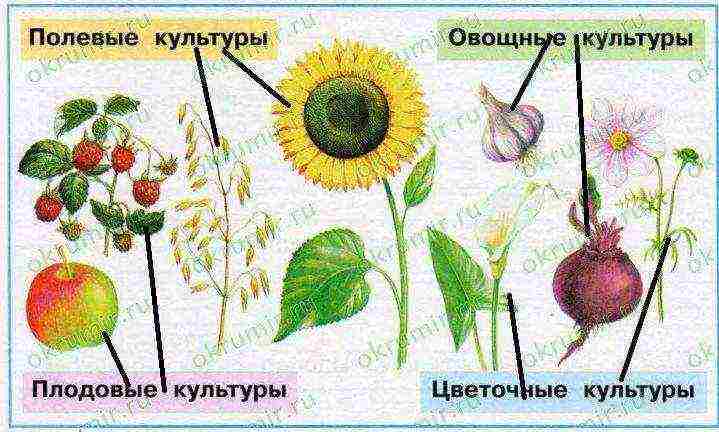
1. Complete assignments for group work.1) Field cultivation.a) Write down the definition. Field cultivation is the cultivation of field crops.
b) Give examples of field crops grown in your area.
wheat, rye, oats, corn, buckwheat, potatoes, flax, sunflower2) Vegetable growing.a) Write down the definition. Vegetable growing is the cultivation of vegetable crops.
b) Give examples of vegetable crops grown in your area.
cabbage, carrots, onions, garlic, tomatoes, cucumbers3) Fruit growing.a) Write down the definition. Fruit growing - this is the cultivation of fruit crops.
b) Give examples of fruit crops grown in your region.
apple, pear, strawberry, cherry, plum4) Floriculture.a) Write down the definition. Floriculture - it is the cultivation of flower crops.
b) Give examples of flower crops grown in your area.
chrysanthemums, asters, peonies, roses, hyacinths, gladioli2. The Wise Turtle wants to know if you can classify crops. Show with arrows which groups the plants shown in the picture belong to. Ask a classmate or teacher to check your work.
3. Cross out the extra word in each row.
Explain your decisions (verbally). Think of a similar task for your classmates with other examples. Write it down. strawberries, currants, radishes, cherries
onions, carrots, tomatoes, rye
tulip, barley, wheat, oatsListen to and evaluate the responses of your classmates.4. As instructed by the textbook (p. 193), observe the spring work in the field, in the vegetable garden, in the garden. Do the work yourself. Write a short report on what you saw and did. You can draw or paste a photo. This spring, I helped my grandmother plant onions in the garden. It was very interesting. First, we took a shovel and dug up the soil under the bed. Then we leveled the ground with a rake and formed a rectangular bed. Then the grandmother took a stick and drew straight longitudinal grooves on the bed. It was in these grooves that we began to plant small bulbs, which my grandmother called “onion-sevok”. Grandma said that all the bulbs should be at an equal distance from each other. We deepened them a little into the ground and made sure that the root was always at the bottom, and the tail with a green sprout at the top. Then we covered the planted bulbs with earth and watered them well from the watering can. Hopefully our bulbs will sprout quickly and we will eat them all winter.
Return - Pleshakov, Kryuchkova, 4th grade. 1 piece of workbook
Plant growing - the science of cultivation of cultivated agricultural plants, as well as such breeding itself. ("Explanatory Dictionary" S. I. Ozhegov) Plants that a person plants himself, takes care of seedlings, reaps crops, uses for food, are called cultural.
Crop production is divided into several main branches: field cultivation, vegetable growing, fruit growing, floriculture.
Plants of the field
A field is an open, treeless space where cultivated plants are grown.
In the Perm Territory, grain crops are cultivated in the fields - rye, wheat, barley, oats, millet and buckwheat; vegetable crops - cabbage, carrots, beets, cucumbers, etc.; fodder crops - clover, vetch, peas, turnips, fodder beets, etc. industrial crops - flax, potatoes.
