Content
- 1 Repaired varieties - what is it
- 2 Repairing raspberries - growing and care
- 3 Pruning
- 4 Spring pruning
- 5 How to cut remontant raspberries
- 6 Polka
- 7 Polyana variety
- 8 Raspberry Hercules
- 9 Shugana
- 10 Indian Summer-2
- 11 Bryansk marvel
- 12 Diamond - a new variety
- 13 Bryansk jubilee
- 14 Monomakh's hat
- 15 Eurasia
- 16 Golden domes
- 17 Morning dew
- 18 Kalashnik
- 19 Apricot
- 20 Gardeners reviews
- 21 Apricot
- 22 Indian summer
- 23 Bryansk jubilee
- 24 Hercules
- 25 Eurasia
- 26 Yellow giant
- 27 Golden domes
- 28 Polka
- 29 Ruby necklace
- 30 Elegant
- 31 How the remontant raspberry appeared
- 32 The best varieties
- 33 Planting remontant raspberries and preparatory procedures
- 34 Reproduction of culture
- 35 Plant care
- 36 Common diseases and methods of control
- 37 Gardeners reviews
- 38 1. "Apricot"
- 39 2. "Bryansk Jubilee"
- 40 3. "Hercules"
- 41 4. "Indian Summer"
- 42 5. "Yellow giant"
- 43 6. "Eurasia"
- 44 7. "Golden domes"
- 45 8. "Polka"
- 46 9. "Elegant"
- 47 10. "Ruby necklace"
Today we will tell you about a group of raspberry varieties that have a unique ability to bear fruit even on annual shoots. We will present you the best remontant varieties of raspberries. You will learn how to care for them, prune them, and increase their yield.
Repaired varieties - what is it
If you look at the English-language publications on gardening, then this name means "continuously fruitful", "fruitful in the fall", "autumn-fruitful". In our reference books of gardeners for such varieties, the collective name "remontantny" was fixed.
It comes from the French "repair", which means - to replenish, to repair. Gardeners in Europe, America and Russia admit that the best remontant raspberry has become an addition to the main assortment of fragrant berries.
Such varieties have been known for more than 200 years, but the older ones are distinguished by a small area of fruiting shoots in autumn. In the 18th - early 19th centuries, more than 20 varieties were described, and by the beginning of the 20th century, more than 60 of them were already known.
Repairing raspberries - growing and care
It is not difficult to care for raspberries of these varieties. Like all plants, it needs watering, loosening the soil, feeding and weed control. Seedlings of remontant raspberry love light and moisture. Their root system is located superficially, therefore, during the dry season, it needs regular watering. It should not be plentiful, since stagnant water can cause the death of small roots. The bush will not die, but it will take about ten days to restore the roots. At this time, the remontant raspberry will experience an acute nutritional deficiency. Growing and caring for it requires careful monitoring of moderate soil moisture.
When loosening the soil, try to be very careful not to damage the root system. From the center of the bush within a radius of a meter, the depth of loosening should not be more than 5 cm. To keep moisture in the upper layer longer, do not neglect mulching with peat or humus.
In the second or third year from the moment of planting, fertilizing with mineral fertilizers is required. At the beginning, immediately after planting, the remontant raspberry grows especially intensively. How to take care of her at this time? The plant should be "fed" with fertilizers containing nitrogen. In the middle of summer, it is necessary to use complex fertilizers containing phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium and trace elements.The gardener calculates the amount of fertilizer based on the instructions on the packages and the level of soil fertility on the site.
The best remontant varieties of raspberries in the middle zone of our country in early spring, after removing the snow, are covered with black film. Under such a "blanket" the sun's rays will warm up the soil much faster, therefore, the growing season will begin 2 weeks earlier than usual. Thanks to this, in the fall, the yield will increase by 500-600 g of berries from every 1 sq. meter of remontant raspberry.
Pruning
In Central Russia, annual shoots of remontant raspberries are cut at the very end of October. But don’t worry if you don’t have time to complete this work within the specified time frame, pruning can be done in early November. In the southern regions, it is held until the end of November.
You should not be in a hurry with this work. It can be performed even when the topsoil is frozen. It is possible to carry out this work after the first snow falls. All this time, valuable nutrients are actively supplied from the shoots to the roots. This provides the plant with intensive development in the next season.
Spring pruning
In some regions, pruning is carried over into early spring. What is the difference between pruning raspberries in spring? For the repaired variety, such pruning is necessary in areas with warm winters. In these areas, after the completion of fruiting, the plant still vegetates for a long time and accumulates nutrients. If, after you cut the raspberry bushes in the fall, the soil does not freeze for 4 weeks, bud germination on the rhizome is possible. This will reduce next year's harvest.
Pruning raspberries in the spring (remontant in this case) is effective for areas with little snowy winters and a harsh climate. Shoots that have finished fruiting will contribute to snow retention. When the buds begin to bloom in the spring, pruning will help the plant receive growth substances that are synthesized in young leaves. The plant really needs them for the spring awakening. This is especially true in the northern regions, where summers are short and common varieties do not have time to ripen.
How to prune remontant raspberries
In the fall, when the entire crop has already been harvested, two-year-old shoots that actively bore fruit in the summer are removed at the root. Overgrown bushes are freed from unnecessary branches. In spring, the upper part of the branches (10-15 cm) is cut from the bushes. This procedure is carried out only once a year, due to which the raspberry tree is renewed and gives an excellent harvest.
Many novice gardeners are interested in which varieties of remontant raspberries are best. We will present you with the most common varieties. Perhaps this will allow you to make the right choice.
Polka
The best varieties of remontant raspberries tend to have large berries and higher yields. For example, the Polka variety, bred in Poland. Today it is the most popular variety in Europe. The main fruiting is given by the shoots of the current year. The plant bears fruit from early August until frost.
Shoots grow up to 1.6 m. They are dense, do not sag under the weight of the crop and do not need additional support. Polka gives about 100 shoots per 1 running meter.
This is an excellent dessert variety that surpasses the Polyana variety in many ways. The berries are quite large, up to 10 g in weight, slightly elongated, dense, shiny, transportable, deep purple in color. They have a pleasant sour taste and a pronounced aroma. Productivity - more than four kilograms of berries from a bush.
Polyana variety
This is a standard remontant grade. He is originally from Poland. Fruiting from the second half of August until the first freezing temperatures, on annual shoots.
The bushes of this variety are powerful, undersized (do not exceed 120 cm). Shoots are erect, they do not need trellises. Shoots that appear in late spring can bear fruit in the same season. Berries of medium size, conical shape, shiny, firm, dessert taste, with a pronounced aroma.In late autumn, the taste deteriorates.
The yield reaches 6 kg per bush. This variety needs slightly acidic soils and good lighting. The first crop appears at the very end of June, the second at the beginning of August. Fruiting will continue until the onset of the first frost. In this case, the best remontant raspberries should be trimmed at ground level or completely mown.
Raspberry Hercules
This is a completely new large-fruited variety, characterized by upright, strong shoots. The first crop is harvested at the beginning of August. The bush is medium-sized, slightly spreading. Shoots of medium thickness, by autumn they turn purple, with a well-visible waxy bloom. The thorns are prickly and rigid, inclined downward, evenly distributed along the length of the branch. The plant has wrinkled, medium-sized, dark green leaves. The berries have an impressive size - up to 6 g, and have a sweet and sour taste. The yield of the variety is 2.5 kg from one bush.
Shugana
When gardeners discuss the best remontant varieties of raspberries, many of them call this one. The variety was bred in Switzerland. Differs in large berries of dessert taste and high yield. Bushes bear fruit from August to October, on the shoots of last year - from July. The yield of an adult plant can reach 9 kg per bush per season.
It is a strong, powerful plant. The bush does not require a garter. The berries are very large, shiny, bright red, conical in shape. On average, their weight is 10 g. After removing the berry from the bush, it remains in its original form for up to 4 days, without losing marketability.
Indian Summer-2
Another new standard remontant grade. It is successfully used in both industrial and home cultivation. It has strongly branching, upright, non-sticking shoots. The berries are not too large (3-3.5 g), pleasant taste, transportable. The variety is quite disease resistant. Differs in high yield (3 kg per bush). Most (80-85%) berries ripen in the first half of September. In the middle lane it gives 90% of the expected yield. Ripening begins in early August, strong shoots withstand the harvest well.
Bryansk miracle
A rapidly ripening remontant variety, with berries weighing 5-6 g. They have an elongated conical shape. They are characterized by excellent taste.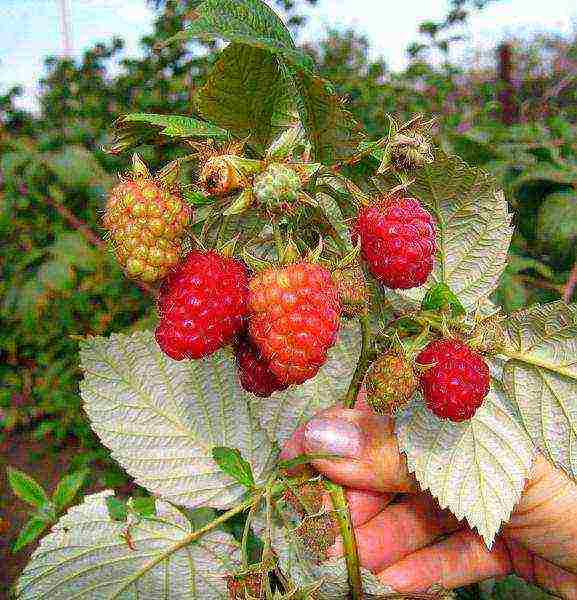
Fruits ripen in mid-August. Before the onset of the first frost, more than 70% of the fruits ripen. The berries do not fall or rot within 5 days. Surprisingly, the berries of this variety ripen, even if the branches have already been cut and placed in the water. This remontant variety is perfectly adapted to drought and heat. Productivity - 4.5 kg.
Diamond - a new variety
The best remontant varieties of raspberries, to which this new variety belongs, often require a garter. His bushes are very sprawling, low. They have 5-6 arched branching shoots.
The harvest begins in early August. Ripe berries remain on the bush for up to 7 days without decaying. Productivity - more than 2.5 kg. Berries of this variety are conical in shape, ruby color (up to 7.2 g). The surface is glossy, with a dessert flavor, but no aroma.
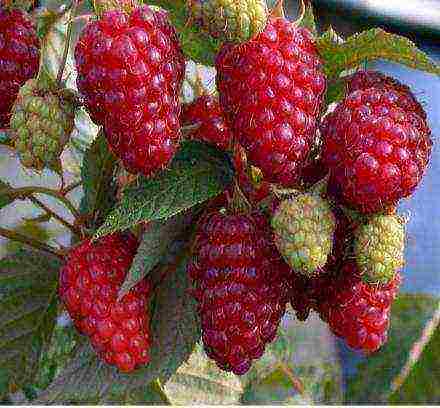

