Content
Many people perceive almost everything that is grown on the earth as food, but this is a misconception. Most of the world's agricultural land is dedicated specifically to the cultivation of industrial crops. Every year more and more goods are produced from them. And it's not just clothes. Soap, tires, medicines, cigarettes, building materials and biofuels - this is not a complete list of the possibilities of such plants. In the commodity circulation of many countries, industrial crops are of the same great importance as oil, iron ore or gas.
Types of industrial crops
Industrial culture is a raw material for industry. For convenience, these crops were classified according to the principle of obtaining finished raw materials from them.
- Starchy crops. They are grown, as the name implies, for the sake of obtaining starch from them. It is usually found in tubers. Examples are potatoes, yams, or sweet potatoes.
- Sugar-containing crops. Plants that are grown to extract sucrose from them. The most famous representatives of such crops in our country are sugar beets and sugar cane. But there are also more rare plants, such as sugar maple, carob or chicory.
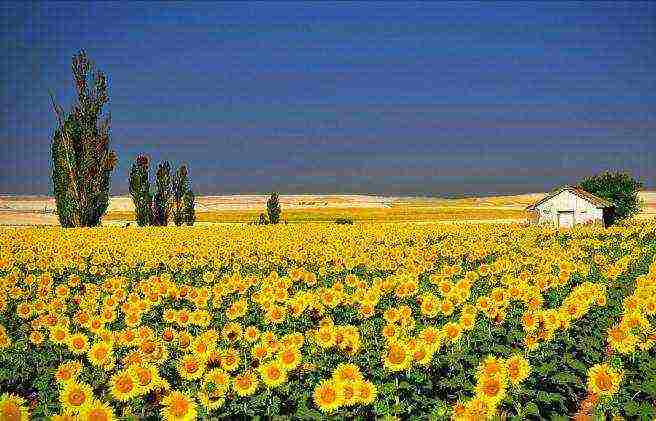
- Oilseeds. This is a large group of industrial crops. Its typical representatives: sunflower, soybeans, peanuts, oil trees, castor oil plants, rapeseed, sesame and others.
- Essential oil. Plants containing essential oils. The group is huge too. Crops such as rose or lavender are world renowned raw materials for the global perfumery and cosmetics industry.
- Fibrous, or spinning. This group also includes bast crops. These are flax, cotton, hemp, kenaf, sisal, ramie.
- Rubber plants. The most famous are hevea and guayula.
- Toning. This group includes all plants from which tea, coffee, coca-cola, cocoa, tobacco are produced.
- Cork or cork-bearing. This includes cork oak and Amur velvet.
- Other groups: dyeing (sophora, saffron, indigo), tanning (badan, oak, spruce), gutta-percha (euonymus, payena), medicinal crops.

Cultivation of industrial crops
Industrial crops occupy a large cultivated area in all countries. Before growing one or another of them, they take into account not only climatic conditions, but also the proximity of processing plants, the market need for raw materials that are produced from a particular crop.
In Russia, industrial crops are not cultivated very actively, since the natural conditions make their cultivation labor-intensive, and large investments are required. In Ukraine, the geographical position of which is favorable for industrial crops, sugar beets, sunflowers and flax are actively grown.
All grain and industrial crops require the use of special harvesting machines and special tools. Usually this is also taken into account when preparing areas for certain crops.
Due to the growing interest of people in healthy, environmentally friendly lifestyles, the cultivation of many industrial crops brings additional profits to producers. An example is the lavender plantation in French Provence. People from all over the world come to admire the flowering of this amazingly beautiful and fragrant plant. Celebrations and festivals are arranged for them, which bring a hefty additional income.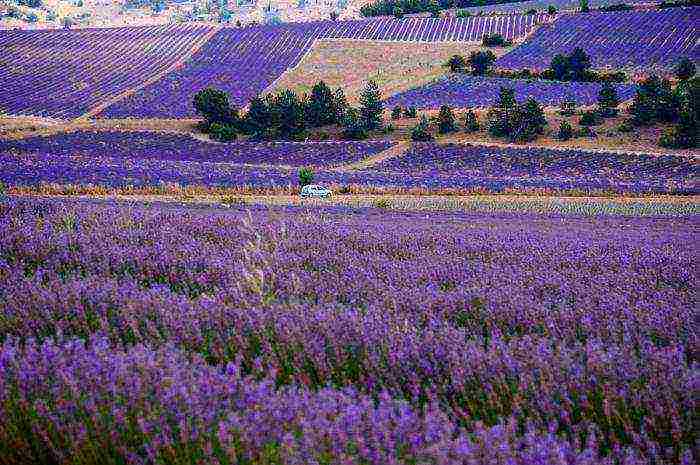
Main industrial crops in Russia
First of all, such industrial crops as sunflower are actively grown in Russia. Our country ranks second in the world for the production of sunflower seeds (Argentina is in the lead). This culture came to Russia under Peter I along with potatoes. At first, the sunflower was grown for decorative purposes, but then they were able to appreciate the enormous benefits of this plant.
