Content
Ventilation is an integral part of the microclimate system.
It is necessary at all stages of production:
1. Dirty area. When manufacturing a substrate using any of the technologies, a lot of steam is released - therefore, it is desirable to have exhaust ventilation in the workshop.
2. In a clean area the ventilation system consists of:
- blower fan,
- coarse and fine filters
- and the air duct inside the room itself, the seed room.
 This air duct is placed either near the doors of the container where the substrate is located (for xerothermia and pasteurization), or above the seeding table (for hydrothermal treatment). A large number of small holes are made in the air duct with a soldering iron.
This air duct is placed either near the doors of the container where the substrate is located (for xerothermia and pasteurization), or above the seeding table (for hydrothermal treatment). A large number of small holes are made in the air duct with a soldering iron.
Before the start of sowing, the clean area is treated with disinfectants, then ventilation is turned on and, due to a small excess pressure, the outside untreated air is not sucked into the seed area.
On the contrary, air is forced through all the slots and passes through the filters. This prevents mold spores from entering the treated substrate.
3. In the incubator the main task of ventilation is timely heat removal from overgrown mushroom blocks. Incubation mainly uses recirculated air. On the 5-6th day of the incubation period (at the peak of heating), to maintain the optimal temperature in the center of the block (30-32 degrees), fresh air is gradually added to the recirculated air - about 10-15%. If this is not enough, turn on the air conditioner. A large amount of fresh air is not used when the blocks are overgrown.
Forced ventilation was built in the incubator according to the same principle as in the growing room:
but). The recirculation system collects air from the room into the mixing chamber, and fresh air enters there. The percentage ratio of recirculated air to fresh air is regulated by dampers (manually or automatically).
b). Behind the mixing chamber are the heat exchangers (hot and cold if you intend to work in the summer), then the blower fan and the humidification system.
in). Depending on the length / width of the mycelium and the method of placing the blocks, air ducts are further bred, or one air duct, the nozzles (holes made from disposable cups) of which are directed along the rows with mushroom blocks - this can be done if the rows are short - no more than 3 meters.
If the rows are long, then the branches from the central duct go to each row. It is possible to make air ducts through a row if the units are suspended or stand on racks, i.e. if the stream flows from below without obstacles.
The main principles by which ventilation is designed for growing oyster mushrooms:
The most important task of ventilation in the oyster mushroom growing room is to create air flows throughout the room, allowing timely removal of the waste products of the fungus from the growing drusen (CO2 and moisture evaporated from the surface of the mushroom cap).
The flow moving through the ventilation system must have certain parameters (humidity 87-92%, temperature 14-16 degrees, the amount of CO2 - from 800 to 1000 ppm).
1. Fan power it is considered to be based on the need to blow 1 ton of the substrate.With intensive loading of chambers (from 160 to 200 kg per square meter) and the simultaneous fruiting of the entire tonnage (for example, with a single-zone method), the calculation is made on the basis of 300 cubic meters. air for 1 ton of substrate. If there are blocks of different ages in your room, and mass fruiting of all batches does not occur, you can calculate based on the figure of 180-220 cubic meters / ton.
2. The fan must be medium pressure.
 3. Air duct diameter - central and outlet - calculated based on the fact that the speed of air movement in them should be 4-5 m / s.
3. Air duct diameter - central and outlet - calculated based on the fact that the speed of air movement in them should be 4-5 m / s.
4. Air duct openings be sure to conical, in order to create directional jets and increase their speed - disposable plastic cups are very suitable for this purpose. The distance between the cups is usually from 0.45 cm to 80 cm.First, according to the formula, the total number of cups is calculated, their diameter is determined (a certain amount of air must pass through the total section of all cups per hour), and then, knowing the total length of the outgoing air ducts, the distance between the glasses can be calculated. The speed of the jet from the nozzle of the glass is 8-9 m / s. With intensive loading of chambers (especially with a single-zone production method), the speed can be up to 12 m / s.
