Content
- 1 Features of keeping and breeding rabbits at home
- 1.1 Biological and physiological characteristics of rabbits for beginners
- 1.2 Rabbit breeding: where to start, the choice of breed for breeding - meat or skin
- 1.3 Home rabbit farm: living conditions, growing and care
- 1.4 Growth and development of rabbits
- 1.5 What rabbits eat, proper feeding
- 1.6 Breeding features of rabbits - how to keep, care for and feed
- 1.7 Disease prevention, vaccinations
Features of keeping and breeding rabbits at home
Rabbit breeding - an interesting, profitable and profitable occupation. This type of household activity is very popular. Rabbits are distinguished by high early maturity and intensity of growth, increased fertility and the ability to reproduce throughout the year. They are unpretentious in the content in cages, they adapt well to the existing conditions, they pay in full for the food spent on them. Breeding and caring for animals is not a difficult task if you know the most important thing about rabbits. This article will show you where to start.
Biological and physiological characteristics of rabbits for beginners
Rabbits are born blind, naked and completely dependent on the mother rabbit. Feed on exclusively with milk. By the 10th - 14th day in rabbits eyes open, by the 16th - 20th they are already leave the nest and begin to taste adult food.
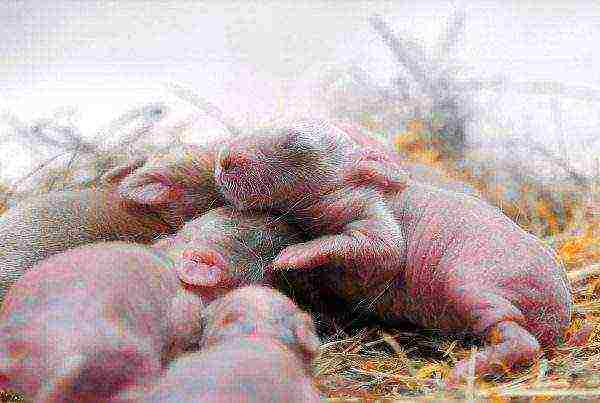

At 1 month old, babies can do without a mother.... By this time, their primary hairline reaches full development and the milk teeth are replaced with molars. Newborn rabbits have 16 temporary teeth. From the 18th day of life their gradual replacement with permanent ones begins. Milk molars fall out on the 20-28th day. After a change, animals have 28, less often 26 (a pair of small incisors in the upper jaw may be missing). By the age of 30 days, the live weight of the rabbits increases 8-10 times.
Rabbits are true vegetarians... They love to eat green grass and prefer high quality hay in winter. With pleasure they gnaw twigs of trees and bushes, gobble up grain, vegetables and fruits. Under domestic conditions, animal feed in the form of nutritional and mineral supplements is also included in the diet of animals.

The digestive system of rabbits is perfectly adapted for eating plant foods. The stomach in animals is single-chambered, has the shape of a horseshoe-shaped bag. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, pepsin and lipase, which quickly dissolve feed proteins, aid in the digestion of fats, and prevent food from decaying. Intestines 8-10 times body length. Rabbit urine is alkaline and contains a lot of nitrogen and sulfur. Daytime feces - dry and hard, night - soft and wet. Natural coprophagia is also a feature of animal digestion.
Rabbits are puberty early... Animals of medium breeds are capable of reproduction at the age of 3 - 3.5 months, large ones - at the age of 3, 5 - 4 months. However, without harm to the health, growth and quality of the offspring, they can occur no earlier than 5 - 6 months, when the period of intensive growth is over. The final development of the organism in rabbits ends by 8 months.
Females bring numerous offspring. In one litter, usually 6 to 9 rabbits are born... The maximum number of newborns is 18. The animals do not have a pronounced seasonal hunting. Females are fertilized all year round, every 5-6 days in summer, and 7-10 days in winter.Bunnies perfectly combine lactation and pregnancy, they can accept, care for and feed both their cubs and from another mother, if the age of the bunnies is about the same.
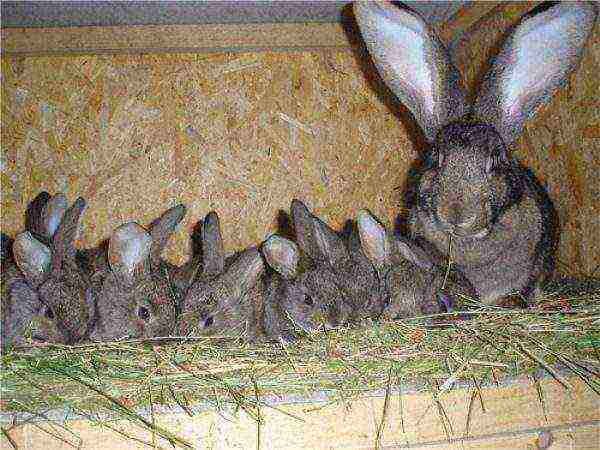
Animals perfectly adapt to living conditions in any climatic conditions, but they are sensitive to extremely low and high temperatures, drafts, infections and polluted air. Rabbits live up to 10 years, after 3-4 years, the reproductive capacity of females and males drops sharply, which necessitates a change in the production composition. Especially valuable animals are used for 5 - 6 years.
Rabbit breeding: where to start, the choice of breed for breeding - meat or skin
Animals are bred for meat and skins. Downy rabbit breeding is less common. Rabbit meat is delicious, nutritious and healthy... It contains a lot of easily digestible protein, 90% of which is easily digested in the human body. The delicate fat does not freeze or leave an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Rabbit meat is used in dietary and medical nutrition... Rabbit dishes are considered delicacies worthy of the attention of real gourmets. The most tender meat is obtained from broilers, which are slaughtered at the age of 70 - 75 days when they reach 2 kg.
The following breeds of animals are suitable for meat breeding:
- flandre;
- French ram;
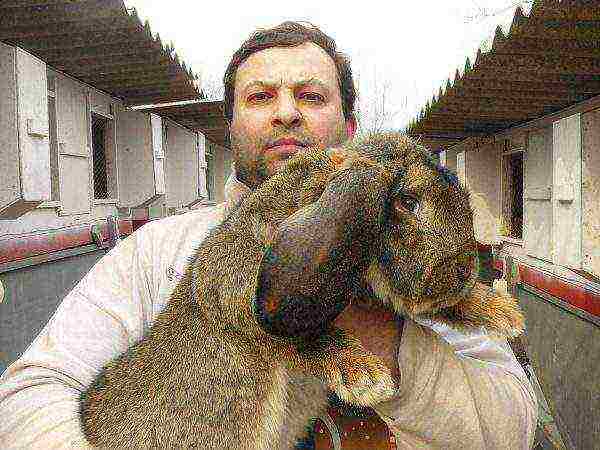

- Californian;
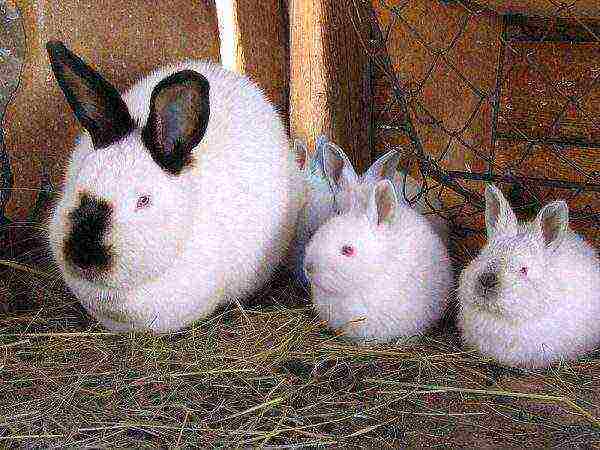

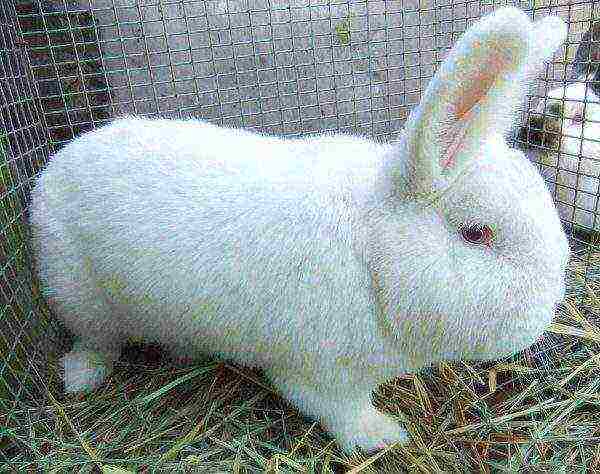
- white New Zealand;

