Content [show]
Garlic is an essential hot spice in cooking. It has a pungent taste and rich aroma and health benefits. Growing garlic is a simple process, therefore, it is on every site. You can find a description of the most popular varieties and varieties in this review.
Varietal variety of garlic
However, not everyone knows that there are more than 70 varieties of garlic! This means that you can choose according to your taste, focusing on the conditions of a particular site with its soil, climate features, location. Moreover growing experience suggests that you should not limit your choice to one or two varieties. It is worth trying a few, and only after leaving the ones you like.
 More than 70 varieties of spring and winter garlic are known
More than 70 varieties of spring and winter garlic are known
Such a variety makes sense, since some ripen earlier and they can be added to dishes already at the beginning - in the middle of summer, used for canning. Others ripen later, but are better stored.
Most popular varieties
Since the varietal variety is great, this article describes popular, popular varieties.
Spring
Spring garlic differs from winter garlic in different planting periods (spring garlic is planted in spring, and winter garlic - in late autumn), yield - spring garlic is less productive, in contrast to winter garlic.
To visually recognize spring garlic, you need to pay attention to the following signs:
- spring garlic without central bararound which the denticles are located;
- themselves spiral teeth - the closer to the center, the smaller they are;
- teeth can differ from each other by size and shape;
- spring garlicno arrows.
Popular varieties of spring garlic:
Victorio
 Spring Garlic Victorio
Spring Garlic Victorio
Mid-season, high-yielding species. No arrows, resistant to pests and fungal diseases... The bulbs are flat-round in shape, the color of the scales is yellow-white.
Yelenovsky
 Spring garlic grade Yelenovsky
Spring garlic grade Yelenovsky
Mid-season, fruitful, round heads. Outside, the color of the scales is whitish, and inside, on the teeth themselves, it is pinkish... Demonstrates resistance to all plant diseases.
Gulliver
 Spring garlic variety Gulliver
Spring garlic variety Gulliver
Considered mid-late. The harvest is good, it produces arrows. The bulb is round, slightly flat. The color of the scales is light, white. Little susceptible to diseases and pests.
Sochi 56
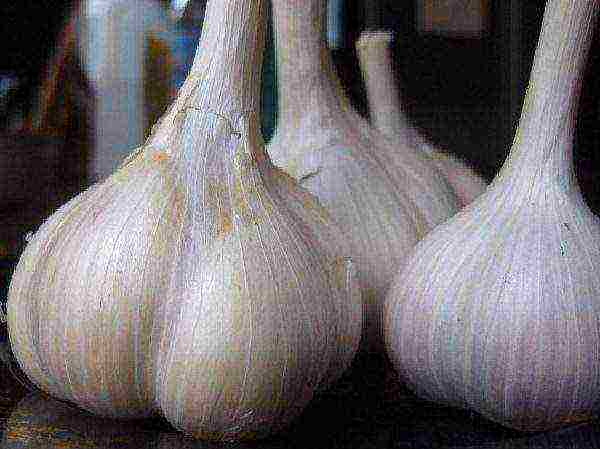 Spring garlic grade Sochi 56
Spring garlic grade Sochi 56
Mid-season, gives a stable and high-quality harvest. The shape of the head is slightly flat, rounded. The color of the scales can be white or purple, and on the teeth themselves - pink with a purple tint. Resistant to disease.
Ershovsky
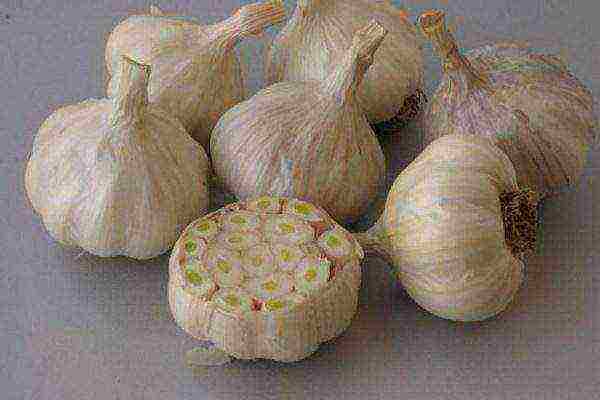 Spring garlic grade Ershovsky
Spring garlic grade Ershovsky
Belongs to mid-season, the bulbs are round, slightly flat. It does not give arrows, the harvest is excellent. Resistant to disease.
Winter crops
For winter garlic, the following signs are characteristic, by which it can be visually recognized:
- rod in the center of the headaround which the denticles are located;
- the teeth are arranged in a circle, in one row;
- teeth the same;
- harvest gives higher;
- in winter crops -arrows grow on which tiny onions are then formed.
