granularity", which is actually bundles of short villi.
Leg: height 6-8, sometimes up to 11 centimeters. The thickness is usually about a centimeter, however, some sources indicate the thickness of the leg up to 4 centimeters. The leg is distinctly ribbed, 4-10 ribs, slightly passing into the cap. Smooth or slightly widening towards the base. Not hollow.
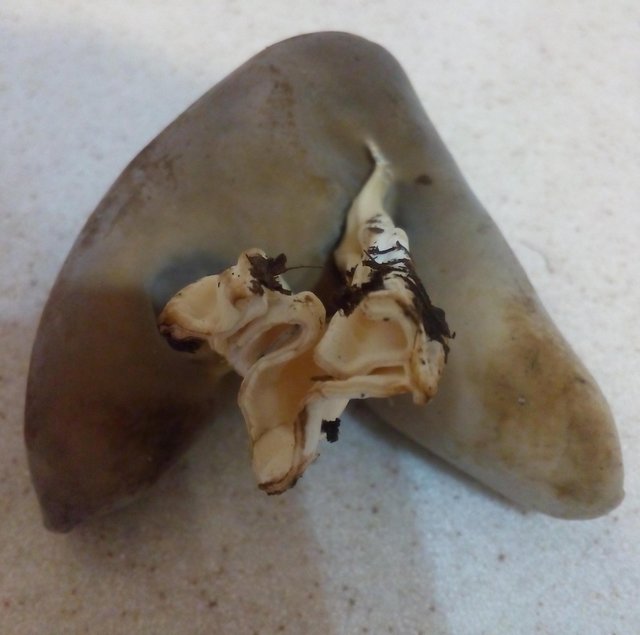
Light, whitish or very pale brown, in the upper part it may be slightly darker, in the color of the outer surface of the cap. The ribs do not break off abruptly when passing from the cap to the stem, but go to the stem, but quite a bit, and do not branch.
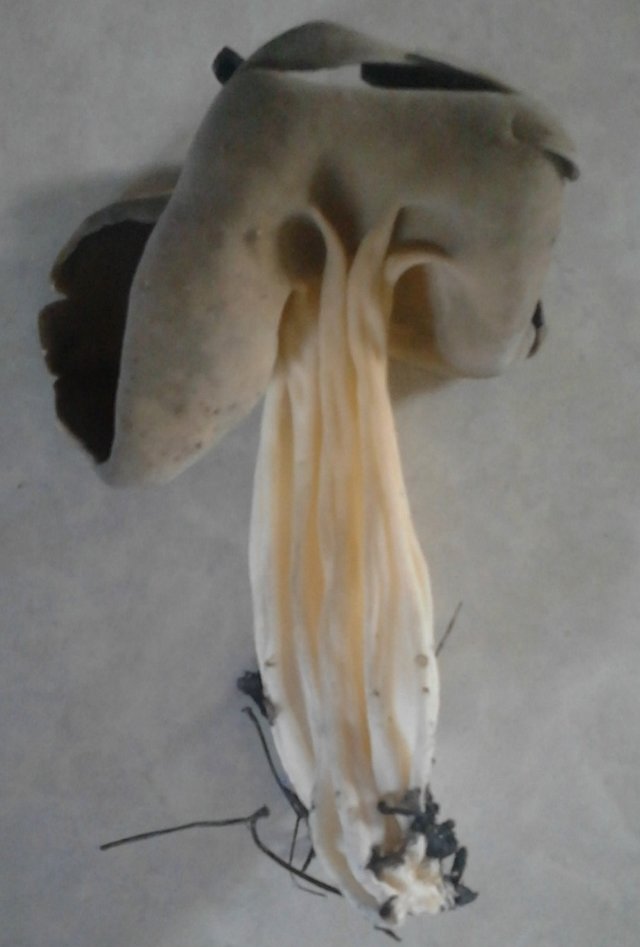

Flesh: thin, brittle, light. Smell: unpleasant.
Disputes 17-22 x 11-14 μ; elliptical, smooth, smooth, with one central droplet of oil. Paraphysis filamentous with rounded apices, which become sharpened with maturity, 7-8 microns.
Season and distribution
Lostweed Kele can be found in spring and summer in various types of forests: coniferous, deciduous and mixed. Distributed in Europe, Asia, North America.
