Content
- 1 What should you consider before growing grapes?
- 2 Step-by-step technology for growing grapes
- 3 How to properly grow and care for grapes?
- 4 Formation of a grape bush
- 5 Tapestry for grapes
- 6 How to tie grapes
- 7 Grape picking
- 8 Preventive treatment and foliar feeding of grapes
- 9 How to treat grapes after rains, when fungicides and solutions of trace elements are washed off?
- 10 What should you consider before growing grapes?
- 11 Step-by-step technology for growing grapes
- 12 How to properly grow and care for grapes?
- 13 Formation of a grape bush
- 14 Tapestry for grapes
- 15 How to tie grapes
- 16 Grape picking
- 17 Preventive treatment and foliar feeding of grapes
- 18 How to treat grapes after rains, when fungicides and solutions of trace elements are washed off?

Growing grapes is not as difficult as it is commonly believed. Large clusters with juicy fruits will brighten up your vineyard if you follow the basic rules carefully, taking into account the advice of experienced growers.
What should you consider before growing grapes?
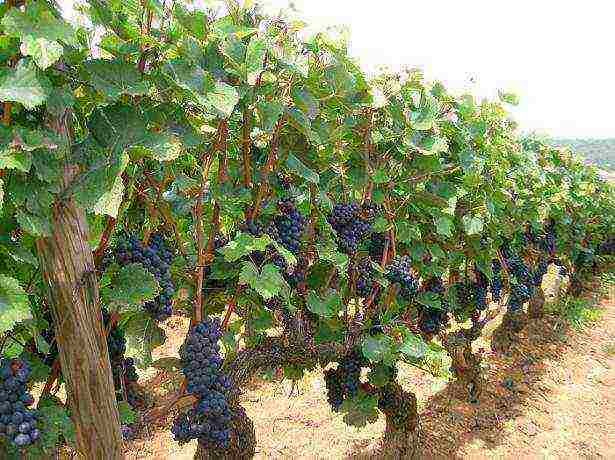

Vineyard photo
Why does not every gardener manage to grow good grapes on their plot so that they do not freeze over the winter, do not rot in the summer and bring a bountiful harvest of decent quality? The fact is that the cultivation of this culture must be taken seriously.
First of all, you should choose a suitable grape variety that will feel comfortable in your area. For instance, growing grapes in the middle lane gives good results only when using winter-hardy varieties with early ripening. Among the new varieties, you will find many excellent options that are resistant to fungal diseases, pests and severe frosts, with high yields and the ability to ripen even in a cloudy short summer.
Video about growing grapes
Black varieties tend to require more sunlight and warmth than light grapes, although there are some hardy black varieties.
Pay special attention to the appearance of the seedling when buying. Look for any mechanical damage, signs of drying or strange spots on the plant? Healthy grape seedlings should have at least three well-developed roots and a shoot about half a meter high. In order not to doubt the quality of planting material, buy seedlings in the nursery, and preferably in a container - this way the plant will take root better.
It will be easier for a novice gardener to plant a ready-made grape seedling, especially if you want to create a vineyard from scratch. Experienced growers can easily cope with cuttings, but those who are not afraid to experiment can try growing grapes from seed.
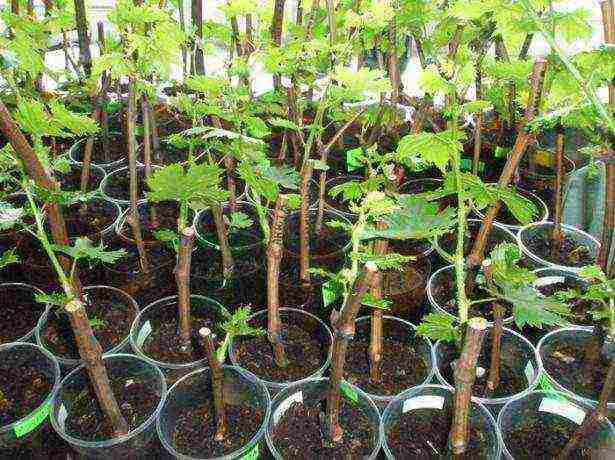

In the photo grape seedlings
Step-by-step technology for growing grapes
When starting to create a vineyard, it is important to take into account the climatic features: if the region is characterized by little snowy winters and severe frosts, it would be preferable to plant grapes in trenches or holes, but if there is enough snow in winter, but the summer is too short and cold, it is better to plant seedlings in bulk ridges. In the pits, the root system will be reliably protected from freezing, and in the ridges, the roots will receive more heat during the summer months.
You can plant grapes both in spring and in autumn, depending on which planting material you have chosen.Consider the most common and simplest option - the autumn planting of grapes with seedlings in planting holes.
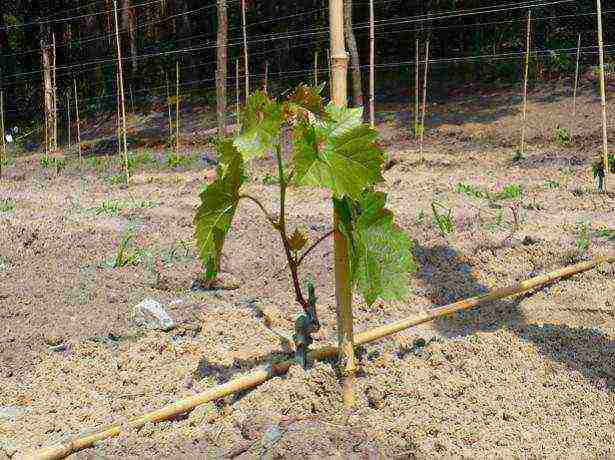

In the photo, planting grapes
Stages of planting a grape seedling:
- choose for planting well-lit by the sun, a flat place where there are no drafts and excess moisture;
- dig a planting hole according to the size of the root system, with a depth of 0.2 to 0.5 m (less for clay soil, deeper for sandy soil);
- mix the soil from the pit with organic and complex mineral fertilizers;
- put a layer of gravel on the bottom of the hole, and put branches or planks on top;
- install a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm or more in order to water the grapes and fertilize the soil through it;
- form a small mound of prepared earth on top of a layer of gravel and branches;
- before planting, dip the roots of a grape seedling in a solution of clay and rotted mullein (clay is twice as much as a mullein);
- cut the shoots into a couple of buds and dip them in melted paraffin;
- place the seedling in the hole, spreading its roots;
- fill the hole with the remaining soil and tamp it carefully;
- pour warm water over the grapes;
- cover the hole with compost or rotted manure.

Photo of watering grapes
If you are going to plant several bushes of grapes, leave at least one and a half meters between them. In this case, it is recommended to arrange plants from the south to the north.
How to properly grow and care for grapes?
For the correct formation of the vines, it is necessary to install a strong trellis. The simplest construction consists of two metal or wooden posts with several rows of wire between them. As the vines grow, they are neatly tied to a wire, giving them the desired direction.
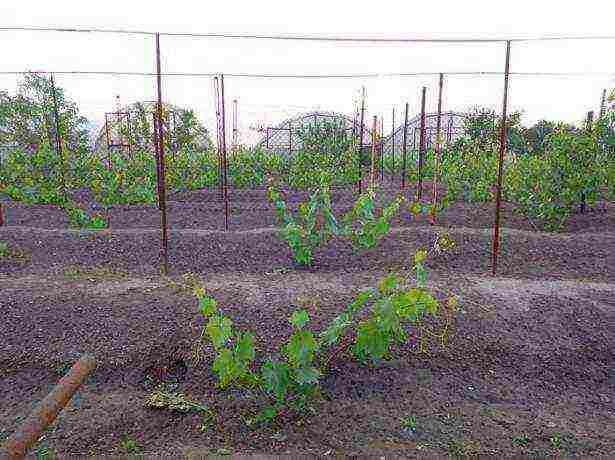

In the photo grapes
In the first three years, pay particular attention to planting: carefully loosen the ground two days after rain or watering, do not allow leaves to wither and dry out the soil from lack of moisture, destroy weeds. Starting from the fourth year, it is sufficient to water the vineyard three to four times per season during the most important phases of development.
Periodically, the vines should be fed through drainage pipes and along the leaves, and treated with suitable fungicides against pests and diseases. Inspect the plants more often in order to start the fight against dangerous enemies of grapes in time and prevent the death of the entire vineyard!
Video about the technology of growing grapes
Prune the grapes every fall after the fall. With the onset of the first night frost, remove the vines from the supports, pin them with brackets to the ground, treat with a solution of copper sulfate and cover with plastic wrap. In spring, do not rush to open the grapes until frosts and sudden changes in temperature stop.
By following the grape growing technology outlined in this article, you can create your own vineyard and enjoy delicious, juicy fruits every year.
Rate the article:
(8 votes, average: 4 out of 5)
The extreme climate of a sunny berry is not a hindrance. And getting a good grape harvest in the second or third year after planting is an achievable goal even for beginners. So how to stop dreaming and start growing grapes ...
First, let's decide on the two most important tasks in growing grapes - we will choose a place for planting grapes and the varieties that we will plant. In principle, the vine will grow almost everywhere (except for a solid shade), and if you take care of it, at the very least it will bear fruit. However, competent planting in the right place will allow you to get really good yields with much less effort. Remember that planting seedlings of low-quality varieties in a vineyard will take your time, energy and good mood. You may be unfairly disappointed in grapes, although the mistake will be entirely yours.
Place for planting grapes
The vineyard should be sunny and sheltered from the wind, for example by the south wall of a house, a barn or a south-facing fence with well-drained soil.If there is a minimum slope on the site, plant the grapes on a gentle southern or south-western slope, orienting the row in the south-north direction. If the plot is flat and the southern walls are occupied, create a place for your grapes by building in any convenient place on the plot a nice solid fence 1.8–2 m high, oriented along the "east-west" line. And you will immediately understand the secret of the monastery vineyards! You can also use for this purpose dense hedges or screens from available materials, for example, from vines or reeds.

