Content
- 1 Anniversary
- 2 Oval
- 3 the globe
- 4 Apple
- 5 Vitamin VNIVI
- 6 Vorontsovsky 1
- 7 Titanium
- 8 Ruby
- 9 Rosehip varieties without thorns
- 10 Rosehip varieties for the Moscow region
- 11 Rosehip: species and varieties
- 11.1 Rosehip varieties by maturity
- 11.2 Large-fruited rosehip
- 11.3 Rosehip varieties for the Moscow region
- 11.4 Rosehip varieties for the northwest
- 11.5 Useful rosehip varieties
- 11.6 Rosehip without thorns
- 11.7 Round Rosehip Varieties
- 11.8 Decorative rosehip varieties
- 11.9 White rose hips: varieties
- 11.10 Rosehip wrinkled: varieties
- 12 Description of the plant
- 13 Varieties popular with gardeners
- 14 Landing procedure
- 15 Care
- 16 Culture propagation methods
- 17 Diseases, pests and control of them
- 18 Gardeners reviews
Rosehip is a great garden plant. During flowering, its bright buds decorate the site and fill the air with the scent of roses, and the ripe fruits are not only edible, but also very useful.
Most varieties of fruit rose hips come from 4 types of roses: cinnamon, wrinkled, dahurian and gray. According to the shape of the fruit, rose hips are usually divided into 2 groups:
- with large fruits (from 4 g or more) with dense skin,
- with small fruits (less than 4 g) with thin skin.
The fruits of the first group look like small apples. It includes varieties such as Jubilee, Oval, Globus, Apple. Berries of these varieties can be eaten fresh, and they also make good jam. Varieties of the first group are distinguished by repeated flowering, which means that they can be harvested several times from August to October.
The second group includes small-fruited rosehip varieties. But that doesn't mean they are less useful. It's just that their yield is less, so if necessary, more bushes will have to be planted. Among the varieties of this group, one can distinguish Vitamin VNIVI, Vorontsovsky 1, Titan, Rubin. Their fruits are great for drying.
Anniversary
The variety is of medium ripening, is a strong and powerful shrub up to 1.5 m in height. The fruits of the plant are large, round-shaped, orange-red, sweet and sour to taste, rich in vitamin C. During flowering, the Yubileiny rosehip is very beautiful: large pink flowers look great on the bush. And the fruits are suitable for jam and for drying.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 1.5 m |
From mid-August |
High |
Oval
A variety of medium ripening. Rosehip bush Oval grows small, flowers are also not too large, white. Fruits are slightly flattened, red, with thick skin and sweet juicy pulp. The variety is frost-resistant, not susceptible to disease, insects rarely damage the bushes. Berries are most suitable for processing, but also suitable for drying.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 1.5 m |
From mid-August |
High |
the globe
The variety is a medium-sized shrub up to 1.5 m high with thick branches and large flowers. Fruits are globular, bright red, characterized by a high content of vitamin C. There are so many ripening of them that the shoots bend under their weight. Globus variety belongs to winter hardy. This rose hip is suitable for making preserves, jams and candied fruits.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 1.5 m |
From mid-August |
High |
Apple
Rosehip of the Yablochny variety usually does not grow higher than 1.2 m, nevertheless, in terms of yield, it is not inferior to tall varieties. The flowers, like the fruits, are dark red. Rosehip berries of this variety are large and often grow in groups of 5-7 pcs. They have a flat-round shape and a sweet and sour taste. A bush with ripe fruits looks very elegant.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 1.2 m |
From mid-August |
High |
Vitamin VNIVI
An early variety of rose hips with large fruits and medium ripening. The bush can grow up to 2 m in height. The flowers are medium-sized, pale pink, collected in inflorescences. The fruits ripen red-orange, oval in shape. Rosehip Vitamin VNIVI is resistant to diseases, tolerates frost well, and is rarely attacked by pests. However, it is worth taking into account that the variety does not belong to self-pollinated, which means that another rosehip bush of a different variety should grow nearby.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
Up to 2 m |
Since the beginning of August |
High |
|
Vorontsovsky 1
The cultivar is an interspecific hybrid of the Webb rose and the wrinkled rose. Oval-elongated fruits are not only high in vitamin C, but also in folic acid. Orange-red berries are good for drying. Up to 3 kg of crop can be harvested from an adult bush. Long-term fruiting. The variety is of medium ripening, relatively cold-resistant.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
Up to 2 m |
From mid-August |
Average |
|
Titanium
A very effective variety with powerful shoots and large fruits. Rosehip of medium ripening. The plant bush can reach a height of 2 m, during flowering it becomes a real decoration of the garden. The Titan variety blooms very beautifully: delicate light pink flowers. Fruits are formed in clusters of 3-5 pieces. The variety is disease-resistant and cold-resistant. The fruit is best for drying.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 2 m |
From mid-August |
High |
Ruby
Rosehip early ripening. Refers to vigorous varieties. The flowers are medium-sized, pale pink. The round-oval orange berries turn dark red when ripe. They have a sweet and sour taste and are well suited for drying.
|
Appointment |
Plant height |
Fruit ripening |
Winter hardiness |
|
|
Up to 2.5 m |
Since the beginning of August |
High |
When choosing a rosehip variety, pay attention to which group it belongs to. So you will know what to do with the fruits: dry or make jam from them. And some growers generally grow rose hips solely for beauty. But it is still better to combine business with pleasure.
Rosehip belongs to the Rosaceae family. During the flowering period, its bright buds decorate the site, but from the end of summer you can already collect its fruits. In this article, we will consider the varieties of rose hips with photos and descriptions, which, according to reviews, are considered the best. Its fruits can be quite large or small, with dense or thin skin.

In the photo, rose hips, which are valued due to their high content of vitamins and biologically active substances
Rosehip varieties without thorns
Almost everyone loves rose hips, but collecting it is a real problem. The thorns of the plant bring a lot of inconvenience. That is why many summer residents are in search of studless rosehip varieties. Let's consider the most popular ones:
- Vitamin. It does not have thorns in the fruiting zone, which makes it easier to collect. The height of the bush is 2 m. The variety is resistant to pests and diseases. The mass of one fruit is 3.5 g. Vitamin is well pollinated, which is rare for a plant.
- Shipless. The name alone indicates that this variety is a real find for the owners of the backyard territory. It is characterized by average yields. There are no thorns at all, and the berries are not large, but sweet, rich in vitamin C.
- Pay attention. The bush is spreading and erect. The weight of the fruit is about 4 grams.It is possible to collect about 2 kg of fruit from one bush. As for the resistance to diseases and pests, it is average.

