Content
- 1 Benefits of greenhouse cultivation
- 2 Pepper and eggplant
- 3 We grow cucumbers and tomatoes
- 4 Greenery in the building
- 5 Harvest of radishes in the greenhouse (video)
- 6 Strawberry harvest
- 7 Seedling flowers
- 8 A bit of terminology
- 9 Why do you need seedlings
- 10 What are the seedlings
- 11 Quality seeds - healthy seedlings
- 12 Soil requirements for seedlings
- 13 Seedling conditions
- 14 Growing seedlings of popular vegetable crops
- 15 Homework
- 16 Popular articles of the site from the section "Dreams and Magic"
 What's growing in the greenhouse? There are many different plants that bear fruit or simply delight the eye with their flowers. And in order for vegetable growing to be truly successful and high-yielding, it is necessary to properly prepare the seeds, soil and correctly calculate the planting time. Depending on the characteristics of the plant, it is grown in the open field with seeds or seedlings, which must be grown in a greenhouse.
What's growing in the greenhouse? There are many different plants that bear fruit or simply delight the eye with their flowers. And in order for vegetable growing to be truly successful and high-yielding, it is necessary to properly prepare the seeds, soil and correctly calculate the planting time. Depending on the characteristics of the plant, it is grown in the open field with seeds or seedlings, which must be grown in a greenhouse.
Benefits of greenhouse cultivation
At the dacha, almost everyone has the opportunity to install a greenhouse. What is the best way to grow in it and what planting scheme will be profitable and effective? Greenhouse designs are very different, so different crops grow well in them. What is the best choice? The choice should be made in favor of such plants that do not grow well in the open field, therefore it is irrational to plant beets or potatoes.
You can plant greens in the greenhouse, which gives a year-round harvest, mushrooms, tomatoes, cucumbers. For planting a garden in greenhouse conditions, preference should be given to melons, raspberries, strawberries.
Growing plants is always the preparation and fertilization of the soil in the greenhouse, seedlings or seeds. If all the conditions for growing a vegetable, fruit or berry are met, you can get a plentiful, early and high-quality harvest.

Why is planting in greenhouses popular even during the summer months? This is due to a number of advantages.
- The greenhouse allows the gardener or gardener to create conditions for the plants that can be controlled and regulated if necessary. For example, drought or increased rainfall. When planting crops in open ground, this cannot be done.
- In greenhouses, you can easily change the air temperature, humidity level.
- In such structures, plants are not threatened by strong winds and other negative environmental factors. Even minor changes provoke a significant increase in the volume of yield, an increase in the degree of its quality.
- Planting plants in greenhouses allows you to get several harvests in 1 season, this is very difficult to achieve with other growing methods.
Pepper and eggplant
You can grow wonderful peppers in a greenhouse.If the structure is not heated, then various varieties grow in it, you can grow hybrid versions of medium-sized and tall bell peppers, which produce large or medium-sized fruits.
You can form a bush of medium and large-fruited peppers in different ways. In temperate climates, the weather conditions change during the summer months. If bushes are formed in an unheated greenhouse in the same way, then large-fruited plants are overloaded. After that, they shed the ovaries, buds fall on the tops of the shoot.
Form a medium pepper in size so that 2 stems remain.At the point where the stem forks, the most powerful shoot is left. Another process is pinched, 1 leaf remains on it, shoots are removed. If the fruits of the pepper are large, 1 shoot should remain.
The conditions for growing pepper should be suitable, this will prevent the appearance of sunburn on the leaves.

What else can you grow? Eggplant grows quietly with pepper. Both of these crops are quite thermophilic. Therefore, you need to allocate a warm place for them with a sufficient level of lighting. The best location is the south side of the beds. If the area in the greenhouse is not large enough, eggplants should be planted at the end of the central garden bed or on its eastern side. Mixing eggplants in the garden with other vegetables is unacceptable. This is due to the high consumption of water and the number of leaves on the stems.
Eggplant grows well in a greenhouse. If the structure is not heated, then first of all you need to take care of uniform fruiting. Planting eggplants in a greenhouse provides for the need to form a plant in several stems, while stepchildren are not left behind. When choosing a plant variety, you need to pay attention to some features. A number of hybrids and certain varieties (chamomile) are characterized by a dense bush shape, which causes some difficulties in leaving.
We grow cucumbers and tomatoes
Planting cucumbers in a greenhouse is very beneficial. Early varieties of culture allow you to get early ripening fruits. There are different hybrids of this plant that can grow even in the shade. Such a culture can be safely planted in a greenhouse. The result is a good harvest. When choosing a specific variety, you should pay attention to the duration of fruiting, the size of the cucumbers, pickling characteristics, the number of fruits in the nodes, the level of branching of the bush.
How to plant cucumbers? It is permissible to plant seedlings or seeds by watering the holes or beds with water. Now there are parthenocarpic hybrids that bear fruit abundantly and do not require insects to pollinate the flowers. Among them are:
- hybrid F1 Goosebump;
- Tournament;
- Erica, etc.
They can be canned and salted.
The newest hybrids may have a female flowering type. Growing them in a greenhouse is convenient for flower formation. How to plant correctly?
These plants need neighbors to pollinate them. They should be about 10% of the total.
Pollinator seeds are usually placed in the package with such a product. There are also hybrids with male flowering. The agricultural technology of growing such plants has changed somewhat. For bunch forms of hybrids, a very high level of productivity is characteristic.
The scheme for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse depends on the area, but you cannot plant them too closely. The greenhouse most often has a ridge several m high. Therefore, it is most rational to choose tomato varieties that belong to the determinant or indeterminate groups. Such plants allow the most optimal use of the area.
There are various methods of growing tomatoes. Some varieties can be planted as a compacting crop.
Planting is carried out along the outer perimeter (row, distance between bushes 23 cm), which will allow you to get a very early harvest. In the greenhouse, you can graft eggplants on tomatoes. How to vaccinate? The procedure is common, which helps to reduce the level of damage to crops by various diseases, while the number of fruits increases.
Greenery in the building
What grows in greenhouse conditions? Greens, but at the same time it is necessary to properly care for it. The peculiarities of growing lettuce are to ensure a suitable temperature regime. This plant grows well at 20 degrees Celsius, while it can be planted outdoors at any time of the year.
It is quite simple to grow a salad in a greenhouse, since it does not imply the preliminary receipt of seedlings and their transplantation to another place after a certain period of time.Since the greens from this category grow quite quickly, the sowing of seeds can occur at intervals of 2 weeks, especially if you use early varieties of lettuce.
The agrotechnology of growing this greenery is quite simple, since it requires fertilization only at the initial stage during planting of seeds. The salad requires minimal maintenance, it belongs to the category of fast-ripening plants.

The technology of growing lettuce consists in good illumination of the crop. In addition, it is necessary to regularly resort to watering (but so that drops do not fall on the leaves of the culture) and loosening the soil. It is worth paying attention to the elimination of weeds that prevent the salad from developing normally.
What else can you plant in a greenhouse from the category of greenery? Parsley is perfect for this, which is distinguished by its useful properties and high taste characteristics. Professional growers use several methods to grow the plant in question. Seeds or root forcing can be used.
Parsley is grown in a similar way to lettuce, as it is not a very whimsical crop. The main thing is to provide her with a sufficient amount of light, moisture and the correct temperature regime.
What else can you plant in the greenhouse? Dill is the type of greenery that tolerates greenhouse conditions well. Features of the cultivation of this culture: the quality of lighting and the correct temperature regime. Vegetable growers should take into account that the ripening of these greens takes place within 2 months. Growing dill in a greenhouse is a profitable activity, because from 1 square meter you can harvest 2 kg of harvest per season.
Harvest of radishes in the greenhouse (video)
Strawberry harvest
What to plant in the greenhouse? Strawberries, especially early varieties, are a good option. This berry is healthy and tasty, so it is quite pleasant to grow it, and the harvest can be obtained in almost all periods of the year.
How to properly plant strawberries in a greenhouse to get a good result? Most often, gardeners resort to the strawberry propagation method. In this case, a certain norm must be observed: there are about 4 bushes per 1 square meter of land.
The technology for growing strawberries in this way is to prepare seedlings. It needs to be kept in the room for about 5 days in pots, so that it begins to get used to the climatic conditions. After this time, it is moved to the greenhouse for further addiction. Then they are planted.
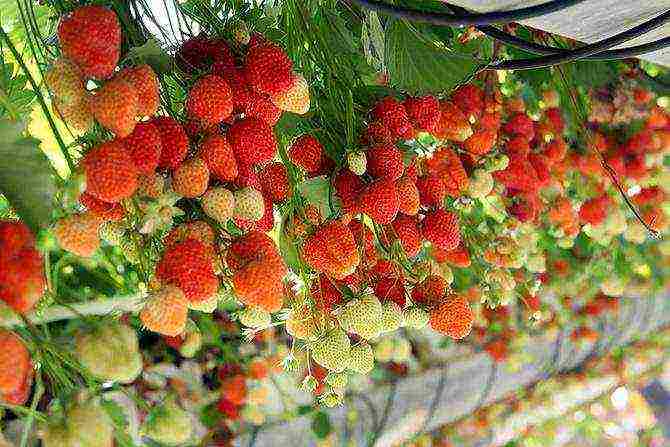

