Content
- 1 Greenhouse requirements
- 2 Selection of vegetables
- 3 Seedling preparation
- 4 Soil and fertilizers
- 5 Care features
- 6 Greenhouse preparation for planting
- 7 Features of planting seeds for seedlings
- 8 Features of growing seedlings in a greenhouse in winter
- 9 Winter planting tips
- 10 What can be grown in a polycarbonate greenhouse?
- 11 Where is the best place to grow cucumbers?
- 12 Soil preparation
- 13 How to get seedlings?
- 14 Planting cucumbers
- 15 How to form cucumber bushes?
- 16 Growing cucumbers in winter
- 17 Correct watering of cucumbers in the greenhouse
- 18 What kind of soil is needed to grow tomatoes?
- 19 Planting tomato seedlings
- 20 Tomato care
- 21 How to grow peppers in a greenhouse?
- 22 Planting peppers in seedlings
- 23 Proper care of pepper
A capital polycarbonate greenhouse allows you not to interrupt the cultivation process even in the coldest time. It is necessary to choose what can be planted in the greenhouse for the winter, based on considerations of economic feasibility, personal preferences and the ability to fully care. It is important to study the needs of the plants, recommendations for ensuring reliable operation and possible difficulties. With a competent approach and investment of certain funds, it is easy to organize even your own business.
Advantages and disadvantages of winter landing
For the winter, seeds of frost-resistant crops are planted in the open ground that can withstand the harsh climate of the cold period without damage. A positive aspect of sub-winter planting is the shift in the beginning of the growing season to an earlier time, which speeds up the possibility of harvesting by two to three weeks.
The seeds undergo stratification at a low temperature and are hardened, the seedlings are disease-resistant and strong, with powerful roots, and are less damaged by pests. The yield of such plants in a greenhouse in winter is usually much higher.
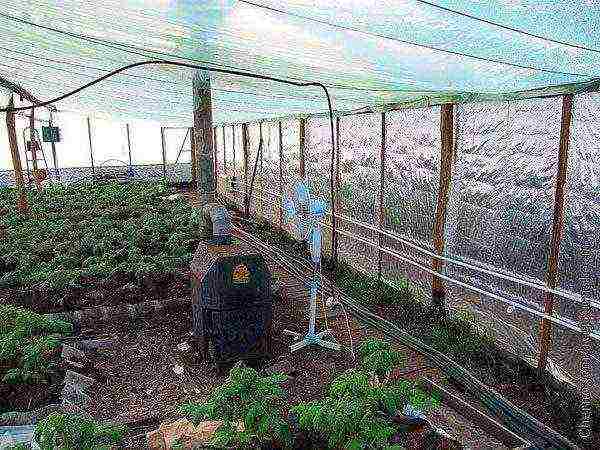

Greenhouse economy in winter
But there is always a threat of complete or partial death of seedlings if the weather is unstable with prolonged warming, contributing to their premature development. Insufficient snow cover may not cope with protective functions. It is necessary to consume more seeds during winter planting, since their germination rate is lower.
This can be avoided by sowing the necessary crops for seedlings or greens in the greenhouse in the fall. Even without heating the room, plants have a chance to get some protection from strong temperature changes, flooding with melt water followed by its freezing, and strong winds. With a sharp cold snap in winter, it is advisable to additionally cover the plants.

Greens in a greenhouse
Greenhouse crops at different times of the year
In the spring-summer period, polycarbonate greenhouses are used for the most capricious southern crops that are unable to ripen in the local climate, as well as for growing planting material for open ground. In winter, plants that are more adapted to the lack of light and heat can be planted, which will allow you to grow vitamin fruits or greens without damage.
Examples of plant selection
What can you plant for your family in the winter in a greenhouse? The main vegetables for all-season greenhouses are cucumbers, zucchini, tomatoes. Eggplants and peppers are more demanding to external conditions and difficult to care for. Not every greenhouse is suitable for growing them. A variety of greens (onions, dill, parsley) are massively grown in winter, even in unheated rooms.

Unheated underground greenhouse
Before winter, you can plant popular root crops in the greenhouse - beets, radishes or carrots, but you should choose the most cold-resistant and early ripening varieties. It is advisable to fill the greenhouse with several types of plants with similar conditions.
Flower lovers can grow suitable varieties of roses, chrysanthemums, asters, lilies, crocuses and other flowering species. Also, in free areas, it is worth sowing vegetable and ornamental crops for seedlings for open ground, so as not to clutter up the window sills in the house.
What should be a winter greenhouse
The greenhouse should be with a strong and stable frame, located on an elevated site or on the south side of the house (outbuilding). It is advisable to deepen the foundation by about 0.8 m and additionally insulate it from the outside. A greenhouse for winter should be well lit by the sun and have a system of protection against flooding by ground and melt water.

An example of a winter building with a foundation
In winter, trouble-free heating systems (water, electric or air), ventilation and irrigation are important (better than drip - saves water consumption). Also, you can not do without installing additional lighting devices (better than LED). It is advisable to use vertical adjustment of the position of the lamps.
In the most severe frosts, the value of the air temperature in the room should not fall below +15 ° С, and during most of the time it should be within + 20-25 ° С.
What to sow in a greenhouse for the winter
Before planting vegetables or other crops in an unheated greenhouse, you need to find out the necessary microclimate parameters in order to contain a particular plant, because the temperature in such a room is low. Conditions in a heated greenhouse vary depending on its design and equipment, the climate of the region. After all, heating devices have a limited resource, which is also affected by the cost of energy carriers.
What can be planted in an unheated greenhouse
The positive qualities of the greenhouse are the exclusion of the negative impact of atmospheric phenomena (strong winds, precipitation). Additional insulation measures (sealing all cracks, deepening the soil, using reflective screens and dark films) improve conditions in the greenhouse in winter. Biofuels are increasingly used, building warm beds on warming mixtures based on manure or straw.
If there are no devices for artificial heating, then the negative temperature in winter, especially in the northern area, does not allow growing any plants. In an unheated greenhouse, various cold-resistant horticultural crops successfully winter, which in open ground can freeze, get wet or weaken.