Bryansk jubilee
This plant grows up to 180 cm, slightly spreading bush. The berries are elongated, bright red, weighing up to 6 g. The taste is pleasant. Differs in high yield - 5 kg or more per bush. Begins to bear fruit from the end of July. On annual shoots, the berries ripen later.
Monomakh's hat
The bush looks like a small tree, up to 150 cm high. It has 3-4 powerful, highly branched, medium-drooping shoots. The thorns are mostly found at the bottom of the branch. The berries are large - the maximum weight is 10 g. Ripen in mid-August.
Eurasia
This variety is distinguished by large berries, early maturity. Ripening begins in early August. Berries do not rot on the branches for a long time. The yield exceeds 2.5 kg per bush. Raspberry Eurasia is resistant to pests and diseases.
Golden domes
Large-fruited remontant variety.The fruits have a characteristic golden apricot color of berries. The bush grows to a height of 150 cm. It is quite spreading, consisting of 5-6 drooping shoots. The berries ripen at the end of summer. The yield is more than two kilograms per bush. The fruits are large (6 g), with a rounded-conical shape. They are unusually colored - when overripe, the color changes to orange. The taste is sweet with a slightly acidic aftertaste.
Morning dew
A fairly "young" variety of remontant raspberries, bred in Poland. Young shoots grow up to 150 cm in height, tough, with thorns. The berries are large, golden yellow, bright, hard, tasty. The variety is poorly resistant to pests and diseases.
Kalashnik
Moscow remontant variety, which is used to get a rich autumn harvest. Kalashnik berries are dark red, blunt-conical, shiny, not very large (2-3 g). Sweet on the palate with a delicate "raspberry" aroma and extremely juicy pulp. They contain a small amount of seeds. Productivity is quite high - up to 3 kg per bush. Although, according to reviews of many gardeners, Kalashnik, with good care, can yield twice as much.
Ripens in early August. Between harvests, you can allow a break of 5-6 days, since the berries do not deteriorate on the bushes for a long time.
Kalashnik raspberry bushes grow up to 2.0 m in height. This is a powerful and spreading plant formed by 10-12 replacement shoots and 10 root suckers, which grow very quickly over the site. The shoots are thick, firm and firm. They are flowing, the upper part is fruiting, covered with a wax coating. The spikes are evenly spaced along the entire length. During the dormant period, they are colored brown.
Apricot
Great variety. During the ripening period, the bush is strewn with bright, large, orange with a golden tint, sweet berries (3.5 g). The plant is slightly spreading, about 150 cm high, shoots are slightly spiny. Its yield is more than 2 kg per bush.
Gardeners reviews
Many gardeners in our country are not very well known for remontant raspberries. The reviews of those who already have such a plant on their site are enthusiastic. Many people note the ease of caring for him. The high yield of such varieties and the size of the berries are striking.
Repaired raspberry varieties are gradually gaining popularity among domestic gardeners. They are distinguished by unpretentiousness, high productivity and resistance to diseases. We have selected varieties that have held the title of the best of the best for several years.
One of the most popular garden berries is raspberry. In the CIS, preference is still given to traditional varieties, although, for example, in Europe, Canada and the United States, up to 90% of plantings are remontant varieties. Their main difference is that they begin to bear fruit in the first year and allow you to harvest a bountiful harvest twice a season - in summer and autumn. Since most of the remontant raspberries come from warmer countries, in the middle lane, before the onset of cold weather, the berry simply does not have time to fully ripen. Recently, however, Russian breeders have bred varieties with a short growing season specifically for the northern regions. We managed to select the best varieties of both foreign and local origin.
Apricot
This is one of the most exotic varieties of raspberries. Although the bushes grow small, they nevertheless need a garter. The berries ripen on them are medium-sized and neat, yellow in color with a pinkish tinge, they are easily separated from the fruit. The shape of the raspberry is blunt-conical, the taste of the berries is reminiscent of apricot. The plant is practically resistant to diseases and pests. Connoisseurs especially recommend making jam of bright amber color from this raspberry.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2,5-3,5 |
3-4 |
1,3-1,5 |
Early August - late October |
||
Indian summer
This is the first remontant raspberry variety bred in Russia. Designed for cultivation in the southern and central regions.The bush is sprawling, rather tall and erect. Berries of medium size, round-conical or spherical in shape. With the onset of ripeness, they acquire a dark crimson color. The taste is sweet and sour, but without a pronounced aroma. The pulp is tender and juicy, no frills. The variety is distinguished by winter hardiness, sometimes the plant is attacked by spider mites, powdery mildew disease and purple spot.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
1-2 |
3-4 |
1,8-2 |
Early June - early July. Early September - mid October |
||
Bryansk jubilee
A repaired early fruiting variety. The bushes are compact, with weak branching. The berries are not very large, beautifully elongated, bright red, sweet and sour. Under suitable conditions, fruiting begins in late July and then resumes in the fall. Productivity and, importantly, crop safety are at a high level. Disease resistance is average, the plant requires regular care, timely watering and feeding.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2-3 |
3-4 |
1,2-1,4 |
Mid July - mid September |
||
Hercules
"Bryansk Bogatyr" is perfectly adapted to the climatic conditions of the middle zone. This variety is suitable for both domestic and industrial cultivation. The second wave of fruiting occurs closer to autumn, when the pests are no longer so active. Berries of intense ruby color with dense juicy pulp are similar to a truncated cone. Their taste is pleasant, sweet and sour. The variety is resistant to most fungal diseases, including gray mold. For the winter, it is advisable to cover the bush so that it does not freeze.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2,5-3,5 |
5-7 |
1,5-2 |
Mid June. Mid August - early October |
||
Eurasia
A large-fruited variety, belongs to the standard varieties and at the same time is absolutely not picky about the composition of the soil and climate. An upright bush reaches a height of 1.5-1.6 m, so it is very convenient to pick berries from it. They are dark ruby in color, conical in shape, can be stored for a long time without loss of marketability. Raspberries taste sweet, but not sugary, but with a slight sourness and traditional raspberry aroma. The plant is quite resistant to all sorts of misfortunes, including temperature changes and pest activity.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2-3 |
3,5-4,5 |
1,5-1,6 |
August - mid September |
||
Yellow giant
This type of raspberry is sometimes called the best variety for the middle lane. The bush has decorative properties, blooms very beautifully and bears fruit, so this raspberry in itself is a decoration of the garden. Neat yellow berries are useful for people with weakened immunity, allergy sufferers and pregnant women. They do not crumble from the bush for a long time and are perfectly stored. The plant has high frost resistance and is practically not afraid of various diseases.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
4-6 |
5-8 |
1,7-2 |
Mid July - mid October |
||
Golden domes
High-yielding variety of Russian selection. The bush is medium-sized, spreading, consists of 5-6 drooping shoots with small thorns. The berries are rather large, round-conical in shape and bright yellow in color, which later changes to apricot. The pulp is juicy, sweetish dessert, with an almost imperceptible raspberry aroma. The plant is resistant to the vast majority of diseases and is almost not attacked by pests. For the winter, it is advisable to leave only the rhizome, removing the entire aerial part.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2-4 |
5-6 |
1,3-1,5 |
End of June - beginning of July. August - mid-October |
||
Polka
This is one of the most popular European varieties, the leader in yield among remontant raspberries.The bushes are practically devoid of thorns, so you can eat fresh raspberries without fear of scratching your hands. By the way, berries are the main advantage of this variety. They are beautiful, large, shaped like a thimble. The berries taste sweet, but not sugary; they are considered the standard of dessert taste. The plant is practically not susceptible to any type of disease. But what is contraindicated for bushes is heat and severe frost.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2-3,5 |
5-6 |
1,5-1,8 |
End of July - beginning of October |
||
Ruby necklace
A high-yielding, transportable variety that is also suitable for industrial production. The bush is medium-sized, slightly spreading, with a small number of shoots. The berries are elongated, regular cylindrical, bright ruby color with a delicate sweet and sour pulp. At the end of fruiting, it is best to cut the aboveground part to ground level to avoid freezing of the plant.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2-3 |
4-5 |
1,3-1,5 |
Mid August - mid October |
||
Elegant
This exquisite variety is appreciated by all lovers of a stable and abundant harvest. It is recommended for cultivation throughout Russia. A powerful bush is not prone to lodging, it grows no higher than human height. The berries are shiny, in the form of a wide obtuse cone, sometimes weighing up to 8 g. The taste is pleasant, the juicy pulp is sweet and sour. The plant practically does not get sick, the crop retains its presentation for a long time and is suitable for transportation over long distances.
| Appointment | Productivity (kg per bush) | Berry weight (g) | Bush height (m) | Maturation (period) | |
|
2,3-2,7 |
4-6 |
1,6-1,8 |
Early August - late September |
||
Repaired raspberry varieties are a real find for summer residents. These plants begin to bear fruit already in the first year, require minimal care, are slightly susceptible to diseases and pests, and at the same time yield up to 2 times a year. Try to plant at least one bush of remontant raspberries and you will not be disappointed.
Having first appeared in the public domain, remontant raspberries immediately became a real sensation. For a while, gardeners simply forgot about the "classic" varieties. But the experience of its cultivation quickly showed that not only solid advantages are inherent in such raspberries. And obtaining bountiful harvests is possible only with competent agricultural technology, because remontant varieties are much more demanding in care than ordinary ones. Therefore, you need to familiarize yourself with all the nuances in advance and be sure to choose the variety reasonably, taking into account not only the size and taste of the berries.
How the remontant raspberry appeared
The property of remontability inherent in some varieties of raspberries means the ability to continuous long-term fruiting. Common varieties yield in just 2-3 weeks, while remontant varieties bear fruit from the first days of August until the temperature drops below 0 ° C. If you do not carry out radical pruning, you can generally harvest two crops. Perhaps this is due to the fact that the fruits are tied not only on overwintered shoots, but also on annuals. In practice, it is often noted that the first summer berries are not particularly sweet and somewhat dry, and the second harvest in a temperate and more severe climate simply does not have time to ripen before frost.
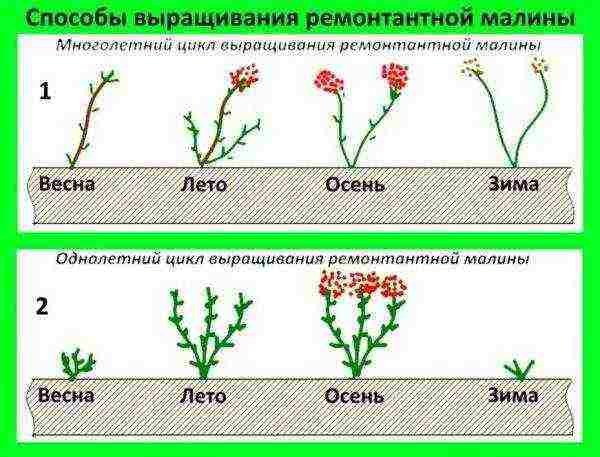
Under optimal conditions, remontant raspberries bring two harvests, but often gardeners donate the first, and there are objective reasons for this.
Video: one or two harvests of remontant raspberries
In Russia, gardeners got acquainted with remontant raspberries relatively recently, only 20-30 years ago. But in Europe and the USA, varieties with the corresponding characteristics have been known for more than two centuries. Botanists noticed that at the end of summer, flowers were blooming on individual shoots. There were such varieties in the south of Russia. The most famous breeder IV Michurin even created the Progress variety.When cultivated in a suitable climate, it produced a small crop on this year's branches in the first decade of September.
Serious work on the breeding of remontant varieties of raspberries in the USSR began relatively recently, in the 70s of the twentieth century. Professor I.V. Kazakov made a very significant contribution to it. The selection was carried out mainly in the Bryansk region. The first achievement was the Indian Summer variety. Currently, not only different varieties of red (common) raspberries are crossed. The emphasis is on interspecific hybridization with the participation of black raspberries, fragrant, hawthorn, wonderful, blackberries and princesses.
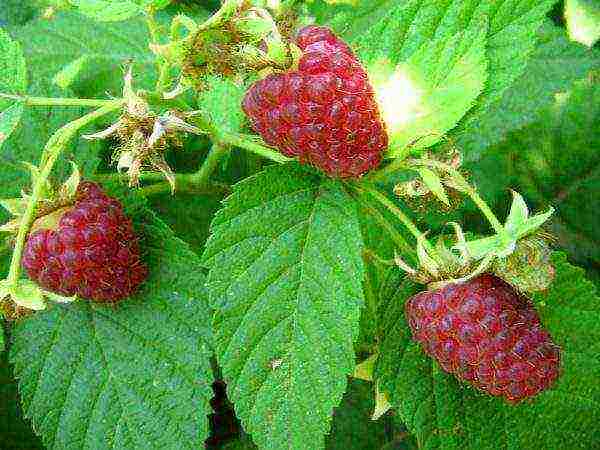

