Content
Symptoms, treatment and prevention of coccidiosis in rabbits
Rabbits are gentle animals that are susceptible to various diseases. Breeding them is not easy, as it might seem to novice rabbit breeders, because often these pets are exposed to such a dangerous disease as coccidiosis. In order to protect your offspring from death, it is important to know how the disease manifests itself.
Knowing the symptoms, it is already possible to carry out the appropriate treatment at the first stage. So what is coccidiosis in rabbits? How to deal with it? Let's take a closer look at the symptoms and principles of treatment of coccidiosis in rabbits.
Coccidiosis in rabbits
Coccidiosis is a disease caused by the unicellular parasite coccidia. They have a damaging effect on the liver and intestines of the animal. Young rabbits at the age of 3-4 months are most susceptible to this disease. But still, adults are not immune from this dangerous infection.
Experts say that parasites of this disease are present in the rabbit's body from the first days of its birth, just like a person is born with worms and other helminths. The presence of coccidia in the body of an animal does not pose a particular danger, the main thing is not to allow and not create conditions for their active reproduction, the development and appearance of the disease coccidiosis.
The affected organ with coccidia will no longer be able to function normally. As a result, part of the food consumed cannot be digested, all useful components will not be absorbed in the body. For this reason, a sick rabbit begins to lose weight, the body becomes exhausted and eventually dies.
Sources and factors of infection
Many coccidial cysts are found in the feces of infected animals. Sometimes pathogens pass through the feces to surrounding objects, food, which ultimately can lead to infection of other healthy individuals. Therefore, the main source of infection with coccidiosis is considered to be contact and fecal-oral.

Sources of infection with coccidiosis include:
- Through feed mixtures, water, as well as through milk, which contains ripe coccidia;
- Infection through the stool of infected individuals;
- From other animals that carry the disease virus;
- Milk of a nursing rabbit who is infected with a disease;
- Various rodents, birds, insects;
- Tools, uniform of farm workers.
Often, animals become infected with the disease on those farms where workers are negligent in their maintenance and appropriate sanitary standards are not observed. Sometimes animals living in uncleaned cages eat feces that contain coccidia and subsequently become infected.
You may also be interested in the following articles on the topic of rabbits:
- How to feed rabbits properly?
- How to use Solikox for rabbits?
- How to properly care for rabbits at home?
Factors that contribute to the development of the disease:
- Keeping rabbits in one cage in a crowded state;
- Failure to comply with quarantine norms during the acquisition of new individuals;
- If the cells are located in the wrong position, which makes it possible for rodents or birds to enter them, carrying infectious agents;
- Failure to comply with sanitary and veterinary rules for keeping these animals.
The disease does not spread by airborne droplets, it is epidemic in nature. Its spread is explained by the fact that when the organisms of pathogens enter the inventory, working clothes of farm workers, feeders, feed and other items, they are quickly transferred to animal cages.
As a result, all offspring that live in these cells are infected. Coccidia are resistant to aggressive substances, sometimes even disinfection does not help remove these parasites. The only thing that kills these parasites is the treatment of the room with hot water.
Disease types
Depending on the area of distribution of pathogens, the disease is of the following types:
- Intestinal coccidiosis;
- Hepatic coccidiosis.
Symptoms of these types of infection are different.... To prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to know the symptoms of the two types of coccidiosis in order to identify it in time and immediately begin treatment.

Rabbit coccidosis symptoms
Coccidiosis is acute and chronic. Coccidiosis in acute form manifests itself on the third day after the defeat.
But coccidiosis in a chronic form occurs when the individual has already been ill and recovered from the disease. Sometimes some of the causative agents of the infection remain in the body, but at the same time it does not harm the tissues of the liver and intestines.
Intestinal symptoms
Intestinal coccidiosis is considered a dangerous form that is developing rapidly. It is accompanied by severe symptoms.