The best-selling varieties of winter garlic are:
Lyubasha
 Winter garlic grade Lyubasha
Winter garlic grade Lyubasha
Withstands severe frosts and dry summers. It is considered quite high - the stem is up to 120 cm. The bulb is round, slightly flat. The color of the scales is light with streaks of violet tones, resistant to diseases. Keeps perfectly. It has a bright spicy taste and is suitable for canning.
Dobrynya
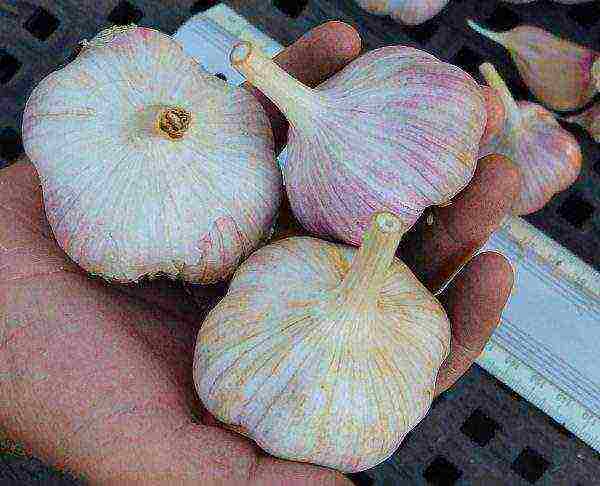 Winter garlic variety Dobrynya
Winter garlic variety Dobrynya
A productive variety, but less frost-resistant than Lyubasha. The heads are large, not too sharp, so it is good to eat it fresh. Ripening period - late. Dobrynya is well kept and is not susceptible to disease.
Sofievsky
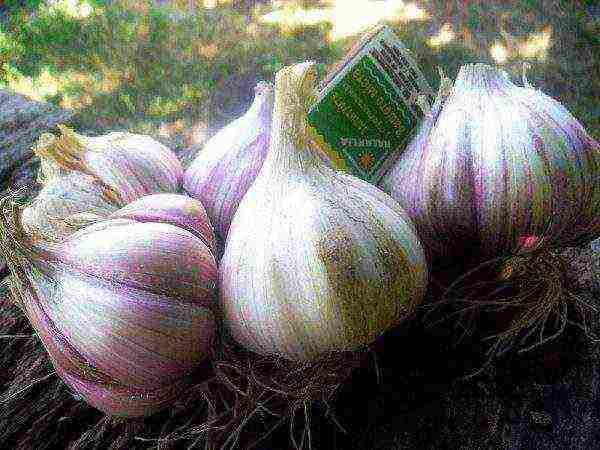 Winter garlic Sofievsky grade
Winter garlic Sofievsky grade
It perfectly tolerates severe frosts, but in summer it is picky about heat and light. Not too high - about 70 cm. Large onion - 100 g with large cloves. The color of the scales is pale purple. Nematode resistant, moderately pungent taste.
Alcor
 Winter garlic grade Alkor
Winter garlic grade Alkor
High-yielding, excellent storage. The color of the bulb is pinkish, and the cloves themselves are closer to gray. Damaged by yellow dwarfism.
Dubkovsky
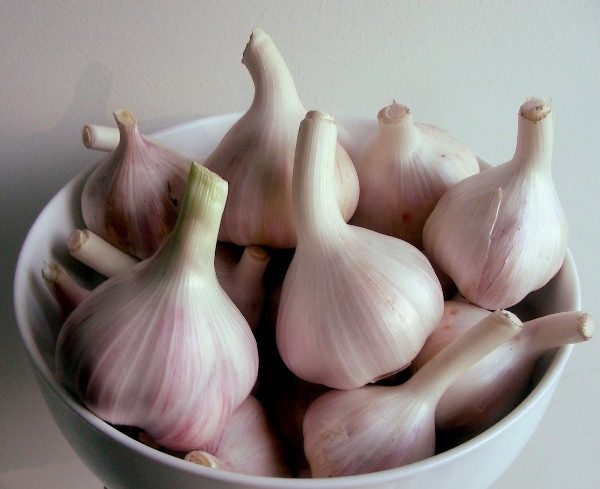 Winter garlic variety Dubkovsky
Winter garlic variety Dubkovsky
High yielding, good storage performance. The stem is of medium height, the bulb is not large, rarely weighs more than 50 grams. It is stored excellently, the taste is spicy.
In winter crops, it is imperative to cut off the arrows at the base, otherwise the head will be shallow. Do not break the arrows so as not to damage the bulb.