Raspberry Indian Summer - the first remontant variety created in the USSR
Modern varieties are self-fertile, they are characterized by the formation of fruit ovaries along the entire length, and not only at the tops of the shoots. Many people think that the taste and aroma of large (weighing 3–6 g) berries are more intense, but this is a purely subjective opinion. The yield during the season can reach 5-6 kg per bush. However, it is imperative to provide the plants with the heat they need and the level of illumination, plant them in fertile soil, regularly feed and water in accordance with the needs of the bush.
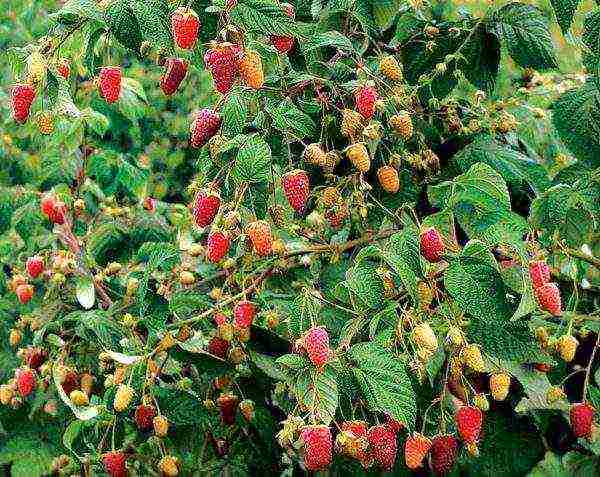

The remontant raspberry bushes are literally strewn with berries, it looks very impressive
Video: the appearance of remontant raspberries and their differences from conventional varieties
The best varieties
Varieties of remontant raspberries, created by both domestic and foreign breeders, are presented in nurseries and specialized stores in a fairly wide range. But when buying, you must immediately take into account that this culture manifests itself in the best way west of the Urals. In regions with a harsher, sharply continental climate, varieties of this category have few advantages over the usual ones. Objectively, perhaps, we can only name the presentability and taste of berries, no need to mess around with the formation of bushes, good frost resistance and higher immunity.
Apricot
Recommended for cultivation in the Central Region by the State Register. The bush is not particularly powerful, slightly spreading. Slightly drooping branches. Thorns are concentrated on the lower third of the shoots.
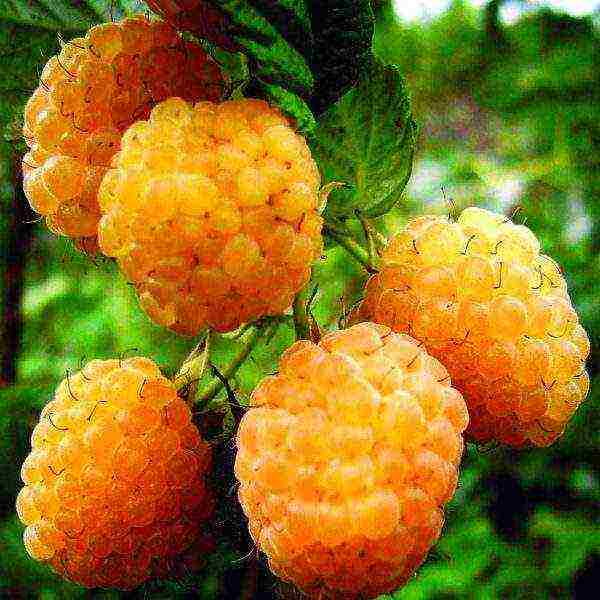

Raspberry Apricot has fairly compact bushes
The average weight of the berry is about 3 g. The pulp is tender, sweet, with a slightly perceptible sourness. The aroma is weak. The taste was rated 4.5 points (the maximum possible is five). Mass ripening of berries begins after August 15. Get about 3 kg from a bush.
Indian Summer 2
"Corrected and supplemented" version of the Indian Summer variety - the first remontant raspberry bred in the USSR. "Parent" is superior in immunity, large-fruited and the presence of a pronounced aroma. The state register is recommended for cultivation in the Central region. The bush grows up to 1.5 m, it is quite powerful, medium spreading. Shoots are straight, densely covered with sharp thorns from top to bottom. The roots do not freeze even in severe winters with little snow.