5. Recirculation -
it is a room air supply system. The recirculation pipe is located before the heat exchanger and fan. It supplies air that mixes with fresh air. This smoothes the jumps in the microclimate - after all, the air from the forcing chamber has already been heated and humidified to the required parameters. Recycling significantly reduces the cost of mushroom production in winter. After all, oyster mushrooms do not need a large amount of fresh air as well-organized high-speed streams. The% opening of the recirculation damper depends on the amount of mushrooms that bear fruit at the same time in the growing room.
A filter is installed on the recirculation pipe to clean the flow that enters the system from fungal spores. Otherwise, the fan blades and heat exchanger fins will become clogged and work worse.
6. Hood should be calculated in such a way as to remove all the air that has entered the room, if the hood is weak, the blower fan will not supply the calculated amount of air, but less. The flow rate will drop, which can negatively affect the shape and condition of the oyster mushroom fruiting bodies.
The power of the exhaust fan is about 90% of the supply fan. With maximum air exchange, i.e. when the fresh air damper is 100% open, the exhaust fan should run at full capacity. When recirculation is in operation, the speed of the exhaust fan must be controlled by a frequency converter as a percentage of fresh air.
The hood, as well as all ventilation, must always work in the mushroom growing chamber if the fresh air damper is open. If the system is in 100% recirculation mode, the exhaust fan is turned off.
Ventilation without ducts
It is possible to make ventilation in a room without air ducts if the chamber load is 1 sq. M. is 100-130 kg, and there are high ceilings.
Or if you practice outdoor cultivation of oyster mushrooms, i.e. blocks stand only on the floor, in one or more tiers. See here for such placement.
It is quite difficult to calculate such ventilation, you have to experiment - in such rooms, axial fans are placed under the ceiling, which accelerate and mix the flows, perfectly removing CO2, and one or more axial fans are placed below, providing exhaust.
Growing chamber ventilation should ALWAYS work, creating a defined, stable microclimate.
No amount of energy savings associated with periodically shutting down fans and humidification systems justifies the loss in yield.Due to the jumps in microclimatic parameters (temperature, humidity, CO2), the oyster mushroom fruit bodies are deformed, and yield losses can reach 5-10% in two waves.
Ventilation calculations for oyster mushrooms.
Oyster mushroom cannot grow without forced ventilation.
If you create natural air flows during ventilation (draft) in rooms where there are bags far from each other on the floor, or are suspended from the ceiling in different corners in the attic or basement, then you can collect a certain amount of ugly dry mushrooms, see the photo below left.
But if we talk about the intensive technology of growing mushrooms, then one cannot do without forced, well-calculated ventilation.
The more the substrate is loaded per square meter, the more intensively the mushrooms exhale carbon dioxide and evaporate moisture. So,
The main task of ventilation in the oyster mushroom growing chamber is to remove the waste products of the fruit bodies from the growing bunches. The air flow must pass at such a speed that it flushes carbon dioxide and moisture directly from the mushroom drusen, and not somewhere around.
Ventilation for mushrooms
The flow rate is created and maintained by a properly sized fan and a system that provides recirculation, fresh air inlet and air discharge from the room - using an exhaust fan.
This is called supply and exhaust ventilation.
In this case, it is very important how the blocks are located - the rows themselves and the distances between them should contribute to the correct passage of the flows.
Here is a photo. On the first two (click to enlarge) there is ventilation only in the wall, there are no air ducts in the chamber itself, the mushrooms pull their leg and fold their caps due to the large amount of carbon dioxide and the inability to evaporate moisture, in the third photo you can see the quality of the mushrooms and the air duct.
The air in the ventilation system must be:
- warmed (cooled) to a temperature optimal for the production of this strain of oyster mushroom. For universal strains, this is from 14 to 16 degrees
- Moistened to the required moisture content, depending on the stage of development of the mushrooms. In the mycelium, where mushroom blocks of different ages are located - you can keep the humidity of 87-89%
- contain an amount of carbon dioxide below 900 ppm - even less for some strains.
I repeat once again - this is how the air should enter the chamber!
It is unacceptable to heat, cool and humidify the air in the growth room itself!
Changes in temperature and humidity have a detrimental effect on the development of fungi - condensation forms on them, or they dry out, or curl up into a tube. In general, we can say that almost all deformations of oyster mushroom fruiting bodies, called "diseases" by mushroom growers, are the cause of improper microclimate control in the growing room.
Calculate and make ventilation for growing oyster mushrooms yourself
I believe that in small myceliums, no more than 10x12 in size, it is quite possible to make a ventilation system in a room for growing mushrooms with your own hands.
How is ventilation calculated?

And why is that ventilation needed? And so everything grows!
Calculations of the fan power and the diameters of air ducts in mushroom rooms are not undertaken even by certified ventilation engineers. Because ventilation of office buildings and industrial structures is considered based on other parameters - mainly from the frequency of air exchange.
In the chambers for growing mushrooms, both oyster mushrooms and champignons, ventilation calculations are not based on the rate of air exchange per hour, but depending on the amount of compost or substrate in the room. Why is that? After all, the substrate itself and the mushrooms growing on it breathe, and the more there are in one square meter, the more moisture and carbon dioxide they emit. Therefore, to remove these waste products of the fungus, a calculated air flow is needed.But in mushroom production, it is necessary to proceed not only from the figures for the ratio of air / tonnage of the substrate.
They are on the Internet: 250 cubic meters. per hour per ton of substrate, the speed from the nozzles is 8-12 m / sec. You can also read my article on ventilation basics here. The mushroom technologist, when calculating ventilation, also takes into account other parameters of the microclimate and uses his knowledge of the biology of fungi.
For experienced mushroom growers who want to expand their production or simply recalculate the correct ventilation in their growing ones, I have created calculators for calculations:
- for myceliums only with a central air duct.
- for chambers with central and side air ducts (with single and double rows of blocks)
On the first page of the calculator, you can enter your data, and on the next page you can see the calculation results. You can read more about it and buy it here.
For those who are just thinking about whether or not to start a mushroom business, I wrote a book with detailed calculations of the location of blocks, a list of all the necessary equipment and a list of monthly production costs. A calculation calculator is included in this book. More details.
I would like to point out that all calculations in this book are based on active inflow, the use of recirculation to stabilize the climate, and active exhaust.
How to calculate the hood for the oyster mushroom growing chamber is described in this book.
I can also calculate the mushroom growing room for you myself.
The cost of this service is dollars for the calculation of one chamber with layouts of blocks, ventilation system, heat exchanger, humidification.
Calculation of small growth rooms up to 35 sq. m. is part of the consultation on the launch of such cameras and costs dollars, cameras ranging from 35 to 100 square meters - dollars. More details.
The calculation includes:
1. Calculation of filling a room with blocks, in pieces and tons, with a block layout diagram, figure,
2. The layout of the ventilation system in the classic version, with recirculation and a mixing chamber, with dimensions and layout of air ducts, with dimensions of the diameters of all air ducts and nozzles - picture,
3.calculation of the throughput and pressure of the fans,
4. terms of reference for the supplier's company for the calculation of the heat exchanger,
5. Description of the humidification system, with the calculation of its capacity. You choose the system yourself (a disc humidifier or a low pressure system, medium or high - it depends on finances and some features of the growing one, we analyze all the pros and cons of the systems).
6. Answers via Skype or Viber to all questions related to the schemes themselves for microclimate systems: their fastening, installation and location
Growing oyster mushrooms is a profitable business that is developing in Russia. Its success for every entrepreneur directly depends on high yield, which is possible only with the creation of the necessary microclimate and competent preparation of the substrate.
It is important to pay special attention to finding a suitable room, choosing tools and equipment for growing oyster mushrooms.

Room for growing oyster mushrooms
Back to content
Premises
For growing oyster mushrooms, you can use both underground and aboveground premises. Garages, hangars or basements are perfect. Among the main requirements for a place, a special place is occupied by:
- good illumination,
- the presence of an optimal temperature regime,
- good ventilation.
The ability of these mushrooms to destroy wood is known, and therefore it is not recommended to grow them in wooden houses or clapboard rooms. The floor can be brick or concrete. Sometimes it is covered with sand. It is advisable to upholster the ceiling with insulation plates.
If the cultivation takes place in large rooms, then it is better to divide them into small ones, which will increase the volume of mushroom production.