Shooters
Garlic that produces arrows is sharper in taste, more productive than varieties without arrows, it is better stored. Among the shooters, the most noticeable are:
Gribovsky jubilee
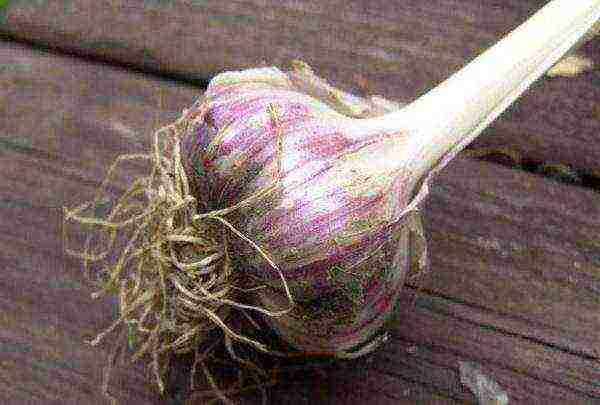 Shooting garlic variety Gribovsky jubilee
Shooting garlic variety Gribovsky jubilee
Medium-sized winter variety. The color of the scales is reddish-purple. Disease resistance - at a high level, stored well.
Gribovsky 60
 Shooting garlic grade Gribovsky 60
Shooting garlic grade Gribovsky 60
Harvest early ripening, resistant to freezing and drought. The bulb is medium in size and keeps well. Not damaged by bacteria and viruses.
Scythian
 Shooting garlic grade Skif
Shooting garlic grade Skif
Frost-resistant variety, resistant to diseases of this plant. The color of the scales is gray with streaks of purple, and the teeth themselves are creamy.
Large-toothed Kiseleva
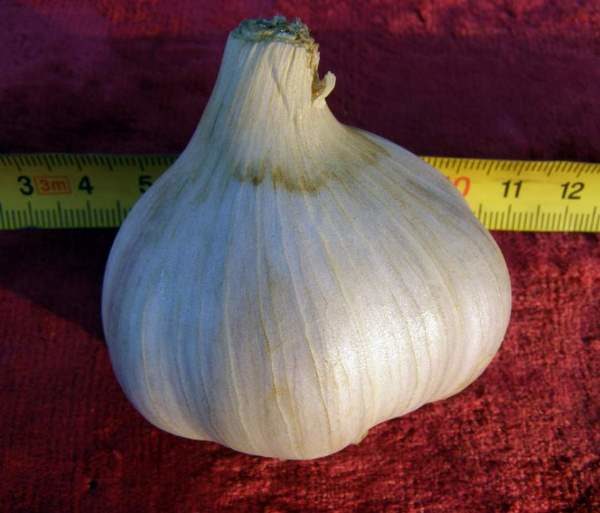 Shooting garlic grade Skif
Shooting garlic grade Skif
Early ripening, the head is more than average, about 80 g, the taste is pleasant, spicy. It is not susceptible to disease, shelf life is long.
Hermann
 Garlic variety Herman
Garlic variety Herman
The bulb is round, conical, the color of the scales is whitish-lilac, and the cloves are cream. Stored up to 8 months, resistant to fungal and bacterial infections.
Non-arrow
Of the non-shooting, the following are popular:
Aleisky
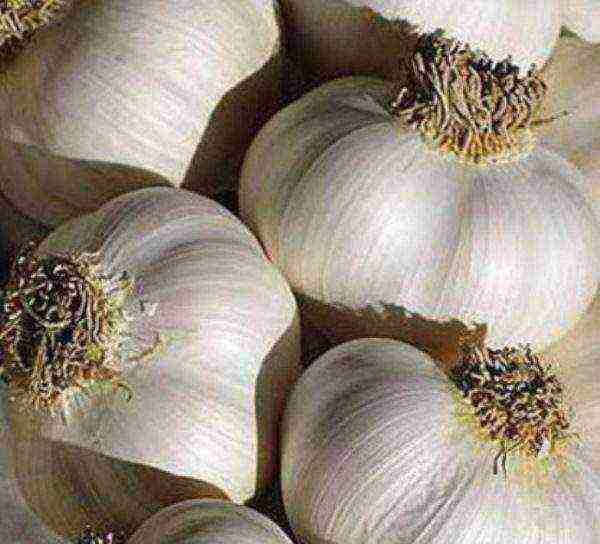 Aleisky garlic variety
Aleisky garlic variety
Mid-season, round bulb, flat, stored until spring.
Moskovsky
 Garlic variety Moscow
Garlic variety Moscow
Mid-season, well kept, not too sharp the color of the scales is light, the teeth are white.
Abrek
 Garlic variety Abrek
Garlic variety Abrek
Similar to Moscow, but the head is slightly larger.
Odessa 13
 Garlic variety Odessa 13
Garlic variety Odessa 13
It happens spring and winter, the color of the scales is white, sometimes with stripes of purple tones, stored wonderfully.
Gafurian
 Garlic variety Gafurian
Garlic variety Gafurian
Medium-sized onion up to 40 grams, round, flat. Resistant to rot, but sometimes it is prone to powdery mildew.
