Content
 The cucumber plant is not endowed with strong roots, therefore it is not able to equally provide all ovaries with sufficient nutrition for their normal development. The procedure for forming a cucumber bush, leaving one main stem, solves the problem. You can learn more about this from the step-by-step description of the process and the video on the topic.
The cucumber plant is not endowed with strong roots, therefore it is not able to equally provide all ovaries with sufficient nutrition for their normal development. The procedure for forming a cucumber bush, leaving one main stem, solves the problem. You can learn more about this from the step-by-step description of the process and the video on the topic.
Varieties and hybrids
All cucumber varieties on the market today can be conditionally divided into:
- traditional;
- new;
- hybrids F1.
Before you start growing, it is very important to study the information about the different varieties and find the right one. The method of forming the bush will depend on the choice, and the quantity and quality of the crop will depend on it.
The formation of a bush is one of the nuances of the correct cultivation of cucumbers. Moreover, varietal cucumbers and hybrids require a different approach. If we bear in mind the former, then female flowers and, accordingly, the ovary are formed on their lateral branches, and only male flowers originate on the central stem. Therefore, most varieties grown in the greenhouse require pinching to enhance branching.

Cucumber ovary
For cucumbers that grow in open beds, pinching the shoots is not effective. Indeed, under these conditions, male and female flowers develop evenly on the branches and on the main stem.
Attention! Removal of excess ovary or branches should be carried out only with a very sharp and sterile instrument. So the plants are practically not injured and the risk of developing an infection is minimized.
Some hybrids throw out only female flowers, so their bushes do not require absolutely any formation. And some of them, in particular parthenocarpic ones, are formed by experienced gardeners into one stem.
Why form bushes
Cucumber plants require formation for several reasons:
- in heavily overgrown plantings, ideal conditions are created for the development of diseases;
- the plant spends a lot of energy on the development of shoots, respectively, the more there are, the fewer ovaries;
- a large number of leaves does not allow light and air to penetrate deep into the crown, which disrupts the process of photosynthesis;
- It is more difficult for pollinating insects to get to flowers through dense thickets.
Advice. During the formation of the bush and harvesting, you should be very careful with the plant, that is, do not turn the whips and leaves in the opposite direction. From such inaccurate actions, the cucumber can stop growth.
The main manipulations carried out during the formation of cucumbers
Garter... Thanks to the well thought-out garter, you can compact the planting without harming the plants. You need to start when the growing cucumber reaches the first support, located horizontally. The process must be very careful so that the cucumber does not break out of the soil by its roots. Then the plant is regularly wrapped around the trellis. The top should not abut anywhere, that is, it should be free.

Cucumber trellis
Lateral shoots can be tied to the main stem, or they can be attached to adjacent trellises with a deflection angle of 30-35 degrees. This way, excess foliage will not form.
Removing leaves... All leaves that touch the ground, that is, the first 2-3-4 leaves, are subject to cutting. Water gets on them when watering, they age early, etc., therefore, it is better to remove them in a timely manner.
Attention! The leaves should not be broken out, but carefully cut out so that a lacerated wound does not form - a notorious source of fungal diseases.
Removing side shoots... In another way, the branches are called stepchildren, and most of them must be removed when a bush of varietal cucumbers is formed. This contributes to an increase in the formation of female flowers and earlier ripening of fruits. Stepchildren are removed when they reach 3-5 cm. If this is done later, the plant becomes depleted and weakens. Accordingly, the yield decreases significantly.
Attention! Many varieties are known in which ovaries are formed only on stepchildren. Therefore, if they are removed, there will be no fruit at all.
Topping... This is the process of removing the top of the lateral branch, which promotes the formation of 2nd and 3rd order shoots.
The main shoot can also be pinched. This is done in order to stop further growth. It is also pinched when a plant is formed in 2-3 stems. In this case, more ovaries will form on the side shoots.