There is also a scheme for planting strawberries according to the Dutch method. For this, the plant is planted in a greenhouse or in certain specially designed blocks. For the plant in question, special conditions are created in the greenhouse. The space should be as illuminated as possible and well warmed up when it comes to the autumn-winter period. Agrotechnology for growing strawberries involves the use of peat and other mixtures that allow you to provide quality nutrition.
Seedling flowers
What can be grown in a greenhouse from flowers? Usually these are plants that are classified as indoor plants, but there are different types of flowers that grow outdoors. It is most profitable to grow early varieties. The methods of growing flowers in a greenhouse are very different. These can be seeds, bulbs, tubers, and other options. At the same time, it is important to provide acceptable conditions for the plants.
You can come up with flower planting schemes yourself. However, the plants should not be cramped, as they will not be able to develop properly. In winter, a reliable heating system must be provided. This is important as most flowers are thermophilic. Another important point is getting enough light. If it is not enough, then additional artificial lighting should be used.

Different ventilation systems, temperature conditions, shading systems may be acceptable for different colors.Therefore, these factors must be taken into account if it is supposed to grow in parallel in the same greenhouse, for example, roses and tulips. In doing so, do not forget that different colors may have different requirements for the level of humidity.
Growing various crops in a greenhouse must follow certain rules to achieve good results. Each plant grows under certain conditions.
"Seedling" is a common term and familiar to many people, even not associated with gardening. The territory of our country is vast and diverse in terms of natural and climatic conditions. However, it is mostly northern, with relatively short summers. This forced our ancestors to learn how to grow southern heat-loving vegetable crops using seedlings, and then the principles they worked out began to be used on other plants, not only from the group of vegetables.

Seedlings are indispensable in our climate
A bit of terminology
Seedling - these are young plants grown thickened in special conditions with a controlled microclimate, intended for subsequent transplantation to a permanent place.
The term is often used in parallel seedlings - these are also young plants, but they are grown for a short time and after the appearance of cotyledons or the first true leaves, they are planted on a large feeding area to obtain seedlings.
Transplanting seedlings and young seedlings onto a large feeding area is called dive.
The period during which the seedlings are grown is called it age, and the period for which the harvest in the open field is accelerated - race... For early crops, the race almost coincides with the age of the seedlings.
Why do you need seedlings
The seedling method allows grow heat-loving crops with a long growing season in places where there are no appropriate natural conditions for them - in regions with short summers and return frosts. For part of the growing season, plants are kept under protection, and then natural conditions are used.

Seedlings allow the cultivation of heat-loving crops in cold climates In addition, seedlings allow receive earlier products by running versus direct outdoor cultivation.
Seedling is a piece product, its use allows a clear calculate the required number of plants per planned planting area, which in turn helps to save seeds, especially expensive hybrid seeds.
And the use of seedlings allows, in some cases, to get several harvests from one area, to better prepare areas for growing crops, not to create tension during the sowing period.
What are the seedlings
Depending on the characteristics of cultivation, there are early, medium and late seedlings. Early seedlings grown for a longer time, usually with a pick, in warm rooms or protected ground structures with heating.
The age (race) of such seedlings is:
- cucumber and zucchini - 30 days,
- tomatoes - 55-65 days,
- peppers and eggplants - 45-50 days,
- early and cauliflower - 45-60 days.
Early seedlings are best grown in pots or containers - this way they are easier to transplant and take root without loss. It is planted not only in open ground, but also in greenhouses, hotbeds and on warm ridges, which further increases the run in the yield of the crop.

Early seedlings are best grown in pots, medium seedlings can also be grown in seed boxes or containersMedium seedlings grown with a dive and without a dive in seed boxes or containers, cassettes are often used. They are grown both in heated rooms and in structures with emergency heating, or they additionally cover the plants with non-woven materials.
Average seedling age ranges from 20-25 days for cucumber and zucchini to 35-45 days for nightshade crops (tomatoes, peppers and eggplants), medium cabbage.In cassettes, the age usually does not exceed 25-30 days due to the small volume of soil in them.
Late seedlings grown with minimal shelter in cold nurseries, greenhouses, warm ridges and on open balconies and loggias. The race is minimal here, and seedling age Usually it is 15-20 days for cucumber and zucchini, for nightshade crops no more than 30 days, for late cabbage - 25-30 days.
Quality seeds - healthy seedlings
When growing seedlings, seeds and their quality are of particular importance. Seed quality includesthree components:
- health,
- sowing suitability,
- grade.
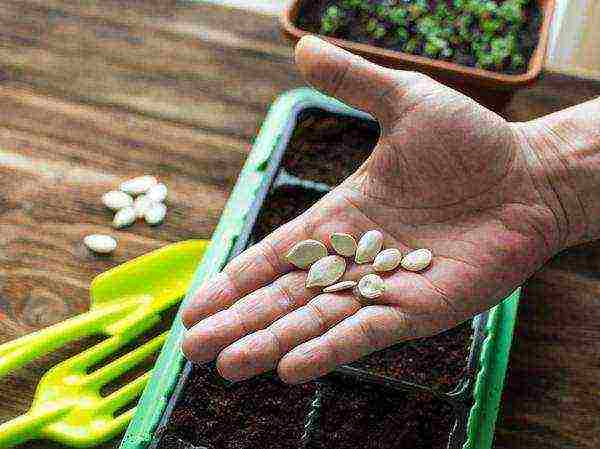

When growing seedlings, the quality of seeds is very important. The last indicator cannot be changed in any way, you only need to use the services of serious companies that guarantee the variety of seeds and the absence of re-grading. Sowing suitability, in turn, has the following indicators:
- germination and germination energy,
- purity,
- humidity,
- weight of 1000 seeds.
Germination
shows how many seeds, when germinating, will give normal seedlings for the time set by the standard (usually from 7 to 14 days), and
germination energy characterizes the amicability of germination and is defined as germination in a shorter period (5-7 days).
Purity indicates the presence of impurities other than seeds, and humidity - the content of free moisture, which should be within the limits that allow the seeds to be stored normally, not to grow moldy and not to germinate.
Weight of 1000 seeds characterizes their size, and as a result - the supply of nutrients and the size of the embryo. Larger seeds are always better to use than smaller ones.
The sowing quality of seeds can be changed by sorting them by size and removing impurities, drying. Treatment of seeds with stimulants can increase their germination and germination energy. Good quality seeds usually do not need to be processed.

The sowing quality of seeds can be changed, but good seeds do not need this. Seed health is determined by the presence or absence of pests and pathogens. According to the requirements of the standards for seeds, there should be no pests in the seeds, as well as the most dangerous pathogens transmitted with the seeds. Some pathogens may be present on the surface of the seeds, and to protect against them, the seeds are disinfected or etched. Protect seeds from infection inside the cells of the embryo, almost impossible. High-quality seed production and protection at the genetic level must work here, and this is inherent in the genes of the variety.
More details about what seeds are, how to choose the right varieties of vegetable crops for your garden, was discussed at the first lesson of our Academy.
Fungi and bacteria are usually located on the surface of the seeds, and viruses are located inside the embryo. Etched seeds, as a rule, during their preparation for sale, which is indicated on the package. Disinfect already before sowing, treating the seeds with special aseptics (hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate) or acting on them with variable temperatures (hydrothermal treatment), various radiation, etc. For an additional guarantee of obtaining healthy seedlings, not only seeds are disinfected, but also premises, growing containers, equipment and soil.
Soil requirements for seedlings
Seedling soil cannot be universal, since individual crops and groups of crops have specific requirements for density, acidity and other soil parameters. But there are several general rules for choosing soil.