Raspberry Indian Summer 2 is valued for its high frost resistance of the root system
The average weight of the berry is 3.6 g, the length is 2–2.5 cm. The pulp is very tender and aromatic, sweet and sour, slightly tart. Its taste is not significantly affected by the weather during the summer. Even with heavy rainfall, it does not become watery. The seeds are small, almost invisible. Taste rating - 4 points. The harvest begins in the second decade of August. Each adult plant produces up to 3 kg of berries.
Hercules
One of the most favorite remontant varieties among gardeners from Russia and the former Soviet republics. It is grown not only for personal consumption, but also on an industrial scale. Officially recommended for landing in the Central Region. When cultivated in conditions of a lack of heat and light, the volume of the crop is sharply reduced, the berries become almost tasteless. The bush grows up to 1.5–2 m, slightly spreading. Shoots are straight, powerful.Hard spines of medium length cover them from top to bottom. Not bad, unlike most remontant varieties, it experiences a moisture deficit, as well as an abundance of precipitation.
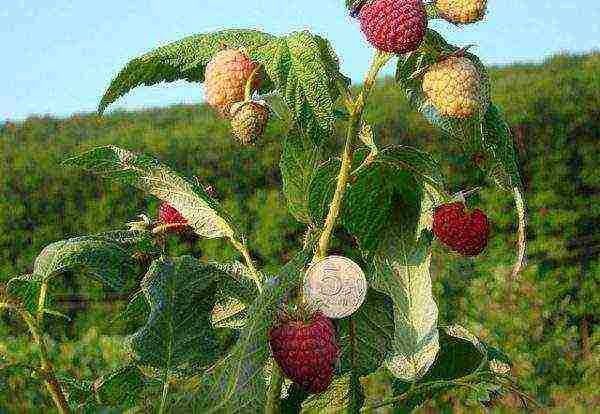

Raspberry Hercules tolerates a lack and excess of moisture better than most remontant varieties
The berries are extremely large (about 6.8 g, some specimens - 10–12 g each). Remove about 4.5 kg from the bush. Pulp of medium density, aromatic, with a refreshing sweet and sour taste. The latter has an assessment of 4 points. But the experience of gardeners shows that it is strongly influenced by the climate and the quality of the substrate. The berries are located mainly on the upper half of the shoot, but are well covered with leaves. This helps to protect the crop from birds.
If, before the first frost, Hercules raspberries do not have time to ripen, the branches with the fruits are cut off and placed in water. They will mature at home.
Eurasia
Has no restrictions on the region of cultivation. Bush 1.3-1.6 m high, standard (looks more like a low tree). Shoots are straight, powerful. Thorns mainly cover the lower half of the branch, but there are also quite a few of them above. It tolerates drought quite well, but not heat. In comparison with other remontant varieties, it is more often attacked by diseases and pests.

Raspberry Eurasia, in comparison with other remontant varieties, has the worst immunity
The mass of the berry is about 3.6–4.6 g. The pulp is of medium density, completely without aroma, the taste is not bad, sweet and sour. The individual drupes are firmly linked. Tasting score - 3.9 points. The fruits are suitable for long distance transportation and mechanized harvesting. The harvest, which is not typical for remontant raspberries, ripens en masse. It is collected from the last decade of August to the 15th of September. Remove about 2.5 kg from the bush.
Golden domes
Included in the State Register for the Central Region. Frost resistance up to -22 ° С. The bush grows up to 1.3–1.5 m, rather actively forms basal growth and replacement shoots. The plant is medium spreading, the shoots are a little dull. Thin and not particularly rigid thorns are not too often located, but along the entire length of the branches.
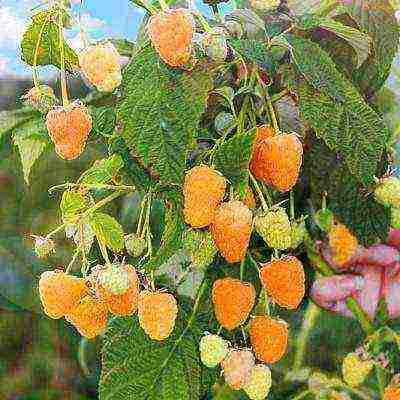

Raspberry Golden domes quite actively form root shoots
Ripe raspberries have a golden yellow skin, overripe ones have apricot-orange skin. Average weight - 3.8 g. The pulp is very tender, sweet, with a barely perceptible sourness. In comparison with other remontant varieties, it contains almost half the amount of vitamin C. An adult plant bears 2 kg of fruit or more.
As with any yellow raspberry, the Zolotye Kupola variety is characterized by an increased content of lycopene and beta-carotene. Also, such berries are much less likely to cause allergies. They can be included in the diet even for young children and pregnant women.
Polka
As the name suggests, the variety originated in Poland. He very quickly gained popularity not only in his homeland, but throughout Europe, where now it is the most common variety grown on an industrial scale. It is considered almost the standard of taste. The height of a medium-spreading bush is 1.5–1.8 m.
Differs in high cold resistance of the plant itself. Fruiting continues even when the temperature drops to -2 ° C. But the roots for the winter definitely need shelter. In general, this is the weak point of the bush, which is also prone to bacterial cancer, root rot. There are practically no thorns. Poorly tolerates heat above 35 ° C and direct sunlight.
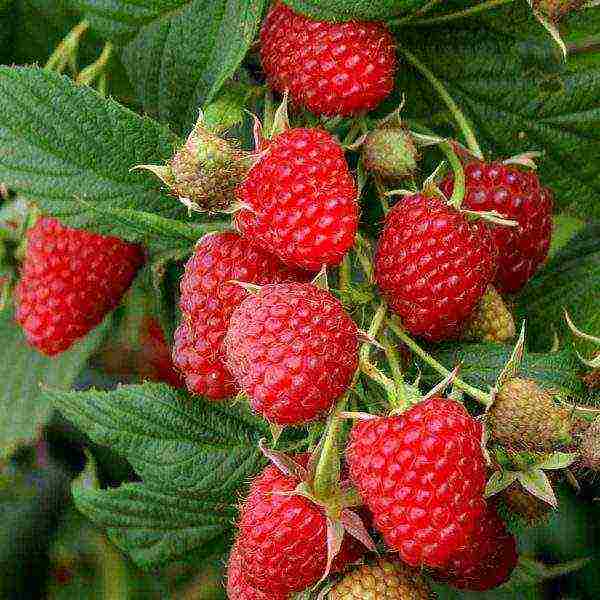

Raspberry Polka is valued for its presentability and excellent taste of berries, but the possibility of growing this variety in Russia is greatly limited by its frost resistance.
The berries are very presentable, weighing about 4.5 g. They are collected in bunches of 6–8 pieces, easily separated from the stalk, ripening, and do not fall off the bush. Drupes are small, firmly linked. The pulp is firm, but very juicy. The taste is appreciated to the maximum. Productivity - up to 4.5 kg per bush. In Russia, the first fruits ripen at the junction of July and August, they are removed until October.Berries tolerate transportation and freezing well.
Brilliant
It manifests itself in the best way in the Central region. The bush is medium-sized, but spreading. Its height does not exceed 1.5 m. Very little root growth is formed. Branches often bend under the weight of the harvest, you will need a trellis or other support. Thorns are not numerous, located at the base of the shoots. It tolerates heat well, drought worse. When planted in the shade, the yield drops sharply.
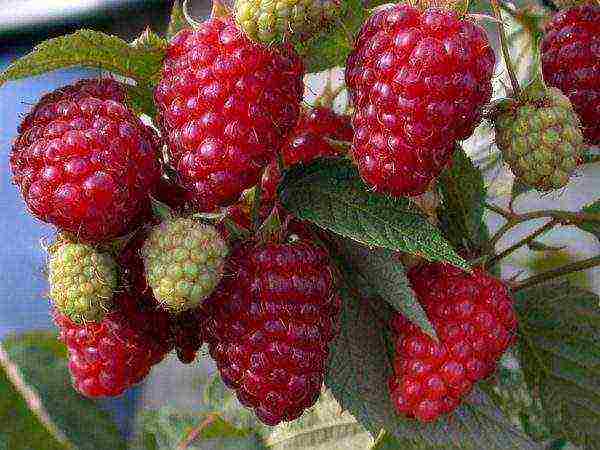

The harvest of Diamond Raspberries is highly dependent on how much sunlight and heat the bushes received.
The average weight of the fruit is 4.1 g. The seeds are large. The pulp is tender, sweet, with a slightly noticeable sourness. There is almost no aroma. The taste is rated at 4 points. The fruits are suitable for transportation. The average yield is 2.5–4 kg per bush.
Penguin
It bears fruit with one of the very first remontant varieties. The state register has not established any restrictions in the area of the cultivation region. The bush grows up to 1.2–1.5 m, standard. The thorns are soft, slightly curved, covering the branches along their entire length. Drought and heat does not tolerate well. He also does not like frost - if you do not cut off the shoots for the winter, they will freeze out above the snow level.

The sour taste of Penguin raspberries is due to the high vitamin C content
Berries weighing 4.2–6.5 g. The content of vitamin C is practically a record - 62 mg per 100 g. The pulp is of medium density, noticeably sour, odorless. The taste is rated at 3.7 points. But it improves significantly when cultivated in optimal conditions and with competent agricultural technology. Productivity - up to 3.5 kg per bush.
Raspberry bushes Penguin are often grown not only for the sake of fruiting. They are widely used for decorative purposes - they are neat, slow-growing, compact. The dark green leaves contrast effectively with the vibrant berries.
Ruby necklace
Approved for cultivation in any regions of the Russian Federation. The bush is not particularly sprawling, reaching 1.5 m in length. Slightly drooping branches. The thorns are not located too often, they dot the shoots along the entire length. He does not like heat and drought. Frost resistance up to -25 ° С.
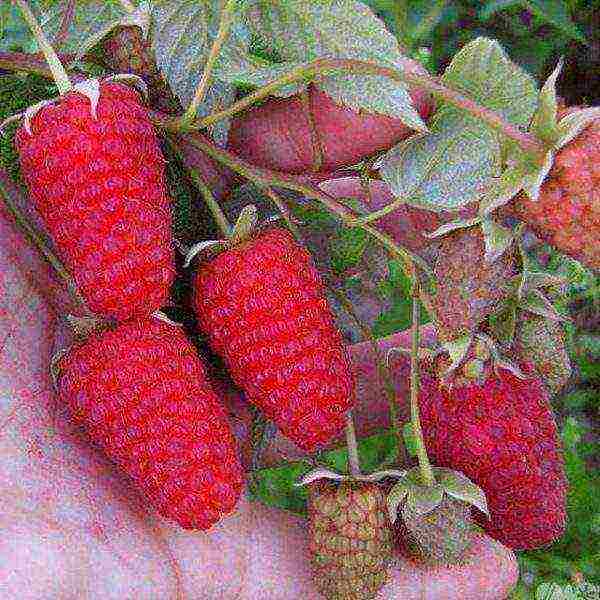