Using the greenhouse for forcing and storing flower crops
During the cold season, the greenhouse can be used as follows:
- sow parsley, lettuce, celery, early carrots and beets, radishes, which are harvested in spring;
- plant onion sets for seedlings or onions on greens;
- store during the dormant period the bulbs of flower crops (hyacinths, crocuses), as well as rhizomes of dahlias, chrysanthemums, followed by their cutting;
- add saffron, iris, daffodil bulbs in February for forcing flowers;
- place two-year-old insufficiently cold-resistant plants for wintering;
- sow flower and ornamental crops - lily, begonia, gloxinia, coleus;
- sow legumes, corn, thyme closer to spring for transplanting to open areas.
Growing greens
The weather conditions must be monitored and in the event of a sharp cold snap in winter, protect the plants in the greenhouse with the available covering materials.
Planting plants in a greenhouse with heating
After harvesting the summer-autumn harvest, thorough cleaning of the soil from plant residues, applying top dressing and sanitary-preventive work, it is necessary to finally decide what is better to plant in a greenhouse in the winter. You need to know the upper limit of the temperature that is stably maintained in the greenhouse. When its value is less than +15 ° С, many plants stop developing and may die or shed fruit ovaries.
A polycarbonate greenhouse with heating can be used for breeding early-ripening varieties of vegetables (cucumbers, tomatoes), getting seedlings, growing greenery or flowers (peonies, roses, dahlias) year-round.Rational use of the area will help the installation of shelving, the use of the trellis method or vertical beds.
A more costly and laborious, but interesting activity is to plant strawberries for the winter. It is worth trying the convenient method of placing the bushes in bags of soil mixture, in pipes, or the Dutch longline technology. It is important to stock up on high-quality seedlings that can give a good harvest, better than remontant varieties.
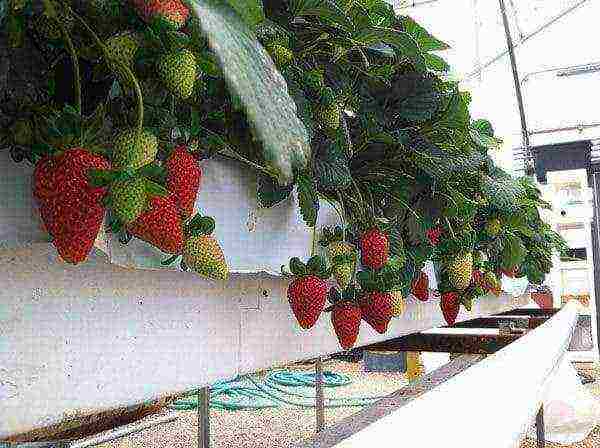

Winter strawberry
In a heated room, the soil does not freeze, which contributes to its disinfection from pathogens and various pests. Planting green manure plants (mustard, rye, vetch) will help improve the general condition of the soil, saturating it with useful substances and microelements, loosening and eliminating insects and weeds.
Growing cucumbers in winter
Growing cucumbers in the autumn-winter turnover, compared to other vegetable crops, is not so troublesome and costly. They are moderately demanding on temperature and its changes, and the yield of high-intensity hybrids, subject to the recommended microclimate parameters, is at least 30-35 kg / m2.
First of all, suitable hybrids are selected. These should be shade-tolerant, fairly compact early ripening varieties. The timing of sowing seeds for seedlings to obtain a winter harvest in the greenhouse should be from mid-October to mid-November. In the first 5 days, seedlings need round-the-clock supplemental lighting, then 16-18 hours.
After 2.5-3 weeks, in the presence of a developed root system and four true leaves, they are planted. The arrangement of the bushes is planned in such a way that the leaves absorb the maximum amount of available light, and do not allow shading. The average planting density is approximately 5 plants per 2 m2.

Growing greenhouse cucumber
They adhere to these basic recommendations for caring for cucumbers in winter:
- maintain the temperature during the day at least + 20-22 ° С, at night - 16-18 ° С, and the relative humidity at the level of 70-75%;
- watered regularly with water at a temperature of + 20-22 ° C;
- bushes are tied up and twisted, all side shoots are removed completely;
- to increase the fruiting period, six leaves are removed weekly, but not more than three at a time.
- the harvest is harvested daily, while making sure that the load on the lashes is not excessive.
Planting greenery in a greenhouse
Even a gardener with little experience can cope with the cultivation of unpretentious greens in a greenhouse in winter - dill or parsley. The yield of these crops is high, and labor and seed and fertilizing costs are low. They have enough ordinary soil, simple care (watering, weeding) and a temperature of about + 15 ° C with a humidity of about 80%.

Growing different types of greens
Dill with parsley grows successfully together with other plants in free areas. Adequate light is required for dill. The prepared seeds are sown directly into the ground, and the crop maturity is reached in one and a half to two months. For continuous harvesting, sowing is done every two weeks.
In winter, green onions can also be planted, which for good development needs a daytime temperature within +20 ° С (at night - 12-15 ° С). Onions need fertile soil, saturated with organic matter and minerals (potassium and phosphorus). Pour cold water on the onion daily. The crop is harvested in about a month.
Heads, leafy and varietal varieties of lettuce thrive in winter indoors. The culture requires a loose soil enriched with organic matter, a temperature of about + 18-20 ° C, ensuring daylight hours within 12 hours, watering two to three times a week. Early maturing species give a harvest in three weeks.