Once upon a time, the British had a monopoly on sugar production, as all the sugarcane crops belonged to them. Already in the eighteenth century, other countries began to look for how to meet the needs of their market for sugar. As a result, in 1747, the German chemist Andreas Marggraf found sugar in sugar beets. Now sugar beet is included in the main crops (industrial) in many countries, and in Russia it occupies one percent of all cultivated land.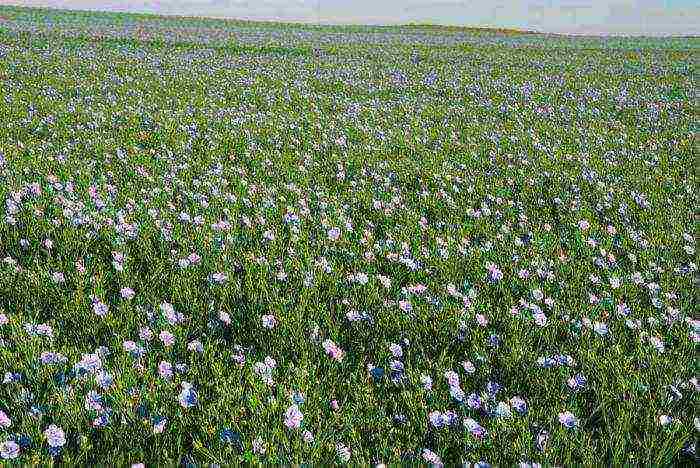
Russia has long been famous for the production of flax. In Belarus and Russia, two-thirds of the world's flax fiber is cultivated. Russia's cool and rainy summers are ideal conditions for growing flax. Although it is a fibrous crop, flaxseed oil has a high nutritional value and is used to make high quality paints. Linen fabrics are very durable, beautiful, they are used not only in light, but also in the aviation and automotive industries.
Industrial crops in the world
More than 20 million tons of cotton are produced in the world every year. It is the main technical culture in the world. One-fifth of the world's total is harvested by the United States and China, ten percent are cultivated by Pakistan and India, and a lot of cotton is grown in Turkey, Uzbekistan, Egypt and Syria. From a ton of cotton, 400 kg of fiber is made, from which three thousand meters of fabric are obtained.
India, China, Bangladesh and other Asian countries are famous for growing jute, sesal, supplying the whole world with burlap, ropes and rough fabrics. In Southeast Asia, hevea grows, from which rubber products are made.
Essential oil and dyeing plants are grown in many countries. For example, almost all of the world's saffron harvest belongs to Iran. It is not only a colorant, but also one of the most expensive condiments in the world. In order to get a kilogram of saffron, you need to collect 200 thousand crocuses.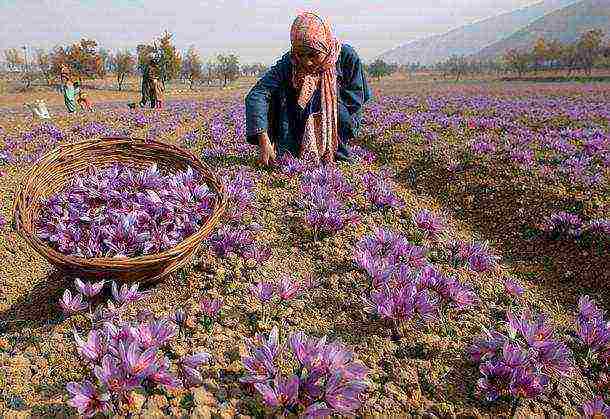
It happens that industrial crops become a symbol of the country. For example, a rose in Bulgaria. In this country, in the Kazanlak Valley, there is a world-famous rose museum. The rose oil produced by the country has brought worldwide fame to Bulgaria.