Raspberry Ruby necklace relatively poorly tolerates summer heat and drought, winter frosts
The average weight of the berry is 4.2–5.6 g, some specimens are up to 8 g. The pulp is tender, aromatic, sweet, with a pronounced sourness. The taste is estimated at 3.8 points. Productivity - 2.5 kg per bush or more.
Planting remontant raspberries and preparatory procedures
Repaired raspberries are very demanding on growing conditions. Therefore, the place for it is chosen so that the bushes necessarily receive enough heat and sunlight. It should be borne in mind that some varieties do not tolerate direct sunlight - the berries are "baked". The place must be protected from the wind - cold gusts and drafts disrupt the ripening process. You can, for example, plant raspberries along a wall, a fence, or create a "curtain" of tall plants (corn, sunflower).
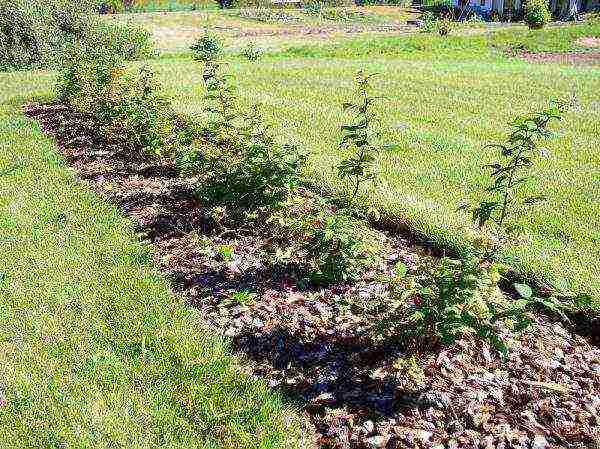

An open sunny area is selected for growing remontant raspberries.
The acid-base balance of the soil for remontant raspberries is only neutral. Dolomite flour, crushed eggshells to a powdery state, are added to the acidic soil during the preparation of the beds, peat crumbs and needles are added to the alkaline soil. The substrate needs light and loose, but nutritious. The best option is chernozem or loamy soil, gray soil. Disadvantages in the quality of a substrate can be slightly leveled by adding clay in the form of powder to the sandy soil, and sand to the clay and peat soil.
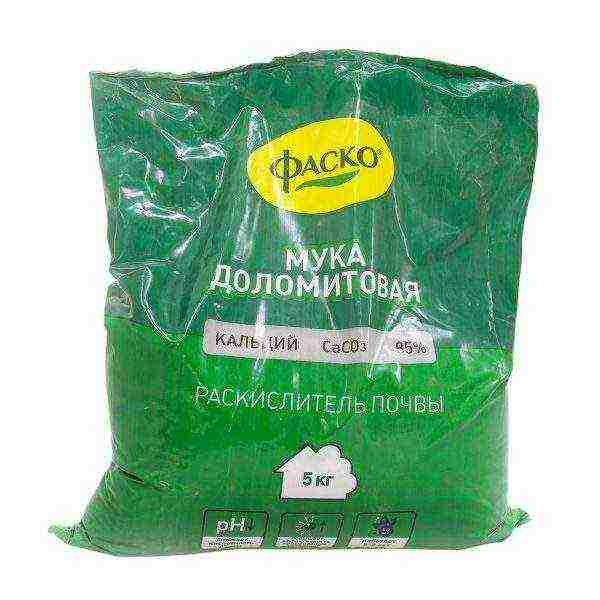

Dolomite flour is a natural soil deoxidizer that does not have side effects when the dosage is observed
The best precursors for remontant raspberries are any siderates (mustard, phacelia, vetch, lupine). The greens then at least 1.5 months before planting can be cut off and embedded in the soil, this is a natural nitrogen-containing fertilizer.Garden beds, where potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers, garden strawberries were grown before, are not suitable for the culture - they greatly impoverish the soil. The raspberry tree is transferred to a new place every 12-15 years.
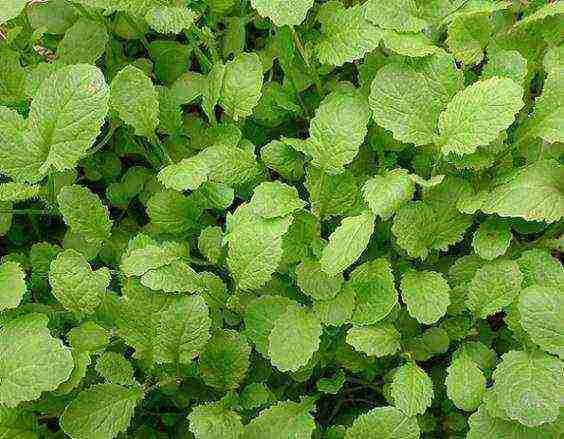

Green manure plants, including mustard leaves, improve the quality of the soil, saturate it with nitrogen
The repairing raspberry loves moisture, but does not tolerate stagnation of water at the roots in principle. If in the area where the construction of a bed is planned, groundwater approaches the surface closer than a meter, you will have to look for another place or build an embankment half a meter or more.
The quality of the seedling is the key to a bountiful harvest in the future. Healthy plants have a developed fibrous root system with a length of 20 cm and a main shoot with a thickness of at least 5 mm. Height - 20-25 cm, no more. Overgrown specimens are worse and less likely to take root in a new place. The wood under the bark is greenish. A reason to refuse a purchase is the presence of less than two buds on the trunk, suspicious lignified growths on the roots (this may be bacterial cancer), flaky bark, spots on it.
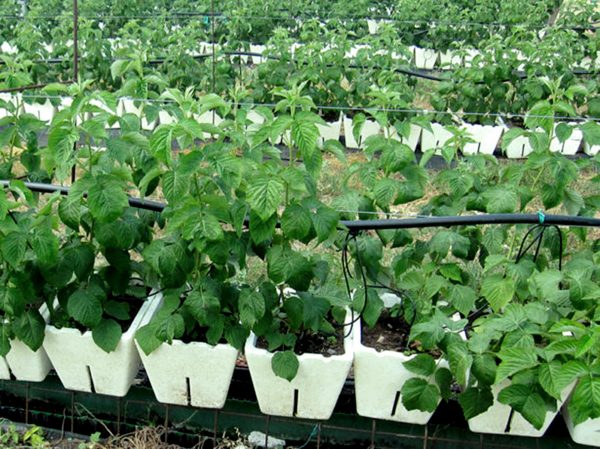

The purchased seedlings of remontant raspberries are carefully examined, if there is any doubt about their quality, it is better to refuse to purchase
Plants can be planted in late spring and autumn, but the most favorable period is the last decade of September or early October. Then the first ripe fruits can be tasted next summer. In areas with a subtropical climate, the procedure can be postponed even until the last days of October.
Bushes in most varieties are rather compact, not spreading, root shoots are reluctant to form. Therefore, when planting, 0.7–0.8 m are left between them with a row spacing of about a meter. Accordingly, if there are more than one seedlings, it is impractical to dig a separate hole for each one. Repaired raspberries are planted in trenches, maintaining the required interval. There are other methods - the so-called curtain (placement of seedlings in groups of 2-3 pieces with an interval of 0.5-0.7 m) and a triangle (the bushes are placed on its tops, the length of the side is 0.4-0.5 m).
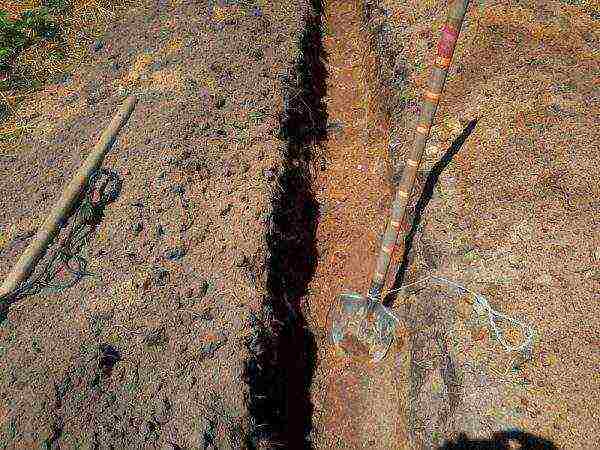

With the simultaneous planting of several bushes of remontant raspberries, it is more convenient to dig one common trench for them
The trench should be dug 3-4 weeks before disembarkation, or even in the fall if you still plan the procedure in the spring. Its depth is 40–45 cm. For each running meter, 10–12 liters of humus or rotted compost, 150–180 g of ordinary superphosphate and 100–120 g of potassium sulfate are added. Or replace individual mineral dressings with a complex product in which phosphorus and potassium are approximately twice as much as nitrogen (150 g). And for lovers of natural agriculture, sifted wood ash (3–3.5 cups) is suitable.
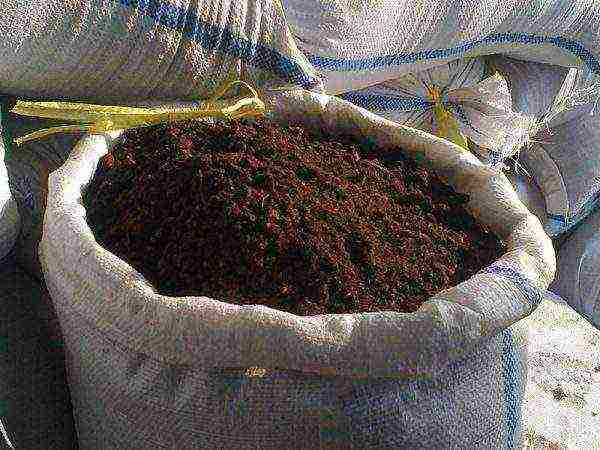

Humus is a natural remedy for increasing soil fertility
Directly planting remontant raspberries in a permanent place does not have any radical differences from the same event for any other shrubs. To make it easier for the seedlings to adapt to the new environment, about a day before planting, the roots are soaked in a solution of any biostimulant. Purchased preparations (Epin, Kornevin, potassium humate) and folk remedies (honey water, aloe juice, succinic acid) are also suitable. In the process, it is imperative to monitor the position of the root collar - it categorically cannot be buried in the ground, unless it is sandy. When properly seated, it is located a couple of centimeters above the ground. After planting, the seedlings are watered abundantly and the root area is covered with mulch. It will help to retain moisture in the soil and will greatly save the gardener time for weeding.