Edibility
The data is inconsistent. The mushroom is considered inedible due to its unpleasant odor and low taste. No data on toxicity.
Similar types and differences from them
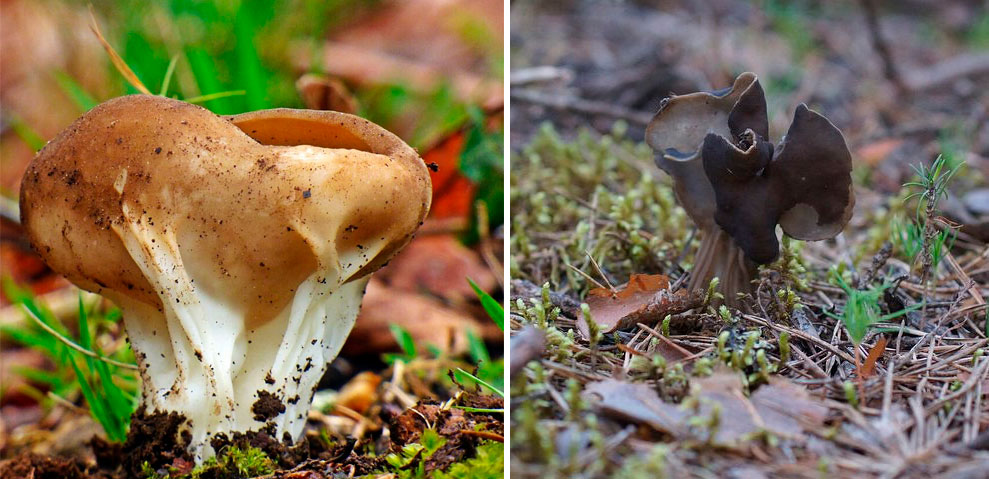
- Saucer lobe (Helvella acetabulum) - the most similar to the Kele lobe, the species overlap in time and place of growth. The goblet lobe has a much shorter leg, the leg is widened to the top, and not to the bottom, like in Kele's lobe, and the main difference is that the ribs go high to the cap, forming a beautiful pattern, which is compared either with frosty patterns on glass or with a pattern of veins. whereas in the Kele lobe, the ribs go to the cap by literally a few millimeters and do not form patterns.
- Lobules (Helvella lacunosa) intersect with the Kele lobster in summer. The main difference: the cap of the pitted lobe has a saddle shape, it is bent downward, while the Kele lobe has a cup-shaped cap, the edges of the cap are bent upward. The foot of the paddle blade has hollow chambers, which are often visible by simply examining the fungus, without cutting.
Other information about the mushroom
The species was named in honor of the mycologist Lucien Quélet (1832 - 1899)