There are both general rules for choosing soil for seedlings, and specific ones - for specific crops.Good soil for seedlings should be:
- loose and easily permeable to water and air (the most porous should be the soil for pumpkin crops that are sensitive to a lack of oxygen);
- free from pathogens, pests and weed seeds;
- provided with readily available food elements - both basic (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) and microelements (copper, iron, zinc, boron, magnesium, molybdenum, etc.);
- with acidity close to neutral (pH 6.0-7.0).
Recently, seedling soils have been produced on an industrial scale and can be purchased.
Seedling conditions
To obtain seedlings, you need to createfavorable microclimate... On window sills in apartments, on loggias and balconies, in special nurseries in rooms, in greenhouses, hotbeds, on warm ridges, special - more comfortable - conditions of temperature, illumination and moisture are provided, in which plants develop for some time, while they are still impossible grow outdoors.
Seedlings can be grown both with and without a pick, placing plants in:
- sowing boxes,
- various containers and pots made of plastic or organic materials (paper, cardboard, peat),
- cassettes with a large number of individual compartments,
- directly in the ground,
- on the shelves of greenhouses and greenhouses,
- on ridges in insulated soil,
- in special nurseries.

Seedlings are grown in various containers, with or without a pick. Separate crops have their own characteristics when growing. For example, celery belongs to the group of cold-resistant crops, but has very small seeds and a long growing season. To get marketable products in the year of sowing, it is sown in January-February, dives twice, ensuring the age of seedlings up to 100 days or more, and only then they are planted in open ground in a permanent place. Heat-loving southern cultures in winter often suffer from a lack of light, and they have to supplement, which also speeds up the run.
When growing seedlings, a certain level of microclimate parameters must be maintained. The main parameters of the microclimate include temperature, humidity of soil and air, illumination... Maintaining these parameters is the most difficult and costly element of growing seedlings. It must be remembered that all factors are equally important, irreplaceable and act in conjunction with each other.
Temperature regime
The temperature around the plants is created by turning on and off various heating systems and using the greenhouse effect. In residential premises, heating of these premises is used, in greenhouses and greenhouses it can be electric heating, stove heating, air heating, the use of natural hot springs and waste heat from industrial enterprises.
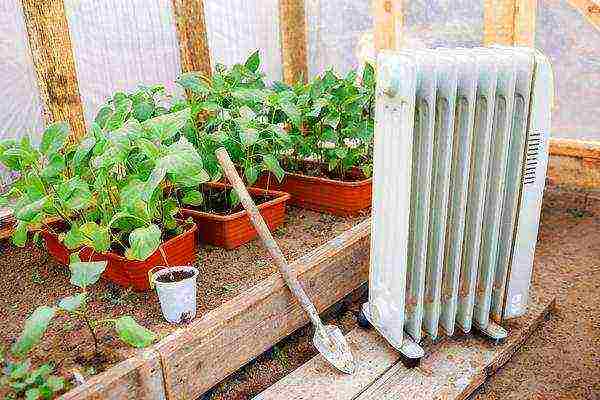

To maintain the required temperature, various available heating methods are used.In rare cases, it is used and biofuel... Manure and household waste, under the influence of microbes, are capable of heating the substrate to fairly high values that allow growing seedlings. When many animals were kept on the farms, this method was the main one.
Greenhouse effect occurs when short-wave radiation penetrates through translucent coatings (glass, film, plastic). The rays are converted into long-wave radiation, which is a source of heat (infrared spectrum). Naturally, such heating acts only on light.
The temperature during seed germination should be the maximum for a given crop. During the period of emergence, it must be reduced by 7-10 days to values slightly below the optimum for each crop. This allows the plant to gradually switch from nutrition due to the supply of nutrients in the seeds to nutrition due to photosynthesis, for which green pigments must appear in the plants, in which new nutrients will be formed.
Further for growth and development every culture will need optimal temperatures, which should be the highest in the light, slightly lower in cloudy weather and even lower at night. The temperature in the root zone should not fall below biological zero for each crop, otherwise the root will stop working.Temperatures above and below optimal ones negatively affect the seedlings, deteriorating their quality.
Correct lighting
Simultaneously with the temperature, lighting also works, without which the seedlings will not be able not only to grow, but also to develop.

As soon as seedlings emerge, the light intensity should be maximized. No light is needed for seedlings to emerge. This process can take place in the dark. But as soon as shoots begin to appear, the light intensity should be maximum. In the winter months, seedlings even supplemented - first around the clock, until the plants turn green and get stronger, and then only during daylight hours, extending the length of the day to 12-14 hours. At a later date, when the length of the day exceeds 10-12 hours, the seedlings are not supplemented.
The higher the temperature, the higher the illumination should be... The length of the day, the spectral composition of light, the change of day and night are important, since light for plants is both a source of energy for the formation of crops, growth and development, and a biological clock with a certain rhythm. Tomato, for example, clearly reacts to the change of day and night, and without this change it counts the entire duration of lighting in one day. Naturally, its size does not increase and development is inhibited. There are plants that bloom better on a short day and form a crop (pepper, eggplant), while others form a food organ (root crop) on a short day, and bloom and produce seeds (radish) on a long day.
In tomatoes, the standard varieties are less stretched, which almost always give high-quality seedlings. These include, for example, Pink Flamingo, Volgogradsky 5/95, Shuttle.
Humidity and proper watering
Moisture is essential for plant growth and development. Due to the small size of the root system, seedlings need to be watered more often than adult plants, but excess moisture should not be allowed, leading to death or poor root development. The higher the temperature and light, the more moisture the plants need..

Temperature, illumination and humidity must be balanced. Air humidity depends not only on illumination and temperature, but also on specificity of individual cultures... Peppers and eggplant need more humidity than tomatoes, and cabbage more than peppers and eggplant.
Stimulants and feeding
The air-gas composition of the atmosphere is also important for plants, in which it is desirable to have more carbon dioxide, but less harmful impurities (ammonia, resins, ethylene). Ethylene is released, for example, by ripening fruits (bananas, apples). Ethylene ages plants, it is an aging hormone for them. Sometimes seedlings are specially treated with some hormones to enhance or weaken growth processes:
- retardants inhibit growth, they are used to prevent overgrowth of plants (tour, anti-yeast, athlete);
- hormones that stimulate root growth are used for better development of the root system in containers (heteroauxin, indolylbutyric acid, root, etc.).
Some brands of fertilizers contain phytohormones and are intended for feeding plants in the seedling phase (raikat start and other complexes marked "starting").

The choice of fertilizers and dressings depends on the characteristics of the culture and the phases of plant development. The seedlings are also fertilized in different phases in different ways. At the beginning of growth, nitrogen and phosphorus should prevail, and a set of all elements, including trace elements, is needed to lay flowers. Complex water-soluble fertilizers with microelements such as Sudarushka, Agricola, etc. are very convenient for feeding seedlings.
One of the lessons of our Academy was devoted to fertilizers and fertilizing - refer to its materials to find out more or refresh the necessary information in your memory.
Hardening of seedlings
Before planting in a permanent place, the seedlings are hardened. Hardening is teaching seedlings to live in a natural climate without regulating it.... Gradually reduce watering; better ventilated; feeding is either not carried out, or they are carried out with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers without nitrogen; periodically, plants are taken out of the premises (meaning the apartment) into direct sunlight. In the case of transporting seedlings to the dacha, they are preliminarily slightly tempered; then this process is continued, partially shading the plants, and only when they get stronger and even slow down their growth, they are planted in a permanent place, watered abundantly, and after 3-5 days they are loosened and already work as usual.

