Content
- 1 Main types
- 2 Grain growing technology
- 3 Sowing dates
- 4 Plowing the land
- 5 Sowing seeds
- 6 Grain care
- 7 Harvest
- 8 Potato cultivation technology
- 9 Land preparation and planting
- 10 Potato care
- 11 Cleaning
- 12 Sunflower cultivation technology
- 13 Technology for growing forage grasses
- 14 Growing sugar beet
- 15 Growing vegetables in greenhouses
- 16 Varieties and hybrids
- 17 Geography and climate
- 18 How the industry developed
- 19 Industry characteristics
- 20 The place of agriculture in the economy of Kazakhstan
- 21 Sectors of agriculture in Kazakhstan
- 22 Agriculture of South Kazakhstan
- 23 Features of agriculture in the western part of Kazakhstan
- 24 Agriculture in the northern part of Kazakhstan
- 25 Features of agriculture in East Kazakhstan
- 26 State policy in the field of agriculture
- 27 Industry development problems
- 28 conclusions
Agricultural crops are called crops cultivated by farmers and large agro-industrial enterprises in order to obtain food, feed for livestock, technological raw materials. There are several main types of such plants. Of course, the cultivation of crops must be carried out in strict compliance with certain technologies.
Main types
Most agricultural enterprises are broad-based and grow a wide variety of crops. It can be cereals, vegetables, fruit trees, root crops, etc. But most often in Russia such agricultural crops are cultivated as:
- wheat, barley, rye and oats;
- potato;
- sunflower;
- forage grasses;
- sugar beet.
These are the main types of agricultural crops in our country. Of course, domestic farmers sometimes grow vegetables as well. Such crops are most often cultivated in greenhouses.

Grain growing technology
When cultivating oats, wheat, barley and rye, agricultural enterprises perform the following activities:
- basic and pre-sowing soil preparation;
- fertilization;
- seed preparation;
- sowing;
- planting care;
- harvesting.
Sowing dates
Grain crops can be cultivated using the winter or spring method. In the first case, sowing takes place in the autumn, in the second - in the spring. The most important task in the cultivation of grain crops is to determine the timing of planting seeds in the soil. They should be chosen so that winter cereals reach the tillering phase before the onset of cold weather and form at least 3-4 shoots. Therefore, the optimal time for sowing grain crops in the non-chernozem zone of Russia is the first decade of September. Sometimes planting is carried out at the end of August. When cultivating spring crops, the sowing time is determined by the condition of the soil. Most often, cereals are planted in mid or late April.
Plowing the land
Soil cultivation before sowing cereals is carried out so that as much post-harvest residues as possible remain on the surface. This is necessary in order to avoid erosion and retain as much moisture as possible in the ground.
For plowing, in most cases, various kinds of mineral fertilizers are applied. Further, early spring harrowing is carried out for spring crops, and pre-sowing cultivation for winter crops.
Sowing seeds
After the soil is prepared, the actual planting of cereals is carried out. In this case, only healthy, undamaged seeds that meet the stipulated standards are used. Before sowing, they are pickled to avoid infection with fungal, bacterial and other diseases. Winter crops are grown from the seeds of last year's harvest.For their storage at agricultural enterprises, special funds are created. Freshly harvested seeds are rarely used when planting. The fact is that they have a reduced germination rate. At the final stage of planting, the seeds are rolled to improve their contact with the soil.
Grain care
Subsequently, to obtain a good harvest, the following activities are carried out:
- Protection of cereals from pests and diseases. As necessary, they are treated with fungicides and insecticides.
- Weed removal. In this case, crops are treated with herbicides.
- Top dressing. Cereals are fertilized during the season, usually using nitrogenous compounds.

Harvest
This operation can be performed in two ways: directly or separately. Two-phase harvesting is performed for unevenly ripened, lodged or heavily weeded crops. In all other cases, the usual direct combining is carried out.