Mushroom photo Helvella Kele from questions in recognition:
Helvella crispa
or
Helvella curly
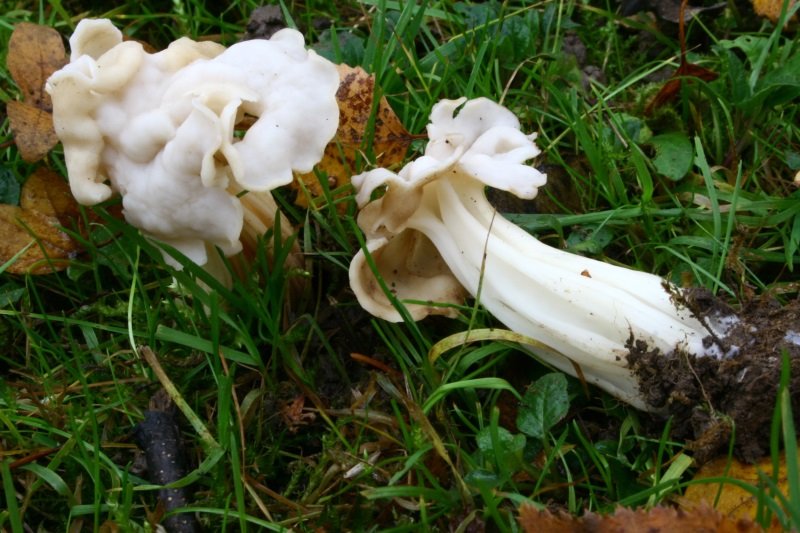

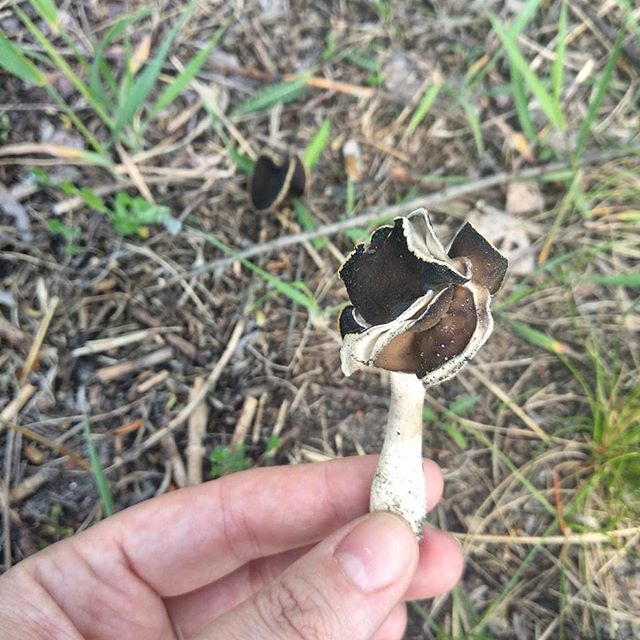
Helvella curly, or Helvella curly (lat.Helvella crispa) is a species of mushrooms belonging to the genus Lostnik, or Helvella (Helvella) of the family Helvellaceae, a lectotype of the genus.
Helwella curly, among the inhabitants of the forest, is one of the few representatives of mushrooms, the Helwell family. And the word Helwella, literally translated from Latin, means: "small vegetable", "greens" or "cabbage" and, in the best possible way, characterizes the very essence of this mushroom. In Russia, the genus Helwell is called differently, they are called blades, because of the characteristic structure of their cap in the form of a propeller blade. This is especially evident in other types of helwell. In total, there are 25 species of such mushrooms and 9 of them grow in Russia. And Helvella curly, among all lobules, is not the most common mushroom. A characteristic feature of all blades (helwell) is the content of a certain amount of toxins in their composition. Some of them contain the heavy toxin gyrometrin, while others contain muscarine, which can