Beekeeping basics for beginners
Bees NOT pets: not a single bee can tell the difference between the owner and the passer-by. And yet they are successfully propagated, produced, and guided. But you need to understand beekeeping, only then you can use their instincts to your advantage.
This article contains basic tips for a novice beekeeper: where to start, how to choose the right bees, the type of hives, proper care, and more.
Where to begin?
With the acquisition of knowledge. It is required to have at least a green (but better - accurate and complete) understanding of beekeeping. Books, articles, advice from beekeepers, and their observations will help here.
It would be nice to enlist the support of an experienced beekeeper living nearby. You just have to try: taking patronage over a beginner means becoming a beekeeper for a year, to which not everyone will agree.

We select a place for the point. Behind the fence, preferably with growing trees (shade in summer helps insects maintain the microclimate of the dwelling), a good food base, next to the house and other buildings - Omshanik, warehouse, workshop.
Do not put an apiary in the lowlands: this contributes to the development of diseases. It is good if buildings or a solid fence cover the hives from the wind.
Tools and equipment are purchased. Some things you can do yourself, some that are infrequently used and relatively expensive (honey extractor, wax melter) things can be borrowed, although it is better to have your own. But it is difficult to do without buying a minimum - a front (preferably two) mesh, a smoker, an apiary chisel, a small amount of foundation, wire for naschivaniya.
We examine the food supply. We take into account the area within a radius of 2 km from the future apiary, this is the radius of productive flight of bees. Bees fly further (up to 5-6 km), but the time and honey spent as fuel, and the troubles that lie in wait during a long flight - birds, cultivated fields, possible bad weather, wasted time - reduce the effectiveness of the takeoff. The frequency of honey collection is also important, significant non-tipping periods lead to theft: insects in search of food are trying to rob neighbors. That can turn into an attack, when the robbed family is destroyed, and the supplies are dragged by the robbers to their nest. Bee wickedness also grows in time without tampering, which can quarrel with neighbors, and the beekeeper himself is not a pleasure. Even in the absence of a bribe, families become swarmed and work poorly.
Free periods can be eliminated in two ways.
- Sowing honey plants, planting nectar-bearing trees and shrubs that bloom at the right time.
- Kochevkoy - moving the apiary to an area with honey plants blooming at this time.
We collect other necessary information.
All beekeeping works, in one way or another, relate to these important dates.
We complete the first aid kit. Not so much for yourself (over time, the sensitivity to bites decreases), as for possible guests or passers-by, stung by your charges. 1-2% of people are allergic to stings, so it's best to play it safe. To avoid possible trouble.
Official registration. The law requires you to obtain a passport for an apiary, even if you keep a single bee colony.
Profitability calculation
Income part. This includes the cost of beekeeping products.
- Honey.
- Wax.
- Propolis.
- Royal jelly.
- Bee packages.
- Uterus.
- Pollen.
- Bee venom.

There are also unreliable incomes, but possible. Payment for pollination or apiary tours (if you find willing to pay). Sale of podmore (dead bees) or wax moth larvae for "medical" purposes. In reality, the healing effect differs little, if at all, from zero, but now the fashion for such a "treatment".
The profit depends on the following factors.
- Directions of the apiary... We work for honey collection or breeding of queens, obtaining milk, pollen or poison.
- Product prices... Moreover, if the prices and demand for honey are relatively stable, then something else ... The price of queens strongly depends on the time of rearing and their purebredness, moreover, it has been documented. Poison and royal jelly, especially the latter, is a very specific product: you need to find a buyer and strictly adhere to the rules for obtaining, since if it is incorrectly selected, it loses all its amazing properties.
- Apiary productivity... It depends not only on the owner. Drought or sudden frosts, like weather in general, are difficult to regulate.
There is also a profitable part, which is difficult to express in coins. The pleasure of fiddling with bees. Increase the productivity of your garden or vegetable garden. A positive effect on the health of one's own and loved ones from honey and pollen, as well as stings (apitherapy is a really effective method).
The consumables are based on.
- Purchase bees and queens.
- Acquisition of hives, tools, equipment or lumber and accessories, if you make hives, frames and other necessary things yourself.
- Construction or rental of premises: warehouse, workshop, Omshanik.
- Price Supplies: medicines, sugar, foundation.
- Wages hired workers.
- If beekeeping is nomadic, add transportation costs, watchmen, fuel.

