Content
- 1 Dates for planting beans in open ground
- 2 Do I need to soak beans before planting?
- 3 Choosing a place for planting beans
- 4 Preparing a site for planting beans
- 5 Planting scheme for beans in open ground and planting depth
- 6 How to plant beans in rows, look at the video:
- 7 Planting corn and beans together
- 8 Planting curly beans in the video:
- 9 Do I need to water the beans after planting
- 10 How many bean seeds sprout
- 11 How to care for beans outdoors
- 12 Useful video about growing vegetable beans:
- 13 Diseases and pests of beans
- 14 Harvest time of beans
- 15 Bean varieties with photos and descriptions
- 16 The many-sided beans
- 17 What you need to grow beans outdoors
- 18 Choosing a method of sowing beans
- 19 Bean care
- 20 The main pests and diseases of legumes
- 21 The nuances of growing in the regions
- 22 Types and varieties of beans
- 23 How to plant beans in an open field or greenhouse
- 24 Outdoor Bean Care
- 25 Harvesting and storing beans
- 26 When to plant beans outdoors
- 27 Are beans afraid of frost
- 28 The most popular varieties for planting
- 29 Planting rules and agricultural techniques for growing in open ground
- 30 Leaving after disembarkation
- 31 Pests and prevention
- 32 The correct timing of harvesting in the country or in the garden
Many people are familiar with such a culture as beans since childhood. Soups are made from it, added to salads, stewed, and prepared. Beans belong to the Legumes family. Grows in the form of a climbing herb or shrub. The color of the fruit can be varied, with a very interesting pattern.
Beans are among the ten most useful foods. Due to the content of about 20% of protein in terms of energy value, it is equal to meat, the balanced composition of the product supplies almost all body systems with useful substances.
Simple agricultural technology and unpretentious care, the possibility of obtaining a generous harvest of useful and nutritious fruits - all this prompts you to set aside a piece of land for beans on your site. Even a novice vegetable grower can handle the cultivation of beans. Beans are successfully cultivated in Belarus, Ukraine, Moscow region, the Urals and even in Siberia.
Dates for planting beans in open ground

Beans planting in spring photo shoots
Beans are a thermophilic crop. They start planting it in the second half of May, when the threat of return frosts has completely passed. The lowest temperature that young seedlings can survive is 0 ° C, at -1 ° C the seedlings die. If the frost was short, then the sprouts will survive, but their development will be slowed down, which will negatively affect the yield.
Covering with a film, agrotextile or the construction of a temporary shelter will help protect against a sudden drop in temperature, as an option - make a fire at night so that it smokes until morning, this will help ward off small short-term frosts.
When planting beans, be guided by the weather conditions:
- At a depth of 10 cm, the soil should warm up by 12-15 ° C (according to popular observations, this approximately coincides with the period of flowering of chestnuts).
- To start sowing a little earlier (in the future it has a positive effect on the yield), the soil should be "warmed up" by covering it with plastic wrap. After sowing, cover the beds again until the night temperature is + 12 ° C.
Erect varieties should be sown first, after a week, start sowing climbing ones. Bush varieties are recommended to be sown in early July (just at this time, the beds will be free after harvesting early-ripening vegetables).
Planting dates for beans in the middle lane and the Moscow region
Experienced gardeners carry out seeding in several stages. From mid-May to early June, you can sow beans every 10 days.
Planting dates for beans in Siberia and the Urals
In open ground, seeds can be planted in early June.
Do I need to soak beans before planting?

How to soak beans before planting and how to process
Seeds are sown directly into open ground without growing seedlings. Whether to soak beans before planting, think carefully: prepared seeds will need to be planted immediately, regardless of weather conditions or sudden cases that have appeared. Therefore, schedule your time so as not to spoil the seed in vain. In addition, soaked seeds should be planted in moist soil, because if there is a lack of moisture, the sprouts will simply die. Therefore, when planting, water the holes and plant the soaked seeds in the mud, or water after planting.
To get earlier shoots and protect young shoots from diseases, it is advisable to pre-treat the seeds before planting.
Start processing in the evening before sowing. The process takes place in several stages:
- For 10 minutes, place in a slightly boron solution of potassium permanganate, then rinse with water.
- Then soak in wood ash infusion for 2 hours, rinse again.
- Wrap in a damp cloth and leave at room temperature overnight.
- Immediately before sowing, dip in boric acid solution for 5 minutes.
When deciding whether to soak beans before planting, consider the following factors:
- If you plant in dry soil and there is no way to water, do not soak it better.
- If it will rain soon and you are sure you will have time to plant, you can soak and not water when planting.
- It is advisable to soak if it is already late, and you want to get seedlings as soon as possible.
- When planting large areas in the field, it is better not to soak, you will not have time to water, and the seeds may die from lack of moisture in sufficiently dry weather.
Choosing a place for planting beans
Illumination
Choose a well-lit place for cultivating beans, avoid drafts and strong winds. Young, immature shoots are very sensitive to this. Beans are often sown along fences, under apple trees.
Soil composition
Clay soils are contraindicated, since they do not allow water and air to pass through well, and the roots of the plant do not tolerate dampness (they will simply rot). Loose soils with a nutritious top layer are best.
Predecessors
Take into account the crops that were previously grown on the site. Excellent predecessors are carrots, potatoes, cucumber, peppers, tomatoes, eggplant.
Preparing a site for planting beans
Site preparation consists in digging to the depth of a shovel bayonet and adding one of the nutrient compositions (per 1 m²):
- Compost or humus (4 kg), 2 tablespoons of superphosphate and dolomite flour, 1 tablespoon of ammonium nitrate.
- About 2 kg of humus or compost, 30 g of superphosphate, 20 g of wood ash.
Planting scheme for beans in open ground and planting depth
Planting bush beans scheme:

Planting bush beans photo
The holes are made at a distance of 20-25 cm, in the aisles they keep a distance of 40 cm, planting depth of beans is 5-6 cm.
Planting curly beans scheme:

How to plant curly beans photo
For climbing varieties, the row spacing should be 45-50 cm. They will need support.
Place a few seeds (5-6 pcs) in each hole, pour warm water. When the shoots appear and give one true leaf each, leave 3 shoots in the hole (the rest can be transplanted or simply removed).
Planting scheme for green beans or asparagus