Today there are over 250 varieties of rose hips. Some of them delight with their fruits, while the rest are decorative
Rosehip varieties for the Moscow region
Today there are over 250 varieties of rose hips. Some of them delight with their fruits, while the rest are decorative. Of course, before buying this or that variety, you need to find out whether it bears fruit well in the area. If we talk about the Moscow region, then you need to carefully choose the variety.
In this area, not all shrubs are accepted and please with their fruits. Pay attention to those of them that, according to gardeners, grow and bear fruit abundantly:
- Scarlet. Winter hardiness, high yield, drought tolerance are the main advantages of the rosehip variety, a photo and description of which is in the article. It is resistant to black spot, mildew and other ailments.
- Vorontsovsky-1. It belongs to interspecific hybrids. Its height is 2.5 m. It is known for its frost resistance, practically not susceptible to disease. The yield from one bush is often 3.5 kg.
- Geisha. This is one of the best large-fruited varieties. Low-growing bush with medium-sized shoots. Summer residents share that the fruits look like small apples. A crop from one bush can be harvested about 5 kg, which cannot but please the owners.
- Hedgehog. Rosehip shoots have thorns, but this drawback is not so significant against the background of the Hedgehog's merits. The weight of one fruit is 3.8 grams. This rosehip variety ripens by mid-August. It is high-yielding, winter-hardy, and is also grown for decorative purposes.
- Victory. The early ripening variety is valued for its stable average yield and winter hardiness. Although there are thorns, they are absent directly in the fruiting zone. The fruits of the plant are large-fruited. The variety is universal, so it can be seen both in the Moscow region and in other regions.
Of course, these are only some varieties of rose hips, which, according to gardeners, have good yield characteristics. There are many others that are grown in the Moscow region: Titan, Rubin, Ural Champion, Yubileiny, Shpil, Globusoni and others.
Video about the best varieties of rose hips:
Rosehip varieties with photos and descriptions are the information that owners of personal plots are looking for on the Internet. Many of them want to plant shrubs that will take root well in the Moscow region, while others are interested in thornless rosehip varieties. In our article you will find a description of these crops with photos.
(
estimates, average:
out of 5)
Rosehip is a wonderful berry plant that can not only decorate the site and play the role of a hedge, but also give a rich harvest of useful fruits. In culture, several types of rose hips are grown at once; many interesting varieties are known.
Rosehip: species and varieties

Rosehip varieties
This beautiful plant belongs to the Rosaceae family - about six dozen of its species grow in Russia. In the wild, bushes can be seen on forest edges and clearings, on river banks, ravine slopes and rocky slopes. Rosehips are of greatest interest to gardeners:
• Thorny
• Cinnamon
• Gray
• Apple
• Wrinkled
• Multi-flowered (climbing)
Each of these varieties pleases with a diverse varietal composition - plants differ in the shape and color of flowers, shape, size and color of fruits, percentage of useful elements.
Rosehip varieties by maturity
The Rubin variety can be attributed to the category of early rose hips. This vigorous plant is covered with thorns, especially at the base of the branches. The fruits are large, red, oval, tasty (with a small amount of acid). The variety tolerates a drop in temperature well.
Middle and late ripening periods are inherent in varieties:
• Titanium
• Ray
• Large-fruited
• Hedgehog
• Geisha
• Crimson
Description of the Hedgehog variety
The plant is weak, with spiny shoots (thorns are yellowish in color). The flowers are very beautiful - large and bright. The oval fruits are creamy orange in color. The plant is winter-hardy, fruitful.
Large-fruited rosehip
A sufficient number of large-fruited varieties are known. The largest berries are produced by apple rose hips - their diameter reaches 3 cm, and their weight is 12 g. The varieties have good indicators:
• Jubilee
• Large-fruited
• Crimson
Description of the variety Large-fruited VNIVI

Rosehip variety Large-fruited
The plant is sprawling, large. Brownish shoots are covered with numerous thorns. The pink flowers are quite large. Red-orange berries are very large, round, sweet and sour. The plant tolerates low temperatures well.
Rosehip varieties for the Moscow region
Almost all rose hips have good resistance to unfavorable weather factors, therefore, in the conditions of central Russia, a wide variety of varieties are successfully grown. The most popular are:
• Russian-1
• Vorontsovsky (1, 2, 3)
• Geisha
• Victory
• Crimson
• Large-fruited
Description of the variety Russian

Rosehip variety Russian
The plant is of medium size. It looks very nice in the garden. The flowers are large, fragrant. The fruits are elongated, red-orange, rather sweet. The plant is resistant to many diseases.
Rosehip varieties for the northwest
In the north-west of the country, good results are shown by such varieties as:
• Bakal
• Ural champion
• Ruby
• Titanium
• Timiryazevsky
• Hedgehog
• Geisha
• Large-fruited
• Ray
• Spire
Description of the Ural Champion variety

Rosehip variety Ural champion
The variety is very winter-hardy, productive, large-fruited (the weight of the berries reaches almost 5 g). The flowers are large and bright. The fruits are rounded and colored red. The berries have a pleasant, sweet and sour taste. The plant is slightly spreading.
Useful rosehip varieties
Berries of all varieties of rose hips are of high value in terms of the content of ascorbic acid and other valuable elements. Nevertheless, real leaders can be distinguished among them. This category includes varieties:
• Vorontsovsky-1 (3900 mg)
• Vitamin (3806 mg)
• Thornless (3110 mg)
Description of the Vitamin variety

Rosehip variety Vitamin
This variety has good winter hardiness. The average height of the plant is 2.5 m. The bush is spreading. Fruits are oval, large, sweet and sour, numerous (up to 5 pieces in a brush). Single thorns.
Rosehip without thorns
One of the most popular varieties of rose hips is Besshipny. The plant has an average yield. The thorns are completely absent. The berries are medium-sized, rather sweet, with a high content of vitamin C.
The varieties Grushenka and Yadviga are also devoid of thorns.
Round Rosehip Varieties
In addition to varieties with elongated berries, there are those that form rounded fruits. Examples of this are:
• Ural champion
• Malets
• Ruddy
• Chelyabinsk vitamin
• The globe
• Anniversary of Michurinsk
Globus variety description

Rosehip variety Globus
This winter-hardy plant pleases with a high yield. The fruits are large, rather sweet, spherical. The plant is resistant to disease.
Decorative rosehip varieties
In the garden, rosehip varieties with climbing shoots and double flowers look very beautiful. Many decorative forms have been developed. The most interesting varieties are:
• Maxima
• Golden Wings
• Fruhlingsduft
• Maigold
• Nevada
Description of the variety Nevada

Rosehip variety Nevada
This variety pleases with the beauty of the flowers - they are large, semi-double, white with a slight pink blush (the color can change depending on the type of soil and can be creamy, pure white or pinkish).
White rose hips: varieties
Terry prickly rosehip is considered one of the most decorative species. The plant has double white flowers.
As for the rosehip varieties, the most interesting for gardeners are the following:
• Alba Mediland
• Climbing Iceberg
• Suaveolens
Description of the Alba Mediland variety

Rosehip variety Alba Mediland
Shoots of this type of dog rose spread (the height of the bush does not exceed one and a half meters). The flowers are very beautiful, double, with white petals. They are small in size and have a pleasant aroma. The plant can bloom twice a season (if conditions are favorable).
Rosehip wrinkled: varieties
In nature, this plant can be seen in the Far East. In culture, it is often grown as a hedge. The most popular varieties of foreign selection:
• Grootendorst (white, pink, suprem)
• Abelzieds
• Ferdinand Meyer
• Agnes
• Hanza
Description of the variety Queen of the North

Rosehip variety Queen of the North
The variety of the Queen of the North is of interest. It is ideally adapted to the conditions of our country, hibernates without shelter. The flowers are double, red-pink, very beautiful.
Each of the rosehip varieties has its own advantages - some of them are grown in order to obtain useful fruits, while others are ideal for decorating the site.
There is hardly a person who has never seen a rosehip. This plant is widely used in landscape design, it is also popular with amateur gardeners. But abundantly flowering shrubs can not only decorate the garden, but also bring a harvest of extremely healthy fruits. There is nothing difficult in cultivating rose hips; even a novice gardener can grow it.
Description of the plant
Rosehip is a numerous genus of deciduous plants from the Rose family. Most of them are shrubs; vines, herbaceous and tree-like plants are much less common. They all have a common feature - the shoots are densely covered with sharp thorns of different lengths. They are even on annual branches, but there they look more like bristles.
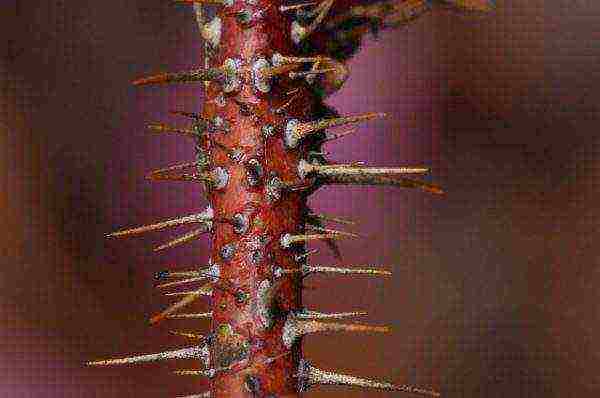
Rosehip owes its name to the presence of many densely spaced thorns dotting the shoots
Rosehips are ubiquitous in the northern hemisphere. He is equally satisfied with the temperate and subtropical climate. It grows almost like a weed, successfully adapting even to unfavorable environmental conditions in cities. In central Russia, cinnamon rosehip is especially common. Among the "relatives", it stands out for the highest content of vitamin C in fruits.

Rosehip is widespread in nature, it grows mainly where the soil is moist and fertile, forming whole clumps and practically impassable thickets
The leaves of the wild rose have a rich dark green color (gray-gray, olive or reddish tint occurs), complex shape (pinnate), not too large (5–8 cm in length). The wrong side is most often pubescent. The edge is cut with small teeth.
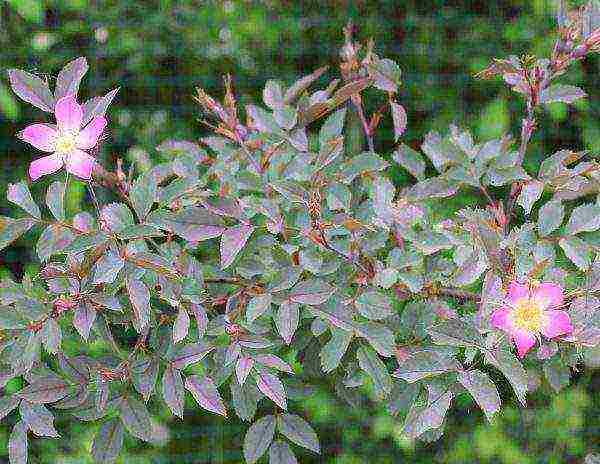

Rosehip leaves, depending on the variety, can cast bluish or reddish
The average height of an adult plant is 1.5–2.5 m. Shoots are thin enough, almost twigs. At the same time, it is rather difficult to break them. The bark is reddish brown, smooth, shiny, sometimes with a greenish or purple tint. The root system is powerful and developed. Taproots extend 2.5–3 m into the ground, adventitious roots reach a length of 25–40 cm.
The plant forms a very abundant root growth, due to which it quickly expands in breadth.

