Content
It turns out that kiwi can not only be grown in a garden near Moscow, but also get your own harvest. Do you want to know how?
Now in any supermarket you can buy kiwi fruits grown on large tree-like vines. They are also sometimes called the Chinese gooseberry, but the correct name of the plant is actinidia chinese delicacy (Actinidia chinensis var. Deliciosa). Upon careful study of the culture, it turned out that in the open field in a place protected from the wind, it can tolerate up to –20 ° С, and under shelter and up to –30 ° С. Therefore, if you "play" with winter shelters, you can try to grow it in the suburbs in the open field, and not at home.
Male and female kiwi plant
I planted the first kiwi seedlings in my garden near Moscow about 10 years ago, but only waited for flowering in 2012, although in the southern regions they bloom in the 3-5th year. First, the male plant bloomed, and the next year, simultaneously with the male plant, the female. Until the moment of flowering, the sex of the kiwi is difficult to determine, but when they bloom, this difference is clearly noticeable: the pistil on the female flowers is much larger.
Varietal affiliation of female plants (variety Hayward) I established only when the plants bloomed and the fruits began to ripen. Not knowing how the local bees and bumblebees would receive the overseas guest, he was a little overcautious: he manually pollinated all the flowers on female vines with a male flower.
The result was not long in coming, and now furry aliens from distant subtropics are ripening in my garden. However, I think that the insects would have done well without my help. For the viability of pollen and the activity of pollinating insects, it is optimal that during the flowering period, which in our area falls on the end of May - beginning of June, the air temperature is + 15 ... + 20 ° С.
Kiwi: planting and care
Kiwis are planted in places protected from the north and north-east winds. Best of all from the south side of the house. Spring planting is preferred. Usually 5-6 female plants are planted per male. Taking into account the fact that kiwi has a superficial root system, the planting pit is made shallow: 0.5x0.5x0.5 m. Kiwis like well-drained humus-rich soils. The best ratio is 1–2 parts of rotted manure or compost to 1 part of garden soil. It is desirable that the root collar is 3 cm above the ground level, since a buried planting can lead to the death of the plant.
Kiwis love abundant watering, but without stagnant water. If the summer is dry, then once a week will be enough 20-30 liters for an adult plant. In a rainy summer, you can water much less often. In the year of planting, you do not need to feed, and in subsequent years - starting from May, about once a month, apply under one plant 20–25 g of nitrogen, 10 g of phosphorus, 10–20 g of potash fertilizers, finishing all top dressing no later than July. Fertilizers containing chlorine should not be applied. Plants are sensitive to high lime content.
Considering that this is a powerful fast-growing vine, for good development it is immediately necessary to install racks (pillars), between which to pull a support: wire or ropes. Kiwi propagated by rooting cuttings, grafting and seeds. However, with seed propagation, the vast majority of seedlings (70–90%) will be male plants, so it is better to purchase seedlings from collectors.
Diseases and pests in our conditions are practically not found on kiwi.
Forming and pruning kiwi
I think the most successful form of growing kiwi is single-tiered and two-tiered palmette.
With a single-tiered palmette at a height of about 0.5-1 m, two sleeves are formed along a wire (rope) stretched between the posts. And with a two-tier one at a height of 1.5–2 m, there are two more sleeves. After planting a seedling from young shoots, the strongest is left and tied to a peg, and the remaining shoots are cut out. If the plant is planted in early spring, wait for the leaves to bloom before pruning. When the shoot reaches the height of the first tier, it is cut off, thus stimulating the growth of lateral shoots, of which two arms are formed. In the spring, only dry branches are removed - at this time there is an active sap flow, and if you cut off living tissue, the cut will "cry" for a long time. In summer or autumn, weak, fertile, thickening shoots are removed, leaving mainly growing horizontally at a distance of 30–40 cm from each other.
Wintering kiwi
My kiwis are planted at a distance of 1 m from the southern wall of the house. In the first years in November, I untied the ropes from the posts, for which the vines were attached, and lowered the whips as low as possible to the ground, trying not to touch it. A trunk circle mulched to a height of about 10 cm. I put two wooden shields in the form of a hut (0.5 m high) over the vines so that the snow falling from the roof would not break the vines, and covered the shields with 2-3 layers of polyethylene on top. The hut was partially covered with snow falling from the roof. In early spring, when the night frosts cease to drop below –15 ° С, I opened the shelter a little so that on sunny days there would be no greenhouse effect and the vine would not wake up ahead of time. For a growing vine, even a small minus is critical. Several years ago, when the frost was -5 ° C (May 8), the vines that had started to grow froze to the ground. Fortunately, they did not die and were fully recovered by August. Mature plants are difficult to bend to the ground. I had to slightly change the design of the winter shelter. In the fall, on the racks to which the vines are attached, I lay cellular polycarbonate, fasten it with one end to the wall of the house and make a small canopy. I untie the vines from the racks and tilt them to the wall of the house. From the outside, I close them with 2-3 layers of polyethylene, which I attach to the racks. In such a winter shelter, without additional heating, vines hibernate almost without damage. Only unripe shoots freeze over. In May, when the threat of frost has passed, I remove polyethylene and polycarbonate.
