Content
1251. The leading place in the export of coal is occupied by
Australia and USA
1252. In the world, most of the electricity is generated by
TPP
1253. The leaders in the export of iron ore
Brazil, India
1254. Bauxite mining is concentrated in rich deposits
Australia, Jamaica, Guinea
1255. In the modern chemical industry, the leading place is occupied by the production of
polymer materials
1256. By the production of products from fabrics, the first place in the world is held by
China and India
1257. In the world condition of fish products, countries stand out
Chile and Peru
1258. Traditional consumer agriculture includes
semi-nomadic animal husbandry
1259. Commercial agriculture includes
plantation economy
1260. The "Green Revolution" in agriculture is called
applying comprehensive measures to increase food
1261. In the world, crop production is based on
cereals
1262. Main grain crop of temperate latitudes
wheat
1263. The most important grain crop of the subtropical and tropical belt
rice
1264. The tonic cultures include
cocoa, coffee, tea
1265. The main countries in Eurasia, where grapes are grown
Italy, Spain, France
1266. About half of the pigs raised in the world are
Asia
1267. Of the countries with the largest number of pigs,
China
1268. In the desert and semi-desert areas of temperate and tropical latitudes,
sheep breeding
1269. The greatest length of railways is
USA
1270. The bulk of international traffic is ... transport
nautical
1271. The major seaport of Rotterdam belongs to
The Netherlands
1272. Straits of great importance for world shipping,
English Channel, Malacca, Hormuz
1273. Countries Leading the World Merchant Fleet
Panama, Japan, Greece
1274. The largest oil pipelines in the world are located in
Russia, Canada, USA
1275. Most of the world trade turnover belongs to countries
Western Europe and Asia
1276. The structure of world trade is dominated by
finished industrial products
1277. Various types of loans between countries are called
international credit market
1278. More than half of all tourists in the world come from countries
Europe
1279. The most visited countries of the world by tourists
Italy, Spain, France
1280. Muslims of the world make pilgrimage to sacred religious places in
Mecca and Medina
1281. From the listed integration groups, choose an industry
OPEC
1282. An EU member state
Portugal
1283. A country belonging to ASEAN,
Philippines
1284. Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries
OPEC
1285. OPEC member country
Algeria
1286. Country of NAFTA,
Mexico
1287. The largest urban agglomeration of Russia
Moscow
1288. In Western Siberia, from all Russian gas production,
90 %
1289. The largest oil basin in Russia
West Siberian
1290. Power plants are built on the Yenisei River
Sayano-Shushenskaya, Krasnoyarsk
1291. Select Russian NPP from the list
Kurskaya, Balakovskaya
1292. In Russia, diamonds are mined at deposits
Sakha Republic
1293. Main grain crop of Russia
wheat
1294. The main mode of transport in Russia in terms of cargo turnover
railway
1295. Kursk Magnetic Anomaly is located in ... economic region
Central Black Earth
1296. Heavy trucks "BelAZ" are produced in
Zhodino
1297. An oil refinery and a petrochemical plant in Belarus are located in
Novopolotsk
1298. In Belarus, among industrial crops, mainly
linen
1299.The largest river in Ukraine that provides hydropower,
Dnieper
1300. Centers of ferrous metallurgy of Ukraine
Kryvyi Rih, Mariupol, Donetsk
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Views: 2 205
Major countries in Eurasia where grapes are grown
Italy, Spain, France
About half of the pigs raised in the world are
Asia
Of the countries with the highest numbers of pigs,
China
In the desert and semi-desert areas of temperate and tropical latitudes,
Sheep breeding
1269. The greatest length of railways is
USA
1270. The bulk of international traffic is ... transport
Nautical
The major seaport of Rotterdam belongs to
The Netherlands
Straits of great importance for world shipping,
English Channel, Malacca, Hormuz
Countries leaders of the world merchant fleet
Panama, Japan, Greece
The world's largest oil pipelines are located in
Russia, Canada, USA
Most of the world trade is accounted for by countries
Western Europe and Asia
The structure of world trade is dominated by
Finished industrial products
Different types of loans between countries are called
International credit market
More than half of all tourists in the world come from countries
Europe
The most visited by tourists countries in the world
Italy, Spain, France
Muslims of the world make pilgrimages to sacred religious places in
Mecca and Medina
Choose the industry sector from the listed integration groups
OPEC
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved May 23, 2016; checks require
17 edits
.