During the intestinal type of the disease, symptoms appear:
- The onset of alternation of acute diarrhea with a rapid course and constipation;
- In the feces of animals, there are mucous and bloody discharge;
- Strong increase in body temperature. The body of the animal is hot enough to the touch;
- Sometimes you notice bloating;
- Poor appetite or no appetite at all;
- Slow growth of the animal's body, its complete stop;
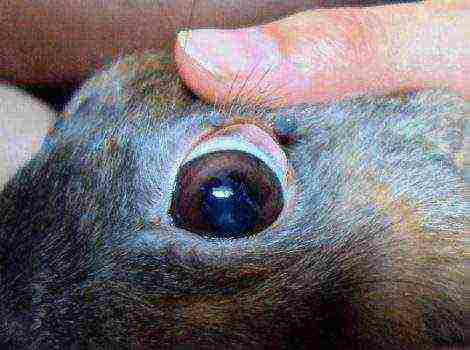
- Purulent discharge from the eyes, nose;
- The wool becomes of poor quality, it looks tousled, without shine;
- The abdomen becomes flabby and saggy.
The rabbit has severe full-body cramps before dying.... The animal can fall on its back, while it throws back its head and makes quick movements with its paws. If you do not take appropriate measures and do not provide appropriate treatment during the time, the individual may die after 2 weeks.
Symptoms of the hepatic form (if there are white spots on the liver)
In contrast to intestinal coccidiosis, the symptomatology of the hepatic form is less pronounced and not so acute. It lasts much longer, from 30 days to 59 days.

In the hepatic form, the animal has signs as in intestinal coccidiosis, only the yellow color of the mucous membrane of the eyes is added, and white spots appear on the liver.
The favorable outcome in the presence of the hepatic form is much higher than in the intestinal form. But often this disease becomes chronic. As a result, the infected individual becomes dangerous to other rabbits, so it should be deposited in a separate place. An infected individual may die or, conversely, recover after a few months.
How can sick animals be treated?
How and how to treat coccidiosis in rabbits? Coccidiosis is well treated with drugs.Medicines against this disease are sold in many veterinary pharmacies. They are used for treatment and prevention.
During the use of drugs, infected individuals are placed in a separate cage. The cage containing sick animals is disinfected and steamed with hot air. If treatment is started from the first days of the onset of the disease, then the chances of recovery will be much higher.... With timely treatment, the survival rate is 75-80%.
How to give the medicine (how to dilute and in what dosage)?
Coccidiosis in rabbits is treated with the following medicines:
- Vetom;
- Baycox;
- Sulfadimetatoxin;
- Sulfapyridazine;
- Phthalazole;
- Furazolidone;
- Solicox.
Rules for the use of drugs:
- Sulfadimetatoxin, Sulfapyridazine. The medicine is given with water. It is added to drinking water. On the first day, 0.2 grams of the drug is given per 1 kilogram of the animal's weight, in the next 4 days of treatment, 0.1 grams of the drug is given per 1 kilogram of the animal's body weight. After that, you need to take a break for 5 days and then repeat the treatment again;
- Phthalazol. To enhance the effect, this drug is best used in conjunction with Norsulfazole. The affected individual is given 0.3 grams of Norsulfazole and 0.1 grams of Phthalazole per 1 kilogram of rabbit weight. The course of treatment with these drugs should be approximately 5 days. After that, you need to take a break for 5 days and the treatment is repeated again;
- Furazolidone... During coccidiosis, the affected rabbit is given daily 30 mg of the drug per 1 kilogram of the individual's body weight. The course of treatment is a week;
- Baycox... This remedy is considered the most effective in treating coccidiosis. It always has a positive effect and in most cases helps to completely cure this terrible infection. Many experienced rabbit breeders claim that even advanced stages of coccidiosis can be cured with this remedy. The instructions for this tool indicate several ways of use. You can inject 2 cubes of the preparation of an infected individual and then pour the medicine into the drinker at the rate of 0.2 ml per 1 kilogram of the animal's weight. Sometimes the medicine is diluted with water and, according to the instructions, is administered to an infected animal at a dosage of 10 ml once a day. The exact application can be clarified at the veterinary pharmacy or read in detail the instructions for use;
- Levomycetin and Sulfadimezin... Sometimes, with coccidiosis, the animal can be given a solution of chloramphenicol, this drug is given in a dosage of 40 grams, or the drug Sulfadimezin can be given in a dosage of 150 mg.