Harvesting kiwi
All kiwi varieties ripen no earlier than December, but can ripen harvested. Therefore, they pluck them before the first frosts and ripen them at home. To speed up ripening, you can put kiwi in one plastic bag with apples (1 apple for 10 kiwi).
Popular varieties of female plants
- Hayward - the most widespread variety in the world. Late ripe. Vigorous. The yield is high. The flowers are white at first, and after 2-3 days - cream, up to 6.5 cm in diameter, solitary, rarely in inflorescences of 2-3 flowers. Flowering lasts 10-14 days. The fruits are large, aligned, oval in cross section. Fruit length up to 6.5 cm, weight up to 100 g. The flesh is strawy-greenish.
- Bruno - early maturing. Vigorous. The flowers are white-cream, with a diameter of 5.5 cm, there are both single and collected in inflorescences of 2-3 pieces. Flowering lasts 10-12 days. Fruits are cylindrical in longitudinal section, round in cross section. Length up to 8 cm, circumference - 12 cm, weight 50–70 g. Green pulp.
- Monty - mid-season. Vigorous. Flowers are white-cream, up to 5 cm in diameter, single or in inflorescences of 2-3 pcs. Flowering lasts up to 12-14 days. Fruits are medium to large, slightly pear-shaped in longitudinal section and oval in cross section. Their length is 6.4 cm, circumference is 13.8 cm, weight is about 30 g. The flesh is greenish-yellow. The taste, in contrast to the listed varieties, is mediocre.
- Abbot - mid-season. Medium-sized. The flowers are white-cream, up to 6.5 cm in diameter, both single and collected in inflorescences of 2-3 pcs. Flowering lasts 10-12 days.Fruits are uniformly colored, elongated longitudinally and rounded in transverse directions. Fruit length 6.6 cm, weight 65 g. Green pulp.
- Jenny - medium early. Medium-sized. Self-pollinated. Fruits weighing up to 60-80 g. Similar to Haywardbut has smaller fruits.
Popular varieties of male plants
- Matua - an abundant and long-flowering variety. Vigorous. Flowers - from single to collected in inflorescences of 3-5 pcs. The villi on the peduncle are single, short.
- Tomuri - blooms a little later than the variety Matua... Vigorous. Long flowering, but less abundant. The flowers are large, from single to collected in inflorescences of 2-7 pcs. The villi on the pedicel are thin and long.
Source
 Many people have an idea of the kiwi fruit thanks to the shops, but few people know how kiwi grows and what kind of plant it is. We will try to fill this gap through an article by the famous Kuban gardener M.V. Konoplyanov, who to the question “is it possible to grow kiwi in Russia»Gives an affirmative answer - you can!
Many people have an idea of the kiwi fruit thanks to the shops, but few people know how kiwi grows and what kind of plant it is. We will try to fill this gap through an article by the famous Kuban gardener M.V. Konoplyanov, who to the question “is it possible to grow kiwi in Russia»Gives an affirmative answer - you can!
Kiwi is the main culture, to which I devoted at least fifteen years, when it was not yet in the Kuban. I have collected many articles about this culture.
Practice has shown that only a few authors were more knowledgeable when characterizing kiwi. And one even writes that kiwi can withstand temperatures down to -1-2 degrees, which indicates a complete lack of knowledge about this culture.
At present, the kiwi is very interested and is being studied at my site by the doctor of agricultural sciences V.A. Gryazev, who rightly claims that kiwi is the future and will take a leading place among fruit crops. The Americans bred the most frost-resistant kiwi variety (up to -40 degrees), and V.A. Gryazev.
Yes, kiwi does not need an article, but a more meaningful book, I hope it will soon appear to the delight of gardeners. Conducting correspondence with almost all corners of Russia, I was convinced that kiwi is grown near Moscow, in the regions of Central Russia and the Volga region, in particular the Volgograd region, and an amateur from Novocherkassk much earlier than I began to harvest this crop on his personal plot (for the winter, kiwi was added, like northern grape varieties).
Until a few decades ago, kiwi cultivated on a limited scale, mainly in New Zealand. However, in recent decades, industrial plantations have been established in many countries of the world, gradually advancing to the north.