Before planting in a permanent place, the seedlings are hardened. Plants transplanted into greenhouses do not need special hardening, except that they are slightly shaded until they take root.
Sowing time for seedlings is determined by the addition of its age and days from sowing to germination. The disembarkation date is the starting point. It is dictated by the average annual terms and the weather of the current season. It is always difficult to determine, especially the arrival of frost. Forecasters are often wrong. You always need to have insurance in the form of a stock of seedlings and the ability to cover the plants with non-woven materials or by arranging a temporary greenhouse or greenhouse.
Growing seedlings of popular vegetable crops
Seedlings cucumber grown with a run of no more than 30 days. No picking, direct sowing in pots or containers. They are planted when the danger of frost has passed.
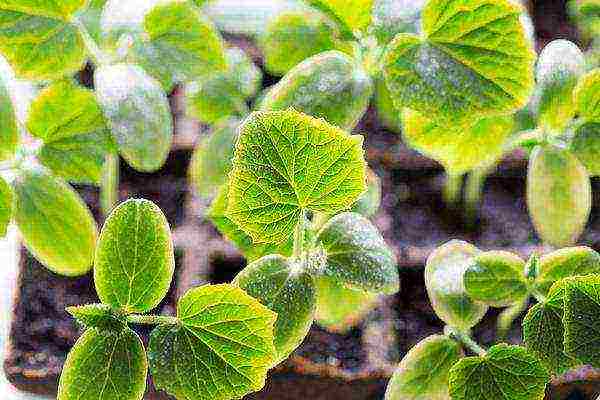

Seedling of a cucumber From sowing to germination - from 5 to 7 days.
Temperature before shoots - + 28 ... + 30 degrees, when shoots appear - + 18 ... + 20 degrees for 10 days, then during the day in sunny weather - + 24 ... + 26 degrees, in cloudy - + 22 ... + 24 degrees, at night - + 18 ... + 20 degrees.
Soil temperature - not lower than +16 degrees.
Watering is frequent, but at small rates.
Seedlings tomato grown with a run of 20 to 65 days. In cassettes - 20-25 days, medium seedlings - 45-50 days, early - 55-65 days. With a dive. They are planted when the danger of frost has passed.
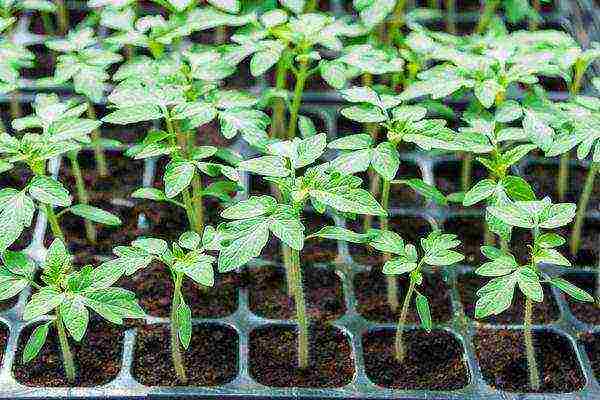

Seedling of tomatoes From sowing to germination - 7-14 days.
The temperature before germination is + 26 ... + 28 degrees, when germination appears - within 10 days + 16 ... + 18 degrees, then in sunny weather - + 24 ... + 26 degrees, in cloudy weather and at night - no higher than +18 degrees.
Watering is rare and abundant.
Seedlings peppers and eggplant grown with a race of 45-55 days, with a pick or direct sowing in pots, containers. Disembarkation - when the danger of frost has passed. From sowing to germination - 14-20 days.
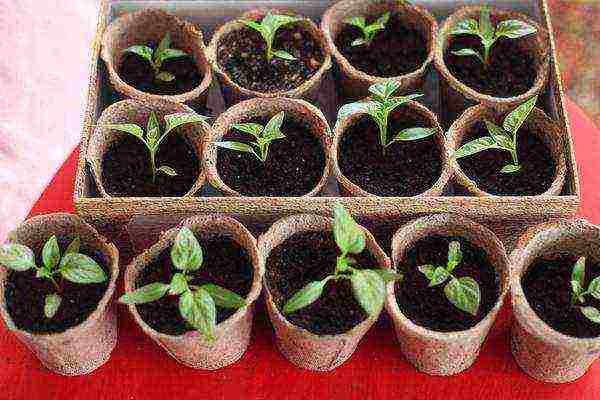

Pepper seedlings Temperature before shoots - + 28 ... + 30 degrees, when shoots appear - 10 days + 18 ... + 20 degrees, in sunny weather - + 24 ... + 26 degrees, in cloudy - + 22 ... + 24 degrees, at night - + 18 ... + 20 degrees.
Soil temperature - not lower than +16 degrees.
Frequent watering, small rates.
Seedlings early cabbage grown with a race of 45-55 days, with a dive into containers or pots. From sowing to germination - 5-10 days.

