Content
- 1 Breeding features
- 1.1 Construction of an apparatus for growing nauplii
- 1.2 HOME BREEDING 1 METHOD
- 1.3 BREEDING ARTEMIA 2 METHOD
- 1.4 Feeding fish with Artemia
- 1.5 VIDEO ABOUT BREEDING ARTEMIA
- 1.6 Part 1 Arrangement of an aquarium for growing Artemia
- 1.7 Part 2 Removing Artemia from eggs
- 1.8 Part 3 Maintaining the right conditions in the aquarium
- 1.9 Part 4 Feeding Artemia
- 1.10 Part 5 Catching Artemia for fish feeding
- 2 Tips
- 3 Warnings
- 4 What do you need
- 5 Artemia - what is it?
- 6 Reproduction
- 7 The benefits of the feed
- 8 Methods for increasing the germination of brine shrimp
- 9 Incubator organization
- 10 How to breed food for brine shrimp?
- 11 Catching brine shrimp for fish feed
- 12 Feeding features
- 13 Finally
Artemia salina is a small crustacean that is found in salt water bodies. Nowadays it is of industrial importance - it is bred and raised as food for fish. First, you need to catch brine shrimp eggs, and then grow nauplii (larvae), which can be used to feed young fish and adults.
Breeding features
The average size of hatched Artemia nauplii is 0.5 mm, their weight is 1/100 mg. In 12 hours their first molt will occur, and before it the larvae will not feed yet. After they move into the second larval stage, water filtration and absorption of bacteria, unicellular algae and detritus will begin. If stored at temperatures above 25 degrees Celsius, nauplii will become adults in a few days, and in 8 days they will molt up to 15. The life cycle of brine shrimp is six months.
Artemia salina is a nutritious food for aquarium and commercial fish. Crustaceans are suitable for feeding sturgeon fish due to their high nutritional value. Nowadays, there are new technologies for keeping crustaceans, in which their mass breeding can satisfy industrial needs. Crustaceans lend themselves to incubation in aquarium farms, and in a house where there is a small aquarium.
Look at brine shrimp under a microscope.
In a city apartment, growing such feed can seem problematic. It is easier for the novice aquarist to catch or buy crustacean cysts and remove nauplii using the Weiss apparatus. Pet stores often sell brine shrimp eggs without capsules, which can be used to feed fry of spawning fish, which are already small in microscopic ciliates.
Larger fry of viviparous fish and large spawning species can eat eggs of brine shrimp or nauplia from the first days of life. Cysts must be outside the capsules (decapsulated). These cysts are harmless. Decapsulated cysts should be poured with water for 20 minutes before feeding. Then rinse them under running water in a net made of nylon or gauze to remove decomposition products that have formed during prolonged storage.
If you give decapsulated cysts to fry, then the prospect of building an incubator disappears. It also minimizes the risk of catching an infection, an attack of live brine shrimp nauplii on fry. Crayfish larvae attacks often occur in saltwater aquariums, where young nauplii grow faster than fry. If you feed with eggs, there will be no danger, but such food has drawbacks. Cysts fall to the bottom, and do not float in the thickness of the reservoir. Over time, some of them will be found by fry, but most of them will have to be removed with their own hands.
Construction of an apparatus for growing nauplii
A surefire way to avoid trouble is to build a Weiss apparatus. As a result, hatched nauplii can be fed prior to feeding. The device allows breeding and rearing many larvae.The equipment is an upside-down plastic bottle with the bottom cut off. A spray bottle must be installed in the cork and neck of the bottle. You will need 2 of these bottles.
In two bottles, you need to pour 1 liter of a solution of table or sea salt without additives and iodine. You need to prepare the solution like this: 3 tablespoons of salt per 2 liters of water. Next, you need to pour Artemia cysts into the container - 1 teaspoon without a top per liter of water. It should be remembered that these crustaceans are prolific, however, breeding at home will give up to 40% of live larvae. Therefore, to get more live larvae, you need to take more eggs. After a day, do the same procedure with the second bottle. A day later, new nauplii are formed in the first container, which are suitable for feeding the fry. New cysts can be poured into the free container.
See how to grow brine shrimp at home.
The air flow to the spray bottle in the bottle must be applied in such a way that the cysts do not settle to the bottom, but are in the water column. The temperature should be kept at 28-30 ° C. Stop the air flow 30 minutes before feeding the fish. Empty shells will rise up and unhatched eggs will sink to the bottom. Nauplii that float in water are best filtered through a dense net, and the strained salt water can be poured back into the incubator.
To wash off the salt again, you can put the larvae in a separate container with fresh water, after which you can feed the fry with them. The most active and hardy larvae can live in fresh water for only 6 hours. If you are going to give this food to the fry of sea fish, then give it a small amount so that the fry can eat all of them. Otherwise, the quickly matured larvae will eat the fry themselves, and the owner of the aquarium is unlikely to expect such a result.
What else you need to know about brine shrimp and larvae:
- Artemia salina never sleeps. They can be at rest, but for full functioning they need constant wakefulness.
- This is one of the oldest animals on the planet, which has existed here for over 100 million years.
- Adult Artemia have three eyes, one appears at the stage of larval development, and two more eyes develop in adults.
- A female's egg sac can contain up to two hundred eggs.
- At home, Artemia larvae need to be fed with baker's yeast. They are introduced into the solution until the medium becomes cloudy. After feeding, the larvae can be fed to the fish after 7 days. They also eat unicellular algae well.
Artemia refers to the gill-footed crustaceans (Anemia salina). Adults reach a length of 18 mm. Artemia is common in salt water bodies in the southern regions of Russia.
There are brine shrimp eggs on sale, from which you can get its larvae (nauplii) and even grow them using specialized feed.