Rosehip is widely used in landscape design
Rosehip blooms in June or early July and lasts 10–20 days. The flowers look very impressive and spread an amazing scent. In wild varieties of rose hips, they are most often simple, five-petaled. The buds are single or collected in 2-4 pieces in inflorescences in the form of a shield or panicle. Breeders have also bred terry rosehip varieties. The color of the petals is very different - from snow-white to dark crimson, almost black. In nature, various shades of pink are common, from delicate pastel to bright crimson. The average flower diameter is 4–5 cm. They open daily from 4:00 to 5:00, and "fall asleep" from 19:00 to 20:00.
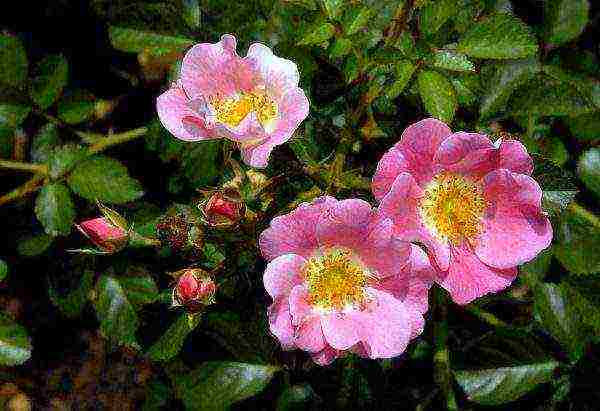

Blooming rose hips decorate the site and spread an amazing scent
Rosehip fruits ripen by the end of summer or in the first half of September. If they are not harvested in time, they will remain on the plant until the first frost. These are almost spherical, sometimes elongated or flattened berries of various shades of red and orange. They are known to botanists as hypanthium, which is formed during the growth of the receptacle. The average diameter is 10-15 mm. The first harvest can be expected in 3-4 years after planting the seedling in the ground. The term of the productive life of the shrub is at least 25–30 years.
Rosehip is a non-self-pollinating plant. Its pollen is carried by bees and other insects. Therefore, if it is planted with the expectation of a future harvest, and not to decorate the site, it is advisable to have several varieties.
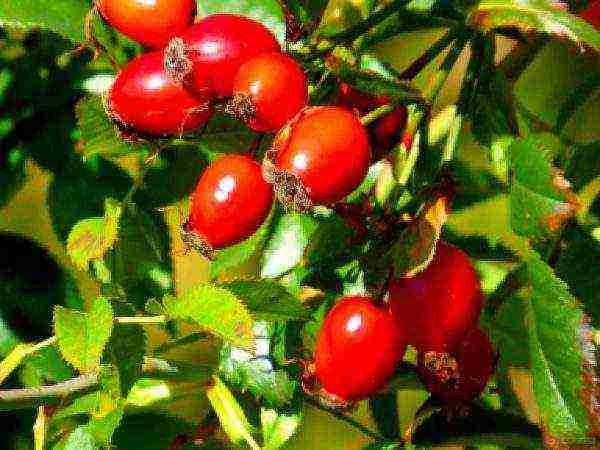

Rosehip fruits look no less decorative than its flowers
Rosehip has a record high content of vitamin C, which has a positive effect on immunity, the general resistance of the body to diseases, reduces fatigue, increases efficiency (both mental and physical), stimulates tissue regeneration and renewal of blood cells. Rosehip seed oil helps with wound healing and any skin ailments.
Contraindication to the use of rose hips - pathology of blood vessels (varicose veins, thrombophlebitis). After using the rosehip decoction, you must rinse your mouth out - otherwise it can cause dental problems.
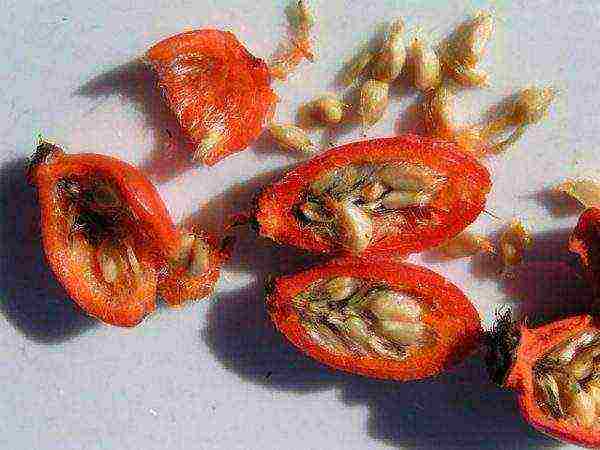

