Content
- 1 Creeping (ground cover) stonecrops
- 2 Tall (shrub) stonecrop
- 3 Unpretentious types of stonecrops
- 4 Rare sedum species
- 5 Heat-loving sedum for growing in containers
- 6 Botanical description
- 7 Types, description, photo
- 8 Rules for planting and care in the open field
- 9 Location selection
- 10 Sedum in indoor floriculture
- 11 Reproduction
- 12 Is sedum useful for humans? What is its use?
- 13 Brief description of ground cover plant
- 14 Variety of sedum types
- 15 What are sedums?
- 16 Conclusion
If you love stonecrops, or sedums, as well as we do, take advantage of our detailed classification of varieties of this plant with photos and descriptions of 47 species.
Sedums, or sedums, are beautiful plants with a rich "pedigree". Among their species there are ground cover and tall bushes; both pale green and bright pink; both unpretentious and capricious. In short, there is a plant for every garden!
Creeping (ground cover) stonecrops
Creeping stonecrops are often also called lodging stonecrops - all thanks to the spreading stems. The height of this type of bushes ranges from 15 to 30 cm.
Shoots of creeping stonecrops easily root, due to which the plants quickly form a thick carpet. Therefore, they like to use them for landscaping roofs and walls, creating frame topiary. Sedum of this group are regulars of rockeries and alpine slides. If desired, they can also be grown in containers (in this case, they grow as ampelous plants).
Many of the groundcover sedums are evergreens, but not all of them tolerate mid-zone winters well.
|
Sedum anakampseros (Sedum anacampseros) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium anacampseros). Forms a curtain with creeping stems that root easily. Leaves are bluish-gray. Peduncles 15-20 cm high. Flowers 0.7 cm in diameter change color from smoky pink to purple. Blooms in July-August. Grows poorly on alkaline soils. |
|
|
Sedum cornflower blue (Sedum cyaneum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium cyaneum). Forms loose sods 8-10 cm high. Leaves are bluish-gray with red dots. The flowers are purple-pink, 0.5 cm in diameter. Blooms in August-September. Requires good lighting, moist, well-drained soil. |
|
| Popular varieties: Rosenteppich, Rose Carpet | |
| Sedum hybrid (Sedum hybridum) | |
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Phedimus hybridus). Forms wide, dense rugs. Creeping stems, well-rooted. The leaves are green. Flowers are yellow. Peduncles grow up to 10-25 cm. Blooms in August-September. Drought and frost resistant. Evergreen. Dry inflorescences with brown fruits can be used in flower arrangements. |
|
| Popular varieties: Czar's Gold, Immergrunchen | |
| Thick-leaved sedum (Sedum dasyphyllum) | |
|
Forms wide, dense rugs. Creeping stems, well-rooted. The leaves are green. Flowers are yellow. Peduncles grow up to 10-25 cm. Blooms in August-September. Drought and frost resistant. Evergreen. Dry inflorescences with brown fruits can be used in flower arrangements. |
|
| Popular varieties: Lilac Mound, Lloyd Praeger, Opaline | |
| Siebold's sedum (Sedum sieboldii) | |
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium sieboldii). Forms wide, dense rugs. Creeping stems, well-rooted. The leaves are green. Flowers are yellow. Peduncles grow up to 10-25 cm. Blooms in October. Winter-hardy. Suitable for growing in containers, creating topiary, alpine slides, rockeries. |
|
| Popular varieties: Dragon, Mediovariegatum | |
|
Stonecrop Kamchatka (Sedum kamtschaticum, Sedum floriferum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Phedimus kamtschaticus). Forms green bushes 15-25 cm high with semi-lying shoots and woody rhizome. The leaves are green, they turn red in the sun. The flowers are yellow-orange with yellow stamens. The fruits are scarlet. Blooms in July-September. Poor drought tolerance. Grows well in partial shade. |
|
| Popular varieties: Variegatum, Tekari Dake. | |
| Sedum kuril (Sedum kurilense) | |
|
Forms a dense carpet up to 10 cm high with lodging stems. The leaves are green. The flowers are yellow. Fruit pods are bright red during seed ripening. Blooms in July-September. Best suited for making rockeries. |
|
|
Sedum lanceolate (Sedum lanceolatum) |
|
|
Forms bushes 15 cm high with lying, slightly raised stems. The leaves are bluish-blue, they turn red in the sun. The flowers are bright yellow. Blooms in June-July. Prefers good lighting, but can grow in partial shade. It propagates well by seeds and dividing the bush. Great for rockeries and rock gardens. |
|
| Sedum false (Sedum spurium) | |
|
Forms loose rugs up to 15 cm high. The leaves are green, after frost they turn red or bronze. There are varieties with burgundy, purple, variegated leaves. The flowers are white, crimson, bright pink or purple, depending on the variety. Blooms in July-August. Evergreen in warm climates. In the middle lane, it drops leaves for the winter. Prefers bright sun. Will transfer slight shading. Used in flower beds, mixborders. Can be grown in containers as long as they are spacious. |
|
| Popular varieties: Album, Bronze Carpet, Elizabeth, Green Mantle, Leningrad White, Pink Jewel, Tricolor | |
| Sedum spatulate (Sedum spathulifolium, Sedum pruniosum) | |
|
Forms rugs about 10 cm high. Peduncles about 15 cm high. Leaves are green with a silvery-bluish bloom. They often turn pink in the sun. The flowers are yellow. Blooms in May-June. In the middle lane in winter it requires a dry shelter, otherwise it freezes in 1-2 years. Used in alpine slides, frame topiary, for landscaping walls. Can be grown in containers. |
|
| Popular varieties: Aureum, Cape Blanco, Harvest Moon | |
|
Sedum multistem (Sedum pluricaule) |
|
|
Refers to the genusOchitnik (Hylotelephium pluricaule). Forms bushes 7-10 cm high. The leaves are greenish-gray, turn pink in the sun. The flowers are bright pink, sometimes snow-white. Blooms in August-September. It grows slowly. Does not tolerate excessive watering and frost. In the southern regions, it can be grown in rock gardens. |
|
| Varieties: Sakhalin (var.ezawe), Edos (var. Yezoense) | |
| Bird sedum (Sedum ornithogalum) | |
|
Forms dense curtains 10 cm high. The leaves are green, they quickly turn red in the sun. The flowers are yellow. The fruits are burgundy. Requires good lighting and soil drainage. With excessive or insufficient nutrient soil, it loses its decorative effect. |
|
| Sedum divergent (Sedum divergens) | |
|
Forms a bush about 5 cm high. Peduncles up to 10 cm high. The leaves are green, they turn red in the sun. The flowers are yellow. Does not tolerate waterlogging. Winter-hardy. Not picky about the type of soil. Suitable for frame topiary, rockeries, roof landscaping. |
|
|
Sedum of the Rural (Sedum selskianum) |
|
|
Forms loose sod 15-40 cm high. Leaves are green, sometimes red. Inflorescences are yellow with gray pubescence. Best suited for growing in rock gardens and rockeries. Needs moderate watering, good lighting. Blooms in August-September. |
|
| Popular varieties: Goldilocks, Spirit | |
|
Sedum of Takeshim (Sedum takesimense) |
|
|
Forms a dense carpet of lodging shoots up to 40 cm long. The leaves are green. The flowers are yellow. Blooms in July-September. In the southern regions it grows as an evergreen. In the middle lane, it retains the color of the leaves until late autumn. |
|
|
Sedum thicket (Sedum pachyclados) |
|
|
Forms dense rugs 3-5 cm high. Leaves are bluish green. The flowers are gray-pink. Blooms in May and September-October. Winter-hardy. Loves good drainage and lighting. Grows rapidly due to rooting shoots. |
|
|
Forster's sedum (Sedum forsterianum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Petrosedum (Petrosedum forsterianum). Forms rugs about 10 cm high. Peduncles 20-30 cm high. Leaves are green, gray-gray, sometimes purple. The flowers are yellow. It grows quickly. Can be grown in containers. Needs regular watering. |
|
| Popular varieties: Elegans, Oracle, Purpureum | |
|
Sedum Ellakombe (Sedum ellacombianum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Phedimus ellacombianus). Forms dense carpets 10-15 cm high. The leaves are rich green. The flowers are bright yellow. The fruits are orange-red. Used in mixborders, rockeries and rock gardens. |
|
Tall (shrub) stonecrop
Perhaps tall stonecrop is the most common sedum species in gardens. For the most part, they are undemanding to the type of soil, although they often prefer lean, rocky soil than saturated with humus. Sedum does not need special care, bloom before the beginning (or even until the middle) of autumn, get along in any garden.
In the case of tall stonecrops, it is important to consider that they do not like drought and most often require more frequent watering than groundcover sedums.
|
Sedum prominent (Sedum spectabile) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium spectabile). Bush 30-70 cm high. The leaves are green, sometimes purple or with a bluish tinge. The flowers are white, pink, crimson, purple. Blooms in August-October. Does not tolerate excessive moisture. Sometimes it gives returnable and chlorophyll-free shoots that need to be removed. Can be grown in a container. |
|
| Popular varieties: Abendrot, Iceberg, Brilliant, Carmen, Crystal Pink, Steven Ward, Neon | |
|
Sedum tenacious (Sedum aizoon) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik(Phedimus aizoon). The bush is 20-50 cm high. Blooms in June-August. Unpretentious. It grows even on sparse rocky soils. Shade tolerant. Needs regular, moderate watering. |
|
| Popular varieties: Auranticum | |
|
Sedum red dot (Sedum erythrostictum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium erythrostictum). The bush is 30-60 cm high. The leaves are bluish-green. The flowers are white, pale pink, sometimes with bright pink pistils. Blooms in September-October. Grows in full sun or partial shade. Requires moderate watering. |
|
| Popular varieties: Mediovariegatum, Frosty Morn | |
|
Sedum ordinary, or telephium (Sedum telephium) |
|
|
The bush is 40-80 cm high. The leaves are purple, crimson, bright pink, green. gray, brown in contrast to the variety. The flowers are pink, crimson. Blooms in July-August. Can be grown in curbs, mixborders, containers. |
|
| Popular varieties: Bon Bon, Jennifer, Red Globe, Raspberry Truffle. | |
Unpretentious types of stonecrops
Sedums of these species are unpretentious in care, not picky about the type of soil and lighting. Their only "whim" is moderate watering and good drainage of the soil.
| Sedum caustic (Sedum acre, S. procumbens, S. glaciale, S. neglectum) | |
|
Forms dense evergreen rugs up to 4-10 cm high. The leaves are green. The flowers are yellow. Undemanding to watering and soil type. Loves good lighting. Winter-hardy and drought-resistant. It spreads quickly, but falls out without difficulty. Valuable honey plant. |
|
| Popular varieties: Minus, Oktoberfest, Elegans | |
| Sedum white (Sedum album) | |
|
Forms dense rugs up to 5-15 cm high. The leaves are green in poor lighting and humid weather, and turn red in the heat and sun. The flowers are white. Blooms in July-August. Undemanding to watering and soil type. Most varieties are hardy. |
|
| Popular varieties: Chloroticum, Bella d'Inverno, Coral Carpet, Faro Form, Goldfinger, Roseum, Rubiflorum | |
| Sedum pale yellow (Sedum ochroleucum) | |
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Petrosedum ochroleucum). Forms a curtain up to 20 cm high with lodging stems. Shoots root well. Leaves are green, brown-brown, with a bluish bloom or two-colored. The flowers are yellow. Peduncles up to 30 cm high. Blooms in July-August. Undemanding to watering and soil type. Most varieties are hardy. |
|
| Popular varieties: Centaurus, Red Wiggle | |
| Sedum spanish (Sedum hispanicum, Sedum glaucum) | |
|
Forms a curtain 5-15 cm high. The leaves are pale green, light yellow, pinkish gray or purple, depending on the variety. The flowers are white or pinkish. Blooms in June-July. In arid conditions, it turns into an annual. It grows rapidly on fertile soils. It reproduces well by self-seeding. |
|
| Popular varieties: Albescens, Aureum, Purpureum | |
| Sedum of Middendorf (Sedum middendorfianum) | |
|
Refers to the genusZhivuchnik (Petrosedum middendorfianus). Forms a bush 8-30 cm high. Peduncles 10-30 cm high. The leaves are green. The flowers are yellow-orange. Undemanding to soil type and watering. Grows in full sun and partial shade. Can be grown in rockeries, rock gardens and containers. |
|
| Popular varieties: Diffusum, Striatum | |
|
Sedum sedum (Sedum sediforme) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Petrosedum sediforme). Forms bushes with woody shoots at the base up to 10-20 cm high. Peduncles grow up to 25 cm, sometimes up to 60 cm. The leaves are dark green with a bluish or brown tint. The flowers are yellow, 0.5-0.8 cm in size. Drought-resistant. Loves good lighting. |
|
| Popular varieties: Aureum, Silver | |
|
The sedum is rocky, or bent (Sedum Rupestre, Sedum reflexum) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Petrosedum (Petrosedum ruperste, Petrosedum reflexum). Forms rugs about 10 cm high. Peduncles 15-30 cm high. The leaves are green or gray. The flowers are bright yellow. Blooms in June-July. Poorly tolerates waterlogging. Winter-hardy. They are used in landscaping walls, roofs, and also as a ground cover plant. |
|
| Popular varieties: Angelina, Blue Spruce, Monostrosum Cristatum | |
|
Sedum trifoliate (Sedum ternatum, Sedum americanum) |
|
|
Forms dense curtains with a height of 7-15 cm. The leaves are green. The flowers are white with purple stamens. Blooms in May. Winter-hardy. Shade tolerant. Needs good soil drainage. Used as a ground cover plant, as well as for greening roofs. |
|
| Popular varieties: Larinem Park | |
|
Sedum narrow-spotted (Sedum stenopetalum) |
|
|
Forms bushes up to 20 cm high. Leaves are light green, turn red during the season. The flowers are bright yellow. Drought-resistant. Winter-hardy. Can be used in rockeries and rock gardens. |
|
|
Sedum hexagonal (Sedum sexangulare) |
|
|
Forms dense rugs 5-7 cm high. Peduncles up to 15 cm high. The leaves are green, arranged in a spiral around the stem. The flowers are bright yellow. Blooms in June-July. Drought-resistant. Shade tolerant. It multiplies rapidly. Can be grown in containers. Suitable for use in frame topiary, roof landscaping. |
|
|
Evers' sedum (Sedum ewersii) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium ewersii). Forms bushes with shoots up to 40 cm long. The leaves are bluish-green. The flowers are pink. Suitable for growing in rockeries and rock gardens, as well as a ground cover plant. Winter-hardy. Unpretentious. Grows best in poor soils. Does not like waterlogging. |
|
|
Varieties: Univalent (S. ewersii var.homophyllum), Round-leaved (S. ewersii var.cyclophyllum) |
|
Rare sedum species
These stonecrops, unfortunately, are not very common in the gardens of the middle zone. And in vain, because they deserve the attention of flower growers.
| Albert's sedum (Sedum affine, Sedum alberti) | |
|
Forms a curtain with short, creeping sterile shoots. The leaves are gray, turn reddish-orange in the sun. Peduncles 15-20 cm high. Flowers are white with purple stamens. Blooms in May. Rarely grown in gardens, most often in rock gardens. Loves good lighting and drainage. Afraid of getting stuck during the melting snow. In the fall, it is necessary to cut the bush to the base. |
|
|
Sedum graceful (Sedum gracile) |
|
|
Forms a dense rug 3-5 cm high. Leaves are light green. The flowers are pinkish white. Peduncles up to 10 cm high. Blooms in June-July. Winter-hardy. Poor drought tolerance. Best suited for growing in the lower tiers of a rock garden. |
|
|
Sedum Lydian (Sedum lydium) |
|
|
Forms a curtain 4-5 cm high with creeping shoots. The leaves are green, they turn red in the sun. The flowers are white with pink veins. Peduncles up to 10 cm high. Grows quickly thanks to easily rooted shoots. Poor drought tolerance. Loves partial shade. Evergreen. Best suited for rockeries and curbs. |
|
|
Sedum vine-shaped (Sedum sarmentosum) |
|
|
Forms bushes 5-10 cm high. Leaves are light green, turn light purple in the sun. The flowers are yellow. Grows quickly thanks to easily rooted shoots. In the middle lane, it requires shelter for the winter, but even with freezing, it grows well with surviving shoots. Can be used as an ampelous plant. Prefers shade and partial shade. Poor drought tolerance. |
|
|
Sedum escaping (Sedum stoloniferum) |
|
|
|
Refers to the genus Zhivuchnik (Petrosedum stoloniferus). Forms dense rugs up to 10 cm high. Peduncles 15-30 cm high. Branched shoots, take root easily. The leaves are soft green. The flowers are pale pink. Blooms in June-August. Unpretentious. Drought-resistant. It takes root well in the middle lane. May replace moss in Japanese-style gardens. |
|
Sedum poplar (Sedum populifolium) |
|
|
Refers to the genus Ochitnik (Hylotelephium populifolium). Forms a bush with woody shoots up to 40 cm long. The leaves are green, poplar-like in shape. The flowers are pinkish-white. Winter-hardy. Shade tolerant. Does not like direct sunlight. Needs good drainage. |
|
| Tatarinov's sedum (Sedum tatarinowii) | |
|
|
Refers to the genusOchitnik (Hylotelephium tatarinowii). Forms a bush up to 15 cm high. The leaves are green. The flowers are white with purple stamens. Suitable for growing in containers, rockeries, mixborders. Requires good drainage. Winter-hardy. |
|
Troll's sedum (Sedum trollii) |
|
|
Forms curtains with a height of 3-5 cm. The leaves are green. The flowers are white. An evergreen shrub. Used in rock gardens and rockeries. Prefers well-drained soil and moderate watering. |
|
Heat-loving sedum for growing in containers
Many "southern" sedums are very beautiful and showy. Unfortunately, in the middle lane, it is almost impossible to grow them outdoors. But, fortunately, no one forbids the use of containers for this.
| Sedum linear (Sedum Lineare) | |
|
Forms a bush with raised shoots up to 30 cm long. Leaves with a bluish-white bloom, green, mint, variegated, depending on the variety. The flowers are yellow. It blooms rarely. In the middle lane, it can be grown in containers and hanging pots as an ampelous plant. |
|
| Popular varieties: Variegatum, Silverstone | |
| Sedum Makina (Sedum makinoi, Sedum obovatum) | |
|
Forms a dense rug with a height of 2.5-5 cm. It blooms almost imperceptibly. The leaves are green. In the southern regions it is used as a ground cover plant. In the middle lane, it is grown only in containers. |
|
| Popular varieties: Kosmosje, Limelight, Tundra Tornado | |
| Sedum polychaete (Sedum polytrichoides) | |
|
Forms rugs up to 10 cm high. Leaves and stems are usually reddish brown. The flowers are yellow. Blooms in August-September. Does not tolerate frost and excessive watering. In the middle lane can be grown in containers. |
|
| Popular varieties: Chocolate Ball | |
| Sedum oregon (Sedum oreganum) | |
|
Forms dense rugs 10-15 cm high. The leaves are green, turning cherry in the sun. The flowers are yellow-orange. Blooms in July-August. Loves good lighting. Does not tolerate excessive watering. In the middle lane it freezes in winter, so it is best to grow it in containers. |
|
|
Sedolum sedum (Sedum glaucophyllum) |
|
|
Forms curtains up to 10 cm high. The leaves are bluish-green. The flowers are white. Blooms in June. Shoots take root easily. Loves loose, well-drained soil, sun or partial shade. In the south, it is used as a ground cover plant. In the middle lane, it is grown in containers, although the Silver Frost bushes can withstand temperatures down to -34 ° C. |
|
| Sedum pretty (Sedum pulchellum) | |
|
Forms bushes up to 15 cm high. It grows as an annual or a juvenile. Leaves are bright green, turn pink during drought. The flowers are white, pink, purple or lilac. Blooms in August-September. Prefers partial shade, good hydration. In the middle lane, it is grown in containers. |
|
What sedum do you like? Do not forget to show off photos of your stonecrops on our forum!