Useful properties of kiwi
The sharp rise in popularity of kiwi is primarily due to the high medicinal value and properties of the kiwi fruit. The high content of vitamin C - 90-120 mg% (daily intake for an adult), that is, 15 times more than apples.
In general, doctors and gardeners who grow kiwi on plots like to say that one kiwi replaces a bucket of apples.
There is a lot of vitamin E in fruits, which is usually (except for avocados, but kiwi twice as much) is absent in other fruit crops. The content of vitamin A is also quite high (175-200 mg%). There are also vitamin B1, niacin, riboflavin.
Another difference between kiwi is that its juice contains the same amount of quinic acid as citric acid (up to 1000 mg%).
The peculiarity of kiwi fruits is also that they mainly contain minus-epicate-chins (and not plus-and minus-catechins, as in other fruits). According to B.B. Kutubidze and G.P. Sadzhveladze, such a content of catechins is optimal for a stimulating effect on the human body.
Kiwi fruits are also valued for the presence of biologically active substances, including the enzyme actinidin, which is similar in action to papain and ficin, the presence of which explains the stimulating effect of kiwi fruits.
The fruits of actinidia kiwi have long been used in traditional Chinese medicine for various disorders of the body and the treatment of many diseases.
They enhance digestion, prevent early gray hair, relieve rheumatic pains, stimulate blood circulation, increase milk production in nursing mothers, they are recommended for hypertension, vomiting and hemorrhoids, and as a tonic.
Kiwi fruit is recommended as a preventive anti-cancer agent in China and New Zealand. The active ingredient is ascorbic acid and actinidia, which directly or indirectly suppress the activity of cancer cells (due to the formation of free radicals that suppress N-nitroso compounds and enhance the formation of interferon).
Kiwi fruit is very valuable as a dietary product as it contains a lot of nutrients per calorie. In addition, they contain many minerals necessary for the body: magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, but primarily potassium, which is necessary in the treatment of many diseases.
By eating one kiwi every day, you avoid many troubles for your health, and the child gets good vitality and harmonious development.
The ecological value of this crop is that it is practically not damaged by pests and diseases. Considering that, moreover, it does not tolerate high doses of mineral fertilizers and, in particular, treatments with pesticides, the cultivation of this crop not only makes it possible to produce high-quality, environmentally friendly fruits, but also makes it possible to generally improve the ecological state of the surrounding area.
Under natural conditions, the wild ancestors of the kiwi grow in the forests of China, along the Yangtze, where cold winters and hot summers are a continental climate, where there are almost no frosts in spring. Some authors claim that kiwi is very photophilous. Years of experience have convinced me that this opinion is wrong: kiwi fruit perfectly, even when almost 70 percent shaded.
Kiwi as a species was formed on forest, well-aerated, humus-rich soil with a low lime content. These conditions favored the positioning of the root system in the superficial, nutrient-rich soil layer. When planting in open ground, it is recommended to create windproof plantings, taking into account fruit plants, trees, vineyards.
These are the biological characteristics and properties of kiwi.
How kiwi grows - growing and caring for fruit
As a fruit crop, kiwi has a number of unusual, unique features peculiar only to it. Firstly, it was domesticated less than a hundred years ago, and industrial cultivation - less than half a century, so it is biologically closer to its wild ancestors.
Kiwi is a liana, therefore it requires support. Shoot growth does not stop throughout the growing season, and appropriate conditions are required to maintain normal growth.
Flowers are laid laterally at the current growth, which is typical for only a few fruit crops. Almost every pollinated kiwi flower produces fruit, but its size depends on the number of seeds set. Kiwi is a dioecious plant.
The root system of kiwi is fibrous. Fleshy roots with a thick phloem occur mainly in the surface layer - up to 50 cm. Already by the 5-6th year, the root system lies on an area up to 5-6 meters in diameter.
At the same time, the proportion of thick structural roots that play the role of a depot of nutrients increases significantly (up to 80% of their total dry weight). These substances are consumed by the plant both at the beginning of the growing season and in the process of fruit formation and ripening.
So, in the first four weeks of growth, the need for basic microelements in kiwi is approximately 30-40% satisfied at the expense of the reserves of the root system. If it is damaged (loosening the soil), the vegetative growth of the plant is enhanced to the detriment of fruiting and fruit quality.
Kiwi does not tolerate tillage, especially near the trunk; very shallow loosening is possible on light sandy soils, where the roots are located at a greater depth. On calcareous soils with a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction, one must be especially careful, since the treatment of such soils leads to an increase in the alkaline reaction, and kiwi prefers a weakly acidic reaction.
Due to the active growth and the large removal of nutrients accumulated by the plant with fruits, leaves, shoots, kiwi requires fertilization.
A number of authors believe that fertilizers containing chlorine cannot be used, since kiwi does not tolerate them. Calcium fertilizers should also be avoided. The crop reacts negatively to high concentrations of nitrogen fertilizers.Should be avoided, especially on neutral and slightly alkaline soils, physiologically alkaline mineral fertilizers.
It is recommended to use sulfate forms of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, superphosphate or complex fertilizers (the recommended formula is 12-12-17), where the release of nitrogen is slowed down. But the best fertilizers are organic (well-rotted manure, peat). They not only provide the plant with nutrients rationally, but also improve the structure of the soil.
Although kiwi can grow and bear fruit on soils with different textures, high yields and fruit quality can only be obtained on light to medium texture soils, well aerated and rich in humus.
On soils with a heavy texture, the root system is poorly developed, even some of the roots emerge to the surface due to oxygen starvation. Soils with a high sand content are also unacceptable - due to rapid drying.
Kiwi can grow and bear fruit normally even on slightly alkaline soil, but its overall pH should not exceed 7.5, since chlorosis begins to progress with an increase in this indicator.
The root system of the kiwi, although buried in the surface layer, is capable of very efficiently extracting nutrients and water from the soil. It has been proven that a plant with a total foliage surface of 16-17 m2 consumes up to 100 liters of water per day. Water is especially needed in the first month or two after flowering, which affects the quality of the crop.
At the same time, the roots of kiwi do not tolerate excessive waterlogging of the soil, as this causes oxygen starvation of plants. Thus, kiwi is a plant with increased requirements for soil moisture levels.
Kiwi is a deciduous vine and can withstand frosts down to -16-18 C (young shoots), -24-30 C (adults, selection from the Hayward variety), but is very sensitive to early spring frosts. This is due to the fact that young herbaceous shoots formed from dormant buds at the beginning of the growing season (or not lignified shoot tips at the end of the growing season) are very sensitive to sudden temperature fluctuations.
This can affect the size of the crop. The negative consequences of exposure to low temperatures can be avoided (weakened) if you do not get carried away by this period in agricultural practices that stimulate vegetative growth (the use of fertilizers containing nitrogen, irrigation).
Kiwi is grown in the open field and in lightweight unheated film greenhouses. According to the data of French researchers, 25-35 t / ha more fruits were obtained in the green field than in the open field. Of course, kiwi is grown indoors mainly in areas with a more severe climate, in Russia - in the middle lane.
Some authors classify kiwi as a subtropical plant, although this is not entirely true. Kiwi is a deciduous crop and requires about 500 hours of freezing temperatures for normal development. Therefore, it is more correct to attribute it to the thermophilic crops of the temperate zone, such as, for example, peach, apricot, etc.
All actinidia are vines, therefore, in natural conditions, they do not have a pronounced trunk. Intertwining and intertwining, numerous kiwi shoots, which do not have support, form a continuous carpet of leaves and shoots.
See also: Growing actinidia - planting care and photos
However, with the appropriate formation and the presence of supports, usually in 25-30 years, the formation of one or several trunks begins. A fairly pronounced trunk with a diameter of 25-30 cm is formed from the central conductor. It can reach a height of 8-10 m.
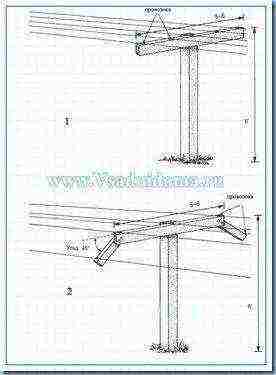
Figure 1. Here are examples of trellis of 2 types on which kiwi cultivation is most successful
1. Ordinary T-shaped trellis for growing kiwi
2. T-shaped trellis with "wings" (more convenient)
Kiwi shoots are divided into two main types: vegetative and mixed. The former are formed from dormant buds on 2-4-year-old shoots, perform a supporting function and do not form fruits.The latter, also called vegetative-generative, are formed on annual shoots of the previous year and perform both a supporting function and a fruiting function. There is also a type of generative or fruit shoots that cannot wrap around the support.
In kiwi, neoplasm of kidneys from the cambial tissues of internodes can also occur. On the cut of the internode, after two to three weeks, callus tubercles appear, from which then the buds of the kidneys (usually 4-6) are formed, and then within one or two months - 1 - 3 kidneys. These buds can later develop into normal shoots.
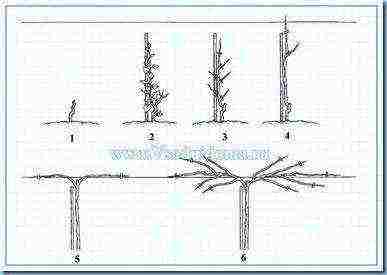
Figure 2. Growing and pruning kiwi
1. Planting a kiwi seedling (one or two late).
2. The first year of growth - leave the central trunk - cut off all others.
3 - 4. Remove all lateral shoots until the tip reaches the top wire in the trellis - then leave another shoot of their buds to grow, which is just below the trellis.