Rose hips are high in vitamin C
Varieties popular with gardeners
Rosehip breeding goes in two directions. Both large-fruited high-yielding varieties with a high content of vitamin C and microelements, and decorative hybrids with unusual color of petals, double flowers are bred.
Of those varieties that are planted for the sake of harvesting, the following are the most popular among Russian gardeners:
- Vitamin VNIVI. Sprawling bush, erect shoots. Thorns on fruiting shoots are practically absent. The berries are almost spherical, weigh an average of 3.5–4 g, and form clusters similar to bunches of grapes or red currants. They are characterized by a high content of vitamin C (4000 mg per 100 g) and carotenoids. The pulp has a pleasant sweet and sour taste. The average yield is 2.5–3 kg per adult plant. The variety is characterized by frost resistance up to -35 ° C, accordingly, it is suitable for growing in the Urals, Siberia, and the Far East. It is also characterized by good immunity to diseases typical of the culture. The presence of pollinating varieties is mandatory;
- Large-fruited VNIVI. The bush is powerful, spreading, and is distinguished by its growth rate. The average height is about 2 m. On young shoots, the bark is greenish; with age, it changes color to grayish brown. The leaves are dark green, the surface is slightly wrinkled. Flowering begins in June and lasts until the first frost. At the same time, the fruits ripen. The flowers are large, the petals are pale pink. The fruits are slightly flattened, the skin is glossy, reddish-orange. Average weight - about 8 g, yield - 3-4.5 kg per bush. A significant drawback is the relatively low content of vitamin C in the pulp in comparison with other varieties. Frost resistance is at the level of -25 ° C;
- Scarlet. The bush is 1.5–2 m high and about the same diameter. The growth rate does not differ. The thorns are rather short and sparse, concentrated at the base of the shoots. Fruits of an unusual pear-shaped shape are located on long stalks. The skin is shiny, bright scarlet. The taste of the pulp is pleasant, sweet and sour. The harvest ripens in the last decade of August. The variety is valued for its high frost resistance and genetically built immunity to powdery mildew, but it often suffers from black spot;
- The globe. The height of the bush is up to 1.5 m, the shoots are quite thick, arched. The bark is greenish brown. The thorns at the base of the branches are densely located, on the tops they are practically absent. The leaves are large, light green. The average weight of an almost spherical berry is 3–3.5 g, the stalk is long, the skin is pale scarlet.The yield is very high - 6-7 kg per bush. It does not differ in particular frost resistance, therefore it is grown in a subtropical climate (south of Russia, Ukraine);
- Ray. Tall shrub, grows up to 3–3.5 m. Shoots are thin, greenish bark. There are practically no thorns, they are concentrated only at the base of the branches. The flowers are pastel pink, the fruits are bright scarlet. The berries have an interesting elongated shape, like a cone. The average weight is 4–4.5 g. The taste is not bad, with a refreshing sourness. The variety is valued for its high yield, cold resistance, and immunity to powdery mildew. Also, it is most often bypassed by pests typical for the culture;
- Oval. A medium-ripening variety, widely grown in Russia on an industrial scale. The bush is low (up to 1.5 m), compact. Shoots are thin, curved, matte bark. The thorns are not located too often, but along the entire length of the branch. The flowers are medium-sized, snow-white. Fruits reach a mass of 8-9 g. The skin is thick, the pulp is sweet, almost without acidity. The variety has a very high frost resistance and is extremely rarely affected by diseases, pests;
- Ruby. The leaves and fruits are large enough. The berries are collected in bunches of 3-5 pieces. The peel is orange; as it ripens, it becomes dark scarlet or crimson, the shape varies from almost spherical to elongated, oval. The pulp tastes sweet and sour. The fruits ripen in the first decade of August, the yield is low - 1–1.5 kg per adult bush. The variety can withstand frosts down to -30 ° C, with good care it rarely suffers from diseases and pests;
- Titanium. Powerful spreading bush, reaching 2 m in height. Flowering occurs in mid-July. The leaves are practically invisible behind the pale pink petals. The berries are collected in a brush of 3-5 pieces, they are stored dry for a very long time. Frost resistance - up to -20 ° С;
- Anniversary. The bush is powerful, but low (up to 1.5 m). The flowers are large, bright pink, the bloom is very abundant. The fruits are shaped like bulbs. The average berry weight is 4–5 g. The skin is shiny, red-orange. The pulp is sweet and sour. The fruits are great for drying, and jam is also made from them;
- Apple. The height of the bush does not exceed 1–1.2 m, but this does not affect the yield in any way. It is comparable to that of tall varieties (4–5 kg). The flowers are large, the petals are dark scarlet. Fruits are colored in a rich bright red, collected in clusters of 5-7 pieces. They are slightly flattened in shape. The pulp has a pronounced sweet and sour taste. The average weight of a berry is 10–12 g;
- Vorontsovsky-1. Interspecific hybrid, "parents" are Webb's rose and wrinkled rosehip. Height - up to 2 m. The yield is not bad, about 3 kg of berries per bush. The fruits ripen at the end of August, they are not only high in vitamin C, but also in E (folic acid). The skin is glossy, orange-red. The shape is almost spherical. Low frost resistance - up to -15ºС. It is a good pollinator for other rosehip varieties;
- Russian-1. The bush is very decorative, graceful, the leaves are pale green. The content of vitamin C is about 3200 mg per 100 g. Fruits are one-dimensional, almost spherical. Productivity - 1.5-2 kg per bush. Bred specifically for growing in the Urals. Has a genetically built immunity against rust;
- Sergievsky. A variety of medium ripening. The bush is compact, 1.5–1.8 m high. It has good frost resistance, disease and pest resistance. Recommended for cultivation in the Volga region. Fruits are bright red, ovoid, weighing 3-4 g. The flesh is sweet and sour. Vitamin C content is about 2500 mg per 100 g.
Photo gallery: common varieties of rose hips
Decorative rosehip varieties are widely used in landscape design both in single plantings and for the formation of hedges. Most of them were bred abroad, so they do not differ in special frost resistance. Most often these are interspecific hybrids obtained by crossing musk and wrinkled rose hips. The most common ones are:
- Jundzilii. The plant is compact, almost spherical. Height and diameter - 0.5-0.8 m. The crown is very dense. It is widely used for the formation of hedges. The flowers are carmine red;
- Nana. Hybrid no more than 0.5 m in height. Flowering is very abundant and long. The petals are pale pink. Semi-double flowers;
- Montblanc. The leaves are small, as if delicate. The flowers are large, with snow-white petals;
- Robin Hood. The flowers are quite modest, pastel pink. Flowering lasts up to 3 months. Simultaneously with them, large scarlet spherical fruits with a shiny skin ripen;
- PiRo-3. The height of the shrub is up to 1.5 m. The flowers are very large, with crimson-pink petals. Against their background, the saffron-yellow stamens, collected in a bunch, stand out sharply;
- Ballerina. Unpretentious hybrid, tolerates partial shade well. The petals are pale pink, covered with brighter specks and strokes;
- Resonanz. The height of the bush is about 1 m. The flowers are very large, double, bloody-scarlet;
- Moje Hammarberg. Due to several waves of flowering, the short shrub is strewn with flowers during almost the entire vegetative season. Their petals are bright pink, the aroma is very rich;
- Red Rugostar. The bush is 0.7-0.8 m high. The flowers are semi-double, dark scarlet. Stamens of a bright lemon shade;
- Thisbe. The presence of several waves of flowering is characteristic. Semi-double flowers, petals of a peach or salmon shade, which is very rare for a dog rose;
- Northern Lights. The bush is up to 0.7 m high. The flowers are semi-double, shaped like saucers. Pale-pearl petals cast salmon, pinkish, pale yellow.
Photo gallery: popular varieties of decorative rose hips
Landing procedure
Rosehip is distinguished by its general unpretentiousness, but a necessary condition for obtaining the maximum possible yields is a sufficient amount of heat and sunlight. The sun is also needed for decorative varieties, otherwise the flowers become smaller, the color of the petals will fade, the flowering becomes not so abundant. Therefore, it is best to place the bush in an open area, ideally on a small hill.
Rosehip soil prefers nutritious, but light enough. Although the plant takes root and bears fruit on any soil, except saline, waterlogged and alkaline, but the best option for it is a loamy or sandy loam substrate. Areas where groundwater approaches the surface closer than 1.5 m are categorically unsuitable. For the same reason, lowlands are not recommended - melt water and moist humid air stagnate there for a long time.
Rosehip yield depends on the availability of pollinating varieties. If several plants are planted at the same time, the distance between them is at least 0.8 m (preferably 1 m). To form a hedge, the interval is reduced by 1.5 times. The distance between the rows of plantings is about 2 m.
Most often, in regions with a temperate climate, rose hips are planted in the spring. In the south of Russia or Ukraine, the procedure can be postponed to the beginning or even mid-autumn. Even in this case, in the subtropics, there is enough time before the first frost. In 2.5–3 months, the seedling will have time to adapt to new habitat conditions.