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
versions
Retrieved May 23, 2016; checks require
17 edits
.
Pigs on a small farm
Pig breeding - a branch of livestock raising pigs. It is most widespread in East Asia (China 49.8% of world production), Europe (25.6% of world production), America (10.3% of world production). This area of animal husbandry is distinguished by high demands, high productivity, high energy value of the products produced and short terms of production of livestock for slaughter. Develops in areas with any climatic conditions. The most important areas of pig breeding gravitate towards densely populated areas and industrial centers, to places of growing and processing grain, to food industry enterprises.
Pig breeding history
People began to breed pigs during the primitive communal system. In the 3rd millennium BC. NS. tribal tribes living on the territory of the river basins. Dnieper, Southern Bug and Dniester (Trypillian culture), pigs were bred for meat and lard; in developed slave states (Egypt, Greece, India), pig breeds were bred.
At the end of the 16th century, Fletcher noted that “the Russians adjacent to them (having become accustomed to their annual attacks in the summer) keep very few livestock, except for pigs, which the Tatars do not touch or steal, because they are of the same religion as the Turks. and do not eat pork meat "
Both N. Ya. Bichurin and Peter Dobel noted the high level of pig breeding in China in the 19th century: “pigs are bred in large numbers, because pork and piglets are the usual tasty food for city dwellers ... Apart from boiled rice and water, pigs are not fed with anything ( I'm talking about those assigned to slaughter): they are kept in stalls, washed daily, even twice a day, and scrubbed clean; thus they remain healthy and soon grow fat. "
In the countries of Western Europe, even in the era of feudalism, there was only primitive pig breeding: pigs grazed in large herds in the forests, kept them in the simplest premises.Pig breeding achieved significant development in the era of capitalism in connection with the growth of cities and the sharply increased demand for meat and other livestock products.
Spreading
Almost half of the world pig population (936.8 million heads, 1997) is in Asia (China, Japan, the Republic of Korea, the countries of the Indochina Peninsula), about 1/3 in Europe (Germany, France, Italy, Great Britain, Russia, Ukraine , Poland) and about 10% in the USA. Due to religious prohibitions, pig breeding did not develop in Muslim countries and Israel.
Pig breeding in Russia
Certificate of the master of pig breeding of the USSR 1958
At the end of 2011, the number of pigs in farms of all categories amounted to 17.3 million heads, which is approximately the same as at the end of the 1950s. The maximum livestock (about 40 million) was reached in the late 1980s.
Pig breeding is most developed in areas with extensive pastures, near large cities, in areas of developed grain farming and potato growing.
The inhabitants of Russia consume about 8 million tons of meat per year, including more than 2 million tons of pork. From 2005 to 2009, the industrial (?) Sector of Russia increased the number of livestock from 7 million to 14 million heads. Pig farming is a fast-return agricultural sector, which is why during 2005-2006 a number of Russian companies announced significant investments in the construction of large pig farms. In 2012, about 2.6 million tons of pork was produced domestically, and about 1.1 million tons were imported. Thus, the share of imports in the consumption of pork was about 30%.
In general, in the period from 2006 to 2012. the increase in pork consumption in Russia amounted to 55.5% in physical terms.
According to the Institute for Agricultural Market Studies, in 2005 the Krasnodar Territory was the leader in pig livestock (950,000), Tatarstan was second (about 600,000), and the Omsk Region was third (about 500,000 pigs).
At the regional level, the Belgorod Region has a strong leadership in the production of pigs for slaughter. For the I quarter. In 2012, agricultural organizations in this region produced 26.0% of the total Russian production of pork in this category of farms. The largest pork producers in the agricultural sector also include the Krasnodar Territory (4.6%), the Republic of Tatarstan (3.9%) and the Lipetsk Region (2.8%). By the end of 2011, the Leningrad Region provided 1.6% of the total Russian pork output in the sector of agricultural enterprises.
There are more than a dozen pig breeds in our country. The most common breed is the Large White. The Kemerovo breed is bred in Siberia. At the pig farms of one of the largest agro-industrial enterprises in Russia - the Siberian Agrarian Group, pigs of three breeds are raised: Landrace, Duroc, Yorkshire.
Age and sex groups of pigs
There are the following age and gender groups (if the farm has a complete production cycle):
- Boars
- basic (18 months and older)
- verifiable (from 12 to 18 months) (“verifiable” because offspring are checked at 2 or 4 months)
- to identify females in the hunt, test boars (both basic and tested, culled)
- repair (from 4 to 10-12 months) up to 150 kg or more, before the first fruitful mating (3-4 months in commercial and 4-5 months in breeding farms).
- Sow
- Replacement pig (from 4 months to 8-9 months, since 6-7 months is the beginning of the hunt, about 3 hunt and fertilization occurs) weight 120 or more kg before the first fertilization
- Checked uterus (from 8-9 months, from fertilization up to 2 month old piglets)
- Major uterus (checked if normal) (from first farrowing to end of use) 2-3 years, 3-4 years.
Physiologically, the same uterus can be:
-
- idle (weaning to fertilization - 21 days)
- pregnant (from fertilization to farrowing - 114-115 days)
- suckling (from farrowing to weaning piglets)
The queens can be single to receive only one farrowing. They are used with a seasonal tour system of reproduction, with a low supply of forage.
- Suckling pigs - piglets that are under the uterus. In small farms - up to 2 months.
- Weaning pigs
- (from weaning to fattening,
- transfer to repair.
- Replacement young growth (from 4 months to 9 months - pigs, boars from 4 to 10-12 months)
- Fattening livestock
- young animals (from weaning, depending on the type of feeding)
- adult animals culled (semi-greasy, greasy)
Terms
- A sow, or just a uterus - a female giving birth
- Farrowing - birth of piglets
- Piglet - baby pig
- Boar - male, sire
- Boar - castrated boar
- A pig is a piglet aged from 4 to 10 months.
see also
- Pig complex
- Domestic pig
- Pigsty (structure)
- Ukrainian Research Institute of Pig Breeding
Notes (edit)
Literature
- Pig breeding / G. N. Dobrokhotov // Safflower - Soan. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1976. - (Great Soviet Encyclopedia: / Ch. Ed. A. M. Prokhorov; 1969-1978, vol. 23).
- Dankvert S.A. and others. Pig breeding of the countries of the world at the end of the 20th century: Reference and study guide. - M., 2004
- Bazhov G.M. and others. Pig breeder's guide. - SPb., 2007
- Sofia Inkizhinova... Produced pigs // Expert, No. 17-18 (849), April 29, 2013.
Links
- Pig, animal characteristics
- Laboratory of Selection and Technological Achievements in Pig Breeding
The modern pig-breeding industry is a highly developed complex of enterprises with colossal production potential.
Achievements of scientific and technological progress in this area have allowed many countries of the world to improve existing and develop new breeds of pigs, which are distinguished by high productive indicators. Efficient production technologies for the in-line production of pork in the conditions of large pig farms have been developed and are being successfully introduced. Many small farms have sprung up. Significant successes have been achieved in breeding and keeping, as well as feeding these domestic animals, which made it possible to significantly increase their productivity indicators.
In the meat balance of many countries of the world and our country in particular, at the moment pork occupies an impressive share of 35-50 percent.

One sow can bring from 18-20 to 25-30 piglets per year, from which, with an intensive feeding method, from 1.8 to 3 tons of meat is obtained with the most economical use of feed and labor resources.
Next, we will consider in which countries pig breeding is developed.
Pig breeding in Europe
On the territory of modern Europe in this industry, there is a different picture in each individual country.