be removed from them only partially and only during the drying process.Helwella curly, as well as common lobster, is considered by some sources to be a conditionally edible mushroom with the taste of mushrooms of the fourth category. This is partly so, but ... and not so. Cases of poisoning with lobules have not yet been recorded, and the degree of poisoning with them directly depends on the number and frequency of their use. Here, for this very reason, Curly Helwell (or Curly Helwell) is best considered an inedible mushroom. And, therefore, it is highly undesirable to use it in food. Yes, and it is extremely rare in our area, and the taste is not at all tasty.
Helwella curly is a rather rare mushroom. And the main places of its growth can be considered deciduous and coniferous forests of Europe and the European part of Russia, in which it is found in small groups, often along forest roads and, unlike the common lobster (Helwella vulgaris), it grows not in spring, but in autumn - from the beginning of August to the end of October.
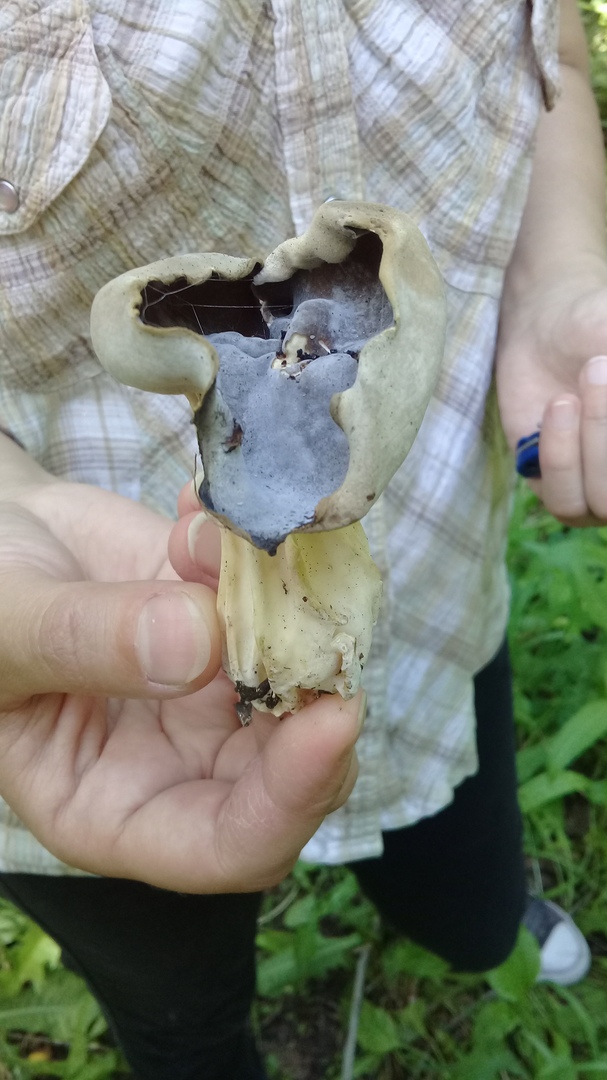
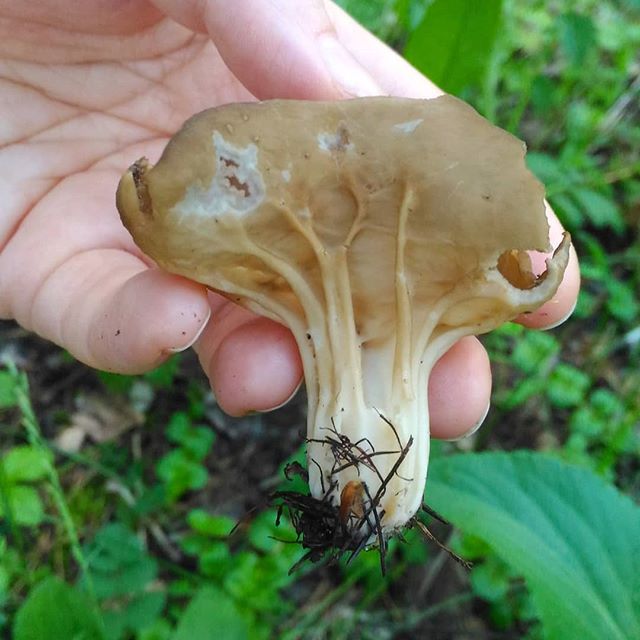
