Content
Rules for breeding earthworms at home
Soil, as you know, is the basis of all living things and developing on our planet, the basis of life. In order not to dry up its strength, soil fertility must constantly be restored, and the most important workers in this direction are earthworms. Everything ingenious is extremely simple - the quality of lands, their fertility and high crop yields directly depend on the waste product of an ordinary earthworm. How to breed it at home, how and what to feed and what kind of care to take will be described further.
Reasons for breeding earthworms at home
Breeding worms at home is not at all difficult. And the case can become a very serious business, and there are at least two good reasons for this:
- creepers multiply very quickly, gain useful biomass and are excellent feed for poultry (poultry farms, poultry farms and egg production);
- the product of active life is vermicompost - the highest quality and environmentally friendly fertilizer for farms and greenhouses.
In addition, in pharmacology, these animal organisms are also used for the manufacture of medicines. The use of vermicompost in personal household plots and in households will significantly increase the egg production of poultry, soil fertility, increase the productivity of vegetables and fruits without the use of chemical fertilizers.
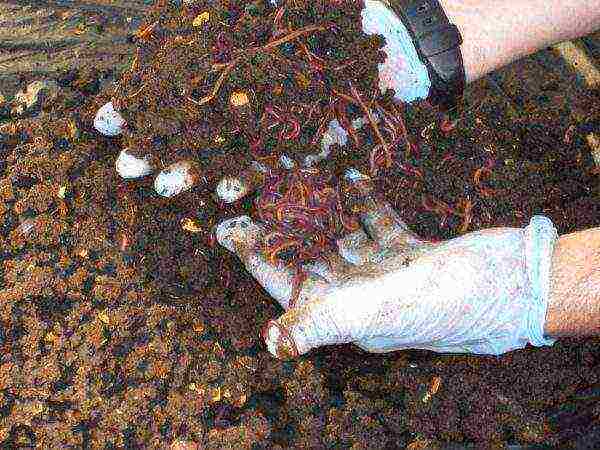

Varieties of annelids
The most common common representative of bristle annelids is the earthworm. But it is they, which are freely found in nature, the least suitable for reproduction in artificial conditions. Representatives of this subspecies reproduce rather slowly, with difficulty adapting to new conditions and unfamiliar food, they live relatively little. They, perhaps, are suitable only for breeding for their own needs of a personal backyard farm.
For industrial cultivation and production of vermicompost, the Russian scientist, Professor AM Igonin bred a special breed "Prospector". By crossing various breeds of species living at a sufficient distance from each other, he was able to get individuals with completely new qualities:
- long life expectancy - from 4 to 16 years;
- multiplies rapidly;
- easily tolerates the change of feed (you can use any type of food - from fallen leaves and grass to human food waste).
Another variety that meets industrial production requirements is the California red worm. Individuals of CCC also reproduce very quickly, increase the useful mass, process various organic waste of human life into vermicompost, serve as an excellent protein feed for agricultural and fish farms.
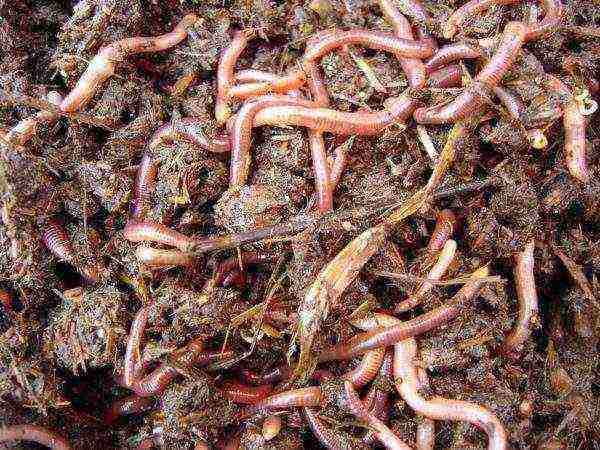

Household breeding technology
Necessary equipment and breeding area
If you decide to start breeding worms, you first need to carry out preparatory work - choose and prepare a place or container. Containers can be wooden, plastic or cardboard boxes (it is clear that cardboard containers will have to be changed often), piles.
They are placed in a shed, garage, any other specially designated place where it is possible to comply with the necessary conditions - the substrate moisture content is at least 70-80% and the temperature is from 12-15OFrom until 22-24OC. You can also breed worms in an ordinary compost heap, a pit.

One convenient option is to use two or three perforated boxes stacked on top of each other. The lowest one - with holes along the perimeter at the top of the sides. This box is intended for vermicelli - a liquid component of vermicompost. A box with perforated walls and a bottom is placed on top of it, a nutrient medium for worms is laid in it and individuals are populated, on top the boxes need to be covered with burlap or other "breathing" cloth, since creepers love dark and damp places.
Making a worm
You can breed individuals on the street, right in the garden, separating a certain place for this and fencing it with boards or other improvised material.
Approximate dimensions of the wormhole: width 1-1.2m, height 30-40cm, arbitrary length. A thick layer of compost is placed on the bottom, leveled and well moistened. Then cover the compost heap with air-permeable material for 5-7 days.
It can be an old burlap, cardboard, a layer of straw, which need to be watered from time to time with rain or well-settled water (at least 2-3 days).
After a week, each square. m, a recess is made in which the creeping ones are placed, and again the wormhole is covered with an air-permeable material.