Sedum, sedum, hare cabbage is an unpretentious succulent plant, the care of which consists in proper planting, timely watering, fertilization and rejuvenating pruning to form a lush bush. During flowering, they form such a lush carpet that, looking at them, a beautifully woven tapestry pattern appears. The charm of a lint-free carpet is given not only by stonecrop flowers, but also by fleshy, dense, spectacularly colored leaves. The sedum is an excellent honey plant, so myriads of bumblebees, bees and butterflies will circle over the luxurious carpet. The ancient Romans firmly believed that sedum protects houses from lightning strikes, so they planted it on roofs and fortifications.
Botanical description
Sedum is a herbaceous, undersized succulent plant. In nature, there are perennial and biennial sedums. All types of succulent sedums can be divided into 2 parts. The first are thermophilic, which in our harsh climate are grown only as annuals. The second are frost-resistant, ground cover.
Under natural conditions of growth, it is widespread in the Caucasus, inhabited the arid regions of South America and Africa, it can also be found here, in Russia
Stonecrop stalks are rather branched; when growing, they form a lush shrub or semi-shrub. The leaves are very dense, adhere well to the fleshy stems. Petiole leaf plates are often ovoid or oval in shape. You can find specimens with swollen, cylindrical, or with flat, disc-like leaves, arranged in whorls or opposite.

During the flowering of stonecrops, you can not take your eyes off the interesting, not similar flowers
Leaf plates can be painted in gray, green, gray-gray, pink... Their color depends not only on belonging to a particular species, but also on growing conditions. The coloration is influenced by weather conditions such as bright sun or partial shade, soil composition, exposure to winds or not. Even one species can have different foliage colors if growing conditions differ markedly. Sometimes reddish streaks may appear on the leaves.
Dense umbellate flowers appear on the plant in the second half of summer, some varieties bloom in autumn... In the umbellate inflorescences, small bisexual flowers are collected, painted in red, blue, yellow and snow-white colors.
The petals are very dense, slightly bent. When growing, they grow together into a narrow tube from which numerous stamens and an ovary peep out. The flowers smell so good that they attract pollinating insects.
Types, description, photo
There are over 500 species of stonecrop in the genus of succulent plants.... Several species are considered cultivated, which, due to their unpretentiousness and colorful appearance, are grown as ornamental plants.
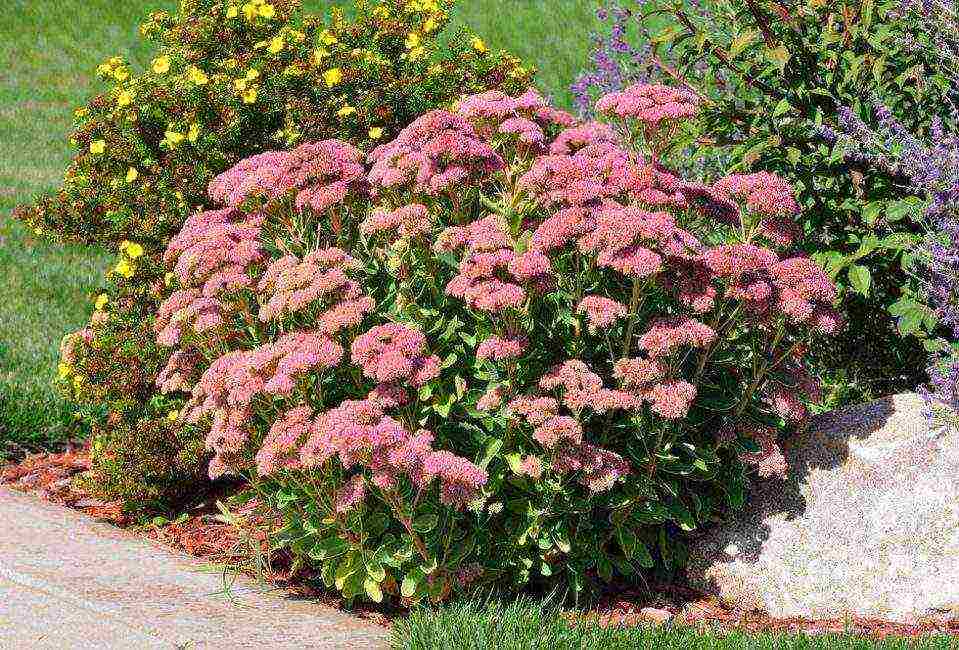
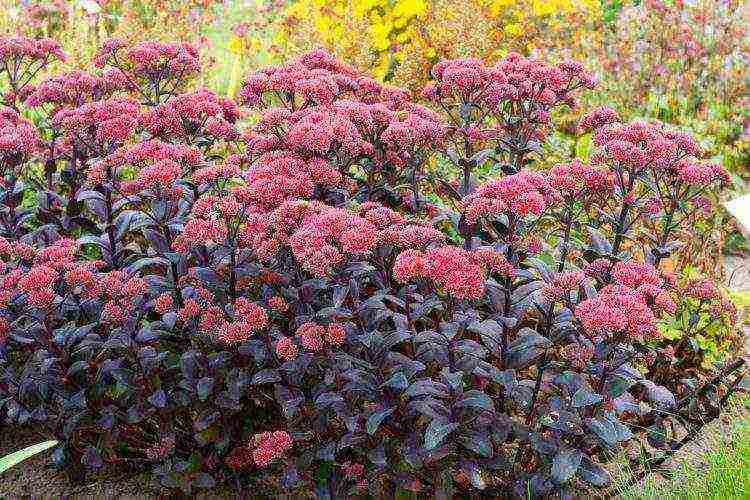
Plain, large or medicinal
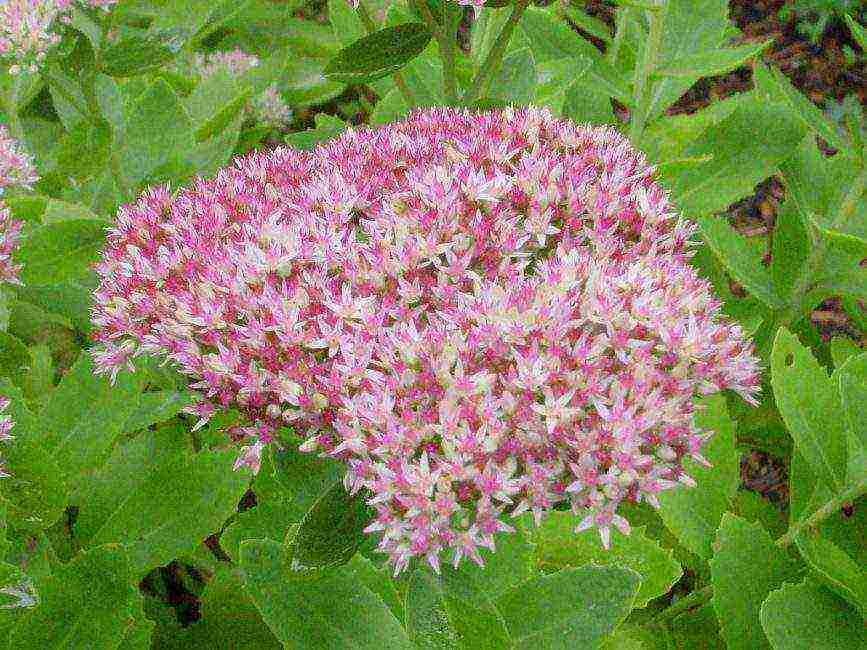