Growing flowers for sale
Growing crops for sale
Even in a small home-made greenhouse, skillful hands can harvest a good harvest with surplus.And a modern and economical polycarbonate greenhouse makes it even more possible to grow greens, vegetables or flowers, not only for personal consumption, but also for sale.
When choosing what to plant in a greenhouse for sale in the winter, one should take into account the economic feasibility of energy costs and the possibilities of a particular greenhouse structure. In the northern regions, the costs are higher, but accordingly the price of fresh products is higher.
To organize a greenhouse business, it is required to draw up planting plans and calculate the necessary costs for planting material, soil preparation and fertilization, provision of agrotechnical conditions (heating, lighting, water), and fight against diseases and pests. It is worth studying the needs of the sales market.

Growing greens
The most suitable market crops are fast maturing and expensive. The most common cultivation in winter is to sell greens (green onions, parsley, dill, lettuce, mint and basil) or seedlings (peppers, tomatoes, flowers). Some people recommend mushrooming, pointing to a profitable and easy marketing.
The flower business is considered the fastest payback. Often flower products (tulips, daffodils, roses, hyacinths, crocuses) are grown for sale on February 14 and March 8.
Video: features of year-round cultivation
With a year-round operation of the greenhouse, additional efforts have to be spent not only on maintaining the optimal temperature regime, but also on supplementary lighting of plants in a winter time poor in sunlight. In order to save and facilitate the operations performed in winter, useful inventions of experienced specialists can be used.
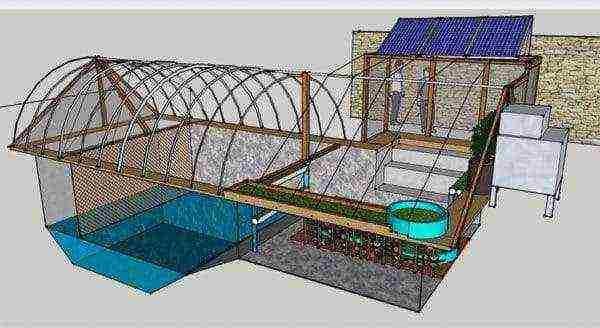
Underground greenhouse
Projects have been developed for structures with high thermal insulation properties that do not require heating devices or with unconventional heating. For example, a thermos greenhouse or a deepening in a foundation pit up to two meters.
Particular attention is paid to the condition of the soil, since during continuous intensive agrotechnical work, its rapid depletion occurs. A modern and convenient way of growing in a greenhouse is soilless, based on a hydroponic system. At the same time, the plants feed on a special solution that contains everything necessary for full development.
Growing vegetables and greens in winter does not negate the fight against harmful insects, since the spider mite and whitefly can be active all year round. Preventive measures should be taken and lesions detected in a timely manner.
Video: What is planted in the greenhouse in the winter
Video: Errors when forcing tulips
Permanent greenhouse owners can get the most out of them in cold weather. It is important to correctly assess the costs, familiarize yourself with advanced technological methods, advice from specialists and experienced owners of household farms. A valuable winter harvest or a bright bouquet of flowers will be a reward for the work done.