Helvella curly refers to marsupial mushrooms, that is, its spores are located in the very body of the mushroom in the so-called "bag". His cap is folded, two to four lobed, irregular and incomprehensible in shape, with wavy or curly edges hanging down and, only in places, growing to the stem. The color of his cap is from waxy beige to pale ocher. The stem of the fungus is short, straight or slightly curved, slightly swollen at the base, with deep longitudinal grooves or folds, it is hollow inside. The color of the leg is white or ash gray. The flesh of the mushroom is thin and very brittle, waxy white in color, with a pleasant mushroom smell. But, all the same, it is not worth trying in the forest the taste of Curly Gelwell in its "raw" form!
Gelvella curly - refers to conditionally edible mushrooms. (4th category)
Edible mushrooms, berries, herbs
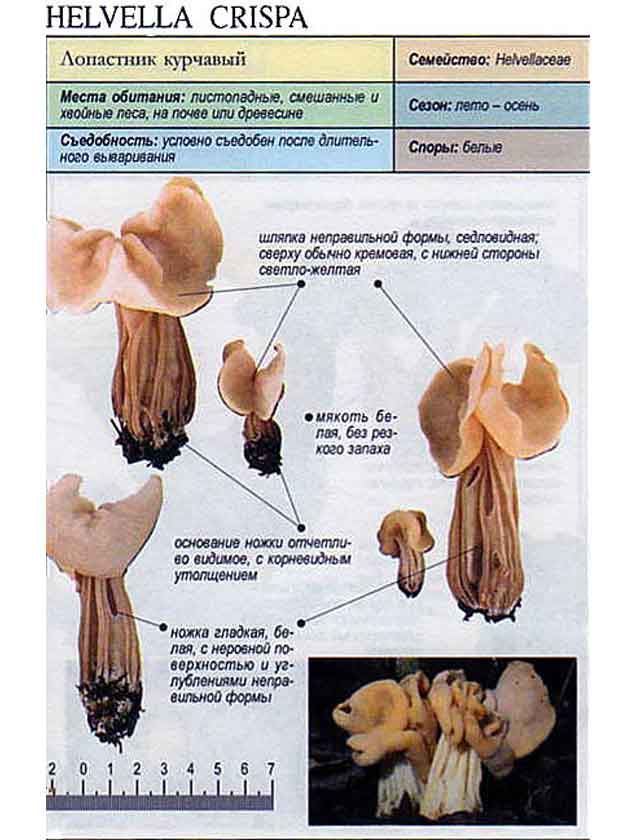
Curly loafer (helvella crispa)
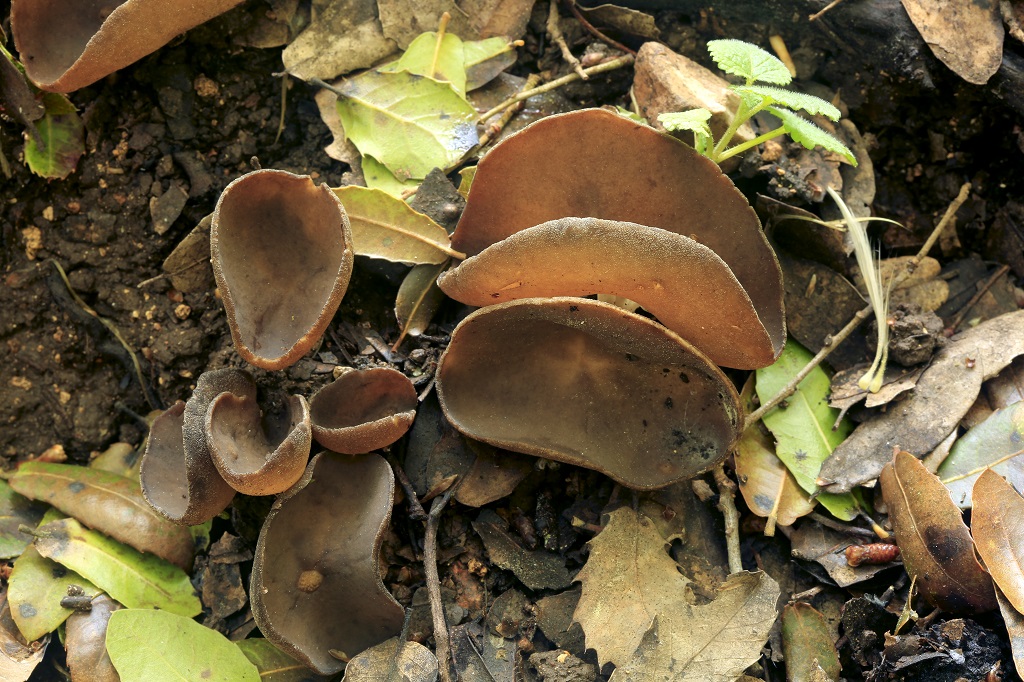
From May to early June and from mid-August to October in deciduous, coniferous and mixed forests, near bushes, along paths and roads, you can meet a mushroom from the Helwell family - curly lobster (curly helvella). The fungus has an irregularly shaped fruiting body with a notched ribbed stem. Grows in groups, rarely singly. preferring the grass cover.