Common sedum
A tall perennial plant with an erect thick stem reaching a height of 25 cm. The leaf plates are dense, flat, petiolate. On the edges of the oval leaves, denticles are noticeable. Abundant flowering occurs in July. A dense scutellous inflorescence appears at the very top, it includes numerous stars-flowers with beautiful stamens. Medicinal sedum is considered a good honey plant.
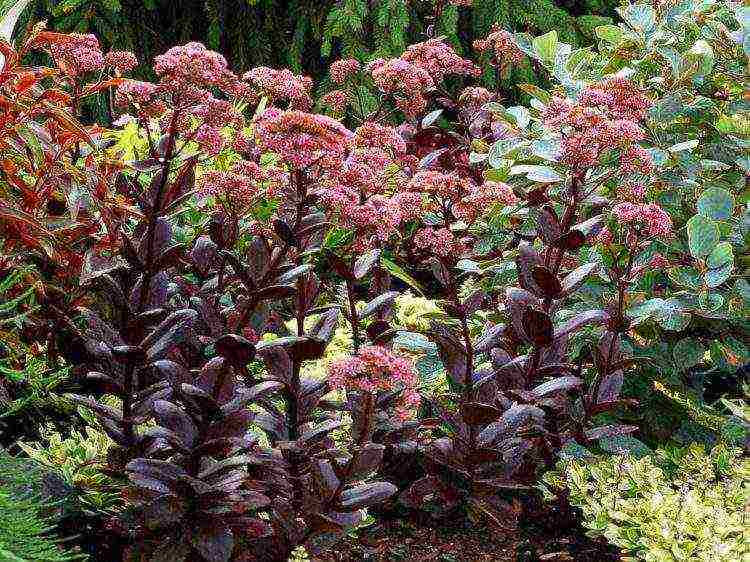
Common sedum is represented by two popular varieties: Matron and Linda Windsor.
The erect stems of the Matrona reach 60 cm in height. Blue-green foliage is covered with a reddish bloom. During flowering, the bush is covered with beautiful light pink inflorescences.
The flowering of stonecrop is somewhat reminiscent of a medicinal plant - St. John's wort.
Linda Windsor

Linda Windsor
Famous for its maroon stems. During flowering, hemispherical ruby-colored inflorescences bloom over the dark red foliage.
Prominent

Prominent
Under natural conditions, it grows in the countries of East Asia. The plant is considered medium-sized, the stems reach a height of 50 cm. The root system of the species is represented by a tuberous rhizome. The bare stems grow straight. They have tight-fitting petiolate leaves. Blue or gray-green plates have a noticeable depression, which runs closer to the center.
In summer, a cap of umbellate inflorescences appears above the wavy, slightly toothed foliage, the diameter of which is equal to 15 cm. Each inflorescence contains lilac-pink star-shaped flowers.
Purple
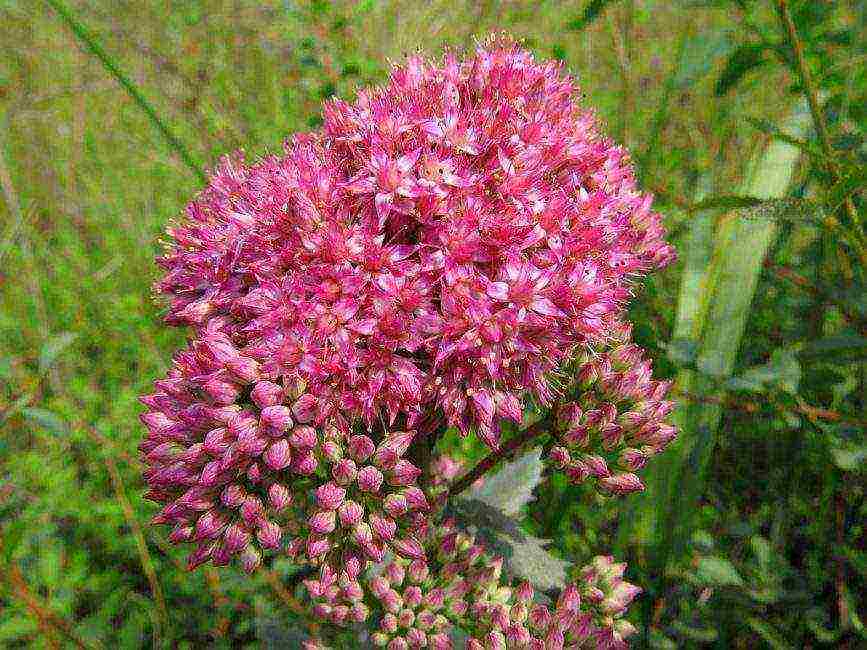

Purple
Perennial succulent plant. Depending on the variety, the stonecrop height varies between 20-65 cm. The dense leaves are evenly distributed on erect stems. Stonecrop is propagated by tuberous rhizome.
The fleshy foliage has a regular arrangement. The length of the leaf plate is from 3 to 9 cm. Above the beautiful foliage, from June to September, umbrella inflorescences of a pale pink or deep pink color appear.
The color saturation of purple sedum flowers depends on the qualitative composition of the soil and growing conditions.
Pungent
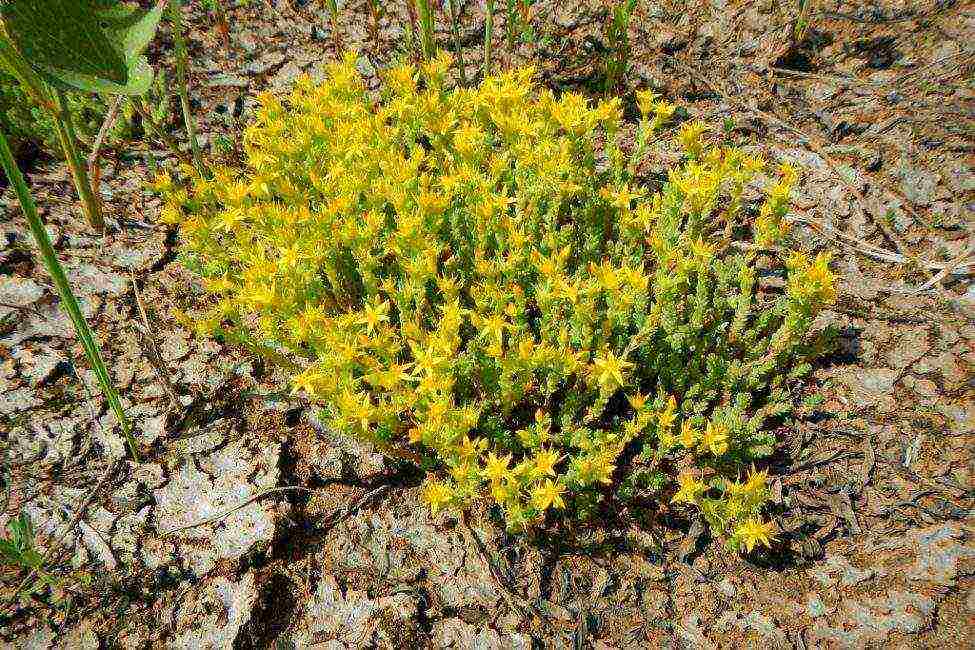

Pungent
The stems of a plant of this species are well branched, they do not exceed 10 cm in height. The oval leaves adhere tightly to the stems, small denticles are clearly visible along their edges.
The leaf plates are small, their length is 6 mm. The shortened stalks boast loose inflorescences in which golden yellow buds sit tightly.
White
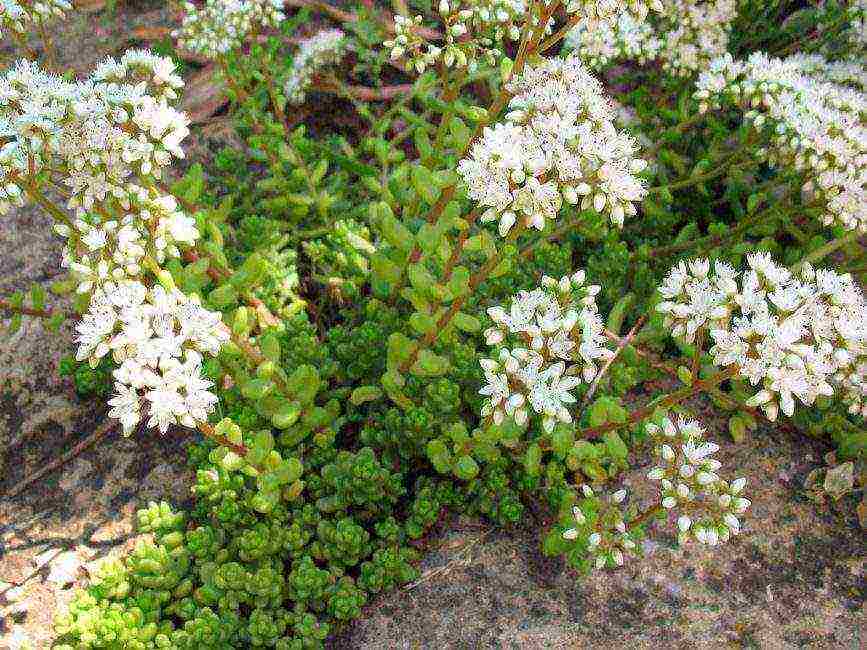

White
Green leaves densely sit on the creeping fleshy leaves of white stonecrop. In shape, the leaf plates resemble numerous cylinders. Over time, the bright green color of the foliage takes on a reddish, purple or pink tint.
White star flowers appear on the plant in late spring. At this time, sedum throws out long, bare peduncles. The diameter of loose inflorescences reaches 12 cm.
False
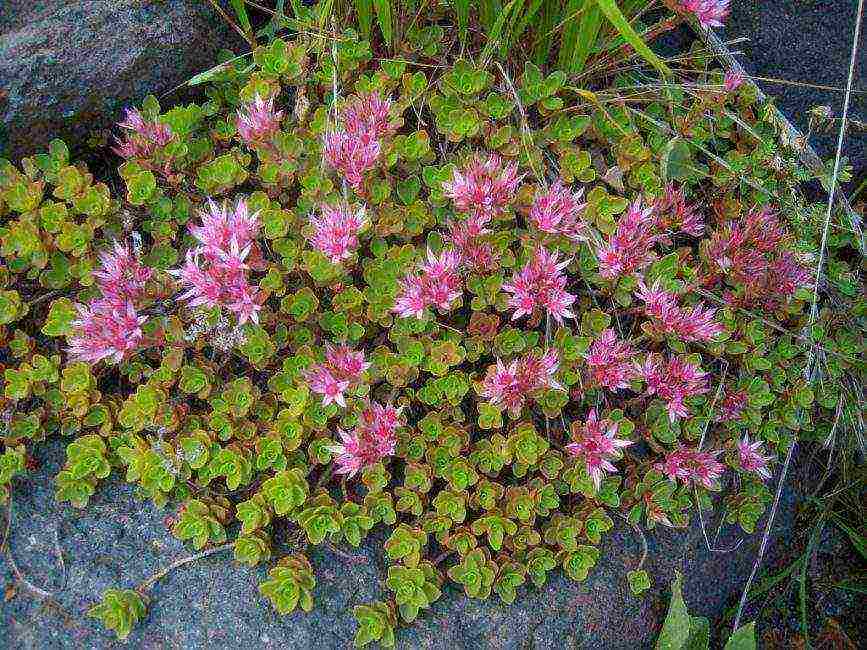

False
The species is characterized by good winter hardiness, has creeping stems and a creeping rhizome. The foliage is dark green, opposite, has an oblong ovoid shape.
Purple or pink umbellate inflorescences appear above the toothed foliage.
Morgana
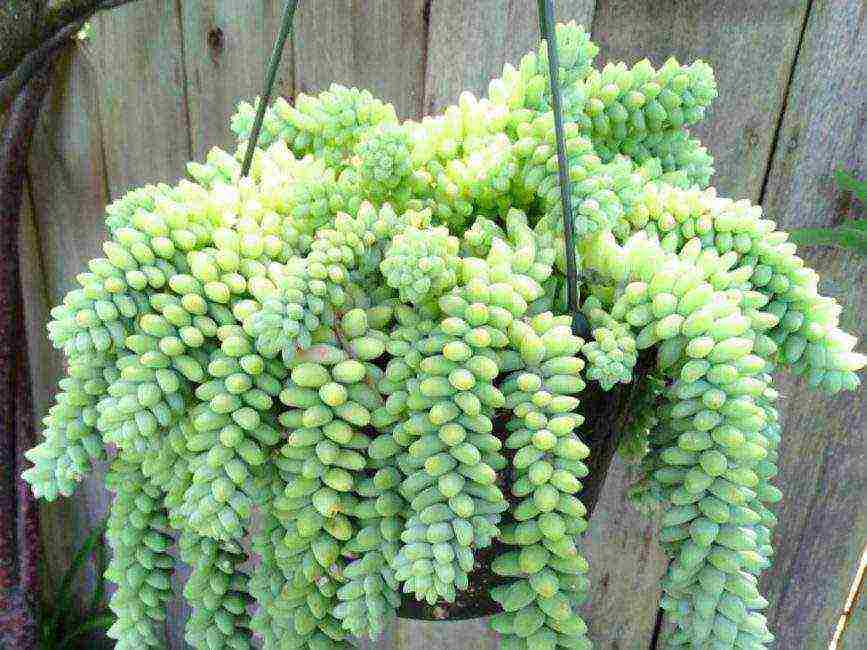