There is nothing difficult in planting remontant raspberry seedlings to a permanent place, even a novice gardener can cope with this task
Reproduction of culture
Most varieties of remontant raspberries are extremely reluctant to form root shoots. On the one hand, this is a plus, because the bushes do not "creep" over the site.But this feature seriously complicates the breeding procedure. Therefore, most often lignified cuttings are used for this purpose.
Planting material is harvested in the fall. When the leaves fall off, annual shoots at least 2-3 mm thick are cut into pieces 20-25 cm long. They can be planted immediately in the ground or allowed to overwinter in a basement or cellar.
In the first case, the cuttings are planted horizontally in humus or rotted compost to a depth of no more than 10 cm. The plantings are watered abundantly, tightened with breathable material (spunbond, lutrasil) and covered with peat chips (at least 8-12 cm in thickness). After the first heavy snowfalls, the garden bed is additionally covered with snow.
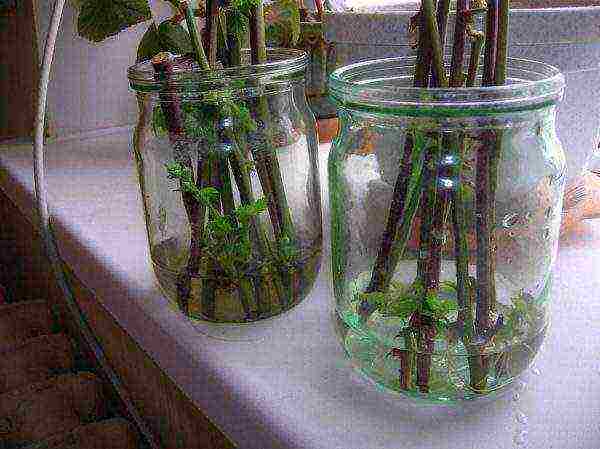

Soaking cuts on raspberry cuttings in a solution of any biostimulant accelerates the process of root formation
The second option is to "plant" raspberries in containers for the winter. The cuttings are wrapped with soft paper or cloth, placed in pots or boxes of suitable size and covered with wet peat or sand. At the beginning of spring, they are transferred to the house, the sections are updated and placed in a container with water, adding any biostimulant. Cover with a plastic bag on top. The water is changed daily. The roots grow in about a month, after another 3-4 weeks the plants can be planted immediately on a permanent place or in a greenhouse or greenhouse. In the latter case, they are transferred to open ground in mid-September.
Breeding with green cuttings is used to propagate especially rare and / or valuable varieties of remontant raspberries. Planting material is cut in late spring or early summer - these cuttings receive the most nutrients. They must have 2-3 sheets, the height - no more than 10-15 cm.

Reproduction of remontant raspberries by cuttings allows you to fully preserve varietal characteristics
The lower sections are dipped in a solution of indolylbutyric acid or Heteroauxin for 16-18 hours. Then the cuttings are planted at an angle of 45 ° with an interval of 10-15 cm in a greenhouse in a mixture of ordinary soil, peat and sand (2: 1: 1). The room maintains a humidity of at least 80% and a temperature of at least 22 ° C. Water is often watered as the topsoil dries up. They are transferred to open ground in the fall.
As practice shows, the bushes of remontant raspberries at the age of 4–5 years give most of the root growth. As soon as the “offspring” grow to 7–10 cm in height, they are buried in, carefully separate the roots from the mother plant with a sharp disinfected knife and transferred to a new place. In the first two weeks after transplanting, the bushes need daily watering. To protect them from direct sunlight, a canopy is erected above them from any white covering material.
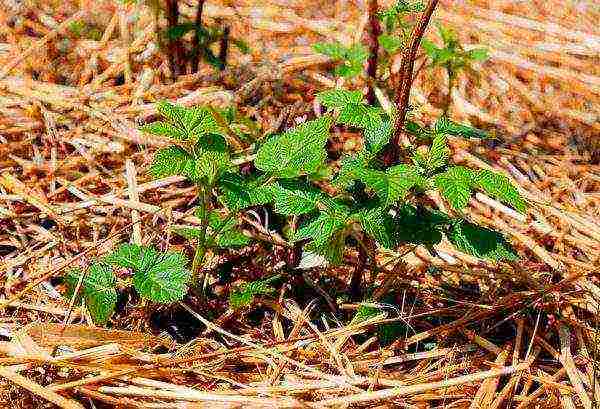

Most remontant raspberry varieties are not prone to root growth, but there are exceptions.
Can be used for propagation and pieces of roots 10-12 cm long and 2-3 mm thick. In autumn, they are planted to a depth of 6–8 cm. Seedlings appear next spring, and the seedlings are transferred to a permanent place in September. Another option is to germinate them at home.

When growing new bushes of remontant raspberries from pieces of roots at home, the shoots appear in about a month.
Video: ways to reproduce remontant raspberries
Plant care
Obtaining the crop volumes of remontant varieties of raspberries declared by breeders is real only with competent agricultural technology. The gardener takes much more time and effort for it than for caring for ordinary varieties of culture.
Repaired raspberry is a moisture-loving culture. The garden is watered at least once a week, in the heat - every two days or even every day. Most of all, the bushes need moisture during the active formation of the green mass, immediately before the opening of the buds and during the period of fruit ripening. In autumn, if it is warm and sparse for precipitation, it is imperative to carry out water-charging irrigation. It helps the roots to overwinter without harming themselves.
The soil must be saturated with moisture to a depth of at least 35–40 cm (approximately 20 l / m²). The best method is drip irrigation. If it is not technically possible to create such a system, it is watered along longitudinal furrows between rows. It is undesirable to pour water under the roots - they are located close enough to the surface, so they easily become bare, dry out. The water must be warmed up to a temperature of 22–25 ° С.
Drip irrigation is a system of rigid pipes and flexible hoses connected to a water tank located at a height of 1.5–2 m above ground level, which allows “targeted” water delivery to the root area of plants without eroding the soil. And if you additionally install a special pump with a timer, the process will generally go without the participation of the gardener. Water is supplied in the form of individual drops or thin streams. It depends on whether drippers or sprinklers are installed.
This method is very suitable for moisture-loving remontant raspberries, because not everyone has the opportunity to live in the garden area permanently. In addition to the undoubted benefits for plants, such a system saves time, energy and water (40–70%). It will last a very long time, the pressure in the pipes does not affect the efficiency of its work, even the weakest pressure is enough. Also, the relief of the site does not matter. The presence of a slope, ledges, and so on will not interfere with the organization of drip irrigation.
The flow of water to the roots of raspberry bushes contributes to the fact that the root system becomes more developed, more fibrous roots are formed. This, in turn, ensures better absorption of nutrients from the soil. The water flowing through the pipes has time to warm up to the optimum temperature. Too cold often provokes the development of root rot in raspberries. Drops do not fall on the leaves, so watering can be done at any time. Accordingly, after foliar dressings are carried out, nutrients are not washed off from them. And when growing raspberries in an open, sunny area, they can act as lenses that cause burns. These drops often contribute to the development of fungal diseases. Immunity in most varieties of remontant raspberries is very good, but it is still not worth the risk.
The experience of gardeners shows that when using this system, the yield of crops, including remontant raspberries, increases by 20–40% compared to sprinkling or conventional watering from a watering can, furrow and row-spacing irrigation. And the limited area of the wetted area effectively prevents the growth of weeds.

Drip irrigation is the optimal method for remontant raspberries, which allows you to evenly wet the substrate
Too zealous with watering is also not worth it. Many remontant varieties do not tolerate drought very well, but waterlogging, which causes root rot, is simply destructive for them.
Video: do-it-yourself drip irrigation system
Ripening large quantities of large berries requires increased amounts of nutrients. If everything necessary was brought into the ground during planting, this will be enough for two years. Top dressing is resumed in the third spring after the transfer of the seedling to the garden bed.
Repaired raspberries respond extremely well to natural organic fertilizers. As soon as the soil thaws enough, the soil in the garden bed is loosened shallowly, at the same time filling it with humus or compost (5–7 liters per linear meter). After about two weeks, loosening is repeated, this time applying any mineral fertilizers with a nitrogen content (12-15 g / m²).
During the active growing season, remontant raspberries are monthly fertilized with an infusion of nettle or dandelion leaves, chicken droppings, and cow dung. The consumption rate of the product is up to 5 l / m². It depends on the age of the bush. Ripening berries need potassium and phosphorus. Therefore, from mid-July, add a tablespoon of potassium sulfate and superphosphate to this top dressing.

Before use, the infusion of nettle is filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 8, and if the raw material was dung, its volume is doubled
You can alternate organic matter with complex fertilizers for berry bushes. Then there is no need for such an additive. At the end of fruiting, sifted wood ash is poured onto the roots.