Potato cultivation technology
Cereals are the main type of plants cultivated by domestic agricultural enterprises. However, potatoes are also quite widespread. The cultivation technology of this crop includes the following stages:
- soil preparation;
- landing;
- plant care;
- harvesting.
Land preparation and planting
Potato plots are usually chosen with loose soil that allows moisture and air to pass through well. Only in such areas can you get good harvests of this crop. The best precursors for potatoes are winter cereals, corn, perennial and annual grasses.
Prepare the soil for potatoes, usually in the fall. At the same time, plowing (autumn) is carried out with the introduction of fertilizers. In April, the soil surface is leveled and early spring harrowing is carried out.
Only healthy, undamaged tubers of large and medium size are used for sowing. 10-12 days before disembarkation, they are unloaded from the storage and sorted out. Further, the tubers are germinated or simply wilted. Sometimes, before planting, potatoes are treated with ash, mineral fertilizers and fungicides.
Tubers are planted only in well-warmed soil. At the same time, 55-60 thousand bushes are placed on 1 hectare. Early varieties are usually planted denser, later ones less often. The landing itself can be ridge, semi-ridge or smooth. The first two methods are more often used on wet or heavy soils. The combs are cut a few days before planting.

Potato care
The first shoots of this culture appear in about two to three weeks. With a smooth planting, harrowing is carried out in agricultural enterprises. It can be performed before germination or after germination. In the future, caring for potatoes is reduced to hilling and weeding. The first operation is performed twice a season: with a height of bushes of 15-18 cm and before flowering. Weeding is carried out as needed. Plantings of this variety, among other things, should be periodically treated against phytophthora (fungicides) and the Colorado potato beetle ("Decis", "Volaton").
Cleaning
The ripening time of tubers depends primarily on the variety of potatoes. To facilitate mechanized harvesting in agricultural enterprises, the tops are usually mown. This operation is performed in 3-5 days. Cleaning itself can be done in three ways:
- direct combining - on light crops;
- by separate technology - on heavy soils;
- in a combined way.
Seed tubers before storage are kept in the light for 10-12 days until light greening. Table potatoes are air-dried for several hours. Of course, like any other staple crop, potatoes must be stored properly. Tubers are laid for the winter in dark cool rooms in bulk or in boxes.

Sunflower cultivation technology
It is customary to grow this crop after winter and spring cereals. Presowing preparation of land for sunflower includes operations such as plowing, harrowing and leveling the soil with special drags. Cultivation is carried out to the depth of planting seeds (6-10 cm). Manure is usually used as fertilizer for plowing. Sometimes mineral fertilizing can also be used (depending on the composition of the soil).
For sowing, seeds of varieties and hybrids entered in the register are used with a germination rate of at least 95%. Planting is carried out in well-heated soil at the rate of 30-50 thousand plants per hectare. Sowing is carried out in a dotted manner. At the final stage, the plots are rolled in.
Sunflower care in our country is carried out using exclusively mechanized methods. The first is such an operation as harrowing before and after germination, with simultaneous weeding and the use of herbicides. Further, sunflower care includes procedures such as:
- Fight against voidness. For this, hives are placed on the allotment at the rate of 1.5-2 per hectare.
- Pest and disease control using chemicals.
Harvesting is done after the back of the baskets turns yellow. The reed flowers should fall off. Sunflower is harvested, like most other agricultural crops, with special combines.
Technology for growing forage grasses
Crops of this group can be cultivated as pasture or for hay or silage. There are many types of forage grasses. But most often in our country alfalfa, clover, vetch and legumes are grown. The technology of their cultivation, like any other agricultural crops, includes soil preparation, sowing, care and harvesting.

A feature of growing herbs is very deep, 25-30 cm, plowing (due to long roots), the possibility of sowing perennial crops under the cover of annuals and fertilizing with mineral fertilizers during the growth period. Plants are harvested in the budding or flowering phase.