The rules for using other drugs for coccidiosis in rabbits can be found in the instructions for them. Usually, the instructions describe in detail the characteristics and rules for taking the drug.
Treatment with folk remedies (iodine)
Many experienced rabbit breeders argue that the treatment of coccidosis in rabbits is possible with folk remedies, for example, with the help of iodine. It stops the active development of coccidia and causes the oxidation of those substances that remained unprocessed by the stomach.
Rules for the treatment of coccidiosis with iodine for rabbits:
- On the 25th day of pregnancy, females are watered with 0.01% iodine solution at a dosage of 100 ml every day;
- On the 5th day after the appearance of the cubs, iodine must be removed from the diet, on the 5th day it is returned again;
- Iodine should be given to individuals for another 15 days.... Every day you need to give 0.02% iodine solution in a dosage of 200 ml. As a result, protection from infection is provided not only for the rabbits, but also for the rabbits themselves, because they receive iodine together with the mother's milk;
- Be sure to immediately after precipitation of the rabbits from the rabbit you need to drink it with a 0.01% solution of iodine. Every day, one individual should be given 50 ml of iodine solution;
- After 10 days, the iodine solution must be removed from the diet;
- About after 5 days, you need to water the animals with iodine solution again... They drink a 0.02% iodine solution at a dosage of 100 ml. The course of treatment should be 15 days.
Disease prevention
Of course, the use of drugs and iodine are mandatory measures in the treatment of coccidiosis, but one should not forget about prevention. Because sometimes the observance of preventive measures can prevent the occurrence of dire consequences for all rabbit offspring.

Remember the following rules of prevention for coccidiosis in rabbits:
- Rabbit cages should be cleaned regularly. They should always be kept clean and free of droppings and food debris;
- It is imperative to thoroughly rinse the drinkers every day and change the water in them as often as possible;
- Feeders should always be clean, all food debris from them should be removed;
- To block access to penetration into the cells of animals by various rodents;
- It is imperative to keep adults separate from young animals;
- Young animals should be kept in spacious cages with no more than 25 heads;
- Constantly, it is advisable to do the treatment of rabbit dwellings every day with boiling water and an ultraviolet lamp;
- Do not feed juveniles with bran, legumes, alfalfa and other feed mixtures with a high protein content;
- Recently purchased individuals are kept in quarantine for a month;
- It is imperative that during feeding it is necessary to ensure that hay, grass or root crops do not fall on the surface of the ground contaminated with feces.
There is a good remedy that is used during the prevention of coccidiosis in rabbits - Zoalen. This medication is given to animals for 10 days. For 1 kilogram of feed, add 250 mg of the drug every day. It is recommended to feed rabbits with special granular feed mixtures, which contain substances necessary for the prevention of coccidiosis.
However, many rabbit breeders cannot always determine the presence of the disease from the first days, so it turns into a severe stage.
In most cases, when the stage is advanced, the animal dies, even if treatment is provided. Many veterinarians advise, even if individuals survived after coccidiosis, it is still better to send them to slaughter. This is due to the fact that the disease may reappear after a few months. But is it possible to eat the meat of a rabbit sick with coccidia? Veterinarians disagree in this case. In any case, it's best not to risk it.
It is recommended to incinerate carcasses that have died after infection, because the infection can spread to healthy individuals.
And finally, a short video on the topic: