A little about our service
In our author's collection of scientific works, on the BYsolo website, at the moment there are only exclusive works made on an individual request for the universities of Belarus and Russia. Our work and work in particular: The company grows watermelons. Fixed costs = 40 CU, the price is 10 CU - there are no duplicates in free abstract banks, so the probability that the work “The enterprise grows watermelons. Fixed costs = 40 unit units, price 10 units ”has already been submitted to your university, is practically zero, in addition, every work, including yours, has passed the most careful selection for quality and relevance at the moment.
Typical exam tasks for the discipline "Economic theory" 2010-2011 academic. year. IMPE
1. A graphical model of the production capabilities of the economy is given. Determine the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of good Y at point A4.
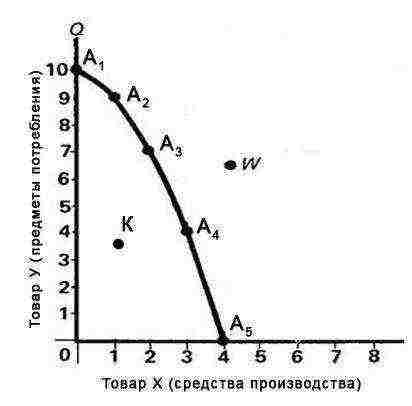
Solution... In order for the production of goods Y to increase at point A4 (3; 4), it is necessary to move to it from point A5 (4; 0). At the same time, the amount of goods X in society will decrease from 4 to 3 units, and the production of goods Y will increase from 0 to 4 units. Thus, the opportunity costs of producing an additional unit of good Y at point A4 = (4-3) / (4-0) = 1/4 of a unit of good X.
2. Reduction of the volume of output of goods A by 25 units. caused an increase in the production of goods B from 0 to 100 units. Determine the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit. product B: a) 100 units; b) 0.25 units; c) 4 units; d) 25 units.
Solution. Opportunity cost (opportunity costs) of production of 1 unit. goods B are calculated as the ratio of the change in the volume of production of goods A to the change in the volume of production of goods B or (25 units) / (100 units -0 units) = 0.25 units item A... Answer: b).
3. In the graph, the original market equilibrium corresponds to point A. If the price rises to the level of P = 33, how much is the surplus of the commodity?
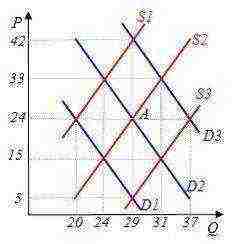
Solution. The surplus of goods is equal to the excess of the volume of supply Qs at a given price over the volume of demand Qd at a given price. According to the graph, we find that at the price P = 33, the supply volume is Qs = 31 (the point lies on the supply graph S2), the demand volume is Qd = 24 (the point lies on the demand graph D2). Thus, a surplus of goods = 31 - 24 = 7 units.
4. The demand curve for backpacks in a small town is described by the following equation: Q = 600 - 2P. The supply curve is described by the equation: Q = 300 + 4P. Determine the equilibrium price and volume of the product?
Solution... At the equilibrium point, the volume of demand is equal to the volume of supply, which makes it possible to equate the functions of supply and demand: 600 - 2P = 300 + 4P; 6P = 300; Pe = 50.
To find the equilibrium sales volume, it is necessary to substitute the equilibrium price value into the demand function or the supply function: Qe = 600 - 2P = 600 - 2 ∙ 50 = 500.
5. Find the coefficient of price elasticity of demand and draw a conclusion about the nature of demand, if it is known that at a price of 7 p. the volume of demand is 5000 pieces per month, and at a price of 4 rubles. is 7000 pieces per month.
Solution. Since changes in the volume of demand and prices are significant, the formula for the coefficient of arc elasticity of demand with respect to price should be used:
Ed = ∆Q / ∆P) ∙ (P1 + P2 / Q1 + Q2) ∆Q = Q2 - Q1 = 7000 - 5000 = 2000 ∆P = P2 - P1 = 4 - 7 = -3
P1 + P2 = 7 + 4 = 11 Q1 + Q2 = 7000 + 5000 = 12000 Ed = (2000 / -3) ∙ (11/12000) = - 0.61.
Demand is inelastic since Ed is less than 1 in modulus but greater than 0.
... If the growth of income by 1.5 times led to an increase in the volume of demand for cell phones by 10%, then what is the income elasticity of demand for cell phones.
Solution. Let's use the formula for the income elasticity of demand in general form, substituting the known parameters into it: Edi = percentage change in demand / percentage change in income or Edi = 10% / (150% - 100%) = 10% / 50% = 0.2 ...
... If the price of cigarettes increased by 10%, and the number of smokers decreased by 4%, then the coefficient of price elasticity of demand is equal to…: a) 0.125; b) 0.25; c) 0.2; d) 0.4.