The best large varieties
Of the varieties with a large head, the following are known:
Alekseevsky (giant)
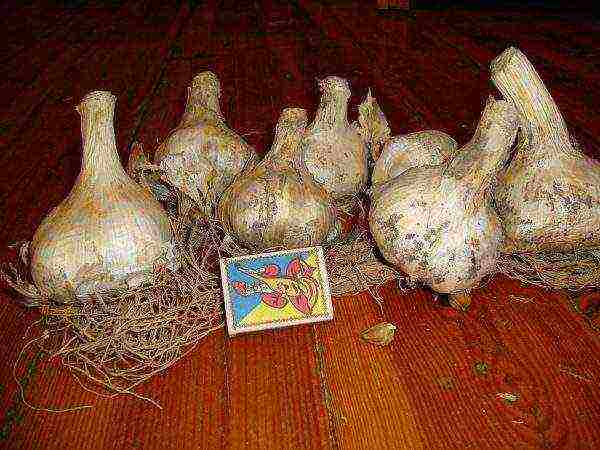 Garlic Alekseevsky (giant)
Garlic Alekseevsky (giant)
The bulb reaches 250 gr. Wherein resistant to diseases and stored for a long time.
Komsomolets
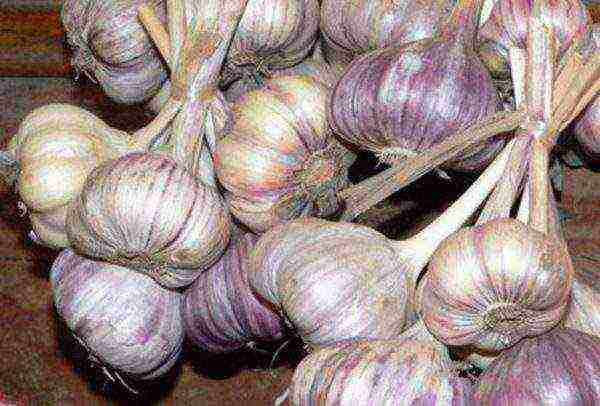 Garlic Komsomolets
Garlic Komsomolets
Shooting, winter, mid-season, flat-round onion, the taste is pungent.
Petrovsky
 Petrovsky garlic
Petrovsky garlic
Looks like Komsomolets, resistant to disease.
Degtyarsky
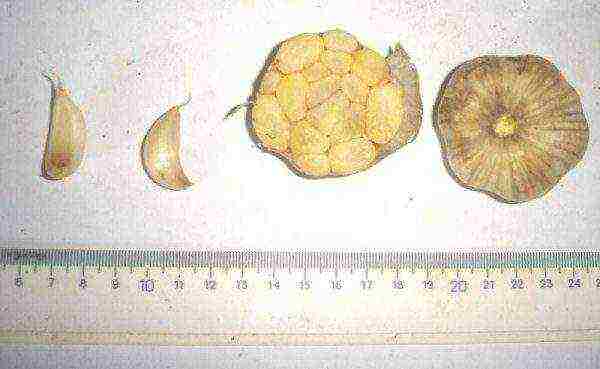 Degtyarsky garlic
Degtyarsky garlic
Spring, without arrows, the taste is moderately spicy.
Orlovsky
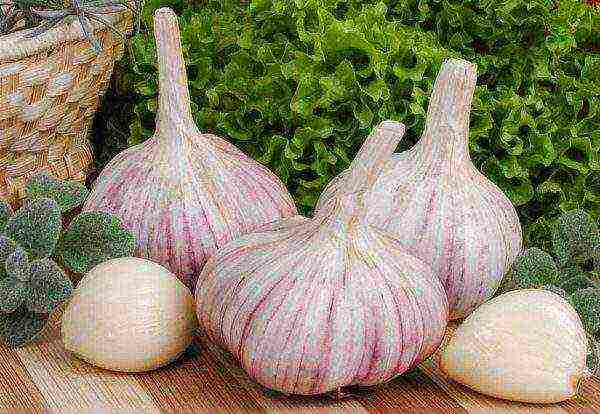 Garlic Orlovsky
Garlic Orlovsky
Spring, does not release arrows, onion over 100 gr.
Conclusion
These are not all varieties of garlic that are worthy of attention. AND do not be afraid to try new selection - there are many good varieties among them!
Foreword
Winter garlic is distinguished by unusually large heads and cloves. And if you also pick up a good variety, the harvest will surprise even experienced gardeners. In this article, we will tell you about the best varieties of winter garlic for different regions of Russia, including the Moscow region, and describe in detail what kind of care this crop needs.
What is the best garlic to plant for the winter?
In varieties of winter garlic, experts distinguish two groups - shooting garlic and non-shooting garlic. True, this division is very conditional, because in the northern regions, arrowhead varieties often stop producing arrows with inflorescences, and in the southern part of the country - on the contrary. It is difficult for breeders to go against nature - most of the winter varieties are still with arrows.