Grain crops occupy the leading place in field cultivation. They are the basis for the development of other branches of agriculture and industry.
Among grain crops, the first place in terms of crops in the region is winter rye... It is cultivated in the north, in the central and southern regions. She is not afraid of cold weather, gives a good harvest and ripens early.
The second place in sowing of grain plants is taken by wheat Is the most valuable grain crop.She loves warmth, so she is cultivated in the southern part of the region.
In the northern regions, they also grow barley and oats. In the south of the region - millet.
All these cultivated plants differ from each other, but their structure has a lot in common. All of them are herbaceous plants, the root is a bunch, the stem is a straw, it is hollow inside, has large nodes, which makes it strong and stable. Leaves are narrow, long. Small flowers of rye, wheat, barley are collected in ears, and millet and oats - in panicles. Later, fruits - caryopsis - are formed from the flowers. Such plants are called cereals.
The grains of these plants are different from each other. For example, in rye, the grain is oblong, darker, in wheat - round, light.
Use of cultivated grains
|
Name of the cultural plants |
What do they get |
|
Rye |
Rye flour (rye bread is baked). The bran is used to feed livestock. The straw goes to the litter. |
| Wheat |
Wheat flour (white bread is baked, confectionery and pasta are made). Wheat groats. Semolina. |
| Barley |
Barley flour. Barley groats. Pearl barley. |
| Oats |
Oatmeal flour. Oat groats. Oatmeal. Hercules. |
| Millet | Millet groats. |
Plants from which bread is obtained are called bread plants.
Farmers have to spend a lot of time, effort and money in order to grow crops, harvest and prepare bread. Therefore, it must be protected!
Vegetable plants
Many vegetables are grown in the fields: cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, carrots, beets, radishes, radishes, onions, etc.
White cabbage often referred to as the "queen of vegetables".
|
Cabbage is very rich in vitamins, it is the basis of many dishes. It is eaten raw in salads, boiled in cabbage soup and borscht, stewed, sauerkraut, pies are baked with it. A lot of knowledge, labor and time must be devoted to the cultivation of this culture. Cabbage loves warmth and moisture. Warm countries are her homeland. Without preparation, cabbage will not have time to ripen during the relatively short Ural summer. Therefore, in early spring, when the field is still resting, people plant small blackish round seeds in greenhouses or hotbeds. They grow light green plants with two leaves (seedlings). |
When it gets warm, the seedlings are planted in fields and gardens. More and more leaves appear in plants. They are pressed closer and closer to each other. This is how a head of cabbage is formed. The inner sheets become juicy and white. There are 40 - 70 of them in the head of cabbage, and sometimes even more, and they hold tightly, clinging to each other. Cabbage is harvested in autumn.
|
Tomatoes love sunny warm weather very much. It was brought to us from South America. Tomatoes, like cabbage, in the Kama region are grown first in greenhouses, and then planted in the beds. On the fragrant, curly bushes with carved leaves, yellow flowers bloom, and from them fruits are formed - round, green. At this time, they cannot be eaten yet. When they turn yellow and red, you can eat them. They become very tasty and rich in vitamins. |
Green cucumbers are a favorite vegetable. They are also good in winter pickled or salted.
|
The homeland of cucumbers is India - a warm southern country. In our conditions, cucumbers give a good harvest if they are grown correctly. Cucumbers, like cabbage and tomatoes, are first planted in greenhouses or hotbeds, i.e. man, as it were, artificially lengthens the summer for them. Then, with the onset of warm weather, they are transplanted to the beds. From the seedlings, low plants grow with creeping fragile stems, rough leaves, then yellow flowers in the form of gramophones bloom, and from them oblong, bright green juicy fruits - cucumbers - are formed. |
Spring seeds carrots, beets, radish sow directly on the beds and watered thoroughly with water. Low plants with green leaves appear. Their roots grow and become thicker and juicier. They accumulate nutrients: sugar, starch, vitamins. A month later, radishes are already ripening, and later - carrots and beets.