5. After the lower shoot has grown, spread them in different directions along the same trellis wire
6. The second and third years of kiwi growth are the formation of a bush.
With a shoot length over 30-40 cm, the shoot tip begins to spontaneously twist around the axis and winds around the support counterclockwise. Mixed shoots are formed on shoots from the previous year. On the shoots of old branches or trunk, they are practically not formed.
Flower buds are laid in the axils of the first 2-8 leaves. The differentiation of the buds into vegetative and generative (floral) occurs in the fall, before the onset of a dormant period.
The main kiwi pruning carried out after the leaves have fallen, but not later than the first decade of January. When forming, the most healthy vegetative shoots are left, on mixed ones - up to five buds, the fruiting shoots are removed to the replacement bud.
Summer pruning (pinching the ends, shortening) is carried out to improve the quality of the crop and complete the laying of the future crop.
See also: Exotic plants: Annona, bigaradia, tangerine, papaya, clementine and nansu mikan
Planting seedlings in a permanent place is carried out taking into account the distance between plants in a row - 3-5 cm. It should be borne in mind that the yield of one kiwi plant reaches 100-200 kg, therefore, powerful supports from pipes 1.8-2 meters high and 2-3 row of wire for trellises.
Kiwi is propagated, like grapes, by cuttings in winter and summer. It must be borne in mind that winter cuttings must be kept buried in the sand until the soil warms up, only then plant a mixture of sand and peat (1: 1) at an angle of 30 °, moderately moisten and slightly protect from the sun for the first two weeks ...
Summer cuttings with a shortened one leaf are placed in a greenhouse. At optimum temperature, light and humidity, roots will form in 3-4 weeks. Excellent results of reproduction - grafting in the split into seedlings from November to December and a scutellum in August-September.
Currently, breeders of many countries have obtained dozens of kiwi varieties, the weight of the fruits of which varies from 30 to 220 grams. The largest varieties are K-10, K-12, K-17.
Kiwi fruits, not removed from plants, are always firm. Usually from October to November (before frost) they are manually removed from the vines. They are laid out in a cool place with a temperature of 0-8 degrees, where they can be kept fresh for up to one year. They are checked occasionally - soft (mature and ready-to-eat) are selected.
To speed up the ripening of the fruits, they are brought into a warm room, where they become soft and very tasty within one to two weeks. Given the high nutritional value of the fruit, one per person per day is enough.
Cakes, salads are decorated with slices of peeled fruits, drinks are made from kiwi, including a wonderful liqueur, jam is made, but how wonderful the fruit is fresh and every day!
When a woman from Sverdlovsk wrote to me that she received the first harvest of kiwi, I realized that there are no boundaries for a purposeful person. According to astrology, the age of kiwi begins.Well, this culture deserves respect, and thanks to her for coming to us. Overwintering kiwi
Corresponding with many amateur gardeners in Russia, I was finally convinced that a culture like kiwi can grow and bear fruit almost to northern latitudes. What kind of subtropical culture is it if it is deciduous and frost-resistant ?! The United States has already received its hybrids with frost resistance below -4 degrees. But let's pay attention to those kiwi varieties that many gardeners in Russia already have.
Wintering kiwi seedlings
The whole difficulty of kiwi cultivation lies in overwintering. It would seem that in terms of frost resistance, kiwi is superior to grapes, but in winter hardiness - the duration of the period of frosty days - it is inferior to him. But for breeders, it's a matter of time.
A gardener from Novocherkassk and a gardener from Volgograd for many years in winter, kiwi shoots were bent to the ground and covered with earth. In the spring, the plants were freed from the shelter. We got harvests annually. But this is a very laborious process!
A very interesting case happened in Volgograd sometime in 1995. A WWII invalid, an amateur gardener, took to the hospital in the fall, having lain in it until the end of winter. Kiwi in the country in the winter did not hide. The frosts were weak before the snowfall, and the snow that fell bent the kiwi shoots to the ground and covered them with its blanket. When the gardener visited the dacha in the spring, he was pleasantly surprised: his beloved kiwi wintered well, although the frosts reached -40 ″ C. It would be worth pondering over this.
But here are some gardeners from the Kemerovo region, residents of the Moscow region, Central Russia adopted the experience of the gardeners of the West. Pieces of pipe half an inch (quarter of an inch) thick, 50-70 cm high above the ground are hammered into the ground, the distance between the stakes is 3-5 m. A wire is pulled from above. Kiwi seedlings are planted along the wire line at an angle to the ground no higher than 30 degrees. In the spring, a two-meter reinforcement is inserted into the stake-pipe, on top of which a wire is also pulled. It is advisable to direct the shoots of the plant during the growing season at an acute angle.
After the growing season, that is, after the first autumn frosts, when the leaves fall off, the kiwi is pruned, leaving up to five buds (seven can be) on the unfruitful shoots of the current year, and up to three buds on well-developed, fruiting shoots after the last fruit.
The armature with the upper wire is folded until the spring of next year. Kiwi shoots are pinned to the ground as close as possible with any hooks (wooden, wire, etc.). The bent shoots of kiwi are covered with any fallen leaves, straw, reeds, sawdust, hay, spruce branches, etc. To prevent the wind from scattering the shelter, cover it with any fabric material on top. It is dangerous to cover with a film, since under the influence of sunny days, the temperature inside the shelter will rise, and the kidneys will begin to awaken. Well, if snow falls on top of the shelter, then frosts even at -50 degrees will not be terrible.
In the same way, figs, pomegranates and many deciduous crops are sheltered in the winter, but planting them at an acute angle is required. In the forties and fifties, they used the trench method of shelter in the winter of citrus fruits: they were not afraid of frosts at -43 degrees.
Growing kiwi - personal experience
Kiwi in the village!
Long gone are the days when kiwi fruits were bought as an exotic gift for a visit. Another thing is surprising: why the cultivation of, say, grapes in the north of the Middle Lane is already considered the norm, but kiwi is not? Imagine a picture: birch, aspen, kiwi, mountain ash ...
This beautiful plant easily withstands frosts of -15 ° and below (in Yalta, for example, in the foothills it happens even at -30 °, and nothing - it grows and bears fruit). Here is another important point: kiwi does not require chemical treatments due to the absence of pests and diseases. In my opinion, it is difficult to come up with a plant more convenient for the summer resident.
But back to agricultural technology. For the Middle Band, three methods are acceptable. I personally tried everything, and therefore I am not telling you to be smart. So.
In containers with a volume of at least 20 liters.With the onset of frost, I transferred the kiwi tubs to the veranda, and for a long time they delighted me with their fancy leaves and delicious fruits. During wintering, I did not forget to periodically water. In early November, I took off the fruits, and they ripened quietly for me for several months. And if they are placed in a food container along with apples, they will become soft and sweet in five to seven days. Growing kiwi in containers makes it possible to use your own cuttings for further propagation.
On a trellis with a vine cover for the winter. Everything is similar to caring for grapes.
In a greenhouse, where emergency heating is designed in case of severe frosts. In the summer, I removed the side walls of this greenhouse for air access.
Kiwi varieties
There are two varieties in my garden Kiwi Hayward (female) and Matuo (male)... I grow rootstocks for seedlings from seeds for two years and then graft with a cultivar. Vaccination methods are generally accepted.
I use both budding and grafting into a cleft with a green cuttings, and into a cleft with a dry cuttings - the choice depends on the specific conditions and the time I have. It must be remembered that kiwi is a dioecious plant.
Fruits are produced only by female plants, but on condition that their flowers are pollinated by male pollen. By the way, I don’t grow “men” separately for myself - they are grafted below on the processes of female plants.
The main advice for amateur gardeners: do not waste time, extract seeds from kiwi fruits purchased in stores, dry, stratify and sow at home in small containers on the windowsills.
The seedling growing technology is the most common. And in two years you will get a lot of good rootstock that can be used for grafting the cultivar kiwi and for planting in the open field for acclimatization.
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
Is it possible to grow kiwi in indoor conditions: Is it possible to grow kiwi in ... 404: not found: We apologize to you ... Growing kiwi - grafting vines: Kiwi - grafting male and ... Growing kiwi at home: Kiwi (Chinese liana) - how ... How to disable ad blockers on our website (AdBlock and others): You have repeatedly requested such requests ... Search +: Advanced search on the site "Garden, ... A flower bed with herbs and aromatic plants - planting scheme: Plants and planting scheme for ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups.
Let's be friends!
It turns out that kiwi can not only be grown in a garden near Moscow, but also get your own harvest. Do you want to know how?
Now in any supermarket you can buy kiwi fruits grown on large tree-like vines. They are also sometimes called Chinese gooseberries, but the correct name of the plant is actinidia chinese delicacy (Actinidia chinensis var. Deliciosa). Upon careful study of the culture, it turned out that in the open field in a place protected from the wind, it can tolerate up to –20 ° С, and under shelter and up to –30 ° С. Therefore, if you "play" with winter shelters, you can try to grow it in the suburbs in the open field, and not at home.