The root system of a rosehip seedling must be developed, healthy
The recommended planting pit depth is about 30 cm, the diameter is 15–20 cm more. It is always prepared in advance, for spring planting - from autumn, otherwise, at least a few weeks before the planned procedure. The top layer of fertile soil is mixed with 2-3 kg of humus, and simple superphosphate and potassium sulfate (20-30 g each) are added.
The natural alternative is about 0.5 liters of sifted wood ash.
Step-by-step planting process
- Before planting, the roots of the seedling are soaked in water, cut to a length of 20 cm, coated with a mixture of powdered clay and manure.
- When it dries up, the plant is placed in a planting hole and covered with earth. It is imperative to ensure that the root collar is 3-4 cm above the soil level.
- The shrub is watered abundantly (25–30 l).
- The trunk circle is mulched, creating a layer about 3 cm thick.
- Shoots are pruned to a length of 10-15 cm, the leaves are torn off.
To prevent the active formation of overgrowth, slate sheets are placed along the walls of the planting pit.
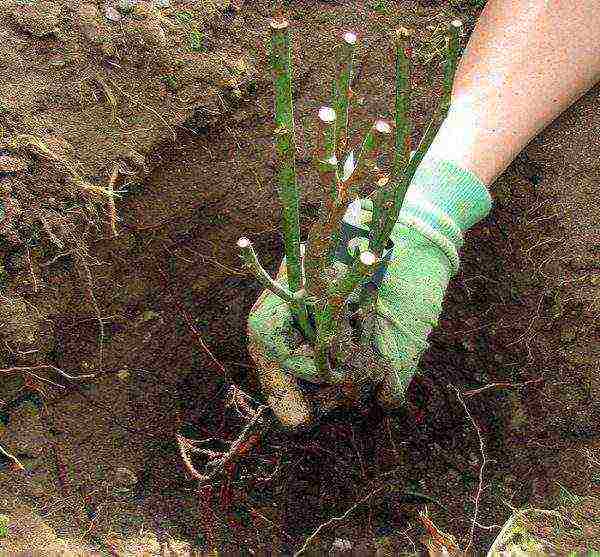

When planting a rose hip, the root collar must not be buried.
Transplant features
To transplant an adult rosehip bush, you need to choose a cool, cloudy day. The roots should not be left in the sun, even for a short time. They dry out quickly, reducing the chances that the rose hips will successfully take root in a new place. The plant is removed from the soil along with an earthen clod. The procedure is carried out either in early spring, before the growth buds "wake up", or in the fall, after harvesting and leaf fall. It is not recommended to disturb flowering bushes.
Care
The plant does not differ in demanding and capriciousness. Care comes down to keeping the trunk circle clean and loosening the soil in it, watering, top dressing and regular pruning.
Watering
Rosehip is a moisture-loving plant, while it categorically does not tolerate stagnant water at the roots. Therefore, the plant is watered infrequently, but abundantly. In extreme heat, in the absence of precipitation, 30-40 liters of water are consumed on a plant before the first harvest every 10–12 days, and 60–70 liters for a fruiting bush. Young seedlings in the first year of life are watered more often, once every 5-7 days.
After each watering, the soil in the near-stem circle is loosened to a depth of 3-5 cm. To retain moisture, it is mulched. Mulch also helps save weeding time by keeping weeds in check.
Fertilization
If the planting pit has been prepared correctly, they begin to feed the dog rose from the second season in the open field. Fertilizers are applied three times.
- The first feeding is carried out 1.5–2 weeks before flowering. The plant is watered with a solution of urea or any other nitrogen-containing fertilizer. Once every 2-3 years, about 20 liters of humus or rotted manure is additionally distributed in the near-trunk circle in the spring.
- The second time fertilization is applied immediately after flowering. Any complex remedy for fruit and berry bushes (Agricola, Zdraven, Effecton) is suitable. In 10 liters of water, 20-30 ml of fertilizer is diluted, the norm for an adult plant is 12-15 liters of solution.
- The last time the rosehip bushes are fed 2-3 weeks after the end of fruiting. Plants need potassium and phosphorus to properly prepare for winter. The solution is prepared by diluting 20-25 g of simple superphosphate and half the amount of potassium nitrate in 10 liters of water. An alternative is complex phosphorus-potassium fertilizers (ABA, Autumn) or an infusion of wood ash.
If the condition of the plant does not suit you, during the growing season after flowering it can be sprayed with a solution of any biostimulant (potassium humate, Epin, Heteroauxin, Zircon) every 2-3 weeks. This has a positive effect on the yield and quality of the fruit.