Growing sugar beet
About 21 thousand hectares of arable land are used for this crop in Russia. The optimum depth of plowing the land for beets is 25-30 cm. Such cultivation of the land is carried out in the fall - usually in September. At the same time, manure is applied in the amount of 40-80 t / ha. For sowing, pickled seeds are used. Planting is carried out to a depth of 25-35 mm, depending on the type of soil, using special seeders. Caring for beets consists mainly of weeding or applying herbicides, as well as protecting plants from pests and diseases using chemicals. Harvesting of this crop usually begins on September 20-25. In this case, in-line, transshipment or combined technologies can be used. The last two methods are usually used with increased contamination of areas.
Growing vegetables in greenhouses
A feature of the cultivation of crops of this variety in greenhouses is the periodic use of fertilizing and land replacement. After all, the soil in greenhouses is very quickly depleted. Also, in such farms, maximum attention should be paid to the fight against pests and diseases. Infections spread very quickly in greenhouses. Seeds of agricultural crops of this variety are necessarily pickled before planting.
Most often, cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers and melons are grown indoors. The greenhouses themselves can be film, glass or polycarbonate. Among other things, when growing vegetable crops, special attention is paid to their selection according to their compatibility. This takes into account such factors as the feeding and irrigation regime, climatic conditions, the need for pollination, the frequency of airing, etc.
Varieties and hybrids
Farms and large agricultural enterprises mainly grow only varieties of agricultural crops entered in the state register. The only exception is experimental stations where breeding work is carried out. When developing new varieties, the following methods can be applied:
- selection with the consolidation of certain valuable features;
- hybridization in breeding nurseries.
The resulting varieties and hybrids are tested and, if the value for agriculture is established, are entered into the state register.

The cultivation of crops, therefore, must be carried out on well-prepared soils, using suitable fertilizers and seeds of the best varieties. In the absence of violations of technology, even in the case of adverse weather conditions, you can get good harvests and at the same time avoid such negative consequences as erosion and soil depletion.
Agriculture in Kazakhstan is one of the most developed sectors of the state economy. In each of the individual regions, conditions are favorable for the cultivation of certain crops. Particular attention is paid to animal husbandry.
Geography and climate
The territory of Kazakhstan is located simultaneously in Central Asia and in Eastern Europe, washed by the Caspian and Aral seas. The continental climate conditions cold winters with little snow and hot dry summers.
About half of the country's territory is deserts and semi-deserts. The western part has mountain ranges. As for water resources, there is a shortage of them due to geographical location. Seven large river arteries and 13 large reservoirs serve as sources of life-giving moisture.  Speaking of vegetation, it should be noted that steppe plants such as feather grass, wormwood and drought-resistant shrubs predominate. Green alpine meadows are found in the highlands. As for forests, they occupy 5.4% of the territory and are concentrated mainly in the north and south of the country.
Speaking of vegetation, it should be noted that steppe plants such as feather grass, wormwood and drought-resistant shrubs predominate. Green alpine meadows are found in the highlands. As for forests, they occupy 5.4% of the territory and are concentrated mainly in the north and south of the country.
Soils are perhaps the most important for agriculture. A significant share falls precisely on chernozems, chestnut and brown soils. There are also gray soils and brown soils.
How the industry developed
It is advisable to consider the development of agriculture in Kazakhstan since the 50s. In view of the economic crisis, the Soviet authorities decided to expand the cultivated areas. Then, virgin lands were actively developed in Kazakhstan and a number of other republics. It is worth noting that it was necessary to develop those areas that were characterized by low moisture content and a tendency to erosion.
It should be noted that the development of virgin lands led to a record grain harvest. At the same time, a sharp decrease in pasture areas was a negative consequence. To prevent a crisis in animal husbandry, specialized collective farms were obliged to increase the number of livestock. The Soviet period in the development of agriculture was also marked by the reform of machine and tractor stations.