Many gardeners use this quality - depending on the selected variety, one plant can produce up to hundreds of seeds, which many call "bulbs". Having sown them before winter, in the next season you can collect a large number of one-toothed, and those, in turn, after a year, will give a good harvest of large garlic bulbs. Just a few arrows are enough to get enough planting material.

Of the shooters, gardeners often prefer varieties such as Krupnozubkovy Kiseleva, Gribovsky 80, Yubileiny, Dungansky local, as well as Otradnensky and Parus. Winter varieties of garlic without arrows are noticeably different from the previous version - although there are many cloves in the bulb, they grow medium-sized and at the same time of different sizes (see photo). Such teeth are arranged as if in a spiral and slightly "overlap" each other. Among those who do not shoot, such varieties of winter garlic as Lekar, Danilovsky local, Shirokolistny 220 and Novosibirsk are in demand.
Nowadays, in stores you can see not only domestic, but also crops imported from other countries. When buying, this should be taken into account, because many foreign farmers in a difficult climate add a large amount of fertilizing to the soil to get a good harvest. Garlic heads have the peculiarity of accumulating heavy metals that are very harmful to the human body, and therefore it is best to eat vegetables in which you are sure - that is, plant and grow the crop yourself.

The stems of this plant can reach a height of about one meter, but the roots are usually located at the level of 30-40 centimeters. It is interesting that when the bulb itself has already reached full maturity, the roots die off, and then new ones appear for the winter. It is also important to know that a shooting plant can simultaneously develop both sterile flowers, which are without seeds, and the very "bulbs". Winter garlic can be propagated with “bulbs” and chives, and non-shooting varieties can be propagated only with chives.
It is better to plant winter garlic only in those regions where it will definitely not freeze, but the spring garlic, which is called spring garlic, is better to plant in areas where the summer is warm, so that the culture has time to ripen in time.

It is the varieties with arrows that are more adapted for planting as winter crops, and those that do not shoot are more suitable for spring crops. By itself, both spring and winter garlic are quite picky about the presence of moisture, but at the same time they do not like strong waterlogging. However, soil too dry by the sun will not suit him. The roots of the bulbs begin to grow even at 1-2 degrees of heat, and the leaves - at 3-4.
Winter garlic - what to choose?
If you decide to plant a spring variety, then its bulbs will probably last after harvest until next fall. But winter varieties are much more difficult to maintain. True, they are more productive - with good care and watering, the heads can be the size of a fist! Such garlic should be planted for consumption in the first place, as well as for use in conservation.

Today it is quite difficult to find breeding varieties. Basically, they buy in Russia the local Bryansk variety, famous for its large garlic bulbs, Breitovsky spring. In the Moscow region, preference is often given to the Podmoskovny garlic variety - it is mid-season and at the same time resistant to various diseases. In fact, this culture does not adapt well enough to changing growing conditions.

Therefore, it is not advisable to plant that winter garlic that was grown in distant lands, even if it is just a handsome man in the photo. Better to buy varieties that are familiar to the local climate. When purchasing planting material, pay attention to the winter hardiness of winter garlic and the early maturity of spring varieties. A reliable choice for the Moscow region is the variety of the same name, in which the bulbs reach a weight of 60 grams, garlic has 5-7 cloves. The variety can yield up to 1.9 kilograms per square meter.
Interesting facts - how and where did garlic come to us?
Garlic itself can still be found in the wild. Historians claim that for the first time this culture began to be grown in Central Asia. It was from there that garlic was brought to Egypt, and then to Ancient Greece and Rome. Since then, it began to be planted and grown in different countries and used in the preparation of various dishes, as evidenced by the old recipes that have survived to this day.

Even in Tibetan monasteries they knew what winter garlic is. Japanese, Indian and Chinese doctors recommended it as a medicine. Nowadays, it is more often used as a spice, although garlic is still used in folk medicine as an effective remedy for many diseases. It was not in vain that they said that winter garlic can cure all diseases, but old age say wait. Many treatises have been written about the magical power of garlic as a means of giving strength and courage, some peoples even perceived it as an effective amulet against witchcraft, evil spirits, vampires - any evil spirits.

Earlier, winter garlic in the villages was also called snake grass and combed onions. Starting from the ninth century, this culture began to be planted in our area. At that time, the main territory for the successful cultivation of garlic was the lands of the Voronezh, Oryol, Tambov and Belgorod regions. We add that this plant, especially when it comes to young garlic, is very rich in vitamins and minerals. Ascorbic acid, sulfur, aluminum, copper, iodine, magnesium, essential oil - this is not a complete list of substances that can be found in cloves.
Rate the article:
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Winter garlic has a high yield and resistance to frost. But how not to get lost among the variety of varieties and choose the best one?
For a good harvest, it is important to be able to choose high-quality planting material suitable grade.
Winter garlic cloves should be:
- no dents;
- no rot;
- no cracks in the bottom;
- about the same size.
It is not worth peeling off the outer shell of the planting material, since in the future a head of garlic that has grown from a "stripped" clove will be poorly stored.
We invite you to get acquainted with the best, according to many summer residents, varieties of winter garlic.
Alcor
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are dense, rounded, pink-purple in color. Hardy, but affected by the yellow dwarf virus.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
4-5 |
13-36 |
good | ||
Belorussian
An early ripening shooter medium-yielding variety of winter garlic. Bulbs are dense, large, off-white scales with a purple tint. Winter hardy, slightly affected by bacterial rot.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
4-8 |
56-78 |
good | ||
Gribovsky jubilee
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are flat-rounded with a run up, purple scales, with dark purple veins. Winter-hardy, drought-resistant, disease-resistant.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
5-10 |
24-44 |
satisfactory | ||
Lyubasha
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are flat-rounded, the scales are white or pinkish with faint blue-violet veins. Winter-hardy and drought-resistant, resistant to fusarium.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
|
|
spicy |
5-7 |
80-120 |
good | |
Sail
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are large, flat-rounded with an upward slope, the scales are off-white with a purple tint. Winter hardy. Peronosporosis affects moderately, stem nematode and bacterial rot - weakly.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
7-10 |
30-47 |
good | ||
Podmoskovny
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are flat-round, white scales with brownish-purple strokes. Winter-hardy, disease-resistant.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
5-7 |
up to 60 |
good | ||
Sofievsky
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are large, flat-round, the scales are light purple in color. Frost-resistant, relatively resistant to nematodes.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
6-8 |
80-120 |
excellent | ||
Saved
Mid-season shooted high-yielding variety of winter garlic. The bulbs are round-oval, the scales are gray with a red tint, as well as with deep purple veins. Frost-resistant, resistant to fusarium and nematode.
| Use | Taste | Number of teeth | Bulb weight (g) | Keeping quality | |
| spicy |
7-10 |
60-100 |
excellent | ||
Only the right choice of variety and quality planting material will help you get a rich harvest of winter garlic.
How to grow large winter garlic? This question worries every gardener who wants to get a high-quality and high yield when planting a widespread and beloved product.
Grow as an annual crop
Garlic is a perennial crop that can grow in one place for several years. This constancy pleases, if not for one "but". The bulbs under such growing conditions will be small, and the size of the cloves will not please. To obtain a marketable harvest, you should know several subtleties of agricultural technology, an important component of which is the cultivation of garlic in an annual crop. How to grow large winter garlic?

Unlike spring garlic, winter garlic is more frost-hardy and is characterized by a high yield. It has large teeth, evenly spaced around the stem. The shelf life is an order of magnitude shorter than that of the spring, maximum until spring. Therefore, it is recommended to grow two types of garlic on the site: winter - for winter pickles and conservation and spring - for long-term consumption.
Location
An important factor in the quality growth of a garden crop and the production of large bulbs is a properly selected soil for winter garlic. For garlic, the most comfortable are sandy loam and loamy soils, without the close presence of groundwater. The area should be well lit, as in the shade the plant will grow weak and depleted.The best predecessors for such a culture are cabbage, cucumbers, pumpkin.
Requirements for planting material
How to determine when to plant winter garlic? Planting winter garlic is best done at the end of September-October, trying to be in time at least a couple of weeks before the onset of the first frost. During this time, the garden culture manages to take root, but does not grow. If the optimal planting dates for winter garlic are met, then we can safely hope for a high-quality harvest next year.
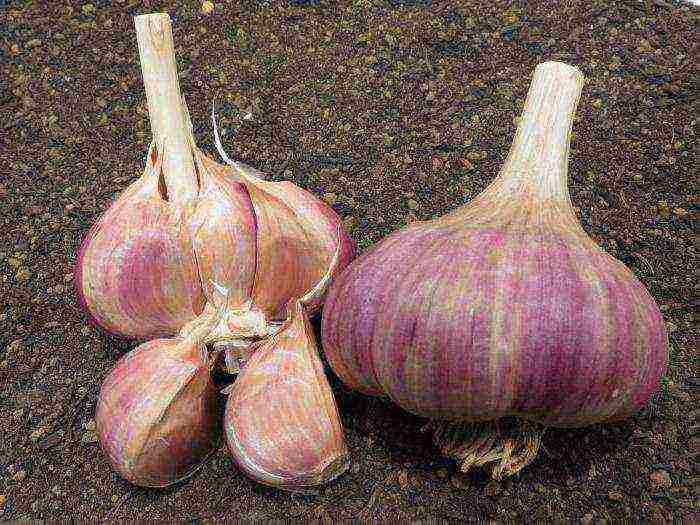

How to grow large winter garlic? You should know that the size of the bulbs of the future harvest directly depends on the state of the planting material. It should be beautiful large bulbs, no dents, rot, cracks, about the same size.
Planting winter garlic in the Moscow region is carried out according to the following algorithm: first, the bulbs should be disassembled into cloves, without peeling off the outer shell, since these manipulations will negatively affect the shelf life of the future harvest. Then land. With ordinary cloves, you can plant air bulbs collected from arrows in the summer. In the first year, whole heads will grow from them (like onions), and in a year - correct ones, consisting of several slices.
Site preparation
The key to obtaining a high-quality harvest will be the preparation of the site, which is recommended to start 1-1.5 weeks before the planting of winter garlic in the Moscow region.
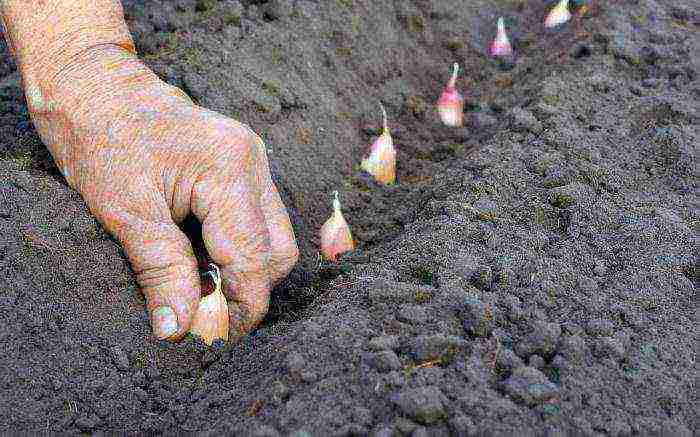

Therefore, care should be taken to fertilize the soil. Before planting winter garlic, the soil should be fed with 5-6 kg of humus, 10-12 g of ammonium nitrate, 30 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium salt per 1 sq. square meter. It is not recommended to apply fresh manure, which causes an increased concentration of nitrogen in the soil. The most comfortable temperature for growing winter garlic is + 18 ... + 25 ° C with its ability to withstand -40 ° C in winter.
Landing features
How to plant winter garlic? With the onset of the planting time, the prepared garlic cloves should be planted in rows, adhering to an interval of 10-12 cm. The distance between rows is 20-25 cm. The planting depth should be twice the height of the clove. With a shallow planting, there is a high probability of freezing of the plant, especially in cold, snowless winters. To avoid hampering root growth, the garlic cloves should not be pressed into the ground too much.

A bed for winter garlic after planting needs a little compaction and subsequent cover with a layer of mulch (leaves, peat, sawdust, humus), on top of which it is desirable to place spruce branches or straw. Such insulating materials trap snow, which is not only a shelter from frost, but also moisture, which is especially necessary in spring.
Growing conditions
Winter garlic does not require any over-maintenance. For high-quality growth, it is enough to carry out several basic activities in a timely manner: watering, weeding, loosening. If the soil is fertile, you can do without top dressing. With increased acidity, it is recommended to sprinkle the beds with ash.
While the plants are young and immature, the weeds can "clog" them, take away the necessary nutrition and light. Therefore, regular weeding is recommended. A little later, simple loosening with simultaneous removal of the grass will be enough, to which the garlic responds with good growth, since it does not like compacted soil.
Watering
Care should be taken with watering. With a lack of moisture, garlic leaves begin to turn yellow and dry ahead of time. With an excess of water, rot may appear, the taste of the cloves may deteriorate and become watery, which will negatively affect the shelf life of the product. Watering should be started when spring moisture has left the soil and completed a month before harvest. In the rest of the period - according to the weather and needs.The next day after watering, it is imperative to carry out loosening, which ensures full access of oxygen to the roots of the plant and preserves moisture. This operation can be dispensed with if the garlic is grown under mulch.
How to grow large winter garlic? As the flower arrows appear, they should be broken out. Several pieces can be left for seeds, as well as for a kind of "beacons" by which it will be possible to determine the beginning of the harvest. Although removing the arrowheads delays the aging of the garlic, it has a positive effect on bulb size. With the arrows left, the garlic heads will be small.
Diseases and pests
Winter garlic, the cultivation and care of which does not cause much trouble, is often affected by pests and diseases, the pathogens of which often persist in the soil. If sore heads are found during the cleaning process, you should start improving the soil.

The simplest method is to sow green manures (plants grown to suppress the growth of weeds and then embed in the soil in order to enrich it with nitrogen and improve the structure). Mustard, calendula, marigolds can be used as such plants.