Plants that eat thickened roots are called root crops.
Onion - a valuable food product. It contains sugar and various vitamins. Not a single meat or fish dish is complete without onions. Even in ancient times, onions were used as a medicinal plant for many diseases. Therefore, the people put together the following proverb: "Onions from seven ailments." Our scientists have found that onions release volatile substances (phytoncides), which kill putrefactive and pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, eating onions has a healing value.
Onions are eaten with green leaves and onions. Dry steppes are the homeland of onions. The plant has adapted to preserve the nutrients in the bulb during the dry season, which has wonderful properties. Many people store onions in the winter, and they do not dry out. In spring, the bulb germinates easily and produces green leaves, and in greenhouses even in winter. She can hibernate easily. Sometimes lek is planted in the beds before winter. When the snow begins to melt, green leaves already appear on the onion.
Potato - a valuable food product. It is often called the "second bread". Potatoes are an important industrial crop. Starch, alcohol, molasses are obtained from it.
|
In spring, a lot of potatoes are planted in the fields and gardens of the region. Herbaceous plants grow in the form of bushes with branched stems. They reach a height of 50-60 cm. In the middle of summer, white-pink and purple flowers are formed on them. Once, for the sake of these flowers, potatoes were grown to decorate clothes, not knowing about the properties of the underground parts of this plant. Observing the flowers, you can see that then round, green, with small seeds, fruits resembling tomatoes appear. They cannot be eaten, they are bitter and poisonous. |
In the underground part, the stalks of potatoes release underground white branches, at the ends of which thickenings are formed - young tubers. They gradually grow and fill with starch. In autumn, a rich crop of potato tubers is usually harvested.
|
The homeland of the potato is South America. Potatoes were not immediately recognized in Russia. In the beginning, it was not the tubers that were mistakenly consumed in food, but the bitter fruits. Therefore, many peasants did not want to plant him. The planting of potatoes was spread among the population by compulsory means, and this caused "potato riots" in ancient times. But gradually people mastered this culture and realized that potatoes are an irreplaceable food product. Now we grow many high-yielding potato varieties. So, potatoes do not eat the fruit, but a modified underground part of the stem, called the tuber. |
Fruit and berry plants
Due to cold and long winters, gardening in the Perm Territory is underdeveloped. But still, gardeners grow sea buckthorn, cherries, garden strawberries, currants, raspberries, gooseberries, plums, apple trees, etc.
|
Garden strawberry |
Cherry |
Raspberries |
Plum |
|
Sea buckthorn |
Gooseberry |
Apple tree |
Currant |
Gardening is concentrated in the south of the region and in the suburbs of Perm, Chusovoy, Krasnokamsk, Okhansk and other settlements. But still, most of the fruits for the population are brought from other countries and the southern regions of our country.
Floriculture
From year to year, our cities and towns are adorned with flowers in the spring and summer. In the spring, when the snow has just melted, the first perennials appear on the garden plots: snow-white narcissuss with an unforgettable delicate aroma, red and yellow tulips, purple irises.
|
Tulips |
Daffodils |
Irises |
Bloom later peonies... They delight with the richness of colors and the size of a saucer of flowers: scarlet, pale pink, white with a pleasant smell.
Then red and white appear carnation, lilies... Tall and slender bloom phloxes: lilac, purple, pink and white. They bloom all summer long.
Carnations Lilies Phlox
In the second half of summer, beautiful dahlias of various colors and shapes bloom and are surprisingly elegant gladioli.
In squares, parks and on the streets, mainly annuals bloom: asters, cosmos, petunias, marigold, colendula and many others.
Calendula Asters Cosmeya Marigolds
In the city of Perm there is an enterprise called Flowers of the Kama Region, where plants bloom in greenhouses all year round, including beautiful roses.
Here, seedlings of annuals are grown for landscaping and decorating the city.