Cabbage seedlings Temperature before germination - + 18 ... + 22 degrees, 10 days after germination - + 10 ... + 12 degrees, then in sunny weather - + 18 ... + 20, in cloudy weather - + 14 ... + 16, at night - +12 ... + 14 degrees.
Frequent watering, small rates.
There are some features of the technology picks of plants of different cultures... In tomatoes and cabbage, the seedling is buried in the soil just below the cotyledons, and in pepper and eggplant - only a third of the hypocotyledonous knee. When pulling out the seedlings, it is slightly poked with a light soil mixture after watering.
For fighting blackleg plants should not be strongly thickened; the surface of the soil can be sprinkled with wood ash, spilled with a pink solution of potassium permanganate, regularly loosen the space between the plants, but trying to damage the roots less. During the period of intensive growth, you can no longer be afraid of this. Protection from pests and pathogens should be carried out according to symptoms, trying to use more biological products and a sanitary regime.
Homework
Tell us about what kind of vegetables you grow through seedlings. What conditions do you create (how do you provide temperature and illumination; where do you place the seedlings; what soil you use, what containers, etc.). What difficulties do you face when growing seedlings? What turns out to be the most difficult in the conditions that you have at your disposal?
In your opinion, is the result obtained justifying the costs of effort, time and money that you have to invest to get seedlings? Are you satisfied with your success in growing vegetable seedlings? What would you like to change and why?
If your seedlings need additional lighting, do not miss the opportunity to purchase phytolamps with 15% discount in the online store of the POISK Agrofirm. To take advantage of the discount, enter when ordering promo code FITOLED (valid until February 28).
Go to the store and choose a phytolamp with a 15% discount
These cultures are newcomers from southern latitudes, they die even with light and short frosts, they practically do not grow and do not develop at temperatures of 10 ° and below, they are very demanding on heat and light, at all phases of their development, even in the middle of summer, they suffer from low night temperatures and cold mornings. In climatic conditions, the Non-Black Earth Region is very often in a state of heat stress, which makes them susceptible to any additional adverse effects and vulnerable to fungal diseases. The gardener's task is to learn how to get stable yields of heat-loving crops in all weather conditions.
7.4.1. Cucumber - a traditional culture for central Russia. Even 20-25 years ago, there were no particular difficulties in the cultivation of cucumbers. On private farms, they were raised mainly in the open field. Seeds, dry or hatched, were sown after June 10, and from the second half of July until the cold weather they were harvesting. However, the general deterioration of the ecological situation led to the fact that the adaptive capabilities of this culture were exhausted, and cucumbers began to be intensely affected by diseases, primarily downy mildew (LMD), as well as powdery mildew (MP) and other diseases. LMR appears from the middle of summer, and it often happens that a culture that has just begun to bear fruit falls ill and dies.
To overcome the unfavorable situation, new varieties and hybrids of cucumber were developed, which are relatively resistant to LMR and other diseases. The strategy for growing cucumbers in the open field has also changed. Techniques that allow to shift the dates of fruit ripening to an earlier period have acquired particular importance: leading a cucumber through seedlings, that is, with a 3-4 week run; the use of temporary film shelters; cultivation of a cucumber in a "warm bed", that is, with heating the soil with biofuel. All of the above methods are not mutually exclusive, and their skillful combination, along with the use of early maturing and ultra-ripe varieties and hybrids of cucumber (Muromsky 36, Monastyrsky, Vyaznikovsky 37, Brigadny F1, etc.) allows you to shift the peak of fruiting to earlier, relatively safe terms in relation to fungal diseases. ...
High yields of cucumber can be obtained if reasonable agricultural technology is combined with a conscious, competent selection of varieties and hybrids.
Probably, for no other crop there is such a variety of varieties and hybrids as for a cucumber. The most significant are the following differences:
1. Type of pollination. Plants can be bee-pollinated and do not require pollination for fruit setting, i.e. parthenocarpic. There are hybrids with partial parthenocarpies. In the open field, bee-pollinated varieties are most often grown, therefore, during flowering, all temporary film shelters should be open to insects.
2. Type of flowering. Plants are monoecious (this means that they bear both male and female flowers), with mainly female or only female flowers. Hybrids with a female flowering type require the presence of a pollinator variety. The best pollinators are the Graceful and Nerosy cucumber varieties.
Table 27. Some varieties and hybrids of cucumber for open ground
Name Beginning of fruiting. after germination, days Length of the main stem Length and weight of the fruit Purpose Resistance to adverse conditions and diseases Remarks Altai 165 35–50 50–100 cm 6–10 cm 60–90 g Salad Relatively cold-resistant. Relatively resistant to fungal diseases. High marketability of fruits. Fruits do not turn yellow F1 Brigadny 37–48 Long-leaved 9–13 cm Salted. Canned food. High-yielding F1 Excellent 43–58 Long-leafed 11–14 cm Salted. High-yielding F1VIR – 522 49–66 Medium-growing 9–10 cm Salted. Canned food. Voronezh 40–61 Long-leafed 9–13 cm 120–150 g Salted. Resistant to olive spot Aquarius 50–60 Up to 100 cm Medium-growing 11–14 cm 100–120 g Salted. Medium resistant to LMR, bacteriosis. High marketability of fruits, fruits without bitterness. High-yielding Vyaznikovsky 35–55 Short-grated 8–12 cm 80–140 g Salted. Resistant to cold and drought, relatively tolerant to bacteriosis Far East 2640–55 Long-leaved 11–15 cm 110–120 g Saline. Resistant to cold and drought, resistant to LMR and MR Decan 42–55 Medium-weighted 11–14 cm 110–150 g Canned food. Resistant to extreme weather conditions. PTO resistant. Medium resistant to LMR and bacteriosis Good keeping quality, suitable for transportation Graceful 44–64 Medium-weight 70–100 cm 10–13 cm 80–120 g Salad. Marine. Relatively cold-resistant. Resistant to olive spot. Tolerant to bacteriosis Is a good pollinator of female flowering varieties
Continuation of table. 27
Name Beginning of fruiting. after germination, days Length of the main stem Length and weight of the fruit Purpose Resistance to adverse conditions and diseases Remarks Competitor 45–50 Long-leafed 8–12 cm Salted. Canned food. Resistant to MR, moderately resistant to LMR, olive. five., bacteriosis Fruits do not turn yellow, similar to Nezhinsky, but fruitful Kustovoy 46–49 Short-leaved 35–60 cm 9–12 cm 100–120 g Saline. Canned food. Medium resistant to MR, bacteriosis Amicable ripening Cascade 35–45 Medium-grained 12–16 cm 110–125 g Salts. Drought tolerant. Resistant to LMR, MR and bacteriosis Do not overgrow - the fruits turn yellow Libella Medium - early Medium-growing 10–12 cm 110–120 g Canned food. Salting. Resistance to LMR is weak Amicable maturation. Fruits do not turn yellow F1 Lord Mid-season Branching medium or above average 10–12 cm Conser. Salting. Tolerant to LMR, resistant to MR, olive spot, VOM-1 Requires intensive mineral nutrition - frequent, fractional dressings. Partial parthenocarp. Long-term fruiting F1Movir 53–57 Medium-growing 10–12 cm 90–100 g Salad. Canned food. Resistant to MR and PTO-1 Long-term fruiting Monastic Early Short-leaved 9–12 cm 100–120 g Salted. Long-term fruiting Mig 35–50 Long-leafed 13–20 cm 120–200 g Salted. Resistant to MR, moderately resistant to LMR. Fruits can be stored for a long time Muromsky 36 Ultra - early ripening 32–56 Short-growing 6–8 cm 50–70 g Salted. Relatively cold-resistant. Resistant to bacteriosis. Amicable fruiting. Do not overgrow - turn yellow quickly; best for lightly salted
Continuation of table. 27
Name Beginning of fruiting. after germination, days Length of the main stem Length and weight of the fruit Purpose Resistance to adverse conditions and diseases Remarks Unbearable 40 43–55 90–120 g Salad. A good pollinator for cucumbers with a female type of flowering Nezhinsky 45–67 Long-leafed 8–12 cm 80–90 g The best variety for pickling Demanding moisture, relatively resistant to fungal diseases Low yield Onyx Early Long-leafed 11–13 cm 80–100 g Canned food. Resistant to LMR Fruits do not turn yellow Obelisk Medium - early Short-leaved 9–12 cm 100–120 g Canned. Resistant to LMR F1 Medium-resistant to MR Common yield F1 Saltan Early-maturing Branching average 9–11 cm Univers. Tolerant to LMR, resistant to MR, olive spot, VOM-1 Female flowering type with partial parthenocarp. Harvestable. Demanding on mineral nutrition F1 Success 221 Medium - early 8–12 cm 70–130 g Salted. Demanding on moisture Do not overgrow Yield 86 Mid-season Medium-climbing 10-14 cm 100-180 g Salts. Drought resistant Universal Early 39–45 100–160 cm 13–16 cm 100–150 g Salad.Salting. Canned food. F1 Farmer Mid-season Branching medium or above average 10–12 cm Canned. Salting. LMR tolerant, MR resistant, olive. five., VOM-1 Requires intensive mineral nutrition, frequent feeding. Partial partheno - carpia Electron Medium early 100–160 cm 8–13 cm 100–120 g Saline. Resistant to MR, LMR, olive spot. Fruits without bitterness. High-yielding - 15
3. Appointment of fruits. Cucumber varieties are salad, pickling, canning and universal. In addition, varieties and hybrids differ in the ripening time of fruits (early ripening, mid-early, mid-ripening), in the duration of fruiting, in the size and shape of zelents, their keeping quality, in the degree of branching and length of lashes, in resistance to cold, drought and other unfavorable factors, for disease resistance.
Table 27 shows varieties and hybrids recommended for open ground (bee-pollinated), some of which, marked with an asterisk, can be used for growing in stationary film shelters, provided that during the flowering period the film is removed for the daytime.