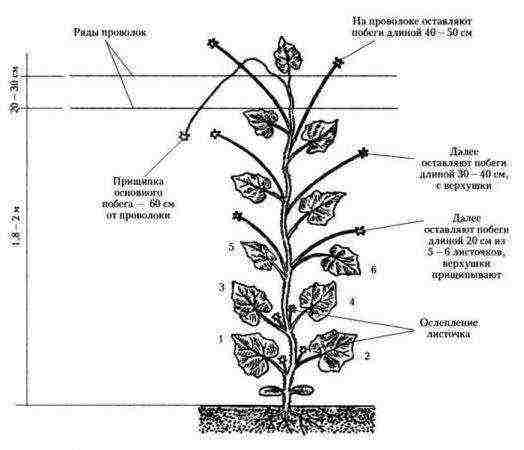
The scheme of the formation of a cucumber bush
The scheme of the formation of a cucumber in one stem
Cucumbers of the parthenocarpic type undergo such a formation, in which all female flowers are located in the axils of the central stem.
- The main stem can only be pinched when it reaches a certain height, for example, the top of the garter.
- All lower leaves must be removed.
- In the above 3-4 leaves, all axillary flowers are blinded. At the same height, lateral shoots are removed, which should not reach 5 cm.
- Further, in 5, 6 and 7 leaves, the lateral branches are pinched, leaving about 20 cm.
- At a height of 1-1.5 m, stepchildren leave 30-35 cm with 2-3 leaves and ovaries in the axils.
- 2 m - shoots 40 cm with 2-3 internodes.
- If the central shoot grows weakly, it is pinched at this height, and if the growth continues intensively, it is thrown over the top of the horizontal trellis and let down.
Attention! Those stepsons who are not removed must be distributed in a checkerboard pattern. So there will be no shading and disturbance of air exchange inside the bush.
You can start forming a young plant only after the appearance of 8-9 leaves. This is about a week after planting the seedlings in the ground. To begin with, it is advisable to stretch the wire along the bed at the level of the top of the grown plants.
How to form bouquet-type cucumbers
This type includes hybrids in which 5-6 ovaries are formed in one node. Due to this feature, it is recommended to form them in only one stem. This reduces the load on the plant and the yield is not lost.

Bouquet-type cucumbers
All side shoots on these hybrids are completely removed up to the upper horizontal trellis. You can leave only 2-3 pieces under the very top, pinching them at the same time over the second sheet. In the lower part of the plant, at the level of 4 leaves, all ovaries and shoots in the axils are removed.
The correct selection of the variety and the concept of the appropriate formation of the bush are the main components of obtaining high yields. There is nothing difficult in this, therefore, everyone can learn simple rules and, following them, get a good harvest of quality cucumbers.
Formation of a cucumber bush in one stem: video
Breeders never cease to amaze gardeners with new achievements. A striking example is the appearance of bundle varieties of cucumbers, bearing fruit in bouquets of strong greens. Disease resistance, abundant fruiting, a wide selection of varieties, unpretentious care - this is an incomplete list of the advantages of this type of green vegetables.
Bunch cucumbers - origin and characteristics
Bundle varieties of cucumbers were named because of the peculiarity of the formation of ovaries in the nodes of the stems. Unlike the usual varieties, which form 1-2 inflorescences, this type of zelents is capable of producing from three to ten ovaries, luxuriantly growing from one node, which gave the second name of these vegetables - bouquet.
The yield of bunch varieties is amazing - with proper care, each plant is capable of producing a harvest of 400-500 fruits per season.
Ovaries in bouquet varieties form bunches of greens in the nodes of the stems
It is clear that such a miracle became possible thanks to the work of breeders, bunch varieties are first generation hybrids. Such hybrids are not suitable for harvesting seeds. Even if it is possible to collect future planting material, there will be no seedlings, or something will appear radically different from what was expected.
Among the representatives of this species are parthenocarpic varieties (F1 Blizzard, Boy with a finger, Robin Hood, Okhotny Ryad), and pollinated ones (F1 King of the Garden, Anyuta, Emerald City, Maryina Roshcha). The choice of the variety depends on where it is planned to grow the crop - in the open field, pollination by bees is possible, in the greenhouse, parthenocarpics are preferable.
One of the defining differences in this type of cucumber is the type of branching:
- Weak branching - lashes form few short lateral shoots, do not require pinching. Early ripening, fruiting up to one and a half months, bring a high yield. These include varieties F1 Alphabet, Bouquet, Balalaika. Representatives of such varieties are good for early harvests.