The power of the influence of flowers on the feelings of people is enormous. They heal us, inspire and improve our mood. They are used to decorate dwellings, streets, parks and gardens. They are presented at solemn events, presented on holidays, laid on the graves of the dead, at the obelisks. On Victory Day, May 9, they are presented to war veterans.
|
Flowers, like people, are generous for good. And generously giving tenderness to people, They bloom, warming their hearts, Like little warm fires. C. Janet |
1. Complete assignments for group work.
1) Field cultivation.
a) Write down the definition.
Field cultivation is the cultivation of field crops.
b) Give examples of field crops grown in your area.
Wheat, rye.
2) Vegetable growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Vegetable growing is the cultivation of vegetable crops.
b) Give examples of vegetable crops grown in your area.
Potatoes, cabbage, carrots.
3) Fruit growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Fruit growing is the cultivation of fruit crops.
b) Give examples of fruit crops grown in your region.
Strawberry, raspberry, apple tree.
4) Floriculture.
a) Write down the definition.
Floriculture is the cultivation of flower crops.
b) Give examples of flower crops grown in your area.
Roses, asters, tulips.
2. The Wise Turtle wants to know if you can classify crops. Show with arrows which groups the plants shown in the picture belong to. Ask a classmate or teacher to check your work.
3. Cross out the extra word in each row.
a) Wheat, rye, carrots, barley.
b) Tomato, cabbage, onion, plum.
c) Apple tree, corn, cherry, apricot.
d) Cucumber, peony, lily, daffodil.
Explain your decisions (verbally). Think of a similar task for your classmates with other examples. Write it down.
Apple, strawberry, raspberry, potato.
Listen to and evaluate the responses of your classmates.
4. As instructed by the textbook (p.193), observe the spring work in the field, vegetable garden, orchard. Do the work yourself. Write a short report on what you saw and did. You can draw a picture or paste a photo.
In the spring, my parents and I went out into the garden in order to prepare the land for planting vegetables. It was mid-April. Dad dug a garden, and mom used a rake to make the beds. They turned out to be even and identical.
I was given a small stick and I made furrows in the beds. Then we filled them with beet and carrot seeds. In the end, we watered our beds with water so that they germinate well and give a crop in the fall.
1. (p. 86) Complete the group assignments.
1) Field cultivation.
a) Write down the definition.
Field cultivation is the cultivation of field crops.
b) Give examples of field crops grown in your area.
Field crops - potatoes, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, corn.
2) Vegetable growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Vegetable growing is the cultivation of vegetable crops.
b) Give examples of vegetable crops grown in your area.
Vegetable crops - carrots, beets, cabbage, tomatoes, onions.
3) Fruit growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Fruit growing is the cultivation of fruit crops.
b) Give examples of fruit crops grown in your region.
Fruit crops - apple, pear, cherry, plum.
4) Floriculture.
a) Write down the definition.
Floriculture is the cultivation of flower crops.
b) Give examples of flower crops grown in your area.
Flower cultures - peonies, lilies, tulips, roses.
2. (p. 87) The Wise Turtle wants to know if you can classify crops. Show with arrows which groups the plants shown in the picture belong to. Ask a classmate or teacher to check your work.
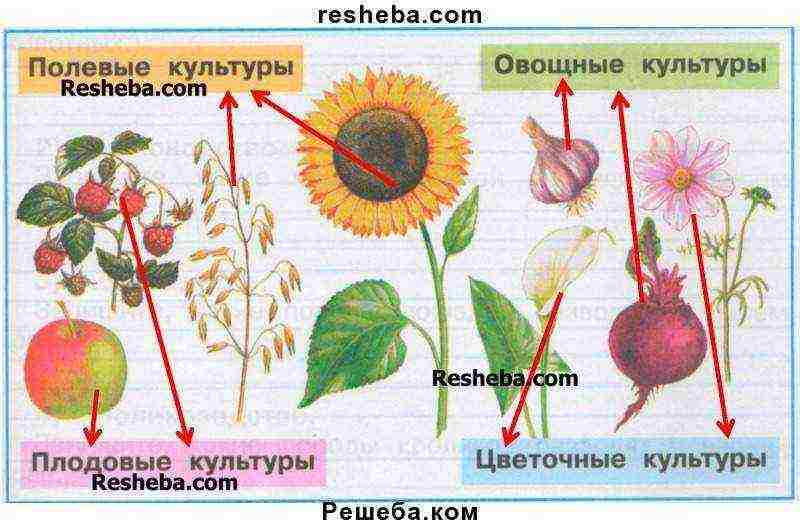
3. (p.87) Cross out the extra word in each row.