- red New Zealand.
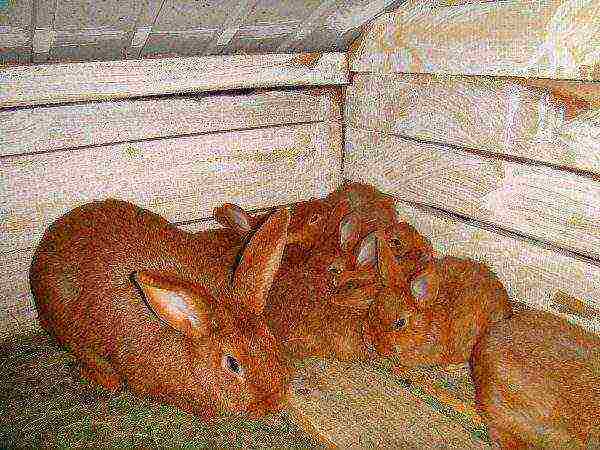

Listed young fast growing, a good set of live weight, optimal feed costs for growth. Marketable products with intensive fattening are obtained by 4-6 months, the weight of rabbits by this time can reach 5 kg.
Animals are raised for skins too... They are used in the light industry for sewing hats, fur coats and in the form of trimming the hoods of products made of synthetic and natural materials. Shoes can also be trimmed with rabbit fur. It is also used to imitate the more expensive mink, arctic fox, sable, fur seal, etc.
Quality skins are obtained from animal breeds:
- Soviet chinchilla;
- gray giant;
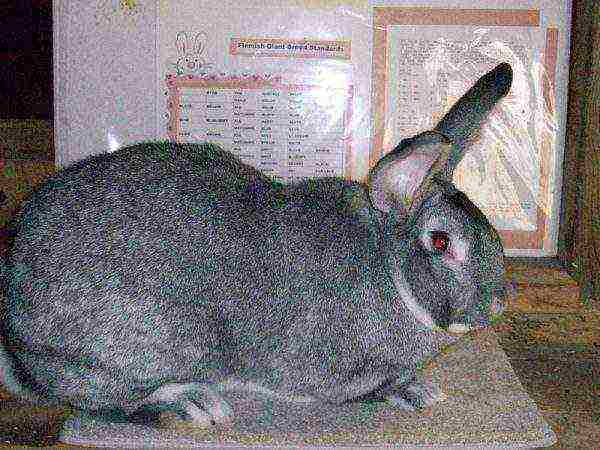