Male and female kiwi plant
I planted the first kiwi seedlings in my garden near Moscow about 10 years ago, but only waited for flowering in 2012, although in the southern regions they bloom in the 3-5th year. First, the male plant bloomed, and the next year, simultaneously with the male plant, the female. Until the moment of flowering, the sex of the kiwi is difficult to determine, but when they bloom, this difference is clearly noticeable: the pistil on the female flowers is much larger.

Varietal affiliation of female plants (variety Hayward) I established only when the plants bloomed and the fruits began to ripen. Not knowing how the local bees and bumblebees would receive the overseas guest, he was a little overcautious: he manually pollinated all the flowers on female vines with a male flower.

The result was not long in coming, and now furry aliens from distant subtropics are ripening in my garden. However, I think that insects would have coped without my help.For the viability of pollen and the activity of pollinating insects, it is optimal that during the flowering period, which in our area falls on the end of May - beginning of June, the air temperature is + 15 ... + 20 ° С.
Kiwi: planting and care
Kiwis are planted in places protected from the north and north-east winds. Best of all from the south side of the house. Spring planting is preferred. Usually 5-6 female plants are planted per male. Taking into account the fact that kiwi has a superficial root system, the planting pit is made shallow: 0.5x0.5x0.5 m. Kiwis like well-drained humus-rich soils. The best ratio is considered to be 1–2 parts of rotted manure or compost to 1 part of garden soil. It is desirable that the root collar is 3 cm above the ground level, since a buried planting can lead to the death of the plant.

Kiwis love abundant watering, but without stagnant water. If the summer is dry, then once a week will be enough 20-30 liters for an adult plant. In a rainy summer, you can water much less often. In the year of planting, you do not need to feed, and in subsequent years - starting from May, about once a month, apply under one plant 20–25 g of nitrogen, 10 g of phosphorus, 10–20 g of potash fertilizers, finishing all top dressing no later than July. Fertilizers containing chlorine should not be applied. Plants are sensitive to high lime content.
Considering that this is a powerful fast-growing vine, for good development it is immediately necessary to install racks (pillars), between which to pull a support: wire or ropes. Kiwi propagated by rooting cuttings, grafting and seeds. However, with seed propagation, the vast majority of seedlings (70–90%) will be male plants, so it is better to purchase seedlings from collectors.
Diseases and pests in our conditions are practically not found on kiwi.
Forming and pruning kiwi
I think the most successful form of growing kiwi is single-tiered and two-tiered palmette.

With a single-tiered palmette at a height of about 0.5-1 m, two sleeves are formed along a wire (rope) stretched between the posts. And with a two-tier one at a height of 1.5–2 m, there are two more sleeves. After planting a seedling from young shoots, the strongest is left and tied to a peg, and the remaining shoots are cut out. If the plant is planted in early spring, wait for the leaves to bloom before pruning. When the shoot reaches the height of the first tier, it is cut off, thus stimulating the growth of lateral shoots, of which two arms are formed. In the spring, only dry branches are removed - at this time there is an active sap flow, and if you cut off living tissue, the cut will "cry" for a long time. In summer or autumn, weak, fertile, thickening shoots are removed, leaving mainly growing horizontally at a distance of 30–40 cm from each other.
Wintering kiwi
My kiwis are planted at a distance of 1 m from the southern wall of the house. In the first years in November, I untied the ropes from the posts, for which the vines were attached, and lowered the whips as low as possible to the ground, trying not to touch it. A trunk circle mulched to a height of about 10 cm. I put two wooden shields in the form of a hut (0.5 m high) over the vines so that the snow falling from the roof would not break the vines, and covered the shields with 2-3 layers of polyethylene on top. The hut was partially covered with snow falling from the roof. In early spring, when the night frosts cease to drop below –15 ° С, I opened the shelter a little so that on sunny days there would be no greenhouse effect and the vine would not wake up ahead of time. For a growing vine, even a small minus is critical. Several years ago, when the frost was -5 ° C (May 8), the vines that had started to grow froze to the ground. Fortunately, they did not die and were fully recovered by August. Mature plants are difficult to bend to the ground. I had to slightly change the design of the winter shelter. In the fall, on the racks to which the vines are attached, I lay cellular polycarbonate, fasten it with one end to the wall of the house and make a small canopy. I untie the vines from the racks and tilt them to the wall of the house.From the outside, I close them with 2-3 layers of polyethylene, which I attach to the racks. In such a winter shelter, without additional heating, vines hibernate almost without damage. Only unripe shoots freeze over. In May, when the threat of frost has passed, I remove polyethylene and polycarbonate.

Harvesting kiwi
All kiwi varieties ripen no earlier than December, but can ripen harvested. Therefore, they pluck them before the first frosts and ripen at home. To speed up ripening, you can put kiwi in one plastic bag with apples (1 apple for 10 kiwi).