a) wheat, rye, carrots (excess), barley;
b) tomato, cabbage, onion, plum (excess);
c) apple tree, corn (excess), cherry, apricot;
d) cucumber (excess), peony, lily, daffodil.
Explain your decisions (verbally). Think of a similar task for your classmates with other examples. Write it down.
a) cabbage, onions, sunflowers, carrots.
b) tulip, rose, millet, lily.
c) cherry, apple, pear, wheat.
4. (p. 88) As instructed by the textbook (p. 193), observe the spring work in the field, in the vegetable garden, in the garden. Do the work yourself. Write a short report on what you saw and did. You can draw or paste a photo.
Spring work begins with land cultivation. These works are most often performed using special equipment. This is followed by sowing seeds and planting cultivated plants. There is a small flower garden near our house. We plant flower crops there with my mother. We planted some of them in the ground with seeds, others with seedlings. Next, we will regularly water the flowers and weed.
EcoMothers
/
Moscow region
/
Agriculture of the Moscow region
/ Crop production in the Moscow region
Grain crops (wheat, barley, oats, rye) are grown on the agricultural lands of the Moscow Region. They occupy about 25% of all sown areas; most of them are located in the southern and southeastern regions of the Moscow region. Approximately 60% of the sown area of the region is occupied by fodder crops (cereals, legumes, beets, carrots and others) for the needs of animal husbandry and industrial crops (rapeseed, flax and others). About 15% of the cultivated area is occupied by vegetables.
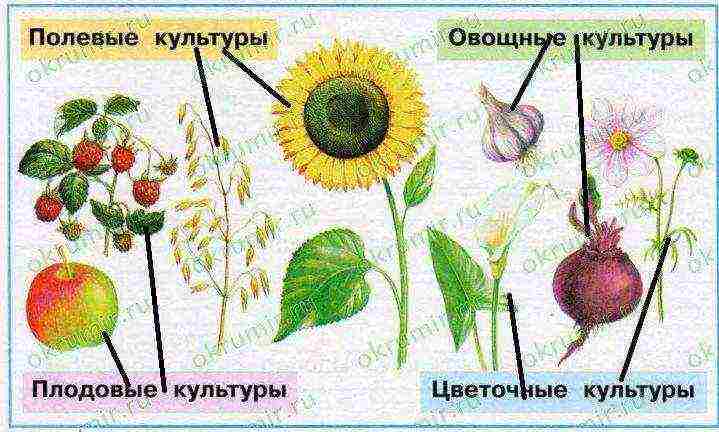
1. Complete assignments for group work.1) Field cultivation.a) Write down the definition. Field cultivation is the cultivation of field crops.
b) Give examples of field crops grown in your area.
wheat, rye, oats, corn, buckwheat, potatoes, flax, sunflower2) Vegetable growing.a) Write down the definition. Vegetable growing is the cultivation of vegetable crops.
b) Give examples of vegetable crops grown in your area.
cabbage, carrots, onions, garlic, tomatoes, cucumbers3) Fruit growing.a) Write down the definition. Fruit growing - this is the cultivation of fruit crops.
b) Give examples of fruit crops grown in your region.
apple, pear, strawberry, cherry, plum4) Floriculture.a) Write down the definition. Floriculture - it is the cultivation of flower crops.
b) Give examples of flower crops grown in your area.