Tips for a new wine grower
-
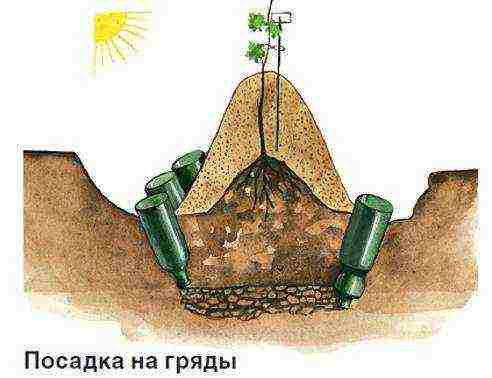
The method of planting grapes depends on the type of soil. Variants are possible, but usually it is recommended to plant grapes on sandy soils in trenches, and on poorly heated loams and clays and in areas with close groundwater occurrence, it is recommended to plant on ridges, which in the old days were called "created".
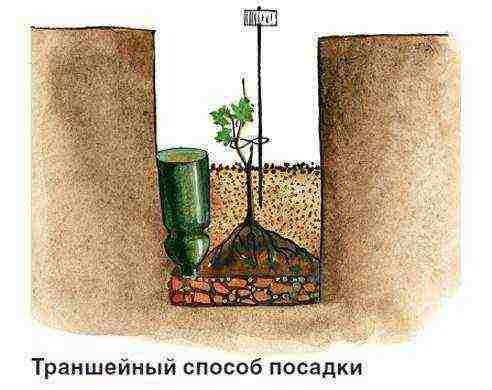
For watering and fertilizing the grapes, I place plastic bottles with a cut-off bottom between the seedlings. For table varieties, as the bushes grow older, I replace them with asbestos-cement pipe trimmings, and for “techies” (wine varieties) I remove them altogether after three years. Mature wine grapes have to get their own water from the soil, and the deeper the roots, the better the wine from its berries.
-
Do not rush to plant seedlings "for permanent residence", especially if these varieties are on trial. Let them live until the first signal brushes in the school (where it is easier to cover). In the first year, some northerner growers do not plant seedlings in open ground at all, but keep them there in mobile containers (for example, in buckets), half buried in the ground. In the fall, containers with seedlings are moved to the basement, and in late spring they are planted. Such seedlings begin bearing fruit earlier.
-
Don't spontaneously plant vines. If your grape bushes are not in a "spot" planting, planning of the vine plot is necessary. Group varieties by purpose, as they have different planting intervals. The distance between bushes of varieties for juice and wine purposes is 0.8 m, for table varieties - at least 1.5 m, between rows - 2–2.5 m. It is advisable to clarify the strength of growth of the selected varieties in order to correctly calculate the right place. Grouping varieties by ripening and frost resistance will facilitate the care of the grapes. You will not need to spray and cover everything to the maximum.
-
Do not plant grafted seedlings (from European and southern nurseries) vertically, but place them practically lying at the maximum possible angle, otherwise there will be problems with the ripening of the vine. Gradually translate them into your own roots.
- Remember that grapes have the property of vertical polarity. When opening, tie a fruitful arrow on a trellis or stakes only horizontally - then all annual green shoots will grow equally. With a vertical garter, shoots grow intensively only from the upper eyes, and from the lower ones, they grow weakly or do not grow.
-
Limit watering. It is only obligatory to water young vines for the first 2 years and water-charging watering, which is common for all varieties, in the fall. Stop watering 7-10 days before the expected flowering, as excessive moisture causes the color to shed and delays the ripening of the crop.
-
Do not use sprinkling, otherwise you will provoke diseases. Arrange drainage channels and place irrigation pipes on the side of the row spacing no closer than 30-50 cm to the base of the bush. Grapes do not like wet leaves and damp ground surfaces. If possible, arrange a visor over the grape bushes.
-
Conduct green operations sparingly and on time. The simultaneous removal of all growth points on the shoot is unacceptable: both the chasing of the top and the pinching of the stepsons. After all, there is a danger that the wintering buds of the bush will start to grow and its potential will drastically weaken. Do not break the stepchildren completely, leave 1-2 sheets. Carry out minting in August, immediately after straightening the crown.
-
Pruning grapes is necessary, otherwise the berries are crushed, and the bush will grow unnecessarily.But in the year of planting, there is no pruning, except for the removal of unripe green parts of the shoots in the fall. From the 3rd year, cut the shoots according to the recommendations (short or long pruning), but do not mindlessly follow the recommended total load, since your conditions - relief, soil, the sum of active temperatures (CAT) - will correct it. Write down from which bud the fruiting shoots grow specifically for you.
Read more: Pruning grapes for beginners .
-
Do not prune in autumn before natural leaves fall or night temperatures are below freezing (early November). Do not prune in the spring, as the "crying" of the vine (sap outflow) weakens the plant.
Read more: How to stop the crying vine>.
-
In the north, it is more reliable to use non-standard formations of a fan or semi-fan type, and not high-standard ones, including for arbors.
Read more: Cordon formation and pruning of grapes.
Read more: Forming grapes for growing on a gazebo>.
-
Winter shelter for the first 2-3 years is needed for all seedlings. The first year the grapes grow tied to a temporary trellis. In autumn, shoots are removed and covered with a two-three-layer air-dry shelter. As a bedding - spruce branches or a board, on top of the seedlings - a layer of spunbond or corrugated cardboard and a film on top (roofing paper, old linoleum). Snow will complete the rest. Leave ventilation slots at the ends of the shelter.
-
Do not remove the cover immediately and completely in the spring. And when removed, leave a couple of layers of spunbond or lutrasil nearby in case of frost.
- Record the timing and characteristics of planting, flowering, ripening, pruning and loading of grapes in a diary. Otherwise, the most valuable information for the analysis of variety testing will be forgotten and lost. And you and the next generation of northern winegrowers, who will definitely come after you, need it so much.
How to grow grapes in the middle lane.
Winter hardy grape varieties
The most necessary requirements for grape varieties in the Moscow region and to the north are frost resistance, the ripening period of the harvest and vines. But you shouldn't put so-called “non-concealment” at the forefront. This concept is relative and does not depend on the variety, but on what are the minimum temperatures in your country house in winter. In the first step, choose the earliest frost-resistant varieties. Later, with experience, an understanding will come that northern viticulture also provides us with certain bonuses, for example, in the form of long daylight hours, which partially compensates for the missing warmth of the grapes. And then you can try growing later varieties.
In addition, in the north, there are practically no diseases and pests of grapes. However, it is always better to prevent danger. There are so-called complex-resistant grape varieties - with high resistance to both frost and disease.
Read more about grape diseases and how to treat them.
Also determine the purpose of the grapes. Why do you need it: for the table, for juice and wine, for decorating the gazebo, or just "so that there was"? Today there are more than 15,000 grape varieties, so there is plenty to choose from.
For beginners, I would advise tasty and unpretentious table varieties ‘Agat Donskoy’, ‘Aleshenkin’, ‘Yubileiny Novgorod’, universal ‘Platovsky’, ‘Crystal’, ultra-early table ‘Krasa Nikopol’, as well as some universal Amur hybrids A.I. Potapenko and F.I. Shatilova. Those who have children should pay attention to the super-early and tender-sweet varieties ‘Liepaja Yantar’ and ‘Early Tsiravsky’ (selected by G.E. Vesminsha), as well as the ‘Krasa Severa’ variety with a high content of useful folic acid. From the listed grape varieties, select no more than four to five for the first planting.