How to plant asparagus beans photo
It is also convenient to plant green beans, or asparagus, in rows: the depth of the grooves is about 5-6 cm, the row spacing is left 40-60 cm wide, in the row between the beans, 10 cm is enough.
How to plant beans in rows, look at the video:
The method of planting beans described in the video is very convenient for use in a summer cottage and a personal plot.
Planting corn and beans together

Corn with beans planting and care photos
Climbing beans are often grown in conjunction with corn. Landing is done under a hoe: shallow holes are made with a hoe, shoveling the earth in one direction, throw 2 corn seeds and 2-3 beans each, rake the hole with your foot and move on. The distance between the rows is 0.7 m, in the row between the holes - 30-40 cm.
Further care of the plants is simple: timely weeding, if it is in the steppe. If at home, you can water occasionally to get a rich harvest.
Planting curly beans in the video:
Do I need to water the beans after planting
When planting in the steppe, the beans are not watered, if this is a personal plot, it is better to plant the beans in the mud and sprinkle with damp earth (before planting, pour some water into the holes or rows). This does not form an earthen crust on the surface, and it will be easier for young tender sprouts to break through.
How many bean seeds sprout
The acceleration of germination is facilitated by the treatment of seeds with a growth stimulator and soaking.
Untreated bean seeds begin to sprout 7-10 days after planting. If the temperature of the air and soil is below the recommended values, then the seeds germinate for 5-7 days longer.
How to care for beans outdoors
Beans are unpretentious in care, requiring minimal effort on the part of a person. It is useful to hud up young shoots in order to give them stability.
How to water
The plant is hygrophilous. It is important to ensure regular, balanced watering if you want to get a lot of beans. Pay special attention to this point during the period of pod formation. Watering is carried out about 1 time per week, determine the rate of water for the bush "by eye", the main thing is to prevent the soil from drying out. For irrigation, it is better to use softened water with a temperature of at least 18 ° C. For this purpose, you can install a barrel in the garden to collect rainwater or settle tap water.
How to feed
Beans are usually not fed. However, a high level of agricultural technology will allow you to get a much larger harvest. The culture is responsive to feeding, but don't overdo it.Otherwise, the tops will actively develop, which will reduce the ovary of the pods.
If you have taken care of laying the nutrient layer during planting, it is enough to feed three times per season.
- The first feeding is carried out 1-1.5 months after germination. Apply a complex of mineral fertilizers with an emphasis on nitrogen and phosphorus. You can add superphosphate (30-40 g per 1 m²).
- For the formation of fruits, a second feeding should be carried out 3 weeks after the first. Add 10-15 g of potassium salt per 1 m² of area.
- The third time is fed after another 3 weeks.
Remove weeds from the area regularly.
After watering, gently loosen the soil in the tree trunk circle.
Useful video about growing vegetable beans:
Diseases and pests of beans
Sources of disease are infected seeds, so discard poor quality seeds (shriveled, darkened, unevenly colored, with strange dots or spots) and be sure to pre-treat. Choose more resistant varieties (we talked about them earlier). In southern regions, sow later so that plants form at 25 ° C. Also, a measure of control against diseases and pests is the observance of crop rotation (in the same place they are grown with an interval of about 4 years).
Bean diseases:

Bean anthracnose
- Anthracnose - the whole plant with leaves and fruits is covered with rusty spots.
- Powdery mildew - recognized by the presence of a whitish bloom.
- Ascochitosis - spots with a black core and a blurry outline appear on the leaf plates. The defeat most often occurs at the fruiting stage - it is too late to heal.
- Rust - the leaves become covered with brown spots, which quickly fill the plant, literally killing it. Most often passes from milkweed weeds. If the disease occurred even before flowering, treat with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid.
- Deforming and yellow mosaic - leaf plates are covered with yellow specks, they become wrinkled, the growth rate slows down. However, the virus may not affect the fetus.
- Bacterial wilting - the edges of the leaves are covered with yellow spots, then they turn completely yellow and fall off. The disease develops in high humidity, so avoid sprinkling.
Bean pests
Pests are not often disturbed. Among them:
- Aphid
- Whitefly
- Bean weevil
- Sprout fly
In addition to the preventive measures described above, timely harvesting (before the pods crack) will help protect the beans from pests. To destroy pests, you should hold the beans in the freezer for 3-4 days.
Before and after flowering, you can carry out treatment with a biological product of a wide spectrum of action.
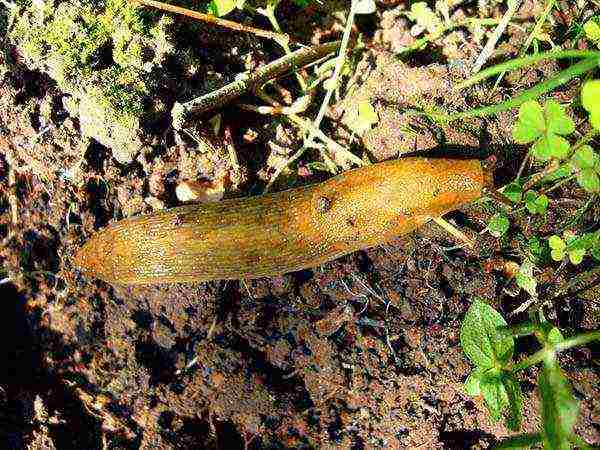
Bean stems and leaves can attack slugs. It is important to carry out weeding in a timely manner, because gastropods love a cool, moist environment. These pests are collected manually or use special traps.
Harvest time of beans
The timing of harvesting depends on the variety and variety of the crop.
Do not overexpose the asparagus beans in the garden - in the dried state, the quality of the product is lost.
If you plan to use the fruit for conservation, it can be picked slightly unripe. To store the beans dry, you must wait until they are ripe. But don't be late so you don't have to harvest beans from the ground.
Ripening can occur unevenly: in the shade of its own tops, some ovaries remain greenish, and at the tops, the pods are already dry. Remove the last, leave the rest to ripen.
It is not necessary to manually remove the beans from the pods. Take a bag or spread a blanket, lay out well-dried pods, and use a stick or other similar object to walk around with moderate effort. Remove the husk and sort the beans, dry them and store them. Store in glass jars with a tight-fitting lid (preferably glass or metal).
Bean varieties with photos and descriptions
The common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) is a cultivated species for the purpose of obtaining a crop of beans. Among the varieties (curly or bush), bush beans are most often preferred.
The variety of varieties complicates the choice. Consider the classification depending on the adaptability of the variety to the specific climatic conditions of a particular region.
Bean varieties for Ukraine, Belarus, Moscow region

Green beans Moscow white beans 556 photos
Moscow white green-leafed 556 - forms bushes about 25 cm high. The beans are covered with a very thin parchment layer (it boils rather quickly). The variety is resistant to both drought and high humidity. The period from sowing to technical maturity is 100 days.

Curly beans Nomad photo
Nomad is a climbing variety with medium ripening periods. The beans are ovoid and have a shade of ocher with a pale purple pattern. They do not have fibers and parchment layers, which makes the structure soft and delicate.
Bean varieties for the middle lane and the Urals
Orange - bush plants 35-55 cm high. Ripening early (80-90 days). The fruits are distinguished by their high taste. With 1 m², you can harvest within 200 g.
Pink - the bush curls, the stems reach a length of about 3 m, needs support. The beans have a marbled pink color and are delicate in texture (fibers and interlayer are absent). It is universal in application (the unique taste is preserved in any form). Ripening period is 65-85 days.
Bean varieties for Siberia

Curly beans with red flowering Photo Winner
The winner is the curly variety. The fruits are large, the length of the pods is about 30 cm. Thanks to good immunity, resistance to cold weather, cultivation in Siberia is possible. The variety has fiery red flowers, which is why it is often used for decorative purposes.

Asparagus beans Butter king photo
Butter king - asparagus beans, ripening period is 1.5 months. Tubular fruits will please even gourmets. The length of the pods is about 25 cm. The application is universal: freezing, canning, preparation of beans in dry form.
Beans are a popular and unpretentious plant. It is pleasant to grow this crop: it grows quickly, and its fruits are used at any stage of maturity. From a variety of varieties with different growing seasons and degrees of resistance, you can choose the one suitable for any region and climate.
The many-sided beans
Beans are valued for their easily digestible vegetable protein, a mass of useful microelements and vitamins. But the plant is beautiful in itself: large leaves resembling lilacs, an abundance of small colorful flowers - from white, pink to purple. And the brighter the color of the petals, the darker the beans.
Flowering begins 40-60 days after sowing and lasts 15-20 days. Gradually, the plant is "hung" with beans or, as they say, pods - flat or round, straight or saber-shaped, variegated or green. And it is not necessary to wait for autumn for the seeds to ripen: immature juicy fleshy shoulder blades of many varieties are eaten in the summer.
A good bonus is that this culture is self-pollinated.

Each variety of beans has a flower of a certain color and original seeds.
Video: the benefits and harms of beans
Bushy and curly
Bush beans are distinguished by their relative cold resistance and earlier ripening periods compared to the curly type. The plant is a branched bush with a height of 25–30 cm to 70 cm. Bush beans are indispensable for growing in regions with short summers, they do not require tying. For better ventilation and lighting, it is recommended to plant such beans in a checkerboard pattern.
Jack and the Bean Kernel: Climbing Plant Varieties
Of course, beans will not reach the sky, as in a fairy tale, but lashes with a length of 3 m or more also look magical. They braid everything that sticks out, stands and grows nearby - hedges, artificial supports, trees.Moreover, a braided fruit tree (beans are friends with an apple tree) does not suffer at all from such a neighborhood. Plant supports are installed prior to sowing.
The beans and leaves of curly beans, or, as it is also called, staked beans, do not come into contact with the ground, therefore they remain clean and healthy. The disadvantages include the relatively late formation of the shoulder blades (2 months after sowing) and increased thermophilicity. Climbing varieties are both green (asparagus) beans and shelling beans, which are grown for the sake of seeds.
Photo Gallery: Curly Bean Supports
What are Asparagus Beans
Cooked whole or cut into pieces, these beans resemble asparagus in appearance, and they are said to taste similar. From overripe asparagus (aka sugar, or green beans) seeds are husked, which are sown the next year or cooked as usual. But the special charm lies in the unripe beans with fleshy pulp and unripe beans. If you pluck the next portion of the pods every 4-5 days, new ones will grow with renewed vigor. Asparagus varieties are both bushy and climbing.

Asparagus beans are surprising in both color and length of the pods
What you need to grow beans outdoors
At first, of course, the earth is warm. In soil heated to + 12–15 ° C at a depth of 10 cm, and at an air temperature of + 20–24 ° C, the germination time ranges from 4–5 days to 8–10 days. The culture does not tolerate frost, already at + 3 ° C its leaves turn yellow, so the planting time is adjusted to match the cucumbers. During the growing season, beans need a lot of sunlight, a minimum of wind, and regular watering.
Comfortable spot
Beans love the sun, so the south side, protected from the north, is the best place for the beds. Combined plantings, tested by our ancestors, are used: bush varieties fit perfectly between potatoes, curly ones let them trudge along the corn. Separately spaced bean beds are protected from strong winds with a curtain plantation. Hot winds dry up the leaves, turning cheerful plants into a lifeless herbarium, and flowers and young tender ovaries fall off. One strip of, for example, the same corn up to 2.5 m high will reliably protect undersized plantings on a plot of land 8–12.5 m wide.

