Content
- 1 General information about the plant Physalis vegetable
- 2 Growing and care
- 3 Physalis in cooking
- 4 Which plant to choose
- 5 Growing physalis seedlings
- 6 Features of growing physalis.
- 7 The use of physalis in cooking
- 8 Physalis is useful for a hundred diseases ...
- 9 One of the three physalis is good for us
- 10 Seven principles of growing physalis
- 11 Physalis vegetable and physalis berry - varieties
- 12 Physalis - growing and care: advice and reviews
- 13 Physalis types
- 14 We plant physalis
- 15 Growing physalis
- 16 Growing physalis in the regions
- 17 Reviews of gardeners about growing physalis
 Physalis vegetable is an unpretentious plant that gives people the healing properties of its bright fruits.
Physalis vegetable is an unpretentious plant that gives people the healing properties of its bright fruits.
It is not clear to the taste whether it is a fruit or a vegetable, especially since in its raw form, it does not have pleasant taste.
But when cooked it has an exquisite unusual taste.
It is pleasant to consider Central America as the birthplace of vegetable physalis.
General information about the plant Physalis vegetable
The name "physalis" is given as a "bubble" from the Greek language.
It is also known by other less common names such as blister grass, mexican tomato, earthen cherry.
Physalis legend
There is even a legend about the origin of Physalis.
It tells how the dragon ate the sun. It became dark in the world and everything began to perish little by little. One young man volunteered to defeat the dragon, he took a lantern and went to battle for the return of the sun.

When he defeated the dragon, and the sun burst out, then from the bright light he covered his face with his hands, dropping the lantern to the ground. But the lantern did not break, but became a physalis berry.
Description of varieties
Now there are about 117 varieties of this plant, it belongs to the Solanaceae family. It reaches a height of 50-100 centimeters, has a powerful branched root system, straight stems and thin oval leaves with jagged edges. Of the large variety of species, only 10 of them are suitable for food.
It is customary to distinguish the berry and vegetable group.
Berry group
Physalis berry varieties are of South American origin. They differ in small pea-sized light green fruits, have a sweet taste and a bright aroma.
Their fruits can be eaten raw or used to make jelly, compote, preserves and other sweets.
There are two popular varieties:
Peruvian physalis - a tall species, has pubescent leaves, demanding on the thermal regime, ripens quite late, therefore it is more often grown only in the southern regions of Russia. Fruits are amber in color. Weighing 7-12 grams.
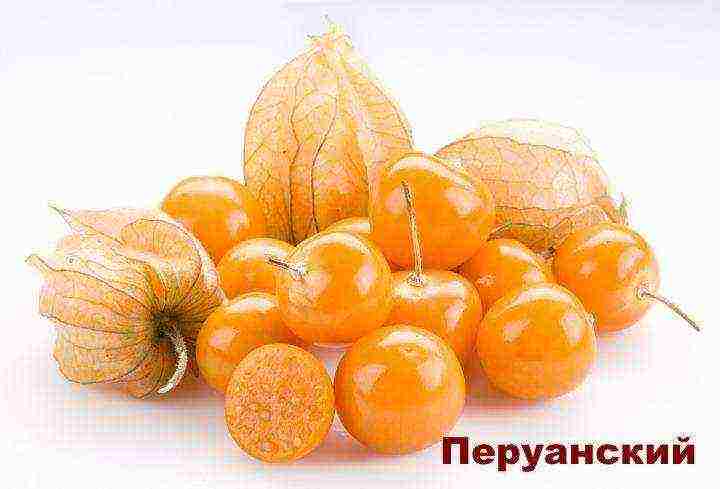

Strawberry Physalis ripens much faster, therefore it is more common in Russia, and not only in the south.

Vegetable group
Vegetable physalis - an annual self-pollinating spreading plant up to 80 centimeters high. Yellow-green flowers appear in the forks of the stems, and the fruits are formed in the flower cups.
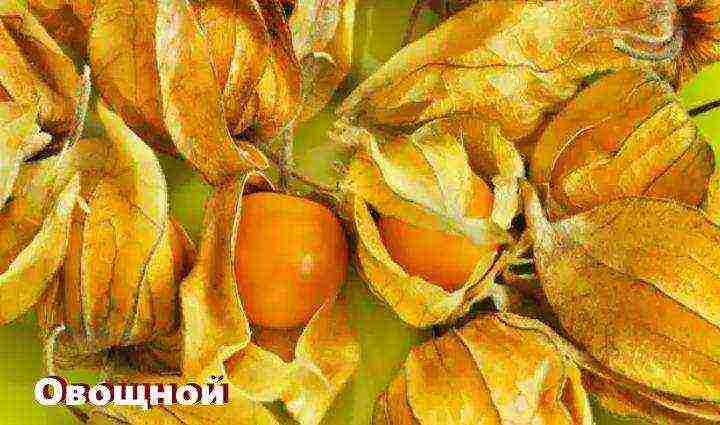

The fruits are similar to small tomatoes and have a variety of colors, you can find yellow, green and even purple berries weighing up to 30-70 grams.

This is one of the most productive types of physalis. Every year it forms up to 5 kg of berries from one bush, which is about 200 units of fruits.
Vegetable physalis are also called Mexican, since Mexico is their homeland. Among them, there are both tall (up to a meter in height) and creeping plants.
The most popular varieties:
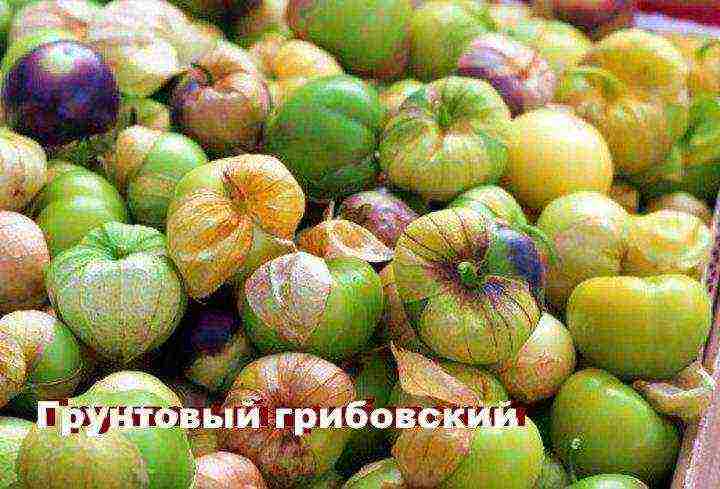
- Ground mushroom - grows up to 80 centimeters in height, has semi-erect shoots, is resistant to cold, ripens early, the fruits are light green sweet and sour in taste, weighing up to 80 grams,
- Moscow early - ripens very early, is a semi-lying shrub, has sweet fruits of light yellow color, weighing 50-80 grams.
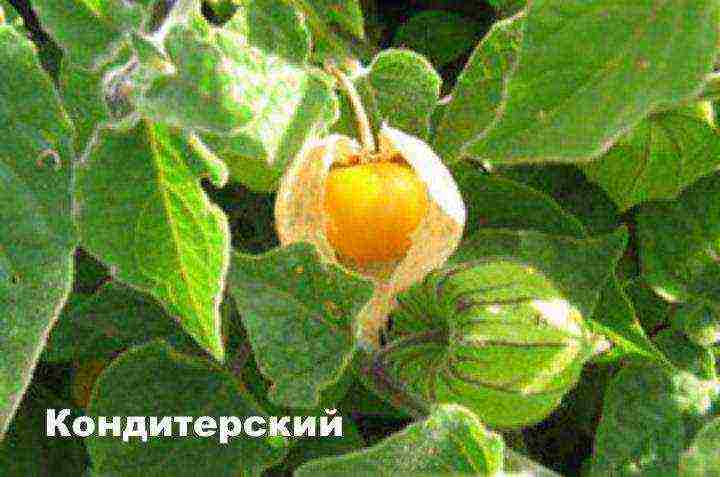
- Confectionery - a highly bushy plant, has sour green fruits, weighing 50-80 grams.



Growing and care
Seat selection and landing
Almost any site is suitable for growing physalis, but if there is an opportunity to choose, then give preference to a sunny site.

Self seeding
Before planting, the plant must be cleared of weeds and loosened well. Physalis can be grown as a self-sown plant, simply by leaving the seeds in the ground from last year, but such crops must be thinned out as they germinate.

It is better to use this method no more than once.
Seedling planting
Physalis is best planted using seedlings. The most suitable time is the second half of April. Physalis seeds themselves are very small, so it is more often planted first in a flat container.
Seeds are evenly distributed over the soil surface, lightly sprinkled with earth. The soil mixture is the same as for vegetable seedlings.
Next, the container should be covered with glass or foil and left for a week, until the first shoots appear. After the appearance of three leaves, the plant can be transplanted into a personal container.

It is better to transplant it into open ground in May, when the plants will have 6-8 leaves. Seedlings are placed in the holes along with an earthen lump to the first green leaf, around the ground you need to tamp and water.
Plants are planted at a distance of 50 - 100 centimeters from each other. Manure and superphosphate must be added to the plant wells. Later, you can feed it with liquid and mineral fertilizers.
If you plant seedlings in the ground in the month of May, the harvest will be early enough.
Care rules
The conditions for growing physalis are quite simple:
- Water on time to keep the ground moist but not flooded
- Weed the weeds
- Loosen up the earth
- Fertilizers can be fed at your discretion.
- For growing branches, create a support or tie up
Pruning
The plant does not need pruning, as this can reduce its fertility, but you can pinch the plant in late summer or early autumn, which will accelerate the ripening of the fruits.
Harvesting
Once matured, flashlights are very easy to find; they change in color and begin to dry out. In this form, they can independently crumble to the ground, and remain unharmed for up to 10 days.