How to buy grape seedlings and rooting cuttings
The most reliable sources of planting material are winegrowers' clubs and forums, where enthusiastic and experienced gardeners and collectors communicate, as well as MOIP and TSKHA.You should not buy seedlings and cuttings at spontaneous roadside markets and exhibitions (of course, this does not apply to the stands of well-known nurseries).
How to buy grapes and choose a good seedling.
You can ask a question to the author of the article, wine grower Olena Nepomniachtchi, here .
You can find out how to grow other plants, what gardening work you need to plan, from other articles on our website. Also, please pay attention to the information block to the left of the text. The links located in it lead to articles of related topics.
 Grown over millennia, grapes have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of a wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large clusters and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing a lot of work and skill in growing and caring for grapes.
Grown over millennia, grapes have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of a wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large clusters and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing a lot of work and skill in growing and caring for grapes.
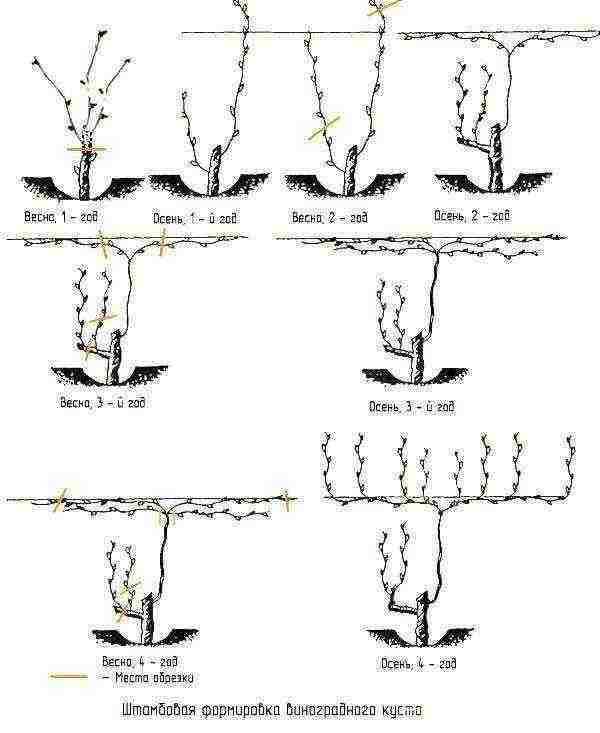
The first, after planting seedlings in the ground, a contribution to the future harvest is the formation of a grape bush, which begins from the first year of the plant's life and, together with the shape of the plant's crown, determines its fruiting.
With a competent approach, by the fourth year the bush takes on its final form, but this does not mean that the work of the grower is completed.
Formation of a grape bush
 The choice of the shape of the grape bush, which determines its appearance, structure and number of both new shoots and green mass, depends on the climatic conditions of growth, soil fertility and the characteristics of the plant variety.
The choice of the shape of the grape bush, which determines its appearance, structure and number of both new shoots and green mass, depends on the climatic conditions of growth, soil fertility and the characteristics of the plant variety.
 The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
- regular and, in accordance with varietal characteristics, bountiful harvest;
- a qualitatively ripening growth at the end of the growing season;
- a plant that tolerates winter without problems and does not suffer from diseases of grapes and its pests common in the area;
- providing a simple care for a grape seedling;
- facilitating the pruning of the vine and its watering, rejuvenation and adjustment of the existing load.
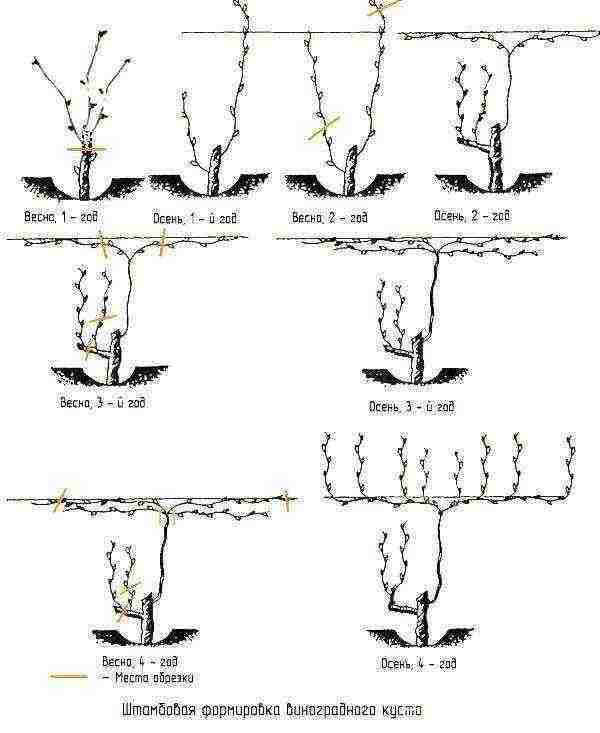
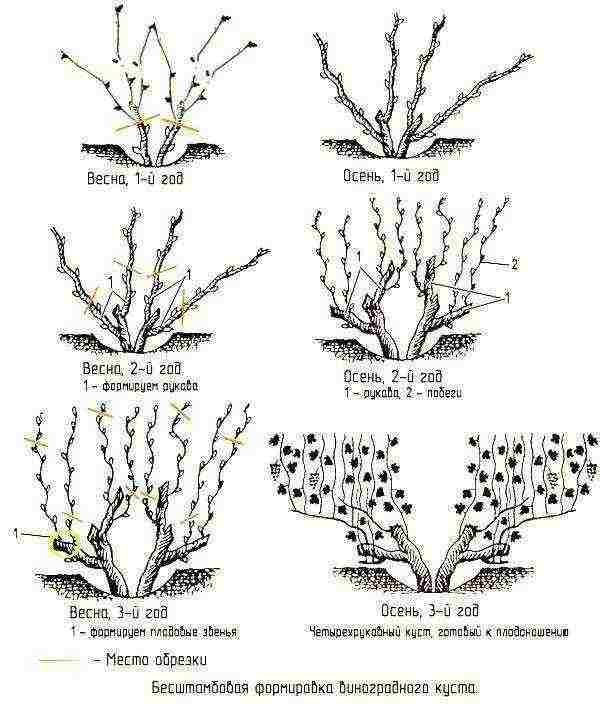
When wondering how to grow grapes, some novice gardeners act on a whim, not paying due attention to pruning the bush. However, there are many well-established options and types of forms that allow you to get good results in a wide variety of farming conditions. With the help of spring pruning, the grape bush is formed with or without a stem of various heights.
Most often, growers give rooting grape seedlings:
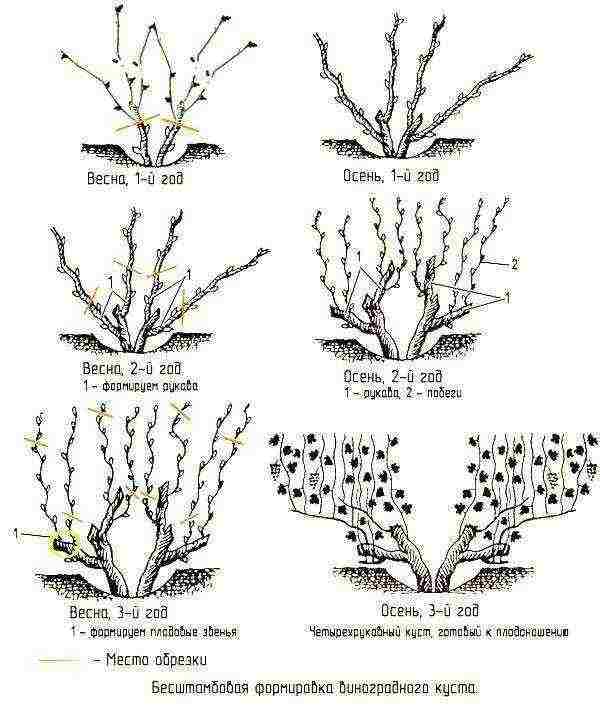
- capitate shape without perennial sleeves, but with a thickened upper part of the stem, from which, due to pruning by 1-2 eyes or per ring, a mass of new shoots grows;
- cup-shaped with sleeves of various lengths extending from the trunk, resting on stakes;
- a form with fruit links directed in one or two directions, the entire growth on which is distributed on a vertical trellis;
- cordon form with one or more perennial cordons, along which fruit links or branches are distributed. This option is convenient in growing and caring for grapes, gives high yields, but is more common in regions with a warm climate, where the vine does not require shelter for the winter;
- fan-shaped and semi-fan-shaped, resting on a trellis and having several sleeves of different lengths and strengths.
It is the various variants and combinations of the fan that have received the greatest recognition of winegrowers in Russia, since such a grape bush is easy to care for.
 The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter.The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, while in the summer excess and overgrowing shoots and stepchildren break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter.The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, while in the summer excess and overgrowing shoots and stepchildren break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
Tapestry for grapes
 Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important for the stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for landscaping sheds, gazebos and other buildings.
Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important for the stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for landscaping sheds, gazebos and other buildings.
Walls, poles, stakes and even trees growing next to the bushes can serve as a support for the vine, but the best solution would be to install a special trellis for grapes.
 In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common.
In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common.
- vertical trellis, where the grape shoots are located in the same plane;
- an inclined trellis, on which the shoots are spaced into two planes at an angle to each other.
 In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the supports of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but for obtaining high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the supports of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but for obtaining high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
To simplify the cultivation and care of the grapes, between the trellises, there are aisles sufficient to remove the bushes and cover them during cold weather, as well as to provide sufficient lighting for the plantings, and the rows did not overlap. It is better if the trellis for grapes on the site will be located from north to south. In this case, the height of the structure is chosen depending on the growth of the grower, the characteristics of the variety and the chosen shape of the bush.
How to tie grapes
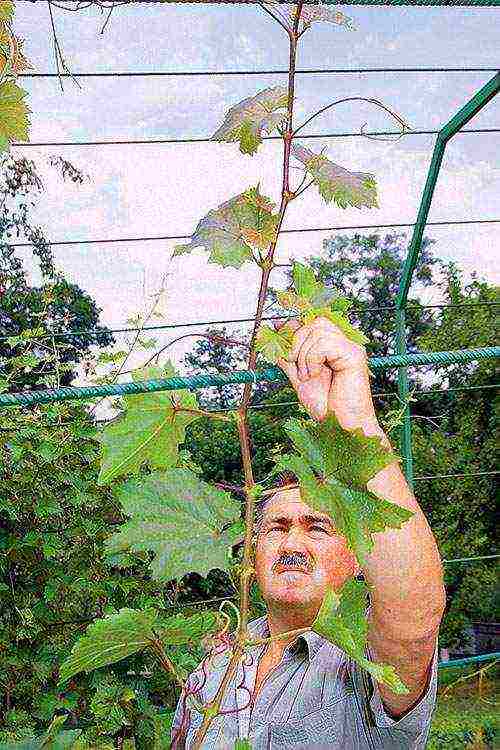 As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
- The plant is provided with the best light and air conditions.
- It is easier to trim and normalize the green mass and ovary.
- Carrying out foliar dressing of grapes, as well as performing "green pruning" is facilitated.
- Vertical shoots grow and mature better.
- The risk of developing grape disease and pest damage is reduced.
- The budding winegrower should know when and how to tie the grapes.
The first time it is necessary to fix the position of the shoots when they are about 40-50 cm long and reach the bottom row on the trellis. Then, as they grow, the stems are tied sequentially to all rows.
As a garter material, it is better to take scraps of textiles or knitwear, natural twine or twine, that is, means that do not squeeze or pinch the growing shoots. It is convenient to use a special tool for tying a grape seedling, freely fixing the shoots with a plastic clip. On trellises, where the wire is stretched in two parallel rows, the shoots only start in such a gap, and the resulting whiskers are firmly fixed on the support over time. If grapes grown on a gazebo or shed are being taken care of, where free growth is provided, then such shoots do not need to be tied up.
Grape picking
 In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant.Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant.Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
If in regions with a short summer, grape pinching consists in the complete removal of shoots already at the initial stages of development, then in the south, especially when growing early varieties, stepchildren are only shortened in order to get an additional harvest of sweet berries by autumn.
And in some cases, for example, when the vine suffers from frost or hail, grapes are not pinched at all. Stepsons replace the lack of green mass on the bush and help to resume the development of the bush.
Preventive treatment and foliar feeding of grapes
 Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Growing on a trellis gives the grower the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Growing on a trellis gives the grower the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
The greatest need for such dressings is for grape bushes:
- before and after flowering;
- during the period when the coloring of the berries begins;
- a few days before harvest.
For feeding grape seedlings and adult bushes, use a solution containing 5% superphosphate, 0.5% ammonium sulfate and 1% potassium salts. When the berries begin to ripen, the vine no longer needs nitrogen, but trace elements, for example, zinc and boron, can be added to the top dressing.
After flowering, the bushes are treated with a 1% solution of boric acid in combination with a fungicide that prevents the development of downy mildew, a disease that occurs in conditions of high humidity and has a detrimental effect not only on the future harvest, but also on the entire grape plant. The final foliar dressing of grapes can be carried out on the basis of the infusion of wood ash. The introduction of such dressings, as well as spraying the bushes with fungicides and insecticides, is carried out in the afternoon, when the temperature drops, the sun cannot burn the leaves and inflorescences or in cloudy weather. The longer the drops of the product remain on the greens, the greater the effect of the procedure.
How to treat grapes after rains, when fungicides and solutions of trace elements are washed off?
In the case of severe precipitation, the treatment is repeated as soon as possible, paying attention to spraying the bushes with Ridomil, especially during the period when the flowering has already been completed, and the likelihood of mildew development is high.
 No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
At the same time, do not forget that the effectiveness of dressings and remedies is really high if all the rules for growing and caring for grapes are followed, weeds and excess shoots are removed in time, air and food are provided to all shoots.
All about planting and growing grapes - video