Industrial crops such as tobacco and hops are also popular in the world. Cuban and Turkish tobacco is prized by smokers all over the world, and Germany is famous for its hop cultivation.
Genetically modified crops and their capabilities
Soybeans are currently the main technical crop in the world. American scientists believe that this will be the main source of protein for humanity. The United States produces three quarters of all soybeans in the world. Every tenth ton of all grain crops is soybeans. It is not only eaten, but also used for technical needs. Soybean oil can be used to make plastics, paints, biofuels.

Scientists are currently working on the widespread use of such a technical culture as lupine. Its possibilities are even wider than that of soybeans. This industrial culture is surprisingly multifunctional: fibers give excellent quality tissue, oil with antioxidant properties is obtained from the plant, and coffee is made from the roots. The world leader in the production of promising crops is Australia.
Gasoline from industrial crops
The earth's oil reserves are running out, and scientists around the world are working to create the optimal biofuel. The best technical culture for this purpose is being sought.
Soybeans, rapeseed and cotton are the leaders in this field so far, but there are also lesser-known plants. Among them are the South American jatropha, Syrian cottonwood, copaiba, which grows in the tropics of the Amazon. In China, they found the plant of the Klabra syndrome.Its juice ignites like oil.
The cultivation of industrial crops has long gone beyond traditional agriculture and is turning into a modern high-tech industry with great prospects. Whoever understands this today will gain a lot tomorrow.
Remember:
1. What types of soils are the most fertile in Russia?
The most fertile soils in Russia are chernozems. Russia ranks first in the world in terms of total reserves of this type of soil (up to 50%). In addition, black soil is the most fertile soil not only in Russia, but in the world in general. This is due to the amount of humus (the top fertile soil layer) - here it is the highest among all types of soils.
2. What types of reclamation contribute to improving soil fertility?
Water reclamation. Irrigation canals were built by the ancient Egyptians, who guessed in this way to increase soil fertility.
Questions within a paragraph:
1. Find these areas on the map of Russia.
Questions and tasks:
1. Name the main grain and industrial crops grown in Russia. Explain the geography of their distribution.
The main grain crops are wheat (the Volga region, the Urals, Siberia and the Crimea), barley (the Central Black Earth region, the Volga region, the North Caucasus) and rye (the middle strip and the north of the European part of the country).
The main industrial crops are fiber flax (northwest of the European part of Russia), sunflower and sugar beet (Central Black Earth Region, North Caucasus and Crimea), potatoes (center of European Russia).
2. What crops are cultivated in your constituent entity of the Federation?
In 2016, in the structure of plant growing in the Chelyabinsk region, the largest share belonged to spring wheat (68.47%), potatoes (37.2%), spring barley (21.73%), vegetable growing (11.87%). In 2016, 1,947.7 thousand tons of grain were produced. At the same time, last year's figure increased by 14.7%. The collection of vegetables amounted to 230.2 thousand tons, and potato production - 722.0 thousand.
3. Describe the impact of crop production on the environment in your subject of the Federation.
1) Agricultural machines negatively affect the soil - with their weight they strongly compact it, which leads to a decrease in its yield by 10-50%
2) The use of chemicals. Useful soil fauna is being destroyed. They can accumulate in the soil layer.
3) Plowing the soil reduces its resistance to blowing and water erosion - soil erosion occurs.
Rastegusha / 17 nov. 2014, 11:06:02 PM
lead the example of the mountains of Russia included in the Pamir-Chukotka belt?
4) What is the oldest era?
5) What era periods are: Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous?
6) In what period, and in what era did the first reptiles appear?
7) In what period of the Cenozoic era did great apes appear?
8) As a result of the activity of which exogenous force, the following forms of relief are formed: kar, carling, trog, circus, moraine, sheep's foreheads, ozy, kama?
9) What is the name of the accumulation of deposits of one type of mineral?
10) What is the name of the long-term weather regime?
11) What is the name of the heat and light emitted by the sun?
12) What is the name of the process of climate change with distance from the seas and okeins, while the amount of precipitation decreases and the amplitude of temperature fluctuations increases?