Growing vegetables in a greenhouse - simple and effective way provide your family with valuable and healthy products. Most of the farm owners uses greenhouses and greenhouses in the spring-autumn period, extending the harvest until frost.
However, an insulated shelter equipped in accordance with all the rules helps to pick fresh vegetables even in winterwhen vitamins are especially needed. The greenhouse will allow you to earn money on growing vegetables in the cold season, when the demand for them is especially high. How to grow vegetables in a greenhouse in winter, we will consider below.
…
Greenhouse requirements
How to equip a greenhouse for growing vegetables in winter? When constructing a year-round greenhouse, it is important to meet all the conditions for successful plant growth: ensuring the required temperature and humidity, the amount of sunlight, the possibility of airing. At the same time, it is necessary to calculate the costs of heating and lighting the greenhouse so that they do not block the benefits of winter vegetables.
Year-round greenhouse must have a solid foundation... To provide the required height for the plants, the structure can be slightly deepened. This little trick will help you save on heating costs and not lose the natural light you need.
It is best to grow vegetables in a medium-sized greenhouse, up to 20 m long and 2.5-3 m wide... The optimal roof structure is pitched. The north wall can be laid out with cinder blocks or wooden beams, protecting the plants from the winter wind. The greenhouse should have a vestibule and double doors. Comfortable air vents.
Most often, capital greenhouses are made on a welded frame with an anti-corrosion coating. Such a foundation will stand for many years, the greenhouse will be strong and reliable. As a coating, you can use dense polyethylene or tempered industrial glass. But the most expensive and high quality material - cellular polycarbonate. It transmits light well and retains heat even in the most severe frosts.
 For heating, pipes on both sides of the greenhouse are suitable. The heat source will be an electric boiler. It is possible to heat the structure with modern wood-burning stoves that save fuel.
For heating, pipes on both sides of the greenhouse are suitable. The heat source will be an electric boiler. It is possible to heat the structure with modern wood-burning stoves that save fuel.
Increasing the temperature inside the greenhouse will help and biofuel - rotted manuremixed with straw. The mixture is laid out under the top layer of soil. Biofuel is suitable for growing cucumbers, radishes and other crops that are particularly heat-demanding.
Selection of vegetables
In a winter greenhouse can grow all kinds of crops, from popular tomatoes to cabbage lettuce and herbs. Among the most popular and fruitful vegetables:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- radish;
- head salad;
- eggplant;
- Bell pepper;
- various varieties of cabbage;
- zucchini.
It should be borne in mind that crops have different requirements for humidity and temperature, so they need to be placed in separate greenhouses. For example, tomatoes and bell peppers require moderate moisture (no more than 60%) and frequent ventilation. Such a regime is destructive for cucumbers, which need a humid and hot atmosphere.
In the cold season, the greenhouse effect with high humidity is easier to maintain.
Therefore, many novice gardeners focus on popular and productive crops that need just this mode: cucumbers and radishes.
Choosing varieties, it is worth giving preference to hybridscultivated specifically for indoor use. These plants have a shortened growing season and do not require insect pollination. Most greenhouse varieties have good yields and pest resistance.
Seedling preparation
Some gardeners buy grown seedlings at markets and other farms. But grow your own seedlings from seed much more profitable... In addition, the process can be started at any time to ensure a year-round harvest.
 It is better to grow seedlings in a separate greenhouse or in a house. Seed germination conditions are different from those to which adult plants exist. In some cases, a lower temperature or higher humidity is required. In the same greenhouse, you can place seedlings of different crops with similar requirements for agricultural technology.
It is better to grow seedlings in a separate greenhouse or in a house. Seed germination conditions are different from those to which adult plants exist. In some cases, a lower temperature or higher humidity is required. In the same greenhouse, you can place seedlings of different crops with similar requirements for agricultural technology.
If there is no opportunity to organize a greenhouse for seedlings, the seeds can be germinated on a separate rack in a common room located as close to the lamps as possible. The seeds can be germinated in peat cups, but this method is not suitable for eggplants and other crops with a weak root system. For year-round cultivation, the conveyor method is recommended.
Seeds are sown every 2 weeks, which makes it possible to get seedlings of different ages. If different crops are planted, after a year it is recommended to alternate them... Eggplant seedlings are planted in the places that were occupied by tomatoes, and cucumbers are replaced with radishes or zucchini.
This technique does not allow the soil to deplete. The first sowing can be started in January. Depending on the growing season of a particular plant, the seedlings will ready for transplant in 3-5 weeks after sowing seeds.
Soil and fertilizers
How to grow vegetables in a greenhouse all year round? Vegetables need light, not too acidic soils. For most crops, a mixture of garden soil, sand and peat is suitable.
Before laying in the greenhouse the soil needs to be calcined or disinfected using an aqueous solution of copper sulfate. Such treatment kills harmful microorganisms and insect larvae.
After processing, ash or a complex of mineral fertilizers can be added to the soil. The mixture is thoroughly loosened and distributed over the ridges. In the greenhouse, you can organize both ground and rack cultivation. The racks are suitable for radishes, head lettuce and other small crops. Some vegetable growers successfully grow tomatoes and zucchini on shelves.
Indoor ground is quickly depleted, so the plants in the greenhouse need to be constantly fertilized. Rotted compost or complex mineral fertilizers are added to the soil. This treatment is repeated every 2 weeks, before feeding the soil must be loosened and weeds removed. During the period of active growth of seedlings, special attention should be paid to nitrogen fertilization, from time to time the plants can nourish with medicinal preparations.
Care features
In winter, you need to maintain an average daily temperature of 18 to 22 degrees. Overheating has a bad effect on tomatoes, eggplants and bell peppers, and a cold snap can have a detrimental effect on radishes and cucumbers. On frosty days, greenhouses are not ventilated, when the outside temperature rises, the vents must be opened 1-2 times a day.
Vegetables in the greenhouse watered 2-3 times a weekwhen the soil dries up a little. It is advisable to use water at the same temperature as the air in the greenhouse. Cold water can cause shock and slow plant development.
 As the plant grows, it is necessary to tie up the stems. Cucumbers need special supports to be mounted on the roof of the greenhouse. With their help, the stems of plants can be directed in the right direction, which is especially convenient for rack cultivation.
As the plant grows, it is necessary to tie up the stems. Cucumbers need special supports to be mounted on the roof of the greenhouse. With their help, the stems of plants can be directed in the right direction, which is especially convenient for rack cultivation.
With the onset of fruit formation it is recommended to remove the lower leaves on the stems. Excessive green mass interferes with fruit development. In addition, this technique will improve air exchange and access to sunlight, plants will not be affected by pests and fungi.
In the greenhouse it is important to maintain the atmospherefavorable for plants. The humidity level will help increase watering of heating pipes and floor with water, as well as placing open tanks in the room. For the successful ripening of tomatoes in the greenhouse, you can put tanks with an aqueous solution of mullein. Good increase moisture and hot water barrels, moreover, they additionally heat the room.
With conveyor cultivation, harvesting takes place all year round. In early summer and late autumn, preventive treatment of premises with partial replacement of soil and thorough washing of all surfaces is recommended. After airing and fertilizing, a new stage of planting begins.
Success growing vegetables in a greenhouse in winter, depends on the region... The most profitable option is to use greenhouses in temperate and climates. Regions with short summers and long frosty in winter will require high heating costs.
In such an area, it is more advisable to extend the summer period until the end of October and practice early planting in heated soil. Using correctly selected varieties of vegetable crops, you can achieve a good harvest.
Simple innovations in the design of greenhouses for growing vegetables all year round, in the video below:
In the fall, it is time for greenhouse owners to consider growing fresh vegetables in the winter. In this article you will find answers to the questions of how to choose the right place for planting seeds in a greenhouse, how to care for seedlings, what you need to know in order to have a good harvest of vegetables in winter, and much more.