Nauplii are excellent food for the young of most aquarium fish, and adults of brine shrimp can be fed to medium-sized fish. It should be noted that brine shrimp nauplii are kept in illuminated places and if the fry hide in the dark, they will be left without food.
Frozen nauplii sink to the bottom of the aquarium, so they are suitable for feeding fry of barbs, catfish and other fish looking for food at the bottom.
100 g of brine shrimp contains: proteins 57.6 g, fats 18.1 g, carbohydrates 5.2 g. 100 g of brine shrimp contains: proteins 48 g, fats 15.3 g, vitamin B12 7.2 microns per 1 G.

HOME BREEDING 1 METHOD
1. A solution of salt is poured into the jar (20 g of table salt per 0.5 l of water), brine shrimp eggs are introduced (a teaspoon without a slide for 0.5 l of solution) and closed with a crumb, in which two holes are made with tightly sitting plastic tubes. On one of them, immersed in water to the very bottom, a sprayer is put on, and the other end is connected to a compressor.The second tube, short, does not reach the surface of the water and serves to evacuate air. A strong air flow ensures that the eggs are stirred. The maturation of the first batch of crustaceans at a solution temperature of 24-25 ° C occurs after 36-40 hours.
To collect them, turn off the air supply for 4-5 minutes so that the crustaceans have time to settle to the bottom. Then put on another cover with two tubes, one of which is connected to the compressor and does not reach the surface of the water. One end of the second tube goes to the bottom of the jar, and the other is brought to a glass jar, covered with cloth Nos 73, 76. The compressor is turned on, and the water is drained into the jar, and the crustaceans remain on the grid. After washing with water, they can be fed to fish. The solution is poured back into the jar, and the operation can be repeated one or two more times. A new solution is prepared for each new batch of eggs. The disadvantage of this method is the not very high percentage of the output of crustaceans from the eggs and the inability to completely get rid of the shells of the eggs, which, remaining in the net and getting into the intestines of the fry, can cause unpleasant consequences
BREEDING ARTEMIA 2 METHOD
Purchase a pack of brine shrimp eggs from a pet store. This food is convenient because it can be stored for years, so do not mind that the eggs are dry. Juveniles of brine shrimp are used as food for the fish. Before hatching brine shrimp, soak the eggs of these crustaceans for half an hour in 5% sodium chloride solution. Then rinse the brine shrimp eggs under the tap for a few seconds and place them in the incubator.
Fill 2/3 a 3-liter jar with settled (chlorine-free) water. Dissolve 3 tablespoons of salt in it. Dip some floating seaweed into the jar. Add a teaspoon of freshly washed brine shrimp eggs to the solution. Dip the hose from the microcompressor with the spray end into the jar. Connect the compressor to the mains and achieve such a flow of air that it does not allow the eggs of brine shrimp to settle to the bottom. Dip a thermometer into the jar. Make a round-the-clock backlight. At a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius, the crustaceans will hatch in 2 days, and at 28 degrees Celsius - in a day. Recreate brine shrimp at the same temperature that is set in your aquarium. In this case, once in the aquarium, they will live longer.
Buy a drip from the pharmacy. Separate the needle, dilator, and clamp from it. When fishing for brine shrimp, use the dropper as a drain hose. Prepare a piece of cloth that is water permeable. Use a hose to strain the required amount of crustaceans to feed the fish. Return the drained salt water back to the jar. If you abundantly aerate the water in the jar, then the crustaceans will live with you for several days. In fresh water, brine shrimp dies in a few hours. To grow a large butPlace a jar of salted water in a jar of salted water, which serves as food for larger fish. When it is overgrown with algae, run the crustaceans there. Algae are their food. You can add orange peels to the water. The crustaceans will begin to grow intensively and even reproduce.
STORAGE OF ARTEMIC
It is not difficult to store brine shrimp eggs; under the right conditions, the "germination" of eggs lasts a very long time. The main condition for successful storage is dryness, because in the presence of moisture, the cysts are not completely dormant and are depleted. It is preferable to store the eggs in the refrigerator in a hermetically sealed bag, then their germination capacity lasts a very long time and the percentage of hatching is quite high.
The fry of many species of spawning fish are fed with brine shrimp nauplii, since the size of the newly hatched nauplii is such that in some cases even small fry can be fed with them from the first day of active feeding. With proper preparation, nauplii can be hatched within 24 hours, which is very convenient, for the constant availability of feed, you can run several incubators and start them at daily intervals to always have fresh feed available.
Feeding fish with Artemia
It's important not just to feed your fish the right food. It is also important to feed correctly. Overfeeding fish is one of the main causes of disease and death of fish. In addition to the fact that overeating fish can easily get stomach inflammation, uneaten food decomposes in the water, which leads to an increase in the level of ammonia, which is toxic to fish. Remember yourself, have you seen a lot of fish that died of hunger? Of course, this does not mean that the fish should be starved. Sometimes the rule is that the fish should be given a volume of food the size of the black pupil of the eye. Acting by this rule, you will starve a hefty frontosa with hunger sooner or later.
A healthy adult fish can safely go without food, especially in an aquarium with plants, for several weeks. This does not apply to fry, which need to be fed a lot to grow up healthy. Therefore, if you are leaving, it is better not to feed the fish than to ask a stranger to give them food and then listen to his explanations about the poor little fish who are constantly asking for food, how can you refuse them. In addition, hungry fish stain the water less, so there is less headache cleaning the aquarium while you are away.
The usual rule, which applies reasonably well to most cases, is to feed once or twice a day as much dry food as the fish eats in five minutes.
Artemia is the only gill-footed crayfish that has adapted to living in salt waters. At the same time, it withstands not only high concentrations of table salt, but also acidic and alkaline environments. In some reservoirs, Artemia is the only representative of the animal world, since no other living creature wants to live in such conditions.