The room temperature depends on the growth stage of the mushrooms. During the incubation period, the temperature should be at least 20 ° C, during fruiting, it is advisable to observe the regime of 15-20 ° C. During the incubation period, the room is sometimes not ventilated.
Equipment
Mushroom farm ventilation system that maintains the set parameters
In a room where mushrooms grow, you need to equip a ventilation system. For this, appropriate motors are usually used. To make exhaust ducts, you should use "corrugation" or other pipes with a large diameter. These channels are laid along floors and walls. Air exchange can take place 3 times a day, the ventilation system must operate at its peak.
Oyster mushroom is a moisture-loving mushroom. In the production process, in the absence of a plumbing, equipment such as hydrophore is used. In the premises where oyster mushrooms are produced, it is required to install several heaters and heating devices. Due to this equipment, the required humidity and air temperature will be maintained. In addition, the substrate for the oyster mushroom will undergo a pasteurization process.
For the convenience of servicing the substrate blocks, it is recommended to use racks.

Developed by I.P. Shapovalov construction for growing oyster mushrooms, consisting of movable mesh containers
Preparation of the substrate for growing oyster mushrooms requires separate equipment. For example, straw choppers are necessary in order to chop the straw and then get the fraction of the desired length. The productivity of this equipment can reach 3000 kg in 1 hour.
In the production of oyster mushrooms, it is possible to use crushers. They allow you to grind sunflower husks, which increases yields, and, therefore, growing mushrooms is more profitable. Also, in the process of their production, chambers are used in which the hydrothermal treatment of the substrate takes place. They combine soft and hard pasteurization treatments.
To form oyster mushroom blocks, a special automatic press is used. This equipment allows you to give the blocks a uniform shape and reduce their density differences. The blocks have 2 flat sides, so that during the cultivation of mushrooms, you can do without shelving. Packers and vibrating tables are also used. They are needed in order to increase the packing density of mushroom blocks.
Back to content
Inventory
During the industrial production of oyster mushrooms, special equipment is used. The kit includes:
- containers in which the pasteurization process takes place,
- bags required for the substrate,
- pitchforks, shovels, with the help of which the crop will be harvested.

The inventory must be carefully treated with a 50% formalin solution, then washed off with clean water. Containers (for example, bags, boxes) must be disinfected.
The inventory is stored only in clean rooms.
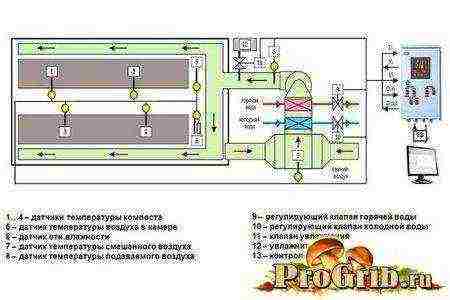
The system consists of:
fan,
distribution duct,
mixing chamber with dampers for fresh air and recirculation air
cooling and heating heat exchangers.
 The distribution of air in the chamber is carried out through air ducts with nozzles, which ensure the movement of air near the mushroom blocks at a speed of 0.2-0.5 m / s.
The distribution of air in the chamber is carried out through air ducts with nozzles, which ensure the movement of air near the mushroom blocks at a speed of 0.2-0.5 m / s.
Calculation of air volume: for one ton of substrate 250-300 m3 / hour.
Optimum speed of air movement from the nozzles: at the top, immediately under the nozzle, at least 8-10 m / s, at the bottom at the floor, at least 0.5-0.8 m / s.
At the same time, the air speed in the air ducts should be half the planned speed from the nozzles. This is ensured by the design cross-section of the air ducts. More details can be downloaded and read here.
The most optimal distance between the nozzles for uniform air distribution is 0.5-0.8 m.In order to ensure such conditions, it is necessary to correctly select the diameter of the nozzle outlet from 0.03 m to 0.07 m.
The fan outlet is connected by a central distribution box through an adapter made of galvanized sheet metal to the cross-section of the box. The cross-section of the box is invariable along its entire length. According to the number of polyethylene hoses, branch pipes are installed according to the calculated diameter of the polyethylene air ducts. The equalization of the air volume in each duct is carried out by reducing the cross-section of the pipes.