If you remove the berries unripe, they will easily ripen at home within a couple of weeks.
You need to harvest every week. The berries must be removed from the bush before the onset of the first frost, since in frozen form they will begin to deteriorate very soon. It is best to pick berries in dry weather.
If you plan to keep the physalis unprocessed, then before storing it you need to dry it well, and then fold it in a thin layer on lattice containers covered with paper.
Ripe berries can be stored like this for up to 2 months, and green ones - until early spring.
Physalis in cooking
Beneficial features
Physalis is used in folk medicine. Medicines are made from the fruits and roots of plants.
Infusion of roots helps with coughs and is a pain reliever.
Fruit use, both fresh and boiled, squeeze out the juice, insist and make ointments. Eating physalis fruits helps to normalize the digestive system and restores the acid-base balance.
It is recommended for those who have problems or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer, gastritis, cholecystitis), as well as diabetes or hypertension.
Compresses from a decoction or infusion of berries are good for bruises and swelling. For cystitis, colds and bronchitis, a decoction of physalis berries is also shown.
Physalis should not be used if ...
Despite all the usefulness of physalis, it has a number of contraindications.
Do not use:
- people with high acidity of the stomach
- people with low blood pressure
- pregnant and lactating women
- people who drink coffee
- people with allergies
- people using diuretics
The rest of the people are strictly forbidden to use physalis in green form without removing the wax film from the fruit, this can lead to food poisoning.
Physalis should be consumed only after removing the wax film, after blanching in boiling water for 2-3 minutes. The taste of vegetable physalis vaguely resembles the taste of tomato.
Varieties
The following varieties are most often used for cooking:
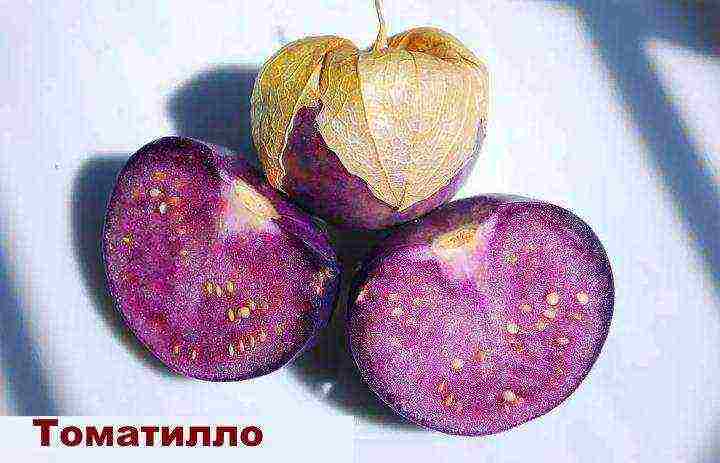
- Tomatillo,
- early Moscow,
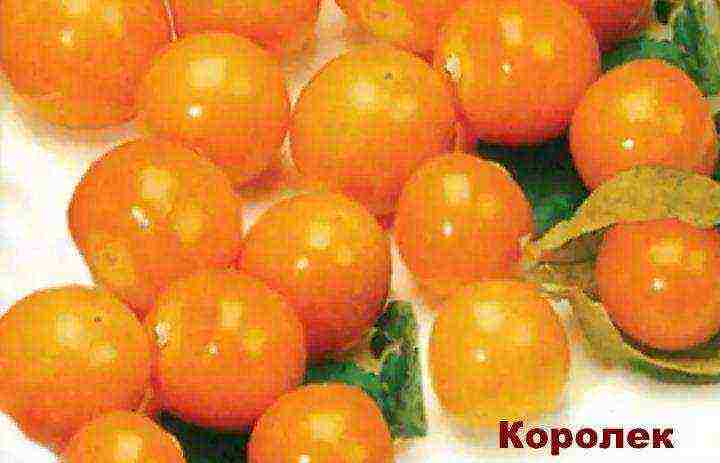
- Kinglet,
- Confectioner,
- Gribovsky soil.



Dishes
Physalis can be used to make:
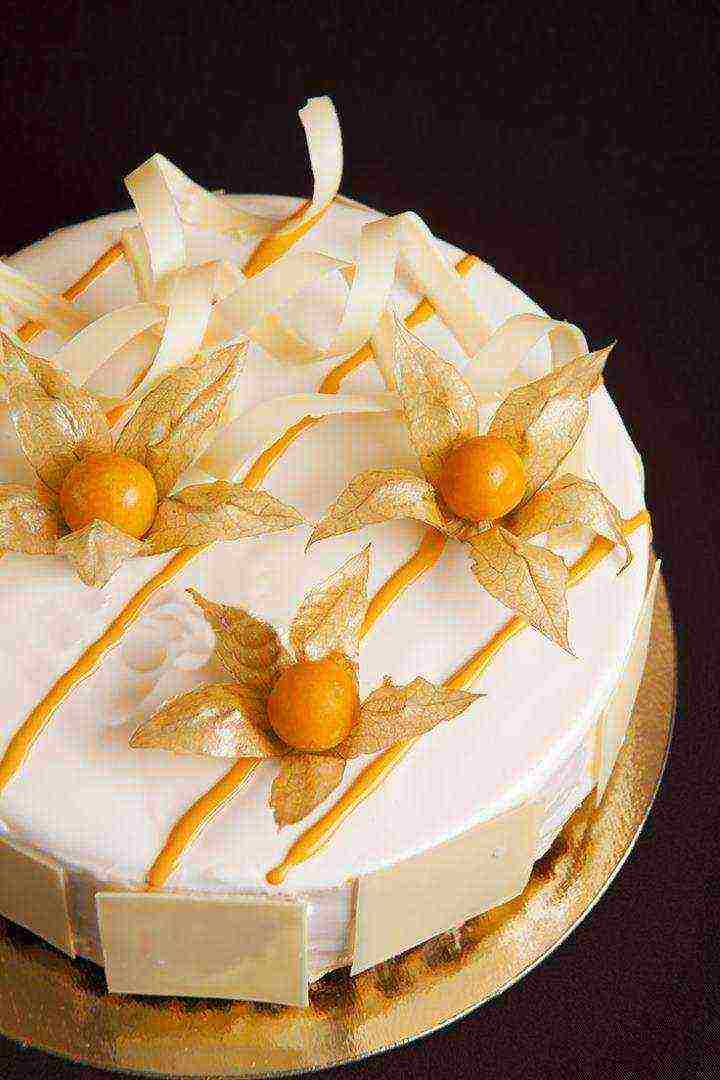 Sweet jam (from the Confectioner variety)
Sweet jam (from the Confectioner variety)- Pickled blanks (from Gribovsky or Moscow early)
- Candied fruits (from the Korolek variety)
- Physalis can be added to salads, first and second courses,
- decorate cakes,
- salt,
- dry like raisins
- make tea from it
- make tinctures
- caviar from berries
Recipes
Pickled physalis
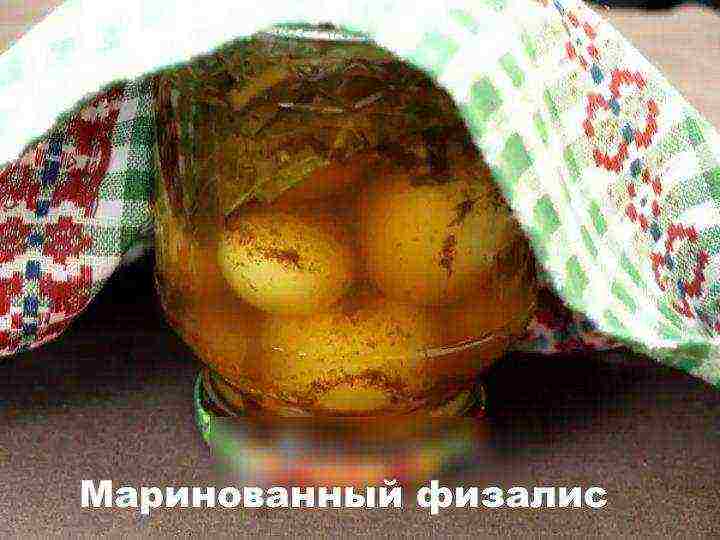

Products:
- physalis vegetable,
- water, sugar, vinegar, garlic,
- spicy herbs: parsley, celery, currant leaves
- at the rate of 50 grams per kilogram of physalis berries.
Preparation:
- Peel the berries from the adhesive film in boiling water, put in layers with spices in sterile containers.
- For the brine, heat water with sugar and vinegar to a boil, in proportion per liter of liquid - 2 tablespoons. vinegar and 50 grams of granulated sugar.
- Pour physalis with hot liquid, drain it after 30 minutes and boil it again.
- Pour chopped garlic into jars, pour hot solution and close the jars for the winter.
Physalis caviar

Products:
- Processed fruits,
- spices (salt, pepper), granulated sugar.
- onions, carrots.
The proportions of ingredients can be taken intuitively, depending on the intended volume.
Preparation:
- Fruits processed with boiling water need to be baked and chopped with a meat grinder or blender, add spices.
- Separately fry the onions, peppers and carrots, puree with a blender or meat grinder, add sugar and stir.
- Roll up in banks.
Physalis in tomato juice
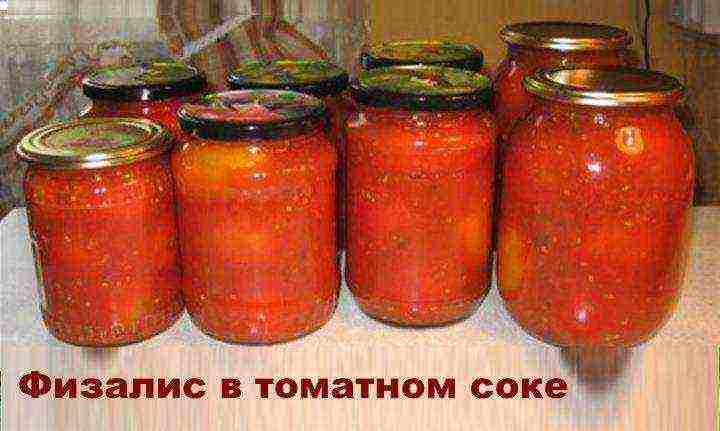

Products:
- Physalis,
- spices of your choice (horseradish root, currant leaf, dill, celery, garlic), 2 pieces of bay leaf,
- 2 tablespoons of sugar and salt,
- juicy tomatoes in an amount sufficient to obtain 1.5 liters of juice,
- black peppercorns a couple of pieces.
Preparation:
- Cut the tomatoes into small pieces, boil them for 20 minutes, rub through a sieve.
- Boil the fruits in boiling water for a couple of minutes to remove the sticky substance.
- The selected spices and herbs are placed in the jars, the physalis berries themselves, you can add greens and pour the tomato juice marinade.
- Close the cans, turn over and wrap them until they cool completely.
Physalis jam

Products:
For 1 kg of physalis, you need 0.5 liters of water and 1.2 kg of sugar.
Preparation:
- Berries processed with boiling water, dry in a colander and place in a saucepan.
- For the syrup, boil half a kilogram of sugar in half a liter of water for 3-4 minutes.
- Pour physalis with it, add another 0.5 kilograms of sugar after 3-4 hours and heat until the sugar is completely dissolved for about 10 minutes. Leave the syrup to settle.
- After 5 hours, add the remaining sugar and cook for 15 minutes.
- The readiness of the jam is easy to determine by its consistency, it should be dense and form a continuous stream when pulled, and the drops will not spread.
- Pour the jam into sterilized jars, roll up and sterilize again from 15-20 minutes.
Candied Physalis

Products:
For 1 kg of physalis, 0.5 liters of water and 1.2 kg of sugar are needed.
Preparation:
- Candied fruits are made from jam, the recipe for which is a little higher.
- Pour the jam into a sieve or colander until the syrup runs off.
- Take out the berries and spread them on paper or a baking sheet, send them to the oven at a temperature of up to 35-40 degrees until tender.
- Ready candied fruits can be sprinkled with powdered sugar and placed in a sealed container.
In this article, we examined the features of caring for physalis at home.
As it turned out, the plant is quite unpretentious in care and gives a very good harvest.
Knowing all the features of caring for physalis, you can please your family and guests with unusual and exotic dishes, which are as easy to prepare as growing the plant itself.
TOP proven suburban shops in the Russian Federation - Choose, buy!
- - "Garden and Vegetable Garden" - Gardens of Russia is an online store of seeds and seedlings.
- - "Becker" is a popular store of seedlings, seeds, bulbs, delivery all over Russia!
Physalis varieties
Rate this post
Which plant to choose

Physalis decorative, or Physalis Franchet (Physalis franchetii) is a "Chinese lantern" that grows in summer cottages. After flowering, its calyx, enclosing the fruit, grows into a thin ribbed red-orange wrapper. This species has perfectly adapted to our climate, easily endures Russian winters, and annually grows from shallow rhizomes. It is undemanding to soils, but prefers calcareous.
Physalis vegetable, or, as it is also called, Mexican - the most famous vegetable. He has large fruits (from 20-30 g to 150 g). Early maturity, cold resistance, high productivity. But the fresh taste of many varieties is quite average. It can turn out to be very pleasant only if the ripening conditions were ideal (sunny weather, a little rainfall), and the fruits set on the first inflorescences and ripened to the end on the bush. Marinated vegetable physalis is much better. And from the fruits, a wonderful jam is made, reminiscent of fig jam. Sweeter fruits in the varieties 'Moskovsky Early', 'Gruntovy Gribovskiy' and 'Korolek'.
Berry physalis inferior to vegetable fruit in size (1-3 g, in some domestic varieties - up to 9 g), but it is much tastier. But early maturity, productivity and cold resistance are low. Among the berry, first of all, it is worth mentioning physalis raisin, or pubescent (Physalis pubescens L.) - variety 'Surprise', Physalis Peruvian (Physalis peruviana L.), varieties 'Kudesnik' and 'Columbus', physalis florida (Physalis floridana) 'Philanthropist' variety.
Have physalis florida the taste is pleasant, sweet, almost without acid and any fruit flavor. With heavy precipitation during the ripening period, its fruits may burst. Jam from this physalis is similar to yellow cherry jam, it is advisable to add odorous geranium leaves to it for flavor.
Have physalis raisin the taste is more refined. It is sweet, with a slight sourness, pronounced fruity aroma and pineapple flavor. And the juice is similar to tangerine, but much richer. From raisin physalis, a beautiful yellow jam is obtained, but almost odorless.And this variety is also best stored: undamaged fruits in their sheaths can lie in a cool dry place for up to 3-4 or even 6 months, withering a little. And if you dry the fruits, you get a real raisin with a weak fruity aroma.
Physalis Peruvian not as sweet as raisin, but it has a bright fruity taste and aroma, and in terms of sugar and acid content, it is close to garden strawberries. The fruits of Peruvian physalis are very tender and therefore poorly stored, although there are exceptions. Berries of the 'Kudesnik' variety are sweet and sour, with a pleasant light bitterness, reminiscent of grapefruit. The fruits are flattened, very large, and the skin and flesh are brownish-orange. Columbus berries smell of strawberries so strongly that the aroma may even seem harsh; the juice tastes like orange, but the bouquet is brighter. It is best to dry the fruits of Peruvian physalis in an open oven at a temperature of 40-50 ° C - they easily rot in the air. Dried fruits resemble dried apricots, but again - the flavor is richer.