Crustaceans feed on algae, as well as bacteria, protozoa, detritus. This is what determines their positive phototaxis.

Crustaceans tend to lighter areas, where there is more algae. The way of feeding is filtration. With a lack of plankton, crustaceans have to stir up the bottom silt with their legs.
Under optimal conditions, the female Artemia lays eggs with a thin shell, which develop in the brood sac and already active nauplii emerge. When conditions worsen, eggs with a strong multilayer shell are formed. It is these eggs that are able to withstand rather harsh conditions for a long time that are used in the aquarium hobby.
The evolution of the genus Artemia went something like this:
The original ancestral bisexual species lived somewhere in the territory of the modern Middle East. Then it spread widely across the globe and about 25 million years ago, there was a division into populations of the Old and New Worlds. The next stage was the isolation in the Old World of parthenogenetic forms derived from European bisexual brine shrimp. At the same time (10-12 million years ago), A. persimilis separated from A. franciscana on the South American continent. The youngest species (subspecies), such as, for example, A. monica, were isolated about 2 million years ago. Thus, on a geological scale, they are our peers.
VIDEO ABOUT BREEDING ARTEMIA
5 parts: Setting up an aquarium for growing Artemia Breeding Artemia from eggs Maintaining suitable conditions in the aquarium Feeding Artemia Catching Artemia for feeding fish
Artemia is a nutritious and easy-to-grow live food for tropical and marine aquarium fish. Despite the wide variety of ready-made dry fish food, it is brine shrimp that will provide your fish with the lipids, vitamins and amino acids they need. In addition, the process of growing Artemia is interesting even for children. Of course, adult brine shrimp can sometimes be purchased at pet stores, but sometimes it is more convenient to grow these crustaceans on your own at home. If you already have experience with saltwater aquariums, it will be a little easier for you to get started.Nevertheless, this article describes in detail everything that is necessary to grow Artemia and maintain optimal conditions for their existence.
Part 1 Arrangement of an aquarium for growing Artemia
-
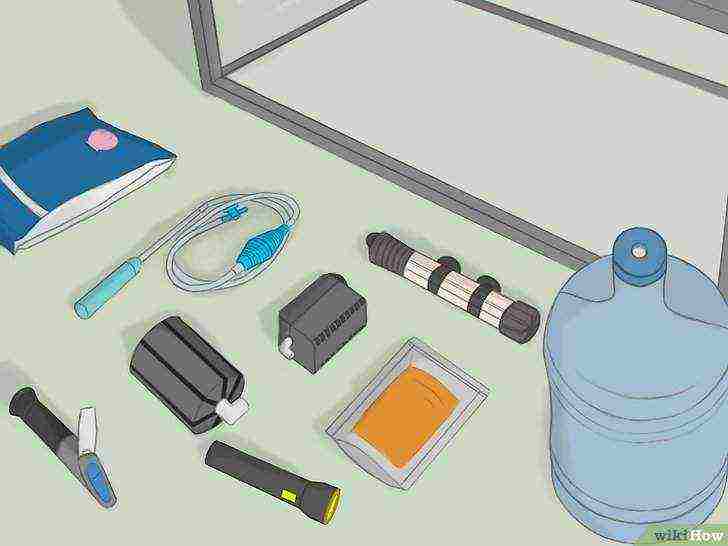 Get everything you need.
Get everything you need.
The materials you need can be found at a regular pet store or a specialized aquarium store. Also, all goods can be purchased online, if it is more convenient for you. To grow Artemia, you will need a lot of items, namely:
- 40 liter aquarium;
- aquarium sponge filter (with tube, sponge and air compressor tube mount);
- air compressor;
- aquarium water heater and thermometer;
- packaging with Artemia cysts (eggs);
- aquarium salt (when preparing a new aquarium, you will need about 300 g of salt for every 10 liters of water);
- 4 liter container with lid;
- 40 liters of reverse osmosis filtered water;
- a refractometer or hydrometer for determining the concentration of salt;
- aquarium siphon for cleaning gravel;
- torch.
-
 Choose the most suitable location for your aquarium.
Choose the most suitable location for your aquarium.
A seawater aquarium should not be placed near windows, doors, batteries and air conditioners, so that the water temperature does not undergo sharp fluctuations. In this case, the aquarium should be located near electrical outlets, since you will need to connect a water heater and a compressor to the network.
- Leave some space between the wall and the aquarium so that you can easily place the compressor there.
- The surface for setting up the aquarium must be absolutely level.
-
Rinse the new aquarium to keep dust out. Then wipe the outer walls of the aquarium dry and place it in the place prepared for it in advance.
-
 Fill the aquarium with a salt water solution.
Fill the aquarium with a salt water solution.
Prepare a saline solution of aquarium sea salt and reverse osmosis water.
Fill a 40 liter aquarium with 35 liters of water so you have room to add salt. Then add aquarium salt to the water according to the instructions on the container.
- The package of salt will definitely contain instructions for calculating the required amount of salt for a certain volume of water.
- Do not be afraid to add too little or too much salt, you can correct its concentration in the water just before adding brine shrimp cysts to the aquarium.