Morgana
A heat-loving species, in natural conditions can be found in Mexico. The sedum of Morgan in our conditions can only be grown as a houseplant.
Hare cabbage grows very long shoots that cover the ground with a dense carpet and reach a length of at least 1 m.The plant produces long peduncles, on the top of which there are dense umbellate inflorescences with reddish or pink flowers.
In one inflorescence, you can count up to 15 buds. The leaves of sedum Morgan are oval or rounded, 5 mm thick, 1.5 cm long, painted in a light green tone.
When grown at home, it is recommended to protect children from contact with Morgan sedum, as its leaves contain toxic substances that can cause severe poisoning.
Evers
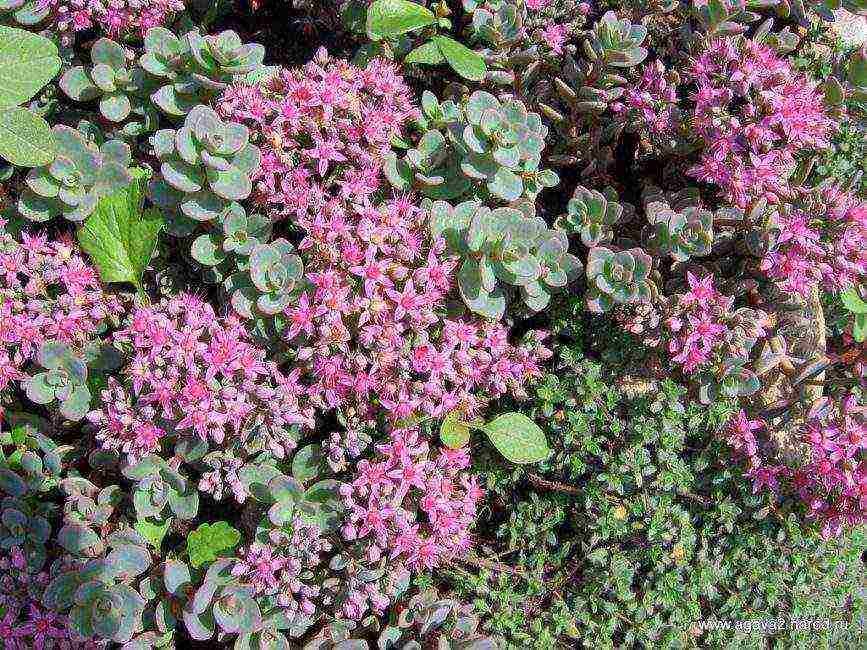

Evers' sedum
The compact bush consists of reddish, well-branched stems, reaching a height of 30 cm. Heart-shaped leaves are located on the stems. Their structure is flat, 2.5 cm wide.
Flowering occurs at the end of the warm season. Large inflorescences with pink flowers cover the plants with a thick cap.A well-visible pink or red edging runs along the edges of the jagged foliage.
Kamchatka
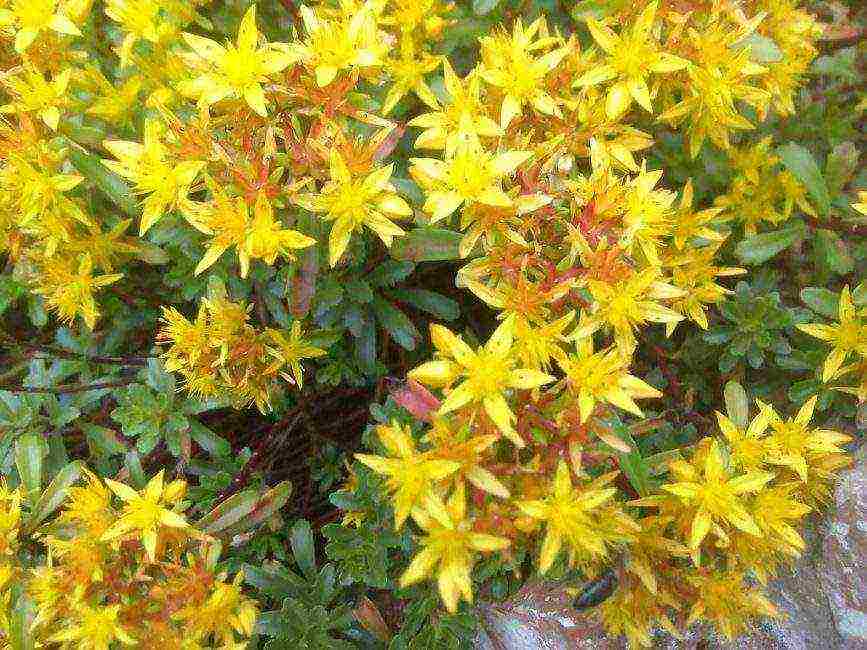

Kamchatka
A perennial plant with a creeping rhizome, thanks to which the species reproduces well and covers the entire area provided to it with a dense carpet.
Oval leaves along the edges have a noticeable smoothness of the teeth. Yellow-orange flowers appear above the beautiful light green foliage.
Bent

Bent
It belongs to the garden variety, has lodging shoots, to which bluish-green, subulate leaves are tightly attached.
Flowering begins in early spring. At this time, the plant produces bare peduncles, on which golden-yellow flowers bloom.
Siebold

Siebold
Indoor variety of a succulent plant. It is grown in a hanging planter as an ampelous plant. Blue-green small leaves adhere tightly to a long, lodging stem.
Leaves are collected in whorls of 3. During flowering, the plant is covered with beautiful numerous inflorescences with bright pink, sometimes crimson flowers.
Weinberg

Weinberg
Sedum has ovoid leaves that are blue-gray. When examining the foliage, a waxy coating is clearly visible.
The stems are erect, however, during the growing season, under the weight of dense leaves, they lie on the ground. Weinberg sedum foliage is collected in a beautiful symmetrical rosette.
Linear Linear

Linear
Indoor miniature plant. The stems are very slender, well spreading. The compact bushes are covered with beautiful foliage.
All types of sedum are beautiful in their own way. Among the variety of species, each gardener can choose the variety and a certain type that can be grown in the open air or choose an indoor flower to decorate the interior.
Rules for planting and care in the open field
The successful cultivation of sedum depends on the conditions that it can provide in a particular area. When planting species, you need to take into account their characteristics of growth in natural conditions in order to try to bring them closer to natural ones.
Location selection

Flowering sedum
Sedum is a native of warm countries, so you need to choose a well-lit area for cultivation., without any shading. If you plant sedum in partial shade, this fact will not affect the growth and development of the plant, but you will have to wait with flowering, and it will not be so lush.
Low-growing sedum is not recommended to be planted in the vicinity of deciduous plants, otherwise the fallen leaves will hide their beauty.
Soil composition
There is an established opinion that stonecrops will grow on any, even sandy soil, you just need to add a little humus to it.

However, in the fertile soil, sedums show themselves in all their glory.
Sedum does not like dampness; excessive soil moisture can lead to rotting of the root system.
Sedum, or hare cabbage, as it is popularly called, naturally grows mainly on sandy or stony soil. Due to the fact that the plant is not demanding on growing conditions, incredible compositions in the form of animals can be created from many varieties.
Without prejudice to growth and flowering, stonecrops can grow in the same place for 5 years.... The overgrown curtain will need to be rejuvenated, divided into several parts and transplanted to another place. Dry fresh earth, gravel and sand to the remaining specimen in the soil.
Fertilization
When planting in a new place, ash and sand are introduced into the soil. For good growth and development, plants need fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers.

Decorative stonecrops need 2-fold feeding for the entire growing season
The first is held in April, the second in August. Better to feed with special fertilizers for succulents. When preparing the solution, it is necessary to adhere to half the concentration.
Perennial stonecrops are fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers only at the beginning of vegetative growth - in the spring... Apply nitrogen in autumn is strictly prohibited, as sensitivity to low temperature conditions can be impaired.
Many gardeners use caustic sedum to control weeds. In addition, traditional healers prefer caustic sedum to all other medicines in the fight against warts.

The beauty and fleshiness of the leaves, as well as their saturation, depends on whether the plants receive enough nutrients.
At the beginning of the growing season, as mentioned, they are fed with organic fertilizers. To do this, use infused mullein. When preparing the solution, the mullein is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. The sedum plant does not like fresh manure.
Transfer
It is better to replant plants in spring.... Humus and mineral fertilizers are introduced into the soil for planting, I dig shovels onto the bayonet and level the surface with a rake. The sedum can be planted in rows. It is advisable to leave 10-15 cm between the specimens, and 20 cm between the rows. This distance will allow the plant to grow well.
The transplant should end with abundant watering. Weekly care consists in loosening the soil, timely watering and weeding the soil from weeds.
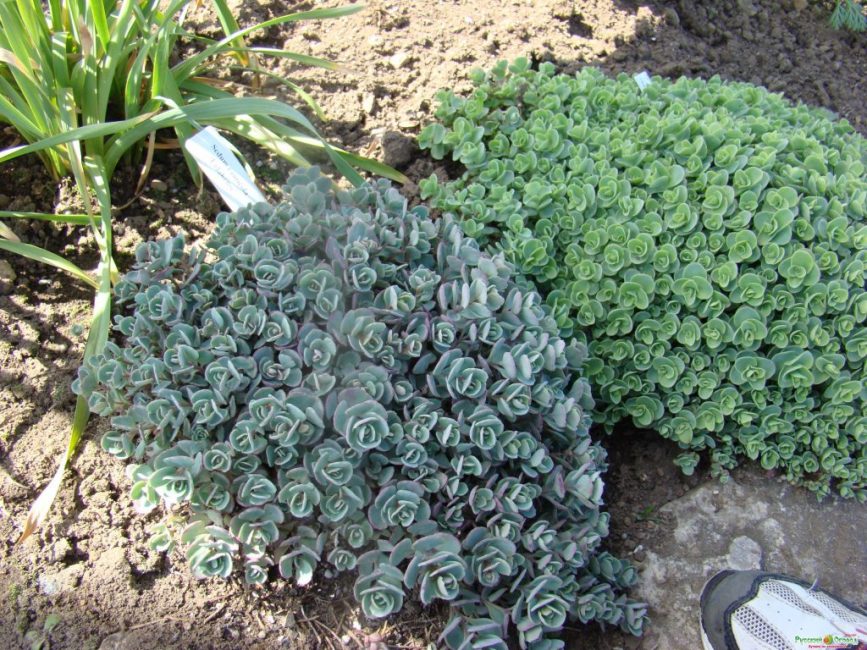

Stonecrops have fleshy leaves that accumulate water "in reserve"
However, prolonged overdrying of the earthen coma can lead to the death of the plant. Abundant watering should be carried out in dry times, when hot, sunny weather is present for a long period.
Excessive waterlogging has a detrimental effect on stonecrops, since the plant can be damaged by fungal diseases.
Trimming stonecrops
The procedure is simply necessary, since the plants grow very quickly, the stems can become bare and the brush takes on an untidy, unkempt look. Therefore, in relation to sedum, it is necessary to carry out formative, sanitary and rejuvenating pruning. The haircut should be regular. When inspecting the plant, it is necessary to remove all damaged and weakened shoots.
Perennial varieties resistant to frosty winters are pruned in late autumn. The optimal time is a strong cold snap. During this period, all stems are cut "to zero" to a level with the soil. The remaining hemp is covered with a covering material or the soil is mulched near the plant. With the arrival of spring, many young stems are formed on the bushes.
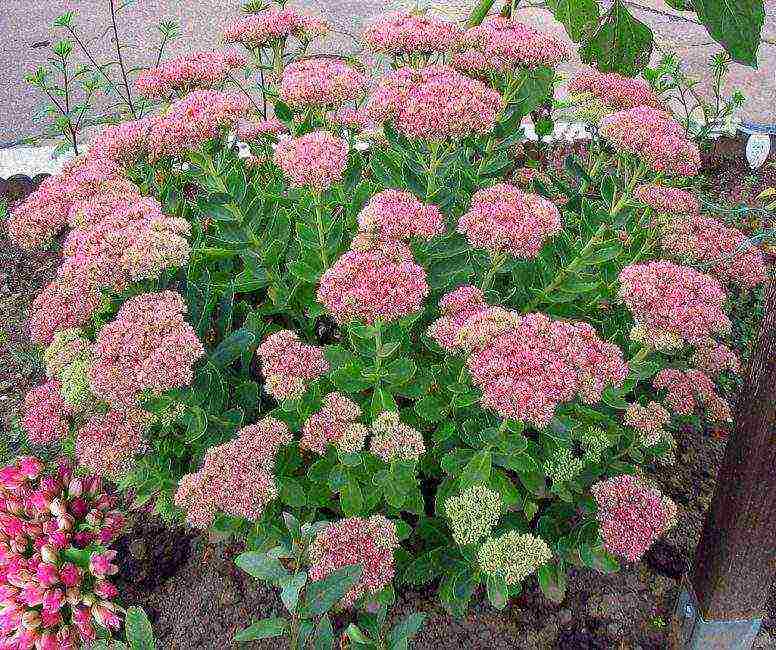

Pruning helps to maintain the decorative shape of the bush, rejuvenates planting
Decorative pruning is carried out in order to give the plant a compact appearance. All manipulations are performed accurately, with sharp and disinfected instruments.
If you find plain leaves in a decorative variety with variegated foliage, you will need to cut them off completely.
Sedum in indoor floriculture
Growing sedum at home is even easier than growing it outdoors. It is only important to choose the right varieties.