The Physalis genus has more than a hundred species. In our country, only three of them are widespread: strawberry physalis (Physalis pubescens), vegetable physalis, or sticky-fruit (Physalis philadelphica), and ordinary physalis, decorative, or garden (Physalis alkekengi). The latter, although inedible, but its overgrown cup looks spectacular in autumn in vases, when the case turns red. The fruit is poisonous as it is saturated with solanine.
Quick reference:
Growing physalis seedlings
Physalis is grown through seedlings. Its seeds are small. They are sown in March, first in cassettes, then diving in the phase of 3-5 leaves into peat pots. This is the way to discard not sprout and weak plants, which is often the case for crops with small seeds. To prevent the seedlings from stretching, the room should not be too hot. The optimum temperature is + 18-20 ° C. After picking, the seedlings are fed with complex fertilizer for vegetable plants.
Landing in open ground
Water the plants 2-3 times a week, so that the soil is soaked through. In April, when the weather is warm, the growing seedlings can be brought out into the fresh air for hardening (during the day). In early - mid-May, it can be planted under film shelters. The age of seedlings for planting in the ground is from 40-55 days. Elongated plants are planted at an angle. Since nightshades do not like high humidity, they try to ensure that the topsoil is not heavily waterlogged under the film.
Physalis - care
Grown plants are fed with complex fertilizer for vegetable plants. To improve fruiting, you can make foliar feeding. To increase the number of fruits at the end of June, plants pinch the growing point. Unlike tomatoes, physalis does not need to be pinned. If there are many fruits on the plants, the stems are tied up.
Fruits are harvested as they ripen, before the first cold weather. They can crumble, but this does not affect the quality - fallen fruits can be collected from the ground. Those who do not have time to ripen must be collected before frost. In a warm room, they will ripen. You can dig up the plants before the onset of cold weather and hang them by the roots in the shed so that the remaining fruits gradually ripen.
Physalis fruits are hidden in caps of yellow-green or orange color. The surface of fruits, especially young ones, is sticky and oily. The most delicious are those that ripened on the plant in summer, in sunny weather. Late fruits are medium in taste, of which it is better to cook jam or pickle.
Before use, physalis is freed from the dry cap and washed with warm water to remove the sticky substance. If not rinsed off, the taste will be bitter. Fresh fruits are stored in a dry room at a temperature of + 2-4 ° C. without losing quality, 3-4 months, but they do not rinse before use for food.
The aromatic fruits of strawberry physalis can be dried in the oven at a temperature of + 40-50 ° C. periodically airing the oven.They will not dry out in the air - they will quickly deteriorate. Dried fruits resemble dried apricots. In folk medicine, physalis fruits are used as a diuretic for kidney and bladder stones. Decoction and infusions of fresh and dry fruits - for inflammation of the respiratory tract, stomach, intestines.
New varieties of physalis - Likhtarik, Zharinka (Ukrainian selection)
| Biochemical composition of physalis fruits (in% to the weight of the fruit) | ||||||
| Variety | Index | |||||
| Dry matter | Sugar (total
amount) |
Acidity (citric
acid) |
Pectin substances
(according to Melitz) |
Tannins | Vitamin C | |
| Moskovsky
early |
8-9,4 | 3,2-3,7 | 0,65-0,73 | 0,25-0,4 | 0,14-0,32 | 24-28 mg% |
|
Ground Gribovsky |
7,2-9,48 |
2,91-3,1 |
0,92-1,32 |
0,24-0,31 |
0,15-0,41 |
17.5-23 mg% |
| Confectionery | 7,66-8,2 | 2,12-2,65 | 0,7-1,37 | 0,3-0,39 | 0,15-0,44 | 20.0-26 mg% |
In detail:
The origin of the vegetable.
Physalis is an annual plant of the nightshade family, which got its name from the rounded shape of the flower calyx (fiza - in Greek means bubble), inside which there is a fruit with numerous seeds.
The Physalis genus is represented by 110 botanical species, most of which belong to wild-growing weeds. Several types of physalis have decorative and nutritional value.
Useful properties and uses. Ornamental types of physalis (common and garden) have small orange-red fruits that can be used as a diuretic, analgesic and hemostatic agent. Physalis garden fruits are used as a harmless organic dye for food products. Winter bouquets are made from branches with orange "lanterns".
Vegetable physalis
This species is more cold-resistant than berry. It tolerates small frosts, so it can be planted in the ground 10-12 days earlier than tomatoes. In addition, it is more resistant to common nightshade diseases, including the most dangerous one - late blight. Vegetable physalis cross-pollinated. Like the decorative one, the cases bloom in the fall, turning bright red. There are varieties of undersized (30-40 cm) and tall (up to 90-100 cm) with intermediate forms.
Strawberry Physalis
These plants are more thermophilic and self-pollinated. Strawberry physalis, popularly called strawberry tomato and dwarf gooseberry, is shorter, with small berries. Vil is less productive and much less common than vegetable, but its taste is more pleasant.
Physalis with edible fruits are divided into two groups. The first is of South American origin, Peruvian and strawberry, which have been known in culture for over 200 years. The fruits of these physalis varieties are very small and therefore not widely used.
The second group of edible physalis includes vegetable species of Mexican origin. They are grown everywhere, including in Russia. They are more productive, less demanding on heat, differ in a variety of economically valuable traits. For this reason, let us dwell in more detail on the physalis of Mexican origin.
At home, vegetable physalis has long been cultivated under the name "tomatil" and "mil-tomato", i.e. Mexican tomato. The local population uses unripe fruits for making hot sauces with pepper, mashed potatoes, boiled and baked, as well as for salting. The fruits of zoned varieties of physalis contain sugar, a significant amount of vitamin C, organic acids, trace elements, pectin substances. Physalis is the only vegetable with a gelling property, and therefore is widely used in the confectionery industry. In addition, its fruits are eaten fresh, used to make jam, jam, jam, compote, caviar, they are salted, pickled.
Biological features.
Mexican physalis is an annual cross-pollinated plant. Insects willingly swarm on its large and fragrant flowers, which bloom before the fall frost.Among the forms of vegetable physalis, there are semi-creeping (30-40 cm high) with a branching angle of up to 140 °, as well as tall (over 1 m), with branches extending from the stem at an angle of 35-45 degrees.
Within a group there can be both early ripening and very late ripening plants with fruits weighing 30-90 g, green, white, yellow, yellow-lilac, dark purple in color; in shape - flat, oval, round, from strongly ribbed to smooth; to taste - from sugary-sweet to spicy-sour with an unpleasant aftertaste. The cups (caps) of fruits are very diverse in shape, color and size - they are either too large, or, conversely, are torn apart by a large fruit.
On the basis of Mexican physalis, domestic varieties Moskovsky early, Gruntovy Gribovsky and Konditersky were created, which can be successfully grown on personal plots. The yield of these varieties with good agricultural technology is 3-5 kg of fruits per bush.
Varieties:
Moscow early.
Plants are semi-recumbent, medium-branching. Leaves are light green, oblong-ovoid, smooth. The flowers are large, yellow, with brown spots in the fauces. The calyx is large, usually covering the fetus. Fruits from flat-round to round shape, 40-55 mm in diameter, weighing 40-80 g. Color of unripe fruits is light green, ripe fruits are yellow to amber. Ripe fruits are sweet, without a sharp sour taste. Early ripening, high-yielding (2-5 kg / m2) variety.
Ground Gribovsky.
Plants are semi-erect, well-branched, 80 cm high and more. The leaves are dark green, smooth, ovoid. The flowers are large, greenish-yellow, with brown spots in the fauces; the stamens are purple. The calyx (cap) is large, multifaceted, completely filled with fruit, sometimes open at the top; brown streaks along the sides of the calyx. Fruits are smooth, from flat-rounded to roundish, light green in color, weighing 50-60 g. The taste of ripe fruits is sour-sweet, without aftertaste. The variety is medium early, cold-resistant, high-yielding (2.5-4 kg / m2).
Amateur vegetable growers will love the promising grade Confectionery, specially created at VNIISSOK for the confectionery industry. Plants of medium vigor, highly branching, spreading. Leaves are ovoid, smooth, dark green. The flowers are greenish-yellow, with brown spots in the throat, the stamens are purple. The calyx is rounded, with dark brown veins, almost always covering the fruit. Fruits are round, green, weighing 30-60 g, with high acidity. The variety is mid-season, high-yielding, easy-going.
Below in the table we give the biochemical composition of physalis fruits according to Alpatiev (1989).
Features of growing physalis.
Mexican physalis is cultivated directly by sowing seeds. Its seeds germinate at a temperature of 10-12 ° C. With the timely implementation of all agrotechnical measures, ground sowing physalis, as a rule, gives higher yields. In addition, such plants do not suffer from picking and replanting, in which a significant part of the roots is lost, and as a result, they develop a more powerful root system and are less sick. However, fruit ripening in them lags behind in comparison with seedling culture.
If an amateur vegetable grower wants to have an earlier crop of Mexican Physalis, it is best to grow it in seedlings. It takes 25-30 days to get seedlings with five to seven leaves. Based on this, the sowing time for each species is determined.
Selection and preparation of a site for planting.
Under the physalis, cultivated, well-illuminated areas are allocated, which are not subject to flooding by melt and rainwater. It can be grown on all types of soil, except for acidic (pH
Any culture can be a predecessor for physalis. However, after tomato, potato, pepper, eggplant, planting it earlier than 3 years later is undesirable, since these related plants are affected by the same pests and diseases.Physalis should not be placed over physalis in order to avoid self-seeding (due to cross-pollination of the Mexican physalis, the offspring may be less uniform).
Physalis loves loose, fertile, well-aerated soil that is not clogged with weeds. Therefore, a plot intended for growing plants is dug up in the spring to a depth of 20-25 cm, after having scattered rotted manure or compost (30-40 kg / m2) over it. Applying fresh manure under physalis can cause adverse effects.
Physalis responds well to the introduction of mineral fertilizers. For soils of medium and low fertility, their approximate consumption (in grams per 10 m2) in terms of the active ingredient is: nitrogen 30-40, phosphorus 10-15, potassium 40-50, calcium 40-45, magnesium 8-10. In the absence of mineral fertilizers in the spring, wood ash is used for digging, rich in potassium, phosphorus, calcium, as well as trace elements, at the rate of 1 - 1.5 kg per 10 m2, or 2-3 glasses per 1 m2.
Preparing seeds for planting
Physalis yield largely depends on the quality of the seed, its ability to provide friendly viable seedlings. For sowing, only class I seeds should be used. They must be large enough, leveled and conditioned in terms of sowing quality.
Preparation for sowing begins with the selection of large and full-bodied seeds, which give a higher yield than usual. To do this, they are poured into a vessel with a 5% solution of sodium chloride or mineral fertilizers and mixed thoroughly. After 6-7 minutes, the lightweight seeds and litter that have emerged to the surface are removed, the solution is drained, and the remaining seeds are washed several times with water and dried to a state of flowability.
When, due to unforeseen circumstances, sowing is delayed, to accelerate the emergence of seedlings, wet after soaking seeds are kept for 4 to 6 days at a temperature of about 20! C. Seeds that have sprouted in warmed-up soil germinate on the 2nd-3rd day. Dry seeds sown at a temperature of 20-25'C germinate on the 7-9th day, while at a soil temperature below 12C they can lie in the ground for a long time without germinating.
To protect plants from fungal and viral diseases, seeds are pickled in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate for 15 minutes, followed by rinsing with running warm water. Disinfection of seeds with a 20% solution of hydrochloric acid is effective against the tobacco mosaic virus (when preparing a solution, hydrochloric acid is carefully poured into the water, and not vice versa).
Growing physalis seedlings.
Physalis seedlings are grown in film unheated greenhouses, greenhouses or in beds covered with transparent film.
The soil mixture for sowing seeds should be loose, without dense inclusions and contain all the necessary nutrients.
Physalis seeds are sown to a depth of 1 - 1.5 cm. In this case, the crops should not be thickened, otherwise the plants are strongly stretched, lodged, and in wet weather they are affected by a black leg. For example, to get 50 plants, 0.2 g of Mexican physalis seeds and 0.1 g of Peruvian and strawberry seeds are required.
With the emergence of seedlings, the temperature is maintained within 15-17 ° C, removing shelters in the absence of frost, so that the root system develops better and the seedlings quickly switch to independent soil nutrition.
In the phase of one or two true leaves, the plants are thinned out or dived into pots or boxes, leaving a distance of 5-6 cm between them, and between the rows 8-10 cm. 1.5-2 hours before this operation, the seedlings are watered abundantly. When picking, in order to better preserve the roots on the plants, the seedlings dig in and pick them up along with the ground. They are placed in small boxes and sorted, discarding the weak, dented, affected by a black leg. Seedlings dive with a pointed peg 10-15 cm long and 1.5-2 cm thick. They make a small hole and plant a plant in it.Then the ground is pressed against the root of the seedling with a peg, and the seedling is supported with the fingers of the other hand so as not to cover the top (growth point).
Seedling care is a crucial period in growing it. At this time, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for the growth and development of plants, for which they include fertilizing, watering, and airing. By the time of planting in open ground, the plants should be strong, unstretched, with a well-developed root system and large buds. Therefore, when the outside air temperature is 10-12 ° C, the frames or the film are removed from the greenhouses and ridges. If the seedlings are grown in boxes, they can be taken out into the open air. However, plants are gradually taught to full light, otherwise they may have sunburn. First, the plants are taken out into the open air by the end of the day, then in the morning and evening hours. Only after 3-4 days on sunny days (on cloudy - earlier) the seedlings are left open for the whole day, and if there is no threat of frost, then overnight.
Water the seedlings in the morning so that the greenhouses or ridges are aired by the evening. Watering is carried out not often, but abundantly. In cold weather, the water is heated to a temperature of 16-20'C. The soil under the seedlings is kept loose and free from weeds.
Top dressing of seedlings is carried out either continuous or selective (plants lagging behind in development) every two weeks. At the first feeding, if the leaves of the plants are pale green and the stems are thin, ammonium nitrate is preferred (15-20 g of fertilizer per 10 liters of water). Feeding with bird droppings or mullein diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15 and 1:10, respectively, is more effective. In this case, one watering can (10 l) of a solution of mineral or organic fertilizers is consumed per 3 m2 of area.
In the subsequent feeding, it is better to use a mixture of mineral fertilizers (10 g of saltpeter and 10-15 g of potassium salt per 10 liters of water) at the rate of 10 liters of solution per 1-1.5 m2. After 10-12 days, the seedlings are fed with superphosphate (25-30 g of fertilizer per 10 liters of water). The consumption rate is 10 liters of solution per 1 mg of plantings. After top dressing, the fertilizer residues are washed off the plants with clean water from a watering can with a mesh to prevent leaf burns.
Before planting, when the seedlings are growing rapidly, the number of watering is reduced, however, preventing the plants from wilting.
Physalis seedlings are planted in open ground in late May - early June (7-10 days earlier than tomatoes). In the morning of the day of planting, it is watered abundantly so that the root system suffers less from mechanical damage. The plot is marked so that there are 3-4 Mexican physalis plants and 5-6 strawberry plants per 1 m2. For better use of the area of the ridge plot, they are compacted with lettuce, radishes, the harvest of which is harvested even before the formation of fruits
physalis. It is best to plant plants in the ground in the afternoon, and in cloudy weather you can throughout the day. After planting, the plants are not watered from above, so that a crust does not form on the soil, which interferes with the access of air to the roots.
In humid areas, physalis is advisable to grow on ridges up to 30-40 cm high in order to avoid the accumulation of stagnant water around the plants.
Growing physalis from seeds. The time of sowing physalis seeds in open ground roughly coincides with the period of planting early potatoes, when the soil at a depth of 10 cm warms up to a temperature of 4-6 ° C. Seeds are sown in loose, well-fertilized soil, free of weeds. Seeding rate - 0.1 g / m2. Since physalis seeds are very small, for a more even sowing, sand or rapidly growing seeds of radish or lettuce are added to them in equal proportions as a lighthouse culture. These plants serve both as row markers for early row spacing and as a compacting crop for additional yield. Sowing is carried out in rows, the distance between which should be 50-60 cm.
With the emergence of mass shoots, the plants are thinned out at a distance of 50 cm, so that by the beginning of flowering there are no more than 4-5 of them per 1 m2.
Planting care
During the growing season of physalis in open ground, the soil is kept loose and free from weeds. Depending on the development of plants, they are periodically watered and fed. The first feeding is given during the period of mass flowering, the second - during fruit formation, the third - after 2-3 weeks, using solutions of mineral fertilizers, as well as slurry (1 part of the fertilizer is diluted with 5 parts of water in dry weather and 3 parts in wet weather), mullein (1:10) and bird droppings (1: 12-15).
To feed physalis with a mixture of mineral fertilizers, 10 g of nitrate, 10-20 g of superphosphate and 10-15 g of potassium salt are dissolved in 10 liters of water. The consumption rate of the solution is 10 liters per 1 m2.
It should be borne in mind that ammonium nitrate with simple superphosphate can be mixed only if the superphosphate is previously neutralized. To do this, add 0.1 kg of limestone or chalk to 1 kg of superphosphate.
Unlike tomato, physalis plants do not stepchild or tie up. On the contrary, it is necessary to strive to obtain more powerful, highly branching plants. Physalis fruits are formed in the places where the stem branches, so the more the plants branch, the higher the yield will be. For amateur vegetable growers, we recommend pinching the tops of the branches in the middle of the growing season in order to enhance branching and increase the number of fruits on the plants.
Plants affected by diseases are removed.
In rainy summers, as well as in low, humid areas, hilling of plants is recommended, which contributes to their strengthening, reducing morbidity and better ripening of fruits.
Recommendations and tips for protecting physalis from diseases and pests
Since physalis is not a widespread crop, it is less susceptible to massive damage from diseases and pests compared to tomato or pepper. However, with an untimely control of them, the yields and quality of the fruits decrease. It is possible to prevent the widespread spread of diseases and pests and reduce the harm caused by them, it is possible with the observance of preventive measures and the application of methods of systematic control of them.
The main and general measures of protection of physalis against diseases and pests are:
- harvesting seeds, if possible, on your site, only from healthy, productive plants after preliminary approbation of sowing;
- seed dressing before sowing;
- compliance with crop rotation;
- systematic control of weeds and pests, which, in addition to direct harm, serve as carriers of many diseases;
- removal of plant residues from the site (into a compost heap) and autumn digging of the soil, contributing to its biological recovery and an increase in crop yield;
- correct agrotechnics, ensuring the normal growth and development of plants.
Phiasis diseases
Blackleg develops with excessive moisture, thickened sowing, poor ventilation of plants. The stems at the root collar turn black, the plants die.
Control measures.
Thinning of seedlings, rare but abundant watering in the morning, airing, loosening of row spacings. Effective disinfection of soil and its components with microgranules (MG) of basamide (50-60, depending on its moisture content).
Mosaic characterized by the appearance of light green spots on the branches. The causative agents of the disease are viruses of perennial physalis, weeds and the remains of pumpkin crops that overwintered in the soil. Infection occurs through insects and mechanically.
Control measures.
Compliance with crop rotation, agricultural technology, weed control.
Streak first appears on plants like a mosaic. In the future, the branches become brittle. Fruits develop poorly, have a lighter color, often with cracks on the surface, tasteless, corky. Control measures are the same as for mosaics.
Physalis pests
Medvedka - an insect of dark brown color, up to 50 mm long, with pronounced digging legs. Most often found in damp places: near rivers, ponds, especially on humus-rich soils. It hibernates in the phase of a larva and an adult insect in soil or manure and begins to damage crops from early spring. Laying horizontal passages at the soil surface, the bear and its larvae gnaw through the roots and stems of plants.
Control measures.
Loosening of row spacings at the end of May and during June to a depth of 10-15 cm to destroy eggs.
One of the most reliable ways to deal with a bear is to set up hunting nests. After harvesting the crop, several holes 40 cm deep and 70 cm in diameter are dug on the site, where several shovels of manure are placed. Looking for warmer places for wintering, the bears climb under the manure, from where they are removed and destroyed.
The smell of kerosene, naphthalene, which is used to treat the places of their accumulation, repels pests.
To protect greenhouses from pests, grooves are dug along them, pouring naphthalene or sand moistened with kerosene into them.
On the subject: My way of dealing with a bear (cabbage)Clickers (wireworms - more details) - beetles 10-15 mm long, of various colors (black, brown and other, with a metallic tint). Distributed almost everywhere. The beetles themselves do not cause significant harm. The most dangerous for plants are wireworms - the larvae of click beetles. They got their name for an elongated solid yellow-brown body that resembles a piece of wire. They prefer moderately moist soil, with drying of the surface layer, wireworms go to the lower layers. They live in soil for 2 to 5 years. The pest gnaws at the root system of plants and penetrates into the stem.
Control measures.
Loosening of row spacings, deep digging of the soil in the fall, in which larvae and eggs die.
Catching wireworms with potato or beet bait buried in the ground (on twigs).
Compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures delays the development of caterpillars of various scoops. Against them, it is advisable to use an egg-eater - trichogram. This useful predator is released in two or three doses during the mass oviposition of the scoop at the rate of 10 insects per 1 m2. For the purpose of prevention, the plants are sprayed with a strained three-day infusion of burdock leaves (1 part of the volume of crushed burdock leaves is poured with 2 parts of water) a week after planting the seedlings.
Harvesting and storage of crops.
Ripening of fruits begins from the lower tiers of plants: the higher the fruits are located, the younger and later they ripen. The moment of ripening can be determined by the drying and lightening of the caps, as well as by the aromatic smell and color of the fruit, characteristic of this variety. Ripe fruits tend to fall off. If the weather is dry, then they remain on the ground without spoilage, especially strawberry and Peruvian physalis, whose caps are much larger than berries. In wet weather, larvae and worms penetrate inside the covers, damaging the fruit. It is not recommended to harvest the fruit after rain. If there is a prolonged rainy weather, then the wet fruits must be dried or freed from the covers, otherwise they will deteriorate during storage. Although physalis fruits are quite strong, nevertheless, precautions are needed to prevent damage, since pectin substances are quickly destroyed by enzymes. Physalis can withstand slight autumn frosts. However, frozen fruits are poorly stored, therefore it is safer to carry out the final harvest before the onset of frost. For long-term storage, the fruits can be removed slightly unripe.
Since immature fruits can grow somewhat on plants, with a small number of plants grown, it is advisable to harvest the fruits together with the plants before frost. Such plants are hung in a dry room or stacked with the tops of the branches inward and the roots outward. From above, the stack is covered with old film or other materials.After one to two weeks, the plants are examined and the grown healthy fruits are collected from them. When plants in a stack freeze, large fruits from them can be used for making jam or for pickling.