-
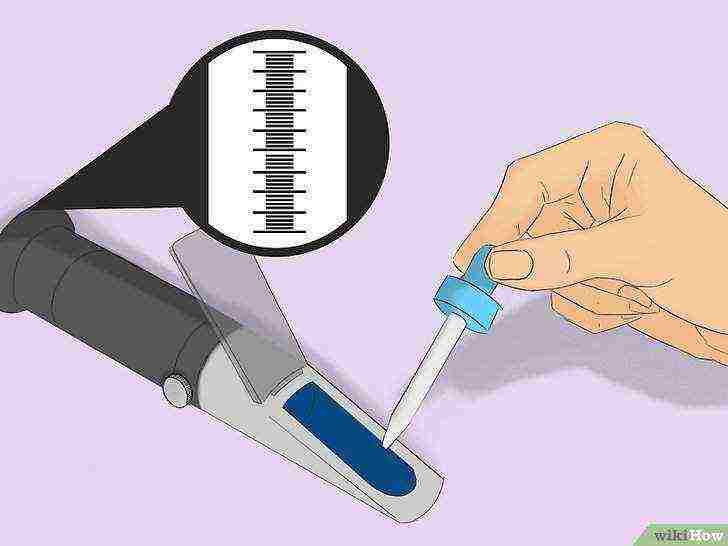 Check the salt concentration with a refractometer or hydrometer.
Check the salt concentration with a refractometer or hydrometer.
The salt concentration in the aquarium should be between 30-35 parts per thousand.
To accurately measure salt concentration, refer to the instructions for your refractometer or hydrometer. Add more salt or filtered water to the aquarium as needed.
- Working with a refractometer or hydrometer involves putting some water into the instrument using a pipette or other handy tool.
- Test the water until you achieve the correct salt concentration.
- If you follow the instructions for adding sea salt to the water exactly, then there should be no problems with the solution.
-
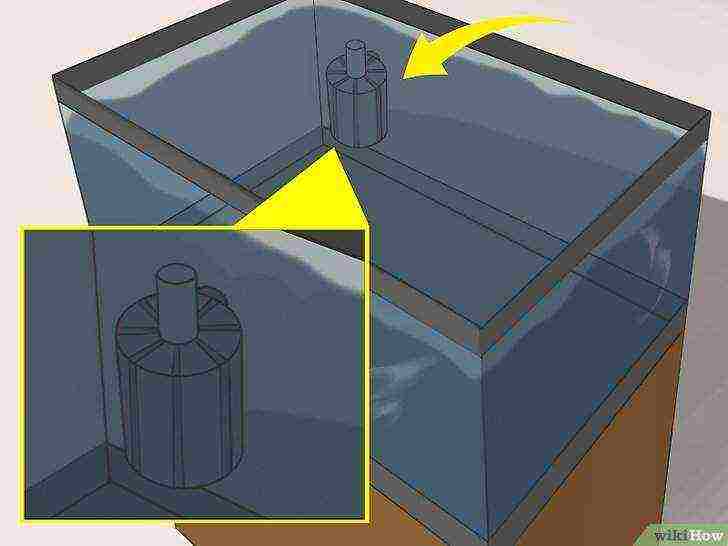 Install a slow sponge filter in the aquarium that is powered by the airflow of an air compressor.
Install a slow sponge filter in the aquarium that is powered by the airflow of an air compressor.
Such a filter is best suited for an aquarium, since during filtration it will additionally enrich the water with oxygen and will not be able to accidentally suck Artemia into itself.
The filter itself should consist of a tube, a sponge and an air compressor tube mount. If the filter does not have a compressor tube mount, buy it separately.
- The sponge filter can be positioned at the bottom of the aquarium or attached to the wall (depending on the specific filter model purchased).
- There are a lot of cheap filters on the market today, but you shouldn't save too much on the filtration system.
- Poor filter performance can lead to the death of brine shrimp.
-
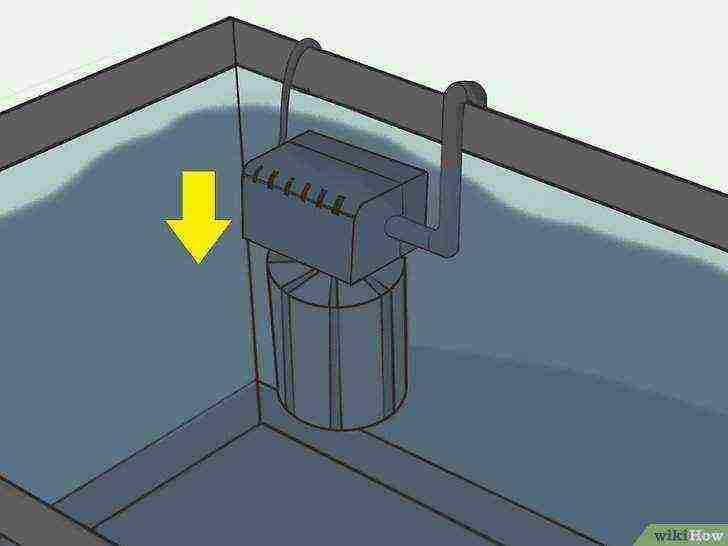 Connect the compressor to the sponge filter.
Connect the compressor to the sponge filter.
Connect the compressor and filter with an air tube.
Connect the compressor to the mains and the filter will start working. Place the running compressor on a secure surface behind or next to the aquarium.
-
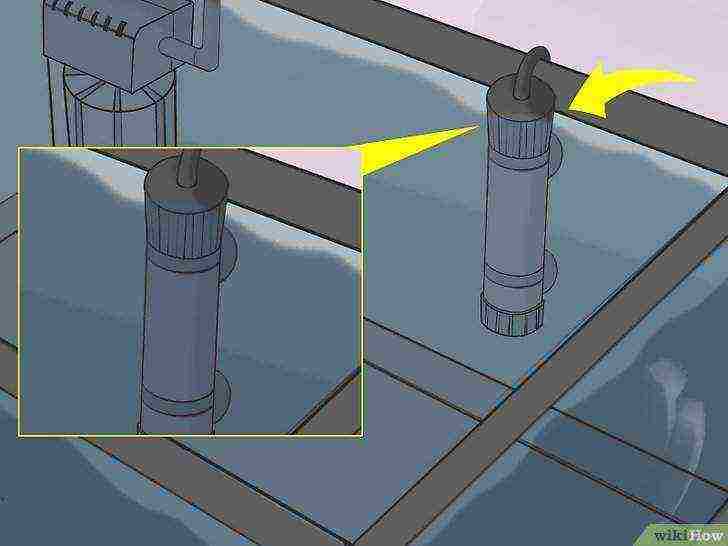
Install a water heater. Install a water heater in the aquarium according to the manufacturer's instructions. Having connected the water heater to the mains, it is necessary to start monitoring the temperature of the aquarium water.