Compost preparation
Mixtures of rotted manure, poultry droppings, peat, straw, leaves and stems of vegetables and weeds, crushed eggshells and food waste can be used as compost for laying in boxes or pits.
All organic materials suitable for breeding are collected on a heap (or in a specially designated place), covered and, periodically moistened, kept for 1.5-2 months.
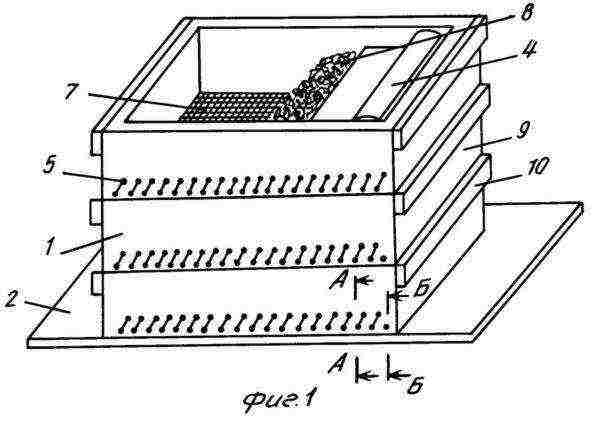
Own vermi farm
If you decide to acquire your own small worm farm, then, first of all, you need to equip a place for keeping worms, stock up on containers, prepare compost and provide comfortable conditions for breeding.
The purchase of the broodstock is of decisive importance. The most suitable species, as already mentioned, are the Californian red worms or prospectors. One family is 1500 individuals. In order to populate 1 cubic meter. m of compost, 1-3 families of broodstock are needed.
Moving into a new location must be done with great care. First, a few individuals are introduced into a small amount of prepared soil in a separate bowl, the soil is leveled and the dishes are closed. After a couple of days, you need to add some feed. If all the worms are active, mobile, with a characteristic red color, the entire livestock can be colonized. If dead individuals are found, then it is necessary to correct the acidity of the soil (the most favorable environment is considered to be an acid indicator of 6.5-7.5 PH).

How to feed earthworms
Ringed earthworms are real vegetarians and they do not tolerate protein foods: meat, fish, eggs. When buying a broodstock, it is necessary to find out what the seller fed his wards, since the most common is the feed that they have tried "from birth". However, they quickly get used to new foods, especially Prospectors. It takes some time to get used to a certain type of feed, therefore, new components should be introduced into the feed base gradually, allowing the worms to adapt.
As a top dressing, plant residues, potato peelings, cabbage leaves, various food waste from the kitchen of plant origin, tea and coffee grounds, straw, grass, dry bread are suitable. Only whatever you add to the compost heap needs to be shredded for easier and faster processing by creepers. Otherwise, the process of acidification, fermentation or rotting of products may begin.

Care and reproduction
The main care in worm farms or in wormhouses is to comply with the temperature regime, timely feeding, and maintain the humidity level when watering with warm rain or settled water.
In favorable conditions, the worms begin to multiply. In the compost, they lay cocoons - small balls of yellow-sandy color. Each of the cocoons contains several eggs, of which small worms appear 2-3 weeks later, and after 7-8 weeks they are ready to produce offspring themselves. The unsurpassed leaders in reproduction rate are the Prospectors - one individual produces 1,500 offspring per year.
Possible sales markets
Growing worms can really be a profitable business if you worry about the market for processed products and increased livestock in advance.
- Vermicompost is an environmentally friendly fertilizer, highly effective in terms of increasing crop yields, growing seedlings, flowers, etc. Therefore, the consumers of vermicompost can be farms, greenhouses, flower greenhouses, as well as private entrepreneurs engaged in plant breeding.
- Live biomass is a valuable nutritious protein feed for poultry and poultry farms.
- Live food in the form of worms is an indispensable nutritious product for fish farms.
- Worms are in great demand as pet food for zoological stores.
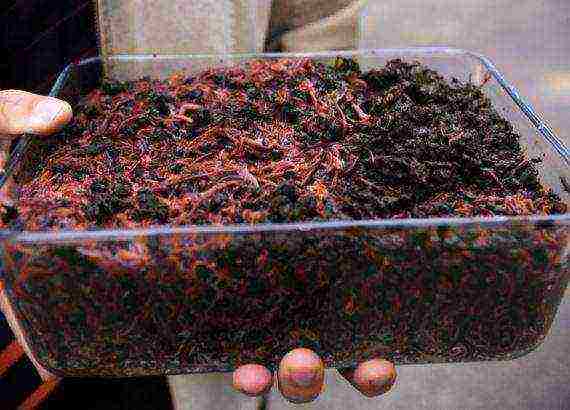

Production profitability
According to the estimates of earthworm farmers, the profitability of the worm farm is in the range of 150%. One Prospector per year gives offspring of 1500 individuals and about 100 kg of the most valuable fertilizer - vermicompost. From 1 ton of harvested compost, you can get up to 600 kg of high-quality fertilizer and 10-15 kg of new individuals.
Farms for growing worms and producing vermicompost is not only profitable and profitable farming, but also enrichment of the environment with useful substances, the possibility of obtaining environmentally friendly food products.