- Limited branching gives a longer fruiting time, few lateral processes. Leaving is not difficult, pinching takes a little time. The cultivars are mainly grown in the greenhouse. Examples: F1 Grasshopper, Cheetah, Trump card.
- Strong branching in varieties that bring greens for a long time, suitable for greenhouse conditions and in the open field. Representatives of this species: F1 Marina grove, Buyan, Boy with a finger, Junior lieutenant, Chistye prudy.
Popular varieties
There are many varieties of bouquet cucumbers, the choice depends on the preferences of the gardener and the conditions in which the cultivation is planned. Breeders have bred many different types of bouquet greens, with different types of branching, early maturity, and duration of fruiting.
Bunch cucumbers for open ground
In principle, many varieties of bunch cucumbers are suitable for cultivation in open ground. The choice is limited by the climatic conditions of the area in which it is planned to plant them. In the middle lane, open ground cucumbers are planted under film shelters or tunnels, in the southern regions they do without shelters.
You can choose a variety depending on what is preferred: early harvest or long ripening of cucumbers. Consider varieties popular with gardeners.
- F1 Green wave - refers to parthenocarpic, pleases with an abundance of fruits. It stands out for its early maturity - you can eat fresh greens in 38-40 days after germination. This option can be grown without shelter, the variety tolerates a drop in temperature, the stem is distinguished by good branching. This representative of bouquet varieties has neat cucumbers, 9–11 cm in length.
- F1 Mother-in-law is a hybrid of the parthenocarpic category. A fresh harvest pleases the owner 45–48 days after germination. Bunches of ovaries (3-4 per node) bring medium-sized cucumbers, 11-13 cm long.
- F1 Zyatek is a pollinated variety forming 6-8 ovaries (female). After 45 days from the day of germination of seedlings, medium-sized (10-12 cm) greens are ready for consumption. Favorably distinguishing nuance - fruiting does not stop with the deterioration of external conditions.
- F1 Little son is a strong branching variety, parthenocarpic. In the axils of this medium-sized cucumber 3-4 ovaries are formed, according to the type of flowering - female. Little son is a representative of early ripening varieties, greens of 6-10 cm in size ripen in 45 days from the emergence of shoots.
- F1 Heroic strength - parthenocarpic. Gives early (37–40 days from germination) results, long fruiting, moderate branching of the stem. Juicy greens ripen from 6-8 ovaries, the length of which does not exceed 13 cm.
The efforts of breeders have instilled resistance to major diseases in bunch cucumber varieties. Even in affected plants, the ability to bear fruit (disease tolerance) does not decrease.
Varieties of bunch cucumbers for growing in shelters
All varieties for open ground are suitable for growing in greenhouses, this is especially true for regions with unstable climatic conditions. But preferable are the types of bunch cucumbers with a moderate or weak type of branching and parthenocarpic type of ovary formation. This is due to considerations of practicality and ease of maintenance.
To optimize the growing conditions, a strong thickening of the plantings should be avoided, this leads to a lack of lighting, which adversely affects the development of plants. With the choice of parthenocarpic varieties, there is no need to worry about pollination of the ovaries.
Indoors, cucumbers are provided with the most favorable conditions
Among the bouquet varieties suitable for growing indoors, consider the following:
- F1 Blizzard is a weakly branching parthenocarpic. The emerged plants give a harvest in 37 days. In each node of 4–5 ovaries, bundles of gherkins develop, the length of which is no more than 8 cm.
- F1 Balcony - as the name implies, the variety is bred suitable for cultivation in small areas - loggias, balconies. Will feel comfortable in greenhouses and temporary shelters. The internodes of this parthenocarpic are short; the stem branches weakly. In 41 days after germination of seedlings, green plants ripen 6-10 cm long, from two to eight in each node.
- F1 Swallowtail is a precocious parthenocarpic, well suited for greenhouses and balconies. The distance between the nodes is small, the shoots grow small (determinant). In the nodes, from 2 to 11 ovaries are formed, which, 40 days after the appearance of the first shoots, give crisp, dense greens 7–11 cm long.