For planting, you need to pick up shallow containers
Soil composition for successful cultivation:
- turf land - 2 parts
- peat - 1 part
- rotted foliage - 1 part
- river sand - 1 part
It is necessary to put expanded clay or pebbles in each pot, because without drainage, the root system of the plant can rot. Before planting, the soil must be moistened, but not to allow the whole earth to be too wet.
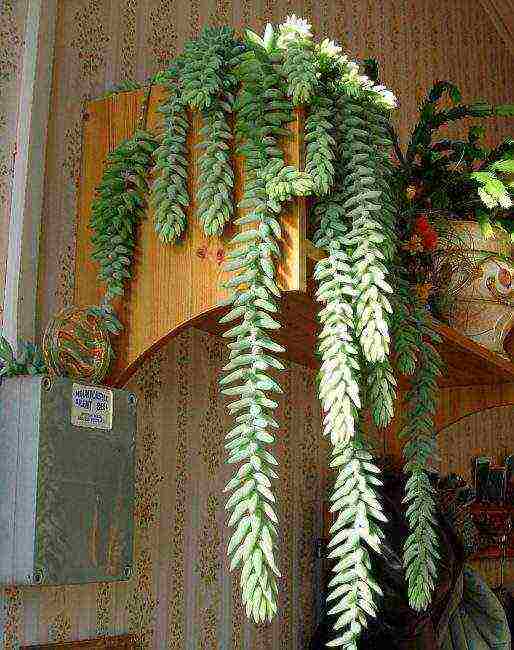

Dangling succulents
The planted plant should not be disturbed at first. Watering is carried out only after the topsoil has completely dried out by 1 cm deep. After planting, young specimens are kept in partial shade. Thus, they quickly adapt to new conditions, move away from stress and begin to develop. Then the pot with the plant is placed on the windowsill so that its beautiful fleshy foliage bathes in the rays of the sun and receives warm baths.
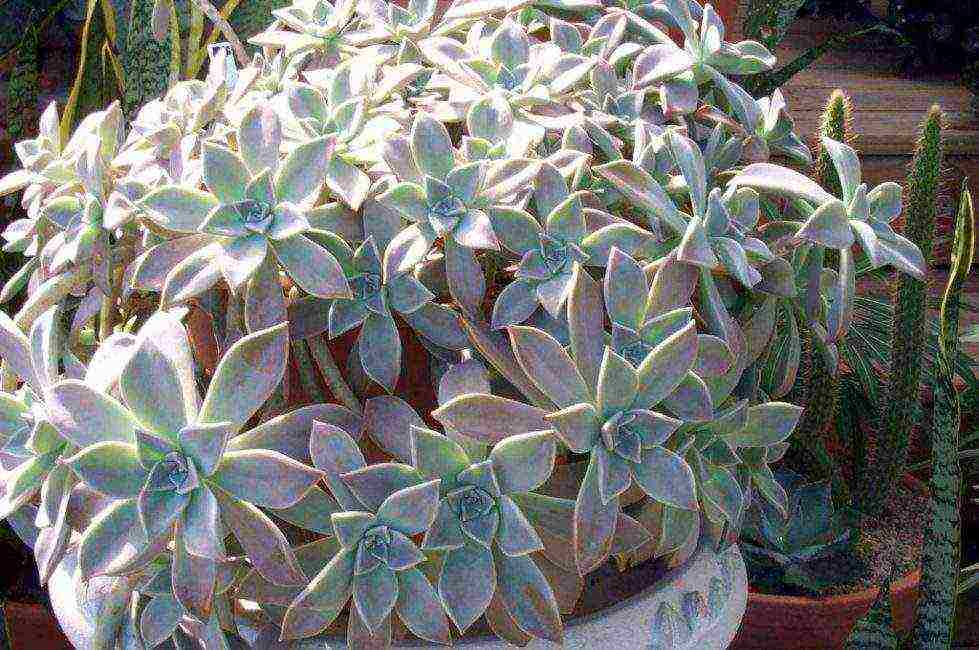

Fleshy rich foliage indicates that the plant has enough mineral and organic fertilizers.
The sedum loves fresh air, so it is recommended to regularly ventilate the room, but avoid drafts... In summer, the pot with the plant can be taken out to the loggia, balcony, terrace or placed in a semi-shaded place in the garden. It is recommended to transplant adult specimens once every 2 years.
Reproduction
At home and when grown outdoors, you can easily get new stonecrop bushes, since they multiply very easily and take root quickly.
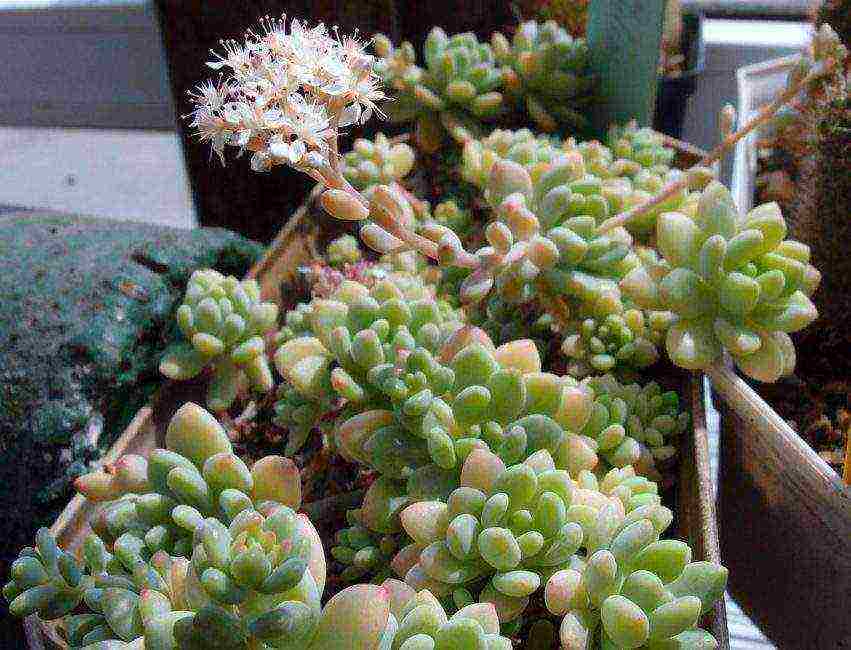

Sedum nail
There are several ways sedum propagates:
- seed propagation
- grafting (variety - winter grafting)
- division of rhizome
Let's consider each method of obtaining new copies in more detail, identify all the positive and negative aspects.
Seed reproduction
For sowing, you can use your seeds collected from plants in a flower bed. You can buy planting material at the store. Bright sunlight and prolonged exposure to the open sun lead to a discoloration of the leaf plates.
It does not lose its decorative effect, on the contrary, it acquires an attractive reddish tint.Seeds can be sown in spring or fall. The containers must be filled with a soil mixture consisting of sand and peat.
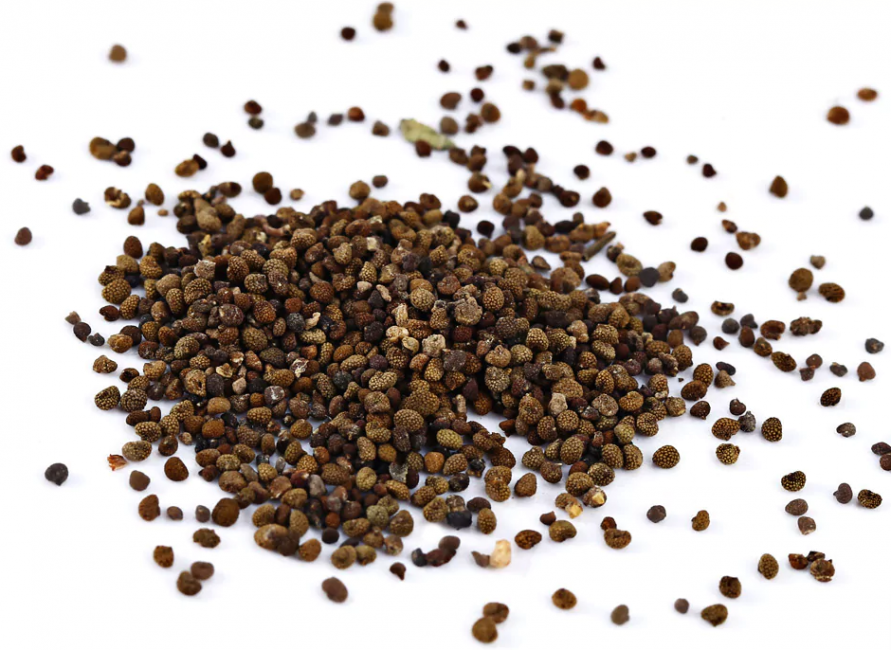

Stonecrops have small seeds, therefore, for their even distribution over the surface of the earth, they must be mixed with dry river sand
It is worth considering that only freshly harvested seeds have good germination, so when buying it is important to pay attention to the expiration date. The earlier the seeds were harvested, the more likely they are to germinate 100%.
Seeds are sown superficially, do not sprinkle with soil. It is advisable to moisten the soil before sowing. So that later, during moistening, the seeds are not buried in the soil. The container must be covered with foil or glass.
Under natural growing conditions, seeds undergo natural stratification - they lie under the snow all winter and are affected by sub-zero temperatures. Home seeds need to create the same conditions. The container with the sown seeds can be placed in the refrigerator for 2 weeks or taken outside and buried in a snowdrift.
Under natural conditions, stonecrops can be found in unusual places, that is, where their growth seems impossible. And they bring plant seeds or stonecrop cuttings into such hard-to-reach places of a bird or mouse.
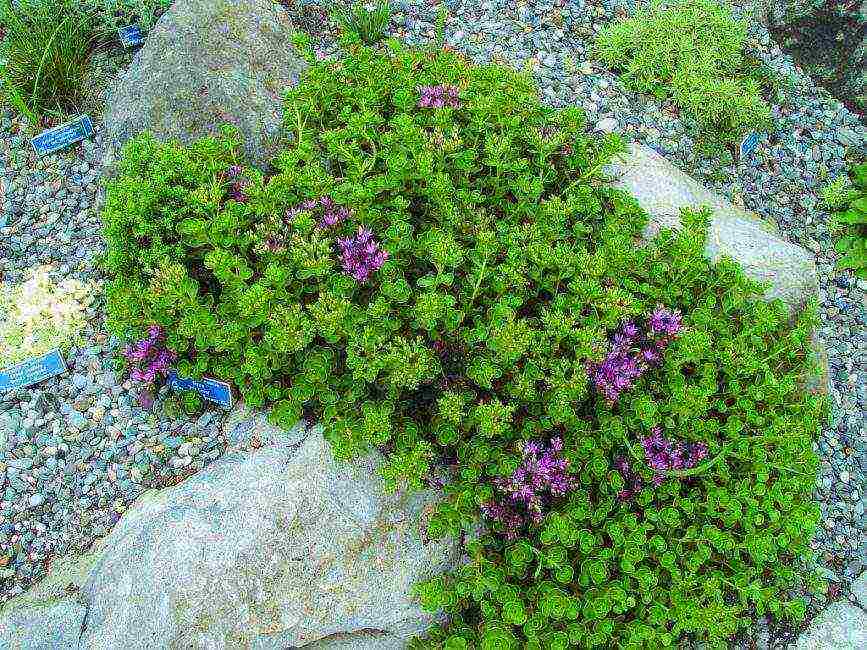

Sedum ground cover
After passing through stratification, a container with seeds is brought into the house and placed on a well-lit windowsill with a room temperature of at least +18 ° C. After about half a month, the first shoots appear. The germination process can take a whole month.
The seedlings are so amicable that the entire surface becomes covered with a continuous carpet. When 2 true leaves develop on young specimens, the young must be cut into separate pots and give him a lot of space for good development.
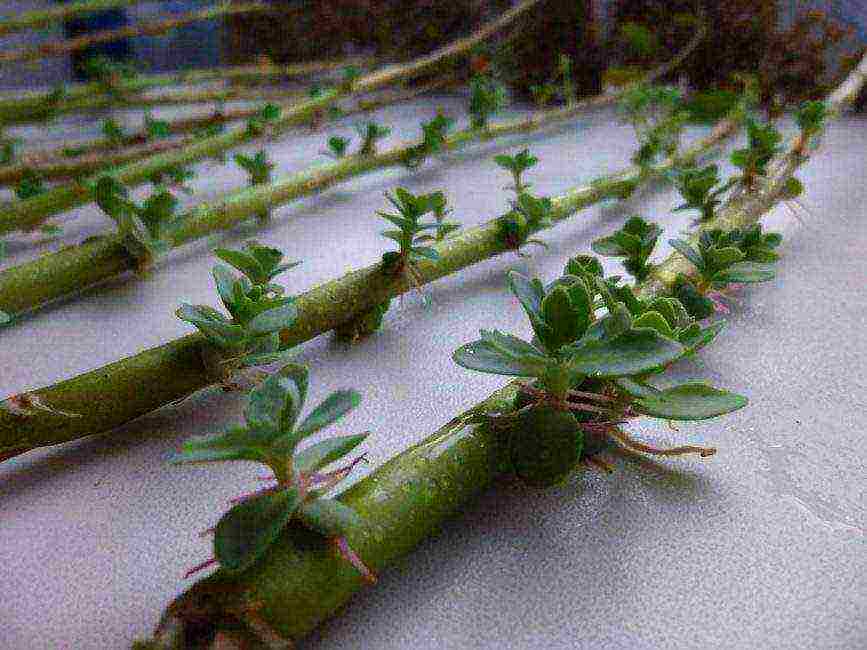
Cuttings
Florists note that propagating sedum by cuttings means saving a lot of time and nerves, since this method is the simplest and most effective... The survival rate is almost 100%. In order for sedum to take root, it is enough for it to touch the ground.

As cuttings, parts of the stem are broken off of various lengths or leaflets are taken for propagation. By the way, they also take root well.
After the cutting is torn off from the mother plant, it is necessary that it lie on the table at room temperature for several hours so that the cut dries out a little.
The stalk is only slightly buried in the soil. Watering should be sparse. When the plant has given its root system, it will begin to massively grow foliage.

Interesting compositions can be created from decorative variegated varieties of stonecrop
Young plants are ready for transplanting into open ground after 2 weeks from the formation of the root system... Further, it does not make sense to grow in containers, since the plants will begin to stretch out and the stem will become bare, unattractive.

Decorative composition
Winter cuttings are used by gardeners to massively increase the collection, that is, to fill large areas with sedum. Landscaping designers recommend using sedum... When it fades, you cannot wait for frost, you should cut off all the shoots and spread them in an even layer in a sufficiently warm room.

While the plants will “bask in the warmth”, they will first lose all foliage and the stems will remain leafless. After a while, young shoots begin to form in place of the fallen leaves.
Now you need to wait until these shoots reach a length of 6 cm. They need to be broken off and buried in the soil for rooting. Cuttings root well at room temperature. They are not afraid of raising and lowering the temperature regime. The only thing that stonecrop cuttings are afraid of is to be in moist soil for a long time at a low temperature in the room. In such conditions, cuttings can rot.
Rhizome division

In addition to seed propagation and cuttings, some varieties reproduce by dividing the rhizome
These include:
- stonecrop
- stonecrop
- sedum red spot
When the plant grows widely, it can be divided and planted in different places, filling the free space with them.... To do this, in early spring, you will need to remove the mother plant from the ground, shake off the ground and divide the bushes in such a way that each division has its own growth points and buds.

Sedum red dot
Places of cuts or divisions of the root system are sprinkled with activated or charcoal, can be treated with special fungicides. Now, before planting in a new place, the cut is recommended to be kept in a cool room for several hours so that the slices dry out a little.
Is sedum useful for humans? What is its use?