Do not be late with cleaning dates
Ripe winter garlic, the cultivation and care of which directly affects the quality of the crop, should be removed and dried in a timely manner. When predicting autumn prolonged rains, it is recommended to dig up the garlic before they start. It is better to harvest the culture ahead of schedule than to overexpose in the garden. Otherwise, overripe heads will crumble, fall apart, and individual slices will not be able to be stored at all. They will only need to be recycled. With a quick rush to harvest, unripe garlic will quickly wither. It is better to harvest the heads selectively, using for preservation for the winter, leaving the bulk to ripen until the correct harvest time.
Ripening signs
How to determine the ripening of garlic? It is believed that yellowing of the leaves is a clear sign (from the top about a quarter of the length). But this assumption may turn out to be erroneous, since the green mass can turn yellow for other reasons: from insufficient nutrition, drought, disease, damage to the root system. You need to focus on the duration of the growing season, which is 100-110 days from the moment the young shoots appear.
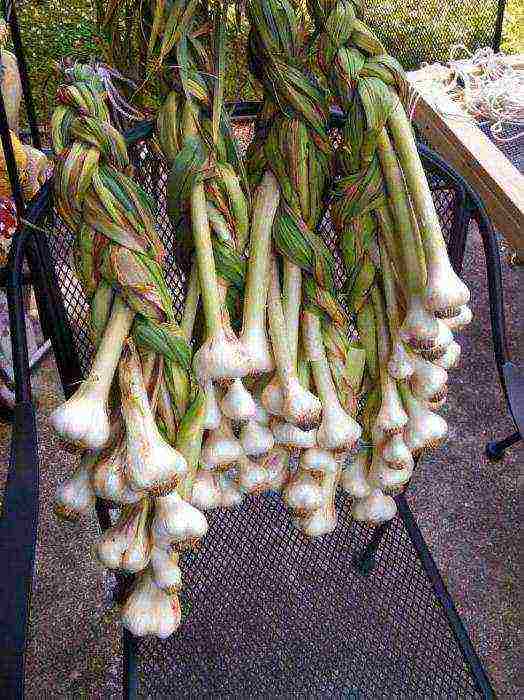

Also, the ripeness of garlic can be judged by its peduncles, "packed" in sheaths. A bursting shell will be a direct sign of the ripening of the garlic.
To correctly determine the timing of harvesting, which is an important fact for its long-term storage, these methods should be considered together.
Winter garlic. Varieties
The largest of them is Lyubasha. Other outstanding representatives of winter garlic are such varieties as Alkor, Parus, Belorussky, Gribovsky Jubilee. These are the best varieties of winter garlic.
- Alcor is a high-yielding, arrowhead variety characterized by dense, pink-purple, rounded bulbs. Frost resistant. The number of cloves in the bulb is 4-5, the average weight of the head is 13-36 g. It can become infected with the yellow dwarf virus, which is carried by several types of aphids. The affected plant is characterized by yellow curling arrows, compacted corrugated leaves with yellow stripes, the inflorescences cease their development, and the plant itself takes on a dwarf appearance.
- Belorussian. Arrowhead variety of early ripening, with dense large bulbs, dressed in off-white scales with a purple tint. Winter-hardy. The number of cloves is from 4 to 8. The average weight of a bulb is 56-78 g. Low susceptibility to bacterial rot, a disease that destroys most of the vegetable product during storage.The presence of the disease can be determined by the presence of brown sores scattered randomly over the surface of the cloves. Garlic cloves may also look frozen or cooked. The defeat occurs when grown on depleted soils, weakening by agrotechnical measures, insufficient maturation, incomplete drying, storage in improper conditions.
- Gribovsky jubilee. Arrowhead garlic with flat-round bulbs, purple scales and dark purple veins. It is characterized by high yields. Disease-, drought-, winter-hardy. The onion, the average weight of which is 24-44 g, contains from 5 to 10 cloves.
- Lyubasha. Extra large. The average weight of the fruit is 80-120 g with the number of cloves from 5 to 7. Arrows. It is characterized by flat-round bulbs. Veins are blue-violet. Weakly expressed. Easily tolerates wintering. Resistant to fusarium - a fungal disease that affects the plant during the growing season and storage. The main signs of the disease are yellowing and drying of the flower-bearing stem, the appearance of a pink coating in the axils of the leaves, decay and complete death of the roots.
- Sail. Arrowhead variety with high yields. The bulbs are flat-round, large, with heavy white scales. It is characterized by a pungent taste. Cloves from 7 to 10. Mass of garlic heads - 30-47 g. Average susceptibility to peronosporosis - a fungal disease, otherwise referred to as "downy mildew". The strongest lesions are observed in areas with a humid climate; the peak of lesions occurs in rainy years. The affected plant is stunted in growth, has a paler color of the aerial part, a change in the shape of the leaves and the appearance of pale green spots on them. The latter, when enlarged, become covered with a gray-violet bloom and cause the death of the plant.