There are also unplanned ones force majeure expenses: payment of a lawyer / analyzes / experts, if there are any problems with the law or additional costs in case of an unexpected illness in the apiary.
Absolutely exactly it is not possible to calculate future profit... If only because the nectar content of the area differs from year to year. But, having taken care of collecting information and planning actions in advance (even better - by concluding a contract for the supply of products), it is easy to estimate future profits, even if not to a penny.
Used hives
Non-collapsible hives (decks, nest boxes, sapets) are little used now, their time has passed. The choice is between vertically (one-, two-, multi-hulls) and horizontally (loungers) stackable hives. And also between made of wood or plastic. Expanded polystyrene hives are becoming more and more fashionable.
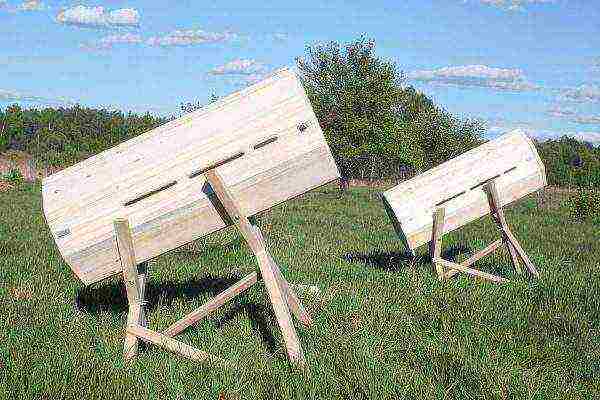

Sun beds have a slight maintenance advantage: no need to lift heavy cases, easier to inspect families. At the same time, they are more cumbersome, more lumber is consumed for production, and worse in transportation.

Ukrainian (Polish, Levitsky - other names for a lounger on a narrow-high frame) are better for wintering, otherwise the same as the more commonly used hives on Dadanovskaya, Rutovskaya, Delonovskaya wide frames.

The choice of a hive is made based on the following considerations.
- Apiary focus: for honey collection or breeding. In the latter case, designs are selected that favor the maintenance of several families in the hive. For cores, special hives are made on a reduced (usually a quarter of a Dadan's) frame. The alpine hive is also good, on the Roger Delon frame: the body is in size and so similar to the nucleus.
- Nomadic or stationary beekeeping supposed.
- Is there (or is it planned to purchase, manufacture) body lift... And is there any strength to lift a full section. If you plan to tinker with bees in your old age, you should not make a choice on heavy wooden cases with 12 Dadan frames in each.
In any case, it is advisable to have the same type of hives for the entire apiary. It helps in the work, bodies and frames are interchangeable, there are no problems with rearrangements.
The biology of the bee colony is the basis of beekeeping
Bee family - a single biological unit. Separately, a bee, a queen, a drone are simply not able to live for a long time, and even more so to reproduce.
Uterus - mother to the whole family: only she lays eggs. All the rest are her children. Up to 3,000 (in the Italian breed, the record holder for this part) eggs are laid per day, the total weight of which exceeds the weight of the queen. The queen is constantly accompanied by a group of bees called retinue: they clean, feed, protect.