Grapes are one of the most beloved treats for people. Aromatic wine is made from it, dried fruits made from berries are added to baked goods, used in cooking. Cosmetics are made from grape seeds. But in order to get all these benefits, of course, you must first plant and grow this useful berry.It would seem that there is nothing easier. You have planted a seedling, and you wait until the fruits appear in a few years. But it’s not that simple. In order for the grapes to grow well and please with a rich harvest, it is necessary to take care of them. How to do this correctly, about the agricultural technology of growing grape bushes will be discussed in this article.
Landing dates
You can plant grape seedlings both in autumn and spring. It is better, of course, to do this in early spring, when the soil after the winter cold has managed to warm up to 6-8. At this time, the "cry" of the vineyards usually begins. That is, the beginning of active sap flow through the plant. Kilchevannye shanks sit down a little later. The soil should warm up to 10-12 degrees. In the southern regions, where the winter is not so harsh and the ground does not freeze too much, the planting of grape seedlings can be carried out in the fall. At a time when the leaves were already crumbling, before the onset of cold weather.
 In spring, the seedling takes root better and has time to get stronger before winter.
In spring, the seedling takes root better and has time to get stronger before winter.
If planting takes place in the fall, then the mounds of land should be larger than in the spring. To avoid frost damage to seedlings.
What to plant
Planting material is cuttings or seedlings (rooted cuttings). Saplings or cuttings are of two types:
- Vaccinated;
- Own-rooted.
In those areas where the soil freezes deeply and there is a risk of frost damage to the roots, the planting of grafted seedlings is practiced. Also, this type of planting material is used in places where the soil is infected with phylloxera. If the weather conditions are favorable, the winters are not too cold and the soil is free of phylloxera, native-rooted grapes are cultivated.
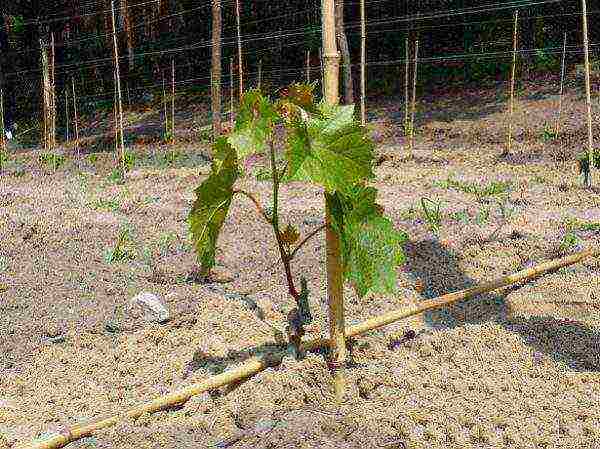 You can plant an already blossoming and strong seedling, or you can also plant a cutting that will begin its growth directly in the open field.
You can plant an already blossoming and strong seedling, or you can also plant a cutting that will begin its growth directly in the open field.
Grafted seedlings are much more resistant to low temperatures and some diseases.
Cuttings (shanks)
Growing seedlings from cuttings is perhaps the main method for propagating grapes. This is a fairly simple method that even a novice gardener can handle. The most important thing is to get cuttings of the grape variety that you would like to plant. In autumn, when the leaves fall off, but even before frost it is necessary:
- Cut from the vine of your favorite grapes cuttings with a diameter of at least 5 mm with 5-7 buds;
- Treat them with a solution of 1% copper sulfate to destroy disease spores;
- Soak for one to two days in water;
- Dry in the fresh air until water droplets disappear and put in a plastic bag, into which, if possible, fill in sawdust.
- Storage temperature 6-7 ° C, humidity just below 100 percent.
 The whole planting process is extremely simple and requires little effort.
The whole planting process is extremely simple and requires little effort.
In the spring, the saved cuttings are kept in water for some time until the roots appear. Then they are planted in open ground.
Graft
It is advisable to graft the grapes in the spring. Of course, each term has its own rules according to which this operation should be carried out. What does the vaccine give? This manipulation allows you to make the grape plant more resistant to various diseases and pests. In addition, grafting makes it possible to get completely different varieties on one root system. With this manipulation, you can rejuvenate the grapes. To develop new varieties with improved taste.
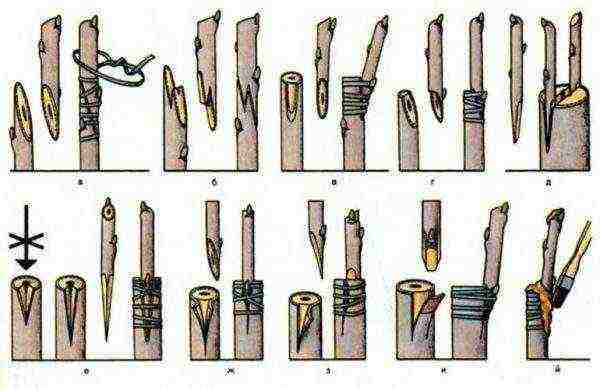 Grafting options for grape cuttings.
Grafting options for grape cuttings.
Grafting grapes is a rather complicated procedure that requires some training and skills.
Layers
Propagation of grapes by layering is a fairly simple method and has been known since ancient times. The advantage of this method is that you can easily renew an old grape bush, grow new seedlings or fill an empty space with a new plant next to the mother bush.
Any healthy and sufficiently developed shoot is selected in the vineyard. A small groove 10-20 cm deep is dug for it. Then the shoot is laid in it, fixed with wire brackets and sprinkled with earth and humus on top. The end of the vine must remain above the ground. It must be strengthened by tying it to a support. Further, the vine planted in the groove must be watered with water, having previously dissolved a small amount of manganese in it. Up to slightly pink. When the shoot has a full-fledged root system, it can be separated from the mother tree.
For propagation by this method, the bushes are formed low, the head of the bush should be as close to the ground as possible and with short sleeves.
In the hot season, the layers must be watered at least three times a month.
How to choose seedlings for a good harvest
The key to a good vineyard is quality planting material. Its further development and yield depends on the correct choice of grapes, the condition of the seedling. It is better to purchase planting material in specialized nurseries that are professionally engaged in breeding certain varieties. Depending on the weather in the region, the composition of the soil, it is necessary to decide what type of seedlings is best to plant. Grafted, which are more resistant to frost and phylloxera, or self-rooted, grown from cuttings.
Landing rules
For the correct planting of grape seedlings, it is necessary to take into account all the details that may affect the future harvest. And this:
- Choosing a suitable place;
- Depth of planting material in the ground;
- Distance between bushes and between rows;
- Soil moisture;
- The thickness of the layer of humus and the introduction of fertilizers necessary for growth;
- Low temperature protection if the grapes are not frost resistant.
Novice gardeners often make a mistake when planting grapes for the first time. The planting material is too shallow in the soil. Because of this, the roots of seedlings, with the onset of frost, freeze out.
Seat selection
Grapes are a sun-loving plant, which means that the sunny, southern side of the garden plot will be an ideal place for planting it. The area must be protected from constant drafts. It is better to plant grape bushes near the walls of the house, along the fence or other buildings on the territory. During the day, the walls warm up a little in the sun and at night give off heat to the plants. In addition, the grapes will be protected from strong winds and low temperatures, which means that the berries will ripen much faster.
 Grapes are an unpretentious plant, but they cannot tolerate shade.
Grapes are an unpretentious plant, but they cannot tolerate shade.
Given that grapes do not like shaded areas, you should avoid planting them near tall trees.
Soil preparation
Grapes grow on almost any soil with the exception of salt marshes. A place where groundwater is too close to the surface is also not suitable. It is advisable to prepare a pit for planting a grape seedling a little in advance. This requires:
- dig a hole 60–70 cm wide;
- pour into it two buckets of rotted manure, two buckets of the top layer of fertile soil, a can of ash from burnt wood, 150-200 grams of superphosphate;
- mix well the soil with fertilizer in the pit.
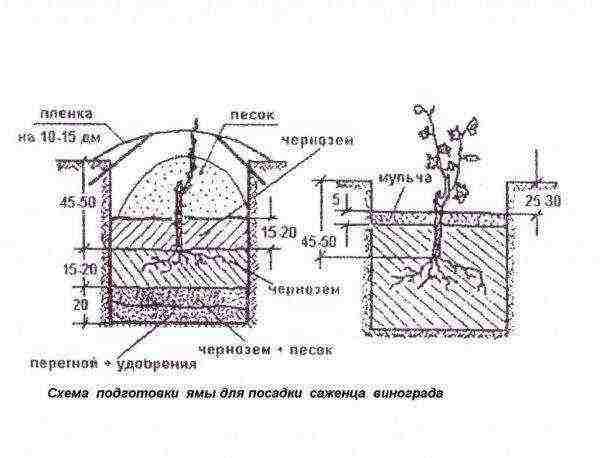