For example, in such a previously developed pig-breeding country like Denmark, the number of farms has recently decreased significantly - to 4,500, of which 40 percent are full-cycle farms with a reproductive herd of 255 females, 13 percent are special reproductive farms, sows with an average of 950 sows, the remaining 47 percent are feed farms with an annual production of 6,800 pigs. It should be said that Danish pig production is highly dependent on the volume of cereals produced. So, in 2008, each pig-breeding farm in this country had an average area of land for scattering manure of about 140 hectares, which made it possible to produce up to half of all feed on the farms themselves. Subsequently, serious restrictions were introduced in Denmark related to the protection of the external environment from harmful influences, including pig manure. This was the reason for the decrease in the number of pig farms.
Despite this, in 2012 alone, the export of piglets from this country to Germany for fattening amounted to more than 9 million units.
A large decrease in the number of farms of this livestock breeding was also noted in the Netherlands. And the number dropped from 25,000 in 1980 to 2,412 in 2012.
Structurally, 75 percent of Dutch pig farms were either reproductive or fattening. The average number of reproductive herds on these farms was 445 sows.
At the same time, following the example of Denmark, about seven million heads of young animals were exported outside the country (most of them to Germany). In this regard, a new Danish-Dutch-German model of pig breeding is traced, in which the first two countries are focused on obtaining piglets, and in Germany they are engaged in fattening them.
The change in direction in Denmark and the Netherlands is due to a number of factors: the impossibility of increasing the number of pigs due to environmental reasons, the lack of free land, the dissatisfaction of the population of these countries with the construction of large fattening enterprises, which resulted in open protests - on the one hand, and the excellent skills of Danish and Dutch pig breeders in pig breeding - on the other. In Germany, on the contrary, a favorable situation has developed for the construction of enterprises for fattening and slaughtering: large available areas of land, availability of labor and its low cost (mainly due to migrants). These factors have played a key role in the significant increase in the number of German feedlots.
French pig breeding is represented mainly by full-cycle pig farms. The average number of reproductive herds in these farms is 196 queens. Most of these enterprises are located in the west of France (Brittany).
On the territory of this European state, rather strict laws on environmental protection are also in force, which explains the impossibility of many enterprises to increase the scale of their production. Research carried out with the participation of 20 percent of the best French farmers has shown that their level of technical skills allows for significantly better results than currently available. Another advantage of French pig breeders is the high level of qualifications of the farm workers. however, this advantage still cannot be realized in practice due to the relatively small size of pig breeding enterprises.
Legislative restrictions have significantly reduced the growth rate of this French livestock industry over the past 10 years. For example, let's say that the size and number of pig farms in France in 2010 remained at the 2000 level.
Pig farming in North America
In the United States, pig production was tied to regions with good grain yields, so it began to develop in the states of the so-called "corn belt".
The basis of the pig-breeding enterprises of this country at that time was made up of small full-cycle farms. According to 1992 data, the share of full-cycle farms in American pig production reached 65 percent.
The replacement of full-cycle factories with specialized ones in the United States began in the nineties of the last century. This process was especially accelerated by the emergence of contracts for the production of pig products. Large business holdings specializing in the production of feed mixtures or the processing of raw materials began to directly conclude such contracts with private farmers.
There was a need to increase productivity, as a result of which the share of full-cycle farms in the total number of pig farms fell from 65 percent in 1992 to 18 percent in 2004.
Historically, the following picture has developed in pig breeding in the United States: selection and breeding work with pig breeds in this country was guided by the phenotype and strong physical constitution.They tried to breed the animals in such a way that they could easily withstand the winter cold. As a result, the thickness of the fat layer increased significantly in such animals. With the advent of large pig-breeding integration complexes, the requirements of breeders to genetics have also changed. The emergence of highly specialized reproductive and fattening enterprises brought to the fore the improvement, first of all, in early maturity and growth rates of pigs.

To this end, the rotation of animals on production farms working on contract terms has significantly increased, which is possible only with high growth rates. If we talk about the fodder base, then, by tradition, American pig breeders tried to grow fodder themselves (grain crops, soybeans, and so on). Own production of feeds made them much cheaper, which reduced production costs. Since the US pig industry was practically independent of changes in world feed prices, growth conversion was not set as the main task for this industry.