Features of seed production.
In order to get a crop of physalis with a higher quality of fruits next year than in the current year, it is necessary to use good seeds. It is not always possible to acquire such seeds, therefore, amateur vegetable growers strive to get them on their site. For this, the best physalis plants are selected, i.e. carry out the simplest type of selection.
From strawberry and Peruvian physalis, they select mainly productive, healthy seed plants with larger and more tasty fruits that ripen well in the area. With good selection, their offspring usually have distinctive features similar to seed plants. This is explained by the fact that in self-pollinating crops, such as strawberry and Peruvian physalis, the genetic characteristics of seed plants are almost completely transmitted to the offspring.
It is somewhat more difficult to select the Mexican physalis, since, due to cross-pollination, its offspring inherit the characteristics of the maternal plant (on which the fruits were formed) and the paternal (from which the pollen was brought to form the ovary).
The biological characteristics of the fruits of the Mexican physalis are determined by the offspring. Since the offspring plants are re-pollinated, the most effective way to obtain plants with valuable qualities is the method of family selection. He
consists in the fact that the offspring from each fruit of a valuable seed mother plant is grown in a spatially isolated area.
An important requirement in the seed production of Mexican physalis is the cultivation of only one variety on the site in order to avoid natural cross-pollination with other varieties of unknown genetic properties. Strawberry and Peruvian physalis do not interbreed with each other, with Mexican, as well as with ornamental garden physalis, so they can not be isolated.
Pollination by insects of various forms and varieties (hybrids) of Mexican physalis is possible at a distance of 1.5-2 km. In order to avoid over-pollination, vegetable growers cultivating Mexican physalis should have seeds of the variety whose seed production is carried out in a given radius.
For the purpose of seed growing, Mexican physalis is grown in seedlings in order to avoid over-pollination of the variety with plants from self-sowing (seeds from past harvest years).
The preservation of the varietal qualities of physalis is achieved by the use of varietal cleanings from the period of growing seedlings to harvesting fruits, as well as the creation of high soil fertility and the timely implementation of the necessary agricultural practices.
The agricultural technique on the seed plot is the same as in the cultivation of physalis for food purposes. Only a strong thickening of crops is unacceptable. For better formation of fruits, and in them seeds, feeding with superphosphate and potassium salt is recommended.
Fruits are harvested first from rejected plants and fallen to the ground, which are used for consumer purposes, and only then from typical plants for seeds.
The collected fruits are sorted, discarding the diseased, and then ripening.
The best conditions for ripening physalis fruits are created in well-ventilated rooms at an air temperature of 20-25 C and a relative humidity of 80-85%. The fruits are laid out on racks in two or three layers in slatted (lattice) boxes.
Seeds are isolated from fruits that have reached full biological ripeness, i.e. having already characteristic color for this variety and seeds with a hardened shell (peel).
If a sufficiently large number of ripe fruits have accumulated, then they are kneaded in glass or plastic dishes. The mass of fruits is kept at room temperature (20-25 * C) for 3-5 days. During this time, it will begin to ferment, after which good full-fledged seeds sink to the bottom of the dish.The top layer is discarded, and the seeds remaining at the bottom are washed several times with water and dried on filter paper or some other absorbent paper. In this case, the seeds are scattered in one layer and kept until completely dry.
It is better to store seeds in a dry room, preferably heated, in canvas or paper bags. Under these conditions, the seeds of the Mexican physalis do not lose their germination within four years, strawberry and Peruvian seeds - within five.
Also on the topic: Purslane Recipes (with Physalis)
The use of physalis in cooking
For processing, you can use both ripe and unripe fruits of the Mexican physalis.
For all types of use of Mexican physalis, first of all, it is necessary to peel the fruit from the caps and rinse with hot water in order to remove sticky and waxy substances from the surface that have an unpleasant odor and bitter taste.
Physalis is salty.
Physalis fruits are salted separately or together with cucumbers. Peeled washed fruits are laid in layers with spices (for 1 kg of fruit - 30 g of dill, 5 g of horseradish root, 3 g of garlic, if desired, 1 g of red capsicum). Other aromatic additives can be used: black currant and cherry leaves, tarragon, basil, mint, parsley, celery.
However, the total mass of spices should not exceed 50 g per 1 kg of physalis fruit. The fruits placed in containers of different volumes are poured with a salt solution at the rate of 60 g per 1 liter of water - for long-term storage or 35-40 g - for a shorter period (2-3 months). After that, the container is closed with a wooden circle with slight oppression and left for 7-10 days at room temperature for fermentation and the formation of lactic acid. Mold that appears during fermentation is removed. After the accumulation of acid, palpable to the taste, the brine is drained, boiled and the fruits are poured hot again. The jars filled with pickles are rolled up and, after cooling, are placed in the cold for storage.
Physalis soaked.
Healthy, fully developed fruits are freed from the caps, washed thoroughly in warm water with a cloth or sponge until the adhesive is completely removed from their surface, rinsed. Then they are placed tightly in glass jars, washed in boiling water or steamed, and poured to the top with brine (for 1 liter of brine, 30-35 g of sugar and 10 g of salt), wooden mugs or sticks are placed on top, a little oppression so that the fruits are kept in brine. In this form, the fruits filled with brine are left for 7-10 days at room temperature (15-20C) for fermentation. After the specified period, the brine is checked for taste: if acid is felt in it, it means that the fermentation process was normal. The jars are closed with plastic lids and placed in a refrigerator or in a room with a temperature not exceeding 6 C. After a month, soaked physalis is ready for use.
Physalis prepared for peeing can be laid in layers in a large volume of cabbage, laid for pickling, and then eaten with it.
Physalis pickled.
Preliminary preparation of unripe fruits (you can also ripe, strong) is the same as for salting and urinating. The washed fruits are blanched (immersed in boiling water for 1 min), then cooled and placed tightly in sterilized liter jars, previously placed on the bottom of spices (%): salt 4-6, sugar 5, vinegar 1.6, cinnamon 0.07 , cloves 0.05 (1-2 pcs. per jar with a capacity of 0.5 l), allspice 1-2 pcs., Bay leaf 1 pc.
Some amateurs add 1 sheet of black currant, small sprigs of tarragon and dill, 2-3 cloves of garlic to a liter jar. Cinnamon and cloves are boiled for several minutes in water, the solution is cooled and then salt and sugar are added. Jars of fruits are filled with hot marinade filling; cover with a boiled lid and sterilize for 10 minutes (at a temperature not lower than 85; C), counting from the moment the water boils in a saucepan in which jars of pickled physalis are installed. Immediately after sterilization, the jars are rolled up with lids.
It is recommended to keep jars of pickled physalis in a refrigerator or a cool room for at least 1.5-2 months to complete the pickling process. At room temperature, the product will be ready for use in 30 days.
Related entry: Vegetable Physalis RecipesVegetable caviar.
To prepare caviar, the washed fruits are baked, passed through a meat grinder and salt, onion and pepper are added to taste.
You can cook caviar with the addition of carrots and onions to physalis. The washed physalis fruits, peeled carrots and onions are chopped and fried in a deep frying pan in vegetable oil until the carrots are soft. Then the fried mass is passed through a meat grinder, salted and added, if desired, a little granulated sugar. Such caviar is used as a side dish or as an independent dish. For 1 kg of physalis take 400 g of carrots, 300 onions and 60 g of vegetable oil.
Jam.
Making Mexican Physalis jam is similar to making it from Berry Physalis.
For cooking Mexican physalis jam, you can use both fruits of full biological ripeness, and somewhat immature ones. First, the fruits are cleaned of caps, sorted, then washed well in warm water, washing off the sticky waxy substance and dirt from the peel. It is advisable to soak the fruits in warm water (at a temperature of 60-70 degrees) or subject them to short-term blanching. If the sticky substances are not removed from the surface of the fruit, then their unpleasant smell and bitter taste can be felt in the jam.
Blanching, especially of unripe fruits, helps to evenly saturate them with sugar syrup. Then the fruits are pricked from all sides with a sharp fork or "hedgehog". Large fruits (over 3 cm) are cut into several parts. Prepared fruits are placed in a bowl, poured with hot syrup (1 liter of syrup is consumed per 1 kg of fruit) and kept for 10-12 hours (fruits must be completely covered with syrup). Then the fruits are boiled (ripe 2 minutes, unripe up to 4-5 minutes), add 100-200 g of granulated sugar, stirring gently at low boil until it is completely dissolved.
After standing, the syrup with the fruits is boiled again and kept for 10-12 hours. If the fruits are ripe, this operation is repeated 3-4 times, and if immature - 5-6 times. When boiling, add 100 g of granulated sugar each time. At the last cooking, you can add vanillin. For 1 kg of fruit, 1 kg of sugar is consumed.
Candied fruit from Mexican physalis is prepared in the same way as from berry physalis.
Candied fruits can also be obtained by glazing fruits. To do this, prepare sugar syrup (for 1 part of water 5 parts of sugar), heat it to a temperature of 120 ° C and cool with stirring until sugar crystals begin to stand out (the syrup becomes cloudy). Slightly dried fruits, cooked as for jam, are immersed in hot syrup, then removed and dried on sieves so that a crust of small sugar crystals forms on the surface of the fruits.
Dried fruits are placed in glass jars and covered with plastic lids. Store candied fruits in a cool place.
Jam.
To prepare the jam, the fruits are cleaned of caps, washed in warm water, small - cut in half, large - into 4 parts or smaller, blanched, poured with sugar syrup (containing 70-75% sugar) and boiled until tender.
Some amateur vegetable growers add 1 glass of water to 1 kg of blanched fruits, boil until the fruits soften, then add 1-1.2 kg of sugar and cook until tender, stirring often to avoid burning.
The finished jam has a jelly-like consistency. The yield of jam is 73-74% of the weight of fruits and sugar.
Puree.
Ripe and fully formed unripe fruits are sorted, removing spoiled ones, freed from caps and washed with warm water. After that, the fruits are blanched (that is, they are immersed in water with a temperature of 80-85 C for 1.5-2 minutes, then the water is drained).This removes the sticky and waxy substances that give the physalis fruit an unpleasant odor and bitter taste.
Next, the fruits are boiled for 15-20 minutes in a little water or scalded. Heating the fruit should not be prolonged in order to avoid the destruction of the gelling pectin. Then the fruits are rubbed through a sieve with a hole diameter of no more than 1.5 mm or passed through a juicer to free the mass from the peel and seeds. The output of mashed potatoes is, depending on the variety, 75-80% of the mass of the fruit.
Store the puree in the refrigerator at a temperature of about 0 for no more than 10 days.
Puree from Mexican physalis is a valuable product for the production of jam and jelly-like confectionery products such as apple marmalade, marshmallow, jelly candies.