Complex fertilizers for berry bushes contain all macro- and microelements necessary for plants
Video: tips for caring for remontant raspberries
When it comes to trimming, there are two ways. The easiest way is to shorten all the shoots to the state of three- or five-centimeter "stumps", but then the next season you will be left without an early harvest. The advantage of this method is not only in its simplicity, but also in the fact that, together with cut off shoots, pathogens, eggs laid by insects. To prepare remontant raspberries for wintering after such pruning, it is enough to cover the "hemp" with a layer of mulch 10-15 cm thick.

For most gardeners in the fall, after pruning, remontant raspberries look something like this
Another option is to leave 10–15 of the strongest and most developed shoots per 1 m² of this season, cut the remaining ones at the root. It should be remembered that not all varieties have the cold resistance required for a given region. While the roots most often tolerate soil freezing up to -25-30 ° С without any problems. The left shoots, if possible, are bent to the ground and fixed, they are thrown over with spruce branches or fallen leaves from above, covered with agril, lutrasil, spunbond. When the snow falls, a snowdrift is built over the bed. In the spring, the frozen branches are cut to a living bud, located above everything.
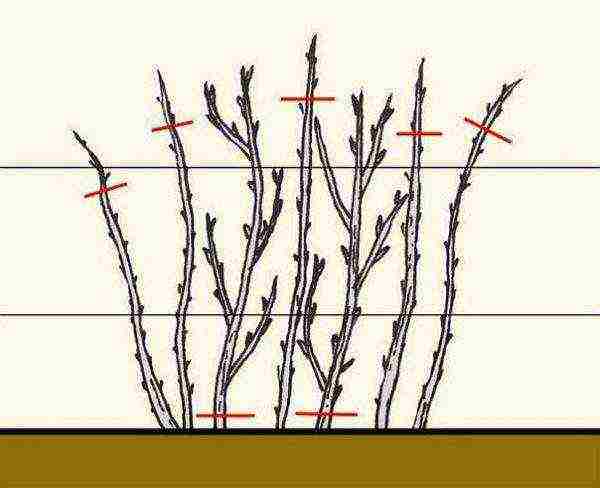
Gardeners who want to harvest remontant raspberries in June thin out the bush and prune the tops of the shoots left behind.
Video: methods of pruning a remontant raspberry bush
Common diseases and methods of control
Most modern varieties of remontant raspberries stand out for their very good resistance to diseases characteristic of the culture. They are much less likely to be attacked by insects en masse than ordinary varieties. Accordingly, simple preventive measures are often enough to protect the raspberry tree.
Fungi do not survive when treated with copper compounds. Consequently, with anthracnose, septoria, powdery mildew, rust, purple and ulcerative spots, all types of rot are fought with the help of fungicides. These can be both old proven effective agents (Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate), and the latest biofungicides (Strobi, Abiga-Peak, Bayleton, Fitosporin-M). Bushes and soil are cultivated by buds in the "green cone" stage, immediately after flowering and 12-15 days after the entire crop has been harvested.

If, after treatment with Bordeaux liquid, the shoots acquire a bluish tint for a couple of weeks, this is normal
The situation with viral (chlorosis, leaf curl, mycoplasmosis, dwarfism) and bacterial (root cancer) diseases is somewhat more complicated. Means for their treatment have not yet been developed. Most likely, they will not kill raspberry bushes, but the yield, as well as the quality of the fruit, will sharply decrease. The best prevention in this case is competent planting care. Plants, where most of the shoots are infected with infection, do not need to be regretted, they are uprooted and burned so that the diseases do not spread further. The soil is disinfected by spilling with a dense purple solution of potassium permanganate.
Of the pests, the most dangerous for remontant raspberries are leaf aphids, gall nematodes, strawberry-raspberry weevils, raspberry flies, and raspberry beetles. Many of them do not tolerate intense strong aromas. It is useful to plant spicy greens, flowers with a characteristic aroma (lavender, marigolds, calendula) next to the garden bed.Sticky tape for catching flies or home-made traps - containers filled with diluted sugar syrup, honey, jam - help well against flying insects. Sprinkle the soil in the garden with crushed chalk or ash. And the plants themselves are sprayed with infusion of onion or garlic arrows, tomato tops, citrus peels every 12-15 days.

Marigolds in the garden are not only beautiful, but also useful, their sharp aroma repels many pests
In those rare cases when infection cannot be avoided, folk remedies are used to control pests (a solution of baking soda or soda ash, colloidal sulfur, mustard powder, vinegar diluted with water or ammonia). A few treatments are sufficient when the problem is not discovered too late. When attacked by many individuals, raspberry bushes are sprayed with universal insecticides (Aktellik, Commander, Mospilan, Iskra-Bio, Admiral).
Gardeners reviews
With proper care and in a suitable climate, remontant raspberries, in fact, give a greater yield than ordinary ones, which bear fruit once a season. But here a lot depends on the gardener. There are enough varieties of culture by breeders so that everyone can find the one that is optimal for him. Agricultural technology mainly includes watering and fertilization, eliminating the need to form a bush.
Raspberries are found in almost any house or suburban area. Some of the difficulty in growing this crop is due to the peculiarities of our climate; mainly in cold winters. The advantage of remontant raspberries over ordinary varieties is obvious - it bears fruit in the same season, and twice. That is, in the year of planting seedlings. How to choose the best remontant raspberries?
You can get a variety of answers to this question. And this is understandable, since everyone has their own criteria for evaluating remontant raspberries - ripening terms, yield, fruit size, resistance to external factors. The list goes on and on - everyone has different preferences. But if you carefully study the materials posted on thematic sites, reviews on the forums, then it is easy to make a kind of rating of the popularity of varieties among our gardeners.
1. "Apricot"
This name was given to this variety not only because of the color of the berries, but also because of the peculiar taste.

The height of the bushes is small (up to 1.5 m), so their preparation for the cold season using any of the practiced methods is not difficult. Berries are medium in size (3.5 g each), and as they say, "calibrated" - one to one. From one bush of this variety, with proper care organization, you can collect about 3.5 ± 0.5 kg. One of the features of the culture is that the berries are very easily removed from the fruit, so almost everyone goes into business, they are not rejected. Connoisseurs of various homemade preparations believe that the most delicious jams are obtained from this type of remontant raspberry.
2. "Bryansk Jubilee"
It is recommended to pay attention to this variety for those gardeners who do not have much free land. The bushes of the Bryansk jubilee 1.3 m high are quite compact, moreover, they do not branch much. Consequently, the planting can be organized quite tightly even in a limited segment of the territory.
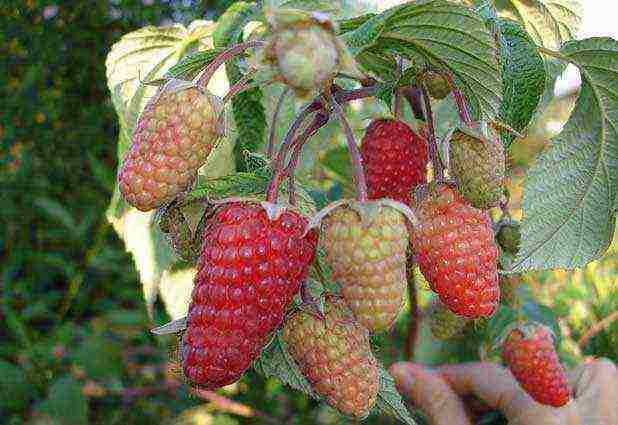

Sour-sweet, slightly elongated red berries are rather large - they weigh about 4 g. For the first time in a season they ripen by the middle of summer, and the second harvest (2.5 kg from each bush) is done at the end of September. The peculiarity of this remontant variety is its stable yield and good resistance to various infections and pests.
3. "Hercules"
For the middle lane - an excellent choice. Dense large berries (6 g each) are characterized by a sweet and sour taste and juicy pulp. Fruiting occurs in mid-summer and late autumn. Good yield - from 3 to 3.5 kg per bush, the height of which is no more than 2 m.
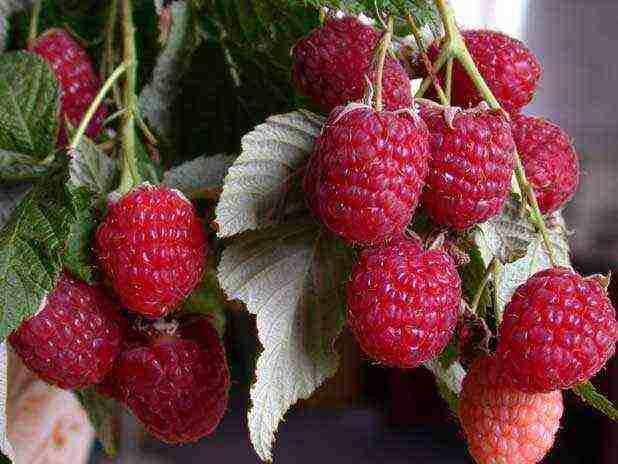