Its own greenhouse at the summer cottage is fresh vitamins on the table at any time of the year.It can grow literally all fruits and vegetables, from greens to potatoes. But potatoes are grown in summer, and the most popular are vegetables such as cucumbers, tomatoes, bell peppers and cabbage, which, if desired, can be had all year round. And now about everything in order.
Greenhouse preparation for planting
We talked about how to process and prepare the greenhouse for the winter season in the article "Autumn preparation of the greenhouse for the next season." It remains to thoroughly ventilate the room, install and connect all heating and lighting devices and rinse the hoses of the irrigation system again. The soil in the beds is also fertilized from its own compost pit. Now you need:
- pick up seeds. When choosing, you can use the information from the article "Features of buying seed in online stores";
- heat the greenhouse to +22 ° С. This is described in the article “Geothermal heating of a greenhouse. We do it ourselves ”;
- in the presence of subsoil heating, achieve the final soil temperature (up to +18 ° C). For more details on the methods of heating the soil in the greenhouse, we have considered in the article “Unusual greenhouses. We are increasing energy efficiency. "
Advice: if artificial heating of the soil is not provided, then before planting the seeds, pour boiling water over the soil and cover the bed (rack) with a film. The soil will warm up within 2 hours. After that, you can start planting seeds for seedlings.
Features of planting seeds for seedlings
In a greenhouse that operates all year round, you should count on more than just planting vegetables for winter cultivation. Vegetables planted in winter will no longer bear fruit by early spring. Therefore, for planting seedlings, you should use the conveyor method. For this, space is allocated on a separate rack, which is closer to the living lighting - to the glass.
Seeds should be "sown" in the place designated for seedlings every 2 weeks. So for 1 sq. m seedlings will grow with different ages.
Since it is not recommended to use the soil for a long time for one type of plants, after 4 stages of growing and transplanting seedlings, cucumbers should be changed with tomatoes, and pepper with cabbage, etc.
Note. After the plants of the 4th stage cease to bear fruit (in June), the greenhouse should be treated as when preparing the greenhouse for winter. After airing, fertilizing the soil and cultivating the greenhouse, the next stage of seedlings can be planted in fertilized places. The next processing of the greenhouse is September-November.
In winter, plants indoors should be more often (than in summer outdoors) replenished with fertilizers, since seedlings require a lot of strength, light and oxygen.
Features of growing seedlings in a greenhouse in winter
Since the soil is fertilized after the autumn preparation of the greenhouse for planting, it is not necessary to heal the seedlings with fertilizers before planting. But after the first stage of planting in a permanent place, the soil should be fertilized. To do this, loosen the row in which the seeds will be sown and add the finished compost.
Despite the distance between plants, in greenhouse conditions they very quickly absorb moisture and oxygen, as well as nutrients. Therefore, the seedlings should be watered as the soil dries up (2-3 times a week). For irrigation, water is used, the temperature of which is close to the temperature of the soil. If the seedlings do not receive a sufficient amount of moisture, they will not stop growing, but, being transplanted, the flowers and ovary will quickly fall off.
Seedlings transplanted to a permanent place must be loosened after each drying out and added compost or nitrogen and, less often, potash fertilizers.
Note. If the greenhouse is small and it is not planned to grow a lot of vegetables, in order to avoid unnecessary loss of electricity, the seedlings are grown in the house, seated in peat cups. They begin to heat the greenhouse a few days before the start of planting, the seedlings are planted together with the container in which the plants are located.
Planting seedlings in a permanent place
It is necessary to observe the conditions required for plants: maintaining a sufficient temperature and humidity in the room, systematic ventilation and watering. It will be good if you organize drip irrigation of plants in the greenhouse. The average soil temperature for all vegetables is not less than +18 ° С, soil moisture is more than 85%, air - + 20 ... + 22 ° С.
In racks designed for cucumbers and other climbing plants, twine is pulled to the ceiling so that the plant can comfortably drag upward. To do this, a hook must be attached from the very bottom of the rack or pins must be initially planned, to which the twine and the plants themselves will subsequently be attached at the stage of growth from seedlings.
Tomatoes also require support with support and twine. This will keep the branches with ripe fruit in place.
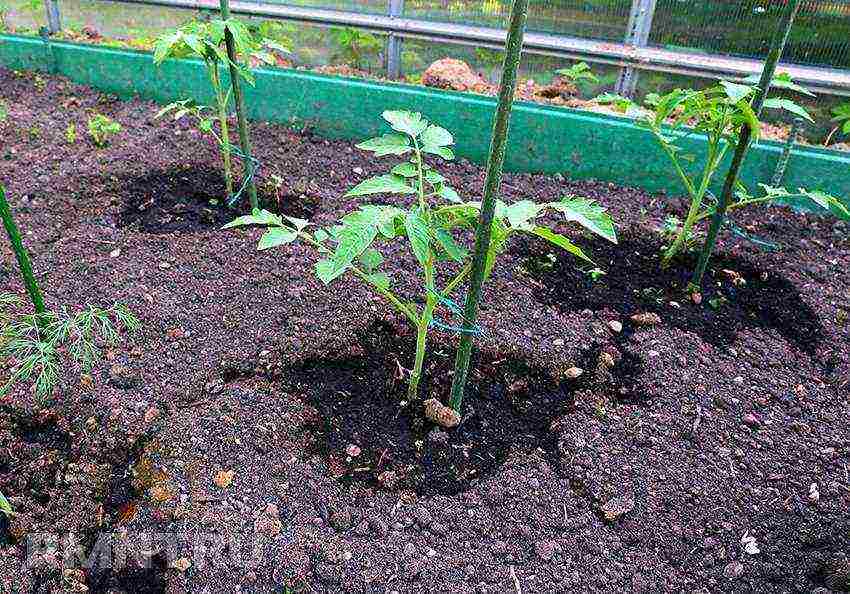

In addition to the fact that twine is attached to the cucumbers, support is still needed. Without it, the stem will tilt and break.

The top rack with cucumbers can be "directed" for growth in different directions.
Pepper, despite the fact that it grows upward, also needs to be strengthened with support. With its help, it will be possible to support the branches with fruits by tying them up. It is necessary to nourish the seedlings by spraying with medicinal preparations (once every 2 months). Pepper fruits suffer in hot weather and require increased attention outdoors. Therefore, it is recommended to continue its summer cultivation in the greenhouse.
Interesting! If you plant bell peppers next to a hot variety, then it will become bitter in taste. Hot peppers will never turn sweet. These two species cannot be planted together. Close proximity to other crops and varieties is also undesirable. Therefore, it is advisable to grow seedlings in a greenhouse between several types of pepper.
Cabbage is the least "capricious" vegetable, so its varieties (early, middle and late) can be planted at the discretion of the owner. It is not necessary to look for varieties specifically for greenhouse cultivation.
Winter planting tips
When the ripening period begins, the lower leaves are gradually removed. But there should be at least 15 leaves on the stem! Thus, the plant will receive more light, improve air access, and good air exchange helps to avoid damage by fungal and viral diseases.
In greenhouses, plants are exposed to diseases only when there is a lack of moisture, oxygen and non-observance of the correct temperature regime!
How to humidify a room in winter
Humidification is done in different ways, depending on which heating system is installed.
If batteries are installed in the greenhouse, there should be containers with water next to them. Pipes need to be watered frequently. Vapors humidify air and plants.
The insulated floor is moistened in a similar way, it is often watered.
Stove-heated greenhouses are humidified by tanks with heated, steam-generating water. In addition, metal barrels or hot water tanks keep the room warm for a long time.
Early ripe varieties of cucumbers for winter cultivation:
| Variety | The beginning of fruiting | Description | Characteristics | Productivity per sq. m |
| Alma-Ata | 50-60th day after germination | Finger-shaped fruits. Weight up to 200 g | Long stems, can be grown on vertical garters | Up to 30 kg |
| Surprise 66 | 50-55th day after germination | Fruits are cylindrical, elongated. Weight 112 g, length up to 18 cm | Stems up to 2.5 m | Up to 40 kg |
| Moskovsky | 50-55th day after germination | The fruits are elongated. Up to 40 cm. Weight from 300 to 600 g | Long-climbing | 28 kg |
| Surprise 66 | 50-60th day after germination | Cylindrical fruits | Stem length 2-2.5 m | Up to 40 kg |
Early ripe tomato varieties for winter cultivation:
| Variety | The beginning of fruiting after germination | Description | Productivity per sq. m |
| Semko-Sinbad F1 | 90th day | The fruits are round. Weight up to 90 g | 10 Kg |
| Typhoon F1 | 80-90th day | Rounded fruits, up to 90 g | 8-9 kg |
| Blagovest F1 | 80th day | Rounded fruits up to 110 g | Up to 20 kg |
| Samara F1 | 85th day | The fruits are round, oblong. Up to 80 g | 10-15 kg |
Varieties and types of cabbage for growing in a greenhouse:
| Variety | Peculiarities | Ripening period |
| Number one K-206 | Simultaneous ripening of the entire crop. Small heads | 120 days |
| Golden hectare 1432 | Head of cabbage weight up to 3 kg | 110-130 days |
| Dietmar early | Super early. Head of cabbage weight 2.5 kg | 50-70 days |
| Chinese cabbage | Early ripening | 20-40 days |
| Cauliflower | Demanding high humidity | Early ripening: 96 days. Mid-season and late: 120 to 200 days |
| Broccoli | Frost resistant | 45 days |
Popular varieties of pepper for growing in heifers:
| Variety | Characteristics | Peculiarities | Productivity from one bush |
| Orange king | Early ripe | Large orange fruits 150 g | 2-3 kg |
| Prince Silver | Early ripe | Fruits are conical, red, 90-100 g | 2-2.5 kg |
| Cow's ear | Mid-season | Juicy red fruits, 120-140 g | 2.5-3 kg |
| Hercules | Mid-season | Dark green or red, 80-120 g | 2.5-3 kg |
| Golden Tamara | Mid late | Fruits are round, large, up to 200 g | 3-4 kg |
Today, in summer cottages and on an industrial scale, various vegetables, berries, flowers and much more are grown on large areas. And what to grow in a greenhouse with a carbonate coating? Read about this in the article.
What can be grown in a polycarbonate greenhouse?
It has long been believed that only tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers are grown here. But this is not the case. What to grow in a greenhouse? In indoor conditions, you can get the following crops:
- Onions - they are grown all year round for personal consumption and for sale. But it should be remembered that the dormant periods during which plants cannot be planted are not the same in time for different varieties.
- Champignons are grown in greenhouse areas unsuitable for other crops. This is a profitable business as mushrooms grow in low light and even complete darkness.