chrysanthemums, asters, peonies, roses, hyacinths, gladioli2. The Wise Turtle wants to know if you can classify crops. Show with arrows which groups the plants shown in the picture belong to. Ask a classmate or teacher to check your work.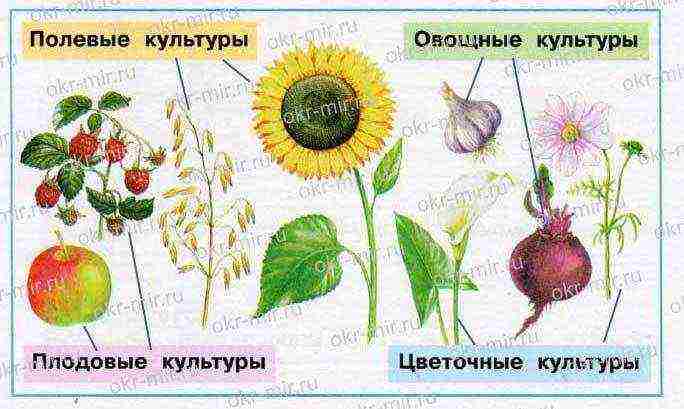
3. Cross out the extra word in each row.
Explain your decisions (verbally). Think of a similar task for your classmates with other examples. Write it down. strawberries, currants, radishes, cherries
onions, carrots, tomatoes, rye
tulip, barley, wheat, oatsListen to and evaluate the responses of your classmates.4. As instructed by the textbook (p. 193), observe the spring work in the field, in the vegetable garden, in the garden. Do the work yourself. Write a short account of what you saw and did. You can draw or paste a photo. This spring, I helped my grandmother plant onions in the garden. It was very interesting. First, we took a shovel and dug up the soil under the bed. Then we leveled the ground with a rake and formed a rectangular bed. Then the grandmother took a stick and drew straight longitudinal grooves on the bed. It was in these grooves that we began to plant small bulbs, which my grandmother called “onion-sevok”. Grandma said that all the bulbs should be at an equal distance from each other. We deepened them a little into the ground and made sure that the root was always at the bottom, and the tail with a green sprout at the top.Then we covered the planted bulbs with earth and watered them well from the watering can. Hopefully our bulbs will sprout quickly and we will eat them all winter.
Return - Pleshakov, Kryuchkova, 4th grade. 1 piece of workbook
1. Complete assignments for group work.
1) Field cultivation.
a) Write down the definition.
Field cultivation is the cultivation of field crops.
b) Give examples of field crops grown in your area.
Wheat, rye.
2) Vegetable growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Vegetable growing is the cultivation of vegetable crops.
b) Give examples of vegetable crops grown in your area.
Potatoes, cabbage, carrots.
3) Fruit growing.
a) Write down the definition.
Fruit growing is the cultivation of fruit crops.
b) Give examples of fruit crops grown in your region.
Strawberry, raspberry, apple tree.
4) Floriculture.
a) Write down the definition.
Floriculture is the cultivation of flower crops.
b) Give examples of flower crops grown in your area.
Roses, asters, tulips.
2. The Wise Turtle wants to know if you can classify crops. Show with arrows which groups the plants shown in the picture belong to. Ask a classmate or teacher to check your work.
3. Cross out the extra word in each row.
a) Wheat, rye, carrots, barley.
b) Tomato, cabbage, onion, plum.
c) Apple tree, corn, cherry, apricot.
d) Cucumber, peony, lily, daffodil.
Explain your decisions (verbally). Think of a similar task for your classmates with other examples. Write it down.
Apple, strawberry, raspberry, potato.
Listen to and evaluate the responses of your classmates.
4. As instructed by the textbook (p.193), observe the spring work in the field, vegetable garden, orchard. Do the work yourself. Write a short report on what you saw and did. You can draw a picture or paste a photo.
In the spring, my parents and I went out into the garden in order to prepare the land for planting vegetables. It was mid-April. Dad dug a garden, and mom used a rake to make the beds. They turned out to be even and identical.
I was given a small stick and I made furrows in the beds. Then we filled them with beet and carrot seeds. In the end, we watered our beds with water so that they germinate well and give a crop in the fall.