Beans grow well among potatoes and corn
Successful predecessors
Although vegetable beans are relatively undemanding to their predecessors, they are worth paying special attention to. Cucumbers, cabbage, potatoes, root vegetables, melons and gourds - extra-class options. Of the siderates, preference is given to lupine, which reduces the acidity of the soil. Beans are not planted after the beans, the culture is returned to its original place no earlier than 3-4 years later, so as not to pick up a "familiar" sore or pest. Onions and beans planted side by side have a mutual depressing effect. But after the legumes, any crops are safely planted. Thanks to nodule bacteria in the soil, "deposits" of nitrogen are formed in an easily accessible form.
Photo gallery: after which crops is it better to plant beans
Suitable soil
The issue of the acid-base balance of the soil is approached with attention, especially when a new site is being developed. Any deviations in the direction of increasing acidity or alkalinity have a detrimental effect on plants, although the latter is less catastrophic for beans. So, on acidic beds, nutrients pass into a form that is not assimilable for plants, fertilizers do not "work", the activity of beneficial bacteria freezes, and on strongly alkaline soils, iron is not assimilated. Beans prefer well-drained neutral (pH 6–6.5) or slightly acidic soils, such as loam and sandy loam.
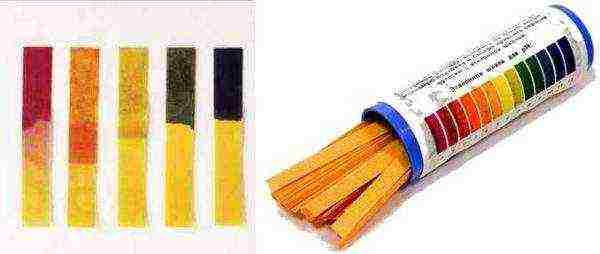
You can determine the acidity of the soil at home using litmus paper
Not the best option for beans and soil with a high salt content - salt lick.To independently determine the pH level of the soil, specialized stores sell litmus paper, which is accompanied by a scale of acidity. If, nevertheless, there is a need to improve the quality of the land, this is done as follows:
- to neutralize acidity, the following substances are scattered over the soil surface without embedding: slaked lime (fluff) per 1 m2 - 0.5 kg of lime for strongly acidic soils, 0.2 kg for slightly acidic; dolomite flour (0.3-0.4 kg per 1 m2), it, among other things, increases fertility, since it contains calcium carbonate and magnesium; chalk - 0.4-0.5 kg per 1 m2 of strongly acidic soil, 0.2 kg - slightly acidic; wood ash - 0.2-0.3 kg per square. On deoxidized soils, do not use ammonium nitrate or ammonium sulfate. Liming is carried out at least one year before planting the beans;
- for desalination (desalination) of the soil in the fall for digging, add gypsum at the rate of 10-30 kg per 1 hundred square meters, watered abundantly; in winter, they provide measures for snow retention, in the spring, digging and watering are repeated;
- the alkaline reaction is reduced by the addition of aluminum sulfate, which is sold in agricultural stores (to lower one pH unit, 550 g of substance per 1 m2 is needed); sublimated sulfur (90 g for the same land area); peat, ammonium nitrate.
The right fertilizers
Soil preparation is carried out either in autumn or early spring. In the fall, compost, peat or humus (4 kg per 1 m2) and 250-300 g of wood ash are applied to soils that are tired or with an insufficient amount of humus. Beans are never planted in the same year on soil fertilized with organic matter; this can be done in 2-3 years.
The roots of beans are inhabited by bacteria that assimilate nitrogen from the air, therefore, the abundance of organic matter rich in nitrogen, or excessive enthusiasm for nitrogen-containing chemistry leads to the fact that the growing season of the culture is stretched, and the crops are lodged. Nevertheless, marginal soils need "starting" doses of nitrogen, which are applied at the rate of 20-30 kg per 1 ha (20-30 g per 10 m2 or 2-3 g per 1 m2).

All legumes, including beans, accumulate nitrogen well in the soil and are good precursors for any plants.
The miraculous ability of these bacteria to enrich the soil with nitrogen for the next season gives the soil a special "taste". For example, beets sown in bean beds become surprisingly sweet, which the author has personally seen more than once.
Beans need mineral fertilizers, which are applied during autumn or spring digging to a depth of 25–27 cm: 30 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium chloride per 1 m2. Immediately before sowing (pre-sowing fertilizer), 30 g of ammonium nitrate is applied to each square. The combination of pre-sowing and pre-sowing soil fertilization contributes to the uniform development of plants and their amicable ripening.
Photo gallery: fertilizer for beans
Choosing a method of sowing beans
There are 2 sowing methods, let's call them conditionally wet and dry.
Wet way
- On the bed, holes are prepared with a step of 10-15 cm with a distance between rows of 40 cm. For vigorous climbing varieties, the distance between the holes is increased to about 80 cm, while increasing the row spacing to 50-60 cm.
- A handful of wood ash and humus, compost are added to each hole.
- The wells are watered with warm water.
- Place 2 seeds in each with the notched edge down. In this position, the tops and roots are already set the correct direction of growth.
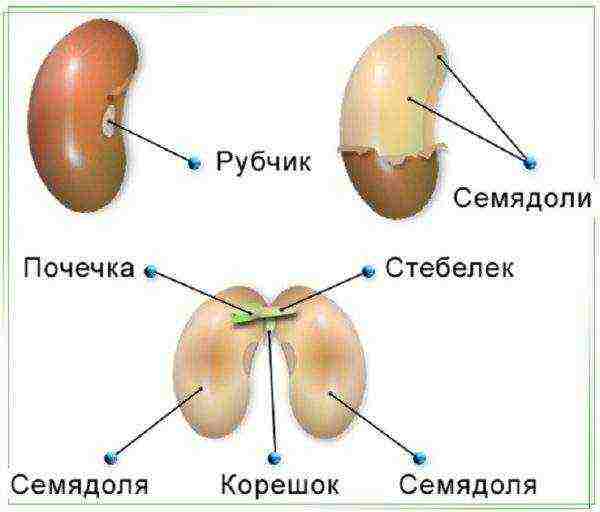
Lower notch position on bean seed saves growth energy
- On "normal" soil, the beans are buried by 2–3 cm, and on dry soil, by 4–5 cm.
- To create a comfortable microclimate, the ground is covered with a film.
- The shelter is periodically raised for ventilation.
- As soon as shoots appear, the film is removed and the soil is carefully loosened.

As soon as bean sprouts appear, the film must be removed.
Dry sowing method
The beds are prepared in the same way, but the holes are not watered... Procedure:
- The seeds are buried in the ground.

You need to put two beans in each hole.
- The holes are designated with sticks.
- And then the entire bed - rows and aisles - is mulched with chopped grass. The thickness of the layer should not exceed 10 cm. Like the film, the mulching layer creates the necessary microclimate, and no crust forms on the ground.