Why is this little nightshade, which grows immediately in the package, is not recognized by our summer residents? It is tasty, healthy, original, unpretentious, not afraid of the cold. However, some physalis fans (there are some!) Are sure that the fruits in the caps can soon squeeze the capricious tomatoes.
reference
Tomato and physalis are the closest relatives and countrymen. Both of the nightshade family, born in the Light of Job. They were brought to us almost simultaneously, after the discovery of America. The first has taken root and is in demand, and the last has remained on the sidelines.
Physalis is useful for a hundred diseases ...
The nutritional and medicinal qualities of physalis are excellent. At home - in Peru, Mexico, Brazil and Venezuela - is in high demand. In recent decades, the same has happened in India, China, South Africa.
In all these countries, it has become one of the main vegetables, occupying vast areas. The reasons for such a triumphant procession are the original aroma, reminiscent of pineapple with strawberries, as well as sweetness, high content of vitamins and other biologically active and healing substances that prolong youth and preserve health.
But its main secret is the unprecedented content of pectin, which is three times more than in apples and currants. Therefore, in many countries, physalis is often used instead of gelatin for the preparation of many dishes and homemade preparations.
The exceptional gelling properties of physalis are supported by the fact that it is able to disinfect and remove from the body almost any poisons and harmful substances, including mercury, lead and radionuclides. And also - kidney stones. Physalis normalizes blood pressure, helps to scar stomach ulcers in combination with the main treatment. It is useful for 100 diseases!
See also: Physalis - growing, planting and care, varieties and cooking
One of the three physalis is good for us
There are 3 main types of physalis, but not all are suitable for us. So, tropical, Peruvian, in the open ground of our latitudes will not be able to live because of the demanding heat and late maturity. Would be suitable for greenhouses, but gardeners prefer to grow traditional vegetables in them.
The second type of physalis is berry, less thermophilic, sweet and smells wonderful, but its fruits are smallish - up to 5-10 g, and the yield is scanty - 300 g per bush.
The third type of physalis deserves wide distribution in our country without reservations. It comes from the cool mountainous regions of Mexico and is called physalis vegetable, Mexican. The optimum temperature for its growth and development is 18-25 ° C, and the seeds germinate in general at 10-12 ° C.
Vegetable physalis is shade-tolerant and undemanding to soil fertility. Its round fruits are large, fleshy, comparable to tomatoes (up to 60-90 g). They have a sticky oily surface that is light yellow, greenish or purple in color. The fruit tastes sweet and sour. Like all other types of physalis, from the moment they are tied, they are enclosed in a dense "sheath", which protects them from bad weather, pests and diseases. The time from germination to the beginning of ripening, depending on the variety, is 90-115 days.
Powerful bushes of vegetable physalis with deep roots are short, semi-creeping or high - more than a meter, erect.They always have many shoots with up to 200 fruits! Until October, they can easily withstand short-term frosts down to minus 2 ° С.