Any universal complex fertilizer for berry bushes is quite suitable for feeding rose hips.
Correct pruning
Rosehip is characterized by a high growth rate and active formation of root growth. Therefore, pruning for him is a mandatory procedure. It is significantly hampered by the presence of thorns. Long-handled pruners are used to avoid injury.
The first time the plant is cut off immediately after planting, leaving no more than 3 growth buds on each shoot. After another 2-3 years, the bush is thinned out, leaving 3-5 of the strongest and most developed shoots. They are shortened to a length of 15–20 cm. A properly formed plant should consist of 15–22 branches of different ages, but not older than 7 years.
Don't forget about sanitary pruning. In the spring, you need to get rid of all the broken, dry, frozen branches damaged by diseases and pests. Also, to the point of growth, weak, deformed, thickening crown, too low shoots are cut off.
It is advisable to reduce the autumn sanitary pruning to the required minimum. Even properly processed cuts do not tolerate the winter cold very well.
The tops of the shoots of the rose hips in the hedge are regularly pinched. This adjusts the height and stimulates more intensive branching.
Preparing for winter
Most varieties of rose hips bred by breeding are distinguished by good or even very good frost resistance, therefore they do not need a special shelter for the winter. Even if the bush suffers from cold weather, it quickly recovers due to root growth. Most often, growth buds on annual shoots freeze slightly.
Decorative varieties of rose hips suffer from cold weather more often. For them, even -15 ° C is a critically low temperature. Therefore, special training is recommended. The trunk circle is cleaned of plant debris, a layer of mulch is created with a thickness of about 15 cm. It is best to use peat, humus, and fallen leaves. As soon as enough snow falls, it is scooped up to the roots. If the height of the bush allows, it can be covered with snow completely.
Harvesting and storage
Rosehip harvest ripens in several "waves". Collect it from August to late September or even early October. It is important to be in time before the first frost. Fruits affected by the cold significantly lose their benefits. When preparing for harvesting, do not forget about personal protective equipment - tight clothing, gloves. You can remove those fruits from which the sepals depart.
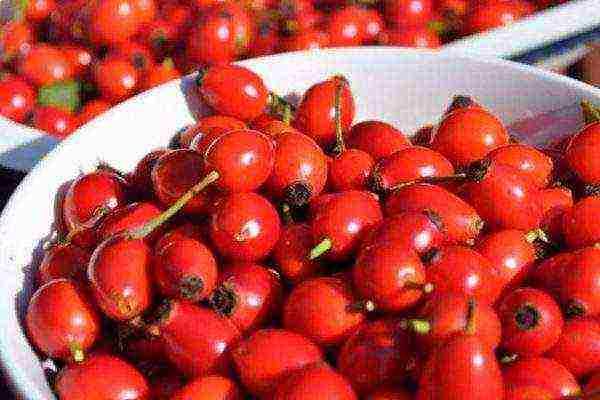

The rose hips must be harvested before the cold weather
For long-term storage, rose hips are most often dried in the oven or naturally. Then the berries are poured into any suitable containers, which must be kept loosely closed. Otherwise, mold and rot quickly develop. To add taste and aroma, the fruits are sprinkled with pieces of ginger, grated citrus zest. After drying, you need to wait at least a week, only then can the rosehip be used to prepare broths and infusions.
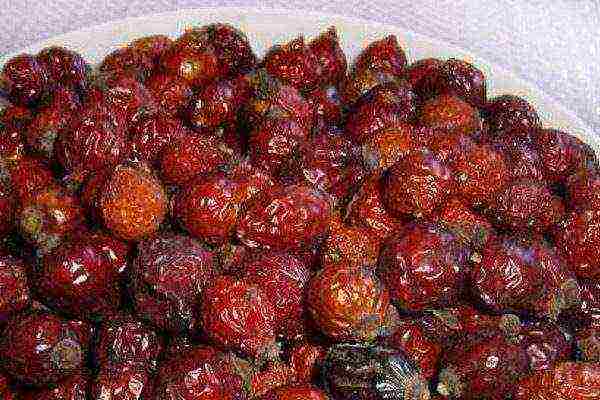

During the drying process, the benefits of rose hips are not lost, and the shelf life is noticeably increased.
Video: growing rose hips and harvesting
Culture propagation methods
Rosehip reproduces both vegetatively and generatively. Amateur gardeners most often use the first option, which guarantees the preservation of the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. Growing rose hips from seeds is a rather lengthy and laborious procedure that does not guarantee success.
Cuttings
Rosehip cuttings do not root very well. This is especially true of decorative hybrids bred with the participation of wrinkled rose hips. The probability of success is no more than 15–20%.
Rosehip stalk is the upper or middle part of an annual green shoot 15–20 cm long, cut at an angle of 45º. They are harvested in the middle of summer. Each must have at least three growth buds.

Rosehip cuttings can be harvested throughout the summer, but the best time for this is July
- Before planting, the lower leaves are cut off, the base of the cutting is immersed in a solution of any biostimulator for 12-16 hours.
- Cuttings are rooted in a mixture of peat with a baking powder (sand, perlite, vermiculite), creating a greenhouse using a plastic bag put on the container, a glass cap, a cut plastic bottle. They are planted in the ground obliquely.
- Next, you need to ensure a constant temperature of about 25 ° C, daylight hours lasting at least 12 hours, bottom heating.
- The substrate is constantly kept in a slightly damp state, the greenhouse is ventilated daily, getting rid of condensation.
- When new leaves begin to appear on rooted cuttings, they can be transplanted into open ground. On average, the process takes 4-6 weeks.
- The seedlings are hardened for 2-3 weeks beforehand, gradually extending the time spent outdoors.
- Rosehip is removed from the container along with a clod of earth. If autumn planting in the region is not recommended, you can wait until spring.
Using root growth
Most varieties of rose hips are found in abundance. This way of getting new plants is provided by nature itself. At the same time, it is not recommended to transfer the seedlings immediately separated from the mother plant to a permanent place. Their root system is weak, not too developed.

Most varieties and hybrids of rose hips are formed in abundance, therefore, a shortage of planting material, as a rule, does not arise.
"Offspring" 25-30 cm high are separated from the mother plant using a shovel. For the transplantation procedure to be successful, about half of the leaves are cut off, the shoots are shortened, leaving 2-3 growth buds. The roots are powdered with Kornevin powder.
An alternative option is to sprinkle the selected "seedling" high in the spring and water it abundantly during the summer, adding humus or rotted compost under the roots about once a month. Hilling stimulates the development of the adventitious root system. In the fall, it is carefully separated from the mother plant, and the next spring is transferred to a permanent place.
Germinating seeds
Rosehip seeds are extracted from unripe brown fruits, while they still have a fairly soft shell. Otherwise, their germination is possible only under the condition of carrying out at least six months of stratification, and the seedlings will have to wait 2-3 years.