13) What is the name of the border strip separating air masses of different properties?
14) When the front is advancing, which front does the rainfall, accompanied by a strong wind, fall?
15) What is the main pattern of temperature changes in summer on the territory of Russia?
16) What is the name of the amount of moisture that can evaporate from the surface under given atmospheric conditions?
17) Define the type of climate in Russia according to the description: typical for the Kaliningrad region; there is a fairly large amount of precipitation throughout the year, not a cold wet winter is replaced by a hot, wet summer?
18) What direction is the wind in Russia?
19) What is the name of the water stream flowing in the deepening-channel?
20) What is the name of the depression in the relief along which the river flows?
21) What is the name of the amount of water passing through the river bed for a certain period of time?
22) What is the name of the temporary rise of water in the river?
23) What is the difference between the height of the source and the mouth of the river?
24) Give an example of Russian rivers with spring floods?
25) Give an example of rivers in Russia with a predominance of glacial feeding?
26) What are the rivers related to the Pacific Ocean basin?
27) Give examples of waste and closed lakes in Russia?
28) Name the reservoir on the Volga River?
29) What is the name of a waterlogged area of the earth's surface?
30) Where are the ice sheets located in Russia?
31) Where is the valley of geysers in Russia?
32) What is the name of the loose surface layer of the Earth, which has fertility?
33) What type of soil is typical for the taiga zone?
34) What is the name in agriculture of the set of organizational, economic, technical measures aimed at improving the soil?
35) What are the types of tundra vegetation?
36) What kinds of animals of the steppe zone do you know?
37) Give examples of anthropogenic, industrial landscapes?
This video tutorial was created specifically for self-study of the topic “Geography of agriculture. Industrial crops and animal husbandry ". On it you can find out which industrial crops are grown on the territory of Russia, in which regions. Then the teacher will talk about the peculiarities of the geography of animal husbandry.
Topic: General characteristics of the Russian economy
Lesson: Geography of Agriculture. Industrial crops and animal husbandry
1. Crop production. Industrial crops
TO technical crops include sunflower, sugar beet, fiber flax, cotton and other crops. The technical species of cultivated plants are used to produce food products (vegetable oil, sugar, molasses), medicines, and light industry products. Russia takes the 7th place in the world in the collection of sugar beets, the second in the collection of flax fiber, and in the collection of sunflower seeds it is in the group of leaders. Despite this, plants do not meet the needs for food and raw materials at the expense of their producers. This is largely due to the fact that industrial crops occupy less area than grain crops, as well as the biological characteristics of plants, which manifests itself in more stringent requirements for natural conditions: the amount of heat, light, moisture and the physicochemical composition of the soil. Complicated by the laboriousness of growing most crops, as well as capital intensity. Virtually every technical culture requires the use of special tools and harvesting machines. Sometimes it is necessary to build special structures, for example, for soaking fiber flax, they equip entire reservoirs and enterprises.
Industrial crops are divided into several groups:
1. Oilseeds (sunflower, castor oil, buckwheat)
2. Fibrous (fiber flax, cotton)
3. Sugar (sugar beet)
4. Essential oil (mint, anise)
Sugar beet is the only sugar-bearing crop in Russia, from which raw sugar and then refined sugar are obtained. Sugar beets are grown not only as a technical crop, but also as a fodder crop. Sugar beets are quite "capricious": they require good cultivated soils, a sufficiently humid climate with a long heat period. It grows best in the forest-steppe zone. Another feature of sugar beet growing is labor intensity. The main areas for growing sugar beets: Central Chernozem, North Caucasian, Volga and south of Western Siberia (Altai Territory).
Rice. 1. Areas of sugar beet growing in Russia
Fiber flax- the most important fibrous culture in Russia. From the obtained flax fiber, linen fabrics are made, which are in high demand in our country and abroad. Flax requires coolness, usually in cloudy weather, is very moisture-loving and does not tolerate heat. In the fields of flax predecessors, it is desirable to have crops enriching the soil with nitrogen. Fiber flax is susceptible to fungal diseases, which reduces the quality of plant fibers, because of this it can be sown in one field no more than once every seven to eight years. This, in turn, limits flax crops, which occupy only 12-15% of the harvested area. The main economic regions for growing fiber flax are Central, North, Volgo-Vyatka, North-West, Ural and West Siberian.