- Lilies, roses and other flowers. It is profitable to grow them in a greenhouse at any time of the year, but especially in winter, since there are few competitors at this time.
- Greens (dill, parsley, celery, lettuce) - it is unpretentious to growing conditions, it can be compactly placed in existing areas. Gives high yields all year round.
Where is the best place to grow cucumbers?
So what to grow in a greenhouse? Modern technologies allow you to grow vegetables all year round in greenhouses. The best option for this is a polycarbonate greenhouse. There are no cracks here, the leaves of the plant are protected from direct sunlight, and most importantly, there are all conditions for the installation of powerful ventilation.
What can be grown in such a greenhouse? Various vegetables, including cucumbers, can grow in this building throughout the year. The main thing is to carry out all the preparatory work before planting seedlings. It should be remembered that cucumbers are native to the tropics; at the genetic level, they do not have protection against diseases and pests of our climate.

If in the previous year the greenhouse beds were occupied by cucumbers, which were repeatedly sick, then the soil is completely replaced, and the interior of the structure is carefully treated with chlorine, then whitewashed with lime.
Soil preparation
How to properly grow cucumbers in a greenhouse? The technology provides for the determination of the acidity of the soil after sanitizing the greenhouse. This indicator should not exceed six and a half units. If more, then lime is added to the soil.
This is necessary in order to create comfortable growing conditions for cucumbers. Vegetables have a bad reaction to the soil with high acidity, since it is a favorable environment for the growth of harmful bacteria. How to properly grow cucumbers in a greenhouse? For this, the beds are prepared before planting seedlings. It is better to apply manure or compost in the spring at the rate of 10-15 kilograms per square meter.

Before planting seedlings, the soil is loosened with a rake, but first you need to evenly scatter a mixture of wood ash and superphosphate over the surface of the soil in the calculation of two teaspoons and two tablespoons, respectively, per square meter.
How to grow properly in a greenhouse vegetables? Only by observing all the rules of the technological process can you get a good harvest. One of them is the saturation of the soil with humus. For this, the beds are watered with a solution: one capsule of the "Energen" stimulator per bucket of water.
How to get seedlings?
For growing cucumbers in a greenhouse on an industrial scale, a seedling planting method is more often used. How to grow seedlings in a greenhouse? To do this, the soil mixture is scattered into peat cups and poured with hot water to kill bacteria.
When the soil cools down and becomes warm, the dry seeds are pressed into it two centimeters and covered with a film. In the morning you can see the sprouts that have hatched. When they grow up, and four to six leaves appear on the stalk, the seedlings are planted in a permanent place of growth.
Planting cucumbers
How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse? To do this, first make beds one meter wide, the distance between them is half of this measurement. Seedlings in each row are planted taking into account 40 centimeters, one bush from another.
Planting of cucumbers is carried out both by seedlings and seed. Planting material must be healthy and prepared before sowing. With the seed method, the plants do not need to be transplanted, since they are already growing in a permanent place. Their delicate roots will not be injured.

Before planting the beds, you need to water and prepare the holes in which the seedlings should be placed vertically. The stem is not covered with earth, and the plants do not bend over. How to grow cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse? In order for the seedlings to start faster, after planting, watering is carried out to the very root, the soil must be well saturated with moisture, since the roots of adult plants go deep into it by twenty centimeters. For irrigation, a solution of water (one bucket) and the preparation "Effekton-O" (three tablespoons) are used. Planting is carried out in soil warmed up to eighteen degrees Celsius.
How to form cucumber bushes?
What can be grown in a greenhouse? It can be vegetables, berries of different types, depending on preferences. Some plants need to form a bush, while others do not. This procedure is necessary for greenhouse cucumbers, they are formed into one shoot.
A week after planting, the plants are tied to supports. When the stems grow to the very top of the support, you need to remove the top of the shoot. In the lower part of the stem, all the rudiments of lateral lashes and inflorescences are cut off. If this is not done, the slow growth of the lower ovaries will affect the growth of the entire plant.
Growing cucumbers in winter
Can cucumbers be grown in a greenhouse in winter? This vegetable feels great growing in a greenhouse with a polycarbonate coating at any time of the year, including in the cold season. We grow cucumbers in the greenhouse in winter, but taking into account some of the nuances of the technological process. So, crop varieties pollinated by bees during this period do not bear fruit, therefore self-pollinated varieties are preferred.
It should also be borne in mind that the winter day is short. In this regard, when choosing a variety, you need to focus on one that can grow in shade and in conditions with low humidity. But in any case, plants need to be provided with sufficient lighting, optimal humidity and nutritious feeding. Otherwise, the harvest will not be seen even from these varieties.
Watering cucumbers correctly in the greenhouse
It doesn't matter what to grow in the greenhouse, but to get a high yield, you need to remember about watering. Otherwise, in the case of cucumbers, this will lead to undesirable consequences: the vegetables will taste bitter. Watering with cold water leads to the same result, so it needs to be heated.
Better to stock up on barrels, put them inside the greenhouse, fill them with water, and the issue is resolved. With a lack of water, the leaves will darken, and with an excess, on the contrary, they will brighten. If the leaves turn yellow, this means that the greenhouse is hot and the plants are running out of water.
You can at least grow something in a greenhouse if you take proper care of the plants.Here are cucumbers, they need to be watered early in the morning or late in the evening when the sun goes down, otherwise the leaves can get burned from direct sunlight. Before the fruiting period, watering is carried out infrequently, once or twice a week, but during it and until the harvest itself - every day, at the rate of seven liters of water per square meter.
What kind of soil is needed to grow tomatoes?
Tomatoes are not recommended to be planted in one place for several years in a row, since the soil is emptied, which is fraught with the occurrence of infectious diseases. To reduce the likelihood of their spread, the topsoil is removed and carried outside the greenhouse. The remaining soil is disinfected with a solution: for a bucket of water - one tablespoon of copper sulfate.