- white giant;
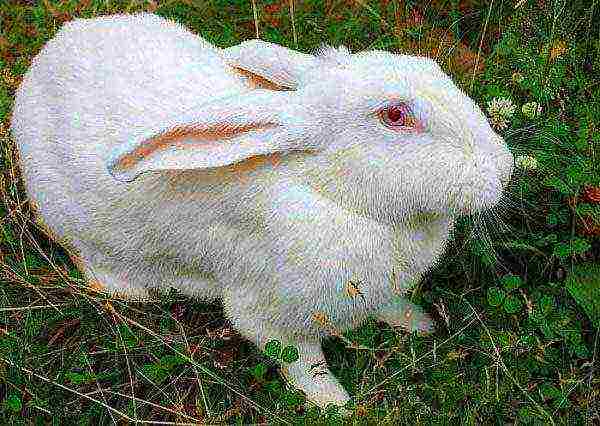

- silver;
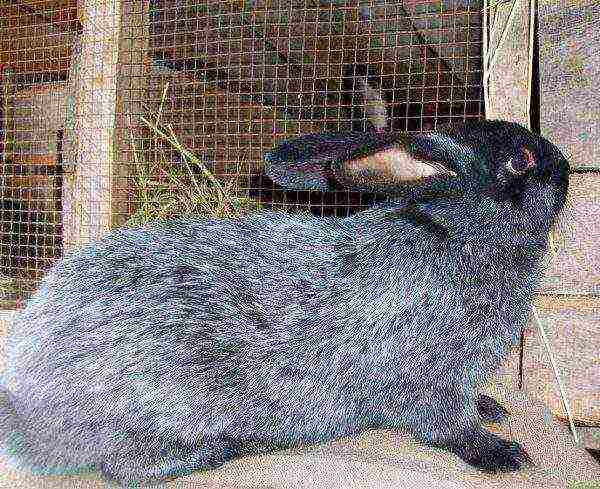

- Viennese blue;
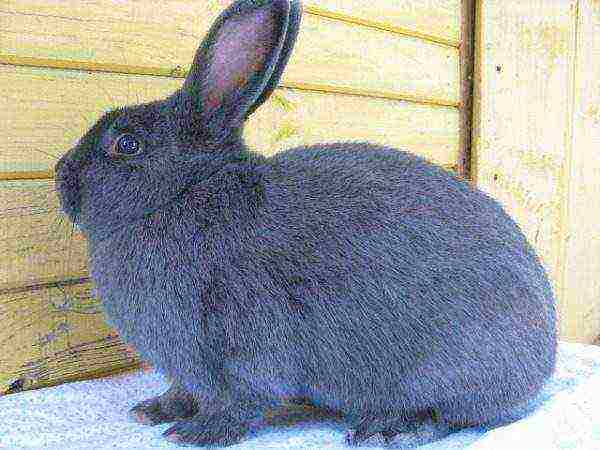

- black-brown;
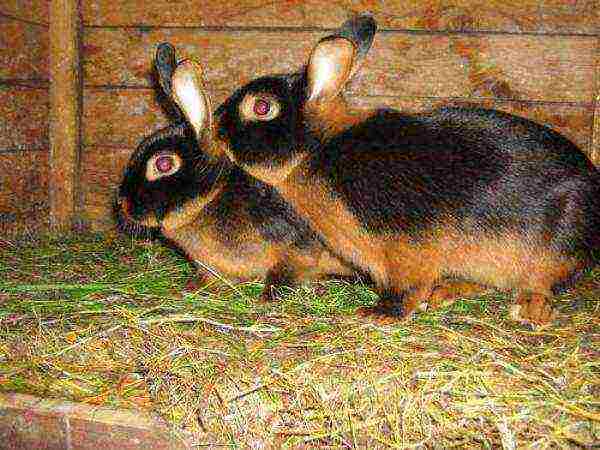

- butterfly;