On narrow ridges 3-4-week-old cucumber seedlings are usually planted. If the landing is carried out before June 8–10, then a film shelter is installed over the ridge; at a later date, protection is not mandatory. Plants are planted in one row along one of the sides. The distance between plants in a row depends on how the culture is carried out - in the spreading or on the trellises. When guiding in the distance, the minimum permissible distance in a row is 25 cm, with a vertical lash tie, the distance can be reduced to 17.5 cm.
With dry seeds, cucumbers can be sown in a film micro-greenhouse (see section 6) starting from mid-May, with germinated seeds - in the third decade of May. Sowing seeds or planting early seedlings does not always bring good results, but they are certainly justified if a narrow ridge is underlain by a layer of biofuel. Seeds are sown frequently (5–6 cm), the seedlings are pulled, leaving the intervals between the plants indicated above.
It is most convenient to carry cucumbers on trellises. To do this, a U-shaped support is installed over the ridge with a horizontal bar at a height of 1.8–2 m and one cord is tied to the bar for each plant. The lashes are tied up at the stage of 3-5 true leaves, covering them at the base with a soft, sliding knot so that the cord does not subsequently pinch the thickening stem. As the main stem lengthens, it is twisted around the cord, guiding it clockwise. The lower lateral shoots are distributed over the surface of the ridge, and the upper ones hang freely from the main stem. The advantages of the trellis method are the best illumination of the plants and the convenience of caring for the crop - it makes it easier to feed, water, collect fruits, and remove old leaves. However, in cold weather, especially in windy weather, the trellis culture remains defenseless. In cold summers, spreading has the advantage. Plants creeping on the ground are less affected by the wind, and if necessary, the ridge can be covered with a film.
The disadvantage of keeping a cucumber in the spread is the difficulty of caring for the crop, the inconvenience of feeding and collecting fruits. In the cold summer, you can use low trellises - slats installed along the ridge at a height of 50-60 cm, through which the lashes are simply thrown without tying them. Low trellises allow you to cover the ridge if necessary and facilitate weekly feeding.
In order to increase the resistance of plants to various kinds of unfavorable influences, diseases and pests, it is advisable to sprinkle the cucumber culture in the beginning of flowering phase with the preparation "Epin" (10 drops per 1 liter of water). In particularly unfavorable conditions, spraying can be repeated at intervals of 10-14 days.In order to prevent fungal diseases, it is recommended to regularly remove old, worn-out leaves from fruiting plants, as well as to spray twice with herbal infusion (in the second decade of July and the first decade of August).
7.4.2. Tomatoes - self-pollinating culture, which does not tolerate prolonged rainy weather, is very sensitive to late blight. These three characteristics make tomatoes the number one candidate for greenhouses. This is more reliable, provides a longer fruiting period, a higher yield, allows a greater variety of varieties and hybrids, but requires a certain skill from the grower. In a greenhouse, without the ability to form bushes, you can get almost nothing but luxurious leaves. It is easier for a beginner vegetable grower to grow tomatoes in the open field, but provided that the variety is correctly selected.
Tomato cultivars and hybrids can be divided into two large groups: indeterminate, that is, capable of unlimited growth, and determinant, in which, at a certain stage of development, growth in height ends on its own and a flower raceme appears at the top of the stem. Indeterminate tomatoes - tall, with an infinitely long fruiting period - are primarily intended for cultivation in greenhouses. For open ground, mainly determinant, and even better super-determinant varieties and hybrids are suitable. Superdeterminate tomatoes are undersized, quickly move to flowering, and give the harvest in unison. Tomato cultivars and hybrids specially oriented for cultivation in the open field are given in table. 28. In order to have a harvest under any circumstances, it is recommended to choose an unpretentious, locally tested variety as the main one, and in addition to test unknown, but somewhat attractive varieties.
It is safer to grow early varieties of tomatoes outdoors. Seeds for seedlings are sown not earlier than the first decade of April; hardened seedlings at the age of 7–8 weeks are planted on narrow ridges in the third decade of May. Temporary film shelters are installed over the plantings. The purpose of the shelter is twofold - protection from possible frost and accumulation and retention of heat in the soil. When the soil temperature drops below 10 °, the roots of tomatoes stop absorbing nutrients from the soil and plant growth stops. If the installation of a shelter is not provided, then the seeds of early varieties for seedlings are sown after April 15, and the seedlings are planted in the ground on June 8-10.
Seedlings of mid-season and late varieties of tomatoes are grown with a long run, sowing seeds for seedlings in March.
Plants of various varieties and hybrids are so different in size and degree of foliage that it is difficult to give. comprehensive recommendations for their location on the ridge and the distance between them in a row. The need for more or less living space depends not only on varietal characteristics, but changes depending on how the bush is being conducted - in one, two or three stems, whether all stepsons are removed; sunny summer or cloudy; whether the site is fully lit or there is little shading; Whether the ridge is evenly lit or the lighting is predominantly one-sided.
Sunlight for tomatoes is a decisive factor in the harvest. If plants have to compete for light, they build up excess vegetative mass to the detriment of fruiting. Therefore, the general rule is as follows: the worse the illumination conditions, the less the gardener has the ability to form a bush, the more grounds for single-row planting and an increase in the intervals between plants in a row in comparison with those indicated in table. 6.
The easiest way is to give recommendations for growing semi-determinant and indeterminate, that is, tall, tomatoes, such as Red Cherry, Yellow Cherry or Giraffe. They are led into one stem (Fig. 10). At the same time, the yield from one bush decreases.But the ripening of fruits is accelerated and the total yield from the ridge increases due to a denser planting of plants (see Table 6)
Table 28. Some varieties and hybrids of tomatoes for open ground
(Varieties and hybrids marked with one star are intended for open ground and film shelters, with two stars - for open ground, shelters and film greenhouses)
Name Beginning of fruiting after germination, days Characteristics of the bush Characteristics of fruits Resistance to diseases Note Agata Early 98–113 Non-standard determinant 33–45 cm 5–11 nests 75–100 g Flat-round smooth High yield, consistent yield, fruit evenness Alpatiev 905 a Early 100–115 Standard determinant erect 46–55 cm 4–6 nests Flat-round 55 –75 to 100 g Medium Cold hardy, very leafy. For 15 days of fruiting, 20–30% of the yield of Argo ripens. Early maturing up to 108 Standard determinant up to 45 cm 90–100 up to 120 g First inflorescence above 8–9 leaves. Good taste, rich in vitamin C (up to 98 mg%) Banana * Early 95 Determinate low-growing Banana-shaped fruits, elongated with dense pulp up to 80 g Ideal for canning. Harvest 2.5 kg per bush White filling Early 100–115 Non-standard determinant 42–50 cm 5–12 nests 90–130 g Relatively resistant to fluorosis The variety is plastic, adapted to different conditions Vonzai ** Mid-season 115 Medium 80–100 cm Pink fleshy fruits 150-200 g Fruits are rich in B vitamins. Yield 3 kg per bush Red cherry. Cherry yellow Early Early Tall Tall Rounded red 15 g Rounded yellow 15 g Fruits contain 3 times more sugars, organic acids and vitamins than ordinary varieties. Yield 1 kg per bush Gavroche Very early 75 Short compact up to 50 cm Red - pink oval 20–40 g No need to pinch. Harvest 1.5 kg per bush. Fruits are suitable for canning Hybrid 15 (Institute Vavilova) Early 105 Determinant compact 50–55 cm In a bunch of 7 fruits 60–90 g Relatively resistant to late blight Newly ripening
Continuation of table. 28
Name Beginning of fruiting after germination, days Characteristics of the bush Characteristics of fruits Resistance to diseases Note Gnome Early 98–100 Determinant compact 40–50 cm 50–60 g 6–7 fruits in a bunch Low-leafed bush, high palatability of fruits Grand Early Ripe Compact 40–60 cm 50–60 g Increased resistance to late blight High palatability Early ripening grotto 108– 110 Non-standard determinant compact 35–45 cm 60–80 g Late blight resistance high Amicable ripening. First inflorescence above 6–7 leaves, 4–5 inflorescences on the main stem Ground Gribovsky Early 90–110 Semi-spreading non-standard determinant 40–52 cm 4–6 nests 55–90 g Relatively resistant to late blight Resistant to unfavorable conditions, cold-resistant. Fresh fruit decay - 2 months Oak (Dubrava) Early maturing 105–110 Non-standard determinant 40–55 cm 90–140 g Resistance to phytophid - torus increased First inflorescence above 6–7 leaves, cold-resistant, fruitful, amicably ripening Giraffe ** Unripe 250 and more Indeterminate vigorous round smooth orange 80–100 g After long-term storage (3–5 months), the fruits acquire an orange-yellow color. Good for solki. Harvest 3.5 kg per bush Corsair ** Early ripening 100–105 Determinant medium spreading 50–60 cm 4–6 fruits per cluster 110–160 g Harvest. Fruits have a high dry matter content F1 Lafania ** Very early Low-growing Rounded smooth 80 g Resistant to TMV, Fusarium, cladosporium Weak leafiness. When dribbled in 1 stem, the distance in a row is 20 cm, in 3 stems - 30 cm F1 Small boy ** Early 100–105 Superdeterminant 50–70 cm On the hand 6–8 fruits 60–80 g Resistant to TMV and cladosporium. harvest - 3.2-4 kg per bush. Supervises fruits in cool weather; if not pinned, then fruiting is later
Continuation of table. 28