Dry grass mulch allows you to create a comfortable microclimate for plants in the garden
- The wells are poured with warm water from a watering can with small holes at the rate of 5–7 liters for each.
- When the sprouts become visible, the mulch is carefully raked off in order to loosen the soil, and then returned back.
Seed preparation before planting
First of all, before sowing, the beans are sorted by hand to find those affected by the caryopsis bug. It bites into the bean seeds, leaving round holes. Dark spots, which are clearly visible only on white beans, indicate that weevils are sitting inside such "burrows".
Various pre-planting methods are used:
- before sowing, the seeds are kept in a 1% (10 g per 1 l of water) solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes, washed with running water, dried;
- soaked in biofungicide (Baktofit, Trichodermin) to prevent powdery mildew;
- immediately before sowing, immerse in an aqueous solution of boric acid (+40 ° C) and ammonium molybdate (2 g per 10 l of water) for 5 minutes;
- spray with a solution of Boric acid: for 1 kg of beans, use 10 mg of the drug, dissolved in 1 liter of water;
- soaked in a material moistened with melt water for no more than 15 hours, and preferably overnight: if you leave the beans to lie longer, they will begin to sour and lose their germination.

When soaking, the beans are covered with a damp cloth or placed on cotton pads
Video: planting beans in open ground
Bean care
The main care consists in weeding, loosening the soil in the aisles and rows, watering. When the plantings grow up, they are mulched: such beds do not dry out, and weeding is minimized. When the beans bloom, they forget about the hoe for a while, so as not to break off the flowers with a careless movement. A variety of supports are installed for curly varieties. If you ignore this technique, then it will be impossible to collect the beans lying on the ground - they will hide under a huge mass of leaves, and the fragile stems will easily break. Hilling plays an important role for bush varieties. Bushes, albeit small, lose stability under the weight of leaves and pods and can fall or break. Therefore, when the sprouts stretch to a height of about 10 cm, they are regularly hilled.
Watering rates
Beans like regular watering throughout the growing season, the water rate doubles during flowering and bean formation. Watering is carried out in the morning or in the evening, consuming about 15–20 liters per 1 m2 in normal weather. If the beans are grown in the steppe area, drip irrigation systems are used.

Drip irrigation of beans is used in the steppe area
What does the violation of the humidity regime lead to:
- watering against the background of low temperatures leads to the threat of fungal infections, and the ovaries and flowers fall off en masse;
- high humidity in autumn slows down the ripening of seeds, worsening their quality: the amount of protein decreases, germination decreases;
- and the lack of moisture leads to a rapid coarsening of the parchment layer of the bean, and the seeds do not grow to the required size.
Top dressing at different stages of the growing season
The choice of fertilizers intended for fertilizing is wide - from ready-made complex to folk:
- 15 g of superphosphate + 5 g of potassium chloride per 1 m2 are introduced under the root in the budding phase;
- Foliar top dressing with complex fertilizer with the formula NPK 5: 7: 10 with boron and molybdenum in a chelated form, which allows plants to easily assimilate the metals that make up the drug. Molybdenum has a beneficial effect on the activity of nodule bacteria and increases the amount of protein in seeds. The first spraying is carried out in the budding phase, the second - after flowering;
- Seedlings and beans in the beds are watered with a yeast solution: dry yeast (10 g) and sugar (50 g) are dissolved in 10 liters of water, left to ferment for 2 hours, and then another 40 liters of water are added to the resulting solution;
- Supporters of organic farming use only mulch as top dressing, which is laid out under the plants and in the irrigation grooves. The mulching layer consists of crushed weeds, green shoots of shrubs and grapes.
Video: what beans love
The main pests and diseases of legumes
The beans have enough enemies: omnivorous bears "mow" the roots of sprouted seeds that curious insatiable crows did not have time to pick out. They use chemical preparations for the bear, for example, Medvetox, Rubit. They are brought in a week before sowing.
And the crops covered with foil will be protected from birds.
The advice to fertilize the earth with organic matter in the fall has another reason - a sprout fly lays eggs in the undecomposed fragments of manure. The larvae gnaw the bean cotyledons, where they pupate. Sprouts from such seeds are rickety, but in most cases they do not germinate. To get rid of flies, before sowing, the ground is powdered with ash, tobacco dust, watered with garlic infusion or planted nearby.
Photo gallery: bean pests
Typical diseases of beans include:
- anthracnose, which consumes the core of the seed;
- putrefactive lesions, gradually destroying the whole plant;
- incurable bean mosaic covering the leaves with a gray-brown sediment.
In warm, humid weather, most of the garden crops are overcome by powdery mildew, which covers the leaves and fruits-berries with a whitish coating. The affected bushes are removed from the garden. You can treat plants using the coolest chemistry, but how then can you eat asparagus beans without fear of poisoning? The use of biological products in accordance with the instructions (Fitosporin, Trichodermina, Pentafaga-S, etc.) reduces this and other risks to zero.
The nuances of growing in the regions
The method of growing beans in the open field is unchanged, in whatever region it is used. Only the approaches to improving the physicochemical state of the soil and the sowing calendar differ.
Northwest region
Soddy-calcareous soils located to the west of the Leningrad region are rich in humus, minerals, their pH level reaches neutral, therefore, the pre-sowing application of mineral fertilizers will be sufficient here. The predominant podzolic soils are poor soils that require regular autumn, pre-sowing and pre-sowing fertilization. The seedling method of cultivation is practiced, when 2-3-week-old seedlings are planted on the beds. The planting date falls on the beginning of June.

2-3 weeks after the emergence of seedlings, bean seedlings are planted in the ground
Volga region
On the floodplain lands of the Volgograd and Astrakhan regions, sowing beans is possible in the second decade of May. The Astrakhan region is located in the desert and semi-desert zone, therefore mulching the beds is a necessary measure. In dry spring 1-2 pre-emergence watering is carried out. Sowing is carried out in early June.

Mulching is a necessary stage of bean farming in the Volga region
Ukraine
The forest-steppe soils of the region are a patchwork of podzolic, gray, peat soils and chernozems. On chernozems (Kirovograd, Poltava, Kharkiv oblasts) it is quite enough to carry out pre-sowing fertilization.
Low-lying peatlands are lime with a complex fertilizer with the formula N20-30P40-60K40-60 and drained to divert high groundwater. Transitional peat bogs are more acidic (pH 3.5–5), so they are calcified.
The optimal first date for planting beans in open ground is approximately May 15, of course, if nature does not present an unpleasant surprise.