Solution... Since we know the percentage changes in the volume of demand and price, we should use the formula for the coefficient of elasticity of demand with respect to price in general form: percentage change in demand / percentage change in price. We have: - 4% / + 10% = — 0,4.│Ed│ is less than 1 and greater than 0. Therefore, the demand for cigarettes is inelastic. Answer: d).
... The figure shows the consumer indifference curve and his budget line. Write the equation of the budget line if the price of product Y is equal to Py = 6 rubles: a) Qy = 10-1.5Qx; b) Qy = 15-1.5Qx; c) Qy = 15-0.67Qx; d) Qy = 10-0.67Qx
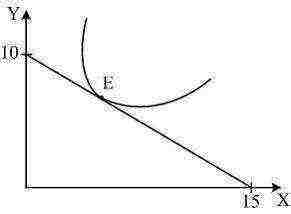
Solution. From the graph we see that if all income is spent on product Y, then 10 units are bought. Since the price is Py = 6, the income I = Py ∙ Qy = 6 x 10 = 60 rubles. The graph also shows that when all income is spent on product X, 15 units are bought. respectively Px = I / Qx = 60/15 = 4 rubles. The budget line equation is I = Px ∙ Qx + Py ∙ Qy or Qy = I / Py - (Px / Py) Qx. Substituting the data, we get: Qy = 60/6 - (4/6) Qх = 10 – 0,67 QNS. Answer: d).
9. The price of product X is 15 rubles. The price of product Y is 10 rubles. The consumer estimates the marginal utility of the product Y at 30 yutils. Find what is the marginal utility of good X if the consumer is in equilibrium.
Solution. In equilibrium, the condition MUх / Pх = MUy / Ru is fulfilled, that is, the weighted marginal utilities for different goods are equal. Hence, MUх = Pх ∙ MUy / Py = 15 ∙ 30/10 = 45 yutile.
10. The enterprise grows watermelons. Fixed costs = 40 CU, price 10 CU How much profit will a farmer make when producing 30 units?
Solution. Profit = Gross Income TR - Total Costs TC. Accordingly, TR = P x Q; and TC = fixed cost FC + variable cost VC. According to the conditions of the problem, P = 10, Q = 30; TR = 10 х 30 = 300 unit units, FC = 40, VC = 110, TC = 40 +110 = 150. We get that profit = 300 - 150 = 150 units.
... The company produces and sells 100 valves per month. If production costs are 12,000 den. units, and the average profit is 50 den. units, then how much is the gross income of the company?
Solution. Average profit is profit per 1 unit of production, that is, average profit = (Gross income TR - total costs TC) / Q. Hence TR = average profit x Q + TC. Substituting the data, we get: TR = 50 x 100 + 12000 = monetary units.
12. The total income of the enterprise amounted to 2,000 thousand rubles, the wages of employees - 400 thousand rubles, the cost of raw materials and materials - 500 thousand rubles, the cost of used equipment - 300 thousand rubles, implicit costs - 200 thousand rubles. Determine the accounting and economic profit of the enterprise.
Solution. Accounting profit = Total income - explicit (external) costs
Economic Profit = Total Income - (Explicit Cost) + Implicit Cost
Explicit costs = wages of employees + costs of raw materials and materials + cost of used equipment = 400 thousand rubles. + 500 thousand rubles. + 300 thousand rubles = 1200 thousand rubles.
Accounting profit = 2000 thousand rubles. - 1200 thousand rubles. = 800 thousand rubles.
Economic profit = 2000 thousand rubles. - (1200 thousand rubles + 200 thousand rubles) = 2000 - 1400 = 600 thousand rubles.
13. In the short run, the firm produces 1000 units of goods, with an average fixed cost of 20 monetary units, and an average variable cost of 100 monetary units. Determine the amount of total costs.
Solution... We are given that Q = 1000 units. goods; AFC = 20 den. units; AVC = 100 den. units Since TC = FC + VC or TC = Q ∙ (AFC + AVC) = 1000 ∙ (20 + 100) = 120,000 den. units
... You are offered to participate in a project that will bring CU 500 thousand in 2 years. income, annual interest rate = 10%. How much money is advisable to invest in this project now.
Solution... The reasonable purchase price is determined by the formula PV = Rt / (1 + r) t, where Rt is the income received in year t, r is the interest rate in unit fractions, t is the number of years after which the income will be received. PV = 500000 / (1 + 0.1) ² = 413223.1 CU
15. Determine how the real wage has changed if the nominal wage increased by 1.25 times, and the rise in prices in the economy for the same period was 10%.
Solution... The relationship between nominal and real wages is determined by the formula: Wr = Wn / P, where Wr - real wages; Wn is the nominal wage; P is the price index for consumer goods and services. ∆ Wr = 1.25 / 1.1 = 1.136 (times) or by 13.6%.