The distance between the bushes should be at least 1.5, and in the row spacing 2 meters.
When planting a seedling near the house, it is necessary to retreat from the wall one and a half to two meters, so that in the future the growing strong roots of the vineyard do not damage the foundation.
Landing time and dates
Grapes can be planted in both spring and fall. An autumn or spring planting has both advantages and disadvantages. A seedling planted in spring does not have to winter in the open field, thereby eliminating the risk of damage from frost. Over the summer, the planting material gains strength and its root system is strengthened. The advantage of autumn planting is that it excludes the possibility of spoiling the seedling during storage due to the lack of storage itself.Planting material, properly sheltered from low temperatures, undergoes a kind of acclimatization in a new place during the winter. Although the roots are not so active, they still grow even in winter, because the rhizomes, unlike the ground part of the plant, do not have a state of dormancy.
 The best time for planting seedlings is the end of May.
The best time for planting seedlings is the end of May.
To get high yields from the vineyard, plants need proper care:
- competent, correct pruning;
- carrying out katarovka at least twice during the summer;
- timely pinching to relieve the bush and garter. The garter should be both dry and green;
- in the autumn and spring, preventive spraying against fungal diseases;
- feeding the vineyard with nitrogen fertilizers before the start of the growing season;
- installation of supports. A strong wire must be stretched between the posts, which can withstand not only the vines, but also the pouring bunches. The first, closest to the ground, is stretched at a level of 50 cm. The second is 25 cm from the first crossbar and the subsequent ones at a distance of 40 cm from each other.
 In the early years, the young vineyard is weeded, loosened and fed.
In the early years, the young vineyard is weeded, loosened and fed.
Grapes also bear fruit on rainfed lands, but nevertheless, for greater productivity and longevity of the plant, it must be watered regularly. The school is watered everywhere. Fruit-bearing vineyards are watered in the irrigated areas of the southern regions of the country. When planting, schools give 25-35 liters of water for each running meter. In the next 5–8 irrigations during the growing season, they provide 400–800 cubic meters of water per hectare. When planting grapes, 20 liters of water are poured under each bush. In fruit-bearing vineyards, 800–1400 cubic meters of water per hectare are used for each irrigation.
 Watering is done only if necessary, if the summer is dry.
Watering is done only if necessary, if the summer is dry.
Many grape varieties do not like excess moisture, so watering the plants should be moderate.
Garter
After the end of the trimming, it is necessary to carry out the garter. This procedure consists in tying last year's vines with twine to a wire that is stretched between the pole supports. The shoots are tied up horizontally so that the uniform development of all eyes occurs. As young shoots grow, they are directed upward. This operation is called the green garter. With the first green garter, young shoots are attached to the second wire from the ground. With further growth, they are tied to the third, fourth. 3-4 green garters are produced during the summer.
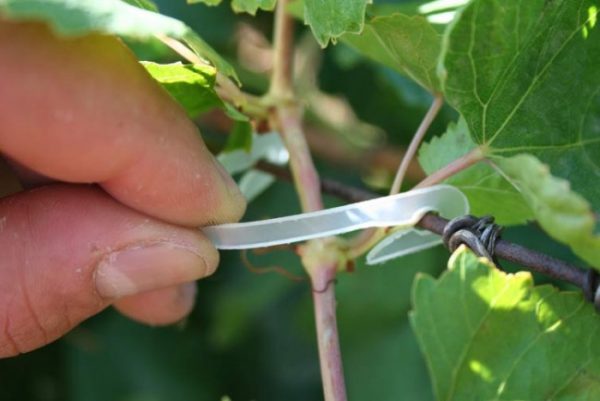 The grapes are usually tied up at the stage of development of their green shoots.
The grapes are usually tied up at the stage of development of their green shoots.
Many grape varieties have bisexual flowers. Sometimes, for physiological reasons, they crumble, and this leads to looseness of the hands.... This disadvantage can be eliminated by pinching the tops of fruiting shoots at the very beginning of flowering or in front of it. This process will be most effective on bushes and shoots with great vigor. After a temporary suspension of growth as a result of pinching, nutrients are not consumed for growth, but are used for the development of inflorescences.
 Pinching consists in removing the tip of the shoot.
Pinching consists in removing the tip of the shoot.
Pinching is not carried out on table varieties for which looseness of bunches is desirable.
Top dressing
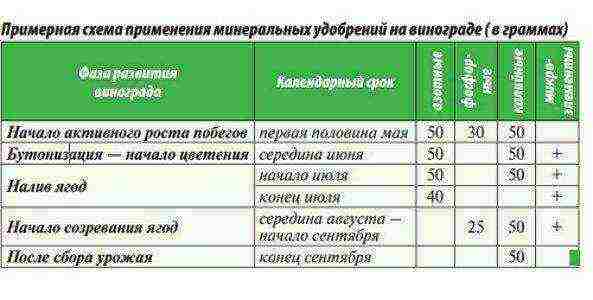
The use of mineral and organic fertilizers significantly increases the yield of grapes. You can recommend the following plant feeding scheme:
- In the southern regions of the country before opening the bushes in the spring, superphosphate, ammonium sulfate (200 g and 100 grams, respectively) are added under each bush. Depth 40 cm.
- Before bud break - nitrogen, phosphoric, and at the beginning of ripening of berries - phosphorus and potash.
- Before flowering, during flowering and at the beginning of ripening, superphosphate, ammonium sulfate, potassium salt (30: 20: 10). In grams for each bush. The depth of application is up to 35 cm. Once every three years, it is advisable to feed the bushes with organic fertilizers.At least 15 kg of humus for each bush. It should be remembered that in the spring, mineral fertilizers are not used in this case.
Pruning
In order to regulate the development of the grape bush and its fruiting, it is imperative to prune the vine. At the same time, young bushes form. When pruning two-year-old and older bushes, you must remember about their load. Pruning happens:
- Short... They try to leave 2-3 eyes. An example of such trimming is a cup-shaped formation, for example, a Crimean bowl.
- Long... Shoots with pruning shears are cut, leaving 6 or more buds on the vine. An example is a large fan formation.
- Mixed. Some of the vines are often cut short enough (knots), and some are long cut for fruit shoots. This pruning is the most common and is called fruit link pruning.
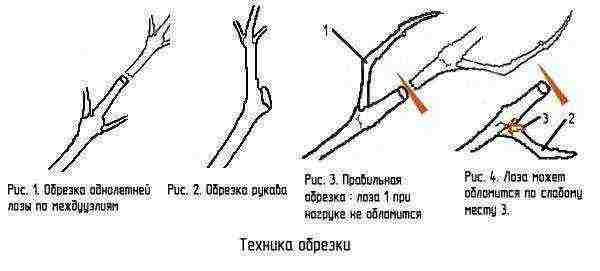
To properly cut the bush, it is necessary to take into account the adopted formation. And also take into account the morphological and biological characteristics of the variety, weather and climatic conditions, the degree of damage to shoots by frost.
Pest control
Diseases and pests wreak havoc on vineyards. Not only the harvest suffers, but the vine does not ripen either. And unripe shoots do not tolerate winter frosts well.
Among the most common diseases are mildew, oidium, anthracnose. And also black, white, gray rot. Even if grapes resistant to diseases are planted on the site, it must be remembered that unfavorable weather conditions can provoke the spread of fungal diseases. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention in the fall, the bushes and the soil around them should be treated with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid. In the spring, before bud break, the bushes should be sprayed with a solution of the same concentration. But if signs of disease appear on shoots and leaves, then a 3% solution of copper sulfate and freshly slaked lime is used. But it is better in this case to treat the bushes with a fungicide.
Video
This video shows the correct planting of seedlings and the correct cultivation of grape seedlings from cuttings.
conclusions
It takes some effort to get a good harvest from a vineyard. Namely:
- Prepare the plot and soil for planting grapes.
- Pick up or grow planting material.
- Observing all the norms plant seedlings in open ground.
After the growth of seedlings, pruning and katarovka. - For unloading bush pinching.
- Increase yield possible due to irrigation and fertilizing with mineral fertilizers.
- Be sure to use for the prevention of the occurrence of fungal diseases, spraying with Bordeaux liquid. But if the first signs of pathology appear, switch to the treatment of the vineyard with fungicides.