-
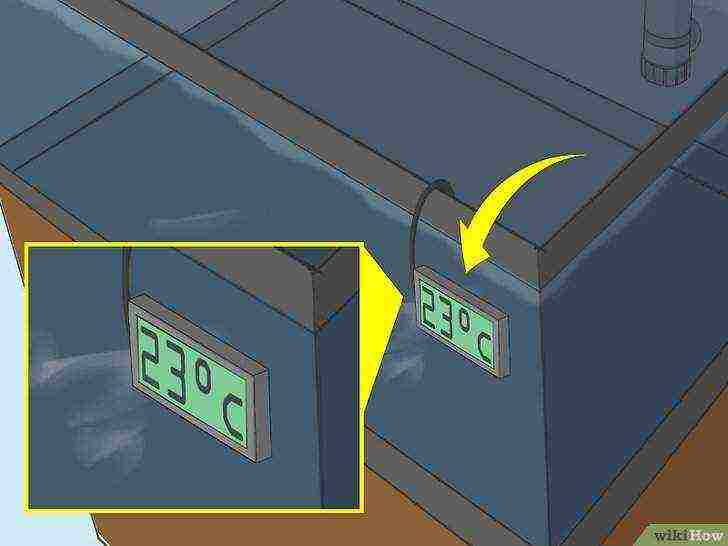 Install the thermometer according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Install the thermometer according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Place the thermometer in a visible place at the opposite end of the aquarium from the location of the water heater.
Having installed a water heater and a thermometer, it is necessary to adjust the operation of the water heater so that the temperature in the aquarium is always kept at 20-25 ° C. Turn the thermostat of the device up or down accordingly.
-
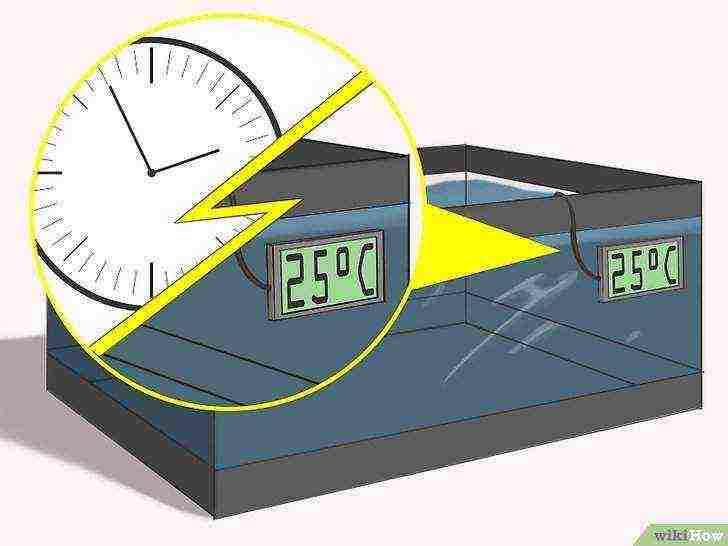
Make sure that the temperature in the aquarium is around 20-25 ° C around the clock. As soon as the temperature in the aquarium is stable within the recommended range, it will create suitable conditions for keeping brine shrimp. Check the water temperature at least twice a day. If the water heater is accidentally turned off or the water temperature changes abruptly, brine shrimp can die.
Part 2 Removing Artemia from eggs
-
 Buy Artemia cysts (eggs).
Buy Artemia cysts (eggs).
Packs of dried Artemia cysts can be purchased at a pet store or a specialized aquarium store.
For a start, one bag of eggs will be enough for you, as brine shrimp reproduce very quickly.
-
 Submerge the cysts in water and they hatch in 15 to 20 hours.
Submerge the cysts in water and they hatch in 15 to 20 hours.
If the correct temperature and salt concentration is maintained in the aquarium, brine shrimp will hatch on the first day. After 12 hours, you will see young crustaceans swimming around the aquarium.
-
 Watch for the growth of brine shrimp.
Watch for the growth of brine shrimp.
Artemia grow and multiply very quickly. From cysts, they hatch very small, and then grow into small crustaceans. They do not need any assistance from you to hatch and grow, as in a well-conditioned aquarium it all happens naturally.
- If brine shrimp does not grow or hatch, check the salt concentration and water temperature to identify possible problems.
- Be aware that part of the Artemia population dies naturally, this is not unusual.
Part 3 Maintaining the right conditions in the aquarium
-
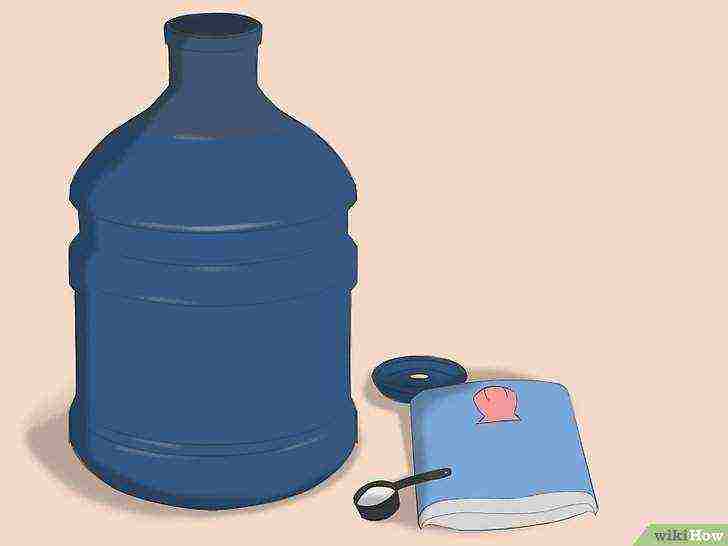 Prepare a supply of salt water.