- Russian ermine.
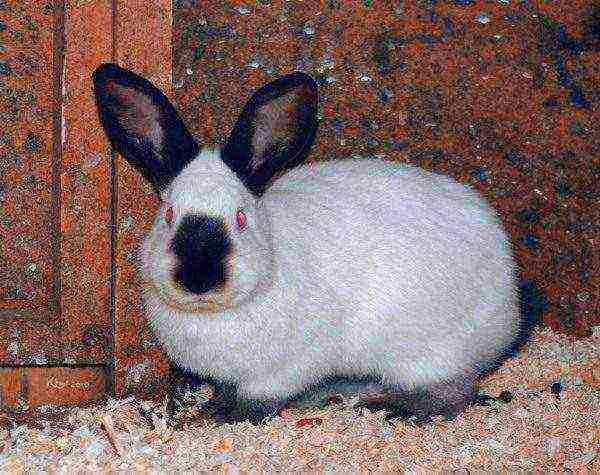

Animals are distinguished thick, soft and beautiful fur with a short awn and strong down... Large valuable skins are obtained from rabbits. Slaughter is carried out after 6 months, when the first adult molt ends.
When choosing animals for a tribe, attention is paid to the health and constitution of the animals. The appearance must correspond to the description of the breed. The male must be energetic, strong, well developed, with a pronounced masculine type. You should not choose small, lethargic, passive, lagging behind in the development of animals. The criteria for selecting females are more varied. The expectant mother should have a light head, strong, but not coarse skeleton, straight back, wide backside, firm, non-sagging belly, strong legs. She must have at least four pairs of evenly spaced and normally developed nipples. This is a guarantee that she can feed and raise numerous offspring.
Home rabbit farm: living conditions, growing and care
In the conditions of private households, they practice both keeping in a barn and outdoor cage keeping of animals... A place for rabbit houses is chosen even, protected from the prevailing winds, with natural or artificial shading. Rabbits do not tolerate overheating well, drafts and do not like moisture, so you should immediately create comfortable conditions for the livestock. The approach to the site must be clear to allow unhindered distribution of feed and cleaning of cages. The breeding backbone and productive young are kept in different sections, although on small farms this is almost arbitrary. Separately, there is a cage for sick animals and a quarantine cage, where newly purchased animals will be temporarily kept, which cannot be immediately placed in the main herd.
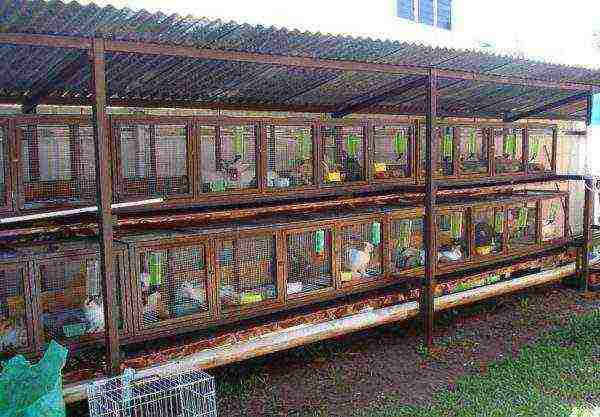

General guidelines for cell design are as follows:
- The best are considered cages made of metal mesh and wood... The back wall and ends are made of boards, nailing parts without gaps, tightly to each other. From the inside, the corners are sheathed with metal so that the rabbits do not spoil the cages. Part of the floor, the front wall and, if desired, the door are made mesh. For these purposes, a chain-link mesh and a fine-mesh construction mesh are suitable. The size is selected so that it is comfortable for the animals to walk without falling with their paws into the cells. Part of the floor is made of solid planks... This is a resting place for rabbits, they can fully rest there, lie down, gnaw on a twig, etc.
- The roofing material is slate, ondulin, profiled sheet... It is practical to make the roof slope slightly towards the back wall to allow rainwater to drain off if the cages are located outdoors. The hinged and hinged design allows you to conveniently clean your rabbit housing when changing livestock.
- Feeders are made removable or stationary, they are placed on the front wall inside or outside the cells. Be sure to put a drinker, preferably an automatic one, so that the rabbits have constant access to water.
- In winter, in severe frosts, the cells are insulated... They use both improvised materials and building insulation. At critically low temperatures, the cells can be sheathed with foam around the outer perimeter, and the facade can be covered with grass mats. In regions where there is a lot of snow, you can simply overlay the cages with it, but do not forget to remove it during the thaw. A plentiful bedding of dry leaves, hay or straw, sawdust will keep the cells warm.
- On small farms cells are placed in one rowe. With a large number of livestock, for ease of maintenance, they are installed in 3 floors one on top of the other. A tray is placed under each tier for collecting feces, urine and feed waste.
Animal cages are made different according to the specification of the use of the room and the needs of the rabbits.
Cages for young animals
Baby rabbits after weaning kept in groups in large spacious cages... Until 3 months, animals are not divided according to gender, then they are transplanted separately. Pugnacious, aggressive animals are isolated from the herd. Fattening and fur young growth contain 6-12 heads in one cage. Repair animals intended to replace the production composition are kept 3 in one house. The living space for a normal rabbit should be 0.12 m², and for reproductive young animals - 0.17 m².
For summer keeping rabbits use a design with two nets on the back and front wall. In such a cage, young animals are comfortable and reliable, the animals breathe fresh air and no harmful gases accumulate inside. It is correct to keep rabbits in a closed cage in winter, lattice only from the facade.
Rabbit mothers
For each female on home farms, a separate cage is allocated. She lives in it and gives birth to offspring. Before the birth of cubs, housing is supplemented with a mother liquor - a closed box with a manhole, in which the rabbit makes a nest. It is made of wooden slats and sheathed with plywood.Box size 300 x 500 x 300 mm. The hole diameter is 150 mm. The lid is made hinged for the convenience of revision in the nest. The mothers are placed either inside the cage at the level of the door, or taken out, providing free passage to the animal. In such an imitation of a mink, it is convenient for a female to raise rabbits. They grow up healthy, strong and strong, and gain weight quickly.
Mating cages
There are no special facilities for crossing animals at home. Everyone does it simply - the female in the hunt for the time of mating is transferred to the male's cage... The whole process takes 10-15 minutes. Mating must be observed. Immediately after its completion, the female is removed from the cage so as not to torment the male. After 5 days, a control mating is carried out. If the rabbit does not allow the male to approach her, she is considered conditionally covered.