Name Beginning of fruiting after germination, days Characteristics of the bush Characteristics of fruits Resistance to diseases Note Moskvich Early 90–105 Standard determinant compact 28–40 cm 3–5 nests 40–50 g Frost-resistant, does not lie down, does not require pinching Nevsky Most early ripening among varieties 75–95 Determinant 25–35 cm 45–50 g Avoids late blight due to early ripening Novelty of Transnistria Mid-season 112–128 Non-standard determinant spreading 40–80 cm 35–56 g Amicable maturation, transportable, lying, suitable for rare harvests Otradny Ultra-early ripening 80–100 Standard determinant compact 35–45 cm Number of nests 4–6. Rounded smooth * 50–70 g Resistance to late blight weak. Fruits are leveled, amicable return of an early harvest, high taste. Can be grown without support. Fruits have a high content of carotene Peremoga Medium early Determinant undersized medium leafy 90–130 g High-yielding Ryzhik Mid-season 115 Medium-sized Round orange 100–130 g High content of B vitamins. nests 6–11 60–90 g Avoids late blight due to early ripening Amicable ripening of an early harvest. High productivity Siberian early maturing Early maturing 96–108 Determinant 30–48 cm Number of nests 5–12 60–115 g Sustainable productivity in different conditions
Continuation of table. 28
Name Beginning of fruiting after germination, days Characteristics of the bush Characteristics of fruits Resistance to diseases Note Sunny Early ripe 93–112 Semi-stem determinant 30–40 cm Number of nests 3–4 Elongated - oval 38–52 g Designed for canning, amicable ripening, high transportability Talalikhin Early Determinant semi-sprawling undersized 76–100 g In favorable years, you can grow without pinching Tamina Apple tree of Russia) Early 85 Tall 70–80 g Torch Mid-season 112–127 Non-stem determinant compact 35–56 cm 4–6 nests 60–90 g Amicable ripening. High yield, suitable for rare harvests Khabarovsk roses Mid-season 116–120 Indeterminate powerful bush 80–115 cm Number of nests 4–5. Pink 60–80 g Stable, but low yield. High quality of fruits Early ripe shuttle 100–105 Determinant standard compact 40–45 cm 4–5 fruits per bunch 50 g Beautiful, plum-like fruits with high taste. Weak breakout force from the stalk F1 Yarilo ** Very early Low-growing Rounded smooth 90 g Resistant to TMV, cladosporium, fusarium Weak leafiness. When dribbled in 1 stem, the distance in a row is 20 cm, in 3 stems - 30 cm
Rice. 10. Formation of a tomato bush (a) - in one stem; (b) - in two stems; (b) - 3 stems.
m - Removed lateral shoots (stepchildren) Arrows indicate saved shoots.
It is also convenient to lead some superdeterminant hybrids into one stem (Malyshok, Lafanya, Yarilo). Although the growth of the main stem stops after 2-3 flower brushes, the growth point is transferred to the lateral shoot, for which a reserve stepson is left in the leaf axil under the upper inflorescence.
When the tomatoes are led in one stem over a row of plants at a height of 2 m, two trellises are pulled, one from the other by 1.0–1.2 m. For each plant, one cord is tied, which gently covers the stem near the soil, and then the stem is guided around cord clockwise. All odd plants in a row are tied to one trellis, all even ones to another. This gives close-planted plants more light and air.
Single-stem keeping requires constant pruning of the bush during the growing season.
1. Remove the lower leaves if they are bent down and touch the ground.
2. Periodically, once a week, remove all stepchildren, that is, lateral shoots growing in the leaf axils (Fig. 11).Small stepchildren are pinched off, and the stepchildren, who have not been noticed before, who have managed to grow, are cut out with a knife moistened with 1% potassium permanganate.
3. To avoid competition for light between neighboring plants, cut off the peripheral parts of the leaves if the leaves of neighboring plants overlap and shade each other.
4. When the fruits are formed on the brush, cut off all the leaves that shade them. Ripening fruits should be illuminated by the sun.
5. If the lash has reached the trellis, but not later than August 1, the top of the main shoot is removed. You should pinch the tip over the brush, the flowers of which have already opened, leaving 1 or 2 leaves above it. In the middle lane in a warm, sunny summer, 6 or even 7 brushes can bear fruit, in cold and cloudy no more than 3-4.
Rice. 11. Stepsons (lateral shoots developing in the leaf axils) should be removed while they are small.
Novice gardeners usually try to avoid the garter and the formation of a bush, so they are attracted by determinant low-growing varieties of tomatoes, which are known to be fruitful without pinching (White filling, Moskvich, Gavrosh, Talalikhin). The main and lateral shoots of these varieties form 2-3 flower brushes, after which they finish their growth. However, even these varieties can be grown without pinching only in warm, sunny years and in the absence of even a slight shading of the garden plot. In unfavorable years, or in conditions of partial shading of the ridge, or in shading caused by too dense planting, the plants stretch out and intensively increase the vegetative mass. The transition to fruiting and ripening of fruits slows down, the danger of late blight of immature fruits increases, which is tantamount to a loss of yield. In a cold, cloudy summer and with partial shading, the harvest can only be saved by pinching and forming a bush.
Grazing of larger determinant varieties (Alpatieva 905a, Korsar, Peremoga, etc.) is a prerequisite for obtaining a harvest even under optimal growing conditions. The more shoots on a plant, the more flower brushes on it and the slower the fruits grow and ripen. If vegetative growth is not limited in time, then the autumn cold or fungal diseases will overtake the culture before it has time to form a crop. Removing the stepchildren, the plants form into one, two or three stems (Fig. 10). Three stems are only permissible under the most favorable conditions.
Rice. 12. Two-stemmed tomato bushes located between and supported by double rows of twine.
Bushes formed into two or three stems can be supported by enclosing them between two rows of twine stretched horizontally (Fig. 12). In a row with plants, stakes (stands) are installed at a distance of 75–90 cm from each other. When the plants reach a height of 25–30 cm, a wide synthetic twine is tied to the extreme post at a height of 20–25 cm and pulled along the entire ridge, from post to post, twisting each post. From the last stand, the twine is pulled in the same way in the opposite direction, but on the other side of the racks. In this case, the plant stems are between two rows of twine. When the height of the bushes reaches 45-50 cm, pull the next 2 rows of twine 20-25 cm higher than the first two rows. As a result, the stems and hands with fruits are supported by twine, without being tied to it. For most "determinant varieties, 2 or 3 double rows of twine are sufficient.
With this method of growing tomatoes, the pruning is less than that of a single-stem crop. It is necessary to remove the lower leaves when they touch the ground, the lower stepchildren and stepchildren of the second order, as well as the leaves shading the ripening fruits.
With standard agricultural techniques, that is, when feeding with a mixture of 2, carried out 1 time in 7-10 days and regular watering, the size of the yield is directly related to the ability to form and cut the bushes.In addition, additional treatments are recommended to achieve maximum yields.
1. At the stage of budding - the beginning of flowering, it is recommended to replace one top dressing with mixture 2 for top dressing with wood ash at a dose of 50 g / m (an incomplete glass of sifted wood ash per meter of a ridge). Feeding with ash (nitrogen-free fertilizer, rich in potassium and trace elements) promotes the transition from vegetative growth to fruiting.
2. At the stage of fruit formation in tomatoes, the need for magnesium sharply increases, which is associated with the intensive formation of chlorophyll in growing fruits. So that magnesium does not become a factor limiting the yield, the culture in the phase of fruit formation is fed with magnesium sulfate at a dose of 25 g / m. Magnesium sulfate is scattered in a strip in the middle of the ridge (same as mixture 2) and dissolved by watering. Top dressing with magnesium sulfate is done between two regular dressings with mixture 2.
3. At the stage of budding - the beginning of flowering, tomatoes are sprayed with Epin (10 drops per liter of water). This increases the immunity of plants, their resistance to any adverse effects, increases the yield. Under stressful conditions, spraying can be repeated at intervals of 10-14 days. The drug "Epin" can be used without any fear: it is useful not only for plants, but also for people.
7.4.3. Bush beans - a small plant with a height of 25 to 60 cm. This crop, exceptional in its nutritional value, is not very common in garden plots, since many believe that it does not ripen in the middle lane. This is completely untrue - early ripening varieties of bush beans in the Moscow region, for example, yield a crop at several planting dates: the first planting is done in the late spring period, the last - in late June - early July.
Failures in growing bush beans among novice gardeners can be associated with the very first stage - the stage of seed germination: in the warmth, seedlings appear after 5-6 days, but if the seeds are planted deeper than 2 cm, if the soil is wet and heavy and if the temperature drops below 11– 12 °, and this is the minimum temperature for germination of beans, then the seeds rot when they swell.
It is possible to improve the conditions for seed germination by covering the ridge with a film immediately after sowing. And yet, the seedling method has undoubted advantages. Seeds for seedlings are sown on May 1-10, and 20-30-day-old seedlings are planted in the first ten days of June or a little earlier, if there is an opportunity to protect the plantings with a film in case of a cold snap. The optimum temperature for the development of beans is 18-24 °.
Varieties of bush beans are divided into shelling, semi-sugar and sugar beans. Hulling varieties have tough bean shells and are grown exclusively for ripe beans. Hulling varieties (Gribovskaya 92, Schedraya, Moskovskaya Belaya) are planted only once - in late spring - early summer, and ripe beans are harvested when the beans begin to dry out. Only fully ripe beans will keep well. In some varieties, fruiting is extended, for example, in Gribovskaya 92. From the first to the last harvest, it takes up to 70 days, and harvests stop only with the onset of frost.