In Ukraine, beans are usually planted in mid-May.
Belarus
Podzolic soils of most of the territory (these are Vitebsk and Minsk regions) require regular application of mineral fertilizers.Organic matter is either applied in the fall a year before sowing the beans, or replaced with compost.
In the east of the country, soddy-calcareous soils prevail, on which it is enough to carry out pre-sowing fertilization. A typical spring in Belarus is stretched out in time; you will not surprise anyone with snow in early May. In such conditions, the beginning of sowing falls on the end of May and the beginning of June.
Moscow suburbs
In the Moscow region, most of the land is sod-podzolic (low-fertile). Obligatory procedures should be regular autumn application of humus, compost and wood ash to the holes, as well as complex fertilizing during the growing season. In late May and early June, beans are sown or planted with seedlings.

In the Moscow region, before planting beans in the soil, it is useful to add wood ash
South of Russia
Salt marshes are a common occurrence for these places, for planting they are cultivated in advance. Sowing in a fertile southern climate is carried out in several stages:
- In the middle of April.
- In the middle of May.
- Closer to June 17-20.
- At the end of June.
In the South, beans are watered more often than usual (about once every 4 days) or drip irrigation is used.
Ural
The scarce podzolic soils, which are in the majority in the region, require systematic application of doses of humus and mineral fertilizers. The beds are heated by sprinkling with hot water. The first time this is done about a week before sowing, covering the ground with a film after watering.
The second time is hot watering of the grooves before placing the seeds in the ground. Beans immediately before planting are dipped for 15–20 minutes in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate, heated to + 60 ° C.

In the Urals, before planting beans, it is necessary to lower the seeds in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate
Sowing beans takes place in three stages:
- the first - at the end of May;
- the second - a week later;
- and the third - in the first half of June, provided that it is an early ripening variety.
Siberia
Sowing with dry seeds gives excellent results in Siberia, which remain viable with a temporary deterioration in the weather and themselves catch a favorable moment for germination. During heavy rains, the leaves and beans of bush beans, in contact with the ground, are subject to decay. To avoid this, twine stretched along the rows at a height of 30–40 cm, to which the shoots are tied, will help.
Considering that return frosts in early June are not uncommon for Siberia, seeds are sown at the turn of May-June. Preference is given to bush varieties that ripen in August. Curly beans in this regard are late for a month, when the threat of the first frost increases.
The yield of beans depends on the acid-base balance of the soil, the favorable geographical location of the site and care throughout the season. The culture performed well in combined plantings. Curly varieties, due to their peculiarity, are used as a decorative decoration.
Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 1 out of 5)
For novice summer residents, their hands rarely reach the beans. Nevertheless, it is quite reasonable to "swing" at this fairly popular culture, which simply has the maximum content of especially valuable vegetable protein, and has stored various nutrients for future use. It is noteworthy that its calorie content is one and a half to two times higher than that of other vegetables. Beans are certainly used both in conservation and in freezing. And the number of fans of the first and second courses with her participation can be frankly envied. In addition, it does not require any wild energy consumption, and the harvest will be enough for the family. You will learn how to plant beans in open ground in the spring, how to effectively care for and store them in this article.

Types and varieties of beans
In appearance and shape of the bush, beans are:
Also, beans can be divided into the following groups depending on the purpose of growing:
Video: types and varieties of beans
How to plant beans in an open field or greenhouse
Seed preparation before planting: treatment
Before planting, it is advisable to soak the beans in a solution of potassium permanganate for 1 hour. Such treatment will significantly increase immunity and germination.
To speed up the process of seed germination, the beans should be slightly held in one of the popular growth stimulants, for example, in Epin or Zircon.
Many experienced summer residents advise simply soaking the beans in plain water overnight. Just do not leave them in water for more than 12-15 hours, otherwise they may simply "choke".

Landing dates
Beans are a thermophilic culture, so they should be planted in open ground along with cucumbers when the air temperature warms up to + 8-10 degrees, and the threat of return frosts will pass. Thus, the optimal time for sowing beans is May-June, depending on the characteristics of your climate. In the Central lane (Moscow region) a little earlier - in the second half of May, in Siberia and the Urals - closer to June. If you are planting beans in a greenhouse, then you should do it earlier, starting already in April.
If you wish, it is much easier to refer to the lunar calendar for specific dates. So, in 2018, beans should be planted in open ground or in a greenhouse on the following dates:
- March - 20-23 (hardly worth it, but it says so on the calendar);
- April - 6-9, 19, 20, 23-26;
- May - 7-10, 19-24;
- June - 4-7.
Garden bed and land
Beans love fertile and loose soil, they will not grow on heavy soil. Since it is a moisture-loving plant, it requires a water-intensive soil. In no case do not plant beans in acidic soil, only slightly alkaline soil is suitable for it. Thus, loamy and sandy loam soil is suitable for cultivation.
Advice! Fertilize the soil with humus before planting, such fertilizing will have a very positive effect on the future harvest.
It is advisable to plant beans in a sunny place near a fence so that the plantings are protected from the wind and there are no drafts. The curly variety can be planted directly on the net, then you don't even need additional support for its garter.

Interesting! Beans are a green manure plant, so they are often planted in the garden to enrich the soil with nitrogen, in other words, to improve the soil.
It is promising to plant beans in the place where onions, cucumbers, cabbage or potatoes used to grow. It is worth thinking about planting it as a sealant for the same cucumbers, potatoes and late cabbage. It is clear that in this case it should be placed along the edges of the seating grooves or between them. The advantage of the situation is that such a close joint arrangement not only does not reduce the yield of the main dominant crop, but also gives a significant yield. In addition, which is also important, it enriches the soil with nitrogen.

By the way! You can also grow beans in a greenhouse, then you will get an earlier and more abundant harvest.

If you decide to plant beans in a greenhouse, then you should place them at the end so that during the day (at noon) it shades, for example, tomatoes or cucumbers.
Video: growing beans in a greenhouse
Curly bean support
If you want to properly grow beans on a support or trellis, then be sure to watch the following videos:
Direct landing
Tips and instructions for planting beans outdoors or in a greenhouse:
- Dig the bed well and make grooves at a distance of 15-20 (many gardeners of practice advise even 20-40) centimeters from each other. Or make small holes. In any case, be sure to add excellent humus to the bottom of the holes or grooves.
- Now you should give free rein to your hands and water the wells abundantly.
- When planting any kind of beans, 2-3 seeds must be put in each hole, the depth of seeding should be 2-3 centimeters. If you are planting in grooves, then the distance between the beans should be about 6-10 centimeters.