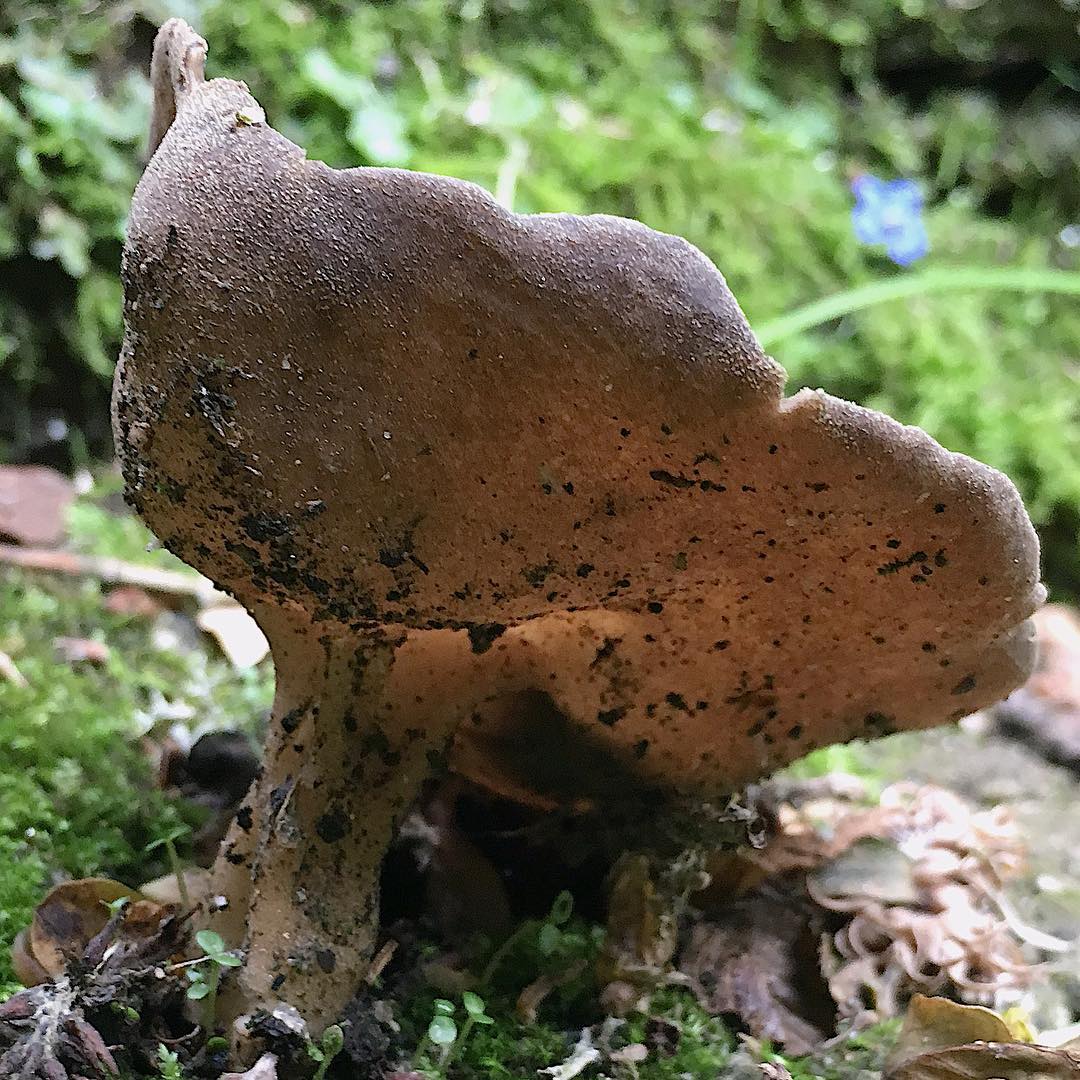
The hat is from 1.5 to 4.5 cm in diameter, two- or four-bladed, usually curved. The edges are wavy-curly, free, adherent in places. The color is light yellow or ocher.
The leg is pitted-furrowed, fusiform, slightly widened towards the base, light white, hollow inside.
The pulp is thin, brittle, whitish, practically odorless.
The mushroom is edible and has low taste and organoleptic qualities. Edible after pre-cooking for at least 12 minutes. In addition to cooking, you can also dry it.
Photos of curly lobe (helvella crispa)




Video about how and in what conditions curly lobes grow, how these mushrooms look in natural conditions
The collected impressive volume of Ivan-tea raw materials or limited free time (sometimes all together) do not allow making Koporye tea by hand using traditional technology. Modern means come to our aid, one of which is a simple electric meat grinder. Tea made in this way is obtained in granular form. (more)
Already in April, delicious gourmet spring mushrooms - morels, represented by three main types: real morel, conical morel, morel cap - begin to grow en masse. Giant and ordinary lines can often be found next to morels. For lovers of exotic dishes, the spring forest also offers the most beautiful sarkoscifs, miniature strobiliurus, and a variety of saucers. In May, the species composition increases significantly: various horned beetles, dung beetles, tinder fungi, champignons, raincoats, May ryadovki, entolomy, pecicia, and spring mushrooms are added.
Edible mushrooms of an unusual shape, found in the European part of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Germany, have been added to the catalog:
| Grifole umbrella |
Descriptions with a photo of the liverwort (liver mushroom) and the sleepy mushroom (scaly saw leaf) have been added to the catalog with edible mushrooms.