In the 60-80s, the most intensive development of agriculture was observed. Cooperative ownership was completely transformed into state ownership, which made it possible to strengthen control over the movement of funds. This led to the fact that many farmers chose to leave the village. The government decided to attract specialists from other republics, as well as to use urgent military personnel.
At the moment, almost all agricultural land is in private hands. And, as in the late 70s, the problem of providing the population with meat and dairy products is quite acute, which indicates the need for reforms.
Industry characteristics
Agriculture in Kazakhstan is characterized by the following distinctive features:
- there is a pronounced zoning (horizontal and vertical) of soil covers;
- more than half of all land suitable for cultivation is in the desert and semi-desert zones;
- 85% of agricultural land is allocated for pastures (this is about 189 million hectares);
- Kazakhstan is one of the ten largest exporters of wheat and flour;
- the largest share of cultivated crops falls on cereals, fruits and berries, oilseeds, as well as cotton;
- in Kazakhstan, the livestock industry is traditionally developed, as well as the production of leather and wool.
The place of agriculture in the economy of Kazakhstan
Agriculture in Kazakhstan is one of the fundamental sectors of the state economy. It is worth noting that it brings 38% of the total national income annually. At the same time, this area employs about 16% of the state's workforce. This is due to the high level of mechanization and automation. It should be noted that there are more than 31,000 agricultural enterprises operating in the country, as well as about 32,000 peasant farms.
It should be noted that the agriculture of Kazakhstan ranks second in the world in the production of grain crops with an indicator of 967 kilograms per capita (leading positions belong to Canada, where this figure is 1,168 kg). At the same time, it is the only post-Soviet republic that is engaged in the export of bread. Nevertheless, the yield and productivity of such an industry as animal husbandry in Kazakhstan is quite low (paradoxically). According to this indicator, the state occupies 142 place in the world.
Sectors of agriculture in Kazakhstan
The agricultural sector is the strongest mechanism that provides not only the internal resources of the state, but also its position in the external market. Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan is traditionally represented by two main sectors:
- Livestock - is developing in such areas as the breeding of cattle (meat and dairy production), sheep, horses, camels, pigs and goats. Poultry farms account for a significant share. A separate, albeit insignificant, niche is the cultivation and commercial fishing of fish.
- Crop production is the backbone of Kazakhstan's agriculture. The largest share is occupied by spring wheat, which is sold not only in the domestic but also in the foreign market. It is also worth noting the prevalence of crops such as rice, buckwheat, barley, oats, millet and corn. Considerable sown areas are allocated for sugar beets and oilseeds (sunflower, rapeseed). Cotton and flax are grown for the textile industry. Crops such as potatoes, apples, melons and grapes are also worth noting.
Agriculture of South Kazakhstan
It is worth noting the diversity of natural and climatic conditions in the republic. Thus, the agriculture of South Kazakhstan operates in conditions of high air temperature in the foothill zone. With a good organization of artificial irrigation, it is possible to achieve high rates of harvesting of cotton, rice, sugar beet and tobacco. It is also worth noting that this is the most favorable place for the development of horticulture and viticulture.
Features of agriculture in the western part of Kazakhstan
Agriculture of Western Kazakhstan is represented mainly by animal husbandry, which is due to large areas of pastures and meadows. The largest share falls on the breeding of sheep, horses and camels. If we talk about crops, then more than 70% of arable land is allocated for wheat. The rest of the area is occupied by barley, millet and rye.
Agriculture in the northern part of Kazakhstan
The agriculture of Northern Kazakhstan is developing rapidly under the influence of favorable climatic conditions. Here, meat and dairy cattle breeding, as well as bird breeding, are most developed.The main industry is sheep breeding. Agricultural fields are occupied by cotton and grain crops. Also, there are very favorable conditions for growing vegetables, fruits and melons.