- When sowing curly beans, the seeds should be planted in nests of 5-7 pieces.We remind you that it is necessary to place such a variety strictly next to the support.
- After planting, cover the holes with earth and level the bed.
Video: how easy it is to plant beans in the country
Video: planting curly beans
In general, planting asparagus beans in open ground is not much different except for a couple of small nuances.
Outdoor Bean Care
The basis of care for growing beans includes regular watering, loosening and weeding of row spacings, and in the case of a curly one - its garter to supports or trellises in the greenhouse.
The first entries appear, as a rule, in 1-3 weeks. Already during this period, the weakest shoots should be removed. And as soon as the bush reaches a height of 10 cm, it should be well spud to give the plant great stability.

Before flowering, the plant is recommended to be watered once a week, and after - 2 times. During the fruiting period, watering the beans should be done more often than usual, but they cannot be poured.

Advice! When the curly beans are about 2 meters tall, you can pinch the top if desired to stimulate the ovary.
Bean feeding is best done with potash and phosphate fertilizers, although this plant is so unpretentious that it should only be fed on rare occasions. For example, on dry and hot summer days, it is good to shed the bushes with an ash solution.

However, if yellow leaves began to appear on the plant, then this is a signal of potassium starvation. It is necessary to fertilize as soon as possible with sulphate or potassium chloride at the rate of 20-25 g per 1 sq. M.

In general, there are no unambiguous solutions, and if you strongly doubt the fertility of the soil, then do not refuse feeding, especially during the growing season. It is advisable to feed the first feeding with urea (10-15 g) during the blooming period of the first true leaf, and the second - during the budding period - the beginning of flowering with superphosphate (20-25 g) and potassium chloride (20-25 g).
On a note! Fertilizers during the first feeding are applied literally 4-6 cm from a row of plants, with the second - within a radius of 8-10 cm.
Interestingly, beans are one of those rare crops that are not susceptible to diseases or pests. The only pests you can see on it are slugs, which are very easy to prevent if you regularly weed the beds.

Harvesting and storing beans
The beans are removed selectively as they ripen. Bushy, in contrast to climbing, gives a crop faster. Grain should be harvested in a timely manner. If you are late, fibers will begin to form in the fruit. The timing of harvesting depends on the specific variety. As a rule, the first crops can be harvested in August-September.
It is advisable to remove the bean pods by carefully cutting with scissors, and not by jerking them with your hands.