Prepare a supply of salt water.
You will need this supply of salt water in order to change the water in the aquarium. If you have about 4 liters of prepared salt water on hand, then changing the water in the aquarium will not be difficult.
- Fill a 4 liter container with reverse osmosis filtered water.
- Add aquarium sea salt to the water according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Place the lid on the container and store in a cool, dry place until you need it.
-
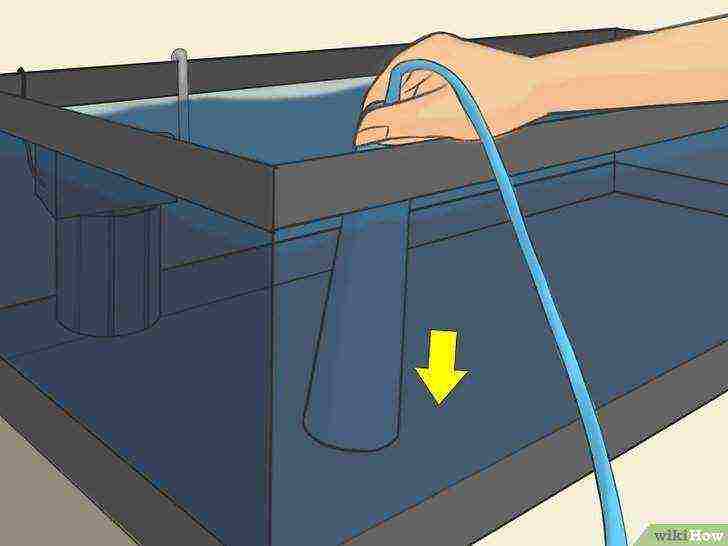 Use a siphon to regularly perform partial water changes in the aquarium (approximately 20% of the aquarium volume or 8 liters per week).
Use a siphon to regularly perform partial water changes in the aquarium (approximately 20% of the aquarium volume or 8 liters per week).
Be sure to turn off the filter compressor before changing the water. Wait for the moment when the water in the aquarium stops circulating and completely stops. Shine a flashlight on the surface layer of water so that all brine shrimp float to the surface.
- Siphon off any dirt from the bottom of the aquarium.
- Then fill up the drained volume of water with pre-prepared clean salt water.
- Check the salt concentration and temperature in the aquarium to ensure that all parameters are within the normal range.
-
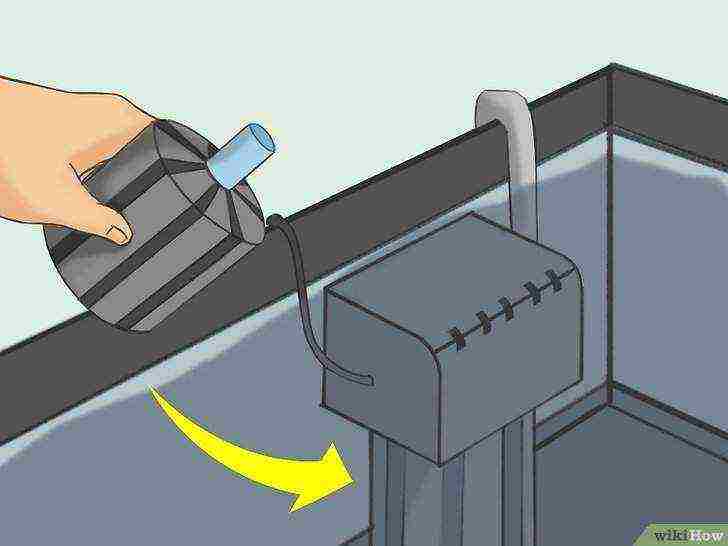 Wash or replace the filter sponge every 1-4 weeks.
Wash or replace the filter sponge every 1-4 weeks.
The filter sponge can become very dirty. To wash (or replace) it, you must turn off the compressor, remove the sponge from the filter and rinse (or replace with a new one).Replace the clean sponge, replace the filter and turn on the compressor. Typically, the sponge needs to be replaced with a new one about once a year.
- When cleaning the filter, use a flashlight to illuminate the opposite side of the aquarium so that brine shrimp does not interfere with you.
- You may need an assistant to remove the filter from the aquarium or illuminate the water with a flashlight.
-
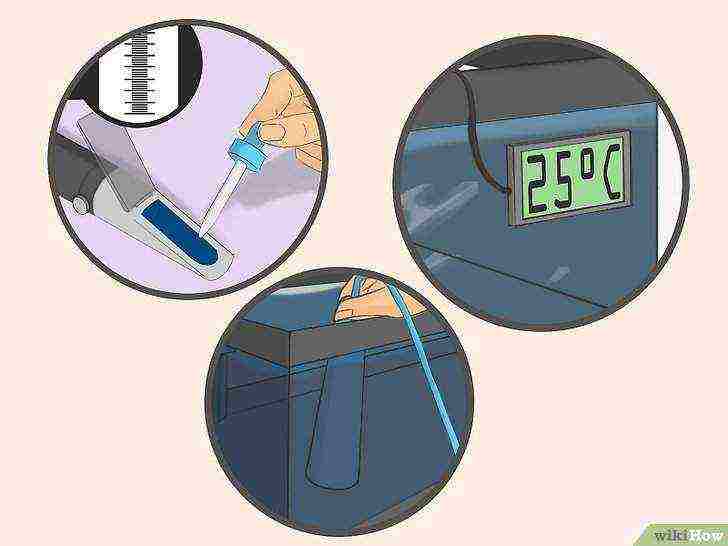
Regularly check the temperature and purity of the water and its salt concentration. All of these parameters are important for a marine aquarium. Make it a rule to check these values in your aquarium weekly.