Sugar varieties (Sachs without fiber 615, Triumphal Sugar 764, Green-pod 517, Kustovaya without fiber 85) have tender pods without parchment and fibrous threads. In semi-sugar beans, the parchment layer is absent in young beans. They are usually grown on a shoulder blade, that is, they are harvested unripe, green beans. Green beans are harvested 8-12 days after the formation of ovaries, when the seeds in them reach the size of a wheat grain. Keep in mind: unripe beans are very poorly stored, they need to be used on the day of harvest, in extreme cases they can be stored for several days in the refrigerator.Even a small ridge of beans will produce more shoulder blades than can be used in soups and main courses in the summer, so the shoulder blades are frozen or canned for the winter.
Only sugar varieties on a shoulder blade can be planted several times per season. The last date for planting seedlings is July 10. At this time, only early-ripening varieties can be planted, in which 50–55 days pass from germination to the first harvest of fruits. It does not make sense to plant beans later, since beans are tied only at temperatures of 15 ° and higher. Ripe sugar beans, as well as shelling varieties, can only be obtained from plants planted in early June.
7.4.4. Curly (code) beans - a more thermophilic plant than bush beans. In central Russia, it succeeds only when administered through seedlings. Seedlings are planted once a season - in the first decade of June. Seedlings are 25-30 days old. The curly bean stalks are very long and by their very nature should curl around the support. Curly beans are carried in a trellis method.
To pull the trellis, T-shaped or U-shaped supports are installed at the ends of the ridges and at a height of 2.2–2.4 m, two rows of large-diameter wire are pulled from one support to the other, one over each row of plants. The wire must be bolted firmly to prevent it from bending. A simpler option is to support half-inch water pipes on supports. Cords are tied to the trellises, around which the whips of beans are twisted. Usually, climbing beans are planted in a row at a distance of 3-5 cm. One cord is tied for 3-4 plants, since several plants can curl around one cord. When the plants reach a height of 15 cm, they gently cover 3-4 neighboring plants at a height of 5 cm from their base with a cord, bring the tops together and guide them around the cord in a clockwise direction.
The period of development in curly beans is more extended than that of bush beans, therefore, only early-ripening varieties of curly beans should be planted in our zone.
7.4.5. Zucchini. Two varieties of zucchini are cultivated - white-fruited (Gribovsky 37, Dlinnoplodny, Sote-38, Yakor, Belogor, Rolik, etc.) and zucchini (Zebra, Aeronaut, Tsukesha, Kuand, Skvorushka, etc.)
The advantage is the seedling method of growing zucchini. Seeds for seedlings are sown in late April - early May, and 25–35-day-old seedlings are planted on narrow ridges in late May - early June.
In order for the zucchini to bear a lot of fruits and not to give excessive vegetative mass, do you need to remove the lateral shoots? and let only the main lash grow. Zucchini squash is more "manageable" than white-fruited; they, as a rule, are weakly branched and among them there are non-branching varieties (Aeronaut, Tsukesha). The formation of a bush in these cases is reduced only to the timely removal of leaves from the part of the stem that has borne fruit. Removing old leaves is a simple and effective technique that increases yields and reduces the incidence of powdery mildew.
To get an early harvest, as well as to increase the yield in cold and rainy summers, it is recommended to practice manual pollination of flowers. The most developed male flower is chosen, the petals are removed and the anther touches the stigma of the pistils of the female flowers. This should be done in the morning, since the period of susceptibility of pollen to female flowers is short - only until noon on the day when the flower blossomed. Petals are also removed from pollinated female flowers.
Large fruits cannot be kept on the bush for a long time, as this inhibits the formation of new fruits.
7.4.6. Squash like zucchini, is a type of vegetable pumpkin. A characteristic feature of these crops is early maturity and high yield. Squash is even more sensitive than squash to low temperatures and frost, so the seedling method is certainly preferred for them. Squash seedlings are planted at the same time as cucumber seedlings.If there is no film, then it is safe to plant seedlings only on June 8-10, but if there is an opportunity to cover young plantings, the dates can be moved to the end of May. Zucchini and squash continue to bear fruit until they die from the first autumn frosts, therefore, the earlier fruiting begins, the higher the total yield will be.
If the beginning of summer is cold, then to accelerate the development of planting, you can grow for a rather long time under the film, until it begins to interfere with the plants. Patissons are bushy plants and usually do not produce long lashes. If the bush is not formed in any way, then in the second half of summer it becomes strongly thickened, which contributes to the occurrence of fungal diseases and makes it difficult for bees to access flowers. Old leaves in the middle of the bush and weak side shoots should be regularly cut. Fruit collection should be carried out at least twice a week, since the best are 2–5-day-old ovaries with a diameter of up to 8–10 cm.
As a rule, gardeners know only the variety of White squash 13. Less known are such interesting varieties as Karavai, Disk, NIO-15. Varieties Disk and NIO-15 are characterized by less leafiness, bushes are better ventilated and less affected by fungal diseases. The early ripening variety Disk is relatively cold-resistant.
Date Added: 2015-03-11; views: 473;
SEE MORE:
Kindergarten.Ru >> Electronic library >> Garden and vegetable garden >>
I.P. Popov, "Growing early vegetables"
Gorky publishing house, 1953
Published with some abbreviations.
OCR Plants grown in a small feeding area and intended to be transplanted to a permanent place of culture, regardless of their age, are called seedlings. The age of the seedlings depends on the purpose and place of further plant cultivation. The younger the seedlings, the better they take root during transplantation, but the later the production of early vegetables arrives. Many vegetable crops are grown in the open field not by sowing seeds, but by seedlings. In addition, in order to obtain an earlier harvest in the open field, seedlings are often grown and those crops that are usually seeded in a permanent place.
In connection with the advancement of vegetable growing further and further north, the seedling method of growing vegetable plants is of great importance. Late spring and early autumn frosts in the northern zone of vegetable growing significantly shorten the even short growing season and prevent many vegetable crops from being sown directly into open ground. The advancement to the north of heat-loving vegetable plants that are more demanding on the heat is possible only with the use of the seedling culture method. In early spring, when the temperature often drops below zero, the seedling method allows plants to create better conditions for growth and development at a young age and makes it possible to start growing plants earlier and shortens the period of growing crops in the open field.
Plants during the seedling period are densely placed and occupy a very small area, which makes it easier to organize the protection of plants from frost and pests.
When growing early vegetables in greenhouses and insulated soil, the seedling method makes it possible to start the culture 20-40 days earlier, and therefore, allows you to get products in a shorter time.
By the time the plants are planted in a permanent place, the seedlings grown in greenhouses or greenhouses reach significant development - they run ahead. Depending on the biological characteristics of plants and growing conditions, the "race" can reach 30-50 days.
The more "run" the seedling has, the shorter the vegetation period of plants in a permanent place after planting will be. Greenhouses, steam beds and insulated beds during this time do not have time to "burn out" - they lose heat, and the planted plants will be in a more favorable thermal environment, they will grow and develop better and faster, and, therefore, the first production will turn out 30-50 days earlier. than from sowing directly to a permanent site.
Planting pre-prepared seedlings in greenhouses and on insulated beds reduces the duration of the plants' stay in greenhouses and makes it possible to use the same area many times, that is, it increases the number of frame rotations and thereby the yield.Thus, crop early vegetables is only possible and economically viable when the vegetables are grown from seedlings.
The seedling method of growing vegetable crops greatly contributes to the elimination of seasonality in vegetable production.
continuation …
Popular articles of the site from the section "Dreams and Magic"
|
|
|
|

When do prophetic dreams come about?
Sufficiently clear images from a dream make an indelible impression on the awakened person. If after some time the events in a dream are embodied in reality, then people are convinced that this dream was prophetic. Prophetic dreams differ from ordinary ones in that, with rare exceptions, they have a direct meaning. A prophetic dream is always vivid, memorable ...
Read completely >>

Why do departed people dream?
There is a strong belief that dreams about dead people do not belong to the horror genre, but, on the contrary, are often prophetic dreams. So, for example, it is worth listening to the words of the deceased, because all of them, as a rule, are direct and truthful, in contrast to the allegories that are uttered by other characters in our dreams ...
Read completely >>

If you had a bad dream ...
If you had some kind of bad dream, then it is remembered by almost everyone and does not go out of my head for a long time. Often a person is frightened not so much by the content of the dream itself, but by its consequences, because most of us believe that we see dreams not in vain. As scientists have found out, a person most often dreams of a bad dream already in the morning ...
Read completely >>
|
|
|
|