With the emergence and development of large companies in the industry, the tasks of breeding work have changed. The main goal was to increase the efficiency of feed use while maintaining and increasing the growth rate
For reasons not entirely clear, the Canadian pig industry has experienced a recession over the past decades. Special programs developed at the state level aimed to stop the decline of this important livestock industry.
For example, the purchase of fattened pigs at the expense of the state treasury was used to reduce the market risks of pig breeders. Currently, Canadian farmers are hoping for a revival of the country's former pig production power. And there are all the prerequisites for this, since this type of animal husbandry in Canada has always been famous for its long traditions and unique technologies.
Pig genetic research in this country has been carried out for more than a hundred years. And the export of both pork and breeding animals to more than forty countries of the world is a significant indicator.
Pig conditions in Canada are some of the best.
Asian pig breeding
The "pig miracle" of the People's Republic of China is known throughout the world. Since 1978, there has been a constant increase in agricultural production throughout the food industry as a whole.
Chinese agricultural enterprises not only began to play a key role in the international market, but also successfully dispelled the myth about the shortage of their land resources and fully provided the domestic market with food. Recently, China has created an efficient food system focused on increasing the share of “highly nutritious boar” in the country's meat balance. The model of development of Chinese agriculture focused on increasing the production and consumption of pork in particular and meat in general.
Compared to 1980, the average per capita meat consumption has quadrupled and in 2009 reached 58 kilograms per person per year.
The fastest growing industries are the processing of fresh meat and its packaging, as well as the receipt of finished meat products with long shelf life, which makes it possible to supply them for sale to various hypermarkets and supermarkets.
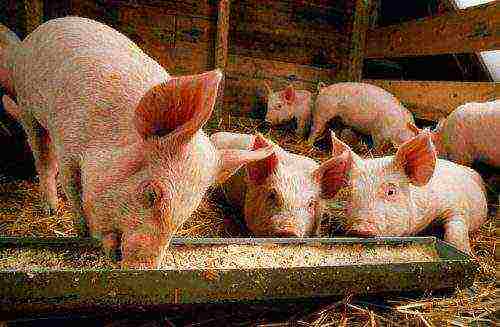
The leading role of China in Asian pig production is due to the rapid growth in production volumes and the popularization of pork in the country itself with its huge population.
Pig farming in South America
Despite the fact that livestock has always been one of the leading sectors of the Brazilian economy, until recently, pig breeding in it occupied a small share (cattle breeding predominated). For example, in the 1950s, Brazil produced only 329 thousand tons of pork, which was 2 percent of the total world production of this meat at that time.
For comparison, China supplied 2 million 200 thousand tons to the domestic and foreign markets (14 percent of the world volume), and the USA was in first place with 4 million 600 thousand tons and 30 percent of the world market.
Serious investments and targeted government policy have led to a real breakthrough in the production of this type of meat over the past decade. For example, let's give some numbers: in just two years (from 2000 to 2002), the volume of exports of pork from Brazil showed an impressive growth - by 270 percent (600 thousand tons in digital terms). This placed Brazil in fourth place in the world among all the leading pig breeding countries, which it successfully holds to this day. The share of Brazilian pork in world exports is 11 percent, and in the total volume of production, this share is 3 percent.
It should be noted that the development of this livestock industry in Brazil cannot be called uniform and constant. Serious recessions in the pig-breeding complex of the country were explained either by the global overproduction of this meat in 2003, or by outbreaks of foot and mouth disease epidemics. Despite this, according to the Brazilian Association of Exporters and Producers of Pork (ABIPECS), over the past five years, despite such constraints as the establishment of sanitary barriers, increased government subsidies to EU pigs and increased competition in the global market for the pig industry, Brazil has managed to increase export performance. for this type of agricultural products by a greater amount than the average competing countries were able to achieve.

The list of regular foreign buyers of Brazilian pork includes more than 70 countries.
The main consumers of these products traditionally include Hong Kong, Ukraine and Russia, although Brazilian pig producers have recently been actively exploring new sales markets, such as the countries of the Middle East and Africa.
Useful video PIG BREEDING AS A BUSINESS Hangar Pigsty fattener video