Growing grapes is not as difficult as it is commonly believed. Large bunches with juicy fruits will brighten up your vineyard if you follow the basic rules carefully, taking into account the advice of experienced growers.
What should you consider before growing grapes?
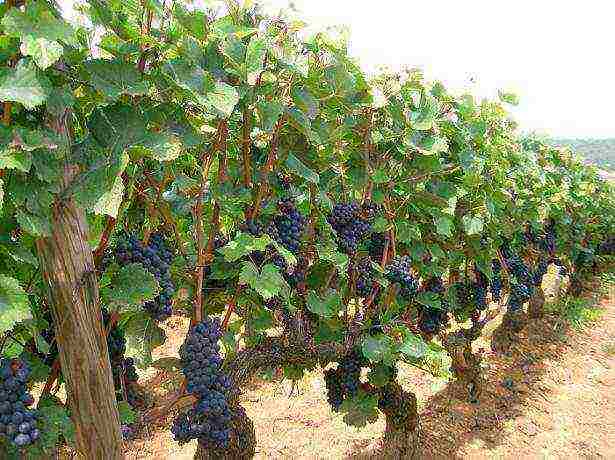

Vineyard photo
Why does not every gardener manage to grow good grapes on their plot so that they do not freeze over the winter, do not rot in the summer and bring a bountiful harvest of decent quality? The fact is that the cultivation of this culture must be taken seriously.
First of all, you should choose a suitable grape variety that will feel comfortable in your area. For instance, growing grapes in the middle lane gives good results only when using winter-hardy varieties with early ripening. Among the new varieties, you will find many excellent options that are resistant to fungal diseases, pests and severe frosts, with high yields and the ability to ripen even in a cloudy short summer.
Video about growing grapes
Black varieties tend to require more sunlight and warmth than light grapes, although there are some hardy black varieties.
Pay special attention to the appearance of the seedling when buying. Look for any mechanical damage, signs of drying or strange stains on the plant? Healthy grape seedlings should have at least three well-developed roots and a shoot about half a meter high. In order not to doubt the quality of the planting material, buy seedlings in the nursery, and preferably in a container - this way the plant will take root better.
It will be easier for a beginner gardener to plant a ready-made grape seedling, especially if you want to create a vineyard from scratch. Experienced growers can easily cope with cuttings, but those who are not afraid to experiment can try growing grapes from seed.
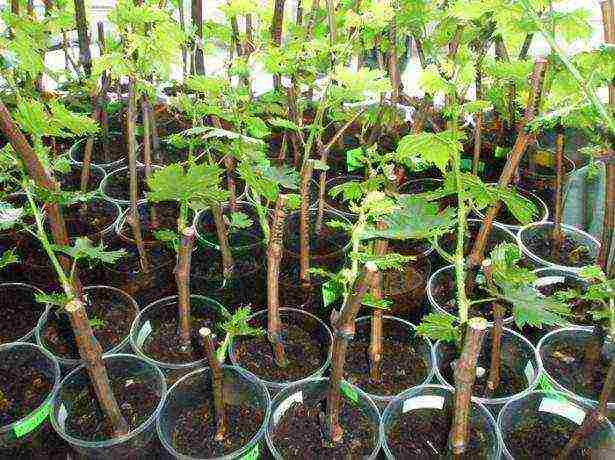

In the photo grape seedlings
Step-by-step technology for growing grapes
When starting to create a vineyard, it is important to take into account the climatic features: if the region is characterized by little snowy winters and severe frosts, it would be preferable to plant grapes in trenches or holes, but if there is enough snow in winter, but the summer is too short and cold, it is better to plant seedlings in bulk ridges. In the pits, the root system will be reliably protected from freezing, and in the ridges, the roots will receive more heat during the summer months.
You can plant grapes both in spring and autumn, depending on which planting material you have chosen. Consider the most common and simplest option - the autumn planting of grapes with seedlings in planting holes.
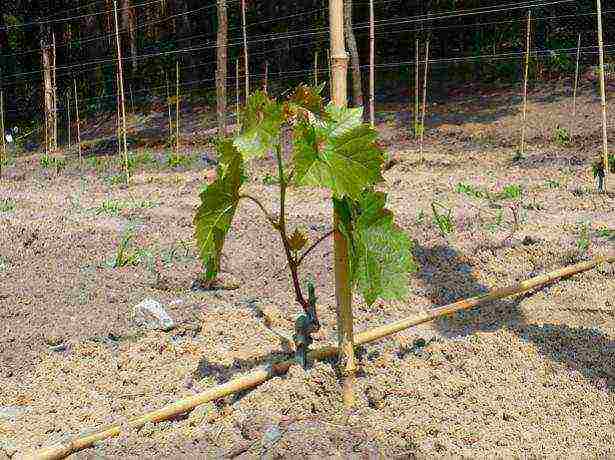

In the photo, planting grapes
Stages of planting a grape seedling:
- choose for planting well-lit by the sun, a flat place where there are no drafts and excess moisture;
- dig a planting hole according to the size of the root system, with a depth of 0.2 to 0.5 m (less for clay soil, deeper for sandy);
- mix the soil from the pit with organic and complex mineral fertilizers;
- put a layer of gravel on the bottom of the hole, and put branches or planks on top;
- install a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm or more in order to water the grapes and fertilize the soil through it;
- form a small mound of prepared earth on top of a layer of gravel and branches;
- before planting, dip the roots of a grape seedling in a solution of clay and rotted mullein (clay is twice as much as a mullein);
- cut the shoots into a couple of buds and dip them in melted paraffin;
- place the seedling in the hole, spreading its roots;
- fill the hole with the remaining soil and tamp it carefully;
- pour warm water over the grapes;
- cover the hole with compost or rotted manure.