Rice. 2. Areas of fiber flax growing in Russia
Sunflower the most widespread industrial crop in Russia and the leading oilseed crop. 90% of Russian vegetable oil is produced from sunflower seeds, 10% of oil is obtained from mustard, flax and other crops. Obtained by processing sunflower seeds into oil and cake - a high-protein concentrated feed for livestock. Green mass and unripe sunflower seeds are used to harvest silage. Sunflower crops occupy more than 70% of all industrial crops. The main areas for growing sunflower: North Caucasian, Volga (Middle Volga region), Central Chernozem, Ural (Orenburg region).
Rice. 3. Areas of sunflower growing in Russia
The cultivation of other oilseeds is less widespread in Russia. Flax curly, or oil flax is sown mainly in the Volga, North Caucasian, West Siberian regions. Mustard - in the Volga region (Volgograd, Saratov regions), North Caucasian (Rostov region, Stavropol and Krasnodar regions). Castor oil plant grown mainly in the North Caucasian region.
2. Livestock
Livestock gives about 60% of Russia's gross product. In recent years, the role of animal husbandry in the agro-industrial complex has been increasing.
In animal husbandry, there are:
1. Cattle breeding (cattle breeding)
2. Pig breeding
3. Reindeer husbandry
4. Poultry keeping
5. Beekeeping
6. Fur farming
Livestock raising is impossible without a serious forage base. Therefore, the placement of livestock complexes is associated with zonal features, for example, dairy cattle breeding is oriented towards the succulent forage of the forest zone, and beef cattle breeding is focused on dry forage of the steppes and forest-steppes. Sheep or goat breeding has always been territorially associated with mountain systems or foothills, where there is enough dry food and space. Cattle are located everywhere, but the main areas of its breeding are Central, Volga, North Caucasian, Ural, West Siberian.
Rice. 4. The main areas of cattle breeding in Russia
According to the ratio of meat and milk in cattle breeding, there are several directions: dairy, milk and meat, meat and milk, meat. Dairy farming concentrated mainly around large cities and industrial centers of the country. The main regions for the production of dairy products are North Caucasian, Central, North-West.
Rice. 5. Areas of distribution of dairy farming
Dairy and beef cattle breeding is widespread. Meat, dairy and beef cattle breeding is developed in the steppe and semi-desert regions of the south of the European part of Russia, the Urals of the Volga region and western Siberia.
Rice. 6. Areas of distribution of meat, dairy and beef cattle breeding
Pig breeding is developing in areas of highly developed grain farming, potato growing or beet growing (North Caucasus, Povolzhsky, Central West Siberian regions), as well as in suburban areas of large cities and food industry centers.
Rice. 7.Pig breeding areas
Poultry farming has reached its greatest development in the main grain regions near large cities. Horse breeding has historically been one of the most important economic sectors in the North Caucasus and the South of the Urals.
Rice. 8. Areas of development of horse breeding
The life of the indigenous peoples of the Far North, Siberia or the Far East has historically been associated with reindeer husbandry.
3. Problems of the agro-industrial complex of the country
The functioning of the agro-industrial complex in recent years has been carried out in difficult conditions. The material and technical base is noticeably deteriorating, the ties of agricultural enterprises are disrupted. As a result, there is a loss of the share of agricultural products in the country's gross domestic product. Serious changes are taking place in the country's agriculture: the redistribution of regions and the privatization of districts. As a result, a part of agricultural products is lost. Russia provides itself with only half of such products as meat, milk, vegetables and 30% provides itself with berries and fruits. The functioning of the agro-industrial complex is impossible without state support. In addition to state subsidies, the agrarian complex requires the provision of material and technical resources, the creation of a favorable environment for foreign investment and the regulation of foreign trade in products in order to protect Russian products. When solving these problems, the agro-industrial complex in our state will produce a sufficient amount of products and fulfill its task of meeting the requirements of the population.
Recommended reading list
- V.P. Dronov, V. Ya. Rum. Geography of Russia: population and economy. Grade 9
- V.P. Dronov, I.I. Barinov, V. Ya. Rom, A.A. Lobzhanidze. Geography of Russia: nature, population, economy. 8th grade
Recommended links to Internet resources
- Unified collection of digital educational resources (Source). Agro-industrial complex of Russia: composition, structure, problems