- F1 Labyrinth - fresh cucumbers of this parthenocarpic appear quite early - 38–40 days after germination. Small fruits, about 12 cm in size, are formed in 4–5 pieces per bunch. The stem has medium branching, few shoots.
- F1 Urban Gherkin - This gherkin is harvested early in 40 days from germination. The cucumbers are thin - 2.1–2.7 cm in diameter and 9–12 cm long. The undoubted plus of this species is shade tolerance, the plant grows well on shaded balconies, it is also cultivated on the windowsill in the apartment. Ideal for greenhouses. The knots form three to nine ovaries.
- F1 A boy with a finger - in the nodes of this parthenocarpic, from two to eight gherkin type zelents 8–10 cm long are formed. Due to the early maturity, they ripen within 36–38 days after the germination of crops.
- F1 Junior lieutenant - interesting for a special property that distinguishes him from the background of the beam counterparts - self-regulation of branching. Ovaries are formed on the main stem, while such a load does not allow lateral shoots to develop. After harvesting from the main stem, lateral shoots also start growing, on which cucumbers also ripen. Between the germination of crops and the ripening of zelents, 40–42 days pass. The number of ovaries in bunches is from 2-3 to 5-7, the cucumbers are juicy, 9-12 cm long.
Cucumbers with slow fruit growth
For those gardeners who come to the plots only on weekends, specially bred varieties with slow growth of zelents are suitable. Breeders have bred a number of varieties that form many inflorescences, when ripe, the growth of the cucumber slows down when it reaches a certain size. This is convenient when it is impossible to harvest the crop regularly every other day.
- F1 Acorn is a bee-pollinated hybrid, a representative of the cucumber type with slow fruit growth. Weakly branching, gherkin type, forms bouquets of 10-12 ovaries in knots. Calmly tolerates the infrequent collection of fruits that stop growth when they reach a length of 8–10 cm. Delicious, juicy greens can be removed after 45–47 days from germination.
- F1 Captain - good yields, bee-pollinated.The branching of this variety is limited, the growth of zelents is slowed down. In the knots, bunches of 2 to 10 pieces are tied, 40–43 days after germination of the seedlings, fruits 8–10 cm in size are ready for harvesting.
- F1 Stay healthy - unlike previous parthenocarpics. It is not a hassle with leaving due to weak branching and slow growth of fruits. The first cucumbers ripen 40–43 days after the germination of seedlings. Each node contains from two to six ovaries. 6-9 cm gherkins are good both pickled and salted.
Video: new varieties of bunch cucumbers
Features of growing bunch cucumbers
Bundle varieties of cucumbers actively bear fruit, forming a large number of ovaries. For their full development and growth, it is important to remember that such a load on the plant requires careful care and makes additional demands on the conditions of detention.
- Plants are demanding for light. It is necessary to arrange bunch cucumbers in well-lit areas, without shading. Insufficient illumination will adversely affect the formation of ovaries.
- Weekly feeding is especially important during the period of growth and ripening of fruits. Nutrients are consumed for the growth of numerous fruits, their lack will lead to a decrease in yield. Cucumbers are fed with small doses of complex mineral fertilizers, using, for example, Crystalon, a solution in the volume of one tablespoon per bucket of water.
- Regular collection of fruits is required for the ripening of subsequent ovaries, usually the collection is carried out every other day. Bouquet cucumbers are grown on a trellis
Formation of bunch cucumbers
Bouquet varieties are rarely planted - one or two plants per square meter.
The formation of bundled cucumbers is carried out in one stem, otherwise the plant's forces will be spent on lateral shoots, which leads to a decrease in fruiting. The four lower nodes of the main stem are "blinded" - flower stalks break off, shoots are removed. Thus, ovaries remain on the stem in each node with one leaf.
Bunch varieties are formed into one stem
Video: forming a cucumber into one stem
What gardeners say
Cucumbers of bundled varieties make it possible to collect bountiful harvests while saving space, and the taste of the fruit will appeal to lovers of juicy vegetables. Perhaps caring for them is burdensome, but choosing the right variety and putting a little more effort, the harvest of strong, crispy gherkins will certainly delight its owner.