Photo of watering grapes
If you are going to plant several bushes of grapes, leave at least one and a half meters between them. At the same time, it is recommended to arrange plants from south to north.
How to properly grow and care for grapes?
For the proper formation of the vines, it is necessary to install a solid trellis. The simplest construction consists of two metal or wooden posts with several rows of wire between them. As the vines grow, they are neatly tied to a wire, giving them the desired direction.

In the photo grapes
In the first three years, pay particular attention to planting: carefully loosen the ground two days after rain or watering, do not allow leaves to wither and dry out the soil from lack of moisture, destroy weeds. Starting from the fourth year, it is sufficient to water the vineyard three to four times per season during the most important phases of development.
Periodically, the vines should be fed through drainage pipes and along the leaves, and treated with suitable fungicides against pests and diseases. Inspect the plants more often in order to start the fight against dangerous enemies of grapes in time and prevent the death of the entire vineyard!
Video about the technology of growing grapes
Prune the grapes every fall after the fall. With the onset of the first night frost, remove the vines from the supports, pin them to the ground with brackets, treat with a solution of copper sulfate and cover with plastic wrap. In the spring, do not rush to open the grapes until frosts and sudden changes in temperature stop.
By following the grape growing technology outlined in this article, you can create your own vineyard and enjoy delicious, juicy fruits every year.
Rate the article:
(8 votes, average: 4 out of 5)
 Grown over millennia, grapes have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of a wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large clusters and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing a lot of work and skill in growing and caring for grapes.
Grown over millennia, grapes have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of a wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large clusters and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing a lot of work and skill in growing and caring for grapes.
The first, after planting seedlings in the ground, a contribution to the future harvest is the formation of a grape bush, which begins from the first year of the plant's life and, together with the shape of the plant's crown, determines its fruiting.
With a competent approach, by the fourth year the bush takes on its final form, but this does not mean that the work of the grower is completed.
Formation of a grape bush
 The choice of the shape of the grape bush, which determines its appearance, structure and number of both new shoots and green mass, depends on the climatic conditions of growth, soil fertility and the characteristics of the plant variety.
The choice of the shape of the grape bush, which determines its appearance, structure and number of both new shoots and green mass, depends on the climatic conditions of growth, soil fertility and the characteristics of the plant variety.
 The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
- regular and, in accordance with varietal characteristics, bountiful harvest;
- a qualitatively ripening growth at the end of the growing season;
- a plant that tolerates winter without problems and does not suffer from diseases of grapes and its pests common in the area;
- providing a simple care for a grape seedling;
- facilitating the pruning of the vine and its watering, rejuvenation and adjustment of the existing load.
When wondering how to grow grapes, some novice gardeners act on a whim, not paying due attention to pruning the bush. However, there are many well-established options and types of forms that allow you to get good results in a wide variety of farming conditions. With the help of spring pruning, the grape bush is formed with or without a stem of various heights.
Most often, growers give rooting grape seedlings:
- capitate shape without perennial sleeves, but with a thickened upper part of the stem, from which, due to pruning by 1-2 eyes or per ring, a mass of new shoots grows;
- cup-shaped with sleeves of various lengths extending from the trunk, resting on stakes;
- a form with fruit links directed in one or two directions, the entire growth on which is distributed on a vertical trellis;
- cordon form with one or more perennial cordons, along which fruit links or branches are distributed. This option is convenient in growing and caring for grapes, gives high yields, but is more common in regions with a warm climate, where the vine does not require shelter for the winter;
- fan-shaped and semi-fan-shaped, resting on a trellis and having several sleeves of different lengths and strengths.
It is the various variants and combinations of the fan that have received the greatest recognition of winegrowers in Russia, since such a grape bush is easy to care for.
 The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter.The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, while in the summer excess and overgrowing shoots and stepchildren break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter.The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, while in the summer excess and overgrowing shoots and stepchildren break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
Tapestry for grapes
 Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important for the stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for landscaping sheds, gazebos and other buildings.
Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important for the stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for landscaping sheds, gazebos and other buildings.
Walls, poles, stakes and even trees growing next to the bushes can serve as a support for the vine, but the best solution would be to install a special trellis for grapes.
 In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common.
In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common.
- vertical trellis, where the grape shoots are located in the same plane;
- an inclined trellis, on which the shoots are spaced into two planes at an angle to each other.
 In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the supports of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but for obtaining high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the supports of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but for obtaining high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
To simplify the cultivation and care of the grapes, between the trellises, there are aisles sufficient to remove the bushes and cover them during cold weather, as well as to provide sufficient lighting for the plantings, and the rows did not overlap. It is better if the trellis for grapes on the site will be located from north to south. In this case, the height of the structure is chosen depending on the growth of the grower, the characteristics of the variety and the chosen shape of the bush.
How to tie grapes
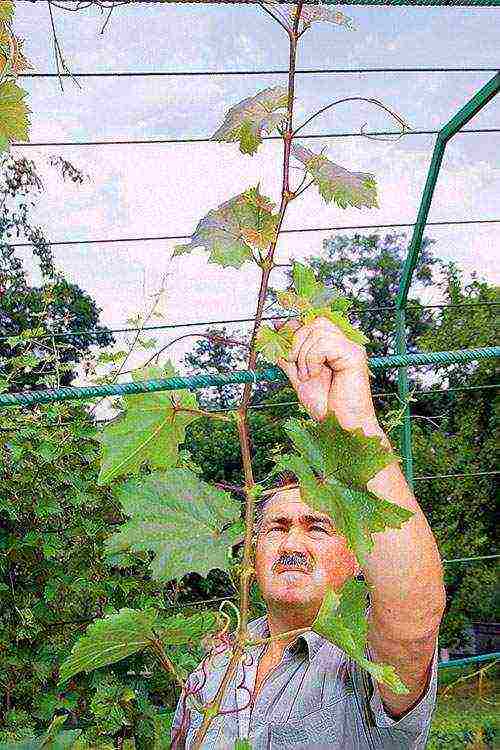 As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
- The plant is provided with the best light and air conditions.
- It is easier to trim and normalize the green mass and ovary.
- Carrying out foliar dressing of grapes, as well as performing "green pruning" is facilitated.
- Vertical shoots grow and mature better.
- The risk of developing grape disease and pest damage is reduced.
- The budding winegrower should know when and how to tie the grapes.
The first time it is necessary to fix the position of the shoots when they are about 40-50 cm long and reach the bottom row on the trellis. Then, as they grow, the stems are tied sequentially to all rows.
As a garter material, it is better to take scraps of textiles or knitwear, natural twine or twine, that is, means that do not squeeze or pinch the growing shoots. It is convenient to use a special tool for tying a grape seedling, freely fixing the shoots with a plastic clip. On trellises, where the wire is stretched in two parallel rows, the shoots only start in such a gap, and the resulting whiskers are firmly fixed on the support over time. If grapes grown on a gazebo or shed are being taken care of, where free growth is provided, then such shoots do not need to be tied up.
Grape picking
 In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant.Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant.Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
If in regions with a short summer, grape pinching consists in the complete removal of shoots already at the initial stages of development, then in the south, especially when growing early varieties, stepchildren are only shortened in order to get an additional harvest of sweet berries by autumn.
And in some cases, for example, when the vine suffers from frost or hail, grapes are not pinched at all. Stepsons replace the lack of green mass on the bush and help to resume the development of the bush.
Preventive treatment and foliar feeding of grapes
 Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Growing on a trellis gives the grower the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Growing on a trellis gives the grower the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
The greatest need for such dressings is for grape bushes:
- before and after flowering;
- during the period when the coloring of the berries begins;
- a few days before harvest.
For feeding grape seedlings and adult bushes, use a solution containing 5% superphosphate, 0.5% ammonium sulfate and 1% potassium salts. When the berries begin to ripen, the vine no longer needs nitrogen, but trace elements, for example, zinc and boron, can be added to the top dressing.
After flowering, the bushes are treated with a 1% solution of boric acid in combination with a fungicide that prevents the development of downy mildew, a disease that occurs in conditions of high humidity and has a detrimental effect not only on the future harvest, but also on the entire grape plant. The final foliar dressing of grapes can be carried out on the basis of the infusion of wood ash. The introduction of such dressings, as well as spraying the bushes with fungicides and insecticides, is carried out in the afternoon, when the temperature drops, the sun cannot burn the leaves and inflorescences or in cloudy weather. The longer the drops of the product remain on the greens, the greater the effect of the procedure.
How to treat grapes after rains, when fungicides and solutions of trace elements are washed off?
In the case of severe precipitation, the treatment is repeated as soon as possible, paying attention to spraying the bushes with Ridomil, especially during the period when the flowering has already been completed, and the likelihood of mildew development is high.
 No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
At the same time, do not forget that the effectiveness of dressings and remedies is really high if all the rules for growing and caring for grapes are followed, weeds and excess shoots are removed in time, air and food are provided to all shoots.
All about planting and growing grapes - video
The extreme climate of a sunny berry is not a hindrance. And getting a good harvest of grapes in the second or third year after planting is an achievable goal even for beginners. So how to stop dreaming and start growing grapes ...
First, let's decide on the two most important tasks in growing grapes - we will choose a place for planting grapes and the varieties that we will plant. In principle, the vine will grow almost everywhere (except for a solid shade), and if you take care of it, at the very least it will bear fruit. However, competent planting in the right place will allow you to get really good yields with much less effort. Remember that planting seedlings of low-quality varieties in a vineyard will take your time, energy and good mood. You may be unfairly disappointed in grapes, although the mistake will be entirely yours.
Place for planting grapes
The vineyard should be sunny and sheltered from the wind, for example by the south wall of a house, a barn or a south-facing fence with well-drained soil. If there is a minimum slope on the site, plant the grapes on a gentle southern or south-western slope, orienting the row in a south-north direction. If the plot is flat and the southern walls are occupied, create a place for your grapes by building in any convenient place on the plot a nice solid fence 1.8–2 m high, oriented along the "east-west" line. And you will immediately understand the secret of the monastery vineyards! You can also use for this purpose dense hedges or screens from available materials, for example, from vines or reeds.