There is only one uterus in the family. In rare cases, a very short coexistence of several is possible: when swarming or in a landfill swarm, when several families have settled on one branch and transplanted into one hive.
A freshly excreted uterus is called infertile.. On the 5-6th day, if the weather permits, it flies out for mating, where several drones are fertilized in flight. After that, she is called fetal. Their semen is stored in special reservoirs called testes.. There are artificial insemination methodwhen the liquid obtained from the drones is injected into an individual euthanized with carbon dioxide with a special syringe. Eggs of two types are laid: fertilized - from them are obtained queens and worker bees, and unfertilized - from these drones.
The uterus is removed from ordinary fertilized eggs, but in special cells of larger volume - mother liquors... It's about food: they are fed with a special biologically active liquid, royal jelly.
Lives for several years, usually two, then replaced by a beekeeper. The reason is that the old uterus lays eggs worse. However, they live longer without a change. Queen can be tagged, a drop of paint is applied to the back, then it is easier to find. Besides, the color of the paint shows the year of breeding: 7 colors are used in 7 years, then the cycle repeats. In nature, the change of the uterus occurs in the following cases.
- Quiet shift. Several (usually 2-3) mother cells are laid, the hatched individual replaces the old, sick or crippled one. Such a change takes place without a noticeable change in the rhythm of the family, often hardly noticeable to the beekeeper. Hence the name.
- Swarm. Several dozen queen cells are laid, the hatched individuals are used for reproduction. On the eve of their exit from the queen cells, part of the bees with the old queen gather full goiter of honey. They fly out of the hive, graft onto an inanimate object (usually a tree branch), hang a little, and go to a new place of residence. The first (with an old, fetal uterus) such a new family is called a pervak swarm. Further - a swarm-second, a swarm-third, and so on. All, except for the first, come out with infertile uterus. The number of swarms released is a breed characteristic. On average, the northern breeds release 1–2 swarms, the southern ones can erupt: they release many small, low-value swarms.
- Fistula. Withdrawal with sudden loss of the uterus. Some cells in a honeycomb with future bees already living in them are urgently altered. The larvae themselves are fed with royal jelly, and instead of bees, queens are obtained from them. The quality is (on average) worse, especially if the older larvae have been eating regular food for some time, rather than royal jelly. Working bees hatch from larvae more than two and a half days old, no matter how they are fed.
Worker bees. Biologically, these are underdeveloped females, they are not able to mate. Do all the work except egg-laying. There are disruptions in the life of the family. If the queen is lost, but it was not possible to bring out a new one, then the part of the bees that ate, due to the lack of brood, the royal jelly produced by them, changes.The genitals are enlarged, the bees are trying to lay eggs. They cannot fertilize, therefore all laid eggs are drone eggs. The drones brought out in bee cells do not fit, they stick out, they have to be sealed not flush with the walls, but with curved, convex lids. Such the brood is called hunchback, oviparous bees - tinder bees, family - rotten. What is sad: without the urgent intervention of the beekeeper, the family is doomed to death, the existing bees gradually die off, and only drones are removed ...
First time - to cleanse the intestines - the bee flies out on day 4... Usually 7-8 days young bees work inside the hive, they are called so - beehives. Then they begin to fly for a bribe, become flight bees. A bee lives from a little more than a month during the main flow period to a little more than six months - hibernating, poorly working bees.
Drone. Male bee, hatched from an unfertilized egg. There is no sting, he is not adapted to any kind of work, and he does not do them. The only function is to see the flying uterus and mate with it. It is in flight that they do not mate in the hive. For searching, it has good eyesight and a good sense of smell, exceeding that of a queen or a worker bee. In autumn, bees do not allow drones to feed and, when they are weak from hunger, are driven out into the street. The presence of drones in a winter club is a bad sign. This only happens in a queenless woman or a family with a very bad, old uterus.
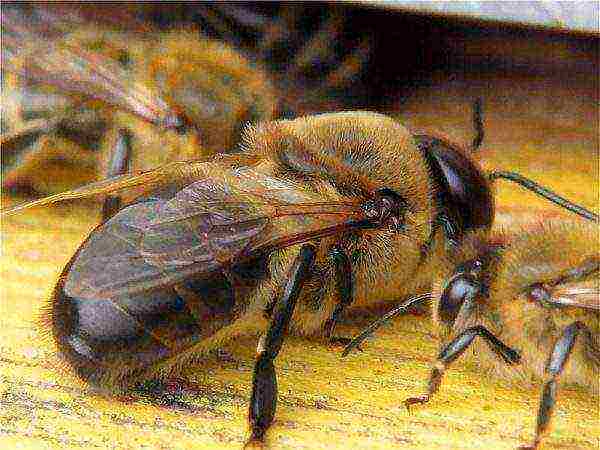