Part 4 Feeding Artemia
-
Use fortified feed. Selcon is a fairly popular brand of fortified fish feed; but there are also many other brands of food available in specialized aquarium stores. If you have any difficulties with the selection of food for brine shrimp, consult with the seller. It is also always possible to purchase feed in bulk via the Internet.
-

Feed brine shrimp yeast, pureed herbs, egg powder, or powdered milk. Artemia is not picky about food, they calmly eat all of the above. Artemia can also be fed with spirulina.
-
Give brine shrimp only a little feed, but several times a day. Don't overfeed your crustaceans! If the water in the aquarium becomes too cloudy and contaminated with food, clean the aquarium and continue to feed less brine shrimp.
Part 5 Catching Artemia for fish feeding
-

After eight days, start catching the grown Artemia. Of course, if you are raising brine shrimp just for fun, there is no need to catch them. Nevertheless, after 8 days the crustaceans will grow to such an extent that they can be easily caught with a net and fed to the fish.
-
 Switch off the compressor.
Switch off the compressor.
After 10 minutes, empty cysts will float to the surface, and non-hatched cysts will fall to the bottom.
Now you can easily catch live brine shrimp.
-

Use a flashlight to light the place where you want to collect brine shrimp. All brine shrimp will float to the light, so it will be easy to catch them with a net.
-
 Trap adult brine shrimp with a net.
Trap adult brine shrimp with a net.
Small brine shrimp will quietly slip through the netting net, but adult crustaceans will not be able to do this. Catch as many brine shrimp as enough to feed your fish.
-

Feed the brine shrimp to the fish. Release brine shrimp into the fish tank. Fish will gladly feast on nutritious crustaceans.
Tips
- Experiment with different ways of hatching and raising brine shrimp. Choose for yourself the one that suits you best.
- Artemy is attracted to light. Highlighting the water with a flashlight will allow you to collect crustaceans in one place and facilitate the catching procedure.
- Sometimes on sale you can find whole kits for growing Artemia, which include everything you need. Typically, these kits are found in specialized aquarium stores.
- If you cannot find a special siphon for cleaning gravel in an aquarium on the market, you can use a kitchen syringe instead.
Warnings
- Be careful when working with water and electrical appliances. Although air compressors are designed to aerate water, they come in different qualities and the electrical part of the appliance should not be submerged in water anyway.
What do you need
- 40 liter aquarium
- Sponge filter for aquarium (with tube, sponge and air compressor tube holder)
- Air compressor
- Aquarium water heater and thermometer
- Packaging with Artemia cysts (eggs)
- Aquarium salt (when preparing a new aquarium, you will need about 300 g of salt for every 10 liters of water)
- 4 liter container with lid
- 40 liters of reverse osmosis filtered water
- Refractometer or hydrometer for determining salt concentration
- Siphon for cleaning gravel
- Torch
Article Information
This page has been viewed 15,513 times.
Was this helpful?
Every aquarium owner who breeds fish understands the importance of using high-quality, healthy food that is offered to fry. Artemia is one of the best options for these purposes. The use of food from such crustaceans offers a wide range of benefits.
What is Artemia fish food? How is this food useful for the inhabitants of the aquariums? How to breed these miniature crustaceans? We will talk about all this in our publication.
Artemia - what is it?
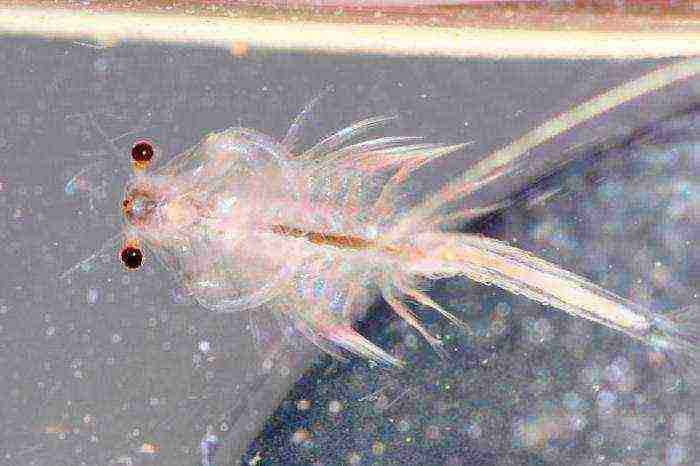

Artemia salina are primitive crustaceans that live in salt waters. Adults are capable of reaching sizes of no more than one centimeter. Such creatures are widespread in the coastal zones of America and Eurasia. They are found in reservoirs, where there are about 300 grams of salt per liter of liquid.
Artemia feeds on organic matter and single-celled creatures, passing a significant amount of water through itself. Thus, the crustacean acts as a real natural cleaner of reservoirs. The shade of these creatures directly depends on the nature of the diet. Artemia can be red to greenish in color.
Large adult crustaceans in natural conditions are prey for numerous inhabitants of reservoirs and birds. Frozen brine shrimp is often used by aquarium lovers. Fish food of this plan can be used for growing crustaceans at home. The procedure does not require any special skills. After all, such creatures are unpretentious to living conditions.