Seven principles of growing physalis
1. These early ripening plants can be sown directly per pound in early May. But for a complete guarantee in a cold spring, it is easy to grow them with seedlings on a window or balcony in individual cups. The seedlings are 35-40 days old.
2. Any type of soil for physalis is suitable, except for acidic ones, which must be limed.
3. Sowing for seedlings is carried out in late March - early April, planning a planting in the garden on May 15-20. Before tomatoes and without shelter. The distance between plants is 50 cm, and between rows - 60 cm.
4. Physalis is especially picky about moisture at the beginning of growth, flowering and fruiting. Then it is watered often - every 3-4 days, and then - once every 1.5-2 weeks.
5. Plants develop faster when fed every 10 days with a weak solution of slurry, fermented weeds and organic fertilizers such as Bucephal and Radogor.
6. It is not required to grow the bushes, but it is advisable to remove at least some of the buds in early August, since they appear in abundance - up to 300 pieces per bush.
7. Ripe fruits quickly crumble. Therefore, they are collected every week. And so that they do not rot on the ground and do not get dirty, the surface of the garden bed is covered with non-woven material or cardboard. Mulch from moss, lawn grass, sawdust is also appropriate.
By the way, in its pure form and without damage, physalis can be stored even at room temperature for 2-3 months or longer. Often, salads from these unusual tasty fruits are prepared for the New Year's table.
It is also convenient that after the first cultivation there are no problems with seeds - now you will have your own and you do not need to buy. In one fruit, up to 400 full-fledged seeds ripen, the offspring of which repeats the characteristics of their "parents". The seeds are very small, but you can pick them out in sufficient quantity with the tip of a table knife. They do not lose their germination within 3-5 years.
See also: Physalis - and flower and plant and berry
Physalis vegetable and physalis berry - varieties
A curious summer resident who is not yet familiar with physalis should try to grow both vegetable and berry varieties. They are different, and the benefits from them are not the same, although any can be salted and pickled. But not everyone has a pleasant tasty taste when fresh.
Vegetable physalis
These varieties are distinguished by a large amount of gelling substances. And their fruits are relatively large, from 20-30 to 150 g, fleshy, akin to tomato ones. They make excellent caviar and even dry wine. Most often, the fruit tastes better when processed.
KOROLEK - early ripe variety (90-95 days after full germination). The height of the bush is 60-80 cm. The fruit is yellow, dense, sweet and sour, weighing 60-90 g. It contains a lot of pectin substances. The yield can reach several kilograms per plant. The variety is very cold-resistant, it can be sown even before winter.
Berry physalis
These plants give small, about 3-9 g, but unusually fragrant fruits, from which jam, jam, candied fruits are obtained. At the same time, they are tasty and fresh.
GOLD SPRAY - early ripe (92-99 days) grade. The bush is 30-35 cm high. The fruit is bright, smooth, slightly ribbed, yellow, sweet and sour, with a strawberry and pineapple aroma, weighing 3-5 g. Yields 0.3-0.5 kg per plant. Not only jam, but also raisins are prepared from the fruits.
SURPRISE - early ripening variety. Sprawling bush up to 70 cm high. The fruit is orange, small, weighing up to 2 g, yellow and sweet. Productivity up to 0.7 kg per 1 m2. The plant easily tolerates extreme conditions.
DESSERT - early ripening variety. Plant up to 70 cm high. Fruits are yellow, small, sweet. Productivity up to 0.7 kg per 1 m2. Endures extreme conditions.
BELL - mid-season variety (120 days). The plant is semi-creeping, up to 100 cm high. The fruit is orange, weighing 7-9 g. Productivity is up to 1.5 kg per 1 m2. Also very hardy.
Reference by topic: Dishes and recipes from vegetable and berry physalis
Berry and vegetable physalis
Today there are varieties that are good in spinning and other processing, as well as a delicacy. These are real generalists!
PHILANTHROPIST - mid-season variety (150 days). The plant is up to 60 cm high. The fruit is brown-orange, weighing 5-10 g, sweet and sour, refreshing, with a fruity aroma and grapefruit bitterness. The fruits also contain a lot of gelling substances. Productivity 0.5 kg per 1 m2.
PINEAPPLE - early ripening variety (105-119 days). The plant is of medium height. The fruit is creamy, weighing 50-80 g, with a pineapple aroma. Productivity 1.4-1.5 kg per 1 m2. Shade tolerant.
JAM - mid-season variety (120-130 days). The plant is tall. The fruit is creamy, weighing 25-40 g, ideal for jam. Productivity 1.2-1.3 kg per 1 m2. Shade tolerant.
MARMALADE - mid-season variety (120-130 days). The plant is undersized. The fruit is creamy, sweet, weighing 30-40 g. Productivity 1.3-1.4 kg per 1 m2. Shade tolerant.
LACOMKA - early ripening variety. The plant is 70-75 cm high. The fruit is yellow in a light cap, weighing 65-80 g. Productivity 3.0-3.5 kg per 1 m2. Drought-resistant, cold-resistant, unpretentious.
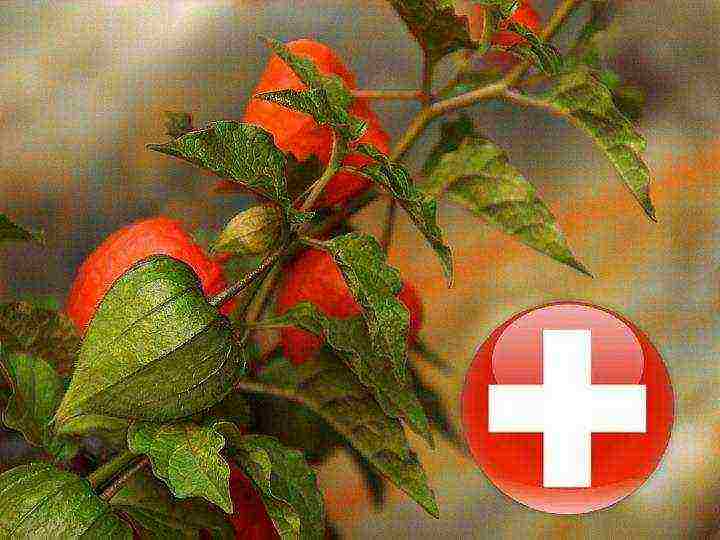
There is also a decorative, or ordinary, physalis - plants with bright orange and red, like paper, flower-boxes that do not fade in dry bouquets in winter. The fruits of this physalis are inedible. Varieties of Chinese Lanterns, Franchetti Zwerg.
Physalis - growing and care: advice and reviews
Lanterns for garden and home
Previously, I admired decorative physalis lanterns only in winter bouquets. She was not going to seriously get involved in this plant - places in the country were reserved, mainly for perennials blooming in the spring and summer.
MY SECRETS
She carefully distributed the seeds over the moistened surface of the soil at some distance, sprinkled it on top with a thin layer of sand, tamped it lightly with her palm and covered it with a plastic bag.
Kept crops on a sunny windowsill at a temperature of +1 8-22 degrees. Seedlings appeared in the second week. She removed the film, periodically sprayed the tender sprouts from the spray bottle.
When the seedlings have grown 3 leaves, I cut them into individual cups with fresh soil. After transplanting, I watered a little, powdered with ash from fungal diseases.
A week later, I fed it with mineral fertilizer with a greater proportion of nitrogen (according to the instructions).
But in March of this year, one of my friends ran into my house for an hour or two, handed a pinch of unknown seeds and took from me a promise to sow them for seedlings. I had to stock up on another bowl with fertile loose soil (soil is suitable for growing seedlings of tomatoes or peppers).
In mid-May, I chose a sunny corner at the dacha, albeit on the very outskirts. I passed the plants into the holes, watered them and almost forgot about them. After all, they did not particularly require attention to themselves. Only twice did I weed out the weeds in this place and once I fed my new pets with fertilizer for flowering garden plants, which was at hand. Somewhere at the end of August, that same friend came to visit. By this time, it had already become obvious what exactly was growing on my site - it was all dazzled with orange fruit beads. Some twigs had to be pinched so that the bushes did not fall apart from the weight. Miraculously, she kept these lanterns until October, but soon she will have to cut them off - in winter, Physalis will decorate the house. And now I can share the collected seeds with other friends!
Irina PUZANOVA, St. Petersburg
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
Growing physalis - variety "Strawberry": Physalis variety "strawberry" reviews about ... Physalis variety "Royal" - reviews, planting and care (Bakshkortostan): Growing physalis varieties Royal I want to write ... Physalis seedlings: Growing physalis seedlings Growing ... and berry physalis: Several years ago, planted near ... Yellow tomatoes are the most delicious varieties: name and description: The best varieties of yellow tomatoes MOST GARDENERS ... Physalis - both a flower and a plant and a berry: How to grow physalis and why ... Bulgarian varieties of vegetables: Bulgarian vegetables - what…
Subscribe to updates in our groups.
Let's be friends!
Bright orange, yellow, emerald lanterns of physalis in flower beds always attract attention. And although this culture was brought to Russia in the 19th century, it has remained exotic. Nowadays, it is most often planted as a decoration for a personal plot.It is unpretentious to climatic conditions and stands out favorably among other garden plants. To appreciate the attractive properties of physalis, you need to get to know this culture better.
Physalis types
Even experienced gardeners and gardeners feel a little confused looking at the counters with physalis seeds. Indeed, today a large number of varieties of this plant are presented on the market. To navigate a gardening center or store, it is important to know which of the three types of physalis is needed for the site:
- Decorative. It is designed to decorate the landscape, it stands out brightly against the background of greenery. Note that decorative physalis is poisonous. During flowering, the physalis forms a neat orange flashlight. It is also called the "Chinese lantern". The Franchet variety also belongs to the decorative type. Its fruits are rich in cherry color. Franchet is less popular in our country than the Chinese lantern. The decorative physalis is perfectly preserved in the form of dried flowers. Often housewives, flower shop owners and designers use it to create flower arrangements, wreaths and bouquets in the winter. The fruits of the ornamental physalis are the smallest. Their weight is only 2 grams.

For its rich orange color, one of the varieties received the nickname "Chinese lantern"
- Vegetable. It is used for pickles, salads and appetizers. The weight of one fruit of vegetable physalis can reach 90 grams. In our country, gluten-fruited vegetable physalis is the most popular. The second name is Mexican tomato.
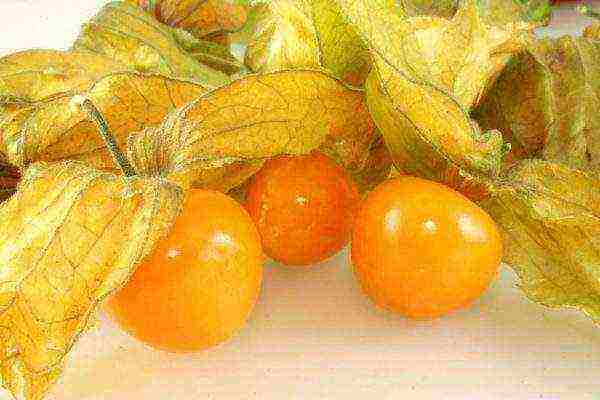

Vegetable physalis - a "relative" of tomatoes
- Strawberry. It is actively used in canning. Jams and preserves are made from it, as well as delicious desserts. The fruits of this species are not large, the weight of one of them reaches 10 grams. Berry Physalis is divided into three subspecies: Peruvian, Florida and Raisin. Peruvian has a rich citrus aroma and flavor, it is dried and jam is made from it. Florida physalis is good for jam that tastes like sweet cherries. Raisin is perfect for drying. The bright tangerine aroma of physalis is preserved even in jam.