Features of agriculture in East Kazakhstan
Agriculture of East Kazakhstan is represented mainly by non-irrigated agriculture. The largest land areas are occupied by sunflower crops. In the river valleys, there are significant fields of wheat, oats, peas, and vegetable crops. It is also worth noting the rapid development of meat and dairy farming. In some areas, irrigated viticulture is developed. Also, great attention is paid to the breeding of pigs and horses. The West of Kazakhstan is characterized by developed beekeeping, fur trade and beekeeping.
State policy in the field of agriculture
The development of agriculture in Kazakhstan is carried out with the support of the authorities. State regulation and reform is aimed at implementing the following main ideas:
- increasing entrepreneurial activity of the population of rural areas, as well as increasing their level of well-being;
- providing residents of agricultural regions with electricity, gas, drinking water and other vital resources;
- construction and overhaul of roads in rural areas;
- modernization of telecommunication systems;
- strengthening health care measures in rural areas (construction or overhaul of hospitals, attracting appropriate specialists);
- reforming education in schools and other educational institutions;
- providing villagers with access to cultural and sports programs;
- improving the level of security in villages by increasing the number of police stations, as well as units of the Ministry of Emergency Situations;
- ensuring environmental safety in rural areas;
- development of policy mechanisms in the field of internal migration in order to reduce the outflow of the population from agrarian regions.

Industry development problems
The following main problems of agriculture in Kazakhstan can be identified:
- insufficient receipt of tax payments to the budget, which is associated with the difficulties of transition from the old state farm form to the modern farm form;
- insufficient amount of financial injections into the industry;
- the deplorable state of the dairy industry (the most vivid illustration of the problem is the forced purchase of products in neighboring Kyrgyzstan);
- the need to increase the livestock population to increase the export of meat products to neighboring countries;
- lack of storage space for crops (the area of elevators must be expanded at least twice to ensure the safety of the crop);
- migration of the population to cities due to the underdevelopment of villages and villages (the population who works in the agricultural sector, basically, does not have the appropriate education and qualifications);
- growth in imports of agricultural products;
- outdated material and technical base;
- insufficient level of development of local science in the field of agriculture.

conclusions
Based on the foregoing, it can be concluded that there is some stagnation in such an industry as agriculture in Kazakhstan. Briefly, the situation can be described as irrational and incomplete use of natural and human resources, as well as insufficient financing of the agricultural sector. The climate and natural resources of Kazakhstan contribute to the development of animal husbandry, as well as the cultivation of grain crops. Thanks to the policy of virgin lands development, which was carried out during the Soviet period, there is a significant area of arable land, which provides Kazakhstan with a leading position in the world grain market.
It is worth noting the exceptional importance of agriculture for the economy of Kazakhstan. This industry accounts for almost 40% of the national income of the state.Considering that less than 20% of the economically active population is employed in this sector, we can talk about a high level of production automation. Despite the existing problems with the yield indicator, the country managed to become the second largest grain exporter in the world. It is the only republic in the post-Soviet space that has the ability to sell grain abroad.
Despite the fact that agriculture is assigned a fundamental role in the economy of Kazakhstan, it has some inherent problems. One of the main difficulties is the incomplete transition to the modern farming form, which makes it difficult to control the payment of taxes. It is also worth noting the lack of investment in the industry. The greatest stagnation is observed in the meat and dairy industry, which leads to the forced import of these products to meet consumer demand. Another key problem that requires an immediate solution is the lack of storage space for the harvested crop.