The fleshy leaves of sedum contain many nutrients. The vegetative part of the plant is used as a medicinal raw material.
Stonecrop chemical composition:
- vitamins
- tanning stuff
- alkaloids
- coumarins
- flavanoids
- glycosides
- saponins
For medicinal purposes, it is necessary to harvest the aerial part during flowering. For treatment, decoctions, tinctures in water and alcohol, healing extracts are prepared.
For the preparation of medicinal infusions and other means, it is important not to miss the preparation time, so that all nutrients do not "evaporate" from the plant.

Sedum white
For the treatment of diseases, all types of sedum are used, except for caustic... This variety should be used with caution or not at all.
Contraindications for taking sedum-based funds:
- pregnancy and lactation
- nervous irritability
- hypertension
- children under 18 years of age
Preparations, which include sedum, have a tonic, anti-inflammatory, healing, analgesic, stimulating, diuretic and laxative effect.
Ingestion is indicated for such diseases as scurvy, atherosclerosis, malaria, nervous shock, constipation, gout. In case of burns, it has a wound healing effect.
Read also:
- Succulents: description, features of growing from seeds, planting, reproduction and care at home, useful properties (70+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
- Types and varieties of home cacti with names and descriptions, care (100+ Photos): flowering, with leaves and without thorns + Reviews
- Coleus: description, types and varieties, growing from seeds, planting and care at home and in the open field (80+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
- Schlumberger is an epiphytic plant, the flowering of which is contrary to all the canons of nature. Features of growing a Decembrist at home (65+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
- Bulbous Flowers Catalog: Description 21 Varieties, for growing in the open field and at home (65 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
8.4 Overall Score
Under good conditions, the plant is almost never exposed to diseases and pests. The only thing is that when caring for stonecrop, it is necessary to constantly maintain its decorative appearance and carry out formative and rejuvenating pruning. Thus, you can get a gorgeous tapestry of beautiful, multi-colored, fleshy sedum foliage with luxurious caps of pink, purple, snow-white, yellow-orange, carmine flowers.
Add your review
A beautiful flower garden is a harmonious and skillful combination of plants on a certain plot of land. Groundcover flowers help fill in the gaps in the ground and create the appearance of a whole picture. Therefore, they are often used in landscape design. Stonecrop flower is one of the brightest and most attractive representatives of this species, although in addition to ground cover varieties, there are also undersized bushes. Before decorating your garden with such plants, you should learn more about them, understand the variety of species and understand the principles of care.
Brief description of ground cover plant
The main feature of the sedum plant is that it can grow almost anywhere. The unpretentiousness to the soil and the planting site makes the flower universal: it can decorate holes around trees, decorate curbs, close too large rockery stones or heavy hatches.
The sedum plant is planted in driveway parking lots, around playgrounds, along the house and in any space that you want to braid neatly and beautifully.
Stonecrop flower fits perfectly into flower beds and rockeries, adjacent to other plants. However, you need to ensure that it does not grow too much and does not interfere with other colors.
Today, no one can say for sure how many types of stonecrops there are, but it is known for certain that there are at least 600 varieties. Several factors contribute to the rapid spread and development of new species. Firstly, sedum, or as it is also called Sedum, can grow in soil of any composition; it does not need special care or greenhouse conditions. Even a soil poor in minerals is suitable for this plant, so it can grow anywhere. Fields, meadows, steppes, mountain ranges - stonecrop gets along well everywhere.
Secondly, stonecrop is easily propagated by shoots and cuttings. Moreover, a dug or neatly cut stalk can be without water for a rather long time, and then be planted and survive. This means that many gardeners bring a tenacious plant to their flower beds, it takes root, grows, and the owner does not always know its name, species or variety.
Many sedum varieties get along well with each other, interbreed and bred on their own. Due to which new plant species appear
To try to differentiate at least the main varieties of sedum, you can learn to distinguish between them in appearance and description.
Variety of sedum types
It is almost impossible to describe all varieties of sedum. However, in latitudes of temperate climates, the same species are often found. Having studied their description, you can learn to distinguish between them and recognize them.
Sedum caustic
This type of sedum is taken from the wild, and to this day it grows in natural conditions. At the same time, low bushes also feel comfortable in personal plots. Growing, caustic sedum forms a solid green dense carpet, which turns bright yellow during the period of abundant flowering - from June to July.
Moreover, its height, as a rule, does not exceed 8-10 cm.
The bright yellow rug expands quickly in size because it can adapt to any soil and growing conditions
Sedum caustic is unpretentious to the conditions and regularity of watering, but prefers well-lit places. Therefore, it takes root well in the steppe area, expanding to all available space.
Another feature of this ground cover variety is the value of the honey plant, bees love it.
White variety
This type of sedum is similar to the sedum variety, but its star-shaped flowers have a snow-white color. The height of a solid rug is also low - up to 7-8 cm. If this variety of sedum is planted in partial shade and watered regularly, its leaves will have a dark, saturated green color. Whereas in the sun, under the influence of direct sunlight, they acquire a reddish tint.
White fragrant flowers, which rise above the stems to a height of 10-15 cm, are distinguished by the white sedum variety.
Both varieties of sedum and white look great along the paths and in the space around the trees, covering the ground first with a green and then a flowering carpet. In addition, its unpretentiousness and vitality captivates. Therefore, many gardeners and landscape designers often use it in the decor of their personal plot.
Evers' sedum
Sedum Evers belongs to shrub plant varieties. The height of its shoots can reach 40 cm, and by the nature of its growth and reproduction, it resembles not a solid carpet, but separately growing bushes. The dense leaves of Evers have a delicate greenish-gray tint.
This variety blooms in July-August with small pink-red buds. which rise above the main bush on long thin peduncles
An important feature of them is their good shearing resistance and fast renewability. Therefore, they are often used as a curb plant or in alpine slides and rockeries with stones. Sedum Evers does not like excessive moisture and grows well on poor soils.
Sedum prominent
The shrub of the Sedum variety can reach a height of up to 80 cm, although as a rule these plants are 50-60 cm. It blooms in the middle of summer and retains a beautiful blooming appearance until the beginning of autumn. This type of plant is used to decorate flower beds and flower beds, where the bush occupies a central place, without clogging other flowers with active growth. Feels good in a sunny area, unpretentious to irrigation conditions.
One of the largest sedum varieties is the prominent sedum - with tall, straight stems, on which lush buds of crimson-red flowers bloom
Sedum hybrid
The sedum hybrid belongs to evergreens and calmly tolerates the winter frosty period. Blooms in bright yellow from August to September. Small buds rise on straight peduncles at a height of 20-25 cm above the bush. This variety tolerates drought comfortably without losing its freshness and attractive appearance.
The hybrid variety Seduma forms dense light green-green rugs, since its stems are well creeping and rooted independently in the available space of the soil
Another feature of hybrid sedum is the ability to stand for a long time in a vase of water. In place of small inflorescences, brown fruits appear, which look original in bouquets and compositions.
The variety is false
Stonecrop leaves have a rich green hue, which becomes reddish-bronze with the onset of the first frost. The stems of the plant are prone to lignification, and when they come into contact with the ground, they sprout roots. Due to this, the sedum multiplies rapidly, occupying all the territory available to it. The resulting rug looks looser than other sedum varieties. Its height is 15-18 cm.
The variety got its name because of the changing color of the leaves, thanks to which it is also called tricolor.
At the beginning of summer, sedum false blooms, and depending on the growing conditions, small buds can be of different colors: from creamy white to dark red and raspberry. Stonecrop blooms until August, keeping the attractive appearance of the flower garden for a long time. It feels most comfortable in the open sun, but it also tolerates partial shade. It is permissible to grow this variety in containers, but on condition that their sizes are spacious enough.
Stonecrop Kamchatka
Kamchatka sedum belongs to ground cover plants, but forms small bushes 20-25 cm high.Their abundant growth and dense arrangement with each other creates the appearance of a solid green rug. In the middle of summer and until the end of August, it blooms with bright yellow-orange buds, from which small scarlet fruits are obtained by the beginning of autumn.
Stonecrop variety, which is more prone to changes in colors and shades than others. Green leaves turn reddish in bright open sun
Kamchatka sedum is one of the few varieties that does not tolerate drought well and needs regular watering. The best landing site for him would be a shaded area. The more the serrated leaves of Kamchatka stonecrop turn red, the more difficult it is for the plant to tolerate the constant direct sun.
Sedum spatulate
Most varieties of sedum are perennial plants, but shovel-leaved sedum loses its attractive appearance every year. Over time, its voluminous rosettes thin out, become loose and shine through with empty space. Whereas at a young age it is distinguished by dense fleshy greenish leaves with a pink tint along the edge of the leaf.
One of the few Sedum varieties that can be grown in a container, limiting the space for propagation and growth
Stonecrop rugs grow low - up to 10-12 cm, flower stalks rise by another 5 cm above them, which bloom in bright yellow from May to June. Such a bright color of leaves and buds is widely used to decorate topiary and alpine slides in early summer. For the winter period, shovel-leaved sedum is best sheltered from frost, otherwise its thinning will begin as early as 1-2 years of growth.
Sedum multi-stemmed
The sedum plant is multi-stemmed - these are small bushes only 8-10 cm high, which grow and form a dense soft mat. The impression is enhanced by the structure of the leaves - fleshy and dense to the touch. Thin creeping stems intertwine to form a tangled, solid carpet, but the growth process is not rapid.
One of the most unusual and bizarre varieties of stonecrop, which is distinguished by the original shape and color of the leaves. Greenish-gray leaves in the open sun acquire a pink tint
The multi-stemmed sedum blooms in late summer and until the end of September, bright white-pink inflorescences remain on the tops of the bushes. It does not tolerate excessive moisture in the soil, and for the winter period it needs shelter from frost.
Siebold's variety
Siebold's sedum belongs to ornamental plants that look attractive in rockeries, on alpine flower beds due to the variegated color of the leaves. However, in the second or third year, the color becomes more and more uniform and dull. Therefore, this variety needs constant transplantation, renewal and multiplication in order to maintain its decorative properties.
Another variety of sedum that amazes with its bright beauty in the first year of growth, and loses its external charm as it grows
Soft creeping stems take root in the ground on their own, thanks to it a dense carpet 10-15 cm high is formed. Peduncles rise above it to a height of another 8-10 cm. They appear in October, have a bright yellow color and decorate autumn flower beds well at the end of the season. A feature of the Siebold variety is frost resistance, therefore, the plant does not need to be covered for the winter.
Sedum Telefium
By its appearance and growth method, stonecrop is a shrub - its thin tall stems reach a height of 50-70 cm. Dense fleshy leaves are evenly located on the stems. The peduncle is formed into a dense ball from light red to maroon color.
Another name for this variety is stonecrop, since it is one of the most common and popular plant species in temperate latitudes.
Forster's sedum
The height of the sedum of this species, as a rule, does not exceed 10 cm, due to which Forster's sedum is often decorated with flower beds, borders and rockeries. Tall yellow peduncles look bright and unusual, which rise 25-30 cm above the general level of grayish-green foliage.Due to its miniature size, Forster's sedum is often grown in pots and containers, especially since it does not grow quickly.
One of the most unusual in appearance plant varieties, resembling a small coniferous shrub, the creeping stems of which form wavy curls
This sedum variety, like some others, loves moisture and regular watering. In dry weather, it withers, loses the saturation of the color of the leaves, the stems with peduncles become soft and fall down.
Variety Spanish
There are several types of this variety of ground cover plants, which differ in the color of the leaves. They can be light green, gray with a pink tint, pale yellow and even purple. It is this property that landscape designers use, planting several different types of Spanish sedum on the same flower bed.
Another representative of undersized miniature bushes is Spanish sedum. Attracts with neatness and grace of thin leaves
The miniature sedum variety blooms with the same small white and light pink flowers that densely cover a curtain 10-15 cm high. The Spanish sedum retains its color for two months in June and July. After that, fruits are formed on the peduncles, which are independently sown into the ground at the end of August. If the stonecrop does not have enough moisture, it dries up by autumn, and new seeds will sprout next spring.
In this video, the authors talk about the basic rules of flower care:
Thus, the variety of species of sedum plant allows you to choose any options for your garden or flower garden that go well with each other and with other flowers. It is important to understand that you can plant next to those varieties that prefer the same care conditions, for example, drought-resistant, or vice versa, requiring regular watering. Then the flower bed will look attractive and delight its owner throughout the warm season.
What are sedums?
Among the variety of sedums there are annuals, biennials and perennials, herbaceous, semi-shrub and shrub forms... It can be ground cover, similar to flowering rugs, varieties, ampelous or erect plants.
 Sedum leaves are characterized by fleshiness, which allows plants to survive in difficult climatic conditions, but the shape of the leaf plate differs. You can find such variations:
Sedum leaves are characterized by fleshiness, which allows plants to survive in difficult climatic conditions, but the shape of the leaf plate differs. You can find such variations:
- Balloons.
- Kegs.
- Needles.
- Spatulas.
Sedums have a variety of flower shapes and colors... In stonecrops, they are small, white, yellow, pale pink and crimson in color, resemble small stars. And among seducers - in the form of bells, but the same color scheme. Flowers in sedums are collected in flat inflorescences (dense or loose).
Further, you can familiarize yourself in more detail with the names and photos of indoor sedums, as well as varieties grown in gardens and other natural conditions.
Groundcover
A very popular plant variety among gardeners. It is very convenient to use when you need to decorate the voids in flower beds or arrange the trunks of garden trees. They got their name for the fact that, growing, they cover all the free land with a continuous low carpet, above which, during the flowering period, flower stalks with numerous small inflorescences rise.
Groundcover sedums can be found both in the wild and in flower beds.... The most prominent representatives are:
- Sedum Lydian (Sedum lydium).
- Sedum False (Sedum spurium).
- Sedum White (Sedum album).
These plants can be found both in the wild and in flower gardens.
To grow stonecrop, you should choose not very rich soil., or artificially limit the area of their growth. Otherwise, these plants will capture all the free space around.
With erect stems
Plants from this group can form dense clumps, but more often only a dense bush is formed, which falls apart by the time the flowers bloom.
Prominent
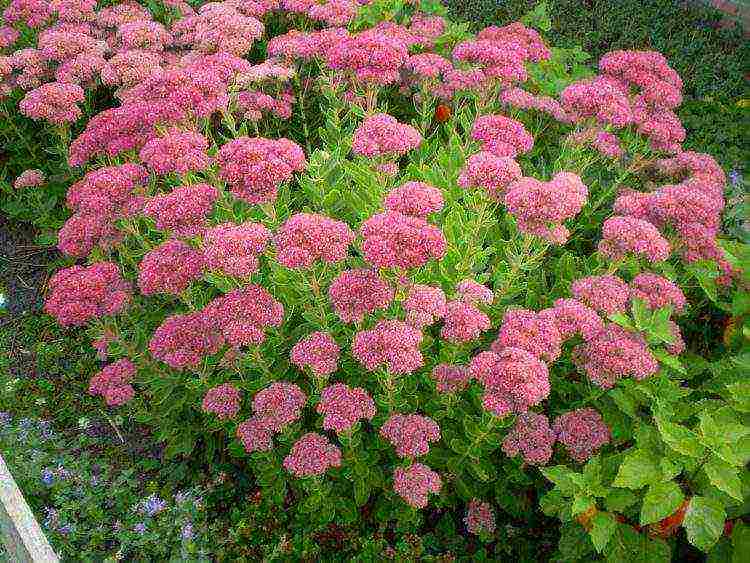

