Content [show]
What is rutabaga and how is it grown
Few people know what a rutabaga looks like, which has special requirements for care, as well as what family it belongs to. The plant is two years old, in the first year it forms a root crop and foliage. The next year, the vegetable grows a stem, which, after flowering, gives seeds that can be planted the next year. The plant is not at all simple, and even capricious, it needs constant attention during cultivation.
What is this rutabaga?
Depending on the variety, the shapes of the fruits of the swede are different:
- cylindrical;
- round;
- rounded;
- flat-rounded.
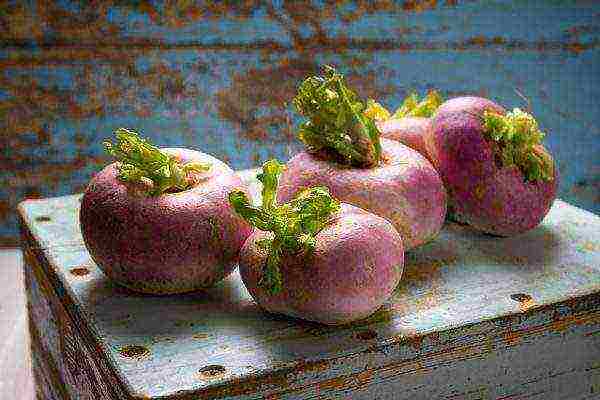
The flesh of the vegetable is firm, it can be light or yellow in color. The size of the root crops is large; during growth, the upper part of them is visible on the surface of the garden. The apical part is dark green, in the lower part it is yellowish or purple with a slight redness.
The plant perfectly tolerates cold conditions, the seeds are able to start growing at a couple of degrees of heat. The sprouts can withstand light frosts, and five-degree frosts are not dangerous for an adult rutabaga.
On the territory of our country, the cultivation of swede has not received mass distribution, but in Western countries its cultivation is developed. For example, the British even consider it their folk dish.
Useful properties and contraindications
The swede contains a large amount of vitamins and minerals. It is noted that even after heat treatment, the vegetable is able to retain its positive qualities.
The presence of vitamin C places rutabagas in the range of foods recommended for scurvy... Freshly squeezed juices are successfully used in wound healing, effectively work as expectorants and diuretics.
Dishes made from this vegetable can improve digestion and are recommended for people suffering from obesity and constipation. The vegetable is also used in the preparation of diets.
It is believed that the root crop is quite valuable for livestock as feed. If you include it in the diet of dairy cattle, you can significantly increase milk yield.

Most popular varieties
The vegetable is cultivated for table and feed needs, therefore it is divided into certain varieties:
— Krasnoselskaya - grown for food use. In terms of ripening, the plant is considered medium early, the growing season lasts from three to four months. The pulp is yellow, sugary. The root crop has a flat-rounded shape, a grayish-green tint with hints of purple. The weight of one vegetable ranges from three hundred to six hundred grams. The culture is suitable for long-term storage;
— dzeltene abolu is a table variety of Latvian selection specialists; it does not differ in good keeping quality. From the moment of germination to harvesting, seventy to one hundred and thirty days pass. The average weight of a vegetable is four hundred grams, the pulp is yellow, firm;
— Swedish - a universal variety, grown for table and feed purposes. The taste is somewhat inferior to Krasnoselskaya. The growing season takes about four and a half months.
- Krasnoselskaya
- Swedish
Timing for landing
Seed in open ground rutabagas should be planted in early May.If you plan to grow a vegetable using a seedling method, then sowing must be carried out in March - early April, so that the seedlings have at least forty days before transplanting to a permanent place.
How to plant seeds outdoors?
The vegetable can grow on both neutral and acidic soils. The land should be sufficiently fertile and loose. Best of all, if it is loamy, sandy loam or peat cultivated beds. The primer should easily absorb and retain moisture.
The best predecessors for this plant are legumes, nightshade or pumpkin.
Rutabaga likes manure, so it is recommended to add it to the soil in the fall, during digging. But at the stage of ripening of a vegetable, such fertilization is contraindicated - the root crop becomes dry and porous. Phosphorus-potassium are best suited as mineral fertilizers. A good solution is to use dolomite flour or lime.
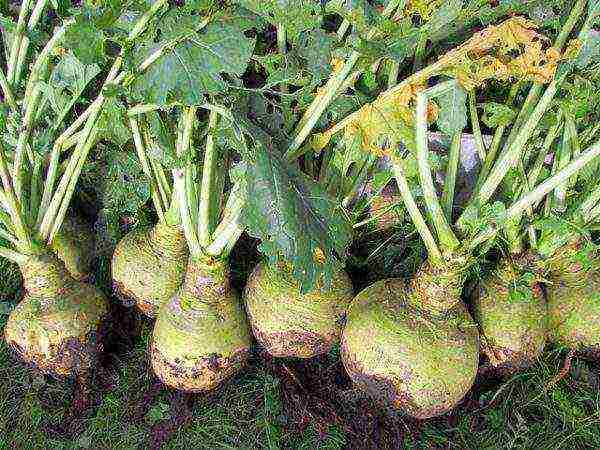

When growing with seeds, it is necessary to prepare the garden bed in the fall. Sowing is carried out to a depth of two to two and a half centimeters, the interval between rows is forty-five centimeters. The emerging seedlings must be thinned out so that there is a fifteen centimeter interval between the plants.
Proper care and cultivation
Growing a vegetable is not difficult. Caring for the turnip is standard - watering, removing weeds, preventing diseases, making fertilizing compositions.
The first decade of seedling growth is slow, it is very important at this time to water the sprouts in a timely manner, remove weeds. After one and a half to two months, the vegetable begins to form root crops, as evidenced by the foliage of the plant, part of which dries up.
Rutabagas are fed twice - a couple of weeks after planting (with manure) and during the formation of the fruit (with complex compounds).
Susceptibility to disease and pests
Like other cruciferous plants, rutabagas can be affected by powdery mildew, ash, linen. Cabbage fly, aphid and keel will not pass by such a culture.
In order not to get into trouble, it is necessary to constantly inspect the plants. Having found the first signs, you should take the necessary measures by treating the plantings with special compounds.
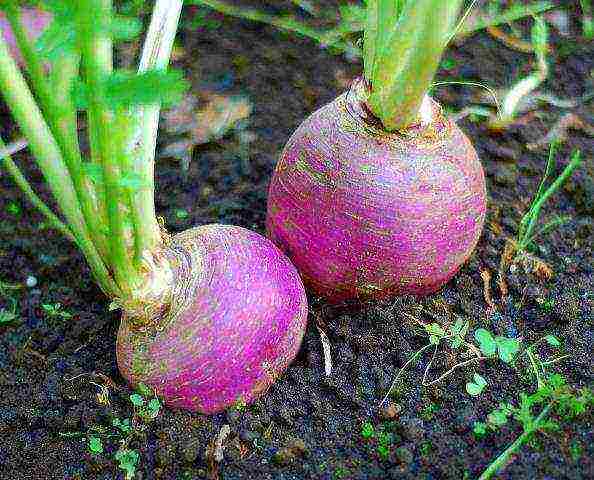

Harvesting
The crop yield is five hundred kilograms from one hundred square meters of planting. The tops are put into silage for livestock, root crops for the winter are stored in piles, cellars or trenches.
As it turned out, it is difficult to find a good variety for growing, but there is always an opportunity to find a suitable option from foreign breeders. With the organization of proper care, each gardener is able to grow this crop on his site.