How to grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse? For this, a place is being prepared in advance. The best option is considered one where the sown area reaches 25 centimeters in height and 85 in width. The soil should be well-drained, loose and moist, but in moderation. Tomatoes need space, so the distance between the rows should be 90 centimeters, no less.
If you are thinking about what is profitable to grow in a greenhouse, remember: all vegetables are in demand with the consumer, but tomatoes are the most beloved and often bought, since their regular use replenishes the missing vitamins and minerals in the human body. Tomatoes grow on soil of any composition, but they are preferable to loamy soil, to which peat, manure or sawdust are added. Vegetables grow well on soil, which contains one part of rotted manure and sod soil, 0.5 parts of river sand. Superphosphate, potassium sulfate, potassium magnesia, sodium nitrate, wood ash are added to this mixture in appropriate quantities: 40:20:20: 2: 500 grams.
Planting tomato seedlings
Have you already decided what to grow in the greenhouse? If you have made a choice in favor of tomatoes, then you need to know that for the successful cultivation of tomatoes in a greenhouse from a polycarbonate coating hybrids work best. They are resistant to diseases and have a small bush size, they are formed into one stem. How to grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse? This process begins with planting seedlings in the ground. Of course, she needs to be raised first. But not everyone does it on their own. Most often, planting material is bought. Before planting, the soil temperature is measured: it should be 13 degrees Celsius.
Plants in which peduncles are formed and the height reaches 40 centimeters will take root better. If tall varieties are used for planting, the distance between them increases, and is about 50 centimeters. For undersized, 40 cm is enough.

For information: overgrown plants have a lower yield. They are planted at an angle, having previously removed the leaves from the lower part of the stem, so that they do not interfere with the deepening into the soil and in the future do not become a source of the spread of the fungus.
Seedlings are planted in prepared holes: the soil is spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate with water to eliminate pathogenic microbes, and fertilized with compost. Plants of normal height are carefully placed in the hole in an upright position and covered with earth, which is slightly compacted and watered around the stem. For two weeks, the seedlings are not watered, and fertilizers are not applied to the soil. This is a prerequisite for rooting.
Tomato care
After two to three weeks after planting, the bushes of the plants are tied to supports. The optimal air temperature is maintained in the greenhouse - 20-30 degrees Celsius, since it is in such conditions that the normal growth and fruiting of tomatoes is carried out.
In winter, additional heating sources are installed to ensure a constant normal temperature regime. To obtain early fruits, self-pollinated varieties are grown.But in order to increase yields, the plants need help. It is enough to shake the inflorescence, spray the plants, ventilate the greenhouse. This procedure is performed in warm and dry weather.
The care involves the formation of bushes, which consists in the removal of leaves and shoots. In order not to shock the plant, in which its growth slows down, strong stepsons are left, only weak ones are removed. During the period of fruit ovary, all the leaves located under the inflorescences are cut off.
When watering tomatoes, it is important not to harm them. Excessive moisture not only causes infection, but also impairs the taste. Tomatoes become sour, their meatiness decreases, they are filled with water.
Top dressing begins when the first small tomatoes appear. To do this, once a week, the soil is watered with a solution of potassium monophosphate. The plant responds well to overhead spraying, which is carried out weekly in the evening.
How to grow peppers in a greenhouse?
Getting a high yield of a vegetable largely depends on the preparation of the soil. It needs to be fertilized with phosphorus and potassium additives, but it is better to refuse fresh manure, since its introduction significantly reduces the yield. Better to fertilize the soil with compost or humus.
Some gardeners practice growing peppers from seedlings in plastic bags filled with nutrient-rich soil. In this case, you do not need to fertilize all the soil, but only the one in the bags.
Planting peppers in seedlings
How to grow peppers in a greenhouse? This is done in two ways: seedling and seed. The first is more popular with gardeners, since already strengthened plants are planted in the ground, and they quickly adapt to new conditions.

When the stem of the plant becomes thick and strong, and more than ten leaves appear on it, the seedlings are planted in a permanent place of growth. The height of the bush should be 25 centimeters, and the temperature of the soil into which it will be planted should be 15 degrees Celsius.
First, the holes are filled, one liter of water is poured into them. When the moisture is absorbed, a plant is placed in the hole and covered with soil so that the first leaves are on the surface of the earth. The soil around the stem is mulched to retain moisture, since the seedlings cannot be watered for a week. To do this, use sawdust, tree bark, dry leaves or straw. Immediately upon planting, a support is installed to each plant.
Proper care of pepper
The soil around the trunk should always be moist. It should be remembered that excessive moisture is detrimental to the pepper. The vegetable needs to be watered no more than once a week or every five days in dry weather. It is good if a drip irrigation system is installed in the greenhouse.
During the flowering period, top watering is unacceptable, since the properties of pollen deteriorate, and ovaries are not formed. Watering the pepper is carried out early in the morning, before the sun rises. During extreme heat, it can be repeated in the evening. It is also important to monitor the humidity in the greenhouse, and the room is constantly ventilated.
When watering, the main thing is not to harm. To prevent a crust from forming on the soil surface, experts advise to water one side first, and loosen the other at this time, and vice versa.
Any plant needs feeding, especially during the growing season. For pepper, potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen additives are especially needed, which can be dry and in the form of solutions. Top dressing is carried out before planting the plant in the ground and during the flowering period.