Reproduction
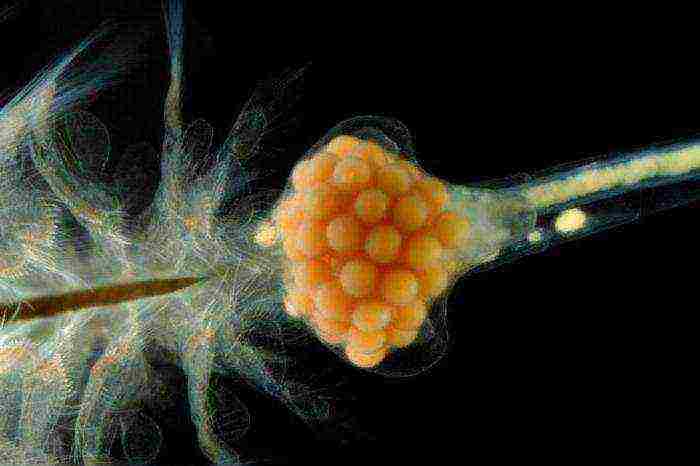
Artemia fish food, a photo of which can be seen in the material, reproduces offspring as follows. Eggs fertilized by males are concentrated in a special sac on the female's abdomen. After a while, nauplia larvae hatch from them.
With the deterioration of environmental conditions, the breeding method changes somewhat. The female lays eggs in a substrate in which the embryos reliably protect the cocoon containing nutrients. In this form, nauplii are able to remain viable for the most indefinite period. As soon as conditions improve, larvae hatch from such a sac. In this case, the minimum number of individuals from the clutch survives. However, this method of reproduction allows brine shrimp to maintain the population.
The benefits of the feed

Food for Artemia fish, a photo of which can be seen in the article, has a number of advantages, among which it is worth noting:
- The possibility of storing eggs for breeding crustaceans in a dry form for the longest period. In this case, the embryos develop normally when they are placed in a suitable environment.
- The incubation of brine shrimp nauplii takes a maximum of several days. Breeding the feed follows a simple and straightforward scheme. Therefore, even with the unexpected appearance of fry of aquarium fish, there will always be something to feed them.
- The benefits of brine shrimp (fish food) are obvious. Such food is well absorbed by young animals. The result of using the feed is a high survival rate and rapid growth of fry.
- The owner of the aquarium can take dry food for brine shrimp and grow the number of nauplii that is required at the moment.
- The organization of the crustacean breeding process requires a minimum of time, investment and effort. To figure out how to grow brine shrimp, just follow the simple instructions.
Methods for increasing the germination of brine shrimp

There are several solutions, the use of which makes it possible to increase the number of nauplii that hatch from eggs. One of the most effective ways is to freeze the seed. Excellent germination is noted after storing brine shrimp eggs in a freezer at a temperature of about -25 ° C.It is recommended to leave the nauplii in this state for several months by placing them in a saturated saline solution. After the specified period has passed, the eggs are removed from the refrigerator and left for a couple of days at room temperature. As a result, the embryos will be fully prepared for effective incubation.
Another way to increase the germination rate of brine shrimp (fish food) is not to use a freezer. The solution requires the treatment of nauplium embryos with non-concentrated hydrogen peroxide. The eggs are placed in a 3% solution of the chemical for about 30 minutes. Next, the seed is thoroughly washed and sent to the incubator. A certain number of eggs can be dried and left to breed for crustaceans in the near future.
Incubator organization

The best option for breeding fish food (brine shrimp) is a spacious container made of plexiglass. Water is poured here, in which salt is dissolved in the amount of one tablespoon per liter of liquid. The incubator provides high-quality round-the-clock lighting. To do this, you can use lamps, the power of which is at least 15 W. Such sources of illumination are located along the walls of the container, which also allows you to heat the water. If the room in which the crustaceans are grown is poorly heated, it is recommended to place the incubator in an insulated box.
Another solution that allows a significant number of brine shrimp nauplii to grow is the use of a conventional plastic bottle with a cut-off bottom. The latter must be moved with the neck down. A sprayer should be installed in place of the plug. You will need several such bottles. Both containers must be filled with an aqueous solution of sodium chloride. It is necessary to periodically supply air to the atomizer that is installed at the necks. This will prevent brine shrimp eggs from sinking to the bottom. You should also warm up the water. Its temperature should not fall below +25 ° C.
How to breed food for brine shrimp?

To begin with, dried eggs are poured into an incubator, which is filled with salt water in advance. As noted above, high-quality lighting is provided here and the optimum temperature is maintained at + 25 ... + 30 ° C. Air is periodically fed into the container, which causes the nauplii to be suspended.
As a rule, the first larvae of brine shrimp begin to hatch from the eggs within a day. After several days, their increased concentration is observed, which is sufficient to catch and start feeding fish fry.
In order for the larvae to remain viable, they must be periodically fed. For this, ordinary baker's yeast is used. The latter dissolve in water to form a cloudy liquid. You should use no more than one gram of yeast per liter of water. This amount of substance is sufficient for nutrition and growth of brine shrimp larvae.
Catching brine shrimp for fish feed

If you follow the instructions for breeding such crustaceans, after a while the nauplii will begin to free themselves from their outer shells, gain body weight and actively move in the water column. To catch them for food, it is enough to direct a stream of air and a lighting lamp to a certain area of the incubator. Adult brine shrimp will concentrate in the presented area, after which they can be removed from the reservoir with a small net. With this method of catching crustaceans, immature individuals will not enter the aquarium with fish fry.
Feeding features
It is necessary to feed brine shrimp to fish in small portions. Crustaceans must be eaten without residue. Otherwise, the nauplii will die, the water in the aquarium will turn sour, which will require regular replacement. In fresh liquid, brine shrimp dies within a few hours. The larvae settle at the bottom and begin to rot.
Finally
As you can see, it is not difficult to grow brine shrimp as food for fish. The main thing is to create optimal conditions for breeding crustaceans. Such creatures act as an extremely nutritious food that provides the inhabitants of the aquarium with a whole range of nutrients, vitamins and trace elements.