The remnants of the peels can be used as fertilizer for tomatoes and peppers, after chopping them up and simply sprinkling the soil around the vegetables.
For seeds, a few pods are left on the plant. They are removed when they have hardened to a golden light brown color.
If you want to preserve any beans (including asparagus), then you can pre-dry and store them at home, or freeze them in the freezer (you don't even need to pre-soak them when cooking).
Video: Tips for Growing and Harvesting Beans
Thus, it is quite simple to grow beans in your summer cottage: the main thing is to plant them correctly, tie them up on time and water them regularly. Then you will definitely get a good harvest.
Beans are among the top ten most useful vegetables, so when choosing crops for growing in your garden, they always have a place. In order for the time and money spent to be rewarded with a generous harvest, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the basic rules of agricultural technology, planting and care for open field cultivation.
When to plant beans outdoors
The planting of beans is planned for May month. You should focus on weather conditions and the correct temperature regime in the soil, which is indicated by indicators 12-15 degrees (at a depth of 10 cm). According to the popular calendar, this period coincides with the flowering of chestnuts.
Erect varieties need to be planted first, and after a week you can start climbing varieties. They plan to plant a bushy legume at the beginning of July... This can be done on the beds from which the harvests of early-maturing vegetables have already been harvested.
Experienced gardeners carry out planting work in several stages: from mid-May to early July with an interval of at least 10 days.
 A bush bean variety must be sown in the ground in early July
A bush bean variety must be sown in the ground in early July
To speed up the harvest, it is recommended to cover the soil in advance with plastic wrap to warm up. After planting the seeds, cover the garden bed again until the night temperature is at least 12 degrees.
Are beans afraid of frost
Beans are a thermophilic culture, so planting is best done in spring. in the second half of Maywhen the threat of frost has passed. Young shoots are afraid even of cold winds, which is why many gardeners find its place under apple trees or along the fence.
The minimum temperature that bean sprouts can withstand does not exceed the mark -3-4 degrees... If the frosts were short-lived, the beans will survive, but their development will be slowed down and yields will decrease.
Agrotextile or film, which are used for construction, will help to change the situation. temporary shelter.
The most popular varieties for planting
Varietal diversity complicates the choice. If there are difficulties in determining the range, it is recommended to give preference to proven varieties that are adapted to the climate and weather conditions of the region.
The best varieties for the Moscow region, Ukraine and Belarus
Moscow White Green Pod 556
 Moscow White Green Pod 556
Moscow White Green Pod 556
Plant mid-early ripening period, from sowing to harvesting 100 days... The bush is formed at a height of only 25 cm, the fruits have a parchment layer, but very thin. The culture is unpretentious, resistant to a humid environment and drought.
Nomad
Curly variety mid-early ripening. The egg-shaped bob is ocher in color with a pale purple pattern. The fruit is free of parchment and fibers, which makes the structure tender and soft. The plant is tolerant to anthracnose, gray rot.
For the Urals and the middle lane
Oran
She R - early maturing ripening beans 80-90 days, recommended to plant in a country house in central Russia. The height of the bushes is from 35 to 56 cm, the fruits are distinguished by high taste.
Productivity from 1 m2 within 200 grams.
Pink
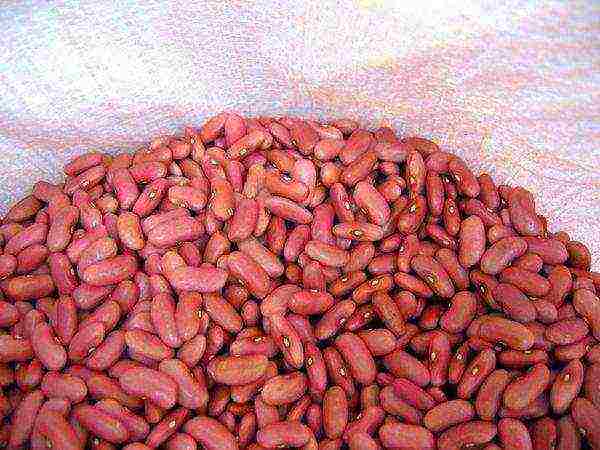 Pink
Pink
Harvesting begins in 65-85 days after seed germination. The climbing bush reaches a height of up to 3 m, so it needs support.
The marbled pink beans are free of parchment and fibers, which gives them a delicate texture. Purple streaks and streaks are visible on the fruit. The application is universal, in any form the beans retain their unique taste.
For Siberia
Winner
 Winner
Winner
Culture is different high yield and the nutritional qualities of the fruit. The length of the pods is about 30 cm, the beans are large. Cold resistance and strong immunity make it possible to cultivate and grow a plant in Siberia.
Feature: lashes with beautiful fiery red flowers can be used as a decorative hedge.
Oil king
 Oil king
Oil king
Bush type of beans with a ripening period 1.5 months... Delicate and pleasant taste of tubular fruits will not leave indifferent any gourmet. The length of the pod part is about 25 cm. The harvest is universal: dry harvesting, freezing, canning.
Planting rules and agricultural techniques for growing in open ground
Seed preparation
To obtain quick shoots and protect young shoots from diseases, the seeds should be prepared before planting.
Soak first in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for about 20 minutes. After the procedure, the beans are washed with clean water and again need to be soaked in wood ash infusion for 2 hours.
At night before sowing, the pea beans are wrapped in a damp cloth for germination at home. And 5 minutes before sowing into the soil, they are dipped into a boric acid solution. This will protect the plant from diseases and pests.
Preparing the soil and choosing a place for sowing
For planting a crop is selected well lit place, but without drafts and strong winds, planting through seedlings is practically not used. The type of soil does not play a big role, but experienced gardeners noted that beans develop worst of all, they can germinate and bear fruit poorly on clay soils. This is due to poor moisture permeability, which causes the seeds and roots to rot.
In general, the preparatory process for the formation of the garden consists in digging the soil to the depth of the shovel bayonet... At the same time, fertilizers are introduced: per 1 m2 add 4 kg of humus or compost, 2 tbsp. l. dolomite flour, 1 tbsp. l. ammonium nitrate and 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate.
 When preparing the soil, you need to dig it up to the depth of the shovel bayonet
When preparing the soil, you need to dig it up to the depth of the shovel bayonet
Another option for enriching the soil with nutrients involves the use of ½ compost (humus), 30 gr. superphosphate, 20 gr. wood ash per 1 m2.
When determining a place for planting beans, those crops that were grown on it last season are taken into account.
Ideal predecessors are: potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, cucumber, pepper, eggplant.
Planting scheme and depth
Shrub varieties of culture are planted according to the scheme:
- seed placement depth - somewhere 5-6 cm;
- distance between holes in a row - 20-25 cm;
- aisle - 40 cm.
Curly varieties are planted in a slightly different way:
- seed placement depth - 5-6 cm;
- spacing between holes in a row - 25-30 cm;
- aisle - 45-50 cm.
 When planting beans, 5-6 seeds are immersed in each hole
When planting beans, 5-6 seeds are immersed in each hole
5-6 seeds are immersed in each hole. After formation on the seedlings, one leaf at a time, only 3 seedlings need to be left, the rest should be removed or carefully transplanted.
According to lunar calendar for 2018 planting beans is recommended:
- March - 20-23 days;
- April - 6-9, 19, 20, 23-26;
- May - 7-10, 19-24;
- June - 4-7 numbers.
Leaving after disembarkation
Unpretentious beans do not require much attention to themselves, but they still need the basic rules of agricultural technology.
Germinating bean seeds
Bean seeds begin to sprout later 7-10 days after disembarkation... If the air and soil temperature is below the recommended values, then the first shoots will germinate after 5-7 days.
The germination process can be accelerated if the seed is soaked in growth stimulants at home. Covering the beds with a film also contributes to this.
Young shoots must be spud to give them stability.
Watering rules and conditions
The plant loves water, so you should not break the watering regime. It is especially important to moisturize the soil during the period of pod formation.
The rate of water per bush is determined by eye, the procedures are carried out Once a week, the main thing is not to let the soil dry out. Precipitation in the form of rain is considered the best irrigation liquid. Experienced gardeners use settled water, the temperature of which not lower than 18 degrees.
 Beans love water, so the soil should not be allowed to dry out.
Beans love water, so the soil should not be allowed to dry out.
What top dressing to use in the garden
The culture is responsive to fertilizers. After preparing the soil for planting, you will need to make at least 3 dressings.
The first procedure is performed 3-4 weeks after germination. It is ideal to use a complex fertilizer rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. Superphosphate is also suitable at the rate of 30-40 grams per 1 m2.
After 3 weeks, you need to feed a second time, this is necessary for the formation of fruits (10-15 grams of potassium salt per 1 m2). The third time the nutrients are administered after 3 weeks.
You should not overdo it with fertilizers, you can provoke the growth of tops and reduce the ovary of pods.
Pests and prevention
Beans are one of the few crops that do not attack pests... Only slugs can appear.
Their invasion can be prevented by timely weeding, since weeds grow and create a favorable habitat for parasites. When slugs are found, you can set several traps, from which you need to periodically remove insects for disposal.
The correct timing of harvesting in the country or in the garden
 Harvest time depends on the type of crop
Harvest time depends on the type of crop
Harvest time depend on varieties and types culture. Asparagus beans should not be overexposed in the beds, as the product loses its value when dried.
If you plan to preserve the legume crop, then you can use any unripe fruits. But for winter preparations, it is better to wait for the pods to dry. The main thing is not to be late, so as not to collect beans from the ground later.
You should not pluck all the pods at the same time on the same day if there are completely dry and greenish ones among them. In the shade of its own tops, some ovaries could develop weaker, it is better to leave them to ripen.
To quickly extract the beans from their "houses" it is not at all necessary to sort each one by hand. The stick will do the job, you can knock out the harvested crop.
To do this, only dried pods are laid out on the bedspread, along which you need to walk with a simple tool with moderate effort. It remains only to remove the dry part of the beans. The selected beans are still being dried and only after sorting are they sent for storage.
The agricultural technology of beans is simple, even a novice gardener can sow and grow it in the Moscow region, in the Ukraine, the Urals or Belarus. By completing all the procedures in a timely manner, preparations for the winter are provided with an incredibly healthy and nutritious product, which also diversifies the menu.