A drone develops longer than the uterus, ready for mating only after 2 weeks (the uterus - 5-6 days after leaving the cell), and in the cell does not develop 16, like the uterus, and not 21, like a working individual, but 24 days. Feed for hatching requires three times more than for a bee.
A normal family consists of a queen, tens of thousands of bees, hundreds of drones. This is in summer, there are no drones in winter. Bees weight - approximately 10,000 per kg. Swarm bees, heavy, which have collected full honey goiters in stock - 7000 / kg.
Species composition
In nature, most species have single bees - leaf-cutting bees, earthen and others, known only to specialists. The reason is that you can't collect honey from them. Leaf cutters are bred to pollinate alfalfa and clover, but infrequently.
Beekeepers work with public bees... Small and (more often) large Indian bee, but most of all - honey bee, in Latin Apis mellifera.
There are many breeds, the differences between them are noticeable. All of them are able to mate with each other, forming hybrids.
When choosing, you should be guided by the local or zoned breed in the place of residence. It is she who is best adapted to bribe and wintering in a given territory, with an alien, even the most remarkable breed, there can be problems. Plus worth considering features of the planned beekeeping... If you are going to grow breeding queens, we buy a specific (exactly the one that you are going to grow) breed. And only her! In order to avoid getting crossbred, not purebred queens. When an apiary is located in the country or when maintaining an apiary as a learning aid (at school, technical school), gentleness is of great importance, even if at the expense of honey productivity.
Acquisition of bees
We omit rare cases (inheritance, donated, orphaned swarm flew to the dacha): they are unlikely. It is really worth considering two ways of establishing.
- Purchase. We receive a specific breed, within the ordered time frame, with documents and appropriate quality. Can be purchased not at firms, but from a familiar beekeeper. Then there is a plus: there is an opportunity to bargain, at the same time get a couple of tips and negotiate help, if anything. Minus - there are (usually) no documents, and the quality of delivery directly depends on the good faith of the seller.
- Catching swarms. Minus - a greater percentage of randomness of the result, the spread in the quality and species of the caught swarms. A plus - cheaper. And the excitement, albeit a little, warms the soul. With the right approach in an area saturated with bee colonies, the method is quite reliable.
Works in the apiary by seasons
Winter. Bees in the club, half asleep, barely alive, are slowly eating honey supplies. Their goal is to endure, to live until spring. In the spring, the uterus begins to worm, the temperature in the brood zone is raised from the winter 14 ° C to the 34 ° C required for the larvae. For bees, winter lasts from the last autumn (usually November) to the first spring (usually March) flyby. It is clear that in different areas in different ways, which applies to all other phases of development.
Spring. Overwintered individuals die off, new ones develop. Families are trying to quickly build up strength and start breeding. In some localities, a commercial bribe from early honey plants is possible, if there are a lot of them. From wild raspberries in Siberia, for example.
Summer. Families are actively collecting food supplies. Also, bees reproduce, release swarms or the beekeeper makes layering.
Autumn. The main task is to grow young, undeveloped insects that will be able to survive until spring and have time to feed themselves a replacement. In rare areas, a late commodity bribe is possible - in the moorlands of Britain, but this is an exception.
Care of bee colonies
Bees do not need guardianship as such, they will survive without human intervention. But a good beekeeper intelligently helps the family, due to which it will collect more honey, and will suffer less from unpleasant factors (winter, illness).
It is not possible to describe all the subtleties of caring for the apiary in the volume of the article. And in short - given what has been written above about the development of the seasons, the beekeeper in each specific period helps the family with minimal losses and with maximum achievements to carry out the necessary work. How? About this - in the relevant sections of our website.
Tips for a novice beekeeper, mistakes, results
Usually novice beekeepersAfter reading, listening, dreaming, they choose in advance the best hive, the best breed, and the best method of beekeeping ...
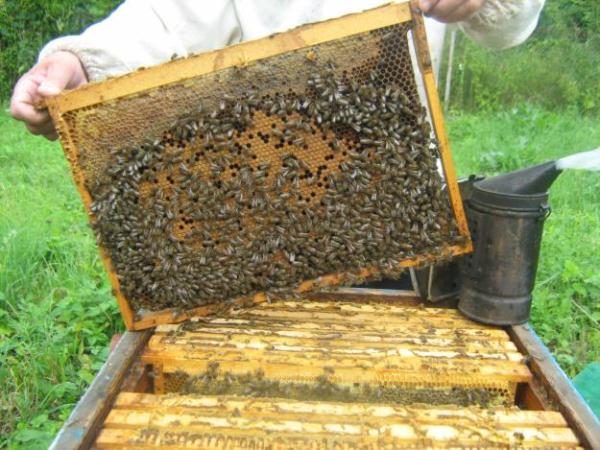

It happens differently: having heard a lot of the conservative beekeeper, in advance they accept innovations with hostility, trying to accurately copy the work in the old-fashioned way of the mentor ...
Truth in the middle. Will be faithful with reason use the experience accumulated by generations of beekeepersboldly experimenting. There are no infallible decisions. There will be diseases, and disappointments, and gatherings of swarms, and unsuccessful seasons, and the death of families during the winter. It is worth setting up in advance for a positive (not ideal) result. With this attitude, beekeeping will bring both pleasure and profit. Necessarily!