Popular varieties of female plants
- Hayward - the most widespread variety in the world. Late maturing. Vigorous. The yield is high. The flowers are white at first, and after 2-3 days - cream, up to 6.5 cm in diameter, solitary, rarely in inflorescences of 2-3 flowers. Flowering lasts 10-14 days. The fruits are large, aligned, oval in cross section. Fruit length up to 6.5 cm, weight up to 100 g. The flesh is strawy-greenish.
- Bruno - early maturing. Vigorous. The flowers are white-cream, with a diameter of 5.5 cm, there are both single and collected in inflorescences of 2-3 pieces. Flowering lasts 10-12 days. Fruits are cylindrical in longitudinal section, round in cross section. Length up to 8 cm, circumference - 12 cm, weight 50–70 g. Green pulp.
- Monty - mid-season. Vigorous. Flowers are white-cream, up to 5 cm in diameter, single or in inflorescences of 2-3 pcs. Flowering lasts up to 12-14 days. Fruits are medium to large, slightly pear-shaped in longitudinal section and oval in cross section. Their length is 6.4 cm, circumference is 13.8 cm, weight is about 30 g. The flesh is greenish-yellow. The taste, in contrast to the listed varieties, is mediocre.
- Abbot - mid-season. Medium-sized. The flowers are white-cream, up to 6.5 cm in diameter, both single and collected in inflorescences of 2-3 pcs. Flowering lasts 10-12 days. Fruits are evenly colored, elongated longitudinally and rounded in transverse directions. Fruit length 6.6 cm, weight 65 g. The pulp is green.
- Jenny - medium early. Medium-sized. Self-pollinated. Fruits weighing up to 60-80 g. Similar to Haywardbut has smaller fruits.
Popular varieties of male plants
- Matua - an abundant and long-flowering variety. Vigorous. Flowers - from single to collected in inflorescences of 3-5 pcs. The villi on the peduncle are single, short.
- Tomuri - blooms a little later than the variety Matua... Vigorous. Long-lasting flowering, but less abundant. The flowers are large, from single to collected in inflorescences of 2-7 pcs. The villi on the pedicel are thin and long.

Learn how to grow figs outdoors in the middle lane.
In our country, there are actinidia colomicta, actinidia Giraldi, acute actinidia and polygamous actinidia. In the center of Russia, actinidia kolomikta is widespread, which can withstand frosts down to -45 degrees.
Actinidia kolomikta - a vine with thin branches, capable of conquering a height of 10–15 m. If a plant is not provided with support, then it spreads along the ground and sometimes does not bear fruit. The berries are smooth, greenish or yellowish with longitudinal dark stripes, oblong and even spherical. Contains many small black seeds.
You can get a crop of actinidia only if a male plant is planted next to the female specimen (one male plant is enough to pollinate five female ones). Another option is to plant 1-2 male cuttings in the crown of a female plant.
Male specimens can be found during flowering. Their staminate flowers are collected in inflorescences of 2-3, and at the end of flowering, the entire perianth falls off immediately (in female flowers, the petals fall off one by one).
Often summer residents are faced with the fact that only "men" grow up on the site, although the seller promised "women". The fact is that male specimens take root better than female specimens, it is much more profitable to graft them, especially if there are no industrial installations of artificial fog.
Actinidia is best propagated by green cuttings in summer or lignified - in early spring.Green cuttings are cut in late June - early July. The leaves are cut in half and planted to a depth of 1.5–2 cm in perlite, coarse river sand or a mixture of peat and sand in a ratio of 3: 1. It is advisable not to water the cuttings, but spray them several times a day from a hand sprayer.
Actinidia should be planted in a moderately lit area with fertile, well-drained soil with a slightly acidic or neutral reaction. Actinidia needs support: they put pillars 2.5–3 m high for it, and after 0.5 m they pull a wire or let it go along the pillars of a garden pavilion. From cats that are attracted by a specific smell, the trunks of plants are protected with a net.
Actinidia care is easy - weeding, feeding, watering. In the spring, at the beginning of the growing season, 15–20 g of ammonium nitrate, 5–10 g of superphosphate and potassium salt (per 1 sq. M) are introduced under actinidia. After feeding, the soil is shallowly loosened, watered abundantly with water, mulched with peat.
After harvesting, fertilizing is carried out with phosphorus and potash fertilizers. It is best to water the plants with a solution of ammophoska (3-4 tablespoons per 10 liters of water).
Care of the aerial part consists in the summer pinching of too long shoots and cutting dry branches. Spring pruning is not recommended: it causes a strong "cry" of plants - an abundant flow of juice through fresh wounds, because of this they lose a lot of nutrients.