Helvella Kele Helvella queletii
Syn: Acetabula queletii (Bres.) Benedix, 1962
Last page update -

The site needs photos of this mushroom All Helvella queletii’s photographs posted on the site you can see here
The description of the mushroom was made by Evgeny Popov with the participation of Alexei Myasnikov, Salavat Arslanov and Irina Ukhanova.
Helvella Kele (Lobster Kele) what it looks like, where it grows, edibility, how to distinguish it, photo
Lobster Kele (Helvella Kele): description and photo
The Kele loafer is a rare type of mushroom. In Latin it is called Helvella queletii, the synonymous name is Helvella Kele. Belongs to the Lopastnik family, the Helwell family. Named after Lucien Kele (1832 - 1899). This is a French scientist who founded a mycological association in France. Actually, he discovered this type of mushroom.

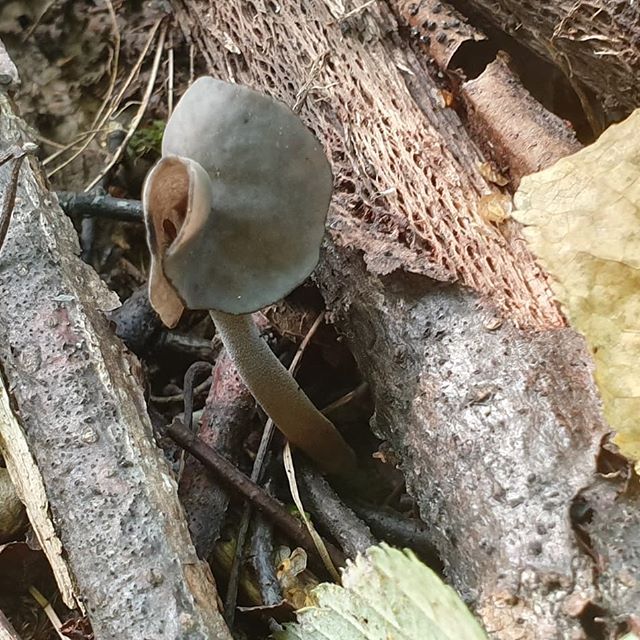
How Kele Helwells look
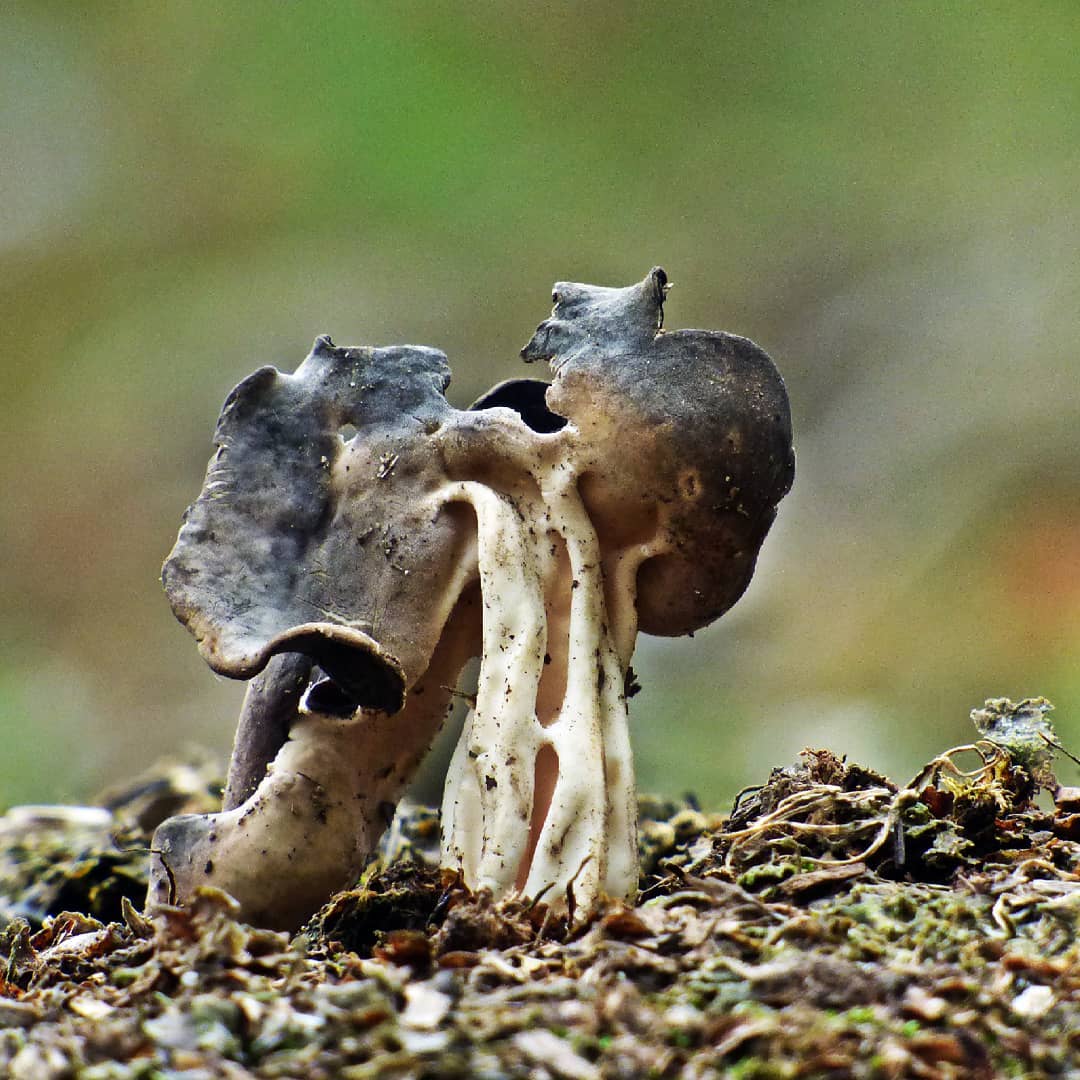
Young mushrooms have cup-shaped caps flattened on both sides. Their edges are slightly curved in the middle. Mature lobes become saucer-shaped, with perfect and solid or serrated edges.
The skin on the upper surface is covered with a pale grayish-brown, brownish, yellow-gray paint. When dry, the cap becomes light gray, a whitish or gray granular bloom looms on it, it is a bundle of short hair. The surface inside is smooth, much dark, can be from gray-brown to almost black.
The leg is pulled up, even, not hollow, grows 6-10 cm in length. Certain sources provide information that its thickness reaches 4 cm, but more often it is very thin, about 1-2 cm. Its shape is cylindrical or clavate, towards the base it can slightly increase.
The leg is ribbed. Number of ribs - from 4 to 10, direction - longitudinal. They do not break off at the transition of the cap to the leg. Its color is light, whitish, below it is quite dark, in the upper tone it is reddish, grayish, brownish, very often similar to the color palette of the outer part of the cap.
The flesh of the mushroom is light in color, brittle and superfine. Fetid odor exudes. Does not represent taste value.
Helvella Kele belongs to the category of marsupial mushrooms. Propagated by spores spread in the fruiting body, in the "bag". They are smooth, elliptical in shape, with one drop of oil in the very center.
Where do Kele blades grow?
Helwella is found in various types of forests: deciduous, coniferous, mixed. She prefers well-lit areas. Grows on soil, less often on rotten wood or dead wood, in most cases singly, or in few groups.
The species is distributed on several continents. Mushrooms can be found in Eurasia and North America. In certain states: the Czech Republic, Poland, the Netherlands, Denmark - Helwell Kele is listed in the Red Book. It is not guarded in Russia. The region of its distribution is vast. The species is found in most regions of the country, quite often in the Leningrad, Moscow, Belgorod, Lipetsk regions, in Udmurtia and in the Stavropol region.
Helvella Kele appears early. The development period begins in May. Fruiting lasts until July inclusive, and in the north it is delayed until the end of summer.
Is it possible to have Kele Helwells
There is no evidence in scientific sources that Helwell Kele can be eaten. The species is not even classified as conditionally edible, there is no description of its nutritional value and belonging to one or another flavoring category.
At the same time, information about the toxicity of fungi has not been demonstrated either. No cases of Helwell poisoning have been reported in the Russian Federation.All the same, the smaller size and fetid smell of the pulp make the lobe unsuitable for consumption.
Conclusion
Helvella Kele are spring mushrooms that appear in forest areas as early as May. Sometimes the species grows within the city. But it will take a lot of effort to find it - Kele's lobe is rare. Collecting it does not make sense and even scary. In European countries, situations of poisoning with blades have been recorded.