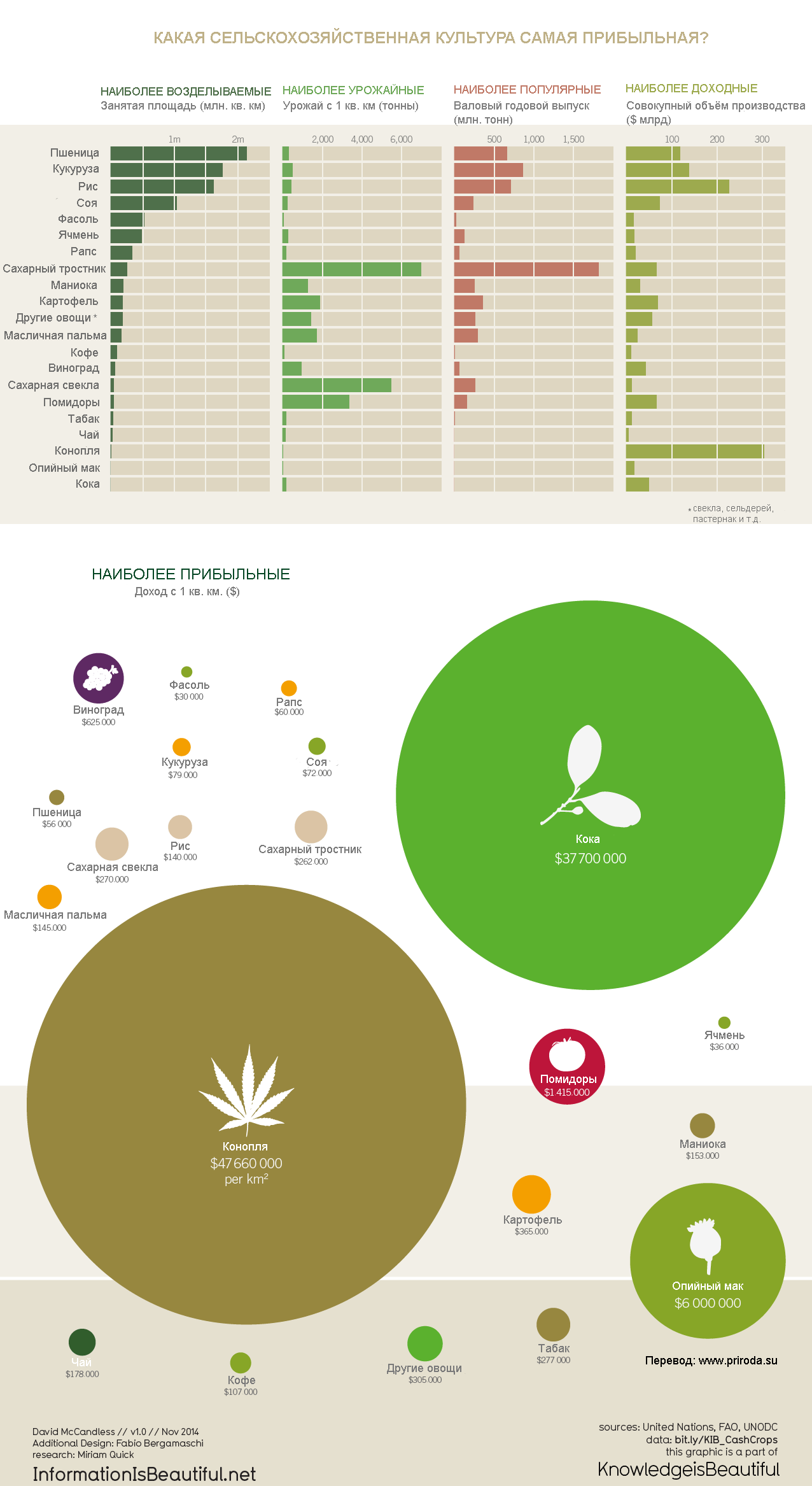
Wheat is the most farmed agricultural crop in the world. More than 2 million square kilometers of the Earth's surface is occupied by this crop. It is followed by corn and rice.
The most productive are sugar cane and sugar beet. About 6,000 tons of these agricultural products can be harvested per square kilometer.
The most popular crop is sugar cane. More than 1,500 million tons of it are produced annually.
The most profitable and profitable plant is parsley. Of the legal agricultural plants, rice is the most profitable in terms of total production, and tomatoes are the most profitable (income per sq. Km).
(Visited 9,957 times, 9 visits today)