Prominent (Sedum spectabile) belongs to the seducers - Prominent ochiner (Hylotelephium spectabile)... One of the most common types with erect stems. Plant height 30-60 cm. Inflorescences are large, dense, consists of small pinkish or purple flowers. The leaves are large, oblong, with a bluish tint. Blooms from late August until frost.
We recommend watching a video about the features of sedum (sedum) prominent:
Tenacious
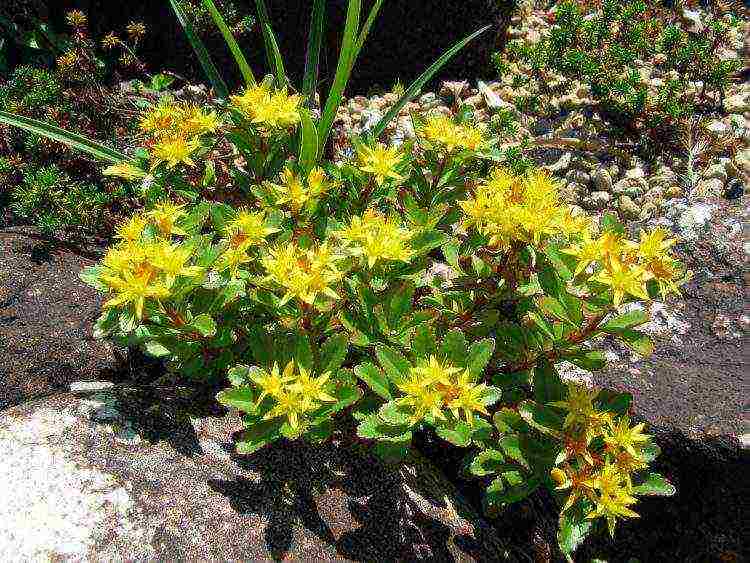

Hardy (Sedum aizoon) is a perennial herb with strong stems, 25-40 cm high. The rhizome is short and thick. The leaves are rhomboid in shape, with small teeth along the edge. The flowers are colored yellow-orange. In natural conditions, it is found in the Far East and Siberia.
Important: Sedum tenacious - a poisonous plant.
Three-leafed fat woman

Now this type of three-leafed, pururic and purple plant is called - three-leafed sedum (Hylotelephium triphyllum).
The plant is erect, 40-60 cm high. The foliage is juicy, fleshy, oblong. The color of the leaves is green or with a purple tint. In winter, the aboveground part of the plant dies off. It blooms in the second half of summer with pink or purple-red flowers, collected in large inflorescences. The plant is unpretentious, tolerates insufficient lighting and soil poverty.
Ordinary

Ordinary, or telephium (Sedum telephium) - perennial with tuberous roots and single, erect stems 40-60 cm high. Leaves are oval-oblong, serrated along the edge. The flowers are red or crimson, collected in a dense inflorescence. Blooms in the second half of summer. The plant tolerates winter well and is distributed throughout almost the entire territory of Eurasia.
Jose Obergin

"Jose Oberdzhin" (Sedum Jose Aubergine) - a perennial plant with a height of 30-40 cm... The leaves are wide, burgundy with a purple tint. The shoots are powerful, erect. It blooms in August-September with small orange-red flowers with white dusting, collected in large loose inflorescences. It is very decorative, unpretentious, tolerates drought and low temperatures well.
Ice Raffles

The Ice Ruffles sedum has strong erect shoots of red color and 30-50 cm in height. The leaves are dark green with a light border along the edge and a red border. Closer to autumn, the leaves turn bronze-red. It blooms from July to September with small cream-colored flowers, collected in dense corymbose inflorescences. Grows well in sunny places, winters without shelter.
Moonlight Serenade
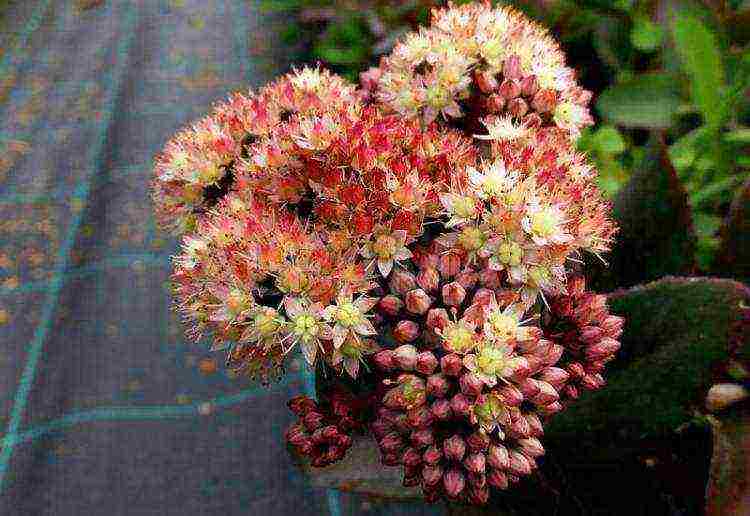
Herbaceous plant about 45 cm high. Stems are erect, foliage is blue-green, turns crimson with age. The leaves are obverse-lanceolate in shape, with small denticles at the edges. The inflorescence is burgundy, the flowers are creamy pink. Blooms from July to October. Sedum loves open, sunny places and moderately fertile soil..
"Bezday Party"

Sedum "Bezday Party" (Sedum Birthday Party) - a perennial plant with stems up to 30 cm high. The foliage is fleshy, purple with brown edges. Blooms profusely in the second half of summer. The flowers are bright pink, collected in large lush inflorescences. The plant grows well in any soil, loves the sun, but tolerates planting well in a shaded area. Does not require shelter for the winter.
Ruprecht's perennial

Ruprecht's ochiner (Hylotelephium decumbens) - perennial with densely leafy shoots 20-40 cm high... Leaves are ovoid, often hugging the stem. It blooms in July - August with white-pink, yellow-white or greenish-white flowers, collected in wide corymbose inflorescences.
Big ochiner

The ochiner large, the largest (Hylotelephium maximum) is a perennial herb with erect stems 60-80 cm high. The leaves are dark green, elongated-oval with a rounded base, slightly toothed along the edges. Blooms from July to September. Small, white-pink flowers are collected in dense corymbose-paniculate inflorescences.
Unpretentious varieties
Sedum is unpretentious in care... Easily adapt to the proposed growing conditions.But there are also particularly tenacious species that are even recommended to grow, for example, on poorer soils. Otherwise, they will fill the entire garden, oppressing neighboring plants.
Pungent
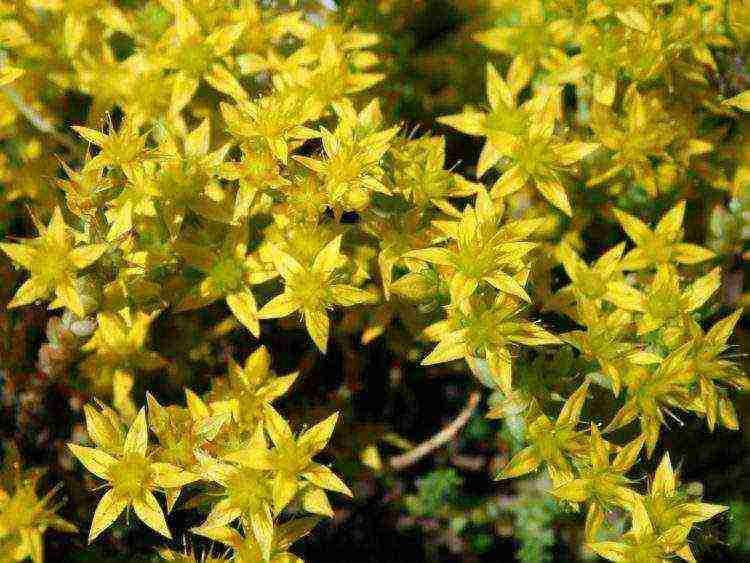

Sedum acre (Sedum acre) is a creeping perennial plant with a large number of thin, branched stems, up to 15 cm high. The leaves are small, fleshy. There are forms with white and yellow leaves. It blooms almost all summer, forming a colored carpet of golden-yellow star-shaped flowers collected in umbrella inflorescences.
This type of sedum is very tenacious, quickly and easily reproduces by self-seeding, prefers dry, elevated places with sandy soil. The sedum (Sedum acre) can release toxic substances that oppress neighboring plants.
The popular variety is Yellow Queen. Leaves are golden green, very densely arranged.
We recommend watching a video about the features of caustic sedum (sedum):
White
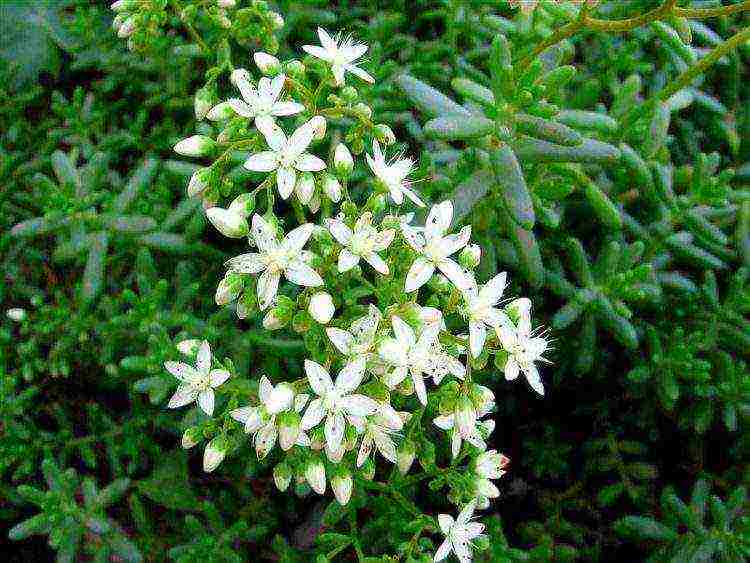

White sedum (Sedum album) - ground cover perennial, forms a flat curtain 15-20 cm high... The foliage is green or red-green, fleshy. Blooms in June-July. The flowers are small, star-shaped, white-pink, collected in large paniculate inflorescences on long reddish stems.
We recommend watching a video about the features of white sedum (sedum):
Spanish
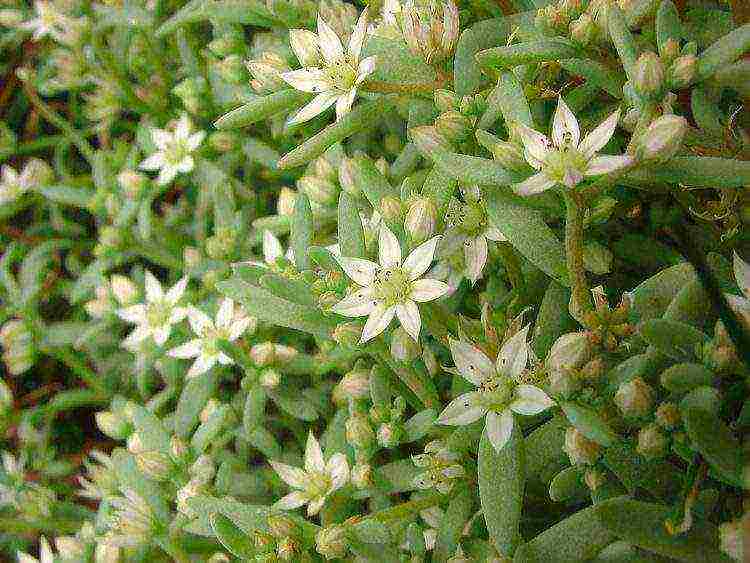

Sedum Spanish (Sedum hispanicum) is a biennial herb. It grows quickly on rich soils. It reproduces well by self-seeding. Forms a curtain 5-15 cm high.
The leaves are pale green, light yellow, pinkish gray or purple, depending on the variety. The flowers are white or pinkish. Blooms irregularly and sparingly in June-July. In the middle lane it hibernates badly, often freezes out or vomits out. Mainly Sedum spanish is used as a seasonal ground cover plant..
Bent
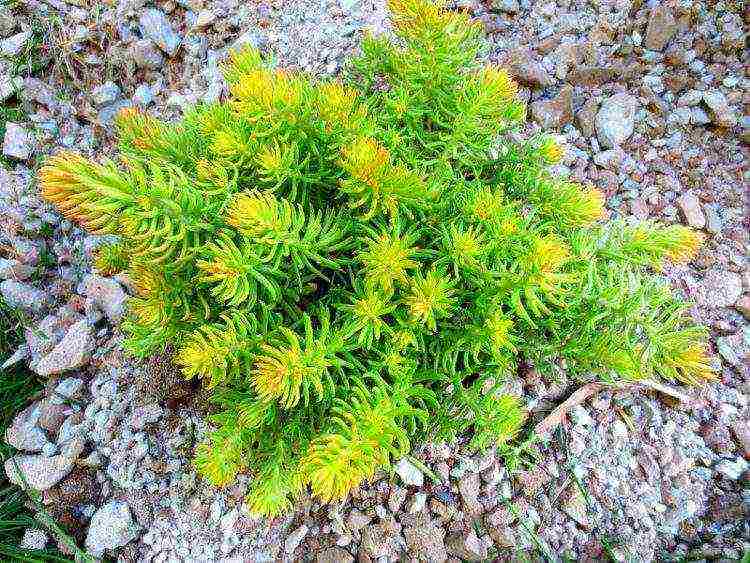