Caring for rabbits consists of distributing food and cleaning the cells of their waste. Feed is given 2 or 3 times a day. Hygiene procedures are combined with morning or evening feeding... On a mesh floor, it is permissible to remove feces once a day.
Growth and development of rabbits
Rabbits give birth at night, lasting from 10 minutes to 1 hour. After that, the female eats the afterbirth and stillborn cubs. Labor causes a feeling of thirst, therefore there must be water in the cells at all timesso that the animal does not compensate for the lack of fluid due to the offspring. The same situation can arise if the mother's body lacks vitamins and minerals.
Young bunnies can throw babies around, so the okrol needs to be watchedbut not interfere with the process. The rabbits outside the nest are folded by hand. If the situation repeats, the animal is discarded.
Females feed the rabbits once a day, rarely twice. Rabbits drink up to 200 gr. milk per day... Well-fed rabbits lie peacefully in the nest, the hungry squeak and try to get out of it. If they climb out of the nest before 14 days, then this means that they do not have enough food. The maximum milkiness level in the rabbit falls on the 20 - 25 day of feeding. The mother herself removes the nest, without the need for a person to make adjustments there.
Females are fed ad libitum during lactation, ideally, if there is always food in the feeder, the animal will choose when and what it needs. The mother will teach grown-up children to eat adult food.
The first selection of animals is carried out at the age of 2-3 months. They are assessed according to the degree of development, compliance with the breed standard, health, desirable traits. Bonitization consists in inspection, comparison with standard indicators. Culling sick, frail, weakened, atypical animals... Rabbits with a rough and loose constitution should also be excluded. For further breeding, the most promising young animals are left, the rest of the animals are allowed to eat meat and skins. The last revision of the future breeding composition is carried out at 6 months.

Rabbits grow intensively up to 4 months... This is the ideal age for slaughtering meat animals, as the profitability of feeding the livestock drops sharply. To obtain marketable skins, you will have to wait for an adult molt. In rabbits, this period is not pronounced. Usually animals molt from March to April, in autumn from October to November. In the summer, there is a partial loss of the awn. The approximate time for slaughtering rabbits for skins - after 6 months. It is not recommended to keep marketable young growth for more than 8 months.
What rabbits eat, proper feeding
A good food base is the key to the prosperity of a rabbit farm. Animals eat a variety of plant foods... Green includes:
- meadow forbs;
- wheatgrass;
- sagebrush;
- corn;
- sainfoin;
- peas;
- sow thistle;
- burdock;
- yarrow;
- nettle;
- rape.
The green mass is dried before distribution, never given wet from the rain... It causes digestive upset in animals, sometimes fatal.
Rough feeds include:
- hay;
- herbal flour;
- branch feed;
- dry leaf of fruit trees.
Hay is harvested during the budding period, forbs and legumes are considered the best in composition. From branch feed, rabbits prefer aspen, willow, mountain ash, maple, acacia. From the garden - apple, pear, raspberry, cherry.
The juicy food menu includes:
- fodder beets;
- potato;
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- cabbage;
- fruits.
Sugar beets are fed in limited quantities mixed with bran... Vegetables are a seasonal crop, so the diet can be varied throughout the year.