Rosehip seeds are extracted from unripe fruits - in this case, they have a softer shell
Rosehip seeds are sown before winter in grooves about 2 cm deep, leaving 5–6 cm between them. From above they are covered with humus and sawdust. In the spring, this section of the garden is covered with plastic wrap until shoots appear. It is removed only when the daytime temperature reaches around 20 ° C.
Seedlings in the phase of appearance of the third leaf dive, leaving only the most powerful and developed plants. Further care for them is no different from what is required for adult rosehip bushes. Next spring, the seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place.
If spring planting is planned, during the winter the seeds are kept in containers filled with a moderately moist mixture of peat chips and sand in a dark place at a temperature of 2-3 ° C. Beforehand, they must be thoroughly cleaned of pulp so as not to provoke the development of mold or rot.
Closer to spring, the seed coat cracks. They are planted in a mixture of peat and sand, providing the same conditions as rooting cuttings. Plants are ready for planting in the ground in 1.5–2 years.
Diseases, pests and control of them
Thorny shoots of rose hips protect the bush well from many pests that can attack garden plants. Also, the culture has good immunity against pathogenic fungi. Nevertheless, the plant does not have absolute protection.
Most often, rose hips suffer from the following diseases:
- rust of leaves. On the seamy side of the sheet, areas of "fleecy" yellow-orange bloom appear. Gradually they turn brown and thicken, the affected tissues die off. For prevention, swelling leaf buds are sprayed with a 2% solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid. During the season, they are treated with soda ash (15–20 g per 5 l of water). Having found alarming symptoms, fungicides (Topaz, Vectra, Strobi) are used twice with an interval of 12-15 days;
- black spot. The disease spreads from the bottom up. Small, gradually growing rounded black-gray spots with a yellow border appear on the leaves and shoots. The affected parts of the plant dry out and die off. For prophylaxis, about once a month, the soil in the near-stem circle is watered with Fitosporin-M, in the fall after harvesting, it is sprayed with a 2% solution of ferrous sulfate. Folk remedy - iodine solution (2 ml per 1 liter of water).For the fight, drugs Topaz, HOM, Abiga-Peak are used, 2-3 treatments are carried out with an interval of 7-10 days;
- powdery mildew. Leaves and shoots are covered with a layer of whitish or grayish bloom, similar to scattered flour. Gradually, it thickens and darkens, acquiring a brownish tint. For prophylaxis, rose hips are sprayed with infusion of wood ash, garlic, mustard powder, a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate, diluted with water with kefir every 10-15 days. They fight the disease using the drugs Topsin-M, Vitaros, Bayleton (according to the instructions);
- peronosporiosis. On the leaves between the veins, lime-colored spots appear with a shiny, as if oily surface. The tissues in these places gradually dry out and crumble, holes appear. For prophylaxis, the soil in the near-trunk circle and rosehip bushes are powdered with crushed chalk, colloidal sulfur, wood ash every 2-3 weeks. To combat the disease, Planriz, Gamair, Alirin-B are used, carrying out treatments no more than once every 2 weeks;
- chlorosis. The leaves are covered with yellow or almost white blurry spots, limited by veins. The most common cause is iron deficiency. To eliminate it, 5 g of ascorbic acid and 2-3 g of ferrous sulfate are dissolved in 1 liter of cold water. The shelf life of the solution is 12-15 days. You can also use Ferrovit and Ferrilene preparations for spraying.
A folk remedy for preventing chlorosis is to bury a few rusty nails under a bush.
Photo gallery: symptoms of diseases dangerous for the rosehip
Most of the pests typical of the culture are also characteristic of roses, which are much more likely to be attacked by them. Therefore, in order to avoid infection, it is advisable to place these crops in the garden as far as possible from each other.
Pests threatening the rosehip:
- spider mite. Young leaves, tops of shoots, buds, are braided with thin translucent threads, resembling a spider web, and are covered with small beige dots. The affected parts of the plant are deformed and dry. For prophylaxis, rose hips are sprayed with infusion of onion or garlic gruel, decoction of cyclamen tubers every 5-7 days. Having found a pest, they apply acaricides (Omite, Apollo, Neoron, Vertimek) with an interval of 5-12 days. Preparations need to be changed so that the tick does not have time to develop immunity;
- rosehip variegated fly. Adults lay eggs in fruit ovaries, hatched larvae eat fruits from the inside, leaving only the skin. For prophylaxis, wild rose is sprayed with Aktellik just before flowering. Chlorophos and Kinmix are used to fight;
- rose-colored sawfly. The larvae feed on leaf tissues, leaving only veins, and eat out longitudinal passages in the shoots. As a result, they turn black and wither. For prophylaxis, leaf, flower buds and fruit ovaries are sprayed with an infusion of wormwood or horsetail. Having found a pest, use Inta-Vir, Aktellik, Fosbecid, Aktara;
- rose leaflet. Adult butterflies lay their eggs in leaves curled up along the central vein. The larvae eat out the buds and fruit ovaries from the inside, then move to the leaves, leaving only veins. For prevention, unblown buds are sprayed with Nitrafen, after flowering, Karbofos is used. They fight caterpillars with Lepidocide, Dendrobacillin, Endobacterin;
- green rose aphid. Small lime-colored insects stick to the underside of leaves, tops of shoots, flowers and buds, fruit ovaries. Once every 5–8 days, you need to spray the rose hips with any sharply smelling infusion. As raw materials, you can use garlic or onion arrows, orange peel, hot pepper, wormwood, tomato tops, tobacco crumbs. Using the same means, they fight the pest, increasing the number of treatments up to 3-4 times a day. In the absence of an effect, any general-purpose insecticide is used (Confidor, Mospilan, Iskra-Bio, Commander).
Photo gallery: what pests typical for the crop look like
Gardeners reviews
Growing rose hips on a personal plot is not very difficult. This plant is less capricious than its "relative" rose, deservedly called the queen of flowers. Rosehip, of course, loses to her in decorativeness, but it has one undoubted advantage - the ability to bear fruit abundantly and steadily. The benefits of its fruits have long been known and scientifically proven. Recently, the culture has become the object of close attention of breeders, who are developing new varieties, focusing on both the visual appeal and the size of the berries.
Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)