Tips for a new wine grower
-
The method of planting grapes depends on the type of soil. Variants are possible, but usually it is recommended to plant grapes on sandy soils in trenches, and on poorly heated loams and clays and in areas with a close occurrence of groundwater, it is recommended to plant on ridges, which in the old days were called "created".
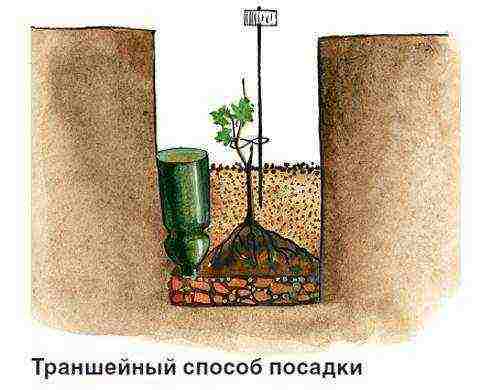
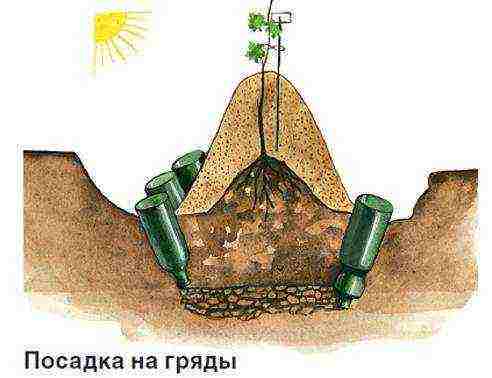
For watering and fertilizing the grapes, I place plastic bottles with a cut-off bottom between the seedlings. For table varieties, as the bushes grow older, I replace them with asbestos-cement pipe trimmings, and for “techies” (wine varieties) I remove them altogether after three years. Mature wine grapes have to get their own water from the soil, and the deeper the roots, the better the wine from its berries.
-
Do not rush to plant seedlings "for permanent residence", especially if these varieties are on trial. Let them live until the first signal brushes in the school (where it is easier to cover). In the first year, some northerner growers do not plant seedlings in open ground at all, but keep them there in mobile containers (for example, in buckets), half buried in the ground. In autumn, containers with seedlings are moved to the basement, and in late spring they are planted. Such seedlings begin bearing fruit earlier.
-
Don't spontaneously plant vines. If your grape bushes are not in a "spot" planting, planning of the vine plot is necessary. Group varieties by purpose, as they have different planting intervals. The distance between bushes of varieties for juice and wine purposes is 0.8 m, for table varieties - at least 1.5 m, between rows - 2–2.5 m. It is advisable to clarify the strength of growth of the selected varieties in order to correctly calculate the desired place. Grouping varieties by ripening and frost resistance will facilitate the care of the grapes. You will not need to spray and cover everything to the maximum.
-
Do not plant grafted seedlings (from European and southern nurseries) vertically, but place them practically lying at the maximum possible angle, otherwise there will be problems with the ripening of the vine. Gradually translate them into your own roots.
- Remember that grapes have the property of vertical polarity. When opening, tie a fruitful arrow on a trellis or stakes only horizontally - then all annual green shoots will grow equally. With a vertical garter, shoots grow intensively only from the upper eyes, and from the lower ones, they grow weakly or do not grow.
-
Limit watering. It is only necessary to water the young vines for the first 2 years and the water-charging watering, which is common for all varieties, in the fall.Stop watering 7-10 days before the expected flowering, as excessive moisture causes the color to shed and delays the ripening of the crop.
-
Do not use sprinkling, otherwise you will provoke disease. Arrange drainage channels and place irrigation pipes on the side of the row spacing no closer than 30-50 cm to the base of the bush. Grapes do not like wet leaves and damp ground surfaces. If possible, arrange a visor over the grape bushes.
-
Conduct green operations sparingly and on time. Simultaneous removal of all growth points on the shoot is unacceptable: both chasing the top and pinching the stepsons. After all, there is a danger that the wintering buds of the bush will start to grow and its potential will drastically weaken. Do not break out stepchildren completely, leave 1-2 sheets. Carry out minting in August, immediately after straightening the crown.
-
Pruning the grapes is necessary, otherwise the berries are crushed, and the bush will grow unnecessarily. But in the year of planting, there is no pruning, except for the removal of unripe green parts of the shoots in the fall. From the 3rd year, prune the shoots according to the recommendations (short or long pruning), but do not mindlessly follow the recommended total load, since your conditions - relief, soil, the sum of active temperatures (CAT) - will correct it. Write down from which bud the fruiting shoots grow specifically for you.
Read more: Pruning grapes for beginners .
-
Do not carry out autumn pruning before natural leaves fall or night temperatures are below freezing (early November). Do not prune in the spring, as the "crying" of the vine (sap outflow) weakens the plant.
Read more: How to stop the crying vine>.
-
In the north, it is more reliable to use non-standard formations of a fan or semi-fan type, rather than high-standard ones, including for arbors.
Read more: Cordon formation and pruning of grapes.
Read more: Forming grapes for growing on a gazebo>.
-
Winter shelter for the first 2-3 years is needed for all seedlings. The first year the grapes grow tied to a temporary trellis. In autumn, shoots are removed and covered with a two-three-layer air-dry shelter. As a bedding - spruce branches or boards, on top of the seedlings - a layer of spunbond or corrugated cardboard and a film on top (roofing paper, old linoleum). Snow will complete the rest. Leave ventilation slots at the ends of the shelter.
-
Do not remove the cover immediately and completely in the spring. And when removed, leave a couple of layers of spunbond or lutrasil nearby in case of frost.
- Record the timing and characteristics of planting, flowering, ripening, pruning and loading of grapes in a diary. Otherwise, the most valuable information for the analysis of variety testing will be forgotten and lost. And you and the next generation of northern winegrowers, who will definitely come after you, need it so much.
How to grow grapes in the middle lane.
Winter hardy grape varieties
The most necessary requirements for grape varieties in the Moscow region and to the north are frost resistance, the ripening period of the crop and vines. But you shouldn't put so-called “non-concealment” at the forefront. This concept is relative and does not depend on the variety, but on what are the minimum temperatures in winter in your country house. In the first step, choose the earliest frost-resistant varieties. Later, with experience, the understanding will come that northern viticulture also provides us with certain bonuses, for example, in the form of long daylight hours, which partially compensates for the missing warmth of the grapes. And then you can try growing later varieties.
In addition, in the north, there are practically no diseases and pests of grapes. However, it is always better to prevent danger. There are so-called complex-resistant grape varieties - with high resistance to both frost and disease.
Learn more about grape diseases and how to treat them.
Also determine the purpose of the grapes.Why do you need it: for the table, for juice and wine, for decorating the gazebo, or just "so that it was"? Today there are more than 15,000 grape varieties, so there is plenty to choose from.
For beginners, I would advise tasty and unpretentious table varieties ‘Agat Donskoy’, ‘Aleshenkin’, ‘Yubileiny Novgorod’, universal ‘Platovsky’, ‘Crystal’, ultra-early table ‘Krasa Nikopol’, as well as some universal Amur hybrids A.I. Potapenko and F.I. Shatilova. Those who have children should pay attention to the super-early and tender-sweet varieties ‘Liepaja Yantar’ and ‘Early Tsiravsky’ (selected by G.E. Vesminsha), as well as the ‘Krasa Severa’ variety with a high content of useful folic acid. From the listed grape varieties, select no more than four to five for the first planting.



How to buy grape seedlings and rooting cuttings
The most reliable sources of planting material are winegrowers' clubs and forums, where enthusiastic and experienced gardeners and collectors communicate, as well as MOIP and TSKHA. You should not buy seedlings and cuttings at spontaneous roadside markets and exhibitions (of course, this does not apply to the stands of well-known nurseries).
How to buy grapes and choose a good seedling.
You can ask a question to the author of the article, wine grower Olena Nepomniachtchi, here .
You can find out how to grow other plants, what kind of gardening work you need to plan, from other articles on our website. Also, please pay attention to the information block to the left of the text. The links located in it lead to articles of related topics.