Sedum folded or rocky (Sedum reflexum) is a perennial herb with weakly branched shoots up to 15-25 cm high. Leaves are fleshy, glaucous, subulate. Blooms in June - July with yellow corymbose inflorescences.
Popular varieties:
- "Angelina"... Leaves are green-yellow with orange tints. In the fall, there is more orange.
- "Blue Spruce"... Sizo foliage is blue.
- "Cristatum"... The stem is strongly thickened and flattened. Leaves are light green, darken by autumn.
- "Sea Gold"... The leaves are gray with reddish-lilac tips; the tips of young shoots are creamy during growth.
- "Atropurpurea"... In sunlight, young leaves become pronounced purple.
Hexagon
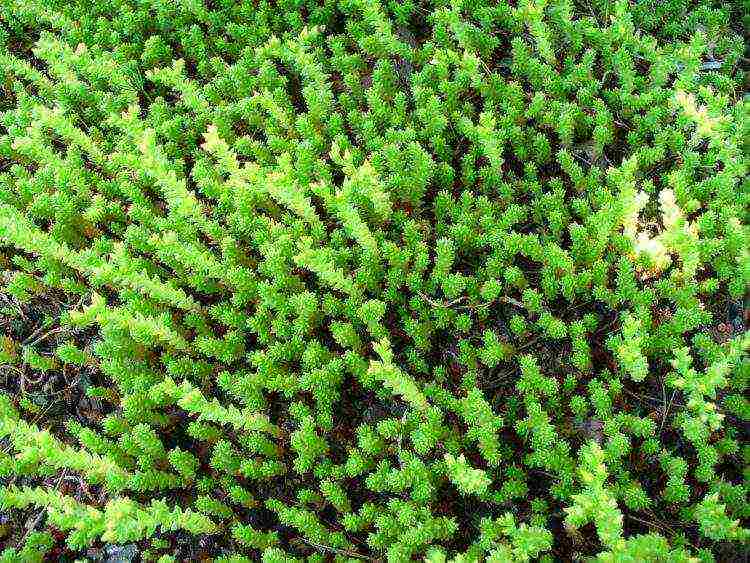

Sedum six-sided (Sedum sexangulare) - an evergreen perennial 15-20 cm high. Shoots are creeping and creeping, slightly raised at the tops. Leaves are fleshy, subulate. The color of the leaves is juicy green, when grown in bright sunlight - reddish. Blooms in July. The flowers of this sedum are yellow and are collected in dense inflorescences.
Red-colored
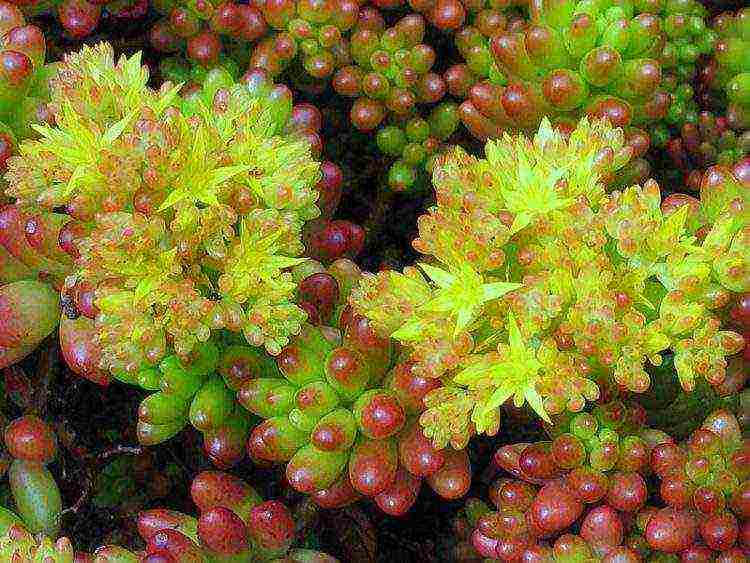

Red-colored sedum (Sedum rubrotinctum) - perennial undersized dwarf shrub with creeping shoots... Leaves, fleshy and reddish, are located in the apical rosettes. The plant acquires a more saturated red hue in bright sunlight. Flowering begins in mid-spring. The flowers are bright yellow with a reddish tint.
Important: Sedum red-colored is poisonous and irritating when ingested or touched.
A popular variety is "Aurora". The variety "Aurora" (Aurora) leaves color pearl-pink with a silvery sheen.
White-pink
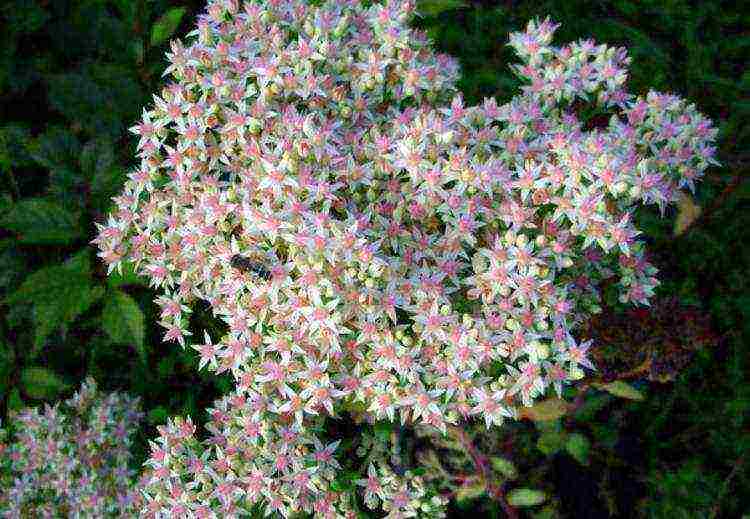

White-pink sedum (Sedum alboroseum) - perennial herb, 35-60 cm high... The stem is powerful, the leaves are oblong-ovate. The inflorescence is umbellate-paniculate, consists of small flowers of white or pink color. Flowering occurs in July-August.
Rare specimens
Lydian
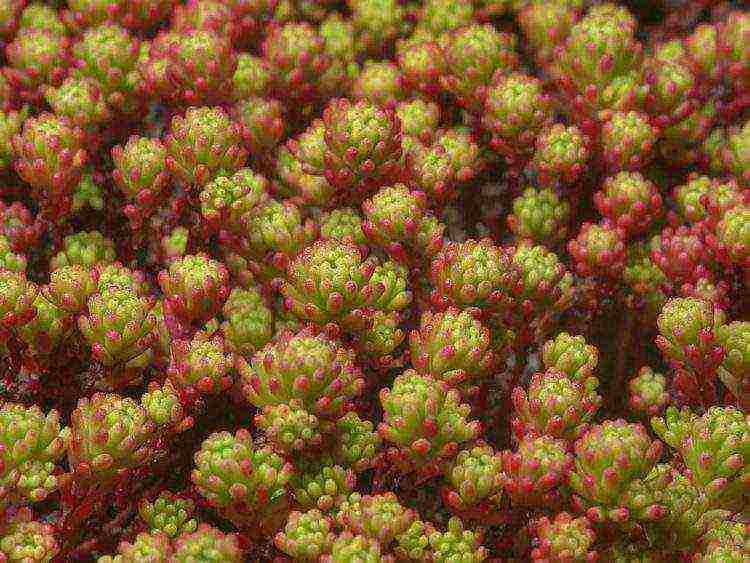

On poor soils, Lydian sedum (Sedum lydium) grows well. It is a perennial evergreen plant. Forms a carpet 4-5 cm high with creeping shoots. The leaves are green, with a large amount of sunny color they turn red. The flowers are white and pink.Flowering begins in May.
Escaping
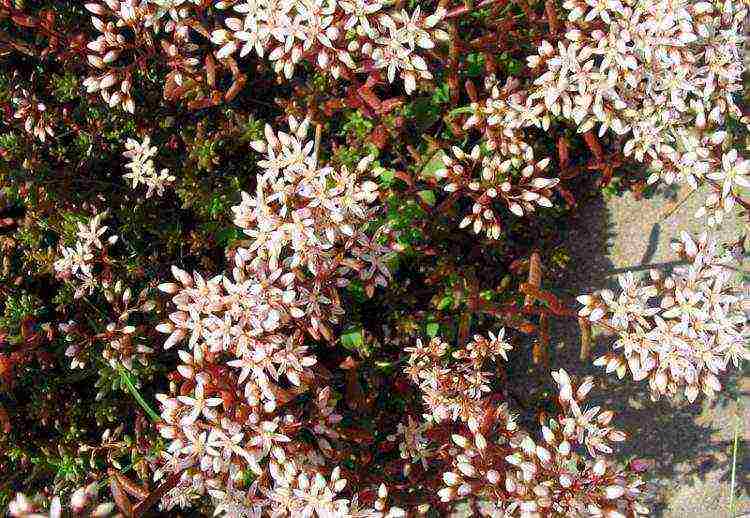

At the present time, the sprouting sedum belongs to the genus "Zapuchnik" (Petrosedum stoloniferus)... Branched shoots, easily take root during transplantation and quickly grows, forming continuous rugs up to 10 cm high. Blooms in June - August. On peduncles 15 cm high, pale pink star-shaped flowers are located.
Plants for containers
For growing in containers and at home, ampelous forms of sedum are most often used. These plants are unpretentious and tolerate the dry air of apartments well, thanks to the moisture reserves in their fleshy leaves.
Small-leaved Makina
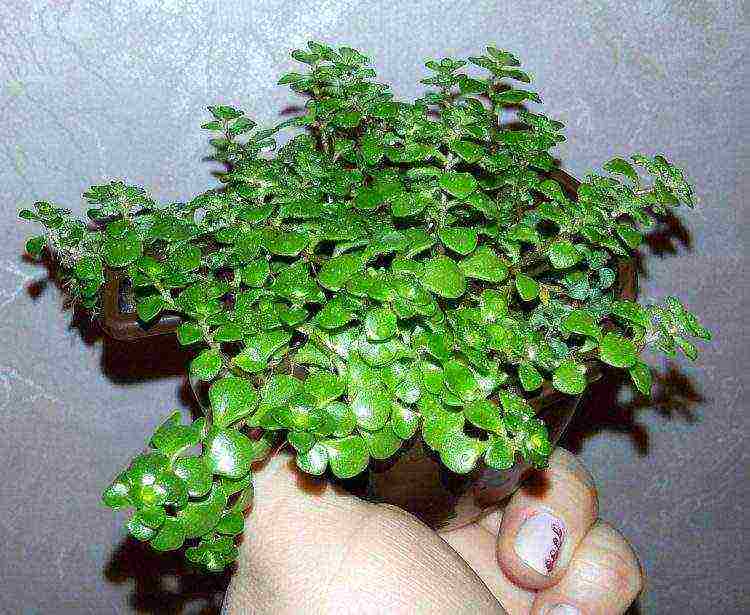

Sedum makinoi is one of the smallest sedum varieties... Used as an ornamental deciduous plant, and flowers that appear in winter are cut off. When transplanting, the plant quickly takes root and covers the entire surface of the container. The color of the leaves may vary depending on the cultivar.
Oregon
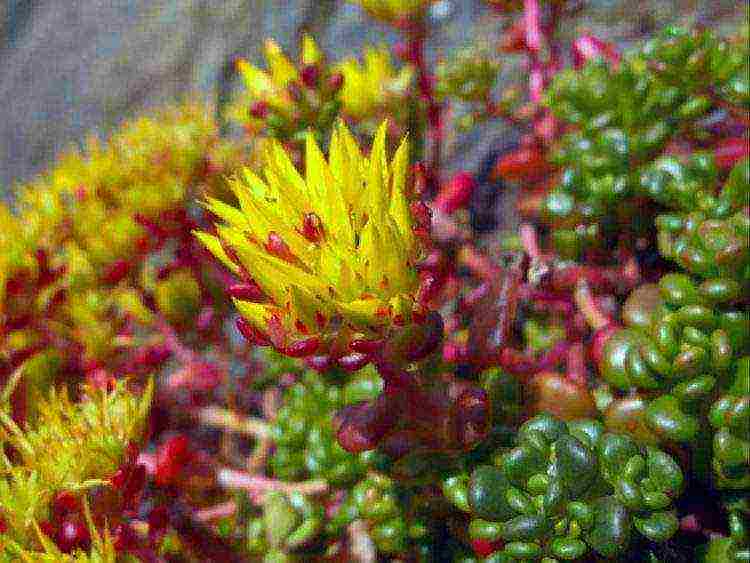

Sedum oreganum (Sedum oreganum) grows in the wild on rocky ledges. Forms dense rugs 10-15 cm high. Shoots are fragile, covered with naked, fleshy rounded leaves. In the sun, the leaves turn from green to red. Blooms in July-August. The flowers are small, yellow-orange, collected in small inflorescences on short peduncles.
We recommend watching a video about the features of sedum (sedum) of Oregon:
Hybrid "Yellow Xenox"

The height of the hybrid sedum "Yellow Xenox" (Sedum hybride Yellow Xenox) reaches up to 40 cm... Leaves are dense, fleshy, greenish-lilac in spring, then dark purple. Inflorescences are corymbose, flowers are creamy yellow, small. It blooms from August to October. Suitable for sunny places with poor soils. Yellow Xenox is prized for its drought tolerance and unpretentiousness.
Conclusion
Sedums can be found in gardens and greenhouses around the world. With their unobtrusive beauty, unpretentiousness, variability of colors, they attract more and more fans. Among the variety of species and varieties of stonecrop, everyone can find the plant that suits his garden.