Rabbits also need grain feed. They willingly eat:
- oats;
- wheat;
- barley;
- corn;
- peas.
Additionally, the diet includes bran, oilcakes.
As a feeding, the rabbits are given:
- salt;
- a piece of chalk;
- meat and bone meal;
- blood and fish meal;
- milk;
- serum;
- yeast.
Granular feed also provides a complete diet... It is bought ready-made in the markets or in specialized stores. The compressed lumps contain everything necessary for the rabbit's body.
In one year a female with an average brood eats up to 1 ton of grass, juicy feed 200 kg, hay 150 kg, concentrates 200 kg and mineral feed 10-12 kg. The data may differ in one direction or the other, it all depends on the climatic conditions in the region, the breed of animals and the diet menu.
Breeding features of rabbits - how to keep, care for and feed
The first time breeding animals are allowed to mate at the age of 5 - 11 months. Disposable females can be used at the age of 5 - 6 months. In healthy, strong, well-fed animals, hunting occurs every 5-6 days, in winter it is somewhat less frequent, so it is easy for a rabbit breeder to plan the time of birth of young animals. 2 weeks before the start of mating, the diet is enhanced with protein and vitamin feed... Males are offered oats, milk, eggs, which increase spermatogenesis and increase the activity of animals. By the time of mating, the breeders should look strong, knocked down, in body, but not greasy.
Mating of animals is fast. For one cage, the male releases up to 2 ml. sperm... In 20 minutes after mating, the sperm penetrate into the female's oviducts. Fertilization occurs 10 to 12 hours later.

Pregnancy in rabbits lasts 26 - 35 days... By the time of their birth, the cubs reach a weight of 50 to 90 g. The weight depends on the breed and the number of rabbits in the litter. In multiple litters, rabbits are born small.
2 - 3 days before the birth, the rabbit becomes restless, runs around the cage, arranges a nest and lines it with down. Signs of impending birth are and a sagging belly of the female, as well as swollen nipples in which milk resides. At this time, the supply of succulent feed is limited and hay is offered to the animals. A few days after okrol, the diet is restored. Lack of milk can be stimulated by giving vegetables and fruits.
Rabbits can produce offspring 4 times a year... With compacted okrol, combined with feeding - up to 6 - 7 times. Often giving birth animals wear out quickly and need to be replaced more often.
Disease prevention, vaccinations
Rabbits are susceptible to disease. Vaccination of animals helps to strengthen the immune system and the body's resistance to infections... The vaccinated livestock is sick less often, while outbreaks of diseases never end with an epidemic.
Vaccination against myxomatosis spend when the young are 28 days old. Live vaccine B 82 is used. The form of administration is intramuscular injection at a dose of 1 cube per head. Re-vaccination is done at the age of 120 days.
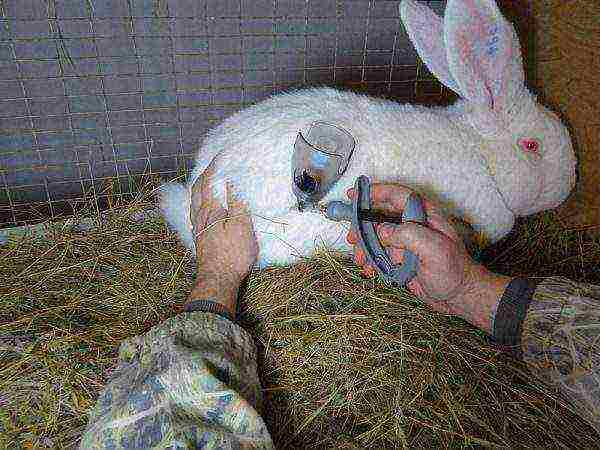
Vaccination against HBV done when babies are 45 days old. Use a fabric hydroaluminum formol vaccine. 0.5 cubes of the drug are administered intramuscularly to animals. At 6 months, the procedure is repeated.
Another option to save rabbits from disease is to use an associated vaccine. It works directly from myxomatosis and VGBK. Rabbits are vaccinated at 45 days. Use 0.5 cube per head. The form of administration is intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
The fight against Pasureliasis begins at 2.5 months... Piperazine is given, which is administered through the oral cavity. The dose of the drug is 0.5 g for each kilogram of rabbit weight.
At 3 months the time comes take action against coccidiosis... They use Baycox, Amprolium. Dilute Amprolium in a liter of water 1, 4 g of the drug. The dosage of Baycox is 1 cube per liter. Drink the medicine at a time.
These measures reduce the risk of developing infectious diseases and keep the rabbits healthy throughout their life.
Breeding and raising rabbits is an addictive business. It is interesting and instructive to do them. For some, it becomes a lifelong hobby. It's not hard to learn everything. For beginners, the main thing is to try, delve into, experiment. And then everything will work out.