All connections must be easily detachable, for washing and replacing plastic sleeves.
A complete calculation of the supply and exhaust of air in the room for growing oyster mushrooms is quite laborious: it includes the calculation:
- power supply and exhaust fans,
- heat exchanger,
- humidification systems,
- diameters of the central and lateral ducts
- device and dimensions of the air mixing chamber in specific conditions
The calculation is carried out taking into account the various options for the placement of mushroom blocks, the height of the ceilings, the size of the chamber, the growing system (with a single-zone, a larger air flow is required).
Calculate ventilation for oyster mushroomsand other systems providing a stable microclimate, our technologists will help. To order calculations, you can write to the e-mail indicated on our store websites.
Climate control diagram
Fresh and recirculated air intake is carried out through pipes of the same cross-section into the mixing chamber. These branch pipes are fitted with dampers that act synchronously; the percentage of opening of the fresh air damper is equal to the percentage of closing of the recirculation air damper.
Next, a cooling heater is installed (if refrigeration equipment is used). Further - a heat exchanger, calculated to warm the air to the optimal operating temperature (22-24 ° C).
Instead of heat exchangers, it is possible to use air conditioners that provide the mode: cold, heat. The air conditioner is located in the recirculation air intake area (wall-mounted) or in the air distribution network (duct).
Further, a supply fan, after which an air humidification system is installed.
Overpressure in the chamber is not permissible! Mandatory forced exhaust ventilation system.
The exhaust fan discharges the exhaust air equal to the volume of fresh air, therefore, when equipping exhaust ventilation, it is necessary to ensure synchronization of the operation of the exhaust fan and fresh air dampers, or adjust the speed of the exhaust fan motor to increase, decrease the air volume through automatic control.
Air filtration:
Filters for coarse and fine air purification are provided on the fresh and recirculated air intake pipes. Filters should have such a pore size to be able to capture spores of 2-3 microns, the efficiency is not less than 95%. Typically, the filter is used for many incubation cycles. The service life of the filters increases with the use of pre-filters for coarse air purification. The difficulty in using filters is their high sensitivity to moisture. The filter must be changed when the air flow resistance has reached the value specified by the manufacturer.
Moisturizing:
1. Steam humidification is most effective for any outdoor air parameters (with the exception of dry hot summer air). This requires the presence of special equipment: a steam generator or steam boiler, a special water treatment station, supply of water and steam pipelines.
2. Humidification by irrigation with water is carried out by placing an aerosol generator or nozzles with an opening providing fine atomization in the air duct after the fan.The effectiveness of this humidification method in summer is ensured by the air warmed by nature, part of the thermal energy goes to evaporate the sprayed water, and part to cool the air.
When using irrigation in winter, the air supplied to the heat exchanger must be warmed to a temperature of at least 40-45 ° C, or the sprayed water must have a similar temperature.
There are various options for obtaining a fine atomization:
- high pressure pumps (120-160 ATM.);
- fogging installations;
- centrifugal trays for special purposes, etc. etc.
Air cooling
Air heat exchangers (air heaters) are the most efficient air cooling elements. Ice water (+ 2-6 ° C), cold water (+ 10-12 ° C) or a mixture of ice water and polypropylene solutions are used as a cooler, which ensures the temperature of the energy carrier is below + 4 ° C, which significantly increases the efficiency of air cooling.
The use of refrigerant (freon, ammonia, etc.) as an energy carrier is very effective when using special equipment from various companies.
When providing data for calculations for air cooling, it is necessary to take into account the heat transfer coefficient of the substrate blocks 1.0 -1.5 kW per ton of substrate, with the allowable heating range of the blocks (30-32 ° C), the set temperature regime of the room, the coefficient of thermal resistance of walls, ceilings, floors.
Air dehumidification
The most effective is the condensation method, which consists in passing air through a heat exchanger with a plate surface temperature below the dew point. By regulating the temperature of the water in the heat exchanger (corresponding to the temperature of the plates), it is possible to regulate the amount of condensate from the air stream.