This type of remontant raspberry is distinguished by its increased resistance to diseases and pests.
4. "Indian Summer"
This raspberry is the first-born among the varieties bred in our country. Judging by the gardeners' reviews, she completely refutes the well-known saying about the first pancake.
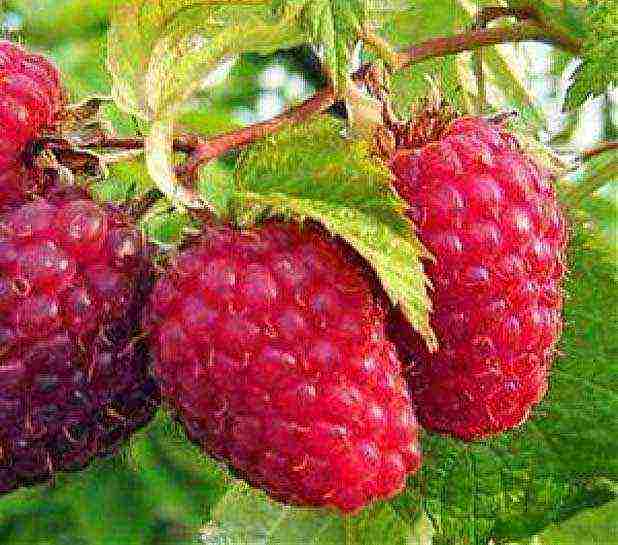

One of the distinctive features is the height of the bush (up to 2 m). Therefore, cultivation in regions with severe frosts is somewhat complicated by the need for complete shelter of the raspberry tree. Although all practiced technologies are quite available for do-it-yourself implementation. Anyone interested in this issue can learn more about it here.
The bushes are quite sprawling, therefore dense planting of seedlings is not recommended - they, growing, will only interfere with each other. But on the other hand, you can collect up to 2.5 kg from each. Moreover, the first harvest will be at the beginning of summer, since this variety belongs to the early ripening ones. The second collection is guaranteed at the end of September, long before the onset of cold weather. Ripe, darkish berries are also somewhat different in taste - they have a pleasant sourness, so the jam prepared from them turns out to be quite original.
5. "Yellow giant"
The berries of this type of remontant raspberry are highly recommended by specialists for allergy sufferers, immunodeficient women, pregnant women and young mothers. A distinctive feature is that the fruits, even when ripe, do not fall off, and after harvesting they remain for a long time without loss of taste.
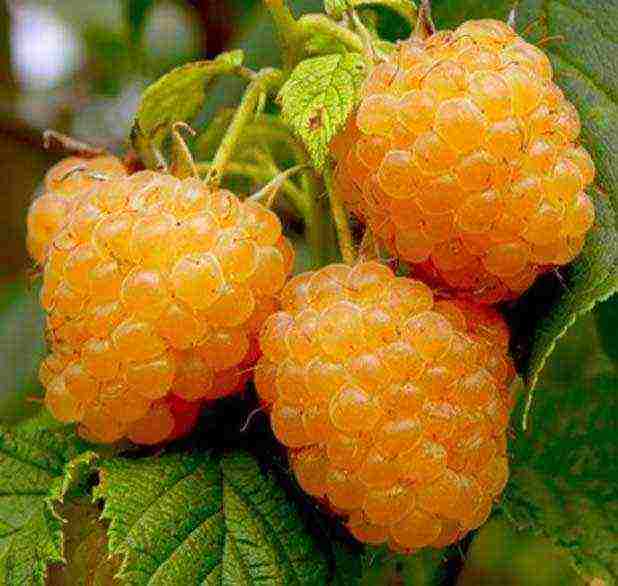

That is why this variety of raspberries is so popular among summer residents who visit the plots only on short visits. But with shelter for the winter, as well as for some other varieties of culture, there are difficulties - the bushes are quite high (up to 2.2 m). But this is leveled by their excellent yield (about 5 kg) and large fruit sizes (7.5 g each). And if you consider that such a raspberry tree in itself is a good decoration of the territory, it is more than advisable to cultivate this variety.
6. "Eurasia"
This variety belongs to the standard varieties, that is, it has a small trunk in the lower part. Consequently, the bush (no more than one and a half meters in height) turns out to be erect, and such raspberries can be planted even in a ventilated area, without additional fencing. In addition, it is quite convenient to pick berries from it. They are characterized by large size (4 - 4.5 g each), dark ruby hue and long-term fresh storage.
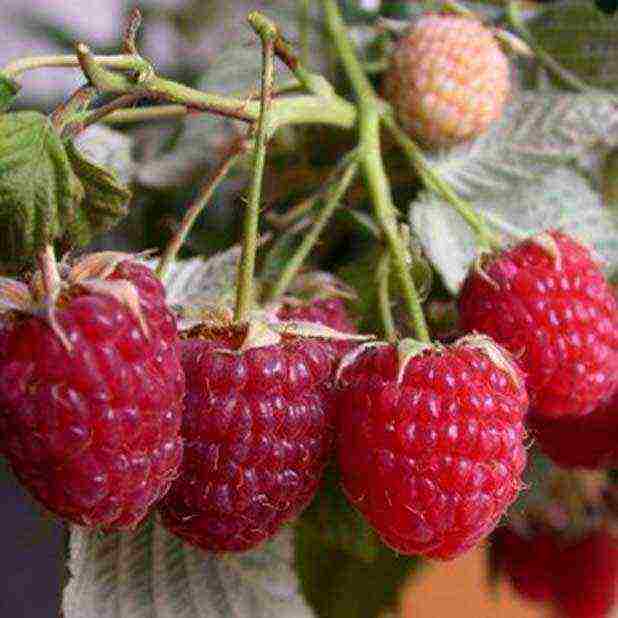

Raspberries of this particular variety are worth paying attention to for novice gardeners. The first reason is that it does not require special care, since it is absolutely inert to external factors (weather and pests). The second - "Eurasia" develops well on almost any soil, so you don't have to deal with increasing (lowering) its acidity, applying specific fertilizers, and so on. The yield of this remontant variety is not less than 3 kg per bush (an additional plus).
7. "Golden domes"
Another sort of remontant raspberry, bred by domestic breeders.

The bushes do not differ in height (no more than 1.3 m), but rather spreading. The yield is not bad - not less than 3.5 kg. Berries are medium in size (5 g each), with a juicy pulp of a sweetish taste (but not sugary). Feature - raspberries are practically not damaged by garden pests. It is noticed that they show no interest in this remontant variety. Consequently, preventive treatment work is kept to a minimum.
For the winter, it is recommended to cut the bushes completely, to ground level, since the stems do not tolerate low temperatures. Accordingly, the raspberry is covered with a "top". If the winter is snowy in the region, then one crust is enough. It turns out that in terms of preparation for cold weather, this variety has advantages over other remontant varieties.
8. "Polka"
The peculiarity of the variety is the almost complete absence of sharp thorns, which distinguishes this raspberry from other berry bushes. The fruits are quite large (up to 5.5 g), sweet, but in moderation.A number of experts consider this remontant variety to be the standard of taste.
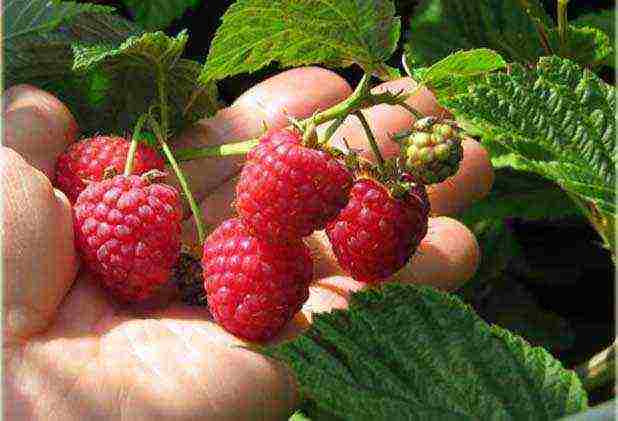

This raspberry is good for everyone, but it really does not like both high (heat) and low (frost) temperatures. In terms of resistance to various lesions, there are some advantages. Neither infections nor garden pests (with the rarest exceptions) are not terrible for this variety. Productivity - within 2.8 kg with bushes up to 1.6 m high. The berry picking periods are mid-summer and late September.
9. "Elegant"
Probably, this is the only one of all remontant varieties that develops equally well in any region.
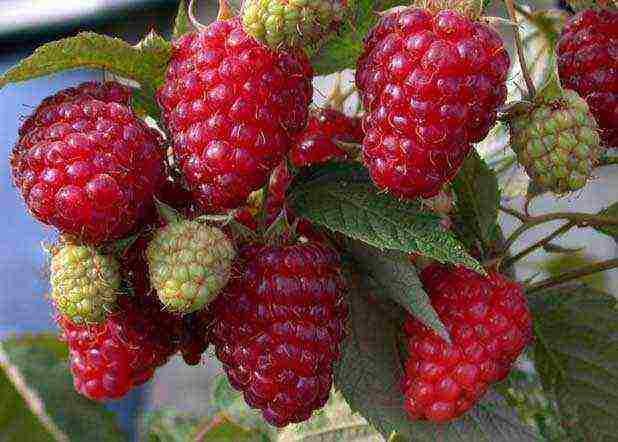

The raspberry grows up to 1.8 m, but the bushes are quite powerful, giving a stable, although not very high (up to 2.6 kg) yield. Medium-sized sweet and sour berries (4.5 - 5 g) are distinguished by good keeping quality, so there is no problem with their delivery over long distances. If we add that raspberries practically do not get sick and need minimal care - a good choice for growing in a garden.
10. "Ruby necklace"
Low bushes (up to 1.4 m) have a good yield (2.5 - 3 kg). The value from the point of view of specialists of this remontant variety is its good transportability. This raspberry can be transported over long distances without losing its presentation, so it is grown not only in summer cottages, but also on an industrial scale.

The berries are quite large (4.5 - 5 g each), with a slight sourness. The first collection is made from the beginning of August, the second - in the middle of October. It does not tolerate frost well, so pruning is done to ground level, and the root system of this remontant raspberry is completely covered.
Well, on which grade to choose, it's up to you, the reader, to decide. The main thing is to determine the priority characteristics, properties of remontant raspberries, depending on the region and personal preferences.


