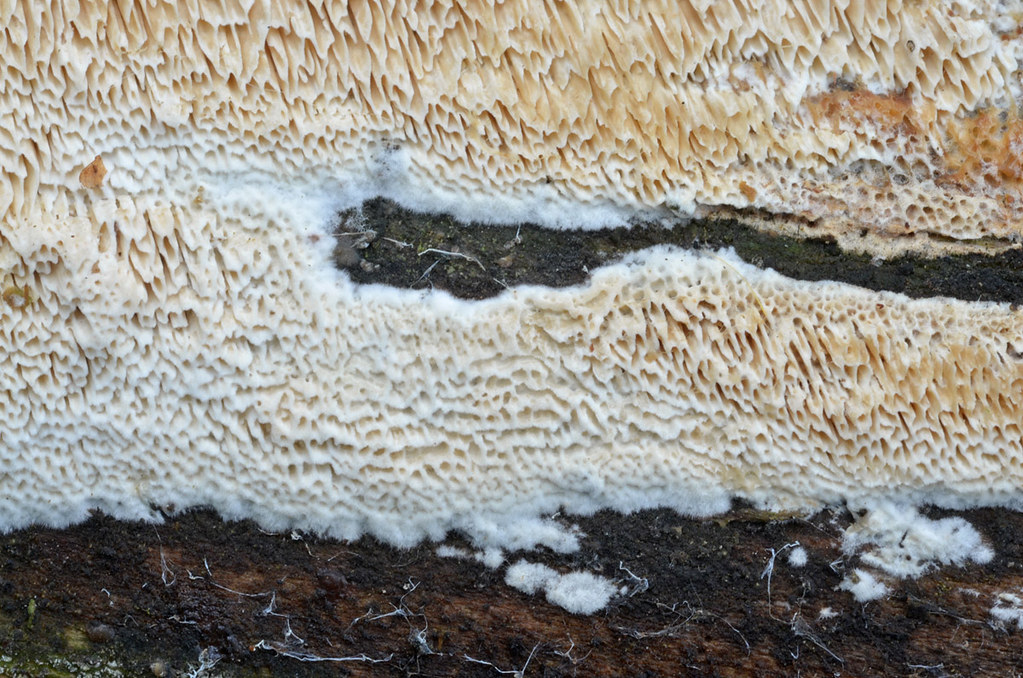
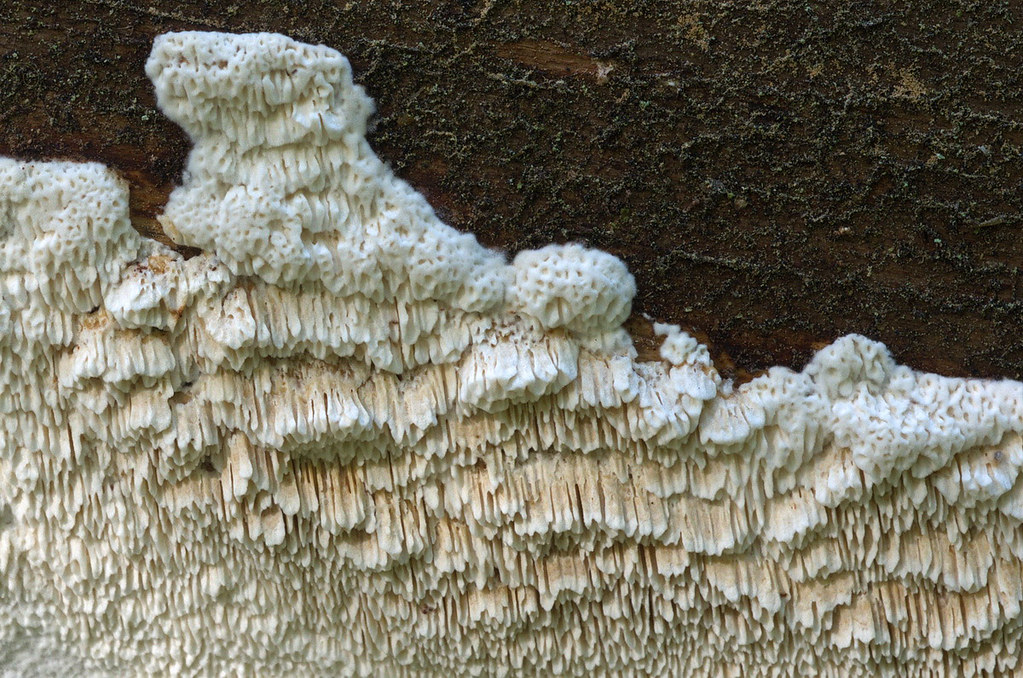
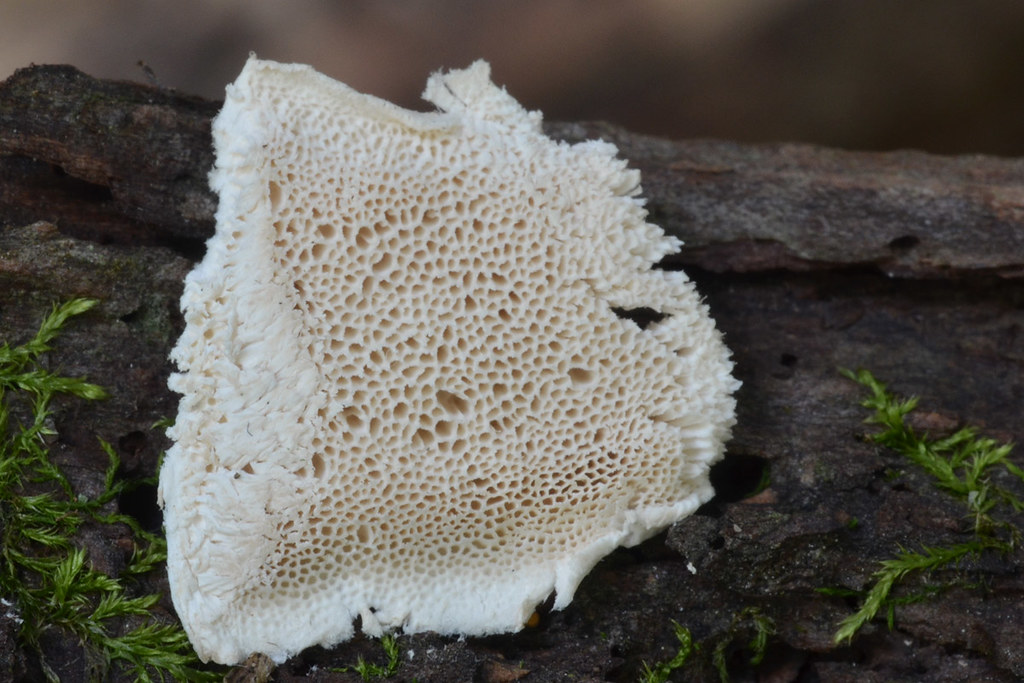
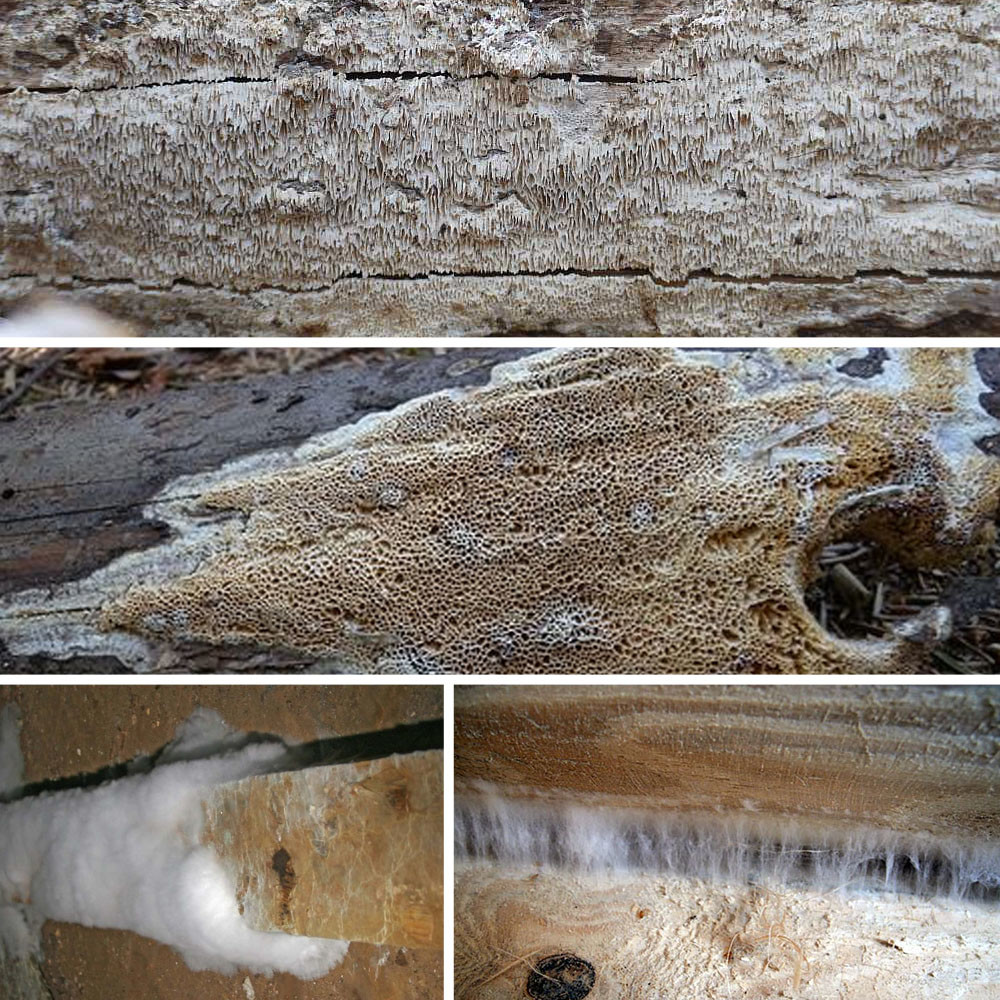
Habitat
The mushroom house has a high degree of ability, characteristic of mushrooms in general, to develop an abundant mycelium in conditions that are not conducive to fruiting. Such conditions are humidity, stale, stagnant air and lack of light. Under these conditions, the fungus quickly and abundantly develops in a sterile form (it was previously called Himantia link) and vigorously pursues the deed of destruction.
Most often, the fungus develops in dark, stuffy and damp cellars and basements, at the base of beams, on the lower surface of floor boards, directly resting on moist soil.
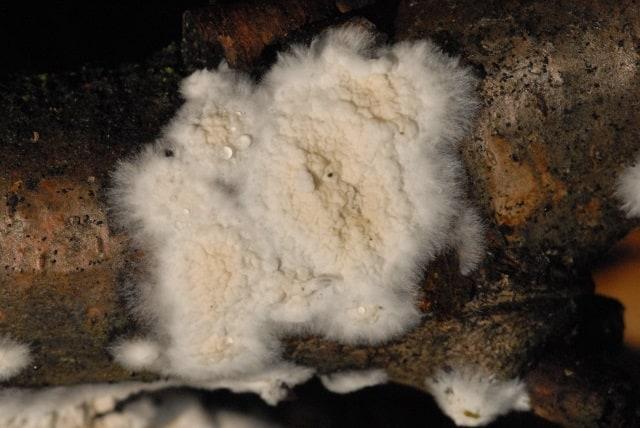
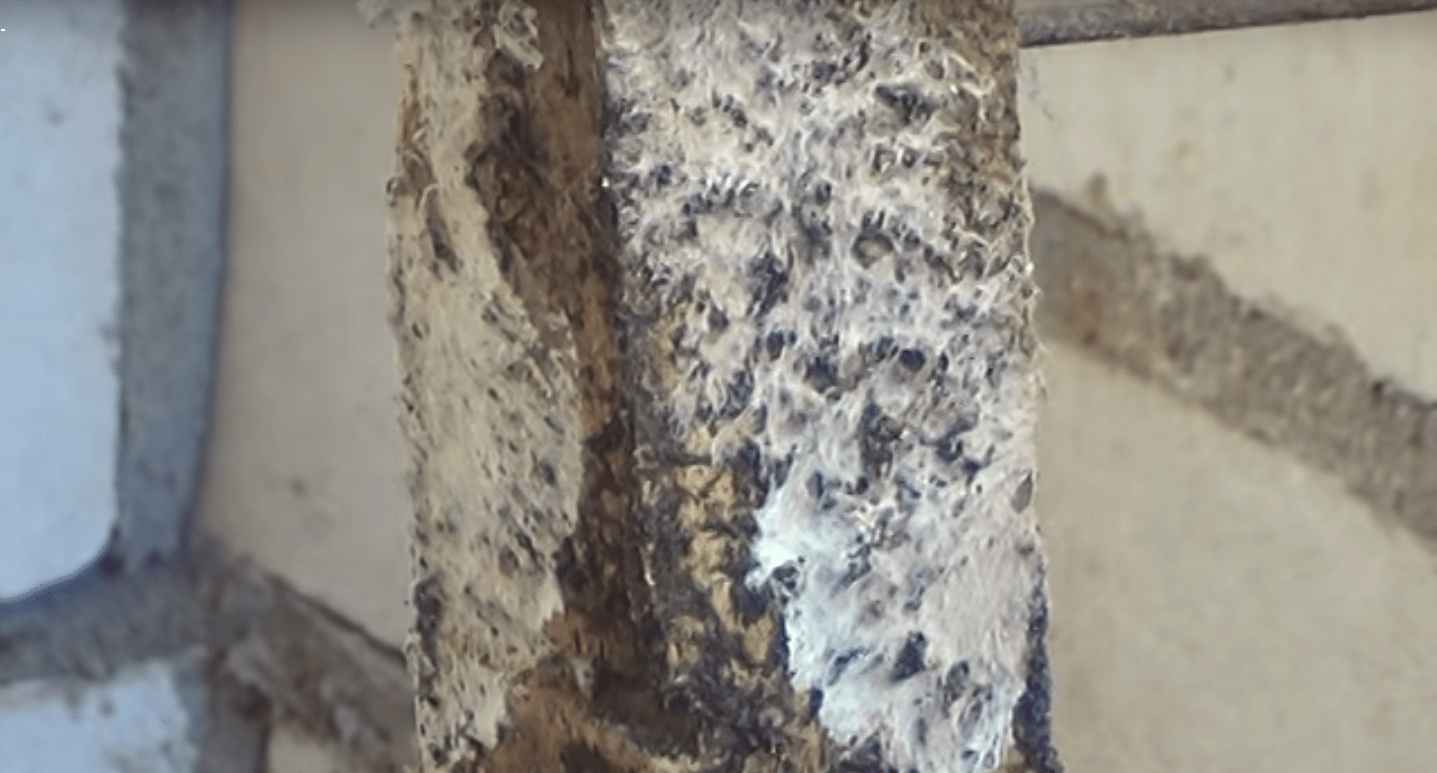
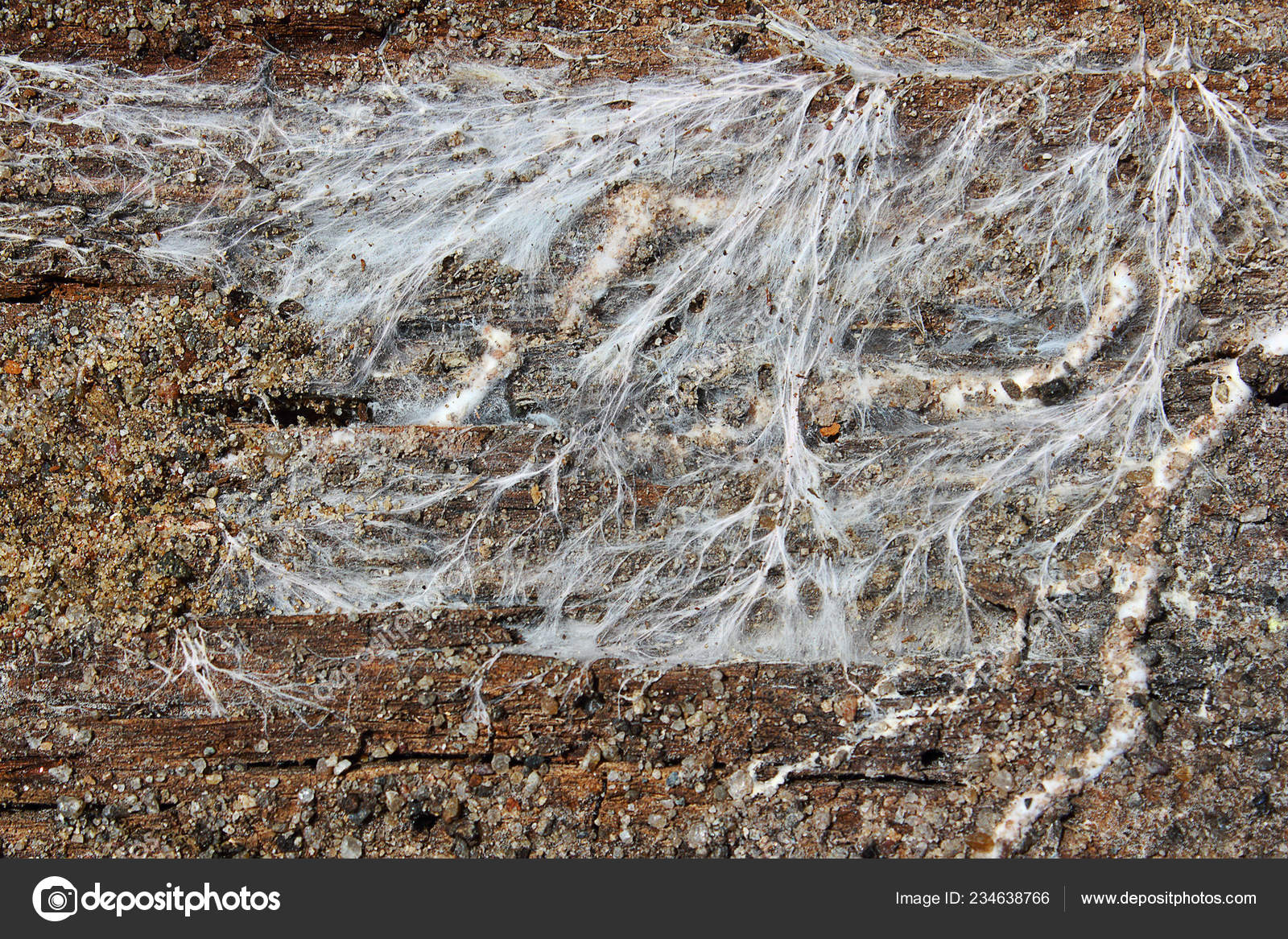
At first, only small white dots are seen on the tree, gradually merging into slimy spots or soft woolly deposits; then a silvery web-like plexus is formed. It grows more and more and spreads over the surface of the tree, becomes thicker, leafy and takes on an ash-gray color and a silky sheen.
From the edges of the mushroom, thin threads extend into spurs, crawling in search of food through the smallest holes and cracks in the stone walls from one part of the house to another. In some cases, the destructive work of the fungus can cause the entire house to fall.
Sometimes other mushrooms come to the aid of D. mushrooms: lat. Polyporus vaporarius, lat. Polyporus destructor and others.
The mushroom house attacks mainly conifers, but deciduous ones (for example, oak) are not immune from it.
The second enemy is mice!
Another possibility of using this homemade product!
After defeating the mushroom house, I hurried to put the lamp in the barn, but in vain!
Autumn was coming to an end and one day before the frost my basement was attacked by rats and vole mice. This night will be remembered by my family for a long time! There was a continuous squeak in the basement, some sort of disassembly took place, glass jars rattled, you could hear how they were eating my potatoes in the basement! Along the entire perimeter of the floor of the apartment, this gray bastard was furiously gnawing new holes, trying to break into our living space! The dog scrubbed the floor and ran around the apartment roaring and barking, children screeching! Swearing, screaming, screeching, barking - urban people faced wildlife :)!
In the morning to work, children to kindergarten and school, 4 am - Corvalol is completely drunk, and we are at war, we are under siege! Neither the banging of a stick on the floor nor the switched on light in the basement gave any result! We were simply ignored, we were superfluous at their celebration of life! I remembered about the lamp, flew after it into the barn, hung it in the basement under the malicious glances of the rodents, closed the hatch, turned it on, I'm waiting! You can hear how the "spectators" are going to look at the "gift" closer to the lamp. After 15 minutes, a weak and alarming squeak gradually turned into a panic! Again the dog rages, children squealing, but already without the mat and yelling! Some kind of races started in the basement, which quickly turned into a stampede! There was silence! The lamp did not turn off all night.
Types of fungi that destroy wood:
- White mushroom house
- Real mushroom house
- Filmy mushroom house
- Mine mushroom
- Pillar mushroom
- Sleeper mushroom
We will tell about each
the form of mushrooms in more detail.
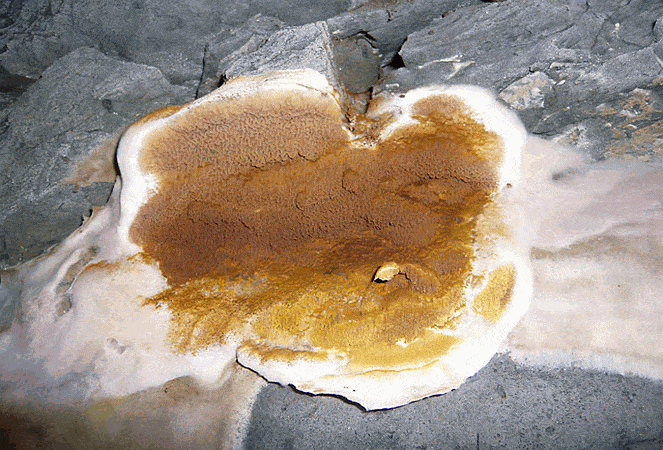
White mushroom house
(Poria Vaporaria)
Conditions for
development of the porcini mushroom are,
wood moisture content 50%, moisture content
air up to 100%.
White mushroom house
stands out with abundant growth
lush, cotton-like white mycelium
colors and is the strongest destroyer
wood. Fungus-Touched Wood
turns brown, becomes covered
cracks that form along and
across the fibers.
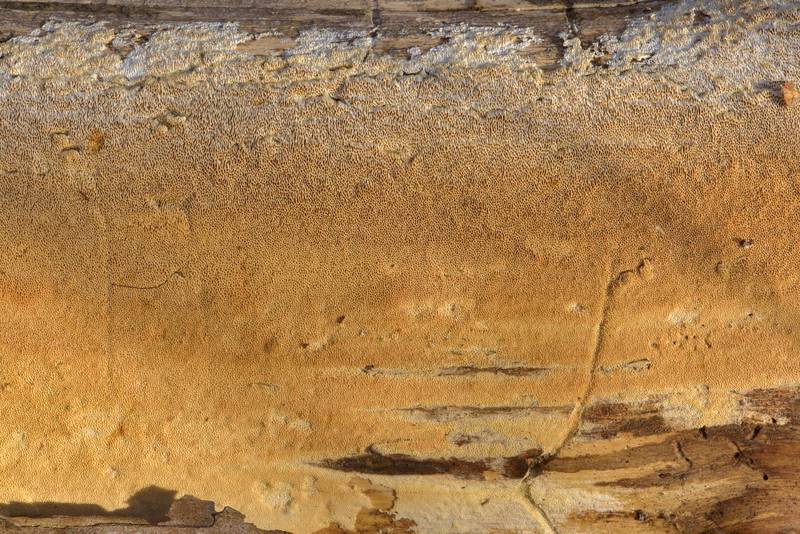
White mushroom forms cream or white bodies. In the form of flat crusts, the surface of which consists of accreted tiny tubes.

Real brownie
mushroom (Merullus Lacrimans)
Same as white
mushroom house, real mushroom house,
in less than a year is able to destroy
wooden structure.
Has a lush,
white, with yellow and pink spots,
blotches. On wood it looks like
gray, dense films with gloss. Conditions
for development real house mushroom
are the moisture content of wood, in the range
20-24%, air humidity up to 95%.
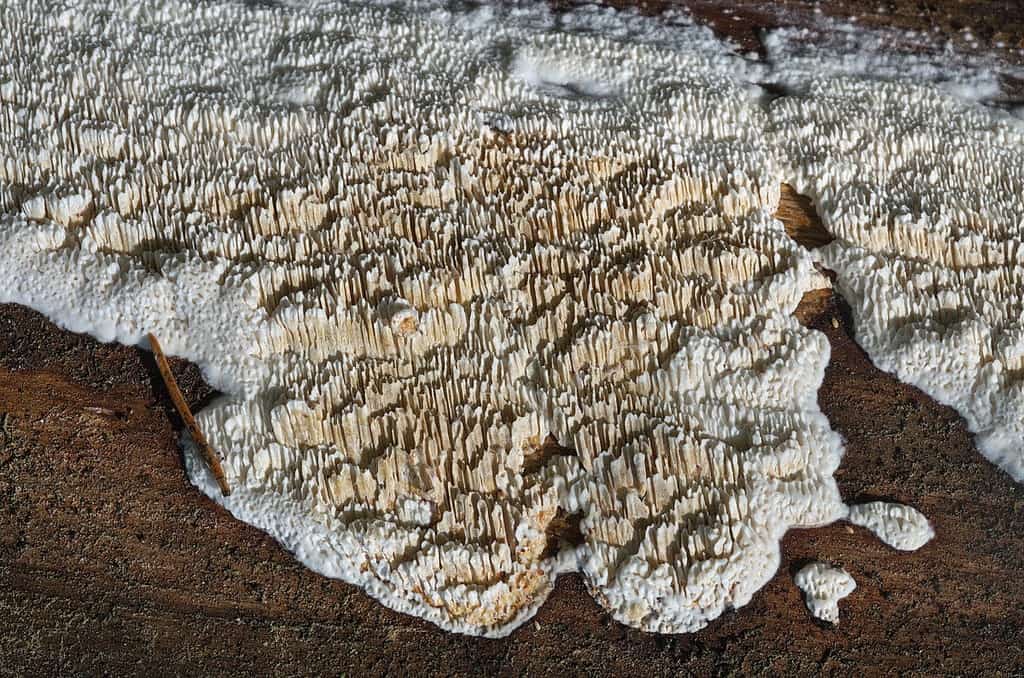
On the surface of the wood, gray dense cords grow over time, which, when dried, become brittle. In adulthood, a real mushroom house forms pan-shaped, wrinkled, fleshy brown fruit bodies with white edges, and over time they dry out and become dusty brown crusts.
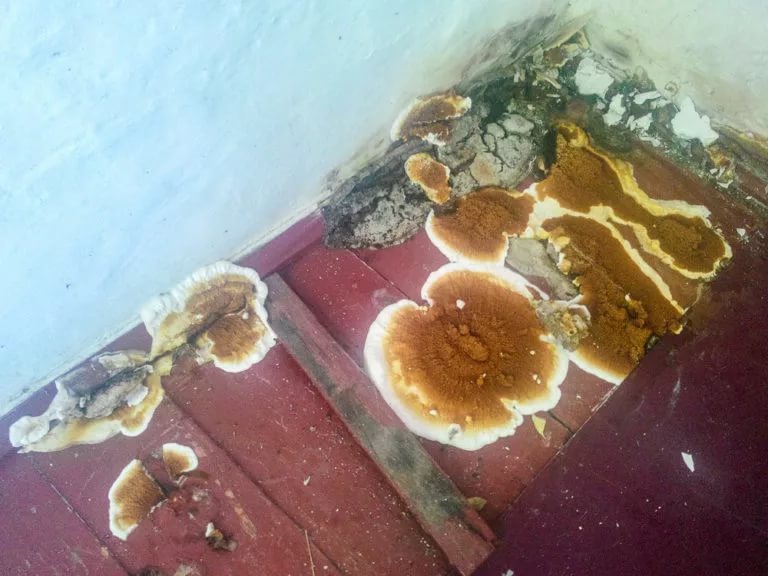

Filmy brownie
mushroom (Coniophora Cerebella)
Condition for
development of filmy house fungus,
is the moisture content of wood in the range
35-45%. Filmy mushroom house in a few
months spreads inside
overlaps and becomes the reason
unexpected collapses of structures. It has
thin light yellow mycelium with branched
a pattern of dark cords.
The fruiting bodies of filmy house mushrooms have the appearance of thin, brown films with white edges.

Mine mushroom
(Paxillus Acheruntius)
For
so that the mine mushroom develops for him
wood is needed, humidity 50-70
percent, air humidity up to 100
percent. This fungus infects wood
which is located directly in
contact with the ground.
The mine room of the mine
mushroom thin and inconspicuous, with cords
yellow-green, fruiting bodies
in the form of fleshy light hats with thin
plates that look like ordinary mushrooms.
The last stage of destruction by the mine fungus is dark brown rot, on wood, with transverse and longitudinal cracks.
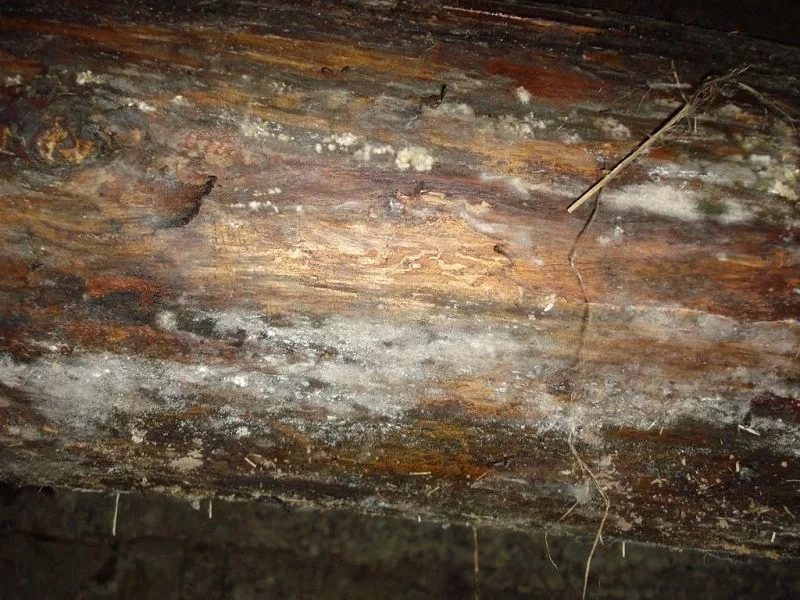

Pillar mushroom
(Lenzites Saepiaria)
Pillar mushroom
affects the wood of outdoor buildings,
including, as power line poles, sleepers, bridges,
overpasses. Rarely, a pillar mushroom gives
external fungal formations that
have the form of lamellar caps, brown
colors, with spores.
The spread of the columnar fungus occurs locally. It appears as foci that grow and merge. Pillar fungus spores penetrate the wood through cracks and attack it from the inside. Affected wood becomes reddish, darkens and breaks down into annual rings. Rotting wood gives off a specific smell.
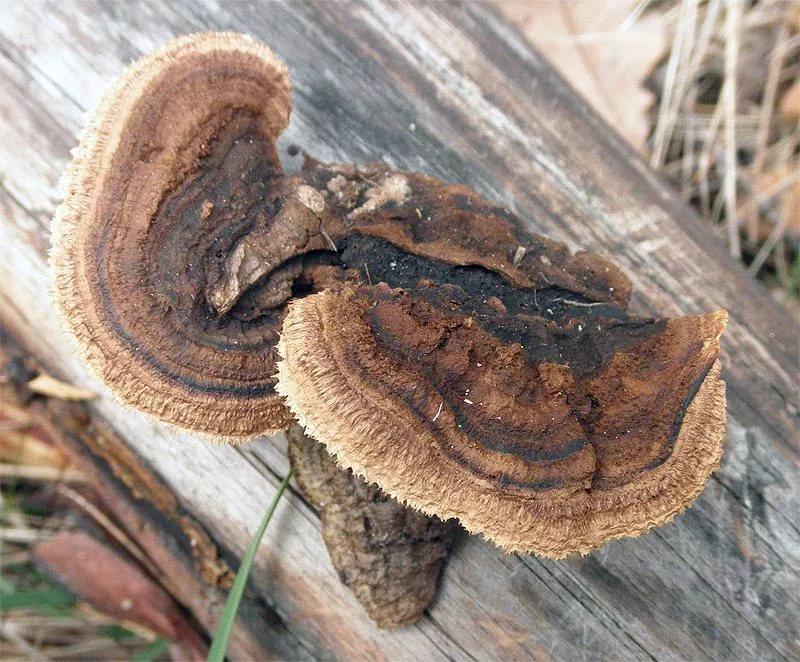

Sleeper mushroom
(Lentinus Squamosus)
Sleeper mushroom,
together with the pillar are often found
in timber yards in open wooden
structures. Sleeper mushroom most often
affects watercraft, iron sleepers
roads. Wood struck by sleeper
the mushroom becomes brown, on it
cracks appear and aroma is released,
vanilla
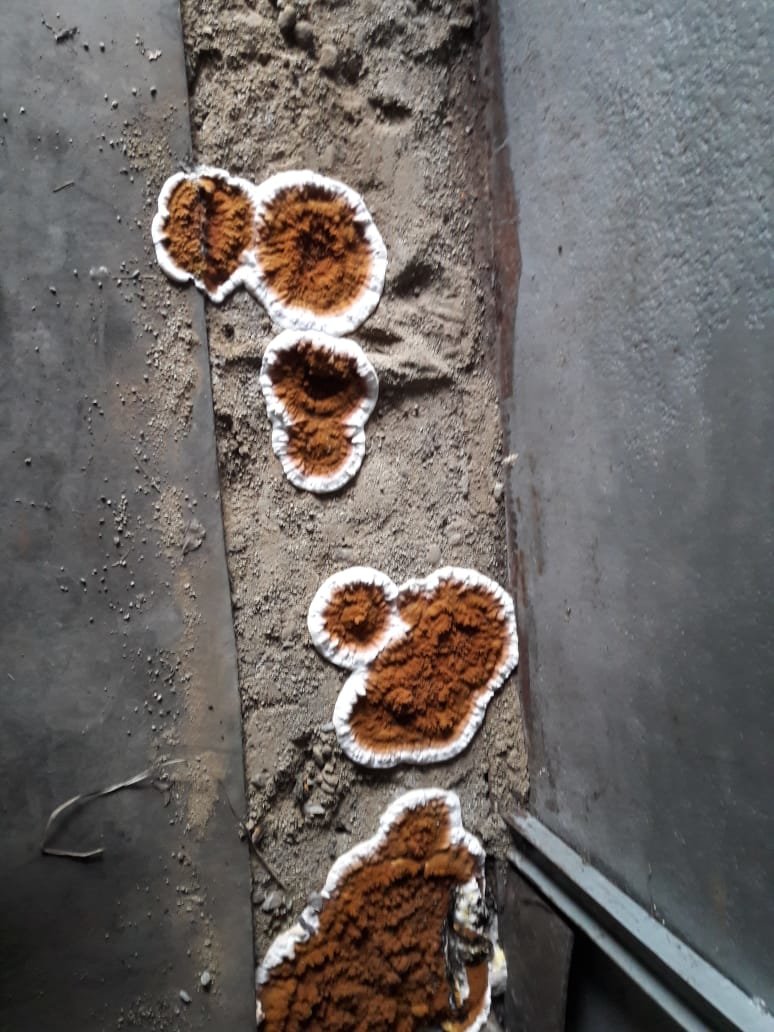
The fruit bodies of the sleeper mushrooms are fleshy mushrooms with dark scales, radial plates with spores and horn-like outgrowths. On the surface of the wood, it forms a mycelium, similar to white felt with brown spots.

To
protect buildings from fungi,
be sure to preserve
wood antiseptics.
What damaging factors led to this result?
- The first is harsh ultraviolet radiation. As is known from physics, ultraviolet light is dangerous to organic life in large quantities. What gets under direct radiation quickly loses the meaning of life!
- Secondly, it is ozone, poisonous in large quantities, a very aggressive triatomic oxygen, which is formed from the attack of oxygen molecules by ultraviolet light. Ozone actively tears all organic matter to shreds, especially if it is in a gaseous state (the smell of rot is organic). Ozone is heavier than air and that living thing that is saved from direct ultraviolet rays is poisoned by ozone (crawling insects). Also a big plus of ozone - it does not live long. Due to the instability of the ozone molecule and always a huge number of objects ready to be oxidized by atomic oxygen, its concentration quickly disappears!
- Thirdly, these are nitrogen oxides, which are formed thanks to ozone and, again, ultraviolet light.Nitrogen oxides have practically no effect on plant organic matter - the concentration is too low. But there is “organic matter” in basements and cellars, for which nitrogen oxides are not the last reason to leave their homes. Read about this "organic" below.
I was prompted to write this article by infa from one of the forums, where the question was asked about the fight against mold and house fungus
I was amazed that the answer was the same that I read in Soviet literature, when few people knew about the Internet! Googling a specific question, I was convinced that all infa on the Internet is a complete reprint of Soviet articles without any comprehension, analysis, taking into account modern realities, practically without warning about precautions when using chemistry. On a rare occasion, it has been reported that a given chemical attack has a short-term effect and must be repeated periodically (for the chemical industry to flourish!)
In the wake of demand, our chemistry (and some garages :)) has launched the production of special formulations to combat mold and house fungus, making money on the lack of education of our people. Along with the struggle for the ecological purity of the environment, we are offered to fill our homes with chemistry, in which we and our children spend most of our lives!
The mistake in combating mold with chemical methods lies in the fact that we forget that mold is the first plant substance that quickly populated our planet at a time when it was impossible to live on it by our standards! Also, the mold will be the last to die before the dying Sun burns our planet! For mold after billions of years of hardening during survival in extreme conditions, our chemistry is like grain to an elephant! So why waste money poisoning yourself and your children?
The choice is yours, everyone will have their own reasons for using this or that method in the fight against this evil.
Poisonous doubles of porcini mushroom
Despite the fact that the porcini mushroom is considered quite common, and it is difficult to confuse it with a toadstool, it has several inedible counterparts. They are extremely rarely fatal, but can still cause symptoms of severe food poisoning.
The danger of false whites is that they grow in the same area as edible specimens, and sometimes in close proximity to them. In order not to accidentally put such a specimen in a basket, you should know the distinctive external signs of poisonous twins.
Gall mushroom (gorchak)
Outwardly, it is very similar to white, but prefers to grow on well-heated clay and sandy soils. Most often it can be found on the edges and clearings of coniferous forests. Based on the place of growth, it should look like a white pine, although in fact, in terms of external characteristics, it looks more like an oak tree (Figure 2).
From the external characteristics of bitterness should be highlighted:
- The hat is convex, brown or brown.
- The stem is thick, cylindrical, covered with a characteristic mesh pattern, which is absent in true whites.
- The pulp is not of a pleasant creamy or white shade, but slightly pinkish or off-white. The flesh of the gallbladder also acquires pink color when cut or broken.
But the main characteristic feature of this poisonous twin is that it has a pronounced bitter taste, from which the mushroom got its name. This taste not only does not disappear, but also intensifies during heat treatment, so you cannot accidentally eat it. It is the bitterness that is the reason why forest animals and insects do not eat it.
Figure 2. Bitterness pulp
Some mushroom pickers advise to lightly lick the flesh of a suspicious specimen to make sure it is edible. We do not recommend doing this, since the toxins contained in the pulp can disrupt the functioning of the liver, and at high concentrations even cause a deadly disease - cirrhosis.
Satanic
Another dangerous double of everyone's favorite boletus.Since it belongs to the same genus, it really resembles white in the shape of the stem and cap. Deciduous forests of regions with a warm climate are considered a common place of growth, and it prefers to grow under linden or hornbeam (Figure 3).
The characteristic features of the satanic look are considered to be a fleshy and velvety hat. Depending on the place of growth, it can be grayish-white, brown or olive. The latter shade is more common in shady areas with dense young growth, while a light cap color is more common in well-lit areas.
Figure 3. Sectional Satanic Mushroom
But the easiest way to distinguish it is by the color of the leg and the tubular layer. The leg has a deep red color, and the tubular layer can be not only red, but also bright orange. If you cut such a specimen, its pulp will turn bright yellow, and after a few minutes it will acquire a bright blue tint.
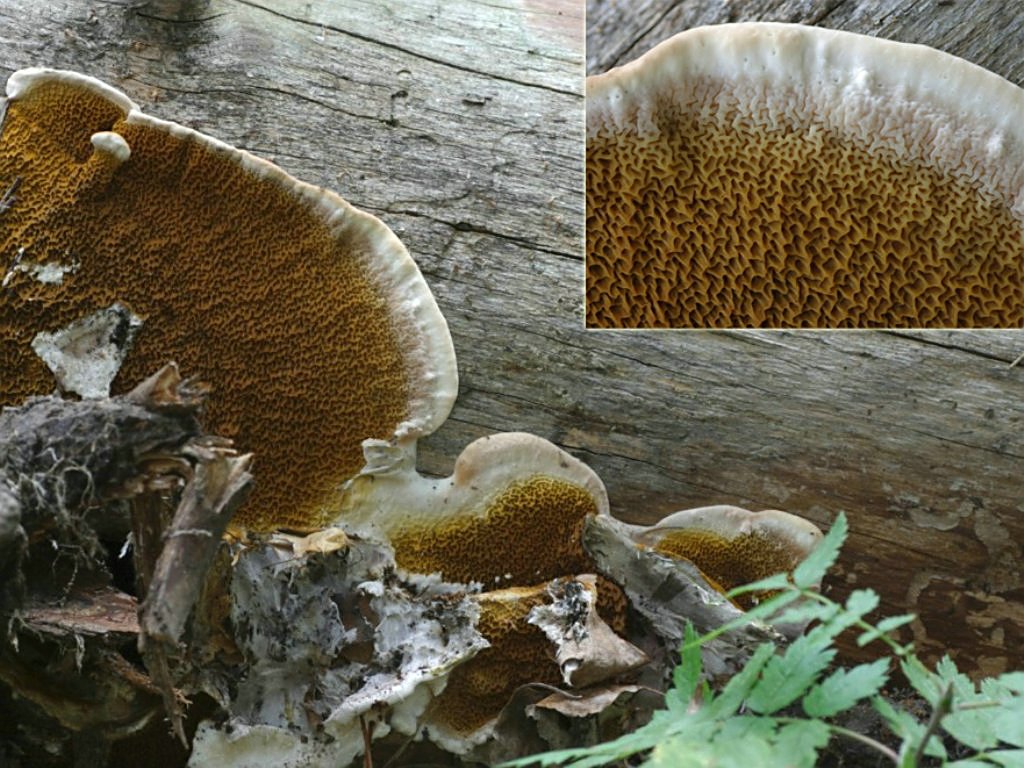
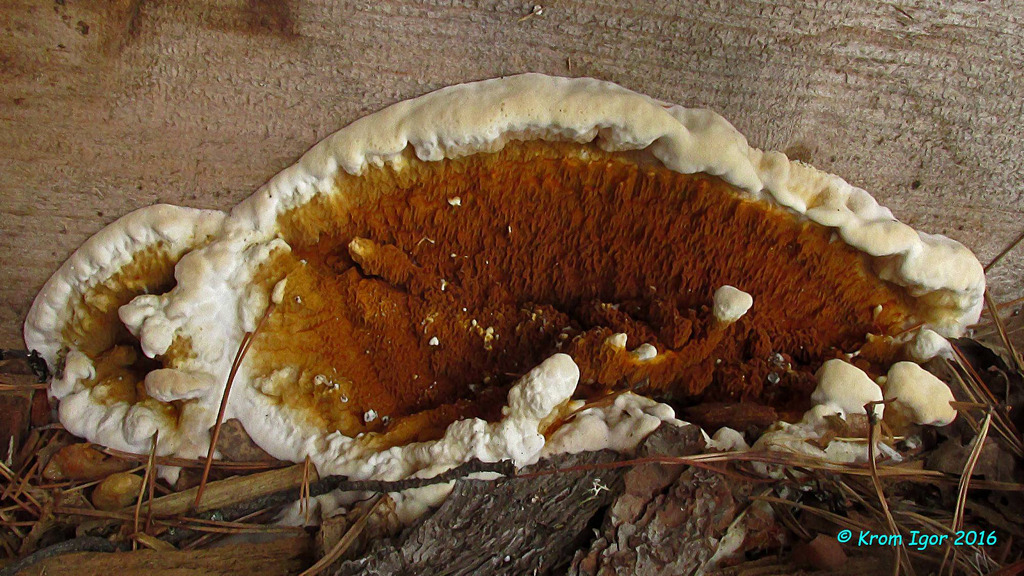
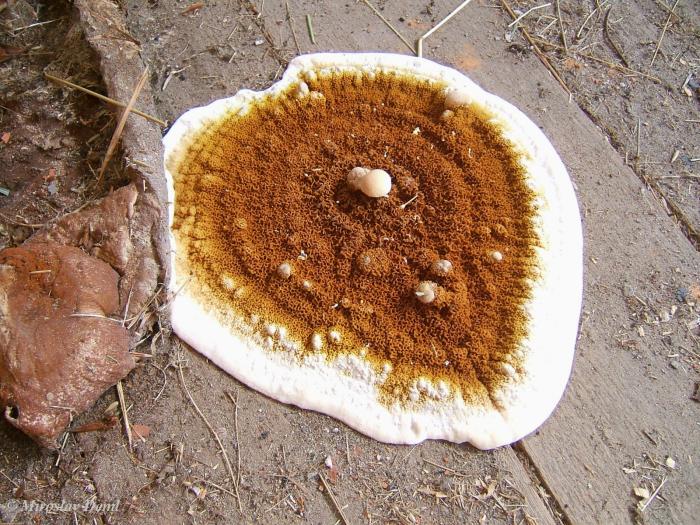
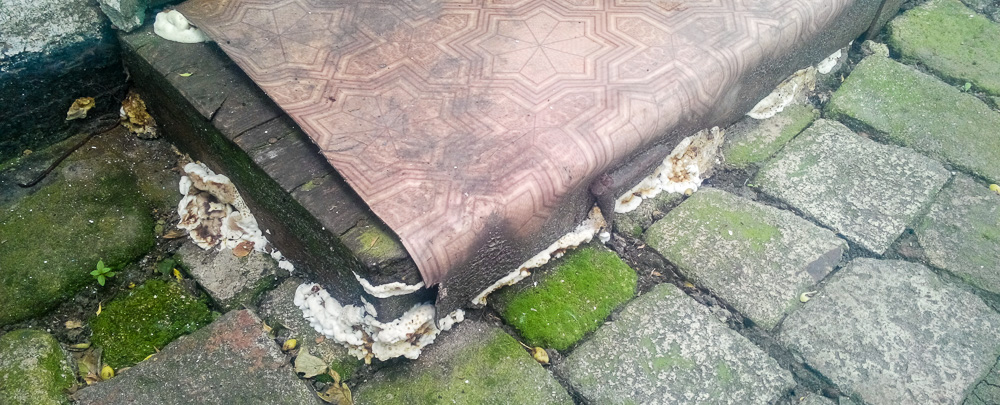
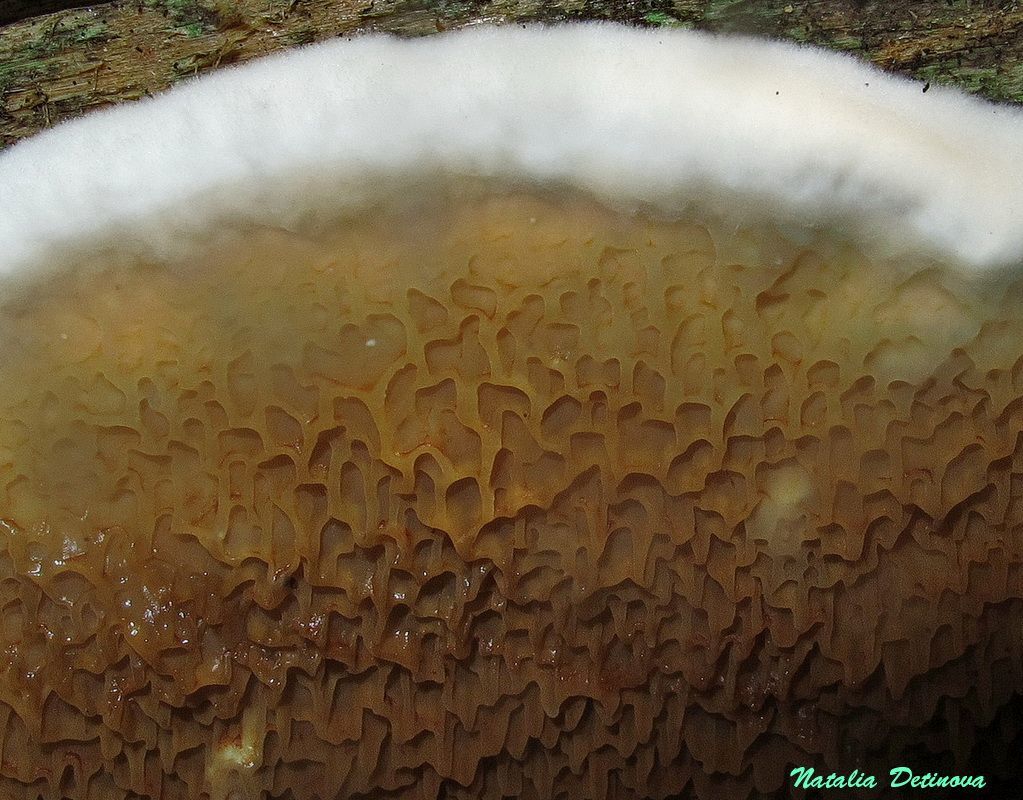
Weeping sickle (Serpula lacrymans)
Fruit body:
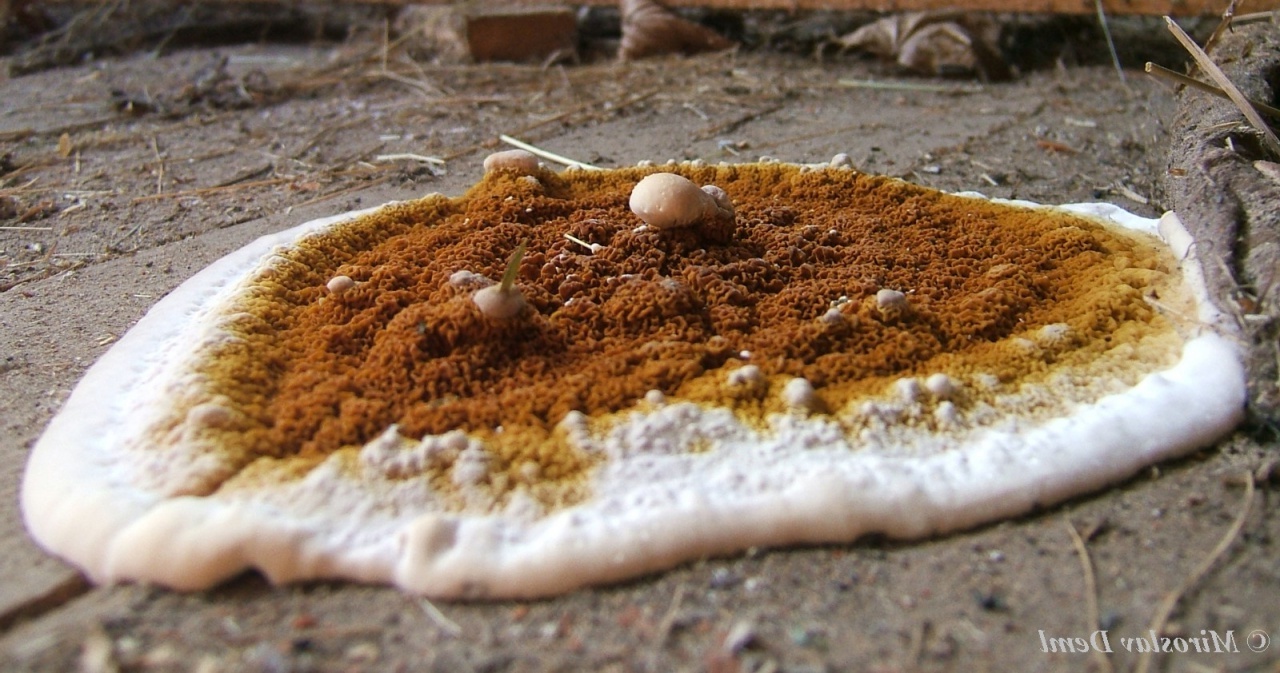
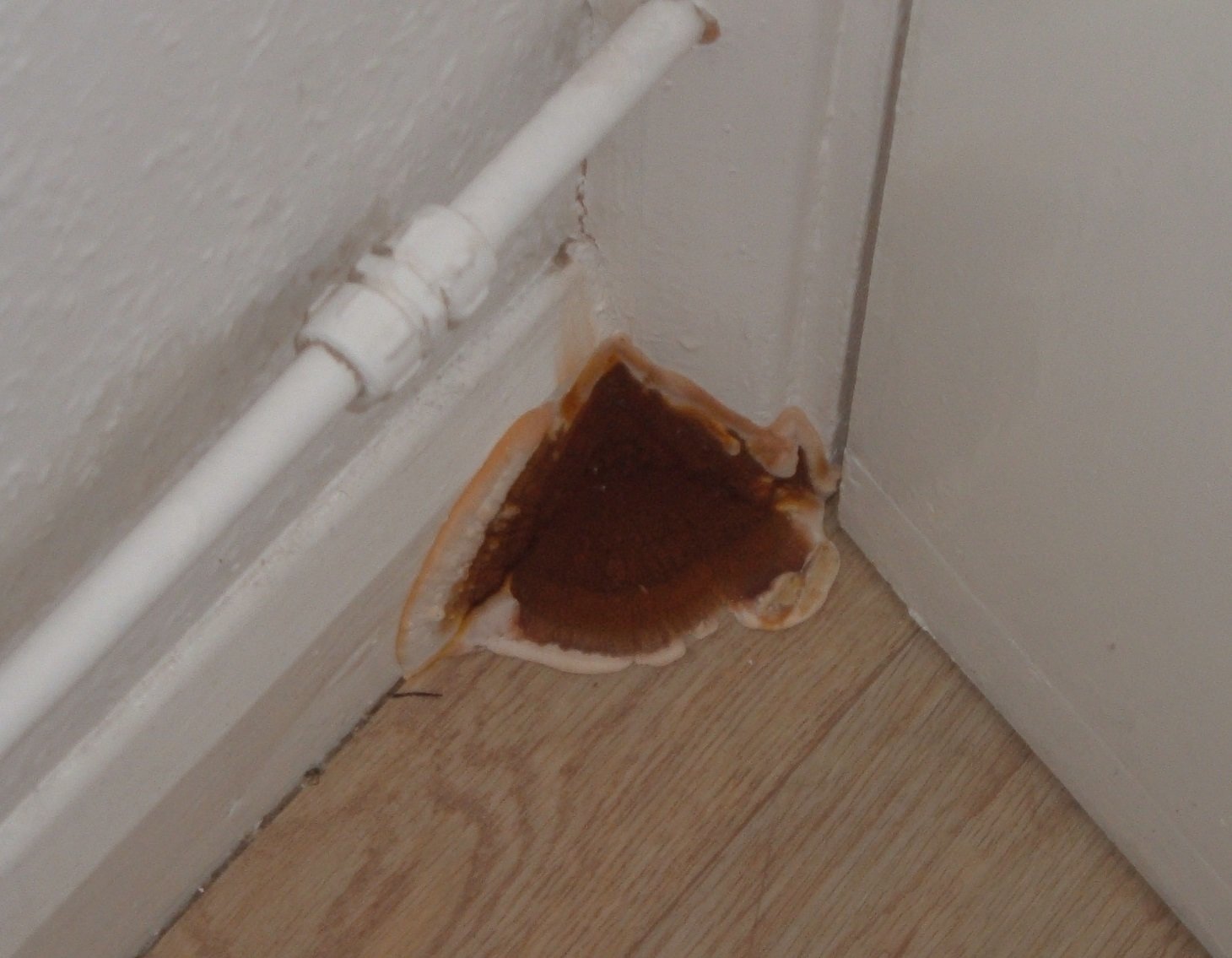
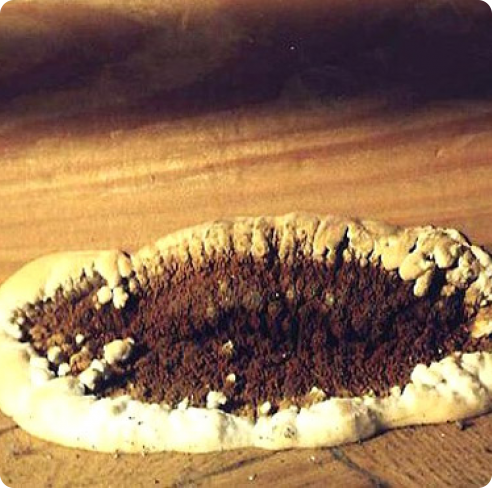
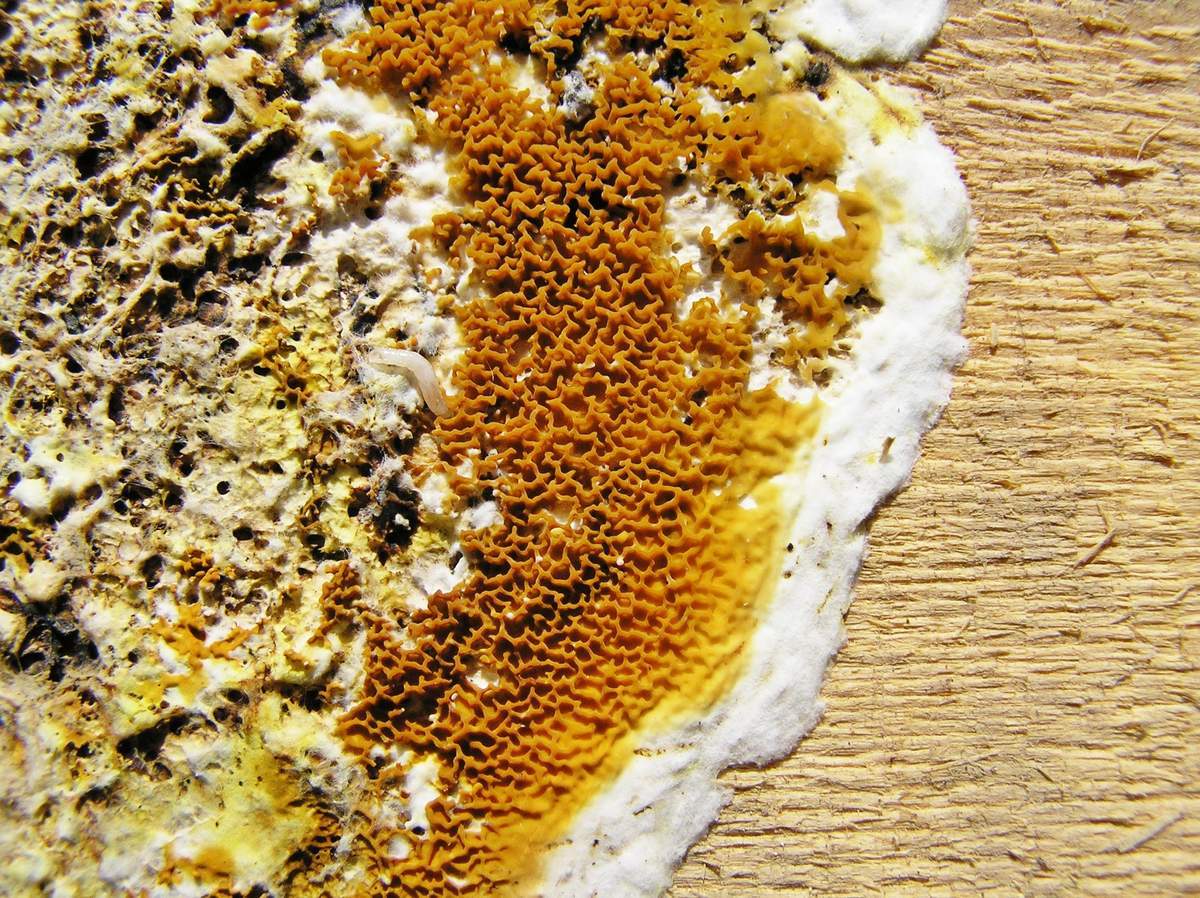
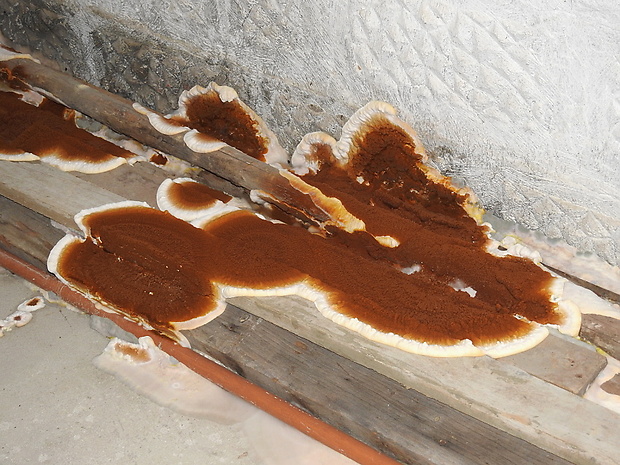
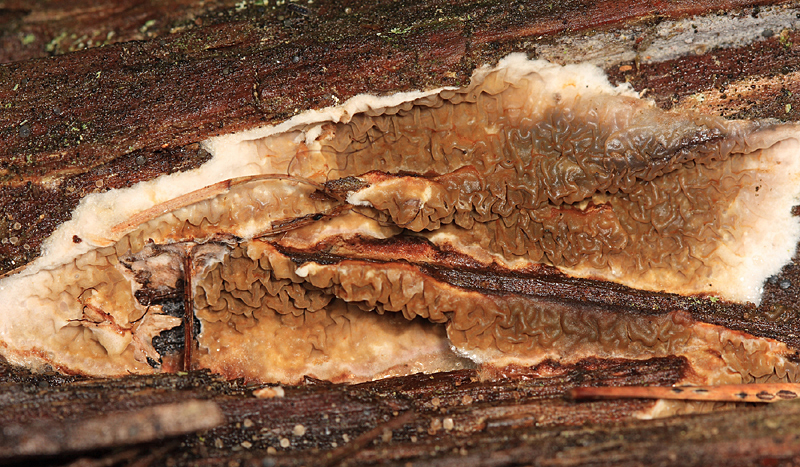
the fruiting body of the Weeping Serpula is rather shapeless and one might even say ugly. On a horizontal surface, the body is prostrate or flowing. On a vertical surface, it is drop-shaped. Sometimes the fruiting body seems to be trying, albeit unsuccessfully, to take the hoof-like shape, traditional for tinder fungus. The size of the fruiting body is from ten to thirty centimeters, while the fruiting bodies can merge, forming a homogeneous mass of the global fruiting body. Young fruit bodies are white and look like formations between the logs. About the same as Yellow Tinder, only white. Then, in the middle part, a tuberous, unevenly tubular brown hymenophore is formed, which produces separate outgrowths, like small fruit bodies with a brown core and a white edge. On the edges of the mushroom, you can see drops of liquid, due to which Serpula Crying received such a name.
Pulp:
the pulp is loose, wadded, very soft. The mushroom has a heavy odor, similar to the smell of damp dug earth.
Hymenophore:
labyrinth, tubular. At the same time, it is considered to be tubular for the most part conditionally. The hymenophore is extremely unstable. It is located in the central part of the fruiting body if the body is in a horizontal position. Otherwise, it is located where it works out.
Spore Powder:
brown.
Spreading:
Serpula Weeping is found in poorly ventilated buildings. Fruiting during the entire warm period. If the room is heated, it can bear fruit all year round. The sickle destroys any wood with great speed. The presence of a mushroom house is indicated by a thin layer of reddish-brown spore powder on all surfaces, which forms before falling onto the plank floor.
Similarity:
Serpula, a completely unique mushroom, is difficult to confuse with other species, especially for adult specimens.
Edibility:
don't even try.
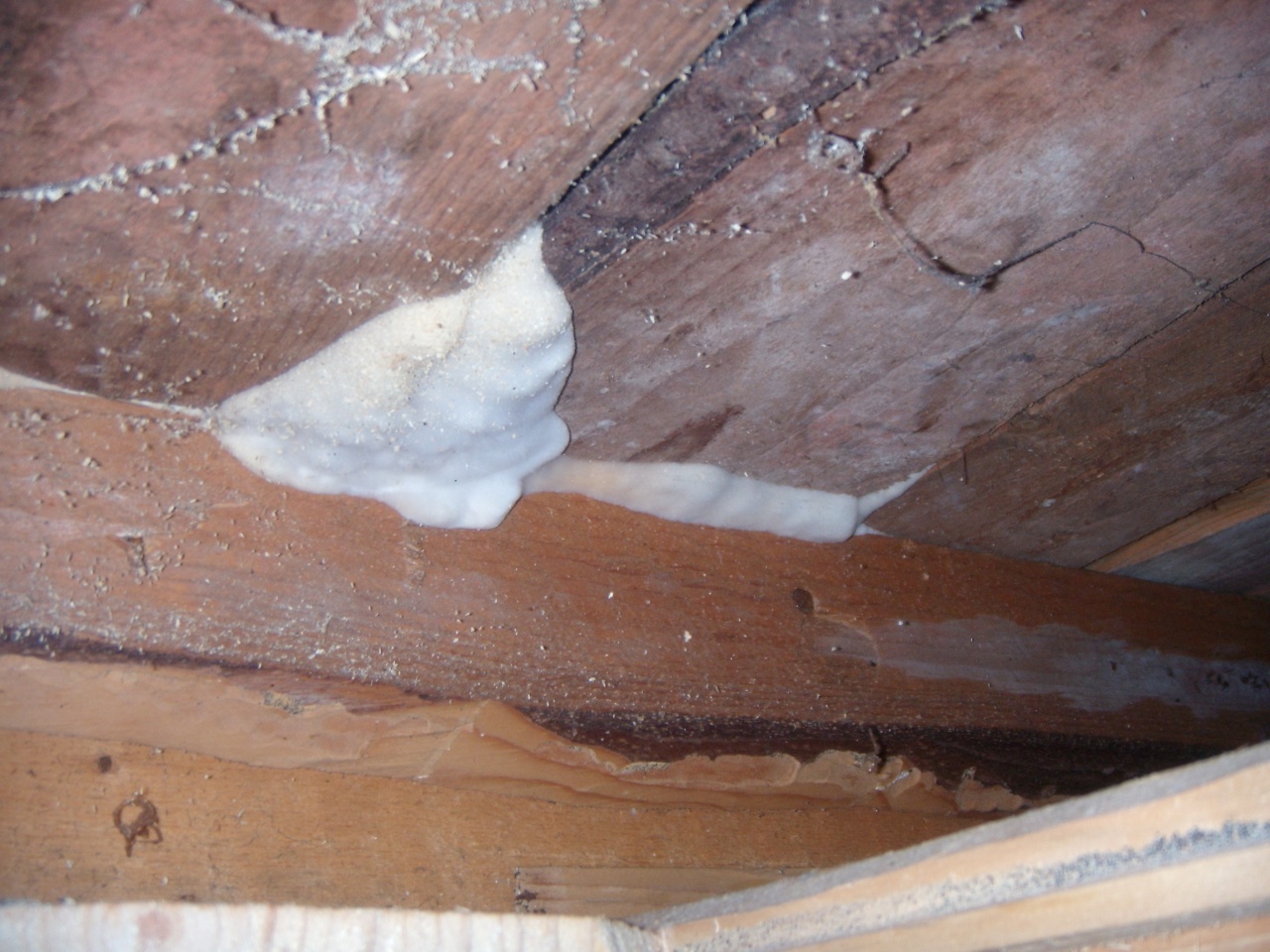
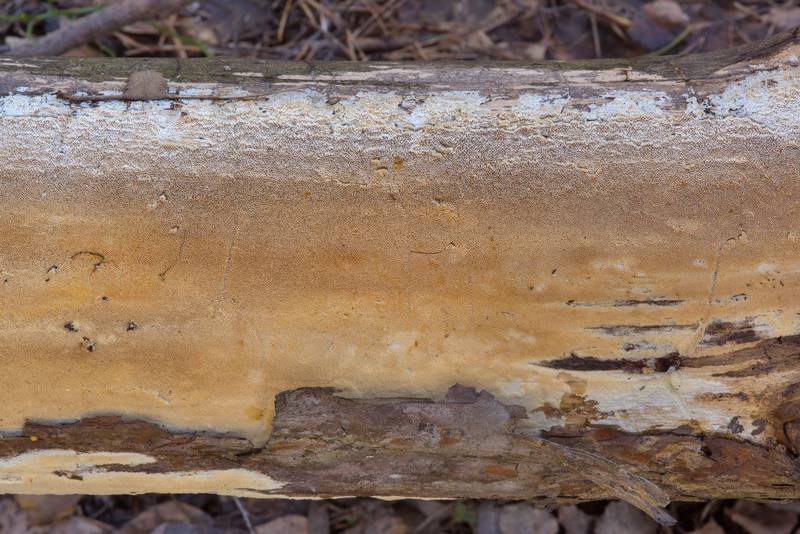
Notes: The Weeping Sickle is a mushroom house that cries crocodile tears. The mushroom is really unpleasant and outwardly ugly. This mushroom secretes a huge amount of spores, even if all the fruit bodies within sight and reach are destroyed, all the same, everything in the house in a short period of time is again covered with a layer of brown spore powder. Serpula is an omnivorous mushroom that is not afraid of anything. He even eats wood pretreated with a protective substance. If Serpula starts up in the house, it is scary to remain inactive, because it is not known where she will cry tomorrow. On the wood affected by Serpula, wadded clusters of mycelium, mycelial cords and fungal films are first formed. First, these formations are white, then they change the shade to yellowish, pinkish or gray.
Effect on wood
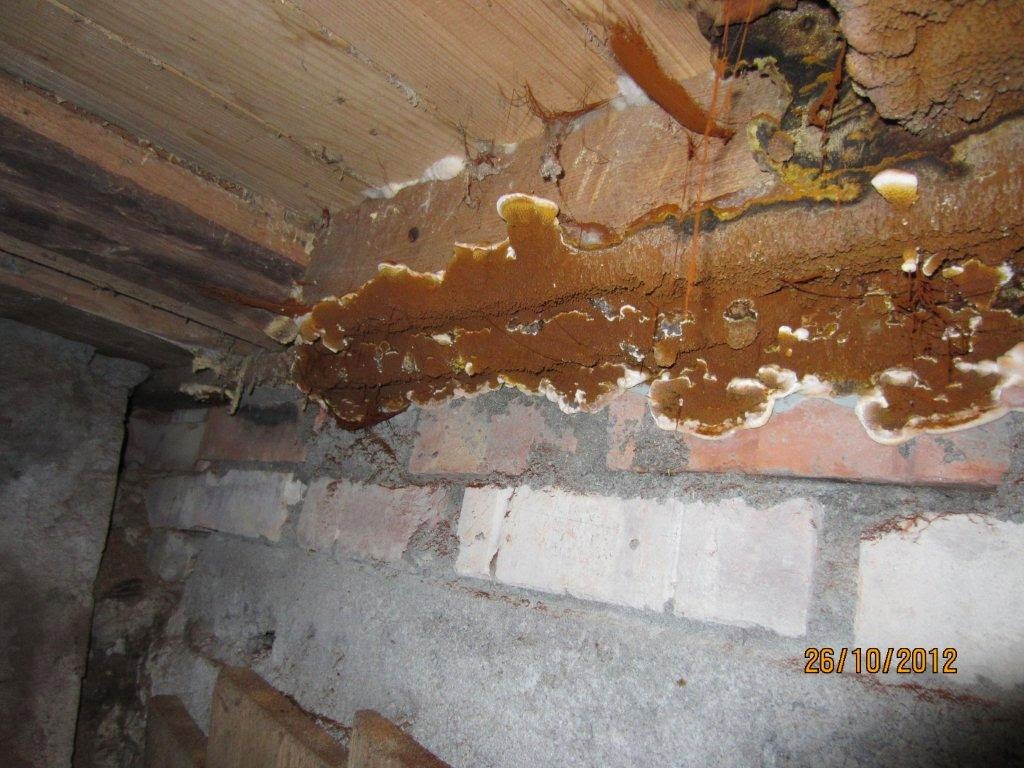
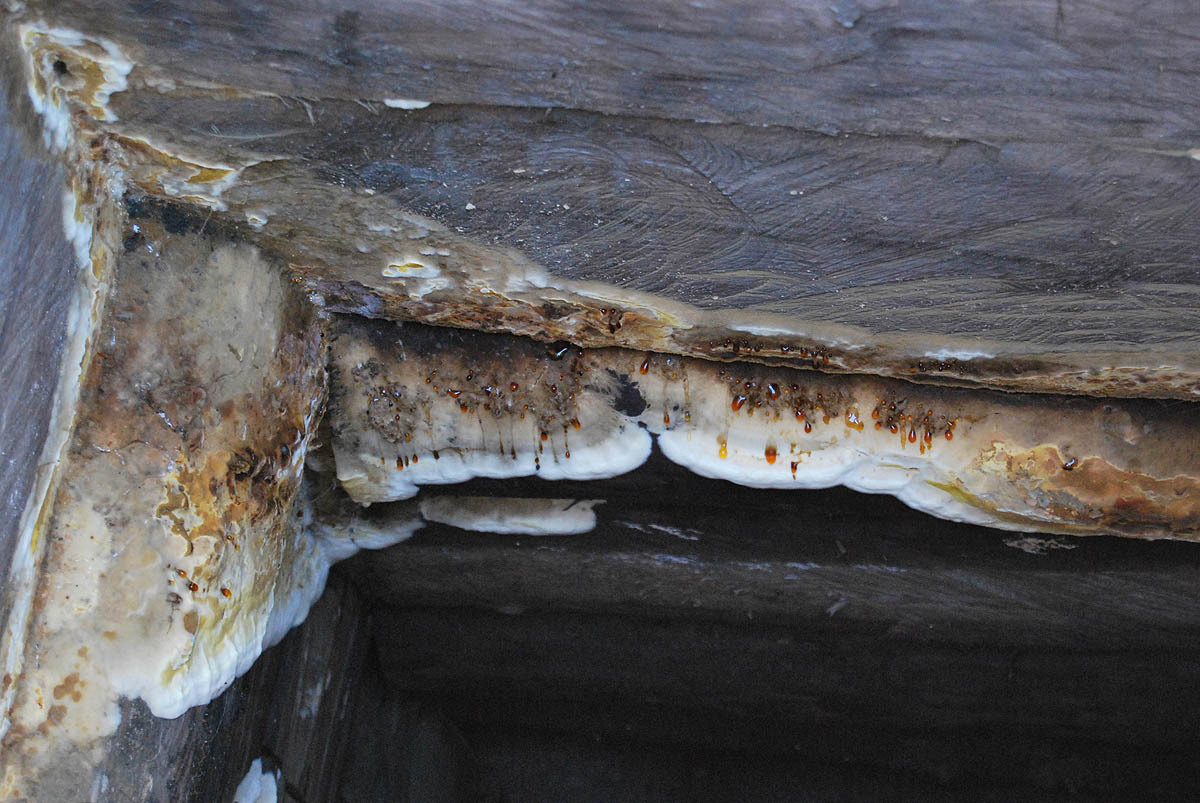
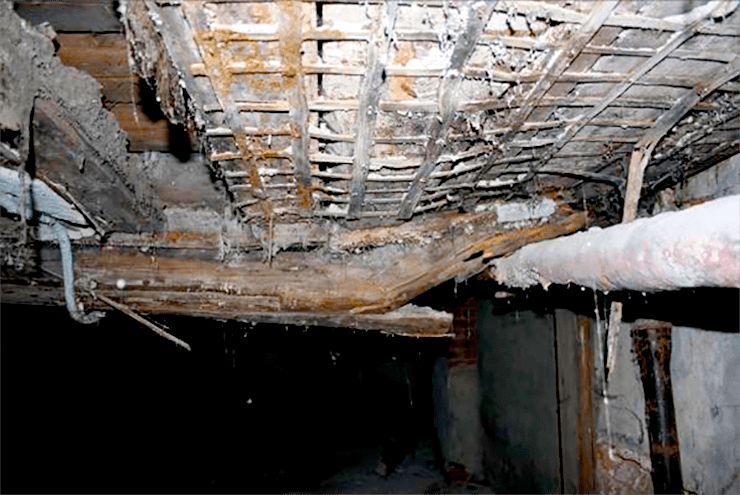
House wall damaged by a mushroom house
According to the research of R.Gartig, the destruction of the tree occurs partly due to the release of special enzymes by the fungus that dissolve the organic matter of the tree at a considerable distance from the mushroom hyphae and turn them into a form that the fungus can digest, partly due to the dissolution of ash constituents (Aschenbestandtheile) cell membranes in places of direct contact of the latter with hyphae.
As the destruction progresses, the tree turns more and more brown and gradually turns into dust; soft when fresh, it becomes dry, brittle, brittle. A floor painted with oil paint is especially easily destroyed by a mushroom house, since the underside of such a floor is protected from light and from drying out.
Presence Merulius lacrymans in such cases, it is recognized by black spots scattered on the upper surface. If the tree is painted with glue paint, then separate fluffy areas of a yellowish color appear on its surface.
Wood infested with house fungus emits a dull sound when tapped, and easily breaks when pressed. The affected tree becomes extremely hygroscopic and eagerly absorbs water like a sponge. In this way, water can be transferred from below to various, often very distant parts of the building, and since the mycelium itself has the ability to easily conduct water and give it to dry wood, the mushroom can make the driest rooms damp and uninhabitable.
To all this must be added the fact that the decaying and rotting fruiting bodies of the fungus emit an extremely unpleasant characteristic odor, harmful to health [clarify].
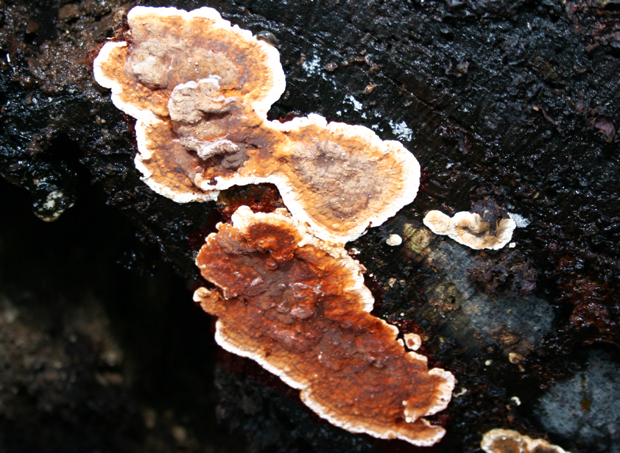
According to the analyzes of Goeppert and Poleck, the water content in the house mushroom reaches 48 and up to 68%. The fruiting bodies of the D. fungus are formed only where the mycelium comes out into the light and fresh air through a crack or crack. Fruit bodies are lamellar, wide, mostly plate-shaped, sometimes up to a meter in size, fleshy leathery consistency, at first white, then reddish-yellow in places, at the end rusty-brown; from above they are covered with worm-like wriggling folds (there are spores on them), from below they are fibrous-velvety with swollen, as if woblock edges of white color. At the edges of the fruiting body, drops of liquid appear, at first transparent, then cloudy, milky in color (hence the specific name M. lacrymans, that is, crying). Brown or rusty-brown spores are elliptical in shape and very small (0.010 - 0.011 mm in length and 0.005 - 0.006 mm in width). The germination of spores occurs, apparently, only in the presence of substances with an alkaline reaction (ammonia and its salts, potassium carbonate, etc.), which cause the spore shell to swell. In the same sense, urine, ash, coke, etc. substances favor the germination of spores, since they contain or are obtained from alkali-reacting substances.
Control measures [| code]
From the dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: “For the extermination of the already appeared house mushroom, a lot of funds have been and are being offered; but, unfortunately, none of them can be considered radical. Satisfactory results were obtained by the 19th century German forester G.L. Gartig, impregnating pieces of wood with creosote or the so-called carbolineum (Carbolineum).
Professor Sorokin recommends covering with ordinary tar; other researchers point to petroleum as a good remedy.
Until the mushroom has become particularly widespread, careful cutting out of the damaged pieces and replacing them with new ones can be successfully applied. "
Currently, a variety of fungicidal impregnations are most often used to combat the house fungus.
However, they are more or less toxic to humans and warm-blooded animals, and should be used with great care inside living quarters.
Harsh ultraviolet radiation kills the mycelium and spores of the fungus.
A promising and environmentally friendly method of combating house fungus can be regular quartzing of premises. Harsh ultraviolet radiation kills the mycelium and spores of the fungus.
Business is possible!
For the most enterprising I give an idea for a small business - the destruction of a mushroom house in basements, cellars, garages.
Most of these places are electrified by the owners, and the technical knowledge and technical curiosity of the population has recently been tending to zero. As a percentage of the entire population, there are now fewer and fewer people who, having seen in fact the device described in the article, will be able to determine what it was before and what can be done with it! Thanks to the modern school Unified State Exam (which teaches you to guess the answers from several possible options) and for the most part "nominal" higher education graduating "conditionally educated specialists" now it becomes possible to profitably use "ancient secret technical knowledge"!
At the end of the article, I can safely say: CHECKED - WORKS!
How to destroy a white mushroom house
Dealing with fungus is not easy. In the initial stages of its appearance, antiseptic agents can be used.

The most effective of them are Neomid 430 Eco and Neomid 400. The first antiseptic is recommended to be used for application to external wooden surfaces, the second - on the internal ones. They will cope with the already developing white fungus and prevent its return for many years.
If the wood material has changed its color under the influence of mold, then it is recommended to use the Neomid 500 bleach. It will return the wood to its previous appearance without making any changes to its structure. It will also provide the processed material with additional biosecurity.
If the wood material is strongly affected by the white house fungus, then the most effective is to remove and burn it.
In this case, the infected wood must be taken out of the room carefully so that as few spores as possible scatter around the room, and it is necessary to avoid even slight contact with healthy wood.
Do not forget about preventive measures. It is constantly necessary to ventilate the premises, periodically treat wooden materials with protective compounds. After all, white house fungus appears not only in old houses, it can also appear in a completely new, only rebuilt building.
Photo: the best formulations for wood pest control.
Semyon Shifner, 48 years old (Tomsk).
LAT Serpula lacrymans Inedible Synonyms: House Sponge (Merulius destruens Pers), Nozdrevik-Destroyer (Merulius vasitator Tode), Tree Mushroom, House Mushroom
Specifications:
| Group: | Smooth |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Absent |
| Colour: | White, yellow-red, rusty |
| Info: | Grows on dead wood |
Systematics:
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Agaricomycetidae |
| Order: | Boletales |
| Family: | Serpulaceae (Serpulaceae) |
| Genus: | Serpula |
| View: | Serpula lacrymans (Mushroom house) |
This mushroom is inedible, moreover, it is a pest that destroys dead wood, which is especially dangerous when it gets into wooden buildings.
Prevention measures
R. Gartig proposes the following protective measures:
Workers who have completed repairs in buildings infested with house fungus should, before further use, possibly thoroughly clean and wash all their tools. Boots and clothing should also be thoroughly cleaned. An old tree, if there are obvious traces of a fungus infection on it, should not go to new buildings. An old, destroyed tree should, if possible, be burned as soon as possible after removing it during repairs. Fresh wood should not be stacked next to damaged wood. The new structure must be protected from all contamination by its workers. The latrines should be arranged in such a way that contamination of the new building does not follow in an indirect way. For a cushion under the floor (lubricants), washed, coarse sand or broken brick should be preferred. It is necessary to avoid coke, ash, etc., as well as masses rich in humus and generally damp. Building wood should be as dry as possible. The new building should dry out sufficiently. Painting floors with oil paint as late as possible.Floors should not be flush with walls
Particular attention should be paid to the arrangement of the correct air draft in the lower rooms and under the floor. Maintain cleanliness and do not allow water and impurities (in laundries, bathrooms, etc.) to fall under the floor.
Observation.
One morning in the yard I found a dead rat on the path. Judging by the trail, she dragged herself away from home with the last of her strength. But I was struck by the condition of her eyes: they were white, like boiled fish! It turns out that even when she was dying, she tried to get away from a dangerous place for her! This observation confirmed my guess that poisoning rodents with poison in such houses is to your own detriment!
I will try to explain.
In case of poisoning or illness, any animal understands that for some time it will not be able to stand up for itself, which means that it needs to find a secluded place where it can lie down without fear of being eaten! What could be safer for a house mouse or rat in the basement of a house, with numerous dug and gnawed passages?
But we poison rodents precisely in order to destroy them! And now the poisoned rat dies under the house or in the passages inside the walls, in the floor and begins to decompose, poisoning the air and making our life unbearable for 2-3 months! Where to find her? To sort through the whole house on the boards in search of a corpse?
The lamp acts the other way around: all its damaging factors let rodents know that this place is very dangerous for them. The smelly mixture of gases easily passes through their passages, expelling everyone outside. The rodents don't come back for the second time! Of course, then new rodents will come to the "free territory", but it's easier for me to plug the plug into the outlet than to look for a new victim of the poison!