Physalis berry varieties taste like strawberries, pineapple and grapes
When choosing physalis for planting in a vegetable garden or garden, it is worth focusing on the early maturity of the variety. For regions with a cold and short summer period, it is worth choosing physalis with an early ripening period.
Popular varieties
No matter how decorative physalis decorates the landscape, most gardeners try to combine the aesthetic appearance of plants and practicality. Therefore, preference for planting is given to a vegetable or berry species. After all, they look no less bright in the flower bed, but at the same time they are eaten. The most popular edible varieties are physalis:
- Gribovskiy 2046. This is a mid-early variety. Physalis is resistant to cold weather. High-yielding. Fruits are yellow-green, round in shape. Slightly flattened.
- Pineapple. The variety is early maturing. The fruits are small, have a sweet taste and rich pineapple aroma. Physalis is used fresh, as well as in the preparation of preserves, jams and candied fruits.
- Marmalade. Mid-season variety. The plant grows up to 1.5 m. Fruits are flat-round, with a pronounced plum flavor. Unripe fruits are green in color. Ripe berries become creamy. The yield of the variety is 1.3–1.4 kg per 1 m2. They are used in the preparation of preserves, candied fruits and jams.
- Strawberry. Plant height 70 cm. Fruits are small, amber in color, with a strawberry flavor and aroma. It is consumed dried, fresh and canned.
- Kinglet. Vegetable physalis, early maturing. The plant grows up to 80 cm. Cold hardy. Grown through seedlings. In the southern regions, it is possible to plant seeds in open ground. Large-fruited. The weight of one fruit varies from 60 to 90 g. Sweet and sour taste. Differs in high productivity: from one Korolka bush, you can collect up to 5 kg of fruits.Practically versatile in cooking. Dry wine, jams, preserves, caviar, marinades are prepared from Korolk.
- Confectioner. Medium early grade. The period from emergence to the beginning of fruiting is 110-115 days. Cold resistant. The bush is 60–80 cm high. Fruits are flat-rounded, yellowish in color, weighing 30–40 g. Resistant to diseases. It is planted with seedlings, in the southern regions it is possible to plant a Confectioner in open ground. After harvest, fruits can be stored for up to 3 months in a cool place. Caviar, candied fruits, dry wines and preserves are made from this variety.
- Wizard. Mid-season variety. Heat-loving. The fruits are rich in pectin and trace elements. Suitable for cooking jams, jellies and marinades.
- Raisin. Early ripe variety. Heat-loving. Raisin prefers well-lit areas. Not picky about the soil. Low-growing plant. The height of the bush reaches only 45 cm. The fruits are considered small. The weight of one fruit is 6–10 g. The color of ripe fruits is yellow.
- Gold placer. The variety is early maturing. The plant is considered undersized, since the height of the bush is 35 cm. It is planted with seedlings. The fruits are golden in color. The mass of one berry is 5–7 g. The yield is high.
- Bell. The variety is mid-season. The plant is highly branched. Reaches a height of 1 m. Fruits are flat-round, orange. The weight of one fruit varies from 7 to 10 g. The peculiarity of the Kolokolchik variety is that it is hardy to adverse weather conditions and undemanding to the soil. Used fresh, in marinades and preserves.
Video: Marmalade, Korolek and Confectioner and other varieties of physalis
We plant physalis
In order for physalis to please in summer and autumn with a good harvest, you need to familiarize yourself with some of the preferences of this culture:
- Physalis needs a lot of sunlight. Therefore, a well-lit place is chosen on the site.
- After precipitation falls, water should not stagnate on the flowerbed.
- A flowerbed for planting physalis must be pre-cultivated. If, before the physalis was transplanted into it, a variety of crops grew in the flowerbed, this will have a positive effect on the growth and productivity of the plant.
- Physalis does not like weeds. After planting, the flowerbed will have to be weeded periodically.
- This plant does not tolerate acidic soil. Physalis either does not take root in such a land, or is constantly ill. To correct the composition of the soil on the site, it is worth worrying about liming in advance. You can add quicklime, wood ash, "Fluff" or dolomite flour to the soil according to the instructions on the package.

In order for physalis to be planted in an area with acidic soil, the soil must be limed
If there is no suitable place for planting physalis in the garden, you can do it yourself. In areas where water often accumulates, earthen ridges should be poured. Or create high beds.

High beds are a great solution for frequently flooded areas.
Physalis grows well in a flower bed after any cultural predecessors, except for nightshades. After growing tomatoes, peppers or potatoes on the site, you need to plant other crops in these places for 2-3 years. Only under this condition, after nightshades, it will be possible to plant physalis.
At the same time, tomatoes, peppers, green onions, lettuce will be good neighbors for physalis. But do not plant peas, beans, cucumbers, aromatic and spicy herbs nearby.
Features of seed reproduction
Physalis is most often propagated by seed. They are planted on seedlings or directly in open ground - depending on climatic conditions. Physalis can be grown in a greenhouse, garden or at home.
To plant physalis seeds, you will have to equip a home greenhouse. You can tighten the box with the sown seeds with an opaque film and put it in a warm place. The seeds are planted to a depth of 10-15 mm. Despite the fact that physalis is not picky about the soil, it must be planted in loose soil. If at home there are no problems with this, then in a greenhouse or garden the soil will need to be prepared in advance.
The earth needs to be dug up to fill it with oxygen. If you plan to plant physalis in the spring, then in the fall the garden can be fertilized with manure, humus or compost. For good germination of seeds, a temperature of 17-18 degrees above zero is required. Physalis seedlings are sown at the end of March. And in open ground, planting is carried out no earlier than mid-May. By this time, the soil should warm up to at least +10 degrees.
Transplanting seedlings into open ground is carried out at the end of May. Plants are planted in the afternoon when the sun is less scorching. This will allow the seedlings to quickly adapt to the new environment. Before transplanting, physalis must be watered abundantly to make it easier to separate the bushes. Strongly elongated seedlings can be lowered into the hole by laying the stem in a spiral. In this case, the lower leaves are removed. Then the plants are covered with earth.
Physalis is not recommended to plant often. This can lead to lower yields.
The distance between the rows must be at least 0.5 meters. In order not to overdo it with the amount of seeds when planting, gardeners are advised to mix the seeds with fine sand. This will help to seed the area with physalis evenly. No more than 5 bushes should grow per 1 m2.
Video: planting physalis seedlings in a greenhouse
Physalis pick
Physalis dive after 2-3 leaves appear in the plant. Before you start picking, you need to prepare pots or plastic cups with loose soil. Only after that do they start planting plants:
- Physalis is watered abundantly before diving. This makes it easier to separate the plant roots from each other.
- With a pointer, a pen or any other convenient object, a depression in the form of a funnel is made in a glass with earth.
- If the seedlings are tall, then the hole can be made to the full depth of the glass. Physalis will subsequently develop a powerful root system.
- Warm water is poured into the hole, to which the growth stimulator HB 101 is added. This is an organic product that promotes active growth and development of plants. For 1 liter of water, 1 ml of the drug is required.
- Plants are divided among themselves. And they sink into the cups. You can plant 1-2 seedlings in one hole.
- The soil is lightly compacted. If the volume of the cup allows, you can add the earth on top.
- Physalis, after a pick, is placed in a warm, but not hot place.
Video: how to dive physalis
Growing physalis
Physalis does not need special care after transplanting into open ground, a pot or a greenhouse. This is a rather unpretentious plant.
Basic conditions for caring for physalis:
- The main requirements are still an abundance of sunlight and warmth.
- Unlike other nightshades, it does not need to be pinned.
- Only vigorous varieties are tied up, reaching 70-100 cm in height.
- Physalis only needs timely watering and weeding.
- The earth is periodically loosened so that a crust does not form and the soil does not crack.
- The plant must be periodically inspected to prevent the occurrence of diseases.
- When diseased bushes are found, the plants are removed and burned so that the disease does not spread.
Video: growing physalis in a pot
Plant agrotechnics
Any plant, including physalis, needs fertilizing. This increases the endurance and yield of the crop. Physalis roots grow deeper, so fertilizers that are on the soil surface are not fully used. Physalis should be fed every 14 days starting in mid-June. You can feed the plants with the following fertilizers:
- Manure solution. The ratio with water is 1: 5.
- Mullein solution. The ratio is 1: 8.
- Poultry manure solution mixed with wood ash. For 1 kg of organic matter, 15 liters of water and 0.2 kg of ash are taken.
- Ash can be replaced with superphosphate (50 g) and add 1 tbsp. l. potassium salt.
- Urea. It is diluted in an amount of 10 g per 10 liters of water.

In the absence of organic fertilizers, urea can be used
As for regular watering of physalis, they are necessary for young plants.An adult physalis needs systematic watering only during a drought period.
Diseases and pests
Of all the nightshades, physalis is the least susceptible to disease. The most common diseases for this plant:
- Late blight. Physalis rarely gets sick with it. This happens when the weather is rainy for a long time. Fogs, high humidity of air and soil can be the culprits of late blight. It manifests itself as brown spots that form under the skin of the fruit. Such berries must be removed from the bushes immediately.
- Blackleg. It affects physalis seedlings. The main cause of the disease is sowing the plants too often. The secondary conditions for the development of the black leg are high humidity and poor ventilation of the flower bed. Fighting this disease is quite simple. It is necessary to thin out physalis, destroy weeds and reduce the frequency of watering.
- Mosaic. To avoid this virus, basic crop rotation requirements must be followed. Physalis can be transplanted to a new place, but it will be possible to return the plant to the previous flower bed only after 4 years.
- Of the pests for physalis, only the bear and the wireworm are dangerous. You can fight them using folk methods. For example, planting lupins, alfalfa, mustard or salad nearby. You can decompose the superphosphate granules by spraying them with a solution of your choice: Decis, Karate, Provotox or Actellik. These insecticides are the least toxic to humans.
Growing physalis in the regions
There are no zoned varieties of physalis for the Urals, Siberia, Ukraine or the Volga region. Gardeners and gardeners are guided by the duration of the warm season, choosing one or another variety for planting. But based on long-term observations and experience of specialists, it is possible to draw conclusions which varieties develop better on the territory of different regions.
Table: Physalis varieties for growing in different climates
Reviews of gardeners about growing physalis
The variety of physalis varieties is good news. But when choosing plants for your garden, it is important to remember that some varieties are decorative. Others can be applied in landscaping, but fully utilized in culinary experiments. After all, this culture is truly unique and deserves due attention.
Photographer, copywriter. Work experience 8 years. Knowledge of English, German. Rate the article:
(1 vote, average: 4 out of 5)

